Abstract
Background: Despite the widespread use of newer basal insulins, Natural Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin still represents a well-established basal formulation with its long history of use, featuring the native form of human insulin. However, NPH insulin exhibits an undesirable peak within hours after a single subcutaneous (s.c.) injection, which may lead to hypoglycemia followed by insufficient basal insulin delivery. This may be attributed to the s.c. enzyme activities degrading the protamine in NPH microcrystals. Methods: A thermogelling block copolymer Pluronic® F127 (PF127) was utilized as a protective carrier for NPH microcrystals and as a modulator for insulin release from NPH. NPH insulin-loaded PF127 gel was prepared with varying concentrations of the polymer (15–25%) under mild conditions. The formulations were characterized for their gelling temperature, morphology, gel erosion, and in vitro insulin release, with trypsin concentrations up to 5 U/mL. Results: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the integrity of NPH microcrystals was maintained after preparation. The burst release of insulin from NPH was significantly attenuated over the course of ~16h in the presence of PF127 with or without enzyme activity. Conclusion: NPH-PF127 successfully resisted the acceleration of NPH crystal dissolution and insulin release in vitro in the presence of protamine-degrading enzyme activity, warranting further testing.
1. Introduction
Insulin therapy is the first line treatment in patients with Type 1 diabetes and it is also given for patients with Type 2 diabetes. Insulin is available in prandial (short-acting) and basal (intermediate or long-acting) forms [1]. The basal insulin is responsible for 50% of the total daily insulin output and is an important player in the long-term management of diabetic complications [2].
Natural Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, introduced in 1946, is among the most widely used basal insulins [3]. NPH, a generic drug, is still among the highly prescribed intermediate- to long-acting insulins worldwide [4]. NPH is a microcrystal formulation in which native human insulin is co-crystallized with zinc, phenolic substances, and the basic peptide protamine (5:1 insulin: protamine molar ratio) at a neutral pH. The function of protamine is to balance the overall charge of the molecule [5].
However, the insulin release kinetics in vivo upon a single subcutaneous injection of NPH are characterized by a peak within a few hours, potentially resulting in hypoglycemia, followed by declining levels in less than one day, which is often insufficient to provide the daily basal insulin requirement from a single subcutaneous dose [6]. This drawback was improved by the advent of genetically modified basal insulins, starting with the insulin glargine (Lantus®) approval by the United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) in 2000. The modification altered the isoelectric point of the protein close to the pH of the tissue injection sites, where the drug can precipitate upon a single subcutaneous injection and act as a depot, featuring a relatively “peak-less” release profile [7]. However, there is ongoing controversy as to whether or not the long-term use of genetically modified insulins increases the risk of malignancies compared to NPH insulin use [8,9,10]. NPH insulin, on the other hand, features native human insulin with a long history of use and still presents itself as a clinically valuable and more economic basal insulin worldwide compared to newer, genetically altered basal insulins. It is worth looking into ways to modify NPH insulin’s release behavior by employing appropriate drug carrier systems.
Several attempts have been made to improve the action profile of NPH. For instance, a lipophilically modified insulin derivative (C8-HI) and protamine were co-crystallized with human insulin to provide a flatter and longer time of action [11]. However, in preclinical studies the formulation did not overcome the problems of higher initial insulin release and peak formation a few hours after administration [12]. Neutral protamine LysPro (NPL) was also developed to provide optimal time action properties [13]. However, the pharmacokinetic parameters and its duration of action profile were rather similar to those of NPH [14].
In insulin delivery, there have been many deliberate efforts to explore alternative routes of administration, such as oral, buccal, pulmonary, and transdermal. However, several challenges and struggles are faced and are yet to be solved in order for it to be as effective and reliable as subcutaneous injection [15,16,17,18]. For example, the FDA approved two inhalable insulins—Exubera (withdrawn) and Afrezza. However, these inhalable forms are not intended to meet basal insulin requirements. The subcutaneous route is still the major route of administration for basal insulin delivery [19].
In a subcutaneous depot system, there are several factors that affect the release and absorption of biotherapeutics. These factors include proteolytic enzymes, physiological pH, blood flow, depth, and volume of the injection. As a result, the fraction of a dose that enters the circulation is usually insufficient or in excess [20,21]. Significant proteolytic activities were identified in the subcutaneous tissue of rats, including cathepsin B, aminopeptidase, and collagenase-like peptidase [22,23]. It has also been shown that the bioavailability of insulin can be enhanced by suppressing tissue proteases in the subcutaneous tissue [24].
Enzyme activities in subcutaneous tissues are thought to facilitate insulin release from NPH crystals due to the splitting of isophane into insulin and protamine fragments [25]. Therefore, NPH microcrystals are dissociated to hexamers and then to dimers and monomers prior to absorption into capillaries. Protamine, where arginine represents approximately 70% of the peptide, can be degraded by several subcutaneous enzymes, such as aminopeptidase, carboxypeptidase, and cathepsin B [26,27,28,29]. Therefore, controlling these tissue enzyme activities is key to improving the insulin release from NPH microcrystals.
The aim of this work is to explore the possibility of altering the dissolution and release of insulin from NPH microcrystals by combining NPH insulins and Pluronic® F127 (PF127) so that the system attains resistance to subcutaneous tissue enzymatic cleavage and that the insulin release from NPH is extended to better mimic physiological basal insulin provision. Herein, the key is to create protective yet erodible surroundings for protamine-insulin crystals by utilizing thermoreversible hydrogel (PF127) as a biocompatible delivery system, where the erosion occurs within 24 h and is rather independent of the biochemical environment (such as pH or enzymes). In this study, we chose trypsin as a model enzyme to represent the tissue enzyme (or tissue fibrinolytic) activity against NPH, because it mainly degrades arginine-rich protamine without significantly digesting the insulin [26,30] to assist the optimization of the NPH/PF127 insulin formulation. The impact of the enzyme activities on the insulin release profiles from NPH/PF127 or NPH were characterized in vitro.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Human NPH insulin (Humulin N®, Eli Lilly, 100 U/mL) was purchased through Henry Schein (Melville, NY, USA). Human recombinant insulin, Pluronic F127 (Kolliphor® P 407), and trypsin from bovine pancreas (2500 U/mg) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monooleate (Tween-80) and the Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). A dialysis membrane 1000KD-1 mL (Spectra/Por® Float-A-Lyzer® dialysis device (Spectrum Laboratories, Rancho Dominguez, CA, USA)) was purchased from VWR. All the aqueous solutions, including phosphate buffer saline (PBS), were prepared using the distilled water Millipore® filter system (Billerica, MA, USA). Other chemicals were of reagent grade and were used without further purification.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Trypsin Activity on Human Insulin
Human insulin powder was dissolved in 50 mM of phosphate buffer 7.4. The concentration of insulin was measured using a spectrophotometer by determining the absorbance at 276 nm wavelength with an extinction coefficient of 1.05 cm−1 (mg/mL)−1 [31]. The samples of 1 mg/mL of human recombinant insulin were incubated with varying concentrations of trypsin (0, 1, 5, 10 U/mL) for 2 h [30]. A calibration curve (peak height vs. standard concentrations) was generated (Figure S1 in the Supplementary Information) and the amount of insulin in each sample was quantified by FPLC (Fast protein liquid chromatograph—Biologic Due Flow, Bio Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) using two serially connected Sephadex G-25 desalting columns (GE Health care, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) to remove phenolic additives. The effluent from the columns was monitored by single-path UV monitor at 280 nm.
2.2.2. Preparation of PF 127 Microcrystals Formulations
Formulations with different concentrations of PF 127 and NPH insulin matrix were prepared. The required amount of PF127 (15, 20, and 25% w/w) for each formulation was carefully weighed and allowed to dissolve directly into the NPH crystal suspension (75, 80, and 85 Unit/mL) in a 10 mL flat-bottomed vial (Table 1). The vial was placed at 4 °C under gentle agitation until the PF127 was dissolved and blended completely with an NPH microcrystal suspension. The samples were refrigerated in tightly closed glass vials. The PF127 concentration in both formulations of gel was always expressed as the weight percentage (% w/w).

Table 1.
Composition of the insulin formulations containing Pluronic F127 (PF127).
2.2.3. Gelation Temperature of NPH-PF 127
The PF 127 solutions were prepared in the concentration range of 15–30% w/w. Briefly, a required amount of PF 127 was gently mixed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) in 10 mL glass vials for 24 h at 4 °C until the PF 127 granules completely dissolved and became a clear solution.
The gelation temperatures of PF 127 (15–33%) and NPH-PF127 (15–30%) were determined using the tube inverting method [32,33]. Briefly, 1 mL of each sample was heated gradually on 8 mL vial with a diameter of 1.5 from 5 to 50 °C at a heating rate of 1 °C/min. The transition from solution to gel was marked by the lack of fluidity when tilting the vial. The gelation temperatures were recorded in triplicate.
2.2.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
The stability of insulin in the matrix was evaluated by obtaining the IR spectra for NPH and PF 127 both alone and combined using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR, Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100 FTIR Spectrometer 76700, Waltham, MA, USA). The samples of the NPH only, PF 127 (25%) only, and NPH-PF127 (25%) were placed on a holder and scanned in wavenumber intervals from 1000 to 4000 cm−1 at 25 °C.
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of NPH-Microcrystals Loaded in PF127 Hydrogel
The morphology of the microcrystals in NPH-PF 127 (25%) was studied using Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy, ESEM (Quanta 200, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) [11,34]. The NPH-PF 127 was compared with NPH alone, and both samples were directly transferred to a specimen holder. Then, the samples were sputter-coated with gold to enhance their observability.
Another NPH-PF127 crystal structure with a different preparation process was investigated. Briefly, a milliliter of NPH insulin was transferred from a vial to a 2 mL Eppendorf microcentrifuge tube. Then, it was centrifuged for approximately 1 min at 5000 rpm, and the supernatant was removed. The retrieved microcrystals were added to PF125 (25%), prepared in PBS as described previously, and left under gentle mixing at 4 °C. The sample was directly transferred to a specimen holder and was gold-sputtered.
