Abstract
Tissue engineering (TE) is one of the most challenging fields of research since it provides current alternative protocols and materials for the regeneration of damaged tissue. The success of TE has been mainly related to the right selection of nano-sized biocompatible materials for the development of matrixes, which can display excellent anatomical structure, functionality, mechanical properties, and histocompatibility. Today, the research community has paid particular attention to zein as a potential biomaterial for TE applications and nanotechnological approaches. Considering the properties of zein and the advances in the field, there is a need to reviewing the current state of the art of using this natural origin material for TE and nanotechnological applications. Therefore, the goal of this review paper is to elucidate the latest (over the last five years) applications and development works in the field, including TE, encapsulations of drugs, food, pesticides and bandaging for external wounds. In particular, attention has been focused on studies proving new breakthroughs and findings. Also, a complete background of zein’s properties and features are addressed.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, nanotechnology is providing new ideas to improve the characteristics and features of different fields, including the tissue engineering (TE). The main objective of TE is to regenerate damaged tissue by using a ceramic or polymeric scaffold at specific an anatomical position. However, the scaffolds must overcome several challenges in order to mimic the cellular environment, such as the establishment of the vascular network, obtain correct pore size to handle the mechanical stress, and maintain the structural integrity of the scaffold, the vascular network issue being the main bottleneck [1,2]. To solve the vascular network problem, it is necessary to preload the scaffold with cells before setting it into the desired anatomic location [1]. Also, to guarantee the proliferation of the preloaded cells, the scaffold must meet conditions of anatomical structure, functionality, aesthetic requirements, mechanical properties, histocompatibility, degradation capacity, growth factors, minerals (e.g., iron which serves as a cofactor on bone TE), and even magnetic forces [1,3,4,5,6]. When dealing with bone TE, the material matrix for the scaffold must come from natural sources due to the fact that it may show potential advantages for the recognition of cells located near to the damaged site without showing any type of rejection. For instance, a natural and potential source for scaffold matrix is bovine collagen. This material generally shows high biocompatibility, unfortunately with poor mechanical properties, leading to its usage in bones that do not provide support to the body [7]. In fact, collagen has been used in a wide variety of TE applications besides bone tissue due to its extensive presence in the human body. There are 28 types of collagen but only collagen types I, II and III have been mostly used on TE applications towards nerves, cartilage, tendon, ligaments, vascular functions and skin [8]. Another example is chitosan, which is the second most abundant biopolymer in the world, and is employed in different types of applications, including membranes [9,10]. It is possible to produce chitosan from the deacetylation of the chitin extracted from shrimps [7,11]. In recent times, due to continuous research of other promising biopolymers, zein has been presented and explored as a potential candidate to be used on TE applications. For example, in the case of the treatment of periodontitis, periodontal ligament stem cells have been grown on scaffolds with a matrix of bovine bone mineral and zein. Both materials had the objective of creating bone, cementum, blood vessel and ligaments [12]. Also, the zein has proved to have several nanotechnological applications including drug delivery, food packaging, and as a raw material for carbon nanodots fabrication or in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) platform for nanosensors [13,14,15,16,17]. Therefore, the goal of this review is to provide an overview of the latest (over the last five years) applications and development works in the field of tissue engineering and specific usage on nanotechnology applications, including encapsulations of drugs, food, pesticides and bandaging for external wounds that, perhaps, can open the door to new ideas and applications in the tissue-engineering field. Particular attention has been paid to relevant results and findings in the field. In addition, an overview about the main characteristics and properties of zein, as well as the different protocols for its extraction, are also addressed. Lastly, future trends are reported and discussed in terms of elaboration of scaffolds with the aid of computational tools and 3D printing.
2. Zein
2.1. Physico-Chemical Properties
Zein is widely found in maize (Zea mays) and constitutes between 44% to 79% of the protein content of the endosperm. Its protein structure can be found elsewhere, as shown Figure 1. This protein has an isoelectric point of 6.2, possesses a hydrophobic composition, and usually is dissolved in ethanol concentration solutions of 60–95% or on alkaline aqueous solutions with a pH of 11. This basic solution is characterized by containing urea or high concentrations of surfactants. The hydrophobic characteristic is derived from the high content of leucine and alanine [13,18,19,20]. Other important characteristics of the zein are low water vapor permeability and a greaseproof property [21]. In the pharmaceutical industry it has attracted the attention due to its natural renewable origin source, biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility [13,22].
