Analysis of Safe Mud Density Window for Enhanced Wellbore Stability
Abstract
1. Introductions
2. Methodology
2.1. Calculation of Rock Mechanics Parameters
2.1.1. Analysis of Principal Stresses
2.1.2. Overburden Pressure
2.1.3. Pore Pressure
2.1.4. Effective Stress Theory
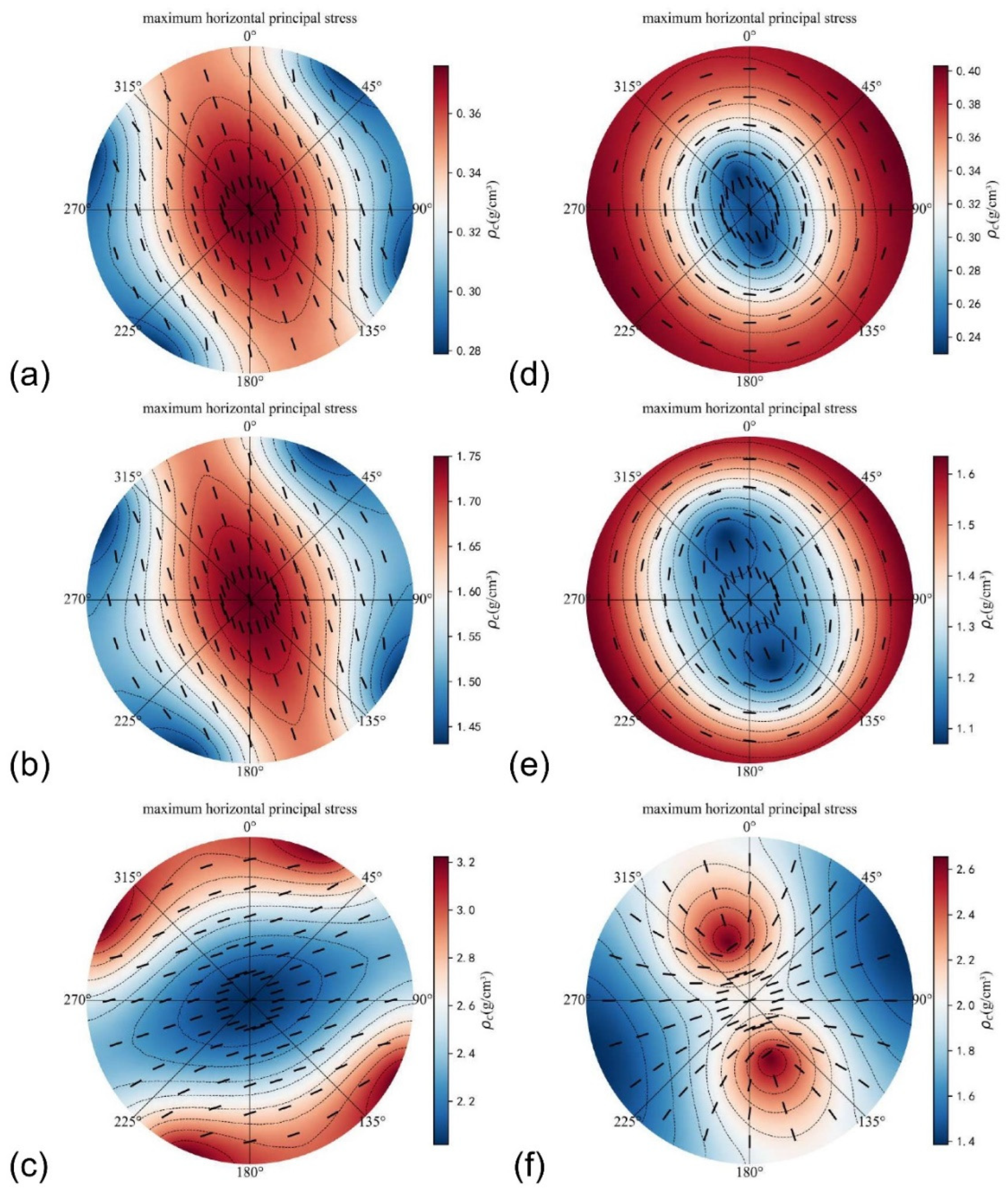
2.1.5. Minimum and Maximum Horizontal Principal Stresses
2.2. Description of Stress Distribution Model in an Inclined Well
2.3. Failure Criterion and Determination of Mud Safety Density Window
2.3.1. Shear Pressure and Collapse Pressure Based on the M-C Criterion
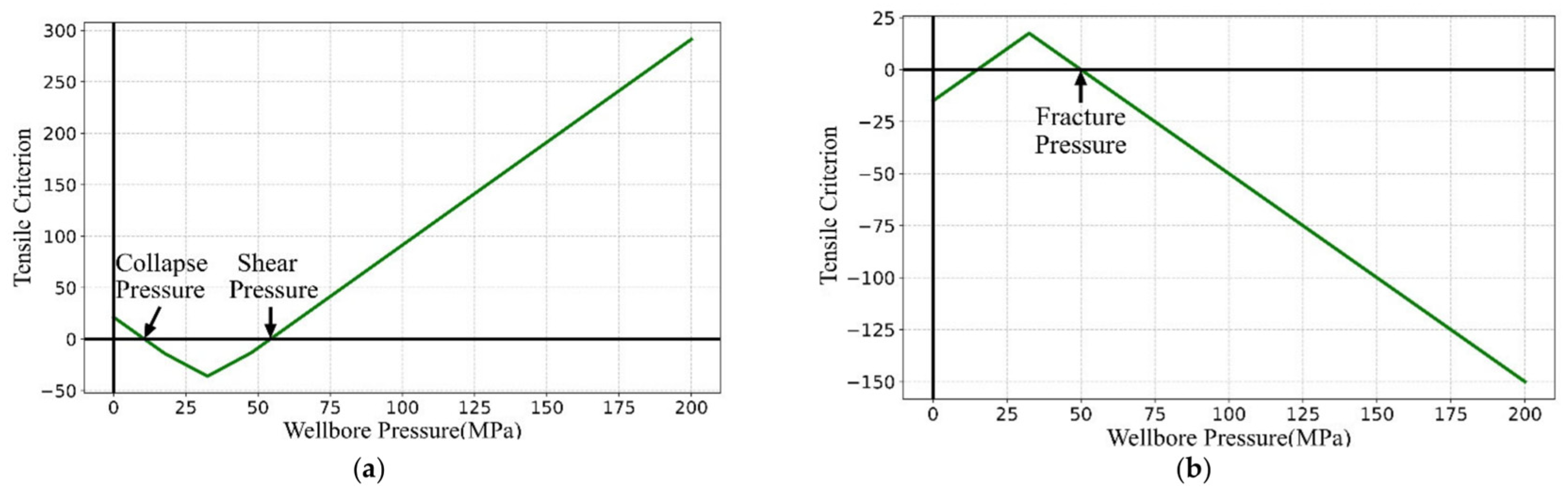
2.3.2. Tensile Criterion
2.3.3. Determination of Mud Safety Density Window
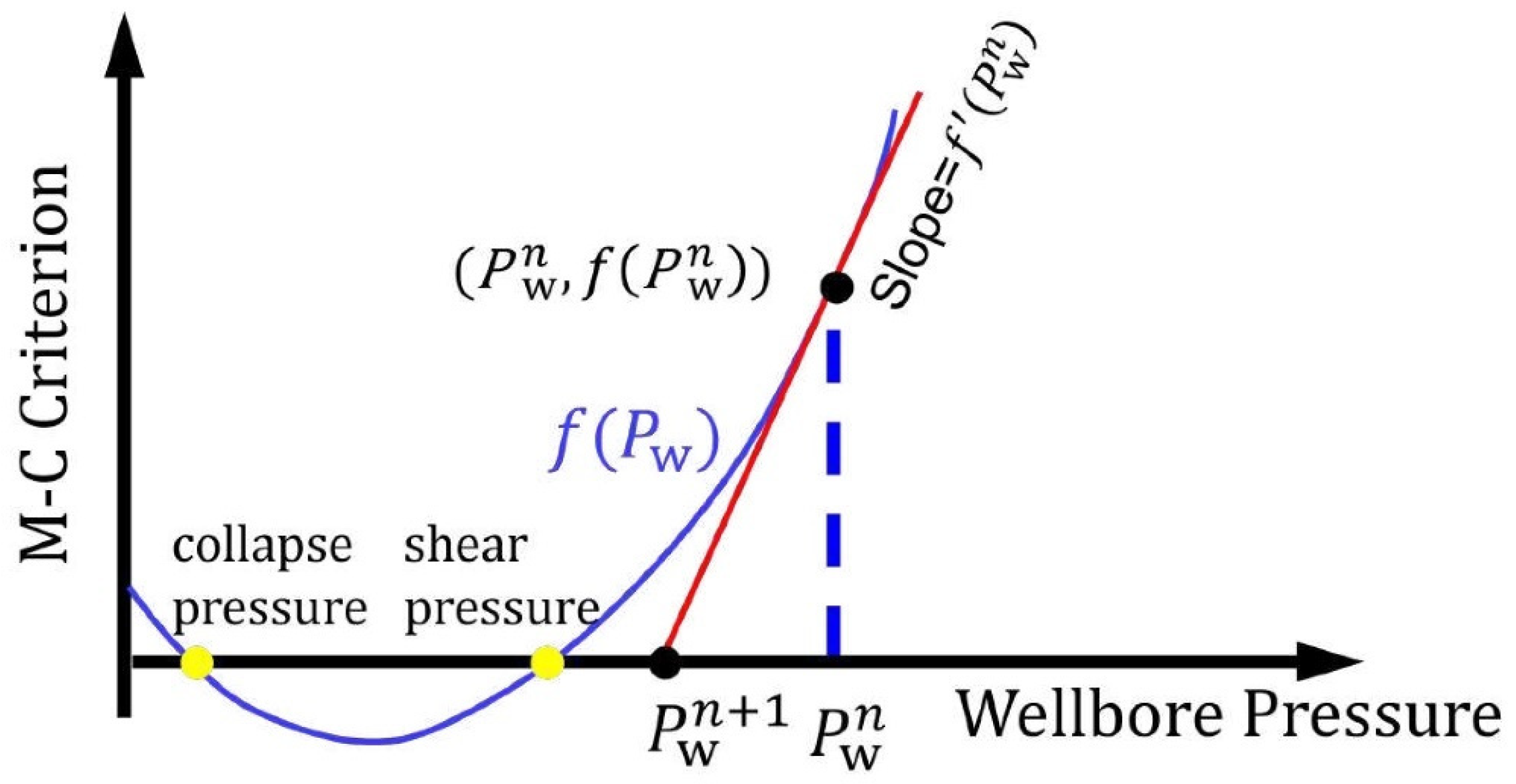
2.4. Calculation of Mud Safety Density Window Based on Newton’s Method
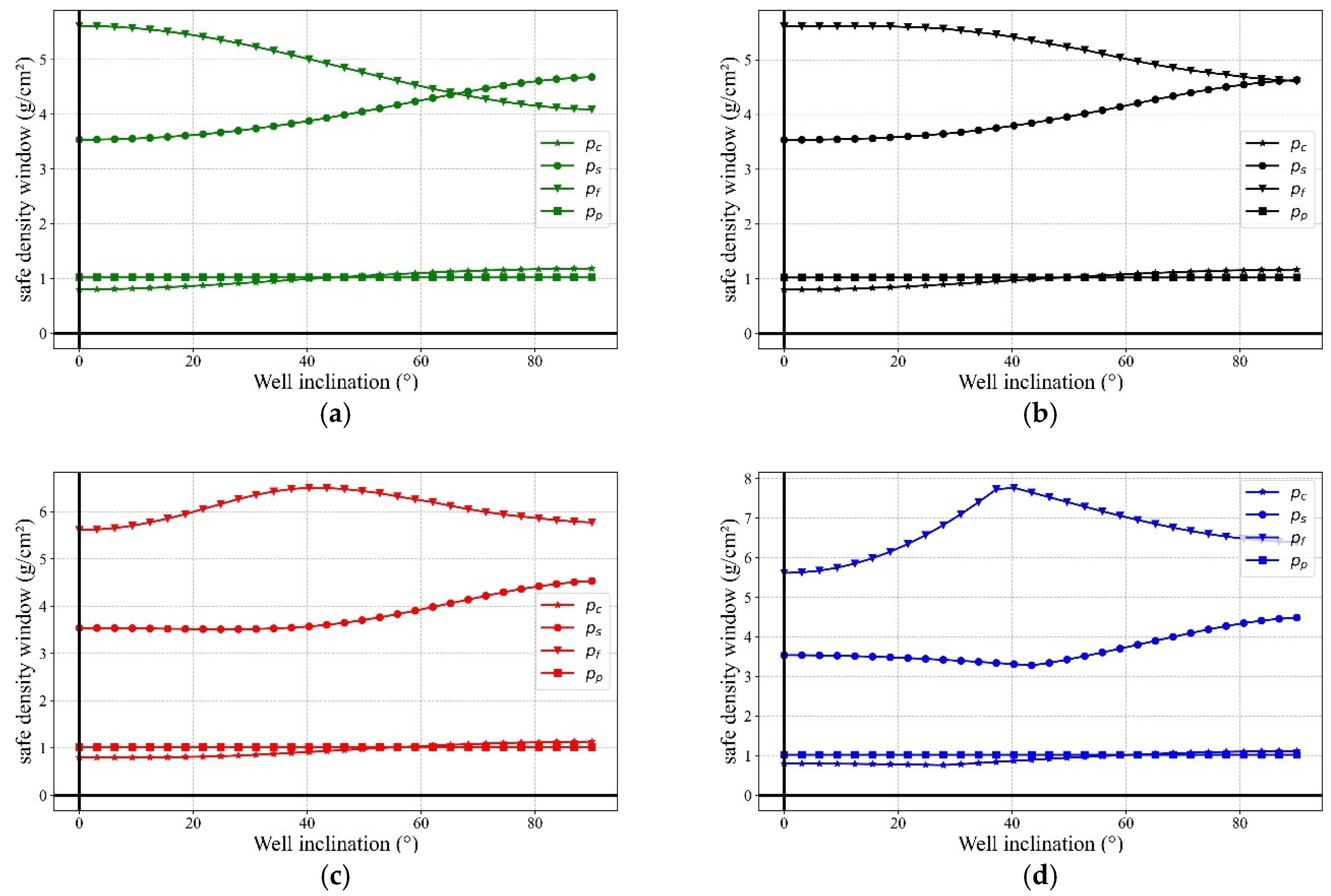
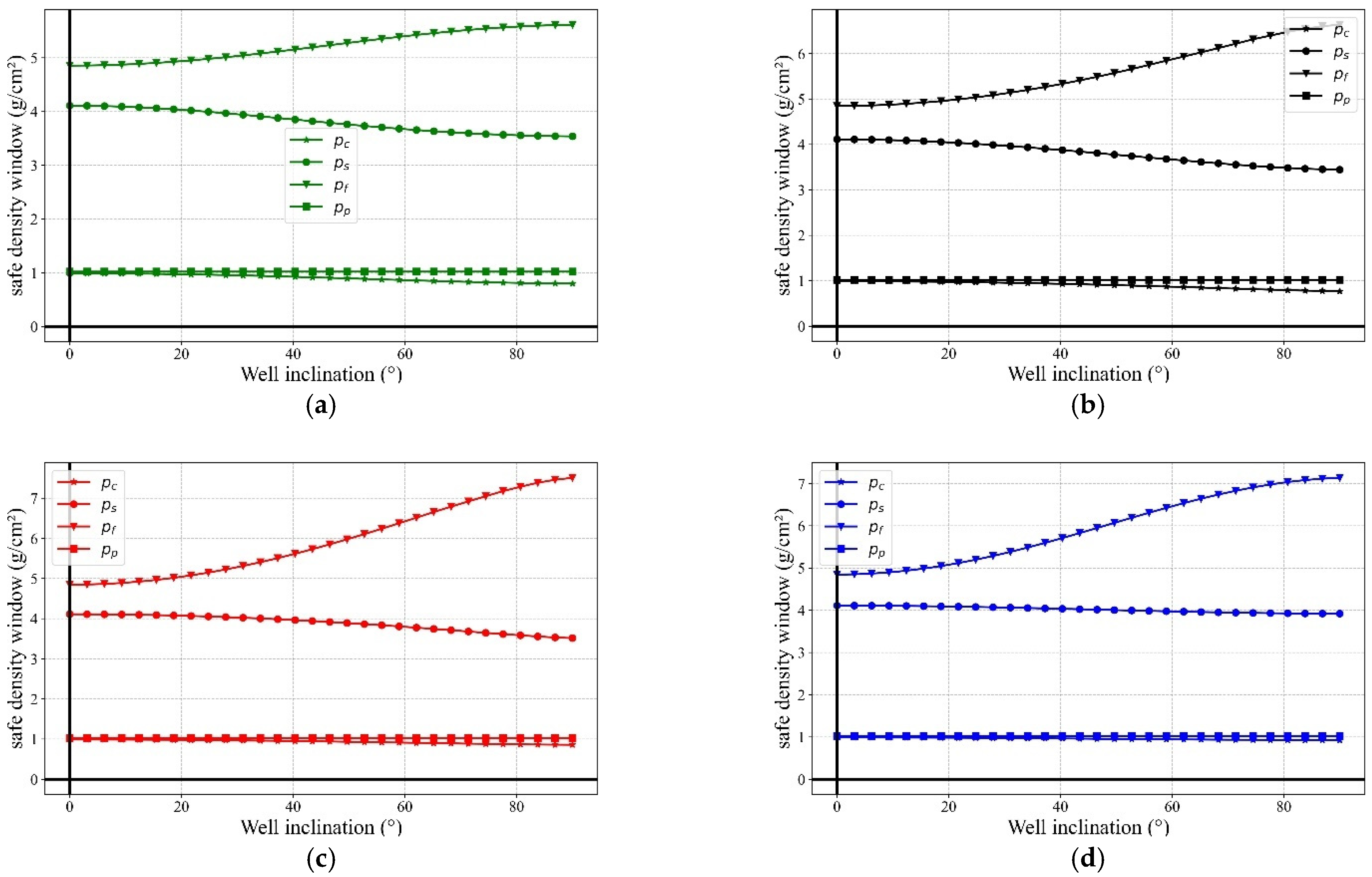
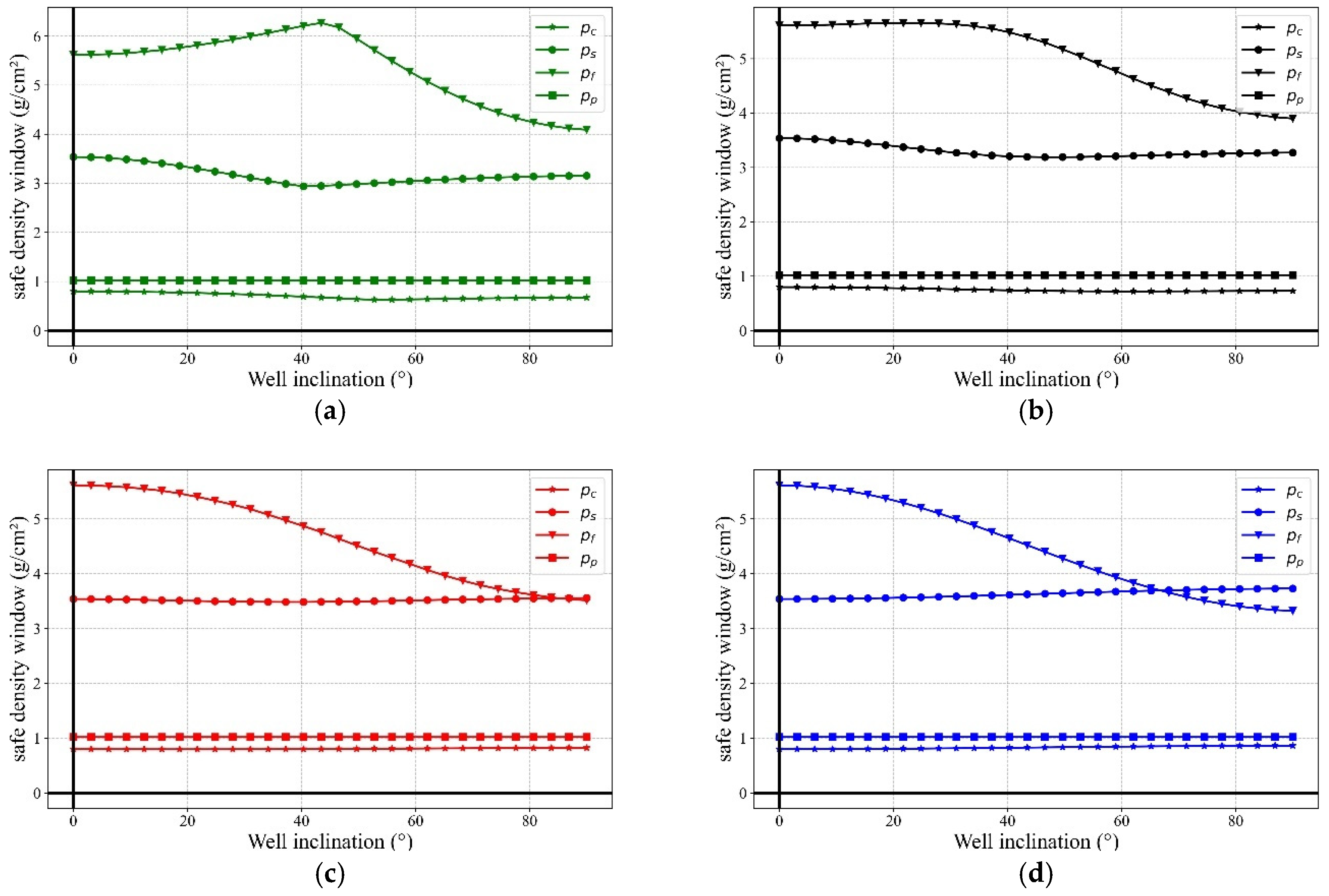
3. Results
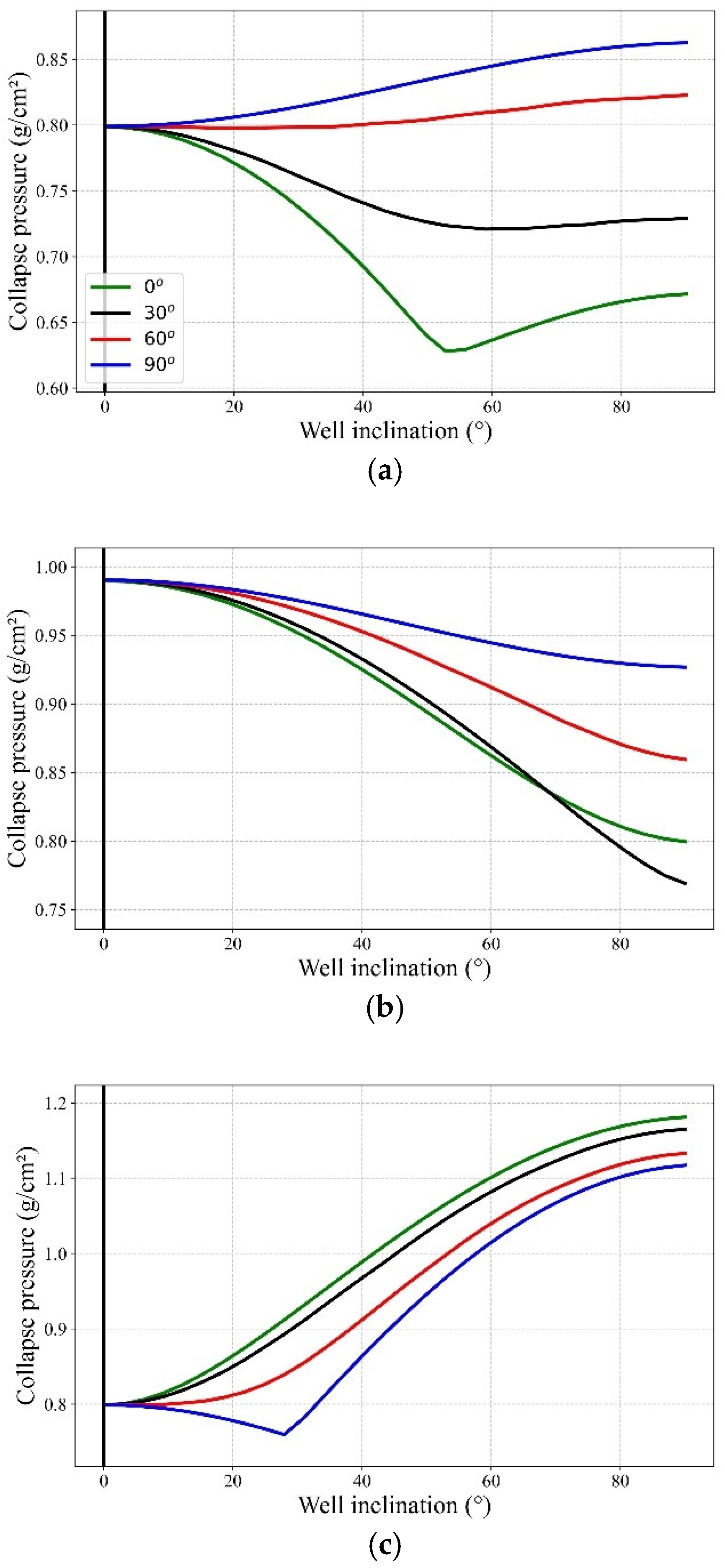
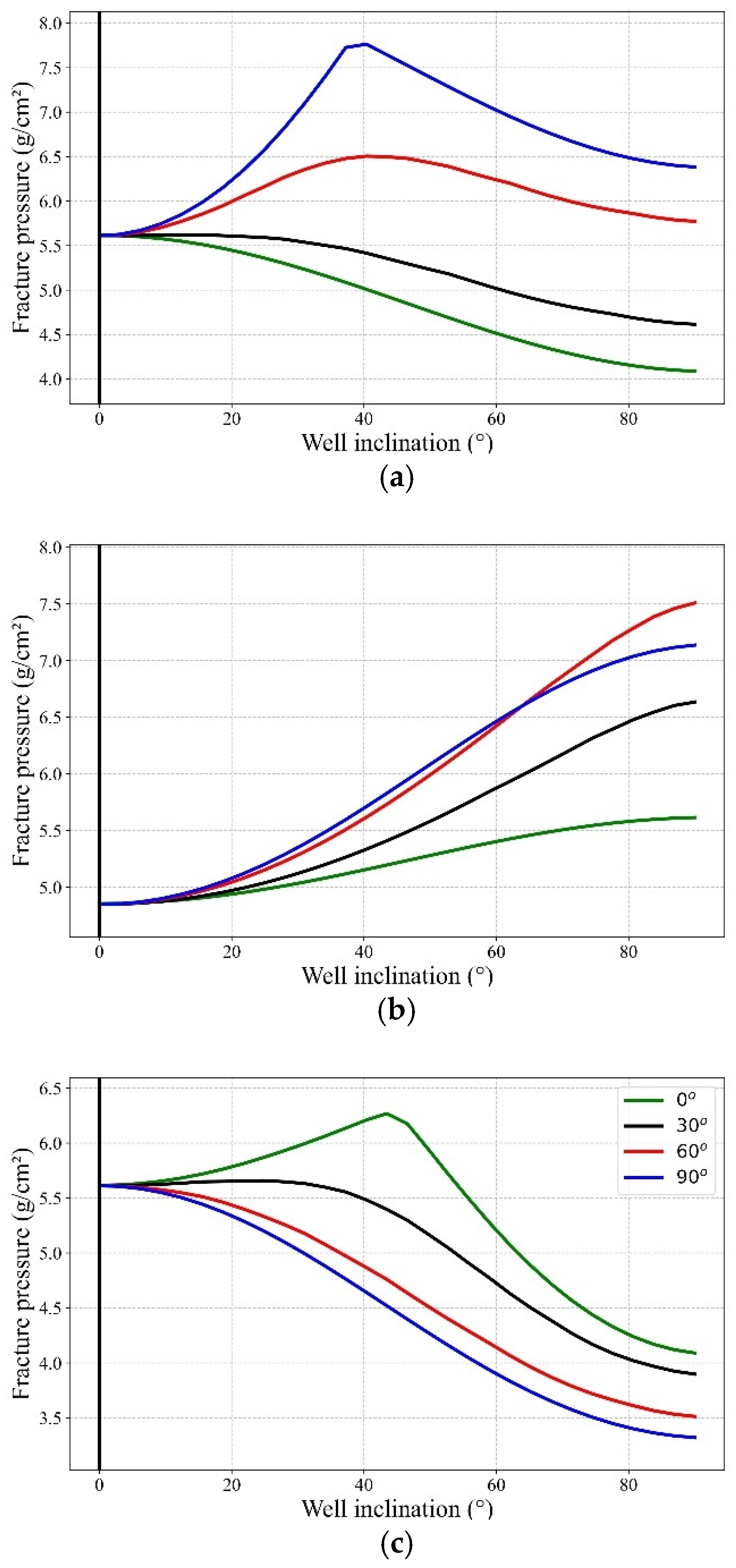
3.1. Safe Mud Density Window Analysis Based on Anderson’s Classification Scheme
3.2. Application to Optimize Drilling in Real-World Operations
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Poisson’s ratio | |
| Young’s modulus | |
| porosity | |
| rock permeability ratio | |
| radius distance from wellbore center | |
| angle measured along the circumference of the wellbore | |
| angle between the overburden pressure and drilling trajectory | |