The effect of trypsin on the microcrystal morphology of both NPH-PF127 and NPH alone was investigated. Briefly, 1 mL of both NPH and NPH-PF 127 (25%) were transferred to Eppendorf tubes, and 10 µL of trypsin (100 Unit/mL) was added to both tubes. After 1 h, drops of the collected samples were affixed to carbon adhesive stubs and coated with a gold prior to SEM observation.
Gel Erosion and Insulin Release In Vitro
All the in vitro release experiments for all formulations were performed at 37 °C using 1 mL dialysis cartridges. Prior to use, all the dialysis cartridges with an MW cutoff of 1,000,000 Da (Spectra/Pop® Float-A-Lyzer® dialysis device, Spectrum Laboratories, Rancho Dominguez, CA, USA) were conditioned by filling the devices with 10% ethanol (EtOH) and submerging in the same alcohol solution for 10 min. Then, using distilled water, the devices were washed, filled, and submerged for 20 min. After pre-wetting, the dialysis membranes were rinsed with PBS. An aliquot (1mL) of each prepared sample was transferred to the dialysis membrane and immersed in a 25 mL release medium PBS (pH 7.4, 0.01% of Tween 80). Experiments was conducted in a water-jacketed beaker at 37 °C under mild shaking of 50 rpm using an orbital shaker (Rotomix 50800 (Barnstead Thermolyne, Dubuque, IA, USA)) (Figure S2 in the Supplementary Information). At pre-determined time intervals, each dialysis medium was collected for analysis and each vial was replenished with fresh medium to assure sink conditions.
2.2.6. Erosion Profiles for NPH-PF127 Microcrystals Hydrogel
The weight of each dialysis device was recorded initially before the start of the experiment and after each change of the release medium. The percentage of gel dissolved (% mass loss) was determined from the difference in weight of the dialysis device between time points according to the following equation:
where W0 is the initial weight of the NPH-PF127 gel, and Wt is the weight of NPH-PF127 at time t. The erosion profile was performed by plotting the cumulative percentage of each NPH-PF 127 gel formulation dissolved against time.
% mass loss = 100 (W0 − Wt)/W0
2.2.7. In Vitro Release of Insulin
The release profiles of insulin from NPH were evaluated concurrently with the erosion profile. The amounts of insulin release from all formulations were determined by analyzing the collected samples using the Pierce-BCA assay kit (Thermo Scientific™). An aliquot of 25 μL each of the standards, controls, and samples was placed in triplicate in a 96-well microplate, and 200 μL of working reagent was added to each well. The plate was mixed thoroughly on a plate shaker for 30 s, incubated at 37 °C for 0.5 h, and cooled to room temperature before the absorbance was measured at 562 nm with a microplate reader (Bio-Tek). Standard curves were prepared by known concentrations of insulin.
2.2.8. Effect of PF 127 Concentration on the Insulin Release from NPH-PF127
The effect of the change in PF127 concentration was studied for the NPH-PF 127 formulations. As described previously, formulations containing NPH and the PF127 concentrations of 15%, 20%, and 25% (w/w) were prepared. Both the in vitro release of insulin and the dissolution of the hydrogel formulations were studied at 37 °C using the dialysis membrane method. Correlation was also performed between the cumulative gel dissolved and the cumulative percent of insulin released.
2.2.9. Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Insulin Release from Both NPH and NPH-PF127
The effect of varying enzyme concentrations on the insulin release from NPH alone, NPH-PF127 (20%), and NPH-PF127 (25%) was investigated. Trypsin was used as a model subcutaneous enzyme. and 1 and 5 U/mL of trypsin concentrations were used. Trypsin was added directly to the dialysis medium.
2.2.10. Effect of Short-Term Storage on Insulin Release from NPH-PF127
The effect of short-term storage at 4 °C on the insulin release behavior from microcrystal hydrogel NPH-PF127 was evaluated for 3 weeks using 25% PF127. Briefly, NPH-PF127 was prepared and stored at the refrigerator for 3 weeks. Samples were taken on day 1, 7, and 21. The insulin release stability was examined using the dialysis membrane method. Release profiles for the analyzed samples were compared.
Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as a mean ± standard deviation. The data were statistically analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with a confidence interval of 95%, followed by Tukey’ post hoc test, and were considered as statistically significant at a p-value of less than 0.05.
3. Results
NPH-PF127, an injectable thermogelling hydrogel loaded with NPH insulin microcrystals, was developed to address the undesirable release profiles of NPH insulin. PF127 was incorporated with NPH to control microcrystal dissolution via protection from the subcutaneous proteolytic cleavage of protamine in the NPH. The microcrystals of NPH-PF127 insulin maintained their morphological and secondary structural integrity. The modified basal insulin has shown a relatively constant insulin release in vitro.
3.1. Trypsin Activity on Human Insulin
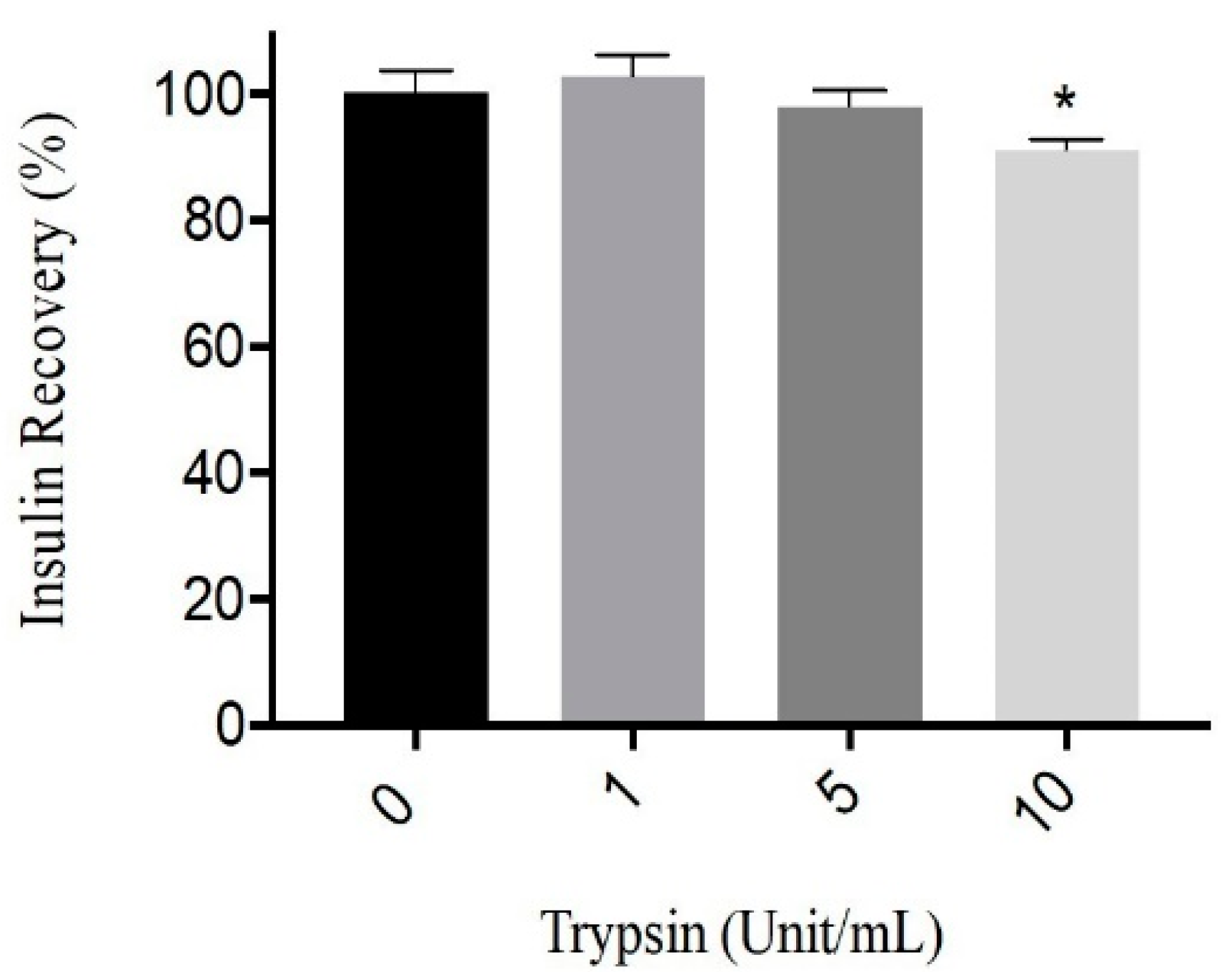
The degradation of human recombinant insulin by trypsin was examined in vitro. Figure 1 shows the recovery percentage of insulin after incubation with different trypsin concentrations ranging from 0 to 10 U/mL. After 3 h of incubation with trypsin (1 and 5 U/mL), the loss appears to be less than 5%. Trypsin has shown an effect on insulin (human recombinant insulin). As the trypsin concentration increased from 1 to 10 U/mL, a decline in insulin recovery was observed. However, the impacts of 1 and 5 U/mL of trypsin on insulin were very low compared to 10 U/mL. It was reported that trypsin itself has a very slight rate of degradation effect on insulin, as it only favors the cleavage of B29-Lys and B22-Arg residues, which are not the dominant amino acids in insulin [30,35]. Our result was consistent with such previous findings, as the percentage of insulin recovery was less affected by the exposure to tryptic activity up to 5 U/mL. This result was used to select the enzyme concentrations to model proteolytic enzymes against protamine in subcutaneous tissues without harming insulin significantly.
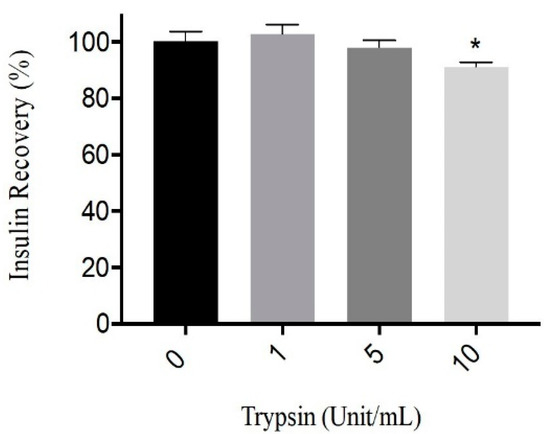
Figure 1.
Insulin recovery percentage after incubation (3 h) with 0, 1, 5, 10 Unit/mL of trypsin at 37 °C, pH 7.4. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3), * p < 0.05.