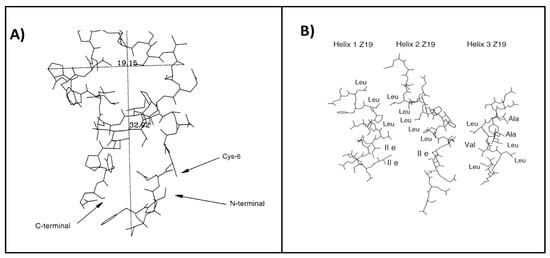
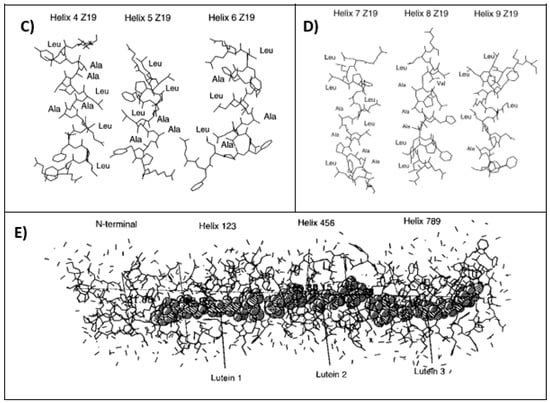
Figure 1.
Protein structure of a 19 kDa α-zein. It is divided into 10 different segments which consist in a N-terminal structures and nine helix segments. The (A) segment is the N-terminal segment, while the (B) segment corresponds the 1, 2 and 3 segments, (C) corresponds to 4, 5 and 6 segments, and the (D) includes the 7, 8 and 9 segments. Finally, (E) shows the whole structure including a lutein structure, which provides stability to zein molecule [23].
Zein is classified into four types, such as α-zein, β-zein, γ-zein and δ-zein. The α-zein represents almost 80% of the total amount of zein, while β and γ-zein are usually present in the range of 10–15% and the rest is δ-zein [18]. The molecular weight of α-zein is about 22 up to 24 kDa, β-zein is around 17 kDa, δ-zein is 10 kDa and γ-zein ranges from 18 to 27 kDa [24]. In general, Table 1 lists some other important properties of zein. Importantly, when dealing with the properties of zein-based films towards biotechnological approaches, the features depend on the preparation protocols and operating conditions of the production process.

Table 1.
Physico-chemical properties of zein materials.
2.2. Zein Extraction
To date, there have been several methods to extract the zein from maize. The first method deals with the use of a single column extraction from distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) [27]. Initially, the first step implies the oil extraction from the DDGS by using a single packed column. The DDGS are later added to the column with n-hexane as the extraction solvent. With the help of a heat exchanger jacket with hot water, the column is heated. The operating conditions are determined as follows: solid mass ratio of 3:1, operation time of 10 min, a constant temperature of 45 °C and a total of four extraction cycles. It is important to point out that this corn oil may also have applications for the biodiesel industry [27]. Once the oil extraction is done, the next step is to take the residue of oil extraction operation. This fresh extract is switched by an ethanol/water solution containing 70% ethanol concentration. Herein, the operating conditions are 40 min of exposure and the temperature is significantly higher ca. 78 °C, and optimal pH of 4. This method requires a total number of three extraction cycles. Subsequently, the solvent is evaporated, and the residues (i.e., zein) later washed with distilled water. Finally, the zein is centrifuged and recovered to be later dried. The yield of zein extraction after the third and fourth extraction is about 30.7% [27].
In a different approach, the zein extraction is performed evaluating 14 different solvents [27,29], including isopropanol, isobutanol, 2,3-butanediol, 1,4-dioxane, ethanol; to mention just a few. Firstly, 1 g of dry DDGS is added to 10 cm3 of an aqueous solution containing 66–73% concentration of the selected solvent and 0.0025 g of anhydrous sodium sulfite. Then, the flask is stirred for 90 min with a temperature ranging from 77–85 °C and a pH condition range of 3.8–4.4. Once the stirring time is over, the reaction product is filtered (Whatman grade-41 filter paper) and then cooled down at a temperature of 4 °C for 6 h. Later, distilled water is added and it is stored at a temperature of 4 °C for 12 h. The last step involves a centrifugation operation of the solution and thus separates the precipitate, i.e., wet zein. Therefore, a drying process must be applied at a temperature of 40 °C. To sum up, the yields of zein extraction are about 36%, 70% and 41% for 2,3-BDO, isopropanol and 1,4-dioxane, respectively (see Table 2). On the other hand, 1,3-dioxolane is considered as a green solvent, which has the objective of reducing the environmental and harmful impact upon human health. It is recognized as non-carcinogenic, non-toxic, and non-explosive. It is typically used within the paint industry as a substitute of toluene and xylene. However, it is likely that an optimization of the process conditions (such as temperature, pH and solvent/water ratio) may enhance the extraction yield [29,30]. The processes can be graphically shown in Figure 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of the different methods and solvents used for zein extraction [27,29].
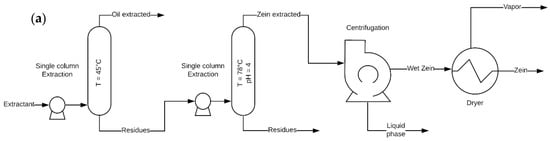
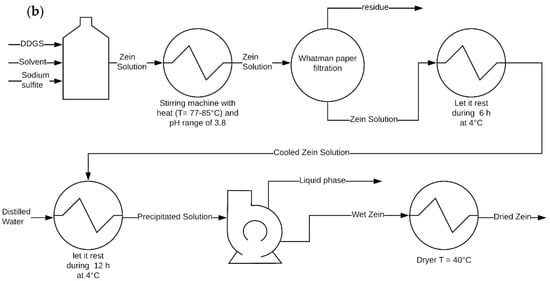
Figure 2.
