Abstract
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage supply chain is recently acknowledged as a crucial method to limit global warming. There is a notable desire to optimize supply chains simultaneously with respect to economic and environmental factors, and the development of a mathematical model integrating the life cycle assessment into source-sink matching is missing in the existing literature. The present work means to fill this gap by using a bi-objective mixed-integer linear programming problem. The case study for this research focuses on a real-life scenario in Germany where carbon dioxide is captured from flue gas and transported to be stored or/and used. The total profit and life cycle GHG reduction are maximized. The results show that the profit per unit of sequestered CO2 decreases from 2014 to −€332 as the rate of life cycle GHG reduction increases from −873 to 52 MtCO2eq/year. The findings from the model can provide valuable knowledge that can be utilized in various countries at different levels, such as at regional, state, and national levels. This knowledge can also assist decision-makers in selecting more sustainable solutions when designing carbon capture, utilization, and storage systems.
1. Introduction
Global warming is considered one of the greatest challenges to humankind due to its significant effect on the global economy and ecosystem [1]. The main cause of global warming is the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG), particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), that emerge from fossil fuels [2]. In 2023, worldwide anthropogenic CO2 emissions reached 37.2 B ton, corresponding to 419.3 ppm CO2 in the air [3]. These increases in CO2 emissions and concentrations have contributed to a rise in temperatures in the Earth’s atmosphere compared with pre-industrial values [4].
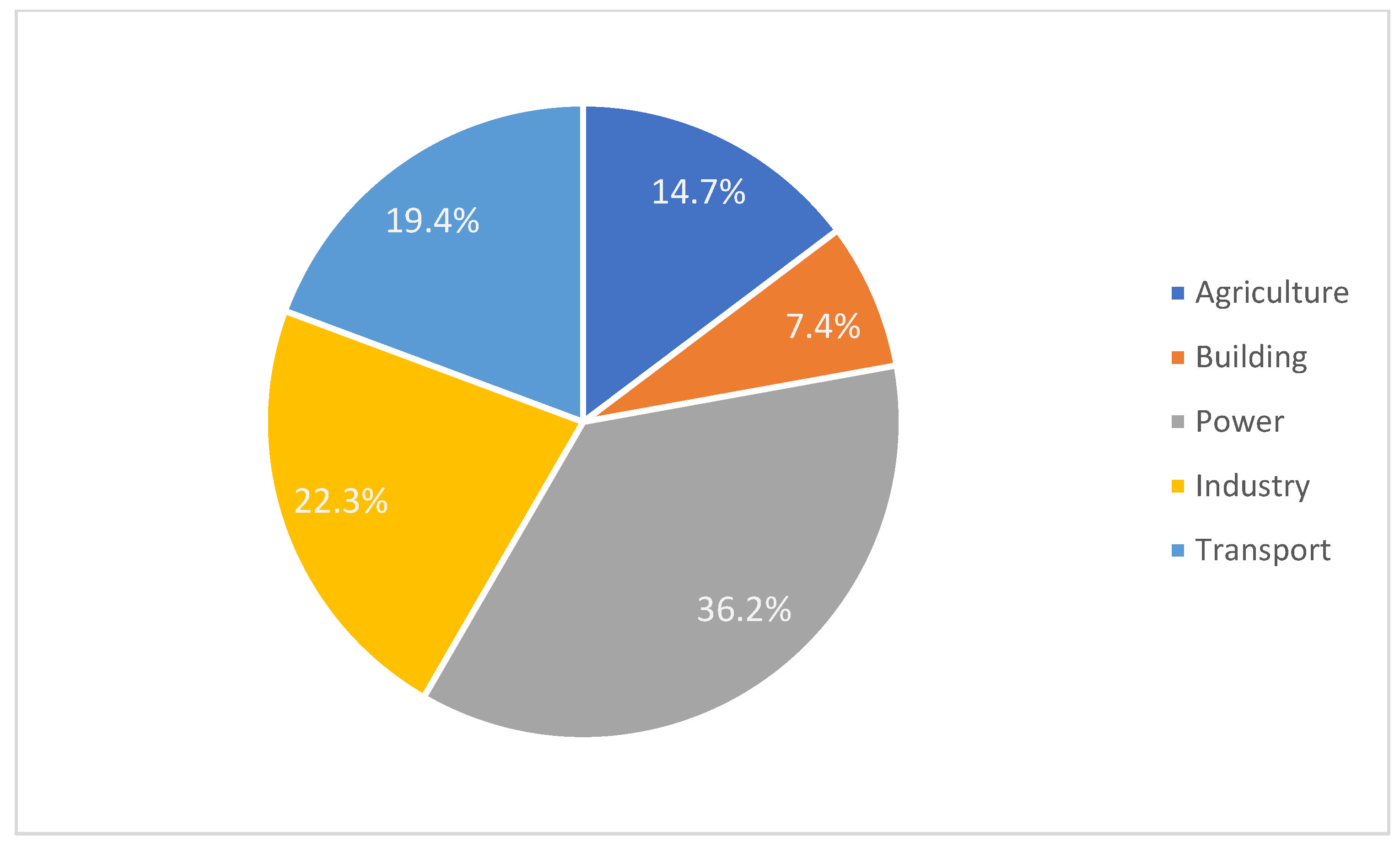
Power plants are the most dominant sector for anthropogenic CO2 emissions, accounting for more than 35% of global emissions. The rest of the CO2 emissions sectors are illustrated in Figure 1 [5]. The European Union set a target to decrease CO2 emissions by a minimum of 40% by 2030 and 80% by 2050, relative to the 1990 level [6]. To achieve this target, several pathways have been proposed by the International Energy Agency (IEA). Some of these strategies can be summarized as (i) enhancing the efficiency of processes, (ii) switching to renewable energies, (iii) using low-carbon fuels, and (iv) carbon capture and storage/utilization (CCUS) systems [7].
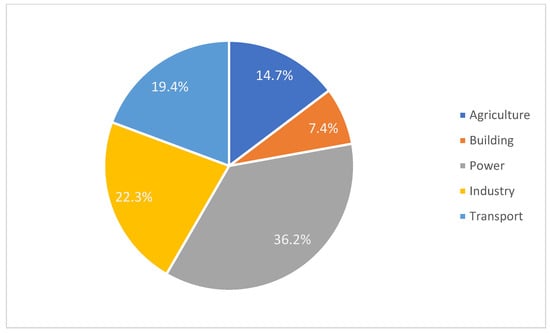
Figure 1.
Worldwide CO2 emission by sector until 2022 [6].
From the aforementioned options, and also according to a political-driven goal, carbon capture storage/utilization has the potential to contribute to mitigating CO2 emissions by at least 20% globally [8]. The expectations indicate that fossil fuels will continue to be the main source of energy until the middle of the century. In this context, CCUS can play a key role in cutting emissions from technologies that depend on fossil fuels. This is due to its capability of being retrofitted perfectly to the existing industries that rely on fossil fuels [9].
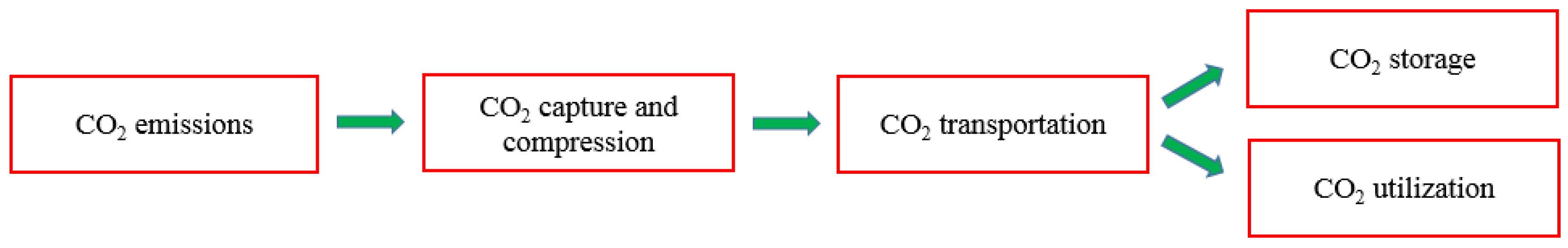
CCUS supply chain comprises four steps: the first is the CO2 capture from the sources; second, the CO2 is compressed to a dense phase to prepare it for the third step. Knowing that the first and the second steps could occur in the same facility, the third step is CO2 transportation through pipelines, rail trucks, or ships. The final step is storing the captured CO2 in geological basins or utilizing it to produce more valuable products [10]. These steps for the supply chain of CCUS are shown in Figure 2.
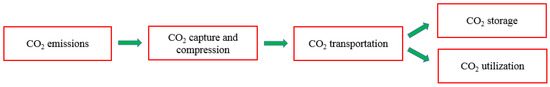
Figure 2.
Scheme for the CCUS supply chain.
In the first step of the supply chain, CO2 is captured via multiple technologies, categorized as post-combustion, pre-combustion, oxy fuels, direct air capture, and chemical and calcium looping [11]. Post-combustion technology is based on separating CO2 from flue gas after combustion using absorption. In pre-combustion, CO2 is captured before combustion [12]: the fuel is pre-treated via the partial oxidation of gasification to generate syngas and CO2. Then, the syngas is converted to a low-carbon fuel such as hydrogen or used for power production. The generated CO2 is separated physically by adsorption, absorption, or membrane separation and captured [13]. Oxy-fuel combustion technology utilizes pure oxygen to combust the fuel completely. Then, the produced CO2 is separated and captured by condensing the co-produced steam [14]. Oxygen carriers are used instead of air in chemical and calcium looping to combust the fuel. Thus, CO2 can be inherently separated from the generated gas by condensing the steam resulting from the combustion [15]. In direct air capture, CO2 is directly captured from the atmosphere [16]. Among all the mentioned CO2 capture techniques, post-combustion technology is the most mature technology [17]. Therefore, most studies on the optimization of the CCUS supply chain have selected it as the CO2 capture step. CO2 capture step shares 70–80% of the overall cost of CCUS [18]. The cost of this step depends on several factors, including the flue gas flow rate and composition, the separation technique used, the emission source, and the fuel type [19].
For the second CCUS supply chain step, CO2 is compressed into the dense phase in order to be transported via pipeline, ship, or rail tanker [20]. Furthermore, multiple options can be used for CO2 storage, including depleted oil reservoirs, deep saline aquifers, and deep ocean storage sites. All these alternatives are essential in the optimization process for the CCUS supply chain, and the risks arising from geological volumes are negligible compared to the overall network costs (always <1% of total cost), although they may be significant locally [21].
On the other hand, CO2 can be utilized in several industries to generate products with more commercial value. For example, in the enhanced oil recovery, CO2 is injected underground to extract the oil [22]. In addition, CO2 can be involved in many processes, including urea production, hydrogenation to methanol, methane, ethanol or formic acid, dry reforming reaction, direct use in food industry, agricultural sector, and even concrete production [23]. Among all these utilization solutions, enhanced oil recovery has the highest potential because it can claim credits for mitigating CO2 emissions due to the long storage time.