3.2. Gelation Temperatures of NPH-PF 127
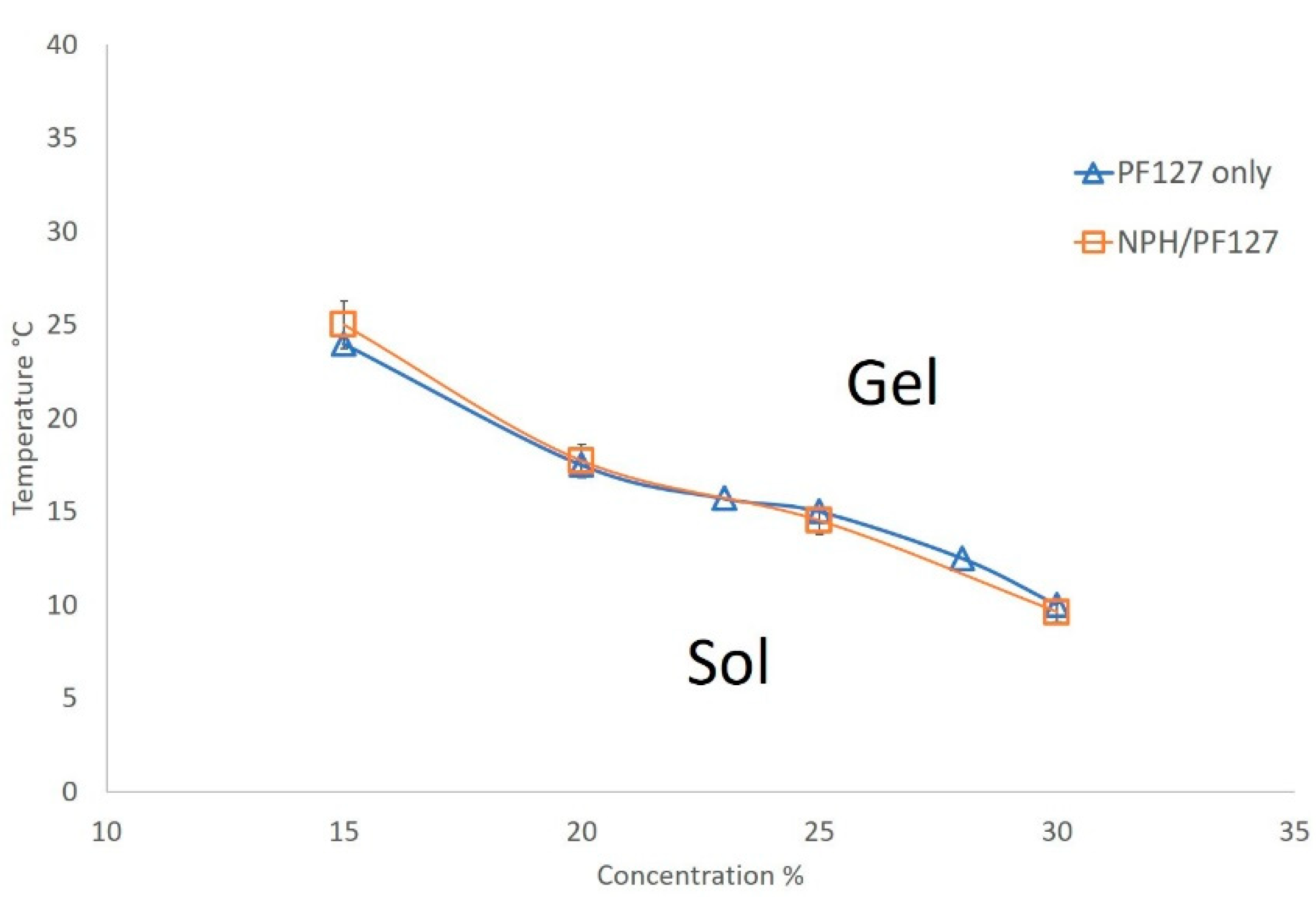
The (lower) sol-gel phase transition curves of PF127 and NPH-PF127 are shown in Figure 2, where the gelation temperatures are plotted against the PF127 concentrations for both PF127 and NPH-PF127. The PF127 concentrations of 15% to 30% display reverse thermal gelation at gelation temperatures ranging from 10 to 24 °C. NPH-PF127 with the concentration range from 15% to 30% exhibited similar gelation characteristics to PF127 solutions. The gelation temperature decreases with an increasing PF127 concentration, which is consistent with published studies [36,37]. The aqueous solution of PF127 is a micellar solution and, upon increase in temperature, micelle packing occurs as a result of the partial dehydration process of both the hydrophilic chain (polyoxyethylene) and the hydrophobic chain (polyoxypropylene) of the copolymer, resulting in a gel state. We have observed a somewhat loose gelation at the PF127 concentration of 15% (w/w) in PBS, which suggests that the concentration was approaching its critical gel concentration (CGC) in the isotonic buffer. In pure water, its CGC is estimated to be ~17 °C [38]. In Figure 2, the upper transition curves (gel to syneresis) were not plotted as those temperatures far exceed the temperature of interest.
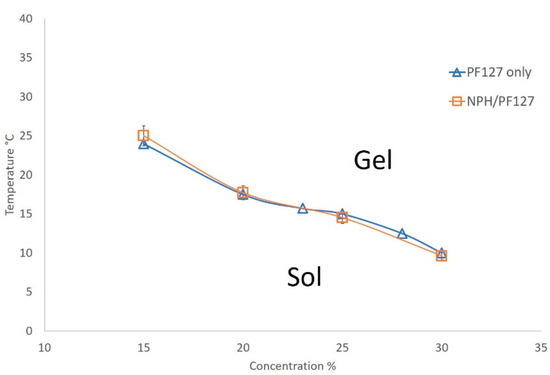
Figure 2.
Phase diagram of the lower sol-gel transition of PF127 in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7.4) with or without NPH. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3).
3.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
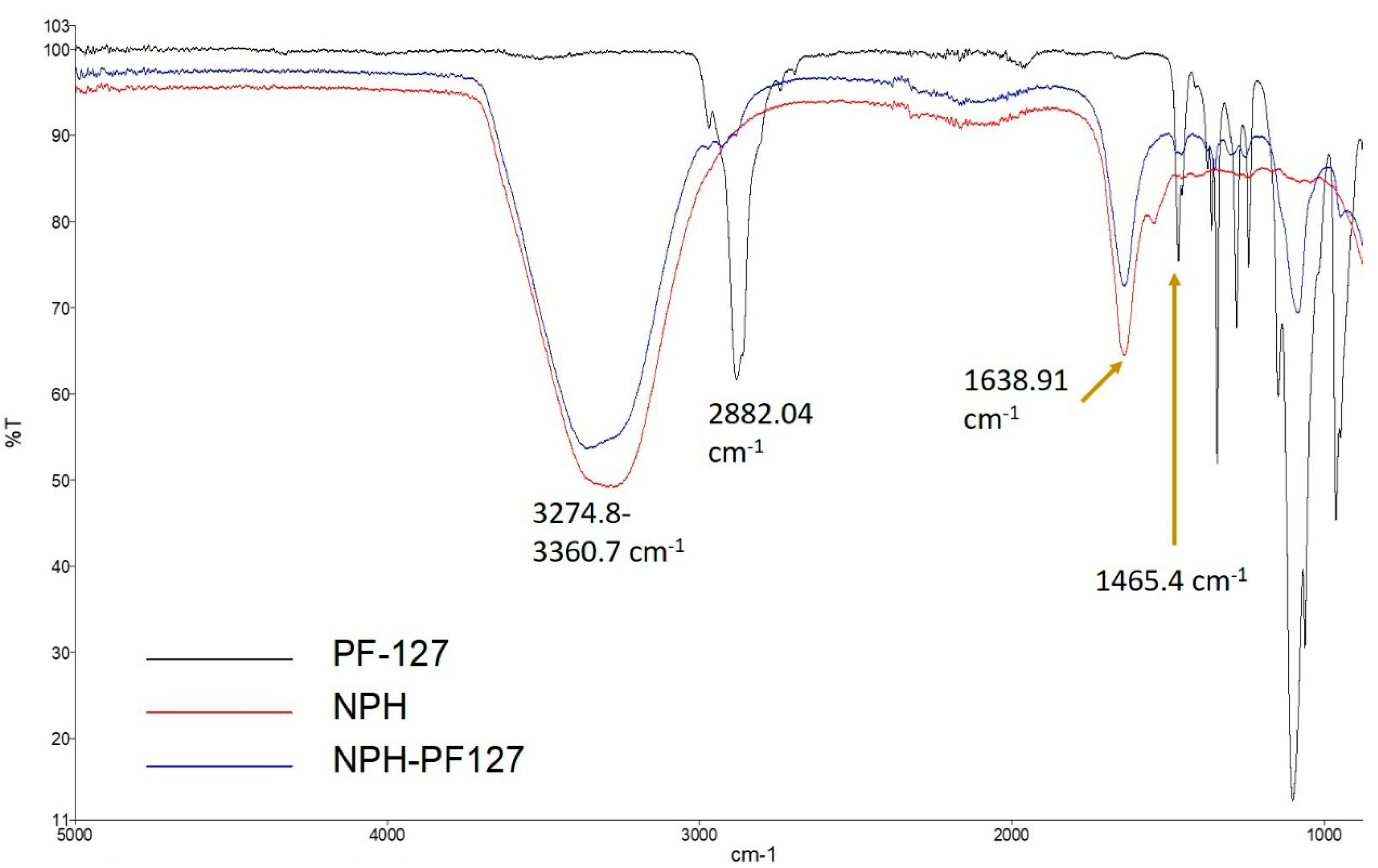
IR spectra were recorded for NPH, NPH-PF127, and PF127 to evaluate any possible interaction during the preparation of hydrogel using a FTIR spectrometer (Figure 3). In the spectra of native NPH (red), the stretching bands at 3274.8 and 1638.4 cm−1 represent the hydroxyl (O–H) and Amide I region, respectively. For the blank PF127 hydrogel (black), a sharp stretching band appeared at 2882.04 cm−1, which reflects the stretch vibrational bands of methylene group (C–H). In the loaded microcrystal hydrogel (NPH-PF127; blue), the shape and position for the peak were similar to those for NPH in the absence of PF127, except for a slight alternation in the position of the stretched hydroxyl group peak at 3360.7 cm−1. This alteration in the NPH-PF127 peak is due to the shift and overlap of the hydroxyl and methylene group peaks of native NPH and blank PF127 hydrogel, respectively. The position of the peaks characteristic of PF127 (2882.04 and 1465.4 cm−1) did not shift in the mixture. Additionally, the Amide I band (~1640 cm−1) maintained the same shape and position in NPH-PF127 compared to NPH only, which appears to indicate the absence of drug–polymer interactions, as all the specific peaks of drug and polymer were present in the composite.