(a) Process diagrams in a single column extraction from distillers dried grains and (b) extraction by stirred glass.
Table 2 shows that the best extraction is done using ethanol (extraction yield ca. 80%) with a stirred flask method, while the worst yield (ca. 31%) is obtained using an ethylic single column extraction. Thus, the best extraction method is that described as the stirred flask method [27,29]. The extraction yield is calculated according to the Equation (1).
2.3. Zein as a Biopolymer
The low degradation of petroleum-based polymers has led to environmental damage due to its rapid and constant production in the last few decades. Microplastics are the most common pollutant in the oceans and they are expected to grow by 12,000 million tons by 2050 [31]. In consequence, bioplastics have emerged as a solution thanks to their non-toxicity, origin from a renewable sources, biocompatibility and biodegradable properties [32]. In particular, zein has been widely used as a biopolymer within diverse industries and scientific fields, and the films and fibers can be fabricated by using electrospinning [15,16,22]. This method can be specially used to create zein-based nanofibers by using an ethanol-water solution at 70% concentration. The voltage required to electrospin the solution is about 15–20 kV. Then, the resulting fiber must be collected by a plate 10 to 12 cm away [15,16,33]. A syringe pump is needed in order to provide 1.244 kPa pressure and an outlet stream of almost 0.9 mL h−1 or less than 3 g h−1. As final step, the fibers are placed in a desiccator for further drying [16,33]. The produced nanofibers for tissue engineering present several advantages, such as high surface area to volume ratio; this characteristic makes them very attractive in several applications, ease of fiber functionalization, ease of material combination, relatively low startup cost, ease of fiber deposition onto other substrates, among others [34,35].
The characterization of the zein-based fibers usually implies two common techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The first allows us to visualize the diameter of the fiber, which can be as narrow as 237 nm, or as wide as 830 nm. The structure can differ when the zein content is low. For instance, the zein structures can transform into ribbons (see Figure 3), and when displaying cylindrical structures, the influence of the magnetic field may produce flat structures [15,16,33,36].
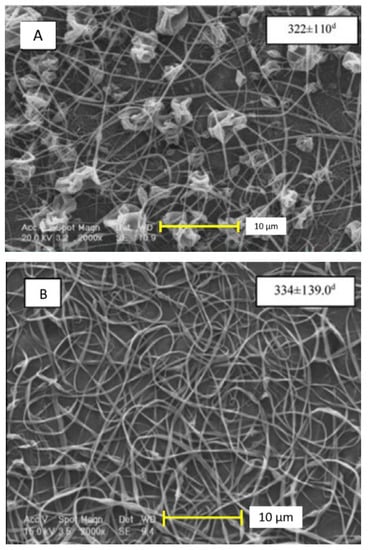
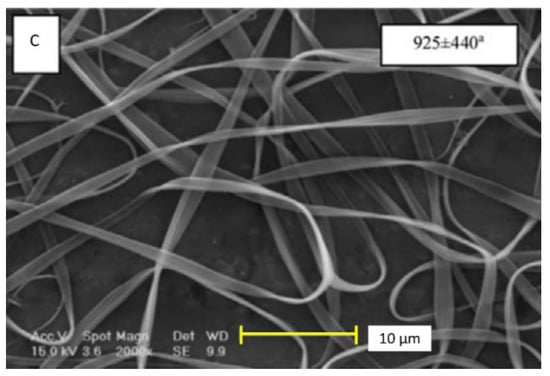
Figure 3.
Different morphologies of zein-based nanofibers, ribbon (A), cylindrical (B), and flat structure (C) [33]. Reproduced with permission from Karim et al., Food and Bioproducts Processing, License number 4921351120034; published by Elsevier, 2020.
By characterizing zein-based films using FTIR, a peak can be observed at a range of 3294–3350 cm−1 which corresponds to the -OH functional groups, while the peaks identified between 2968–2922 cm−1 correspond to C–H groups, 1538–1546 cm−1 for N–H, 1649–1653 cm−1 for C=O and 1428–1451 cm−1 for C–N [15,33,36].