The scientific community has shown interest in formulating mathematical models to evaluate and determine the optimal configuration for such carbon networks.
Among the mathematical models developed in the literature, economic concerns are regarded as the unique goal through the minimizing of overall costs [10,19,24,25,26].
These studies mainly focus on using CO2 to enhance oil recovery, and according to Hasan et al. [19,24], by lowering 50% of emissions, it is possible to reach a total expense lower than 30 USD/tCO2 captured. Hasan et al. [25] later discovered that the cost of the CCUS network falls between 58.1–106.6B USD/year when emissions are reduced by 50–80%. In contrast, Hasan et al. [26] attained a reduction of 80% in CO2 costs, utilizing a CCUS infrastructure that cost around 44 USD/tCO2 recovered. Zhang et al. [10] found that the carbon structure can achieve a 50% reduction in CO2 emissions. This comes at a cost of 2.3B USD/year but also generates 0.77B USD/year in income from oil recovery.
While minimizing the overall cost, other CO2 utilization options have been considered in the literature. Bique et al. [27] produced methanol through CO2 hydrogenation in Germany: The results indicate that the network could generate profit when green hydrogen is provided without any associated expense. Methanol is also produced via methane dry reforming in Leonzio et al. [28] for a CCUS supply chain located in Germany. A significant quantity of methanol (203 Mt/year) was generated to reduce emissions in this study.
Different CO2-based products are considered in Leonzio et al. [28] for a supply chain in Germany: methanol, concrete, wheat, lignin, polyurethane, calcium carbonate, urea, and concrete by red mud. The findings indicate that the overall costs amount to around 98B EUR/year, and the payback period is approximately three years [29]. On the other hand, only methane is produced through a power-to-gas system from CO2 in the study by Leonzio and Zondervan [30], who presented a mathematical model that aims to produce methane from CO2 with minimum overall costs in Italy through the power-gas system. According to another study by Leonzio et al. [31], as the economic analysis is conducted, calcium carbonate is identified as the most suitable product for carbon sequestration in the UK.
CO2 utilization for mineralization is considered in the work of Ostovari et al. [32], where CO2eq abatement costs of individual mineralization plants in the supply chain range from 110 to 312 EUR/tCO2 avoided. In Sun et al. [33], a CCUS framework for China was developed to minimize costs: At a 90% capture rate, storage and enhanced oil recovery costs 20.3 USD/tCO2, while the annual emission reduction is 212 MtCO2 more.
Other mathematical models for carbon supply chains have optimized the net present value (NPV) [33,34,35]. In addition to the NPV, the profit has been considered in the optimization of carbon supply chains.
In Kegl et al. [36], the results show that CCUS technology is only profitable if the price of CO2 emissions is higher than 110 EUR/tCO2 emitted. In Nguyen et al. [37], the production of various CO2-based chemicals results in a yearly income of 162.21B EUR/year, achieved by a 40% reduction in emissions. Rakhiemah and Xu [38] optimized the productivity of a carbon network by extracting oil from CO2 sequestration. The researchers discovered that at an oil price of 40 USD/bbl, the levelized net profit amounts to 3.13 USD/tCO2.
Some works in the literature consider the amount of captured CO2 as the objective function, as in Fan et al. [39], where the CCUS cost is a constraint in a supply chain for China. The results show the optimal amount of stored CO2 in the saline aquifer and the amount of oil recovered.
Social aspects could also be considered in the optimization, as in Derakhti and Gonzales [40].
Today, many researchers have tried to enhance the efficiency of CCUS systems by considering simultaneously various factors, including mainly economic and environmental effects.
In the study conducted by Leonzio et al. [41], the objective was to optimize overall expenses and the quantity of collected CO2 in the CCUS network. Similarly, it was conducted by Zhang et al. [42], where the findings indicate that the most economically efficient option’s levelized expenses and CO2 emissions are around 25 USD/tCO2 and 37 MtCO2eq, respectively. Conversely, these factors for the most environmentally efficient option amount to 67.84 USD/tCO2 and 19.36 MtCO2eq, respectively.
There is a notable desire to optimize CCUS supply chains simultaneously with respect to economic and environmental factors, and the development of a mathematical model integrating the life cycle assessment into source-sink matching is missing in the existing literature. The present work means to fill this gap.
In addition, the exact geographical locations of emission sources, use/sequestration sinks, and details of different CO2-derived synthesis routes and chemical products are also incorporated into the CCUS system in order to provide more practical and meaningful solutions.
2. Methodology
2.1. Problem Description
In this paper, the primary purpose is to develop an optimization for planning and constructing a large-scale and complete CCUS infrastructure for a given objective function in Germany. The overall network scheme of the carbon infrastructure includes CO2 sources from flue gases, CO2 capture facilities, CO2 transport modes, CO2 storage/utilization sites, and different CO2 utilization paths and CO2-based products.
Given:
- Locations, types, annual quantities, and flue gas properties of CO2 sources;
- CO2 capture technologies/materials and correlations of capture cost;
- Cost function of CO2 transportation;
- Locations of CO2 utilization sites, parameters of different CO2 conversion process paths, and annual market demands for various CO2-based products;
- Location, correlations of CO2 storage cost, storage capacity, and limit of storage site.
Determine:
- Which emission sources are selected with the corresponding amount of CO2 captured by employing which capture technology/material combination;
- Which sites and conversion paths are chosen for producing CO2-based products, and how much these products are produced per site;
- Which sites are selected for injecting and storing CO2, and the quantity of CO2 that is chosen for each site;
- Type of CO2 transport and then the overall system topology.
To formulate a mathematical framework for the CCUS network, several assumptions must be made:
- One-to-one coupling refers to a situation where there is a single emission source that is connected to a single capture node, and there is only one capture node that is linked to a single source node.
- A capture plant is established at the same site as an emission source for preventing the transportation of flue gases.
- The pipeline is considered as the unique transport in CO2 logistics.
- The CCUS infrastructure keeps unchanged over the 30 years and is in steady state conditions.
- All CO2-based synthesis processes use the feed at 1 bar, 40 °C, and 90 mol% purity of CO2.
- Different CO2-based products can be synthesized at the same utilization sites and within existing chemical plants.
- Due to stationary conditions, the market quantities and prices of CO2-based products are constant over time
- The specified production sites are considered to have a high or infinite production capacity.
- The distances between various points are determined by utilizing their respective latitude and longitude coordinates.
2.2. Model Formulation
2.2.1. Sets, Parameters, and Variables
The MILP model is composed by indices, parameters, and variables. An index is used to describe every component of the supply chain network model: emission sources are denoted by “i”, capture plants by “j”, sequestration and utilization sinks by “k” and “a”, respectively, CO2-based products by “p”, utility consumption types and raw materials for CO2 synthesis processes by “u” and “r”, and CO2 conversion paths by “m”.
Binary and continuous variables are employed to characterize and enhance the system’s efficiency. The binary variable reflects the decision of a particular source i, and capture facility j when it equals 1. The continuous variables , ranging from 0 to 1, quantify the quantity of CO2 gathered from source i using technique j and either stored at site k or utilized at plant a to make the product p.
Several parameters are defined in the overall MILP model for each section of the supply chain as reported in the Supplementary Files with their respective values.
2.2.2. Equality Constraints for the Economic Model
Regarding the economic analysis, the CCUS infrastructure mathematical model includes several equations.
The overall yearly cost (€/year) of the overall carbon system comprises CO2 capture and compression cost CO2 transportation costs , CO2 storage costs , and CO2 utilization costs (Equation (1)).
Capture and compression costs (€/year) for the sequestration and utilization units are assessed using the subsequent equations (Equations (2)–(4)).
with as the flue gas dehydration costs for the sequestration and utilization stages, respectively, in €/year (through the absorption of the tri-ethylene glycol of €9.28/tCO2, involving capital and operating costs [43], the capture investment costs for the sequestration and utilization stages, respectively, in €/year, and the capture operating costs for the sequestration and utilization stages, respectively, in €/year.
The annual capital and operating costs of the capture technology are determined by the subsequent relationships, which depend on the flue gas flow rate and CO2 concentration [20,25] (Equations (5) and (6)).
with as the capture technology-material related parameters [25] supported in the Supplementary Files, and the quantity of flue gas mitigated and transported to the sequestration and utilization sites, respectively, in mol/s.
CO2 transportation costs (EUR/year) are determined by adding together the annual costs for investment and operation, according to the next correlation (Equation (7)).
with as the capital cost recovery achieved by applying a 10% interest rate over a period of 30 years, the capital costs (M EUR), and the operating costs (4% of the investment cost) (M EUR/year).
The transportation capital cost is calculated by the cost of transportation to the storage and utilization stages [44](Equations (8)–(10)).
with as the coefficients of 0.019 and 0.533, respectively [44], the distances calculated based on the latitude and longitude, the overall CO2 emission from the source i in t/year, the continuous variables ranging from 0 to 1 and quantifying the fraction of CO2 gathered from source i using the technique j and either stored at site k or utilized at plant a to make the product p, a terrestrial factor of 1.2 [45], and 16 the Km incorporated into the main distance as a result of account extra paths associated with the process [46].
Total CO2 storage costs (EUR/year) are calculated by the capital (€) and operating (EUR/year) costs [43] (Equations (11)–(14)).
with as the model parameters equal to 1.53M EUR/km and 1.23M EUR, respectively [44], the well-depth of 3 km [27], the number of wells needed for storage k [25,47], and the maximum injection capacity of a well of 912.5 KtCO2/year [27].
The cost of utilizing technologies primarily consists of capital expenditure and the expenses for raw materials and utilities. However, reliable capital expenditure data for most CCU technologies are unavailable [48]. Therefore, the utilization cost (EUR/year) is only calculated by the raw materials and utilities costs in this study [48,49] (Equation (15)).
with as the prices of raw material and utility, respectively in EUR/t or EUR/GJ, the amount of raw material r of synthesis route m in t/year, and the consumption of utility u of synthesis route m in GJ/year.
The CCUS network can create some benefits through the sale of CO2-based commercial chemicals. The total annual revenue (EUR/year) is determined by adding up the production quantity of each primary product (t/year) and by-product (if it exists) (t/year) by the selling price of each product (€/t) as presented in Equation (16).
The overall annual profit (EUR/year) of the CCUS supply chain network is therefore determined by subtracting the overall annual cost from the overall annual revenue (Equation (17)).