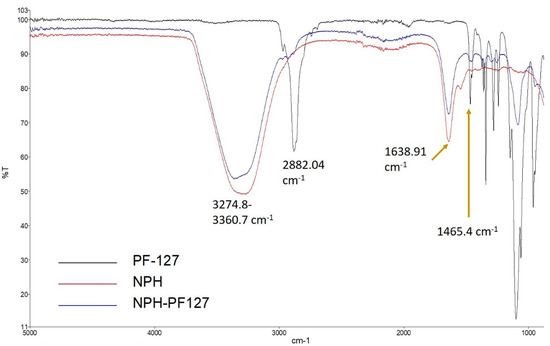
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of NPH, NPH/PF127, and PF127.
3.4. Microcrystals Morphological Characterization
The crystallization of isophane insulin (NPH) is mainly about the complexation of protamine and insulin hexamers with at least two zinc atoms. The rod-like tetragonally bi-pyramidal morphology of NPH microcrystals, with dimensions of approximately 0.5 to 1 µm in width and 5 to 10 µm in length, has a morphological structure that is distinct from other crystalline insulins [11,39,40].
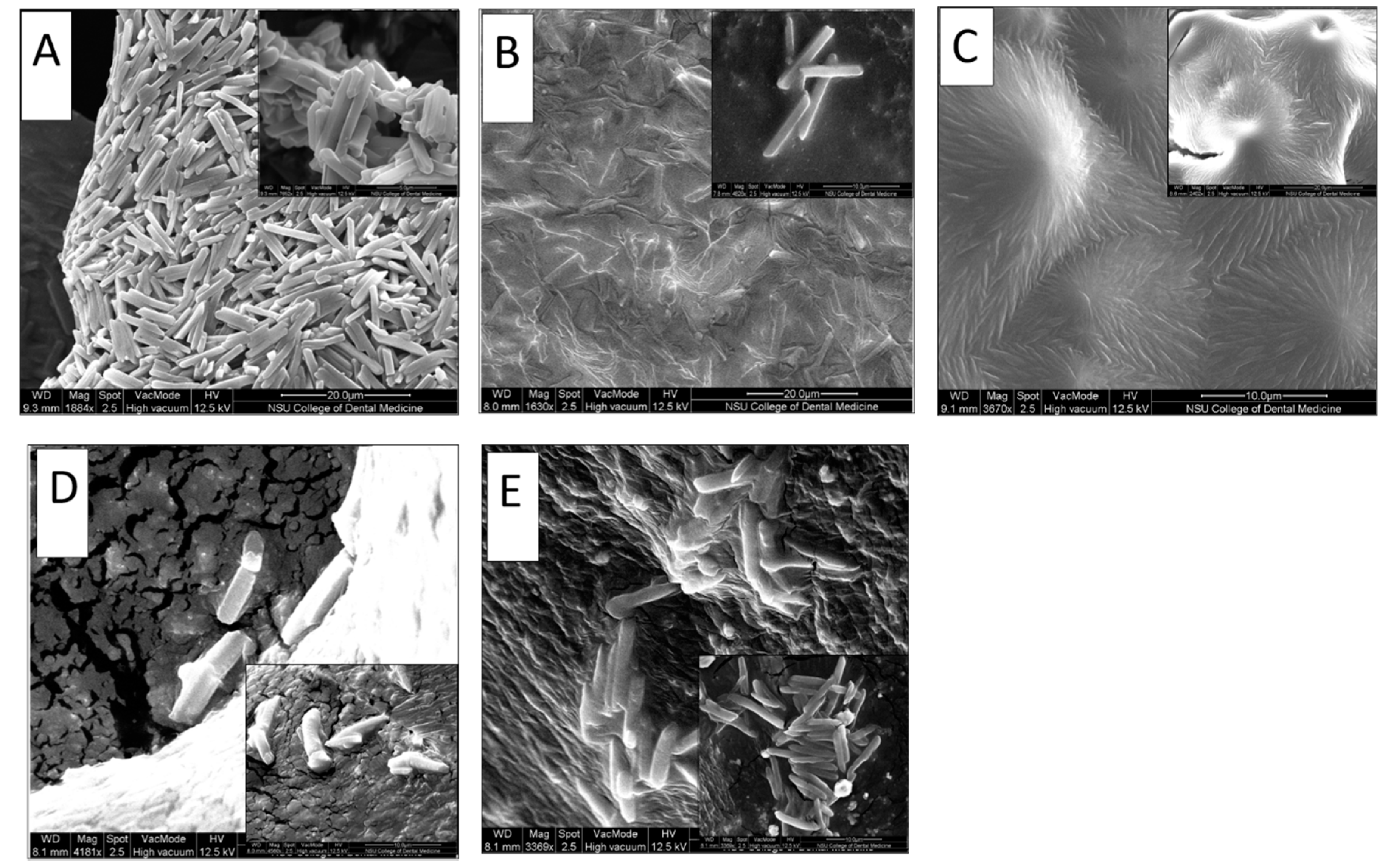
The morphology of microcrystals of NPH-loaded PF127 hydrogel was examined using Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy. NPH-PF127 samples (with and without centrifugation) were compared to commercial NPH. Another comparison was conducted between NPH-PF127 and NPH in the presence of trypsin. Figure 4B shows that the NPH loaded in PF127 (in which PF127 was directly dissolved in an NPH suspension) appears to have preserved the morphological integrity of the crystals, as the shape was similar to the microcrystals in NPH alone (Figure 4A) with the tetragonal rod shape with approximately similar dimensions. Figure 4C shows the NPH-PF127 crystals which underwent centrifugation in the preparation process. Although the elongated crystal shape was retained, these crystals appear to lack the clear definition of the original tetragonal rod-shape characteristics of the NPH insulin microcrystals.
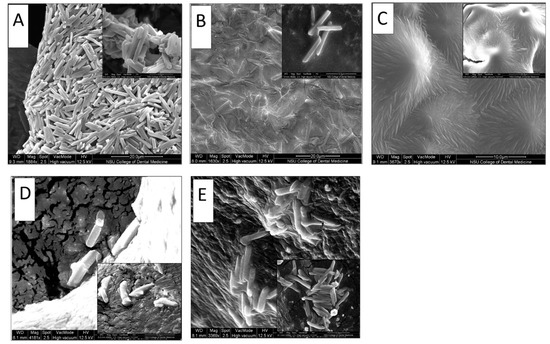
Figure 4.
SEM images for (A) NPH only, (B): NPH-PF127 by direct dissolution in PF127, (C) NPH-PF127 by the centrifugation of NPH, (D) NPH in the presence of trypsin (1 U/mL), (E) NPH-PF127 in the presence of trypsin.
Figure 4D,E display insulin crystals in the NPH and NPH-PF127, respectively, after 1 h of incubation with trypsin (1 U/mL) as the subcutaneous model enzyme activity against the protamine moiety. The morphological features of the microcrystals were better preserved against the same duration of tryptic activity in the NPH-PF127 in comparison with NPH alone. It was observed that the crystal morphology in Figure 4E was consistent with NPH-PF127 (Figure 4B) and with NPH (Figure 4A). Presumably, loading the microcrystals in PF127 hydrogel was accomplished when they were prepared with a gentle direct mixing without centrifugation, and ultimately they retained the same characterization as NPH original crystals because of the relatively minor physical alteration. The other preparation of NPH-PF127 shown in Figure 4C was apparently impacted by the centrifugation process, and the crystals lost their integrity due to the possibly harsh conditions of enrichment.