3. Uses of Zein in Tissue Engineering: Current State of the Art
3.1. An Overview of Tissue Engineering (TE)
Tissue engineering (TE) has been defined as the usage and merging of cells, materials, engineering and other physicochemical factors to enhance and replace biological tissue. To date, TE in bone is likely the most explored and developed application in the field [37]. However, TE is also applied in other biological tissues, such as soft tissue [38], organs [39], eyes [40], cardiac and vascular systems [41], and connective tissues, such as articular cartilage [42], which may be affected by several factors, e.g., traumas, degenerative or age-related disease. For instance, the bones of the skeleton provide support for the body and protect the organs found within it. However, similar to any other anatomic part of the human body, the bone tissue may suffer complete or partial damage, which in many cases must be attended to as soon as possible. Thus, it is necessary to find adequate material in order to fill or replace the bone [43]. At this point, it can be possible to find different sources, e.g., those that are autologous, which are referred to as the cells of the patient. By contrast, we can find allogeneic cells that come from other patients, and finally, xenogeneic cells which are coming from other species [44].
Unfortunately, the main limitation found in bone transplantation is the lack of autologous bone sources. However, this overcomes the antigenicity present in allogenic bone. This issue has been successfully overcome by using TE. For instance, the scaffolds are used on bone tissue engineering (BTE) to achieve the mechanical strength and also for delivering an operation of stimulus and thus achieving bone regeneration [43,45]. The scaffolds display the ability to rebuild organs with a normal function. This is because they allow migration and then cell attachment. Today, a scaffold prepared by printing 3D structures can meet the shape and size required by the patients [1]. An example of a compound that can be utilized on bone TE is the hydroxyapatite, which is used to avoid post-operative infections that are commonly caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus and Enterobacter. Hydroxyapatite is a calcium phosphate with similar crystallinities as are present in the bones. With the aid of Ag and CeO2, hydroxyapatite may even show antimicrobial properties [46]. Commonly, bones are classified as connective tissue; however, there some other tissues categorized within this group, such as ligaments, tendons and the dermis. All these connective tissues, which are typically formed by of cell-associated and aligned collagen fibers, play an important structural role in the body and may need surgical repair [47]. In these approaches, reinforced polymers for connective tissue are needed, e.g., glass fiber poly(etherimide) (PEI) composites, poly(methyl methacrylate) [47]. As one of the methods used in connecting TE, cell-sheet technology has been involved in the regeneration of myocardial, vascular, cartilage, bone, tendon/ligament and periodontal areas [48].
When dealing with the implementation of TE in organs, the pelvic organ prolapse may produce a herniation of the organs found into the pelvis that affects 30–40% of the women. In this case, autologous tissue must be replaced by mesh to treat the pelvic floor-damaged structures. The synthetic mesh-like polypropylene displayed a good mechanical property. However, it can present low degradation and poor compatibility with tissues causing erosion, exposure, and infections. On the other hand, biological meshes, also known as implants from a natural source biomaterial, which are an extracellular matrix used on bone and cartilage reparation, were found as an alternative for the post-operation issues of the synthetic mesh despite having a poor mechanical property, causing the resurgence of the herniation [49,50]. The materials for natural source mesh are divided into two classifications. The first are protein-based biomaterials which include collagen, silk, fibroin, gelatin fibronectin and keratin. The second group englobe polysaccharides, such as hyaluronic acid, cellulose, glucose, alginate, chondroitin, chitin and chitosan. In the specific case of mesh used in pelvic floor reconstruction, some of the natural sources of the materials needed are silk, cellulose and collagen type I, II and III. Thus, the use of scaffolds can be a better alternative for the repairing of the pelvic floor tissue [50]. Today, the TE in organs is aided by using organ printing, which involves three fundamental sequential steps: (i) pre-processing or development of ‘blueprints’ for organs, (ii) processing or actual organ printing, and (iii) postprocessing or organ conditioning and accelerated organ maturation [39].
Soft tissues are present throughout all of the body, such as muscle, fat, blood vessels, fibrous tissue, lymph vessels and nerves, to mention just a few areas. Such soft tissues surround, support and connect organs and some other tissues in body. To develop and substitute such damaged biological tissues, several polyester elastomers, which are recognized as soft, biocompatible and biodegradable, are usually used in various biomedical applications, especially for TE in soft tissues, including ophthalmology, cardiac and vascular systems [41]. In this regard, Ye and co-workers [41] have substantially reviewed the role of such polyester elastomers (such as aliphatic polyester and polyhydroxyalkanoate-based elastomers, poly(polyol sebacate), poly(diol citrate), poly(trimethylene carbonate), poly(caprolactone fumarate) for soft tissue engineering. Importantly, all these polymer-based materials may need to be processed by various techniques and protocols (e.g., electrospinning, replica molding, 3D printing, photolithography and laser microablation) for use in soft tissue regeneration [51]. It is important to point out the ability of polyesters in regenerating sensitive soft tissues, such as vascular tissues (including blood vessels, arteries, veins).