2.2.3. Equality Constraints for the Environmental Model
In this model, the research utilizes the life cycle GHG emission evaluation method to measure environmental impacts for the entire CCUS system. In particular, the environmental impact reduction of the framework compared to the conventional production process is evaluated in this research. To this aim, Equation (18) calculates life cycle GHG emission from each section of the CCUS network. It is important to note that this research explicitly examines the potential emission decrease of the carbon system with and without CO2-based conversion technologies by using Equation (19), which computes the GHG emission of conventional synthesis processes for the same products. Therefore, the overall life cycle GHG reduction concerning a business-as-usual (BAU) level is presented by Equation (20) [48]. Additionally, this paper does not consider the indirect carbon emissions associated with the construction, operation, and disposal of the equipment in the carbon system.
with as the GHG emission coefficients of CO2 capture, transportation, and storage steps, respectively, in tCO2eq/t [50], the GHG emission coefficients of raw material r, and product p, respectively, in tCO2eq/t [48], the GHG emission coefficient of utility u in tCO2eq/GJ [48], the GHG emission coefficient of product p by the reference conversion path in tCO2eq/t [48], the GHG emission coefficient of CO2 utilization path m in tCO2eq/t [48], and the amount of CO2 captured by the CCUS network in t/year. All coefficient values can be found the Supplementary Files.
2.2.4. Inequality Constraints
Different constraints are used in the resolution of the MILP model for the carbon supply chain. As defined here, each source can only be assigned a single capture technology-material combination (Equation (21)).
with as the binary variable reflecting the decision of a particular source i and capture facility j when it equals 1.
The quantity of CO2 injected is restricted to the annual maximum capacity (assuming 508 Mt [27]) of the sequestration site (Equation (22)).
The selection of capture technology-material combination for every source is determined by the concentration of CO2 in the feed as controlled by the limitation below (Equation (23)).
with as the CO2 concentration in flue gas from the source i in mol%, the lowest CO2 concentration processing limit for the capture facility j in mol%, and the highest CO2 concentration processing limit for the capture facility j in mol%.
To transform the non-linear mathematical problem into a linear one, the Glover linearization constraint is utilized in the subsequent equations (Equations (24)–(26)). In this study, a constant value of 0.9 is employed to ensure that the maximum CO2 removal of 90% is achieved for every source.
The Glover linearization is due to the fact that in the capture cost, there should be a product between a continuous and binary variable. To make it linear, it is possible to consider the binary variable in the product, but it is necessary to constrain the continuous variable between the corresponding binary ones. Errors due to this linearization are neglected.
For this research, the amount of raw material and utility consumption of each synthesis path is assumed to have a linear relationship to that of the primary product [48]. Notably, each conversion path only has a single primary product, referred to as the main product, while others are considered by-products. The provided equations (Equations (27)–(29) for raw materials (including CO2) and utility consumption, respectively, while Equation (30) is for by-product production quantity) are used to determine the various aspects of each synthesis process.
with as the consumption coefficients of CO2, raw material, and utility per unit of the primary product, respectively in t/t or GJ/t while is the production coefficient of by-product per unit of the primary product in t/t [48]. All coefficient values can be found in the Supplementary Files.
To guarantee the mass balance of CO2 in the supply chain, Equation (31) is introduced, while Equation (32) ensures that captured CO2 is delivered to the utilization sites. Equation (33) is utilized to restrict the production capacity of product p, while satisfying the annual reduction target of CO2 emissions requires Equation (34).
2.2.5. Objective Functions
The proposed CCUS system aims to optimize (in particular, to maximize) simultaneously both the total annual profit and the overall life cycle GHG reduction , which can assess economic and environmental outcomes when planning the CCUS infrastructure. The general bi-objective model can be expressed as follows (Equations (35)–(37)):
s.t
with as the continuous variables, the binary variables, and the integer variables of the problem. The problem is defined as a mixed-integer linear programming model (MILP) and can be addressed by obtaining a set of Pareto optimal solutions, which demonstrates the trade-off between environmental and economic considerations in the case study. The bi-objective problem is typically solved by two main methods: the weighted-sum method and the ε-constraint method [51]. In this study, the ε-constraint method is selected because it is rigorous for the nonconvex problem. As a result, the bi-objective model is expressed below (Equations (38)–(41)), according to the formulation of the ε-constraint method.
s.t
The ε-constraint methodology facilitates the transformation of a bi-objective into a single optimization problem in which the additional target is treated as a new constraint within a specified ε range [52]. As a result, the graph of the Pareto front, consisting of non-dominated or non-inferior solutions, is generated by varying ε values. In this study, the objective function is to maximize the total annual profit, whereas the inequality constraint is the overall life cycle GHG reduction.
2.3. Case Studies
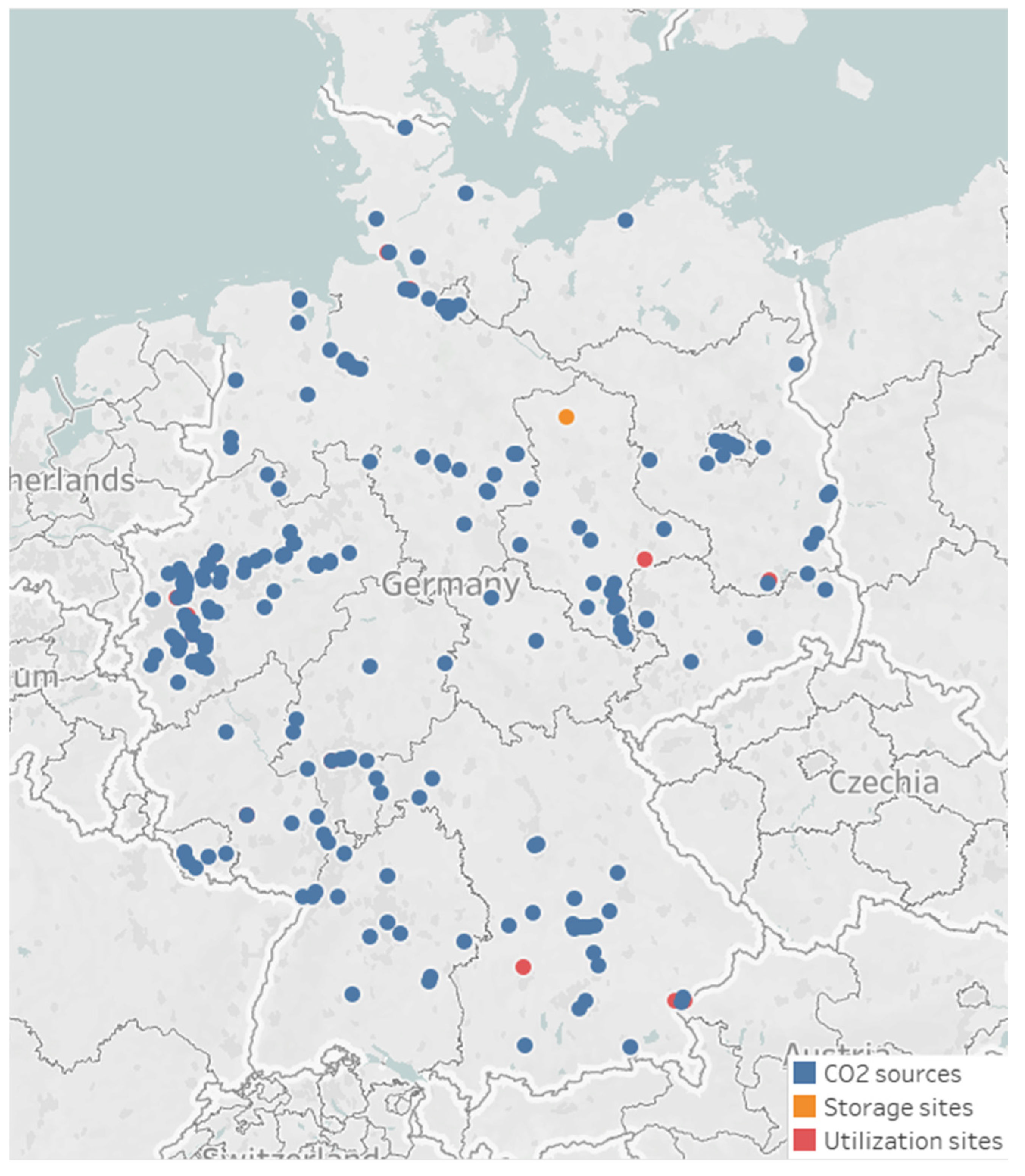
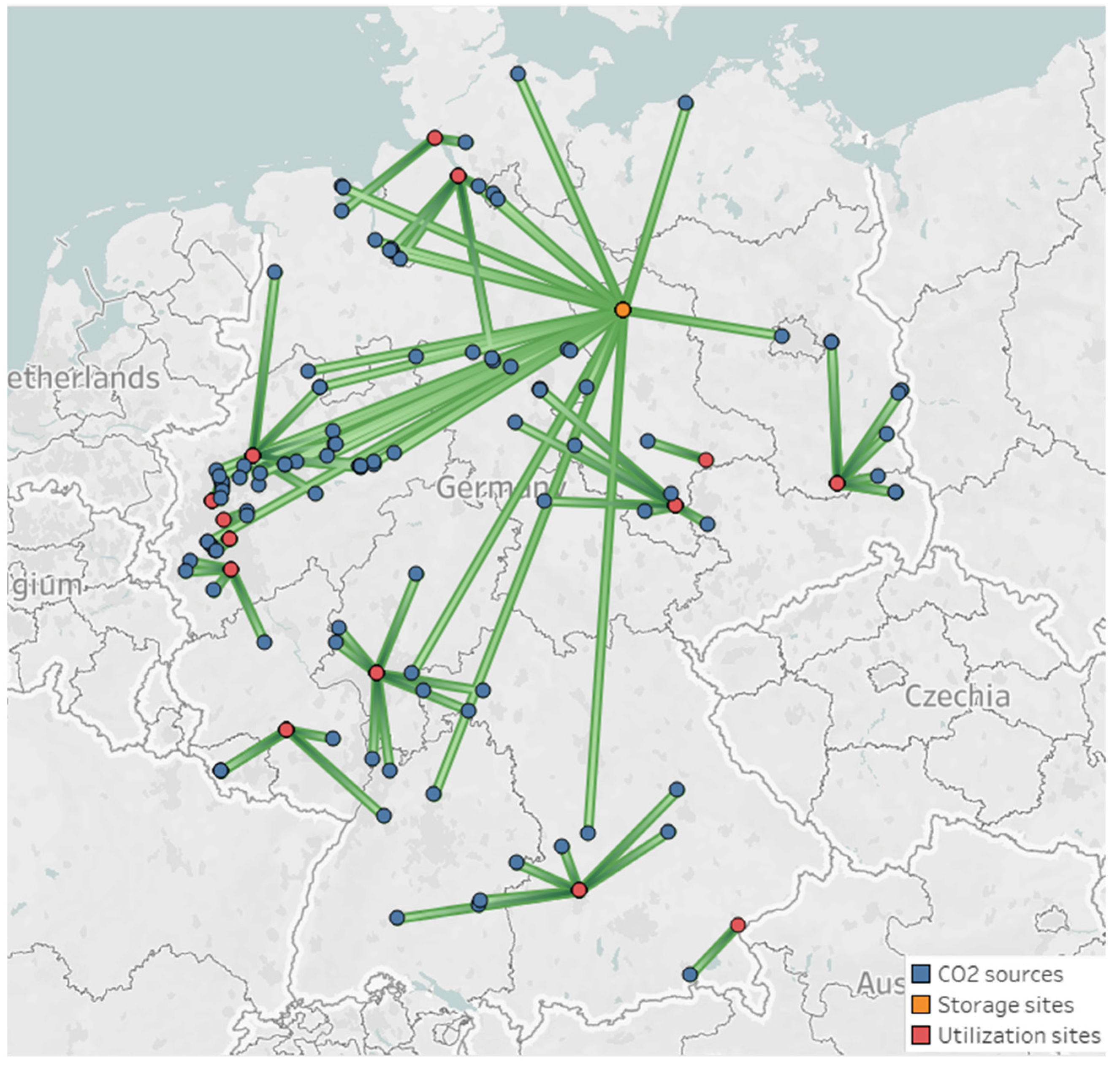
This part examines a practical case study of significant sources of emissions in Germany to verify the efficiency of the planned CCUS infrastructure. Nguyen et al. [37] provided information regarding the details of emission sources and sequestration/utilization sinks in Germany. The distribution of all CCUS system elements across Germany is presented in Figure 3.