3.5. Gel Erosion and Drug Release In Vitro
3.5.1. Erosion Profiles for NPH-PF127 Microcrystal Hydrogel
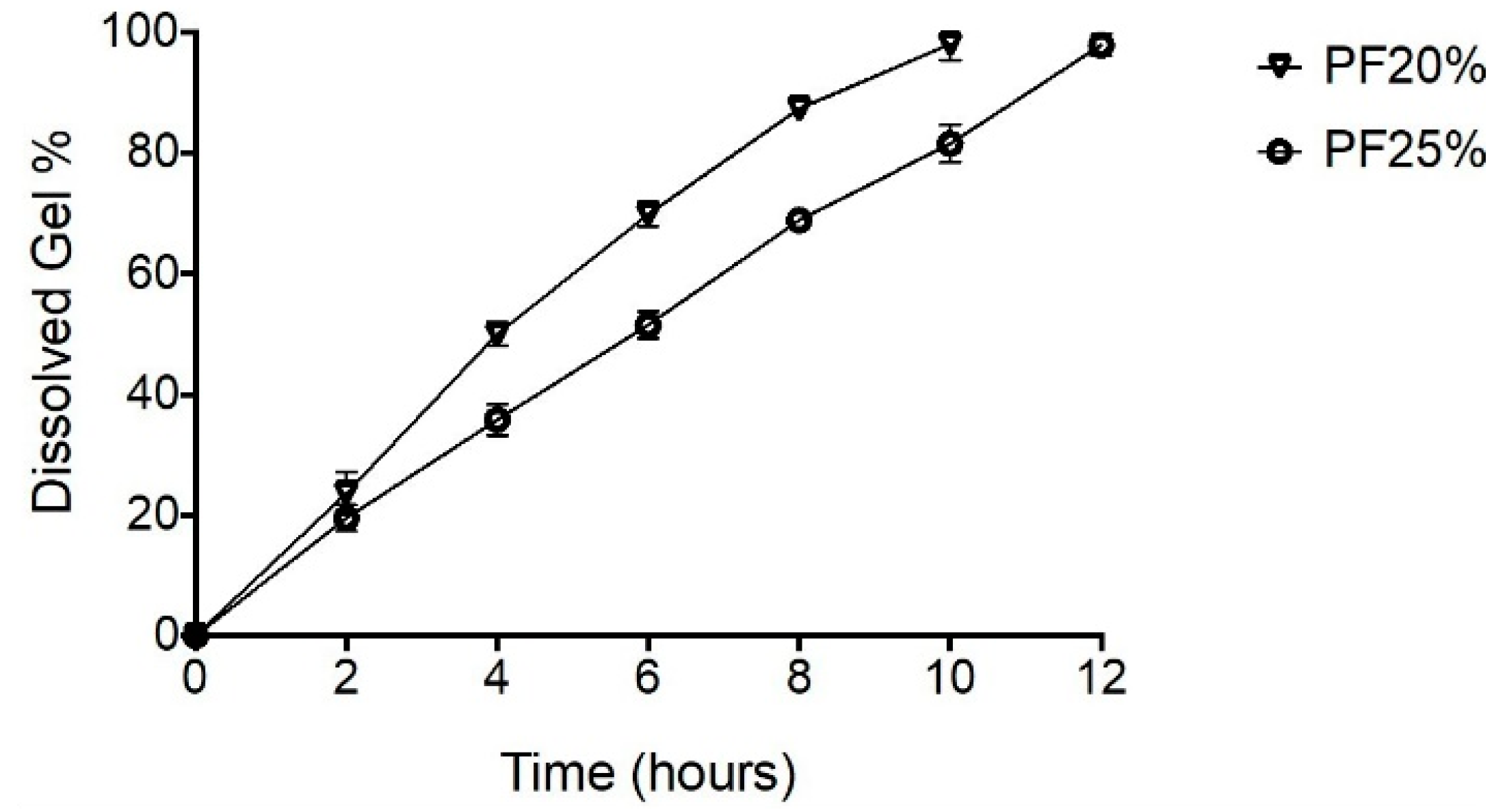
The erosion rate of NPH-PF127 hydrogel was investigated in vitro using a dialysis membrane by measuring the mass loss of the insulin microcrystal-loaded gel over time. As shown in Figure 5, increasing the PF127 concentration correlated with decreasing the percentage of dissolved gel for all time. The % mass loss of the NPH-PF127 gel followed a zero-order kinetics exhibiting linearity for all the hydrogel concentrations. The erosion kinetic results are in agreement with those of other studies [36,37]. The aqueous gel viscosity increased as a result of increasing the PF127 concentration, at which the penetration of the dissolution medium through the hydrogel surface is thought to be more restrictive.
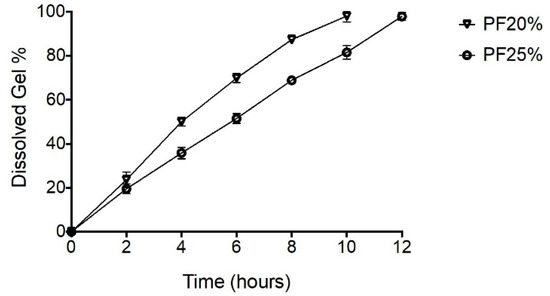
Figure 5.
Degradation and erosion behavior of different concentrations of NPH-PF127 using the dialysis method at 37 °C. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3).
3.5.2. In Vitro Release of NPH Insulin from PF127
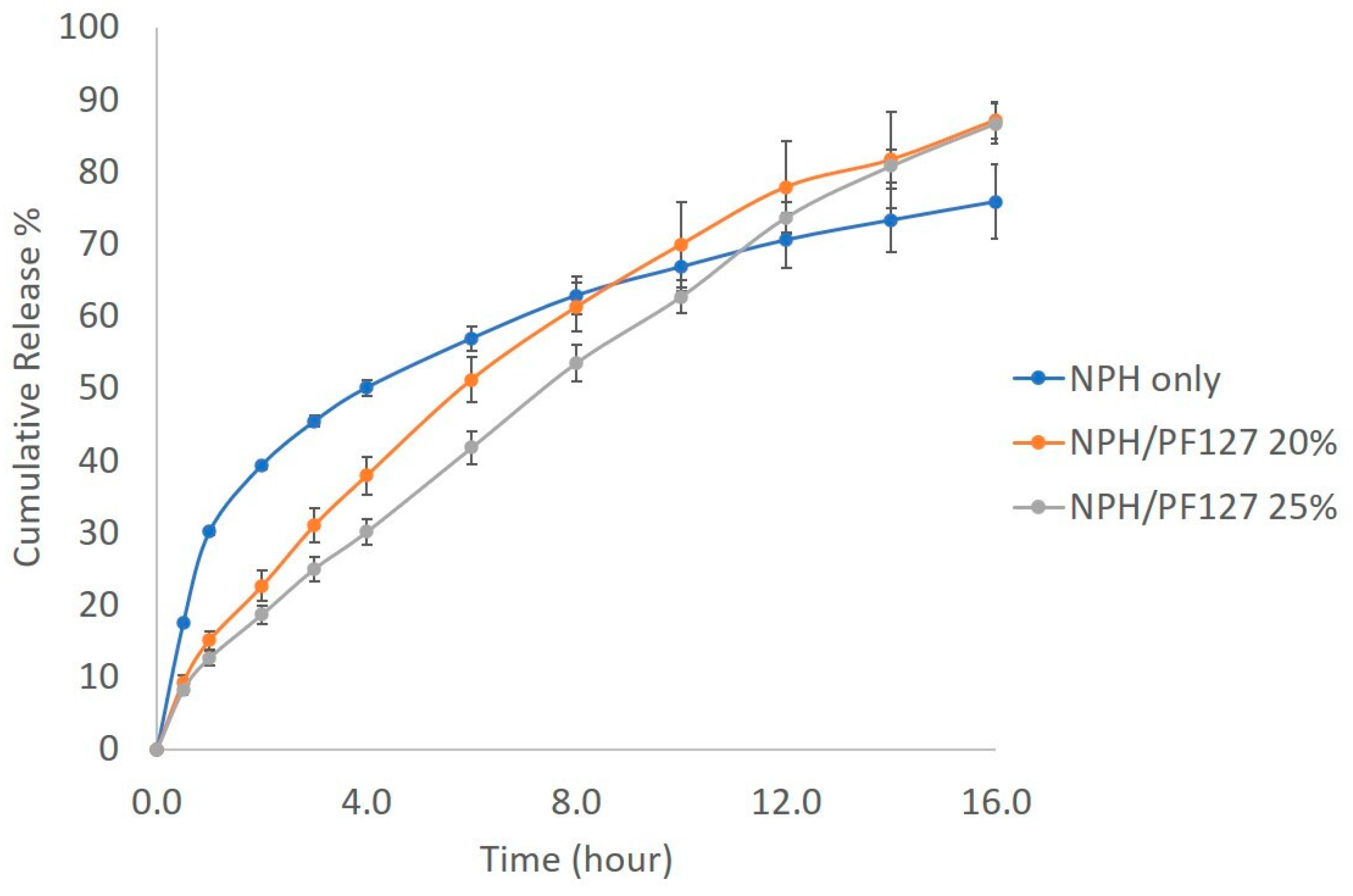
The in vitro insulin release from NPH alone and NPH loaded PF127 was investigated using the dialysis method at 37 °C. Figure 6 shows the initial burst release of 40% of insulin from NPH microcrystals during the first 2 h, followed by a relatively flatter release profile until the end of the experiment. The release of insulin from NPH microcrystal hydrogel (NPH-PF127) was steady and slow. The presence of PF127 reduced the burst of insulin release by 20% during the first 6 h in comparison to NPH only and, unlike the NPH only, the drug release from PF127 (both 20% and 25%) was more continuous, reaching a higher cumulative percent release at the end of the experiment. In both polymer concentrations, the drug release was well-correlated (R2 > 0.99) with the mass loss of the polymer (see Figure S3 in the Supplementary Information).
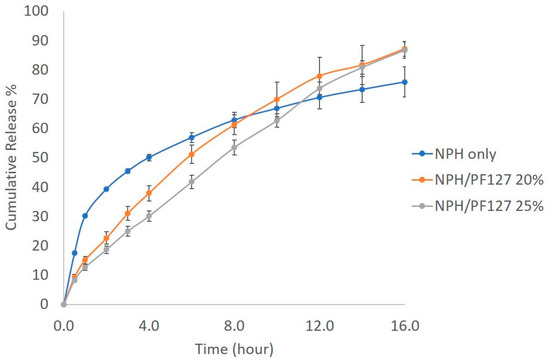
Figure 6.
In vitro insulin release profile of NPH, NPH-PF127 (20%), and NPH-PF127 (25%) using PBS at pH 7.4 as a dialysis medium.