| azimuth angle | |
| the wellbore radius | |
| effective stress | |
| wellbore pressure | |
| shear pressure | |
| collapse pressure | |
| fracture pressure | |
| pore pressure |
References
- Mohiuddin, M.; Khan, K.; Abdulraheem, A.; Al-Majed, A.; Awal, M.R. Analysis of wellbore instability in vertical, directional, and horizontal wells using field data. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 55, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Numerical insights into factors affecting collapse behavior of horizontal wellbore in clayey silt hydrate-bearing sediments and the accompanying control strategy. Ocean Eng. 2024, 297, 117029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Cao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. The Crack Propagation Behaviour of CO2 Fracturing Fluid in Unconventional Low Permeability Reservoirs: Factor Analysis and Mechanism Revelation. Processes 2025, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peška, P.; Zoback, M. Compressive and tensile failure of inclined well bores and determination of in situ stress and rock strength. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1995, 100, 12791–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireille, C. Essai sur une application des règles de maximis & minimis à quelques problèmes de statique, relatifs à l’architecture. Rev. Fr. Géotech. 2003, 175, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declan, G.; Winthrop, D. Mohr circles of the first and second kind and their use to represent tensor operations. J. Struct. Geol. 1984, 6, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littke, R.; Sachsenhofer, R.F. Organic petrology of deep sea sediments: A compilation of results from the Ocean Drilling Program and the Deep Sea Drilling Project. Energy Fuels 1994, 8, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N. The shear strength of rock and rock joints. International Journal of rock mechanics and mining sciences & Geomechanics abstracts. Pergamon 1976, 13, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Yu, H.B.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas field in offshore Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Jin, Z.K.; Yan, W.; Zhu, X.; Xu, X.; Peng, B. Influences of overpressure on reservoir compaction and cementation: A case from northwestern subsag, Bozhong sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Du, X.F.; Liu, X.J.; Xu, W.; Hao, Y. Formation mechanism of high-quality deep buried-hill reservoir of Archaean metamorphic rocks and its significance in petroleum exploration in Bohai Sea area. Oil Gas Geol. 2020, 41, 235–247, 294. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xie, R.J.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J. Progress and prospect of CNOOC’s oil and gas well drilling and completion technologies. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2022, 9, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.A. The equation for geopressure prediction from well logs. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, TX, USA, 28 September–1 October 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.P.; Bao, H.Z. Advances in calculation method for rock mechanics parameters. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2005, 33, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Leopold, M. Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1969; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.M.; Mackenzie, A.S. Prediction of pore fluid pressures in sedimentary basins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1990, 7, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, C.M.; Johnson, G.; Denyer, G. Predrill pore pressure prediction using seismic data. Geophysics 2002, 67, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Pore pressure prediction from well logs: Methods, modifications, and new approaches. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 108, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Erdbaumechanik auf Bodenphysikalischer Grundlage. 1925. Available online: https://scispace.com/papers/erdbaumechanik-auf-bodenphysikalischer-grundlage-539sbnypud (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Biot, M.A.; Willis, D.G. The elastic coefficients of the theory of consolidation. J. Appl. Mech. 1957, 24, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Shen, J.; Qin, Y.; Meng, S.; Wu, C.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, C. In-situ stress state in the Linxing region, eastern Ordos Basin, China: Implications for unconventional gas exploration production. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 86, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Z. A model for predicting formation fracture pressure. J. Univ. Pet. China 1984, 4, 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Thiercelin, M.J.; Plumb, R.A. Core-based prediction of lithologic stress contrasts in east texas formations. SPE Form. Eval. 1994, 9, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shuai, D.; Qi, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, S. Using 3d seismic data to estimate stress based on seismic curvature attribute of HTI medium: Application to the weiyuan, southern sichuan basin, china. J. Geophys. 2024, 67, 1970–1986. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A. Curvature attributes and their application to 3d interpreted horizons. First Break 2001, 19, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, G. Die theorie der elastizität und die bedürfnisse der festigkeitslehre. Z. Des Vereines Dtsch. Ingenieure 1898, 42, 797–807. [Google Scholar]