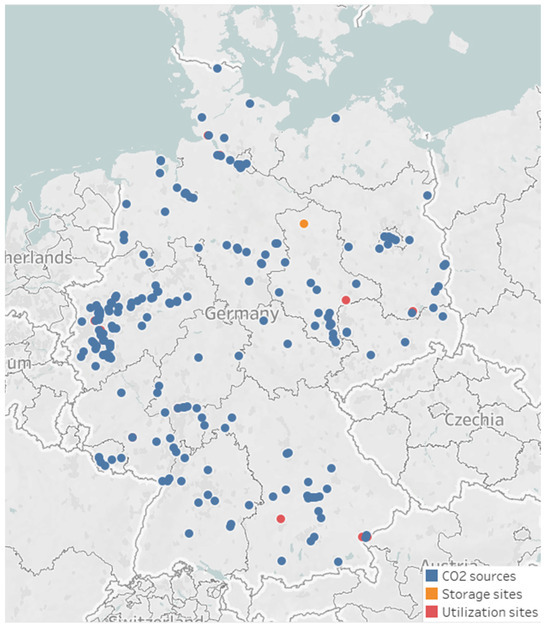
Figure 3.
The location of all emission sources, storage, and utilization sites in Germany.
The research focuses on the 241 primary stationary sources of CO2 emissions, which collectively generate around 405 MtCO2/year. These sources account for around 45% of Germany’s yearly CO2 emissions. The specified flue gases can have a CO2 content ranging from 1 to 60 mol%, which differs based on the industrial applications. The storage facility is settled in Altmark [27] with a storage capacity of 508 Mt, while 15 chemical parks serving as production sites are expected to have the capability to create all CO2-based chemicals through 15 candidate synthesis routes in which two or more routes can be used to synthesize the same product. The details for the characteristics of the selected emission sources, as well as storage/utilization sites in Germany, are shown in the Supplementary Files.
Various technology-material combinations are taken into account for the capture of CO2. The proposed materials for absorption technology include monoethanolamine (MEA) at 30% wt and piperazine (PZ) at 40% wt. The membrane technique considers the use of POE1, POE2, and FSCPVAm. In addition, this work utilizes 13X, AHT, MVY, and WEI zeolites for pressure- and vacuum-swing adsorption (PSA and VSA) technologies. Note that the pipeline is recognized as the primary means of transportation of captured CO2.
The captured CO2 is converted into eight valuable primary chemicals, which encompass synthetic gasoline and diesel, methanol, acetic acid, dimethyl ether (DME), dimethyl carbonate (DMC), formic acid (FA), and succinic acid (SA). In addition, the synthesis processes also produce by-products such as liquid propane gas (LPG), ethylene carbonate (EC), and ethylene glycol (EG). The details for the characteristics of the targeted conversion paths are presented in the Supplementary Files.
3. Results and Discussion
The ε-constraint technique is exerted to deal with the bi-objective model for optimizing the structure of the carbon system in Germany. The target is to maximize the total annual profit and the entire life cycle GHG reduction. The model is implemented and addressed in the Advanced Interactive Multidimensional Modeling System (AIMMS) software with the CPLEX 22.1 solver on a laptop equipped with an Intel Core i7 processor, 3 GHz, and 32 GB RAM. The national CCUS supply chain network comprises 4,718,531 variables (3133 integer variables) and 5,659,167 constraints.
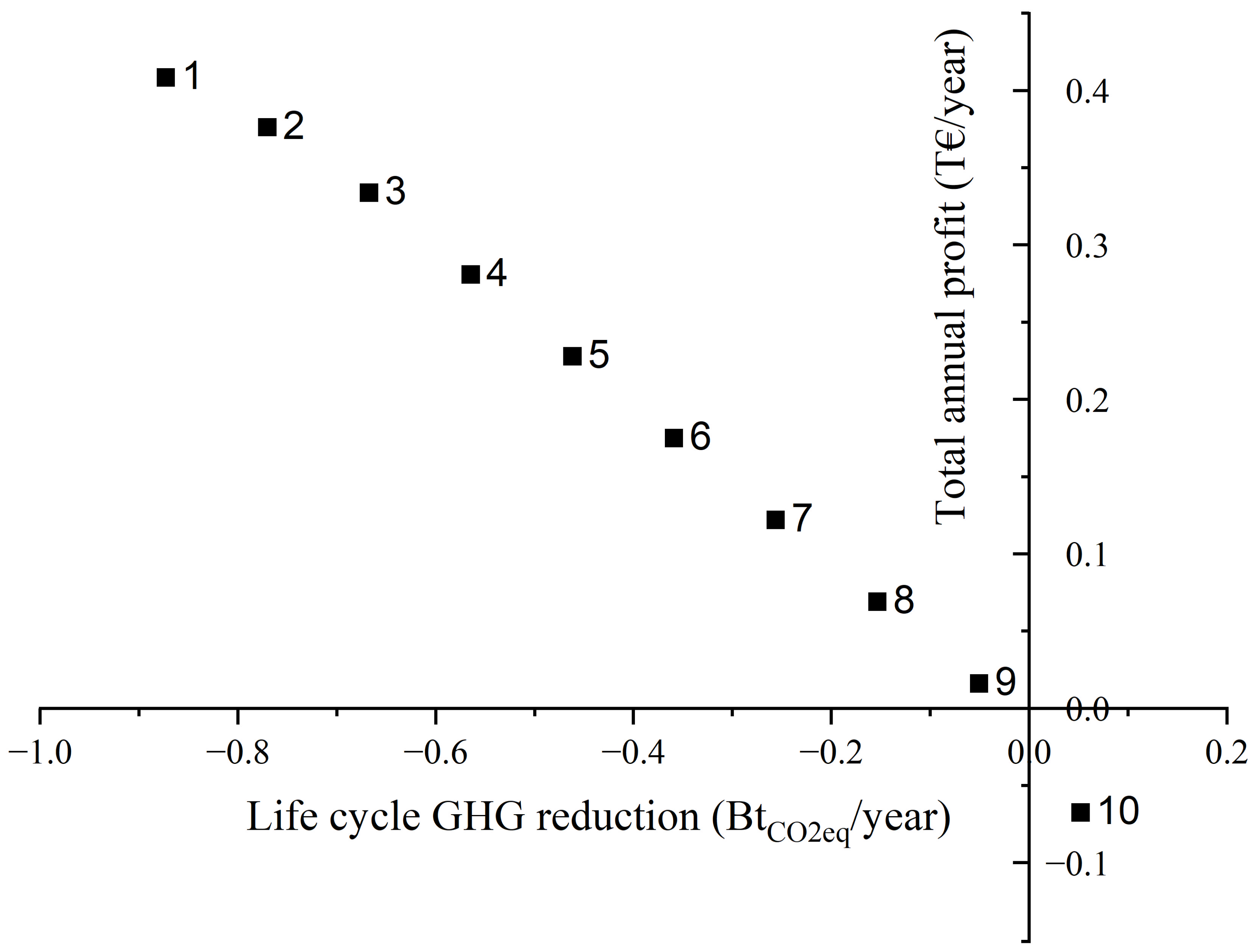
Figure 4 depicts the Pareto graph derived from addressing the bi-objective model. It is noted that each point corresponds to a distinct supply chain structure in relation to network development and a set of decisions. The network topologies on the left are typically more economical, while those on the right aim to maximize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions across the whole life cycle. Within the set of Pareto-optimal solutions, two extreme points (Points 1 and 10) located on the far left and right sides are considered too extreme as they completely ignore the impact of the opposing target.
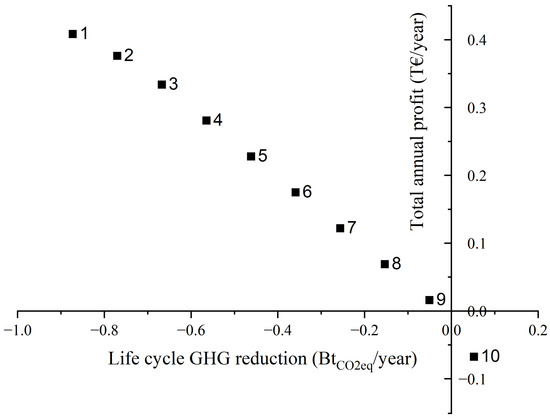
Figure 4.
The optimal Pareto curve for the bi-objective problem (total profit vs. life cycle GHG reduction).
The Pareto curve demonstrates a clear correlation between the rise in the overall life cycle of GHG reduction and the drop in profits. More precisely, the total annual profits for CO2 capture decrease from 409 to −68B EUR/year when achieving reductions of GHG emissions from −873 to 51 MtCO2eq/year, respectively. Consequently, the implementation of measures to reduce the environmental impact would result in a decrease in the overall annual profits. Undoubtedly, the two targets have trade-offs, as reducing one target requires compromising the other.
3.1. Cost-Optimal CCUS Supply Chain Network
To meet Germany’s aim of cutting greenhouse gas emissions by 50% by 2030, 203 Mt/year of CO2 is mitigated, and it costs about 166B EUR/year in the most cost-efficient supply chain of CCUS (Point 1 of the Pareto front with the corresponding topology shown in Figure 5). Therefore, the supply chain effectively prevents the release of GHG emissions at an average cost of 817 EUR/t CO2. The primary factors that contribute to the cost of reducing CO2 emissions in the CCUS network are raw material costs—around 85% of the total cost (141B EUR/year) and utility costs—about 11% of the total costs (19B EUR/year). Interestingly, the yearly expenses for capture and compression in this study only account for 3% of the total costs, corresponding to around 5.42B EUR/year. When operating, the network generates an annual revenue of 574B EUR/year. As a result, the benefits of selling CO2-based chemicals allow the CCUS supply chain to capture 203 MtCO2/year at a total yearly profit of 409B EUR/year or 2014 EUR/tCO2. Notably, the manufacture and sale of gasoline are the primary drivers of both the expenses, which comprises over 96% or 160B EUR/year, and the profit, which is the only source of income (gasoline was selected as the only product in this case). This could be explained by the exploitation of inexpensive raw materials like natural gas [48]. CCUS technology is a method of reducing emissions; however, there are CO2 emissions connected to each stage of the supply chain. Similar to the costs, the GHG emissions from the utilization stage are still at the dominant share, making up 99% or 1242 MtCO2eq/year. On the other hand, the capture, transportation, and injection processes result in minimal emissions due to their tiny contribution (6.8, 3.04, and 0.01 MtCO2eq/year, respectively). Consequently, this approach has a detrimental effect on reducing GHG emissions, leading to a decrease of −873 MtCO2eq/year. In summary, the cost-effective supply chain network can achieve the government’s aim of reducing 203 Mt of CO2 each year with a profit of 2014 EUR/tCO2, while the life cycle GHG reduction of this supply chain is −873 MtCO2eq/year.