The use of TE in ophthalmology has been widely explored over the last few years. Here, specific polymer-based materials, like poly(glycerol-co-sebacic acid), are used to improve retinal tissue [52], while poly(propylene fumarate) has been utilized in drug delivery systems and eyelid reconstruction [53]. Very recently, gelatin, identified as a protein-based material produced from the hydrolysis of collagen, has been also pointed out as a promising component within ocular TE applications due to its multiple advantages, such as excellent biocompatibility, ease of processing and availability at low cost [40]. Interestingly, TE in ophthalmology has found a place in the market in specific products, such as Surodext™ and Ozurdexs®, which are both biodegradable, dexamethasone-eluting, suture-less implants manufactured by Allergan Inc. Specifically, Surodex™ has reached phase 3 clinical trials in the US and has been approved for use in the treatment of post-cataract surgery inflammation [41]. In addition to this, the commercial product is approved in other countries like Mexico, China and Singapore. Ozurdexs® has been already Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved in the treatment and control of macular edema and uveitis [54].
To date, several examples of TE can be found on the regeneration treatment of the bones, cartilage, pancreas, and vascular system, but there are still challenges to face, including the lack of patients in which can be applied. Also, TE techniques have had limited trials. Xenogeneic cells may be dangerous because of the endogenous factors, e.g., the retrovirus that comes from the pig. In the case of autologous cells, older patients do not have the ability to harvest a high number of cells. At this point, a challenge that the scaffolds or extracellular matrix must overcome is the biological requirements that must be provided to the cell [44]. However, a positive characteristic is shown with the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells on bone tissue. For instance, In vivo tests were carried out on rabbit femurs, showing no inflammatory responses after 6 weeks [28]. In the electrospinning technique, this has been employed in other several TE applications, such as cartilage, vascular, cardiac, nerve and skin. Such a technique presents the advantage of creating micro or nanofibers that possess beneficial features for regenerative medicine [55]. For the specific application of cartilage TE, a wide number of biodegradable and bioresorbable materials, together with scaffold designs, have been experimentally investigated. Regarding the scaffold design in cartilage, ideally, a promising scaffold must have the following features: (i) three-dimensional and highly porous structure together with interconnected pore network for cell growth and facilitated transport of nutrients and metabolic waste; (ii) biocompatible and bioresorbable properties with a tuned degradation and resorption rate to match cell/tissue growth in vitro and in vivo; (iii) proper surface chemistry for cells during their attachment, proliferation, and differentiation; and finally (iv) impressive mechanical properties to match with the tissues at the specific site of implantation [42]. The future of the TE regards also the creation of complex structures of several tissues, specifically liver, neural and cardiac tissue [56]. The latest (cardiac TE) has been addressed due to the current lack of heart organ donors and multiple bottlenecks in terms of immune suppressive treatments. Herein, TE uses biodegradable-based polymers to create in vitro cardiac TE scaffolds for culturing artificial cardiac tissue, as well as the manufacture of cardiac patches for the efficient delivery of cells and regeneration of damaged heart tissues in vivo [57].
Cardiovascular diseases are a main concern due to high mortality rates. Hence, TE has been addressed by creating cardiac grafts and repairing the tissues without side effects. For this purpose, synthetic polymers, such as polyglycolic acid, polylactic-l-acid and polylactic glycolic acid, have been used together with collagen type I and III [58]. The materials used on nerve TE are polycaprolactone, collagen type I, silk fibroin and chitosan. Here, TE tries to address the issue of creating an effective and accurate connection [59].
For a couple of decades, skin has been the first engineered organ. The main reason to address skin reparation is the fact that it is the largest organ in the human body, and it comprises 15% of the total weight of adults. Also, the economic impact is considerable, for example, skin wound treatment costs almost $20 billion dollars in the USA each year [60]. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and produce novel nanostructured biocompatible surfaces [61], which could be commercially available, implying less cost.