- Haimson, B.; Fairhurst, C. In-situ stress determination at great depth by means of hydraulic fracturing. In Proceedings of the 11th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS), Berkeley, CA, USA, 16–19 June 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu, Y. Stress Around a Shaft or Level Excavated in Ground with a Three-Dimensional Stress State; Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyoto University: Kyoto, Japan, 1962; Volume 24, Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2433/280512 (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Hiramatsu, Y.; Oka, Y. Determination of the stress in rock unaffected by boreholes or drifts, from measured strains or deformations. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1968, 5, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, W.B. Failure of inclined boreholes. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1979, 101, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuz, J.; Zang, A. Mohr-coulomb failure criterion. In The ISRM Suggested Methods for Rock Characterization, Testing and Monitoring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, D. The tensile strength of rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1964, 1, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E. Fracture of anisotropic rock. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1964, 64, 501–518. [Google Scholar]
- Pašić, B.; Gaurina, M.; Matanović, D. Wellbore instability: Causes and consequences. Rud.-Geološko-Naft. Zb. 2007, 19, 87–98. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/19296 (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Li, S.; George, J.; Purdy, C. Pore-pressure and wellbore stability prediction to increase drilling efficiency. J. Pet. Technol. 2012, 64, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galántai, A. The theory of newton’s method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 124, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M. The Dynamics of Faulting and Dyke Formation with Applications to Britain; Oliver and Boyd: Edinburgh, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.B.; Macdonald, D.; Zhao, X.; Vincent, S.J.; Brouet-Menzies, C. Early Cenozoic two-phase extension and late Cenozoic thermal subsidence and inversion of the Bohai Basin, northern China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1997, 14, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, L.Y.; Graham, S.A.; Tilander, N. Seismic reflection imaging of a major strike-slip fault zone in a rift system: Paleogene structure and evolution of the Tan-Lu fault system, Liaodong Bay, Bohai, offshore China. AAPG Bull. 2004, 88, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Shedlock, K.M.; Hellinger, S.J.; Sclater, J.G. The north China basin: An example of a Cenozoic rifted intraplate basin. Tectonics 1985, 4, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, B.N.; Biddle, K. Deformation and Basin Formation Along Strike-Slip Fault; SEPM Special Publications: Claremore, OK, USA, 1985; SP 37. [Google Scholar]





| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 m | 35 MPa | ||
| 1 | 40 MPa | ||
| 30° | St | 5 MPa | |
| 20 MPa | 0.25 | ||
| 45 MPa | 0% |
| Regime | Stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | |||
| Strike-slip | |||
| Reverse | |||
| (MPa) | (MPa) | (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | |||
| Strike-slip | |||
| Reverse |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, R.; Feng, J.; Qin, L.; Yuan, J.; Guo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, S. Analysis of Safe Mud Density Window for Enhanced Wellbore Stability. Processes 2025, 13, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041046
Xie R, Feng J, Qin L, Yuan J, Guo Z, Yu Y, Yuan S. Analysis of Safe Mud Density Window for Enhanced Wellbore Stability. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041046
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Renjun, Jianxiang Feng, Lu Qin, Junliang Yuan, Zhiwei Guo, Yue Yu, and Sanyi Yuan. 2025. "Analysis of Safe Mud Density Window for Enhanced Wellbore Stability" Processes 13, no. 4: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041046
APA StyleXie, R., Feng, J., Qin, L., Yuan, J., Guo, Z., Yu, Y., & Yuan, S. (2025). Analysis of Safe Mud Density Window for Enhanced Wellbore Stability. Processes, 13(4), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041046