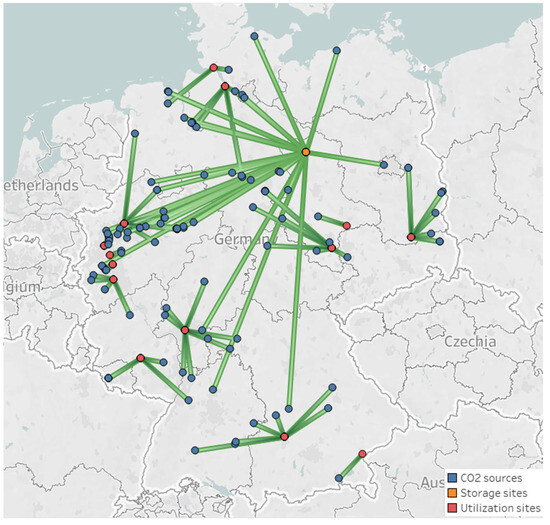
Figure 5.
Mapping of the optimum network at a maximum total annual profit (green lines: connections among sites).
In this design, a total of 106 sources and 14 utilization sites have been chosen. Among the selected CO2 sources, the optimum CCUS network utilizes 76 emission sources exclusively for gasoline production, accounting for the highest CO2 consumption. It is worth noting that the majority of the captured CO2 is transported to the nearest utilization sites to minimize the expenses associated with pipeline construction and operation. Meanwhile, only 31 sources are needed to sequester CO2 into storage locations. As a result, only 0.2 Mt/year of CO2 (0.01%) is directed towards the storage sites, whereas 202.8 Mt/year of CO2 (0.99%) is diverted into utilization sites. In this case, most CO2 tends to be chemically converted rather than stored, primarily due to economic considerations. Interestingly, in this case, only three capture techniques are selected among 14 technology-material combinations. Out of 87 sources, the MVY-based PSA method is the most favored for CO2 capture. It is followed by AHT and WEI-based PSA technologies with fifteen and four sources, respectively. The results are justifiable due to the preference for adsorption-based techniques over the alternatives, resulting from selecting sources with moderate and high CO2 concentrations [42,49].
In order to examine the impact of the supply chain on the economic aspects of specific emission source plants, the study now focuses on several exceptional emission source plants (as shown in Table 1): Kraftwerk Neurath, Kraftwerk Schwarze Pumpe, Kraftwerk Lünen, and Kraftwerk Moorburg. The Kraftwerk Neurath plant has the most considerable amount of captured CO2, with 28.86 MtCO2/year. The significant mitigation of CO2 emissions at the Kraftwerk Neurath plant can be attributed to two factors: (a) its strategic position and (b) its effective integration into the supply chain. Specifically, the Kraftwerk Neurath plant is not only located near the utilization site but also available for the highest CO2 capacity. On the other hand, the configuration of the CCUS supply chain allows the Kraftwerk Neurath plant to mitigate as much CO2 as possible. Nevertheless, producing the enormous amount of conventional gasoline from the Kraftwerk Neurath plant leads to the lowest reduction of life cycle GHG emission (−124.38 MtCO2eq/year), which makes it have the most detrimental effect on the environment. With 2030 EUR/t of CO2 captured, the Kraftwerk Schwarze Pumpe plant has the highest profit in the supply chain for the cost-efficient scenario. However, this plant exhibits a negative value of life cycle GHG emission of −47.49 MtCO2eq/year, which is around 2.6 times lower than that of the Kraftwerk Neurath plant as a result of its lower CO2 captured. Unlike previous plants, the Kraftwerk Lünen plant has the lowest CO2 captured profit and highest CO2eq abatement cost of −34.34 EUR/tCO2 and 38.96 EUR/tCO2eq, respectively. This can be blamed on the fact that all captured CO2 from the Kraftwerk Lünen plant is sent to the storage site that is not only far from the emission source but also lacks economic incentives. The Kraftwerk Moorburg plant avoids the most CO2eq in total, with 0.012 MtCO2eq/year. The favorable location (due to its proximity to the storage site), combined with the supply chain design, results in high avoided CO2eq per ton of CO2 mitigated (0.881 tCO2eq/tCO2) and, consequently, the lowest CO2eq abatement cost for the Kraftwerk Moorburg facility (36.41 EUR/tCO2). It is interesting to notice that all chosen plants are power plants. This is supported by the fact that power plants are the primary contributors of CO2, constituting approximately 75% (or 153 MtCO2/year) of the total CO2 mitigated.

Table 1.
Outstanding emission source plants in the cost-optimal scenario capturing 203 MtCO2/year.
3.2. Climate-Optimal CCUS Supply Chain Network
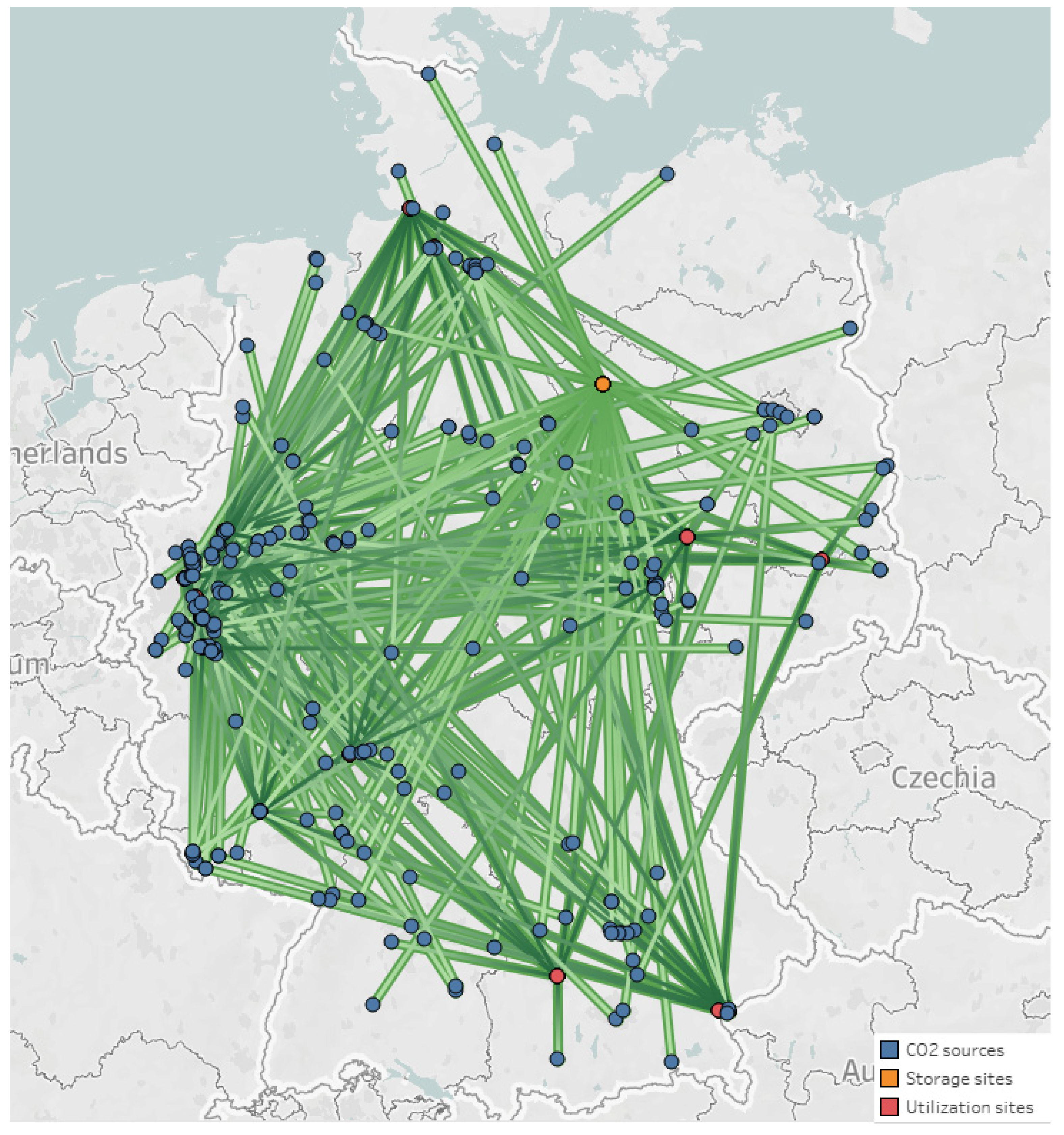
The climate-optimal and the cost-optimal supply chains have the common goal of mitigating 203 Mt of CO2 annually. This case corresponds to Point 10 in the Pareto front, and the corresponding configuration is presented in Figure 6. To achieve the reduction target from the Germany government, the CCUS supply chain necessitates a yearly expense of 148B EUR or around 728 EUR/tCO2 to execute the capture and usage/storage procedures. Among these costs, the most substantial portion (around 94% of the total), amounting to 139B EUR/year, is attributed to the production expenses associated with CO2 utilization. Meanwhile, capture and compression costs rank second with 8.24B EUR/year, followed by transport and injection costs with 0.3B EUR€/year and 0.75M EUR/year respectively. The CCUS network also earns an annual income of 80B EUR/year by selling CO2-based products. Consequently, operating the climate-optimal CCUS supply chain requires a mitigation cost of 67B EUR/year or 332 EUR/tCO2, which can be explained by the rapid income drop in this case while the total costs remain high (equal to 14% and 89% of the corresponding values of Point 1). This scenario is a substantial attempt by the CCUS supply chain to mitigate life cycle greenhouse gas emissions. Similar to Point 1, life cycle emission of the utilization section is still the most significant contributor, accounting for 97% or 274 MtCO2eq/year. However, along with relatively little change in life cycle emission of the capture, transportation, and injection sections, a slump in GHG emissions of the utilization section (by 78% as compared to Point 1) allows the CCUS supply chain to obtain a dramatic reduction of 51 MtCO2eq/year in life cycle emissions. This could be explained by the fact that the CCUS network, in this case, employed sustainable synthesis paths in which renewable hydrogen is frequently promoted for CO2 hydrogenation due to its superior performance in mitigating CO2 emissions and its increased potential in forming a carbon cycle loop [48,49]. To summarize, the climate-optimal supply chain network can successfully meet the government’s objective of capturing 203 MtCO2/year and avoiding 51 MtCO2eq/year at an average sequestered cost of around 332 EUR/tCO2.