3.2. Zein on Tissue Engineering
As is well known, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is composed of diverse biomolecules, such as proteins, polysaccharides, proteoglycans, among others, which promote the attachments of the cells and their proliferation, differentiation, and migration. With this new and artificial environment, the cells must be capable of displaying the same functions and regenerate the lost tissue or healing the damaged tissue [62]. It is feasible to elaborate the ECM matrix by the electrospinning method due to its inexpensiveness and adaptive technology to produce the fibers. Furthermore, it is possible to combine nanofibers from natural and synthetic origins and thus provide a synergistic effect. Importantly, synthetic materials lack binding from the cells and the production of acids but have sufficient mechanical stability. Natural-based fibers may show a loss of mechanical strength during the biodegradation process. However, the ECM from animal source nanofibers may show a potential immune response or transmission of diseases. Thus, plant-based nanofibers have been studied, showing more benefits than the animal source. Zein has been used in TE, displaying resistance to microorganisms, flexibility, compatibility with the human body and biodegradability [26,63,64,65,66,67]. In addition to such properties, electrospun zein has also shown antimicrobial activity [68,69,70]. It is possible to elaborate scaffolds with other fibers from the cellulose acetate, polyurethane, and gum arabic. This last one shows similar characteristics compared to zein, but a combination of factors in a fragile skin regenerator. Due to that issue, polycaprolactone (PCL) has been presented as an alternative to solve the fragility issue. PCL is also biocompatible, nontoxic and possesses excellent mechanical strength [67]. For instance, Pedram Rad and co-workers fabricated and fully characterized polycaprolactone (PCL)/zein/gum arabic electrospun nanocomposite scaffold, which was proposed for skin TE. Each component possesses a specific function on the scaffold. Zein and gum arabic provide protein and polysaccharide content for skin regeneration and support, respectively, while polycaprolactone provides the mechanical elasticity and strength needed [71]. It is important to mention that scaffolds are defined as physical substrates for cell attachment, proliferation, differentiation, and ultimately conduction to the regeneration of tissues [72]. In Padram Rad’s study, it was found that the porosity in all PCL/zein/gum arabic scaffolds were higher than 77%, which is suitable and recommended for cells infiltration. Moreover, such a composite scaffold demonstrated antibacterial properties due to the presence of cyanogenic glycosides in gum arabic, together with enhanced hydrophilicity. Importantly, the hydrophilicity is relevant to a TE scaffold since it enhances the cell viability and proliferation [73,74]. It is worth mentioning that cell affinity towards synthetic polymers is typically poor due to their low hydrophilicity and lacking in cell recognition sites [72]. However, there are hydrophobic synthetic polymers, such as poly(ethylene), poly(ester amide) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide), which may allow cell proliferation. On the other hand, polymers coming from natural sources have a better interaction with cells due to the interaction with the membrane receptors [75,76]. It is also supposed that zein may be a potential candidate for cardiac TE applications when zein is blend with poly(glycerol sebacate) for the production of fibers with the electrospinning technique [77].
When dealing with the target of improving the mechanical strength of scaffolds, authors have proposed preparing composites based on graphene oxide, TiO2, carbon nanotubes and hydroxyapatite. The process of loading nanoparticles, like hydroxyapatite, can also improve the regeneration rate and decrease the degradation rate of the scaffold [78]. The combination of zein with hydroxyapatite has also shown a specific improvement in the osteoblasts [79]. The hydroxyapatite itself can carry drugs, e.g., vancomycin, which is an antibiotic-loaded with a negative charge, and its release can be controlled by the hydroxyapatite [78]. When growth factors are loaded to the nanofibers, there is an improvement in the differentiation and promotion of the proliferation of osteoblasts. The recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (rhBMP-2) and dexamethasone (DEX) enhance the TE differentiation efficacy. Herein, it is necessary to maintain the release of the stable factor [80].
Electrospinning is the most versatile technique for scaffold elaboration, but there are other methods to tailor scaffolds, such as melt-drawing, centrifugal spinning, freeze-drying, 3D extrusion, among others. The centrifugal spinning is a method that can be used to create a gelatin-based scaffold. Gelatin is a natural polymer that comes from the hydrolysis of the collagen. Due to its poor water resistance, this material is quickly degraded. Thus, the hydrophobicity of the zein can lead to enhancement of this gelatin’s property. The resulting material can be potentially used for scaffolds preparation and then implemented for drug delivery, hernia repair and TE. Mamidi and co-workers developed a homogeneous blending of gelatin/zein (1:4), which resulted in improved tensile and good hydrophobic properties (water contact angle of 115 °C). The cell viability was also investigated with human fibroblasts and a low cytotoxic effect was noted. Interestingly, the ability of the aligned scaffolds for berberine drug release was measured and sustained release rate was observed over 15 days [81]. It is also possible to elaborate scaffolds based on a zein/gelatin complex via a co-electrospinning technique [12]. Clear improvements, contributed by the gelatin on the resulting nanofibers, were the increase of elastic modulus, enhanced hydrophilicity and cytocompatibility, but the use of a high concentration of gelatin may result in weak membranes. Specifically, the electrospinning technique allowed control of the porous surface, cytocompatibility, mechanical strength, shape of the fibers, as well as improvement of the cellular adhesion. The results showed that the scaffolds were smooth and homogeneous, except for A, which is beaded, as shown in Figure 4. The diameter of fibers increased from 69 ± 22 nm to 950 ± 356 nm when the ratio of gelatin increased. The cell affinity of zein/gelatin nanofibers was tested by using human periodontal ligament stem cells [12].
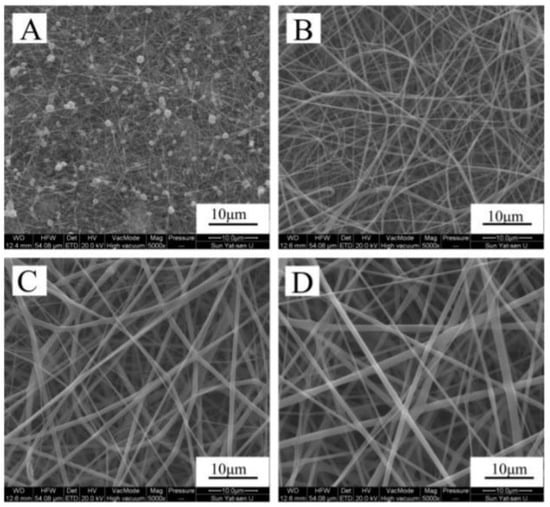
Figure 4.