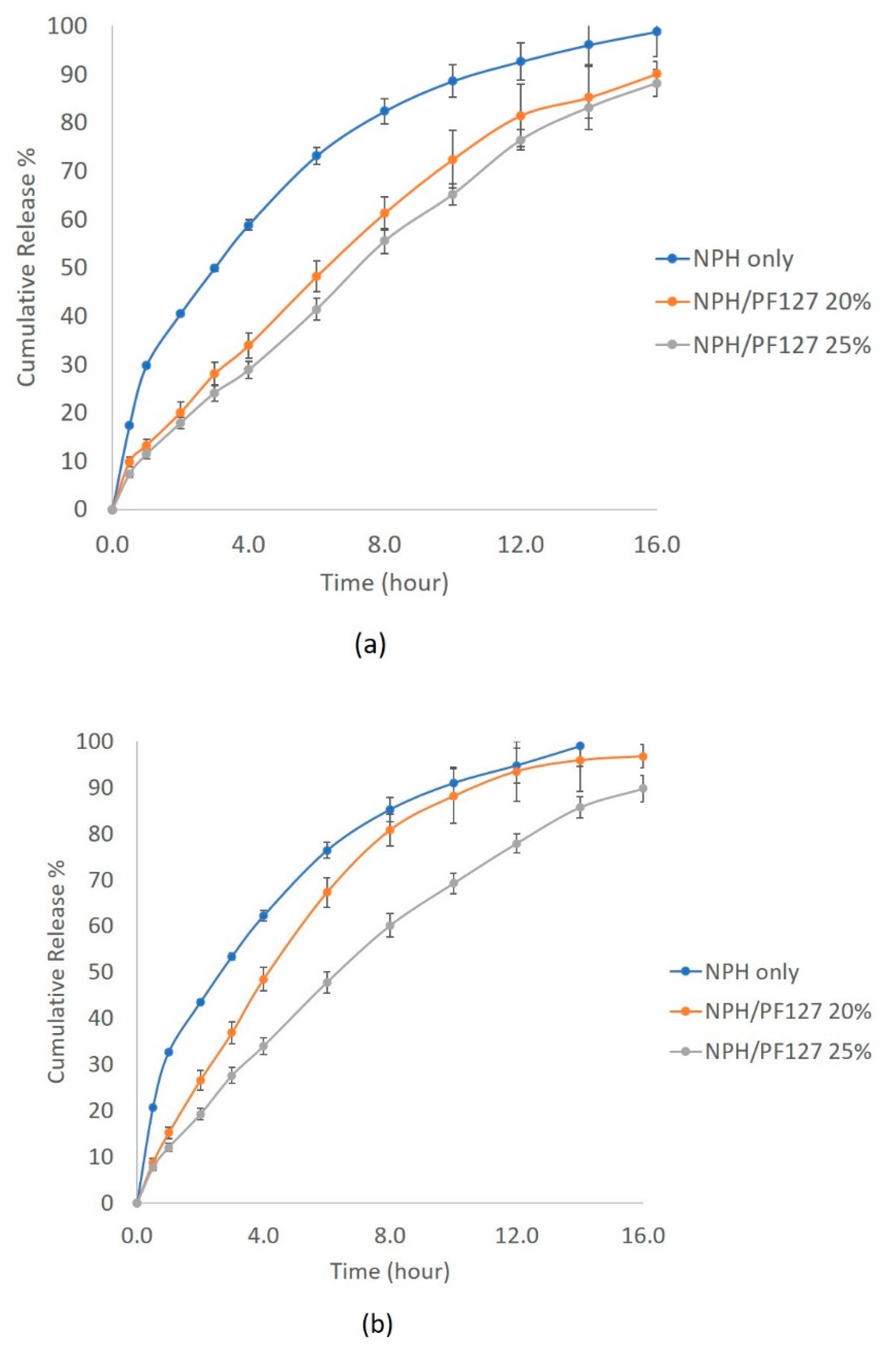
The influence of subcutaneous enzyme concentrations on the dissolution of NPH and NPH-PF127 was tested in the trypsin concentration range of 1–5 U/mL. As presented in Figure 7a, the dissolution of NPH crystals was highly enhanced, and more than 70% of the insulin was released after 6 h in the presence of 1 U/mL of trypsin. At the same concentration of trypsin, the presence of PF127 in the NPH-PF127 significantly attenuated the crystal dissolution and the burst release over the duration of the release study. Approximately, there was a 50% reduction in insulin released from NPH-PH127 (25%) compared to NPH during the first 2 h.
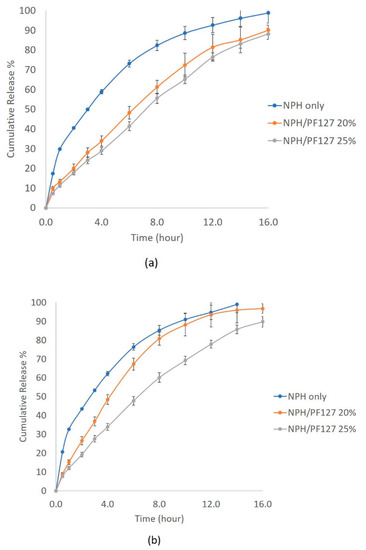
Figure 7.
In vitro insulin release profile from NPH, NPH-PF127 (20%), and NPH-PF127 (25%) using PBS (pH 7.4) with trypsin concentrations of (a) 1 U/mL and (b) 5 U/mL.
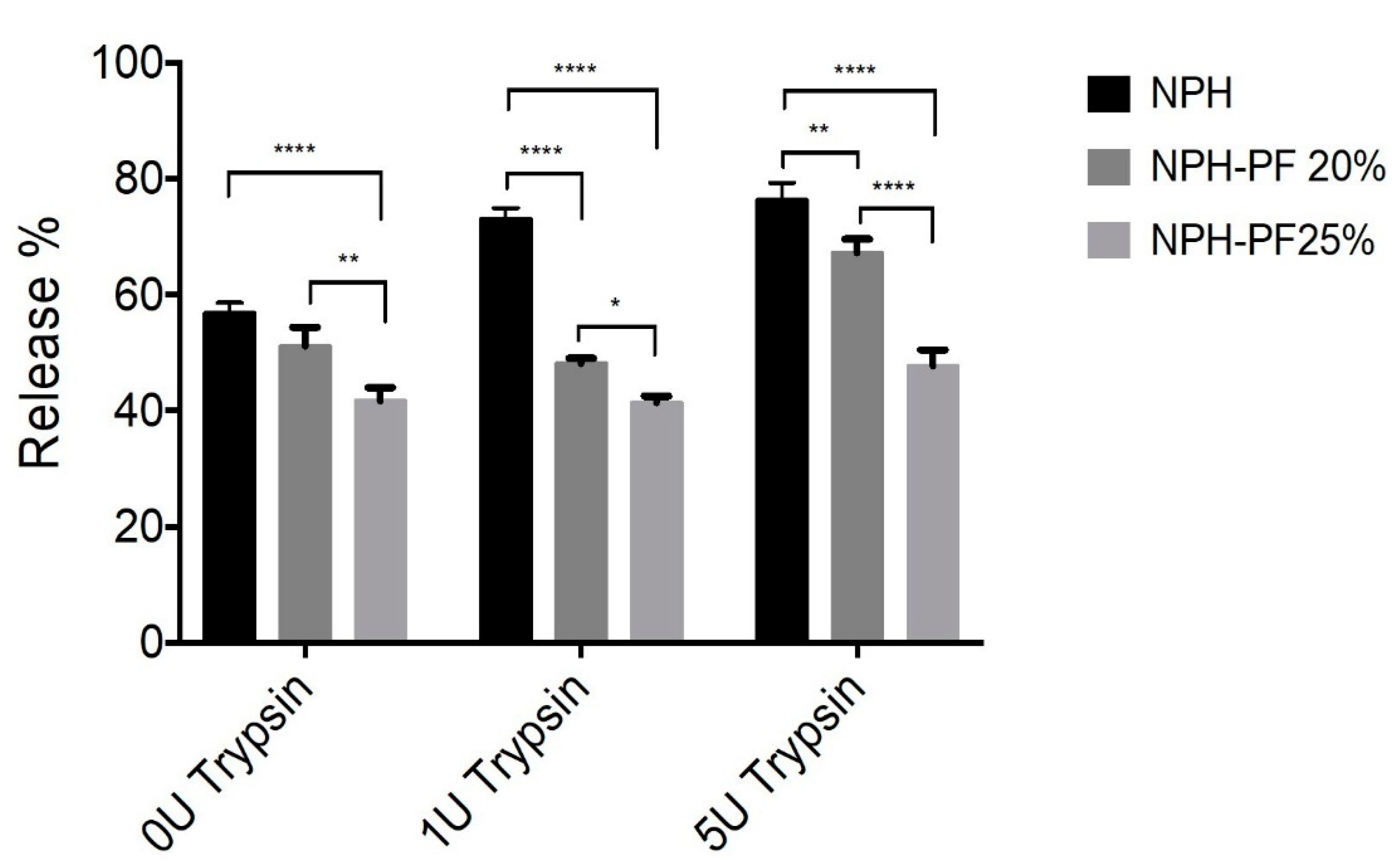
As shown in Figure 8, the presence of trypsin concentration of up to 5 U/mL had a significant effect on the dissolution of NPH alone, which led to a release of more than 70% of insulin 6 h after the drug release commenced. The addition of 5 U/mL of trypsin to the release medium resulted in a 75% insulin release from NPH alone as compared to 65%, 45% in the NPH-PF127 20% and NPH-PF127 25%, respectively. The percentage of insulin release from each insulin formulation in the presence of various trypsin concentrations after 6 h of in vitro release is shown in Figure 8. A highly significant (p < 0.0001) decrease in the total insulin release percentage was observed when the insulin was set as the NPH-loaded PF127 (20% or 25%) gel formulation compared with the insulin release from the NPH suspension in the presence of trypsin (1 U/mL). In the absence of trypsin, a significant (p < 0.0001) increase in insulin release was observed in the NPH-PF127 (25%) gel formulation compared to that of the NPH suspension. With the addition of 5 U/mL, while the insulin release from NPH-PF127 (20%) was significantly accelerated compared to 1 U/mL, the insulin release was significantly attenuated for NPH-PH127 (25%).
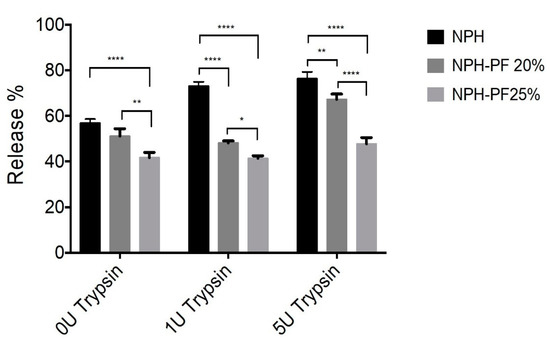
Figure 8.
Comparison of the insulin release in vitro at t = 6 h: NPH, NPH-PF127 (20%), and NPH-PF127 (25%) without and with (1–5 U/mL) trypsin. Values represent the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). Statistically significant differences (**** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, and * p < 0.01) in the % release values (at t = 6 h) between each paired group were obtained using Tukey’s post hoc test.