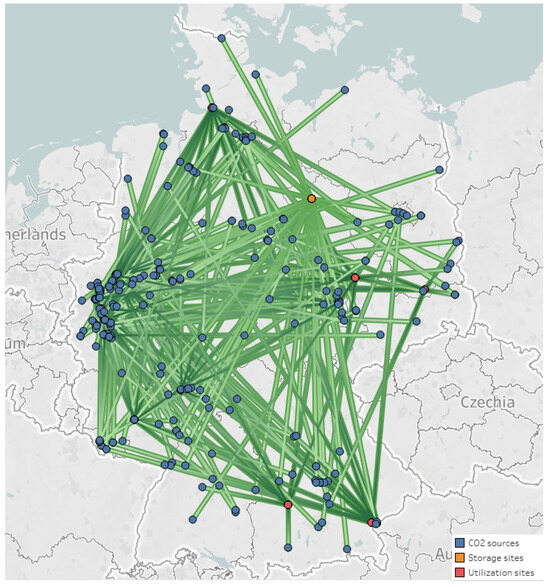
Figure 6.
Mapping the optimum network at maximum life cycle GHG reduction (green lines: connections among sites).
In this case, all emission sources and sequestration sinks are considered. Similar to Point 1, most CO2 is often chemically converted with 202.5 MtCO2/year (99.73%) and 187 sources rather than stored with only 0.54 MtCO2/year (0.27%) and 56 sources, although the quantity of CO2 being transported to storage sites in this case is nearly triple of that in the most profitable scenario. This can be explained by the fact that utilization can transform a huge amount of captured CO2 into valuable chemicals, creating a carbon-neutral cycle [48,49]. In particular, CO2-based chemicals in the CCUS network mainly focus on methanol (with a production rate of 99 Mt/year), with 137 selected sources contributing 157 Mt/year of captured CO2. Consequently, the sale of methanol generates an annual revenue of 48B EUR/year, accounting for approximately 60% of yearly total sales. On the other hand, acetic acid production (24 Mt/year) involves 35 sources and results in 26.5 MtCO2/year. Acetic acid manufacture ranks second in revenue, contributing approximately 28% of the total revenue (equivalent to 22.2B EUR/year), while the remaining 12% (around 10.1B EUR/year) comes from other products (such as DME (6.9 Mt/year), DMC (1.6 Mt/year), and formic acid (1.3 Mt/year)). In contrast to the cost-effective situation, more capturing techniques and materials (specifically, four out of thirteen alternatives) have been selected. Specifically, there are 150 sources that use 13X-based VSA, 47 use WEI-based PSA, 31 use PZ-based absorption, and 13 use POE2-based membrane methods. Contrary to Point 1, the reason for such changes in this case is that the capture cost is determined by both the emission source composition and the quantity of mitigated CO2 [49]. This also emphasizes the significance of carefully choosing materials and technologies in the CCUS supply chain network. Interestingly, in contrast to the cost-effective supply chain, the climate-optimal supply chain focuses on integrating new sources of CO2 into the supply chain to prevent GHG emissions.
Similar to the cost-optimal scenario, the study also analyzes the influence of the supply chain on the economic features of certain emission source facilities in the climate-optimal case. These plants include Kraftwerk Weisweiler, Kraftwerk Ibbenbüren, Anlage zur Papierherstellung, and TRIMET Aluminium SE, as indicated in Table 2. It can be seen that this case is entirely different from the previous case. All source plants possess the ability to decrease their life cycle greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, all selected plants are employed to synthesize sustainable CO2-based chemicals. The Kraftwerk Weisweiler facility holds the record for the highest quantity of captured CO2, with an annual volume of 13.04 Mt. However, this plant only achieves a reduction of 1.63 MtCO2eq/year in life cycle emissions, which leads to a low avoided CO2eq per ton of CO2 captured (0.125 tCO2eq/tCO2). In addition, the profit generated from the sale of green methanol (synthesized from CO2 and renewable hydrogen) is insufficient to offset the expenses incurred for CO2 mitigation, resulting in capture and abatement costs of 442.5 EUR/tCO2 and 3534 EUR/tCO2eq, respectively. In fact, the abatement cost of this facility is significantly higher than those of technologies implemented by 2030, as indicated in the IPCC report (around 210 EUR/tCO2eq). Meanwhile, the Kraftwerk Ibbenbüren plant has the highest total CO2eq avoidance of 2.59 MtCO2eq/year while capturing 3 MtCO2/year. The favorable location (due to its proximity to the production site) of this plant, combined with the high market price of acetic acid, results in a captured profit of 381.82 EUR/tCO2 and a mitigation benefit of 441.62 €/tCO2eq. Notably, the Kraftwerk Weisweiler and Kraftwerk Ibbenbüren facilities are power plants that remain the biggest sources of CO2 (with 129 sources and 140 Mt/year of CO2 captured) in the climate-optimal case. The Anlage zur Papierherstellung plant, like Kraftwerk Ibbenbüren plant, is used to produce acetic acid with the highest captured profit and a mitigation benefit of 386.64 EUR/tCO2 and 447.19 EUR/tCO2eq, respectively, and consequently a relatively high avoided CO2eq per ton of CO2 captured (0.865 tCO2eq/tCO2). With 482.54 EUR/t CO2 captured and 3873 EUR/t CO2eq avoided, the TRIMET Aluminium SE facility has the highest captured cost and abatement cost in the supply chain for the climate-optimal case. The high captured and abatement costs of the TRIMET Aluminium SE facility are due to (a) its location and (b) its high methanol production capacity.

Table 2.
Outstanding emission source plants in the climate-optimal scenario capturing 203 MtCO2/year.
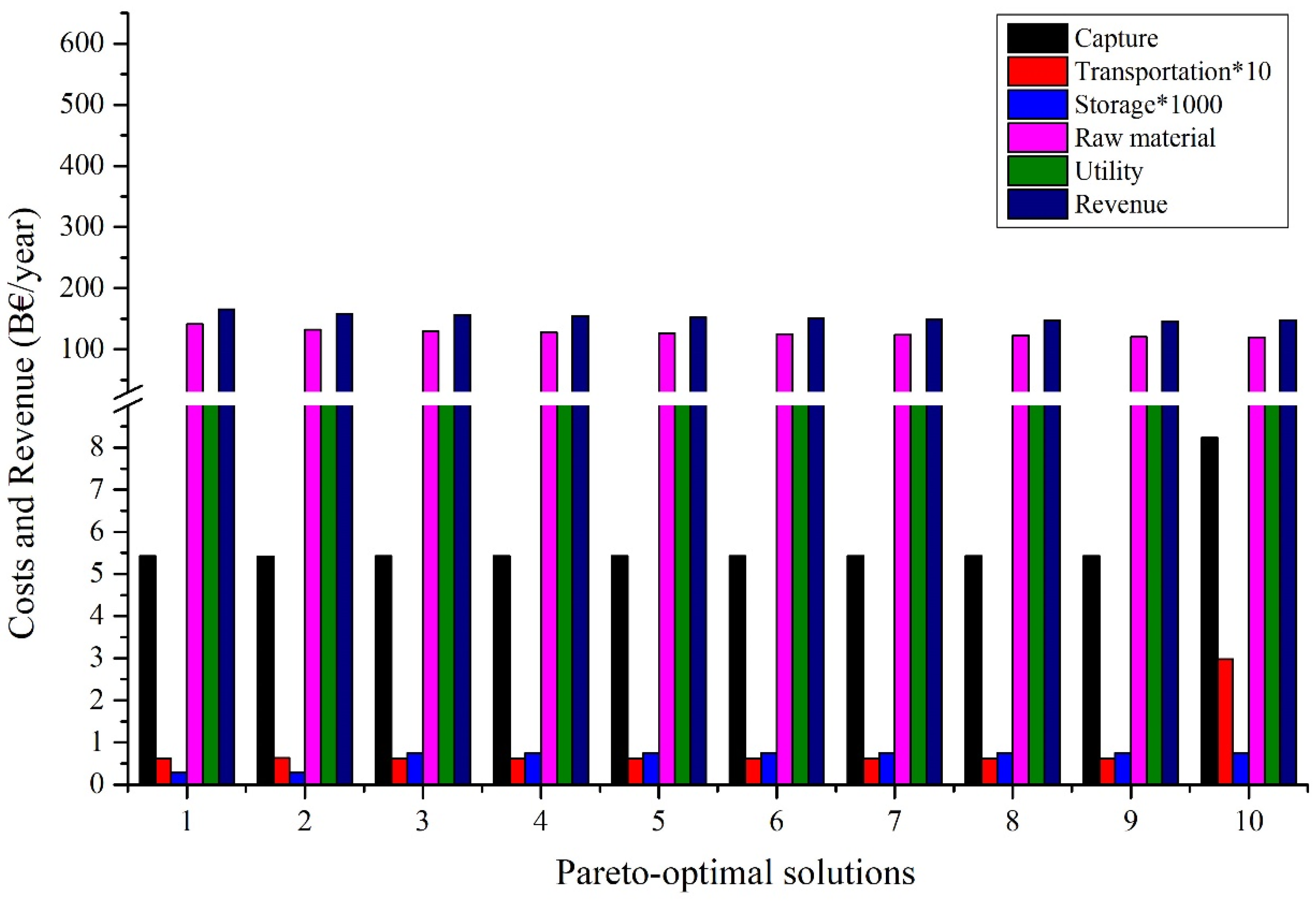
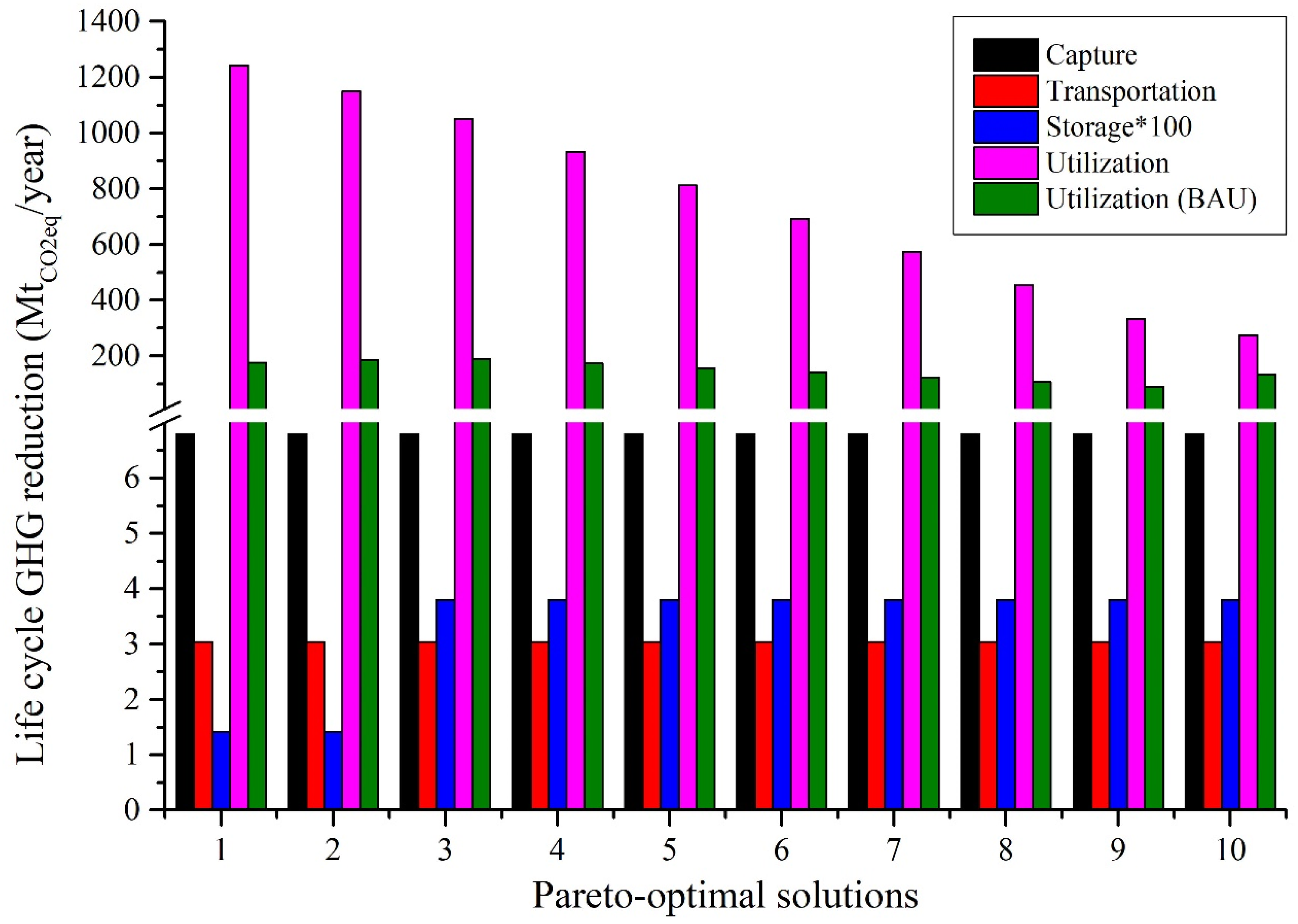
3.3. Cost and Life Cycle GHG Reduction Distribution