Morphological analysis of zein (A); zein/gelatin-1 (B); zein/gelatin-2 (C); and zein/gelatin-3 (D) electrospun nanofibers. Taken from [12].
It has been well documented that the crosslinking protocol is a latent way to improve the mechanical properties (e.g., tension strength) in membranes [82]. Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) is an example of a cross-linker agent in zein-based nanofibers. Also, the incorporation of plasticizers, such as palmitic and stearic acids, is recommended. For instance, the optimal concentration of palmitic acid/zein (1:2) and stearic acid/zein (1:4) allowed enhanced mechanical properties to be obtained in zein nanofibers. If there is a higher concentration, the mechanical strength decreases. Thanks to a better distribution through the zein fibers, the palmitic acid has shown a better plasticization. A similar result can be found when using clays, as these composites can improve the mechanical strength in the zein fibers. Other materials, such as mica, kaolinite, montmorillonite, and zeolite, offer similar findings to clays in zein fibers [28].
Poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) is a bacteria synthesized thermoplastic that is compatible with the human body and degradation. Some applications of this thermoplastic polyester deal with packing, orthopedic and wound treatment. Thus, the blending of poly(3-hydroxubutyrate-co-4-hydroxubutyrate) (P(3HB-co-4HB)) and zein was performed in N,N-dimethylformamide, and subsequently electrospun for fiber preparation. Ultra-thin fibers of 60–650 nm were obtained with an increase in the tensile strength from 4.8 to 7.1 MPa, and an elongation at break between 15% to 69%. This improvement was achieved by having a content P(3HB-co-4HB) that ranged from 20% to 80% [83].
Very recently, Mariotti and co-workers developed zein-based electrospun fibers containing bioactive glass with antibacterial capabilities. In this study, the authors were also addressing the main drawback of zein regarding its poor mechanical properties. Here, inorganic compounds (e.g., bioactive Cu-based glasses) have been implemented in combination with zein to obtain composite materials with improved mechanical properties. Such composites were assayed in TE applications. Cell culture studies using MG-63 and C2C12 cells released promising insights, demonstrating increased cell proliferation and growth for fiber mats containing both types of bioactive glass. Moreover, through an evaluation with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacteria, the study confirmed that the inorganic composite scaffolds had antibacterial activity. Cu has imparted antibacterial properties without influencing cell behavior [84].
There are even some natural composites that can be loaded on the zein scaffolds. One example is Aloe vera that has been used to treat skin-related disorders and burns. Aloe vera enhances collagen synthesis and can increase adhesion and cellular growth. Also, Aloe vera has antibiotic and antifungal properties towards Streptococcus pyogen, Enterococcus faecalis, Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus [63]. Therefore, by researching more about how the zein works as a carrier, it may be possible to introduce more bioactive compounds to understanding the action mechanisms. Some examples of using zein as a wall material in nanoencapsulation can be found in the pharmaceutical, food and pesticide areas [85,86,87].
4. The Role of Zein in Nanotechnological Applications
In principle, a nanomaterial must possess a size between 1 to 100 nm, having a large surface area per volume. A comparison with biocomposites and microorganisms can be made to realize the real dimension of a nanomaterial. For example, a nanocomposite can be 300 to 3000 times smaller than a bacteria, close to the size of the proteins (3–150 nm) and even the size of a DNA strand which can be 2 to 3 nm. One important fact is that nanomaterials, used as additives, may lead to improvement of the properties in other materials [85]. Considering the molecular weight of zein (ca. 22 kDa), zein nanoparticles (average size of 114.9 nm) can be prepared and thus implemented within different nanotechnological applications, including as a way of packing drugs, food, nutrients and even pesticides, as well as bandages for wound treatment [85,86,88,89,90].
4.1. Zein-Based Delivery Systems
Drugs are compounds used in treatment, control and disease prevention. Nowadays, their therapeutic efficacy must be increased, and there are advances to create powerful drugs with the help of bioinformatics. Even with the aid of technological advances, there are still failures in solubility, stability, and toxicity. Thus, this situation has encouraged scientists to find a way of improving drug efficiency by creating a carrier that releases the compound at a controlled rate with low toxicity. This can be achieved with biopolymer-based proteins. Such polymers tend to offer advantages, such as being easy to produce and having high loading capacity. The most common proteins used for such purposes are gelatin, albumin, keratin, casein, silk protein and zein. Nevertheless, these biopolymers may undergo structural changes, and therefore, the protein function may be lost and rapid degradation can occur [86].