3.6. Effect of Storage on Insulin Release from NPH-PF127
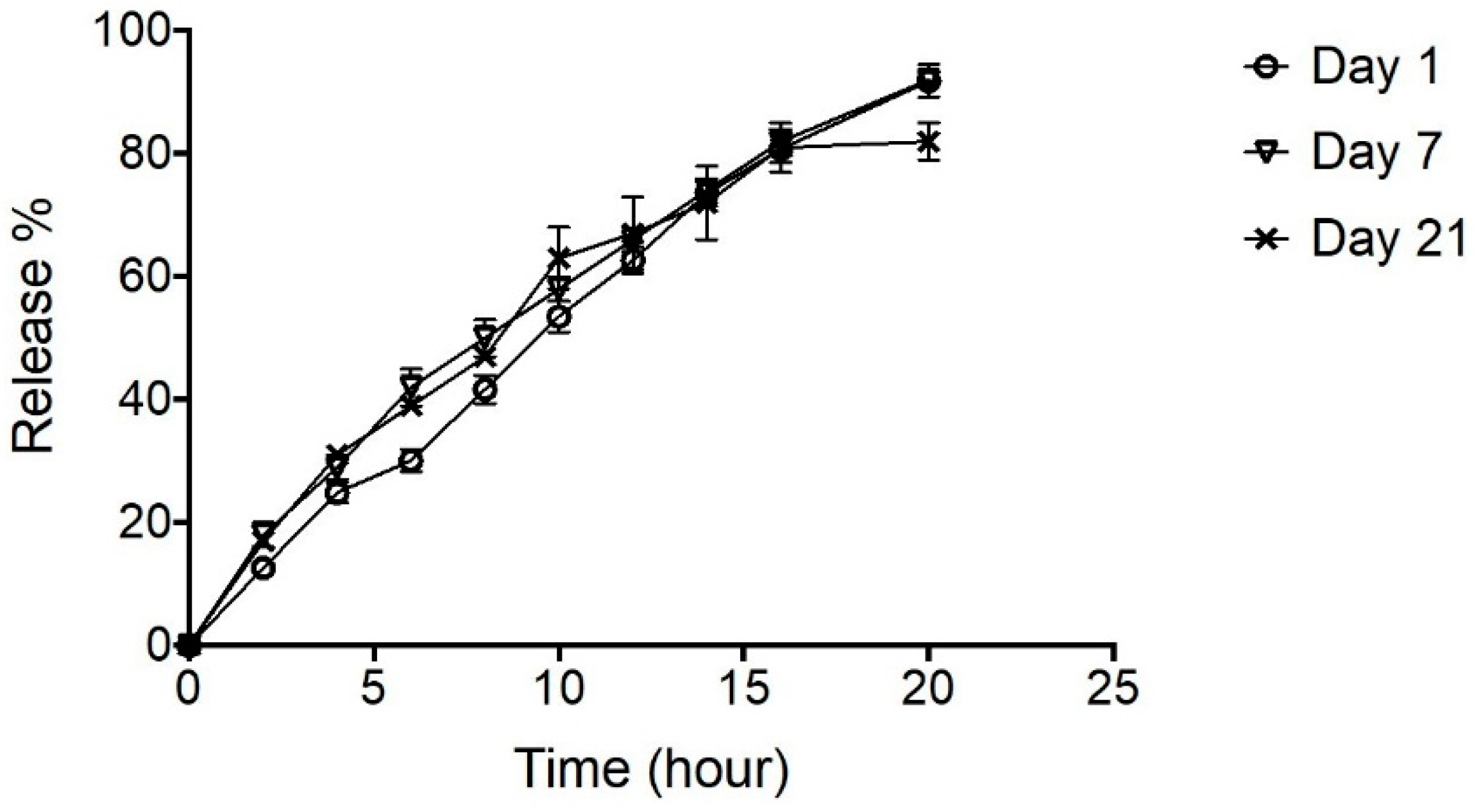
The effect of short-term (3 weeks) storage at 4 °C on the performance of NPH-PF127 (25%) was evaluated by conducting the in vitro release for the same preparation at different days (1, 7, and 21 days). Overall, the release profiles from all three cases retained similar insulin release patterns to those shown in Figure 9. Approximately 100% of the initial loading was released equally with a constant release rate for the samples analyzed on days 1 and 7. On the other hand, the insulin release appeared to be stagnant at 80% for the sample after 3 weeks of storage in this particular study.
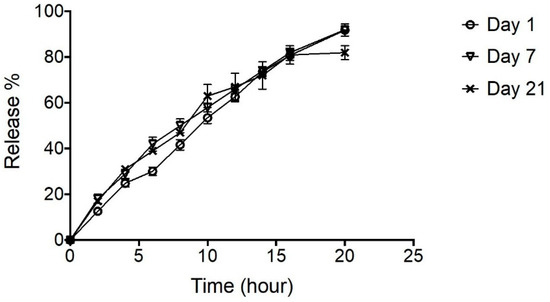
Figure 9.
In vitro release of insulin (NPH- PF127 25%) at day 1, 7, and 21 upon storage at 4 °C. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3).
4. Discussion
Several approaches have been introduced to provide controlled release systems for protein delivery via the subcutaneous route [17,19,41]. However, due to the instability concerns for a long-term protein release system using biodegradable polymers, an injectable hydrogel depot using biodegradable (tri)block copolymer materials has been explored for the controlled and longer-term delivery of therapeutic proteins, including insulin [42,43,44,45].
Pluronic F127 (PF127) can serve as another type of biocompatible injectable depot that has been widely studied for parenteral and other applications for insulin delivery for the last two decades [46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. Pluronic F127 (PF127) is a nonionic triblock copolymer that consists of 70% polyoxyethylene and 30% polyoxypropylene segments (PEO-PPO-PEO). The thermoresponsive aqueous solution of PF127 has been utilized to control and modulate the release of loaded drugs [37,45]. However, the hydrogel formed by PF127, unless chemically modified, can only last ~1 day at most due to surface erosion and was deemed unsuitable for a drug release system beyond 1 day.
The main question we are trying to answer in this study is whether we can modify the clinically undesirable action pattern of NPH basal insulin, which involve a nonconstant release. The aforementioned “negative” property of PF127 hydrogel (lasting only a matter of a day) is in fact a desirable property to modulate insulin release on an hourly scale in such a system. If the carrier erosion occurs within 24 h, it leaves nothing behind, which is a key property for a once-daily formulation.
As mentioned in the introduction, tissue enzymes are involved in the insulin release from NPH microcrystals by degrading protamine, an essential component of NPH insulin. Although mainly found in the digestive tract, trypsin is a good model enzyme to represent any tissue enzyme activity to degrade protamine without significantly degrading insulin itself in the NPH microcrystals, under the concentration of 5 U/mL (Figure 1). Using the trypsin-containing medium, we were able to characterize and adjust the compositions. The FTIR study suggests that the interactions between the PF127 polymer and NPH insulin are minimal (Figure 3). The peaks characteristic of PF127 (2882.04 and 1465.4 cm−1) appeared to be attenuated in the NPH/PF127 mixture without a change in position. This observation is consistent with other solid-phase drug-loaded PF127s, in which those peaks were attenuated with an increasing drug payload in solid state. The lack of shift is indicative of the lack of strong intermolecular interactions between PF127 and its payload [53]. This feature is in fact desired in our application, as the polymer does not disrupt the property of the microcrystals. PF127 hydrogel is serving as a depot system, providing a diffusion barrier to rapid insulin release as well as a physical barrier for penetrating enzymes to come into contact with NPH microcrystal surfaces.
As a means to increase the loading, we initially considered a loading process in which the microcrystals were enriched after centrifugation (5000 rpm for 5 min), followed by the removal of supernatants and loading the enriched microcrystals into a pre-formed PF-127 aqueous solution at 4 °C. However, this method resulted in compromising the integrity of NPH microcrystals, as shown in the SEM observations (Figure 4C). Therefore, we chose a direct dissolution of PF127 at 4 °C into NPH microcrystal suspensions (100 U/mL) overnight under mild agitation conditions. Indeed, this milder process helped to preserve the morphological integrity of the NPH microcrystals (Figure 4B).
The in vitro release results indicated that the enzyme-induced dissolution of NPH microcrystal was significantly attenuated due to the protective role of the PF127 gel structure surrounding the microcrystals. Without PF127, NPH in a tetragonal cube crystal form is assumed to be degraded from the outside surface [54]. The dissolution of NPH microcrystals involves the release of auxiliary substances, protamine, and insulin hexamers, which further dissociate to dimers and monomers in an equilibrium reaction [25]. For an NPH crystal dissolution in PBS (pH 7.4) without the addition of enzyme, the release of insulin is slower because the diffusion of protamine, insulin, and auxiliary substances under sink conditions is the primary factor for crystal dissociation and insulin release. In the presence of protamine-degrading enzymatic activity, the rate of insulin release can drastically change. Simulating protamine-specific activity by using trypsin in the release medium indeed accelerated the aforementioned crystals dissolution process. Protamine is the key factor in the crystal dissolution due to its basic nature originating from a high arginine content, which can be favorably targeted by enzymes in subcutaneous tissues [55].
It is noteworthy that when the PF127 concentration was 25% (w/w), the cumulative insulin release at the 6th hour point was not only attenuated compared to NPH, but also exhibited resistance to the acceleration of insulin release when the trypsin activity in the release medium was increased from 1 to 5 U/mL (Figure 9). The formulation with a lower PF127 concentration (20%) failed to demonstrate such a protective effect. This may be explained by the lower polymer density in the 20% hydrogel that allowed the easier penetration of trypsin at a higher level. On the other hand, we considered using 30% PF127 formulations to further increase the protective effect of PF127 toward NPH insulin. However, the viscosity of this formulation and the lowered gelling temperature presented an inconvenience to practical application. Therefore, we select NPH-PF127 (25%) as the formulation worthy of further testing.