Figure 7 and Figure 8 provide a detailed analysis of the costs and environmental outcomes of all the Pareto optimum cases. As can be seen from Points 1 to 10, it is apparent that there is a dramatic increase in the reduction of life cycle GHG (from −873 to 52 MtCO2eq/year), while a slight decrease is seen in the total annual expense (from 166 to 148B EUR/year or by 11%). This tendency is also evident in the primary components of the overall cost, including the raw material and utility costs. However, there is a notable rise of 1.5, 4.8, and 2.7 times in the expenses associated with capture (from 5.42 to 8.24B EUR/year), transportation (from 0.06 to 0.3B EUR/year), and injection (from 0.28 to 0.75M EUR/year). Furthermore, the CCUS network has experienced the most significant decline in sales, from 574 to 80B EUR/year. This phenomenon can be linked to the pursuit of a considerable reduction in GHG emissions throughout the life cycle. As discussed above, the CCUS system often employs renewable hydrogen as a primary resource in such cases. While renewable hydrogen has a lower carbon dioxide footprint, it is nevertheless costly. As a result, this substantially reduces GHG emissions across the life cycle but with low profitability. The findings of this research indicate that, in all cases, the production and sale of critical CO2-derived chemicals could be a better solution than solely injecting CO2 for storage purposes. However, to lower the life cycle GHG emissions of the whole CCUS system, the CO2 storage option tends to increase its role, in addition to the utilization of CO2.
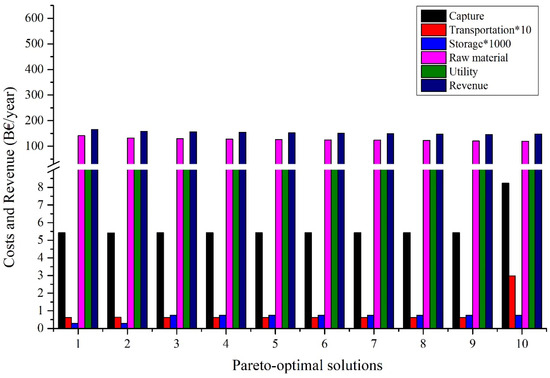
Figure 7.
Cost distribution for different points of the Pareto curve.
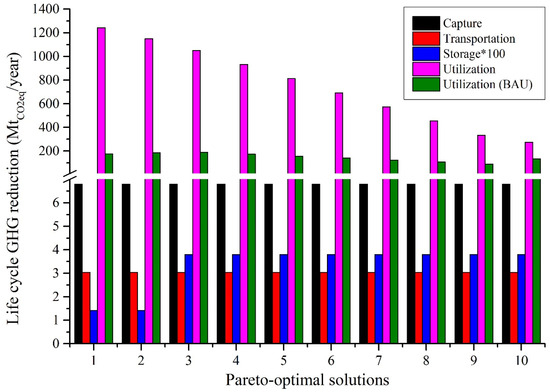
Figure 8.
Life cycle GHG reduction distribution for different points of the Pareto curve.
As shown in the previous results, the network structure will be heavily influenced by the greenhouse gas emission reduction level. Interestingly, as discussed before, there are two extreme case studies (Points 1 and 10). However, the middle points (Points 2 to 9) are other optimal solutions as they balance costs and environmental considerations. The resulting trade-offs will offer valuable insights into the CCUS design problem that could potentially enhance both cost efficiency and environmental sustainability.
4. Conclusions
A comprehensive bi-objective mixed-integer linear programming model was advanced in this work to find the maximum annual profit and life cycle GHG emission reduction for a CCUS supply chain in Germany.
Specifically, this research integrates the life cycle assessment (LCA) approach into the entire procedure of the complex CCUS system that involves actual geographical locations of several emission sources, capture plants, sequestration and utilization facilities, and details of various CO2-based conversion paths and chemical products.
The outcomes indicate that the profit for the most cost-effective option is 2014 EUR/tCO2 at a life cycle GHG reduction of −873 MtCO2eq/year. Conversely, achieving a decrease of 52 MtCO2eq/year in greenhouse gas emissions during the whole life cycle would need an investment of around 332 EUR/tCO2. Therefore, decision-makers should carefully choose to balance emission reduction goals with economic constraints. Additionally, it is evident that the utilization stage plays a crucial role in both the economic and environmental aspects of the CCUS network. As a result, the primary necessity in the design of CCUS is the development of more sustainable pathways for CO2–based chemical production.
The results of this research emphasize several significant practical implications of considering environmental effects when implementing a large-scale carbon network in Germany. On the one hand, a correlation between two primary objectives—economic and environmental—is established. This relationship could function as a decision support system for policymakers to decide the most effective strategies for deploying CO2, including identifying optimal locations and methods for capturing CO2 as well as proper pathways for utilizing CO2. On the other hand, incorporating environmental impacts as a measurable criterion can generate additional potential network configurations. By following this approach, a diverse range of Pareto-optimal solutions can be created and chosen based on the decision-makers’ desires. Furthermore, the case study of a carbon statewide supply chain in Germany serves as a suitable reference example before implementing the whole CCUS system at different levels and in various countries.
There are multiple restrictions in this research. One issue is that it neglects to include uncertainty analysis. This analysis operates under the assumption that the parameters of economic costs, source emissions, raw materials, and utility consumption are unchanging. In fact, these parameters can be influenced by factors such as the circumstances of carbon sources and sinks, transportation routes, and technology advances, resulting in a broad range of possible outcomes. Moreover, a shift in manufacturing methods and the adoption of clean technology will have a profound impact on the distribution of carbon emissions in Germany. Therefore, implementing proposed CCUS techniques may not be suitable for practical management in this context. Finally, the CO2 emissions linked to the construction, operation, and disposal of equipment in the supply chain have been excluded in this study.