We also briefly looked into the short-term storage stability of NPH-PF127 (25%) in refrigerated conditions. As shown in Figure 9, after 3 weeks of storage the insulin release pattern appeared to begin deviating from those with a shorter storage time toward the end of release. More comprehensive study is needed to better characterize the impact of storage conditions on this formulation, as our attempt was based on a very limited number of tries. The observation may be attributed to insulin trapped in aged polymer during storage or the potential chemical degradation of insulin during storage. In fact, even for commercially available NPH insulin, it can only be refrigerated for approximately a month after opening the vials. We also need to consider optimizing the additive concentration, which was not done in this study. It is reported that phenolic derivatives in the NPH suspension not only function as a preservative but also stabilize the interactions between dimers in each hexamer [7]. During the NPH-PF127 preparation, the injection solution was not discarded; rather, it was used as solvent to dissolve the PF127. This changes the overall volume of the formulation by about 25% and the preservative concentrations, which may affect the quality of the formulation in the longer run. The further optimization of additive concentrations is desired regarding the longer-term storage stability of the formulation.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, we conclude that the appropriate combination of NPH insulin microcrystals and PF127 hydrogel offered the protection of NPH insulin and the modulation of the insulin release in vitro in the presence of simulated tissue enzyme activity. Through this in vitro study, we optimized the formulation for further testing.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/8/10/1320/s1: Figure S1: schematic of instrumental setup for in vitro release studies; Figure S2: insulin concentration plotted against absorbance peak height (calibration curve) for insulin recovery study; Figure S3: correlation of cumulative % insulin release vs. % gel mass loss for NPH/PF127.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M.K.; methodology, M.H.S., Y.M.K.; formal analysis, M.H.S., W.A.M.; investigation M.H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.M.K., M.H.S.; supervision, Y.M.K.; project administration, Y.M.K.; funding acquisition, Y.M.K. and M.H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part by Nova Southeastern University, Health Professions Division Grant, and by Jazan University through the Saudi Arabian Cultural Mission (SACM) assigned to M.H.S.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Niswender, K.D. Basal insulin: Physiology, pharmacology, and clinical implications. Postgrad Med. 2011, 123, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petznick, A. Insulin management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 4, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, K.; Jeitler, K.; Berghold, A.; Ebrahim, S.H.; Gratzer, T.W.; Plank, J.; Siebenhofer, A. Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH insulin (human isophane insulin) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, CD005613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubner, K.; Molz, K.; Kerner, W.; Karges, W.; Lang, W.; Dapp, A.; Holl, R.W. Daily insulin doses and injection frequencies of neutral protamine hagedorn (NPH) insulin, insulin detemir and insulin glargine in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A multicenter analysis of 51 964 patients from the German/Austrian DPV-wiss database. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2014, 30, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, R.D.; Cole, S.A.; Ozawa, H.; Magdoff-Fairchild, B.; Eggena, P.; Rudko, A.; Low, B.W. Precipitation and crystallization of insulin in the presence of lysozyme and salmine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 200, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, M.; Pampanelli, S.; Fanelli, C.; Porcellati, F.; Bartocci, L.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Bolli, G.B. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of subcutaneous injection of long-acting human insulin analog glargine, NPH insulin, and ultralente human insulin and continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin lispro. Diabetes 2000, 49, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenfeld, R.; Seipke, G.; Berchtold, H.; Owens, D.R. The evolution of insulin glargine and its continuing contribution to diabetes care. Drugs 2014, 74, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Azoulay, L.; Majdan, A.; Boivin, J.F.; Pollak, M.; Suissa, S. Long-Term Use of Long-Acting Insulin Analogs and Breast Cancer Incidence in Women with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, J.C.; Conlin, P.R.; Gellad, W.F.; Edelman, D.; Lee, T.A.; Pizer, S.D. Long-term outcomes of analogue insulin compared with NPH for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Manag. Care 2015, 21, e235–e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redwan, E.M.; Linjawi, M.H.; Uversky, V.N. Looking at the carcinogenicity of human insulin analogues via the intrinsic disorder prism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brader, M.L.; Sukumar, M.; Pekar, A.H.; McClellan, D.S.; Chance, R.E.; Flora, D.B.; Myers, S.R. Hybrid insulin cocrystals for controlled release delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrman, M.; Hubalek, F.; Schluckebier, G. Structural characterization of insulin NPH formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFelippis, M.R.; Bakaysa, D.L.; Bell, M.A.; Heady, M.A.; Li, S.; Pye, S.; Frank, B.H. Preparation and characterization of a cocrystalline suspension of [LysB28,ProB29]-human insulin analogue. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, J.; Fogelfeld, L.; Guerra, Y. Cumulative clinical experience with use of insulin lispro: Critical appraisal, role in therapy, and patient considerations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2012, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.S.; Larsson, M.; Hsiao, M.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Roding, M.; Nyden, M.; Liu, D.M. Injectable insulin-lysozyme-loaded nanogels with enzymatically-controlled degradation and release for basal insulin treatment: In vitro characterization and in vivo observation. J. Control Release 2016, 224, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, P.; Araujo, F.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. Oral insulin delivery: How far are we? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, W. Challenges and recent advances in the subcutaneous delivery of insulin. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, R.I. Inhaled insulin-intrapulmonary, intranasal, and other routes of administration: Mechanisms of action. Nutrition 2010, 26, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Burke, P.A.; Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: Formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.F.; Bhansali, S.G.; Morris, M.E. Mechanistic determinants of biotherapeutics absorption following SC administration. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.F.; Jacobsen, B. Subcutaneous absorption of biotherapeutics: Knowns and unknowns. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, F.; Okumura, K.; Hori, R. Fate of porcine and human insulin at the subcutaneous injection site. II. In vitro degradation of insulins in the subcutaneous tissue of the rat. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1985, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Okumura, K.; Komada, F.; Hori, R. Fate of porcine and human insulin at the subcutaneous injection site. I. Degradation and absorption of insulins in the rat. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1985, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyama, M.; Ishida, T.; Kokubu, N.; Komada, F.; Iwakawa, S.; Okumura, K.; Hori, R. Enhanced bioavailability of subcutaneously injected insulin by pretreatment with ointment containing protease inhibitors. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeborg, T.; Rasmussen, C.H.; Mosekilde, E.; Colding-Jorgensen, M. Absorption kinetics of insulin after subcutaneous administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 36, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, J.; Qin, W. Potentiometric determination of trypsin using a polymeric membrane polycation-sensitive electrode based on current-controlled reagent delivery. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 88, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mort, J.S.; Buttle, D.J. Cathepsin B. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernigora, A.N.; Gengin, M.T. Basic (cleaving arginine and lysine residues) metallocarboxypeptidase of mammalian tissue: Structure, properties, and function. Ukr. Biokhim. Zhurnal 1998, 70, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, M.; Blass, J.; Detruit, H.; Aime, L.; Baudet, B.; Fiancette, J.Y.; Verriest, C. Determination of “in vitro” degradation of protamine in plasma by three different methods. Thromb. Res. 1986, 41, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, R.J.; Mitra, A.K. Degradation of insulin by trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, M.; Craparo, E.F.; Podesta, A.; Bulone, D.; Carrotta, R.; Martorana, V.; San Biagio, P.L. Kinetics of different processes in human insulin amyloid formation. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, W.L.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhou, T.Y.; Zhang, Q. Controlled delivery of recombinant hirudin based on thermo-sensitive Pluronic F127 hydrogel for subcutaneous administration: In vitro and in vivo characterization. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Wang, Y.L.; Qu, Y.; Liao, J.F.; Chu, B.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Qian, Z.Y. Synthesis, characterization, and application of reversible PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA copolymer thermogels in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.R.; Macphee, C.E.; Miller, A.F.; Dunlop, I.E.; Dobson, C.M.; Donald, A.M. The formation of spherulites by amyloid fibrils of bovine insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14420–14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.A.; Dodds, E.C.; Phillips, D.M.; Stephen, J.M. The action of chymotrypsin and trypsin on insulin. Biochem. J. 1948, 42, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.; Rehman, K.; Li, N.; Gpao, J.Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, S. Sustained delivery of IL-1Ra from pluronic F127-based thermosensitive gel prolongs its therapeutic potentials. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 3475–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Hsiao, W.L.; Pan, W.; Yang, Z. Thermoreversible Pluronic F127-based hydrogel containing liposomes for the controlled delivery of paclitaxel: In vitro drug release, cell cytotoxicity, and uptake studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Hatton, T.A. Poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (propylene oxide)-poly (ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: Thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balschmidt, P.; Hansen, F.B.; Dodson, E.J.; Dodson, G.G.; Korber, F. Structure of porcine insulin cocrystallized with clupeine Z. Acta Cryst. B 1991, 47, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brange, J. Galenics of Insulin; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1987; pp. 18–100. [Google Scholar]
- Pisal, D.S.; Kosloski, M.P.; Balu-Iyer, S.V. Delivery of therapeutic proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2557–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, S.W. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature 1997, 388, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, S.; Koh, J.J.; Lee, M.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, S.W. Controlled release of insulin from injectable biodegradable triblock copolymer. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, S.W. Biodegradable triblock copolymer microspheres based on thermosensitive sol-gel transition. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Qi, T.; Wei, X.; Qu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Thermosensitive polymeric hydrogels as drug delivery systems. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barichello, J.M.; Morishita, M.; Takayama, K.; Nagai, T. Absorption of insulin from pluronic F-127 gels following subcutaneous administration in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 184, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wong, B.C.K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lin, C.; Riaz, M.K.; Tyagi, D.; Lu, A.; et al. Long-lasting Insulin Treatment Via a Single Subcutaneous Administration of Liposomes in Thermoreversible Pluronic® F127 Based Hydrogel. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 6079–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Development and in vitro evaluation of insulin-loaded buccal Pluronic F-127 gels. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2010, 15, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Statistical optimization of insulin-loaded Pluronic F-127 gels for buccal delivery of basal insulin. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, F.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, A.; Khan, J.A.; Khan, A.; Khuda, F.; Zakir, S.; Yousaf, N.; Khan, I.; Shah, Y.; et al. Development and evaluation of pluronic- and methylcellulose-based thermoreversible drug delivery system for insulin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Barichello, J.M.; Takayama, K.; Chiba, Y.; Tokiwa, S.; Nagai, T. Pluronic F-127 gels incorporating highly purified unsaturated fatty acids for buccal delivery of insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 212, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chu, M.K.; Lu, B.; Mirzaie, S.; Chen, K.; Gordijo, C.R. Enhancing thermal stability of a highly concentrated insulin formulation with Pluronic F-127 for long-term use in microfabricated implantable devices. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolewicz, B.; Górniak, A.; Owczarek, A.; Żurawska-Płaksej, E.; Piwowar, A.; Pluta, J. Thermal, spectroscopic, and dissolution studies of ketoconazole–Pluronic F127 system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 2487–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.; Gryniewicz, C.M.; Pringle, T.; Cunningham, F. Insulin temperature and stability under simulated transit conditions. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röder, P.V.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).