To modify the model to align with the progress of CCUS, future research should examine the optimization model in the dynamic state to forecast the outcomes of CCUS technology during various time periods. Besides, further sensitivity studies can be performed to investigate the effects of other parameters, such as the selling prices of the CO2-based products and process-specific parameters of the synthesis technologies, on the optimal solutions. The social benefits of deploying CCUS technology, including its impact on local job creation and economic development, also should be considered.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr12081575/s1, Table S1: Estimated parameters for the cost model for the capture and compression; Table S2: Upper and lower bound for 14 capture technology-material combinations; Table S3: CO2 sources: type, composition, emission and geological information; Table S4: Potential reservoirs: type, capacity and geological information; Table S5: Potential utilization sites: geological information; Table S6: Summary of CO2-based synthesis routes; Table S7: Raw material consumption (t of raw material/t of primary product); Table S8: Utility consumption (GJ of utility/t of primary product); Table S9: Production and emission (t/t of primary product); Table S10: Raw material - Lifecycle GHG emission in production and market price; Table S11: Utility - Lifecycle GHG emission in production and market price; Table S12: Product - Lifecycle GHG emission in production (via conventional means), market price, and global market demand; Table S13: Emission factors for the CCUS supply chain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L.; Methodology, T.B.H.N. and G.L.; Formal analysis, T.B.H.N.; Data curation, T.B.H.N.; Writing—original draft, T.B.H.N.; Writing—review & editing, H.Y.M.B. and G.L.; Supervision, G.L.; Funding acquisition, G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
Sets
| CO2 emission sources | |
| CO2 capture technology/material | |
| Storage sites | |
| Utilization sites | |
| CO2-based products | |
| Utility consumption types | |
| Raw materials | |
| CO2 conversion paths |
Variables
| Overall yearly costs (EUR/year) | |
| Capture and compression costs (EUR/year) | |
| Transportation costs (EUR/year) | |
| Storage costs (EUR/year) | |
| Production costs of various CO2-derived chemicals (EUR/year) | |
| Total annual revenues (EUR/year) | |
| Total annual profit (EUR/year) | |
| Capture costs for CO2 from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product (EUR/year) | |
| Dehydration costs for CO2 from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product (EUR/year) | |
| Capture capital costs for CO2 from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product (EUR/year) | |
| Capture operating costs for CO2 from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product (EUR/year) | |
| The quantity of flue gas from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product (mol/s) | |
| Fixed investment costs for CO2 transportation (M EUR) | |
| Operating costs for CO2 transportation (EUR/year) | |
| Transportation capital costs for CO2 from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product (M EUR) | |
| The fraction of CO2 from source , mitigated by facility and transported to storage node or utilization node to create product | |
| Fixed investment cost of CO2 storage at storage node (EUR) | |
| Operating costs for CO2 storage at storage node ( EUR/year) | |
| Number of wells needed for storage node | |
| 1 if CO2 is mitigated from source by facility , 0 otherwise | |
| The quantity of raw material of synthesis route (t/year) | |
| The consumption of utility of synthesis route (GJ/year) | |
| The production quantity of primary product of synthesis route (t/year) | |
| The production quantity of by-product of synthesis route (t/year) | |
| Life cycle GHG emission rate of the CCUS network (tCO2eq/year) | |
| GHG emission rate of conventional synthesis processes to create product (tCO2eq/year) | |
| Overall life cycle GHG reduction rate of the CCUS network (tCO2eq/year) | |
| The amount of CO2 captured by the CCUS network (t/year) |
Parameters
| Capture technology-material related parameters for CO2 at facility j | |
| CO2 transportation cost related parameters | |
| Distance between source and storage node or utilization node (km) | |
| Overall CO2 emission from the source (t/year) | |
| Injection well characteristic parameters | |
| The depth of the well at storage node (km) | |
| The maximum injection capacity of a well (t/year) | |
| The price of raw material (€/t) | |
| The price of utility (€/GJ) | |
| The price of product (EUR/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of CO2 capture step (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of CO2 transportation step (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of CO2 storage step (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of raw material (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of product (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of utility (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of product by the reference conversion route (tCO2eq/t) | |
| The GHG emission coefficient of CO2 utilization route (tCO2eq/t) | |
| Maximum capacity of storage node (t) | |
| Highest CO2 concentration processing limit for capture facility (mol%) | |
| Lowest CO2 concentration processing limit for capture facility (mol%) | |
| CO2 concentration in flue gas from the source (mol%) | |
| The consumption coefficient of CO2 per unit of the primary product p of synthesis route (t/t) | |
| The consumption coefficient of raw material per unit of the primary product of synthesis route (t/t) | |
| The consumption coefficient of utility per unit of the primary product of synthesis route (GJ/t) | |
| The production coefficient of by-product per unit of the primary product (t/t) | |
| Production limit of product (t/year) | |
| Annual reduction target of CO2 emissions (t/year) |
References
- Sivalingam, S.; Harish, A.; Selva, M.R. Chapter 5—Environmental and health effects of global warming. In Health and Environmental Effects of Ambient Air Pollution; Dehghani, M.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 109–129. [Google Scholar]
- Letcher, T.M. Chapter 1—The root causes of global warming and the new normal. In Living with Climate Change; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2023; IEA: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kiehbadroudinezhad, M.; Merabet, A.; Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H. Chapter Twelve—Health impacts of greenhouse gases emissions on humans and the environment. In Advances and Technology Development in Greenhouse Gases: Emission, Capture and Conversion; Rahimpour, M.R., Makarem, M.A., Meshksar, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 265–291. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. (Eds.) Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Odenberger, M.; Kjärstad, J.; Johnsson, F. Ramp-up of CO2 capture and storage within Europe. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2008, 2, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA (International Environmental Agency). 20 Years of Carbon Capture and Storage; International Environmental Agency Paris: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli, P.; Gazzani, M.; Mazzotti, M. The Role of Carbon Capture and Utilization, Carbon Capture and Storage, and Biomass to Enable a Net-Zero-CO2 Emissions Chemical Industry. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7033–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Du, J. An optimization model for carbon capture utilization and storage supply chain: A case study in Northeastern China. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Mohapatra, P.; Joshi, A.; Joshi, R.K.; Fan, L.-S. Chemical Looping for CO2 Conversion and Utilization—Recent Advances and Perspective. In Advanced Materials for Multidisciplinary Applications; Wu, M., Gao, W., Li, L., Lu, Y., Liu, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, M.; Adjiman, C.S.; Bardow, A.; Anthony, E.J.; Boston, A.; Brown, S.; Fennell, P.S.; Fuss, S.; Galindo, A.; Hackett, L.A.; et al. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): The way forward. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1062–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahzad, H. Chemical Looping Water Splitting for Hydrogen Production, Decarbonised Steel Production and Energy Storage/Generation In-Situ with CO2 Capture. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.J.; Lewis, N.S.; Shaner, M.; Aggarwal, S.; Arent, D.; Azevedo, I.L.; Benson, S.M.; Bradley, T.; Brouwer, J.; Chiang, Y.-M.; et al. Net-zero emissions energy systems. Science 2018, 360, eaas9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahzad, H.; Katayama, K.; Boot-Handford, M.E.; Mac Dowell, N.; Shah, N.; Fennell, P.S. Iron-based chemical-looping technology for decarbonising iron and steel production. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 91, 102766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, M.; Bui, M.; Mac Dowell, N.; Fennell, P. Geospatial analysis of regional climate impacts to accelerate cost-efficient direct air capture deployment. One Earth 2022, 5, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiquier, S.; Patrizio, P.; Bui, M.; Sunny, N.; Mac Dowell, N. A comparative analysis of the efficiency, timing, and permanence of CO2 removal pathways. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 4389–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomen, E.; Hendriks, C.; Neele, F. Capture technologies: Improvements and promising developments. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; Baliban, R.C.; Elia, J.A.; Floudas, C.A. Modeling, Simulation, and Optimization of Postcombustion CO2 Capture for Variable Feed Concentration and Flow Rate. 1. Chemical Absorption and Membrane Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15642–15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Caramanna, G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amore, F.; Sunny, N.; Iruretagoyena, D.; Bezzo, F.; Shah, N. European supply chains for carbon capture, transport and sequestration, with uncertainties in geological storage capacity: Insights from economic optimisation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 129, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, J.C.; Rubin, E.S.; Mazzotti, M.; Herzog, H.J. On the climate change mitigation potential of CO2 conversion to fuels. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.M.; Samsatli, S. Technologies and infrastructures underpinning future CO2 value chains: A comprehensive review and comparative analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 85, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; Baliban, R.C.; Elia, J.A.; Floudas, C.A. Modeling, Simulation, and Optimization of Postcombustion CO2 Capture for Variable Feed Concentration and Flow Rate. 2. Pressure Swing Adsorption and Vacuum Swing Adsorption Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15665–15682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; Boukouvala, F.; First, E.L.; Floudas, C.A. Nationwide, Regional, and Statewide CO2 Capture, Utilization, and Sequestration Supply Chain Network Optimization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 7489–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; First, E.L.; Boukouvala, F.; Floudas, C.A. A multi-scale framework for CO2 capture, utilization, and sequestration: CCUS and CCU. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2015, 81, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bique, A.O.; Nguyen, T.B.H.; Leonzio, G.; Galanopoulos, C.; Zondervan, E. Integration of carbon dioxide and hydrogen supply chains. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Friedl, A., Klemeš, J.J., Radl, S., Varbanov, P.S., Wallek, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 43, pp. 1413–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Leonzio, G.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. An outlook towards 2030: Optimization and design of a CCUS supply chain in Germany. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 125, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. Sustainable utilization and storage of carbon dioxide: Analysis and design of an innovative supply chain. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 131, 106569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Zondervan, E. Analysis and optimization of carbon supply chains integrated to a power to gas process in Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Bogle, D.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. Optimization of CCUS supply chains in the UK: A strategic role for emissions reduction. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 155, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovari, H.; Kuhrmann, L.; Mayer, F.; Minten, H.; Bardow, A. Towards a European supply chain for CO2 capture, utilization, and storage by mineralization: Insights from cost-optimal design. J. CO2 Util. 2023, 72, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Adenutsi, C.D. Source-sink matching and cost analysis of offshore carbon capture, utilization, and storage in China. Energy 2024, 291, 130137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klokk, Ø.; Schreiner, P.F.; Pagès-Bernaus, A.; Tomasgard, A. Optimizing a CO2 value chain for the Norwegian Continental Shelf. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6604–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-H.; Kim, J.-K. Techno-economic evaluation of CO2 enhanced oil recovery (EOR) with the optimization of CO2 supply. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2017, 58, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kegl, T.; Čuček, L.; Kovač Kralj, A.; Kravanja, Z. Conceptual MINLP approach to the development of a CO2 supply chain network—Simultaneous consideration of capture and utilization process flowsheets. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.H.; Leonzio, G.; Zondervan, E. Supply chain optimization framework for CO2 capture, utilization, and storage in Germany. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2023, 8, 1685–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhiemah, A.N.; Xu, Y. Economic viability of full-chain CCUS-EOR in Indonesia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 179, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-L.; Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. How can carbon capture utilization and storage be incentivized in China? A perspective based on the 45Q tax credit provisions. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhti, A.; Santibanez Gonzalez, E.D.R. A bi-objective optimization approach for carbon capture and storage supply chain network combining with pricing policies: Economic and social aspects. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. Multi-objective optimization of CCUS supply chains for European countries with higher carbon dioxide emissions. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2023, 8, 1593–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Tao, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, J. Multi-objective optimization for the deployment of carbon capture utilization and storage supply chain considering economic and environmental performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanarengan Ravi, N.; Van Sint Annaland, M.; Fransoo, J.C.; Grievink, J.; Zondervan, E. Development and implementation of supply chain optimization framework for CO2 capture and storage in the Netherlands. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 102, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, J.; Morbee, J.; Tzimas, E. Technical and Economic Characteristics of a CO2 Transmission Pipeline Infrastructure; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek, M.; Brederode, E.; Ramírez, A.; Kramers, L.; van der Kuip, M.; Wildenborg, T.; Turkenburg, W.; Faaij, A. Designing a cost-effective CO2 storage infrastructure using a GIS based linear optimization energy model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 1754–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, J.J.; Dahowski, R.T.; Davidson, C.L.; Bachu, S.; Gupta, N.; Gale, J. A CO2-storage supply curve for North America and its implications for the deployment of carbon dioxide capture and storage systems. In Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies 7; Rubin, E.S., Keith, D.W., Gilboy, C.F., Wilson, M., Morris, T., Gale, J., Thambimuthu, K., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 593–601. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn, M.; Förster, A.; Großmann, J.; Lillie, J.; Pilz, P.; Reinicke, K.M.; Schäfer, D.; Tesmer, M. The Altmark Natural Gas Field is prepared for the Enhanced Gas Recovery Pilot Test with CO2. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 6777–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, K.; Al-Hunaidy, A.S.; Imran, H.; Lee, J.H. Optimization-based identification of CO2 capture and utilization processing paths for life cycle greenhouse gas reduction and economic benefits. AIChE J. 2019, 65, e16580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, J. Optimization-based approach for CO2 utilization in carbon capture, utilization and storage supply chain. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 139, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Cai, G.; He, J.; Wang, S.; Bai, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Z. Economic costs and environmental benefits of deploying CCUS supply chains at scale: Insights from the source–sink matching LCA–MILP approach. Fuel 2023, 344, 128047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrgott, M. Multicriteria Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brisset, S.; Gillon, F. 4—Approaches for multi-objective optimization in the ecodesign of electric systems. In Eco-Friendly Innovation in Electricity Transmission and Distribution Networks; Bessède, J.-L., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 83–97. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).