Breast carcinoma is the most dominant cancer in women. In the early stages, breast cancer is local but once metastasis starts, it spreads all over the human body. In fact, 90% of the cases of breast cancer deaths are related to the metastasis process. Therefore, there have been new advances to treat this disease through novel drug-delivery systems with zein and hyaluronic acid. This complex has the goal of successfully delivering Honokiol. Besides of anti-carcinogenic activity, it displays anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective properties. Honokiol targets the CD44 receptors that are overexpressed on cancer cells. The success of the complex hyaluronic acid–zein–honokiol reduces tumor growth by 77.3% based on tumor weight, which represents three times more inhibition than that provided by only free honokiol with only 25.8% of tumor inhibition [91].
Recently, Labib (2018) has reviewed the current developments and advances at using zein as a natural pharmaceutical excipient in drug-delivery systems [92]. The author highlighted that zein has some unique advantages over other available biomaterials including biocompatibility, safety, lower cost, and it is adhesive and easily shaped, displaying a ductile and soft nature, having vast applications as a biomaterial. Unfortunately, its application as nanocarrier is still a challenge but the research community is promoting its implementation. For instance, curcumin is a bioactive compound which display antioxidant properties together with anti-inflammatory benefits. These properties can be enhanced and maintained by blending with zein. Curcumin, as a typical polyphenol, is generally used to treat prophylaxis, chronic diseases related to the inflammatory process, antibacterial and antioxidant agents. Its characteristics include poor water solubility, low chemical stability, and poor pharmacokinetics. Due to these factors, its bioavailability is less than 1%. In order to solve this situation, a series of packing methods have been undertaken for curcumin including microcapsules, micelles and inorganic nanoparticles. Of course, zein has also been proposed for such a purpose, a conjugation of curcumin with zein-poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) has resulted in the enhancement of stability, cytotoxicity of cancer cells and pharmacokinetics. However, the resulting micelles showed a low macrophage activation and long-circulating property (exceeding 72 h in mice), but they can be sensitive at pH changes, thus nanoencapsulation can be an alternative thanks to its pH stability. Towards the enhancements of particle stability, the size of the zein-based nanoparticles coated with curcumin has been reported about 65.17 ± 0.32 nm. However, the curcumin/zein nanoparticles can be recoated with sodium caseinate and sodium alginate in order to provide more stability and boost the size of the particle up to 200.67 ± 0.65 nm [93,94].
Similarly, resveratrol displays low solubility and bioavailability [95]. The importance of such a substance is related to its potential to treat and prevent gastrointestinal cancer. This cancer is recognized as the third most lethal cancer. By 2030, it is expected to have led to 2.2 million new cases and 1.1 million deaths. Resveratrol can be naturally found on grapes, berries, and peanuts, however, after their consumption, they are quickly metabolized into glucuronides and sulfates, and ultimately excreted [96]. In addition to this, changes in heat, light and the exposure to enzymes can degrade resveratrol. To avoid this issue, resveratrol can be preserved by nanoencapsulation, thereby improving the oral administration of the drug. With the help of a pectin-based shell, the zein can act as a core and avoid aggregation caused by pH concentration, high salt concentration and high temperatures [97]. Such a study was carried out by Huang and co-workers, who fabricated zein–pectin core/shell nanoparticles loaded with resveratrol by combining antisolvent precipitation and electrostatic deposition protocols. Interestingly, the antioxidant activity of resveratrol was greatly improved when it was encapsulated into the biopolymer-based nanoparticles [97].
4.2. Zein-Based Nanoparticles in the Food Industry
A nano-food may have a higher nutritional value compared with common food, but there is a risk that the nanomaterials may show toxicity. In the case of the zein, it has not been reported to have any toxicity. In fact, it is considered as GRAS additive (i.e., generally recognized as safe) by FDA. In this way, zein-based nanoparticles have been used to carry flavors, food colorants and bioactive compounds [85].
Cinnamic aldehyde belongs to the flavor compound groups of interest in the food industry. This compound has also antioxidant properties but high sensitivity to humidity, oxygen, light, and high temperature [87]. Therefore, its encapsulation may protect the high-added-value compound and thus extend its use. Karim et al. used zein as a wall material for encapsulating cinnamic aldehyde into hydrophobic nanofibers, which were tailored with named needle-less electrospinning. Such nanocapsules loaded with cinnamic aldehyde were added on sausages to decrease the use of nitrite. The resulting sausages exhibited an increase of hardness from 9.76 to 15.2 N during storage, meaning that there was less humidity. Also, there was no significant change in sensory analysis. On the other hand, the nanoencapsulated cinnamic aldehyde had bactericidal activity against E. coli O157:H7 and S. aureus PTCC 1337 [98].
In a more macroscopic approach, it is possible to create an edible packing to replace the traditional plastic materials. Today, there is great interest in replacing chemically synthesized food packing materials. By creating a zein-starch bilayer film it is feasible to have a better lamination with enhanced mechanical and barrier properties, as demonstrated by Chen et al. The mechanical properties were enhanced thanks to the hydrogen bonding among hydroxyl groups and amino (carboxyl) groups of starch and zein molecules, respectively. Finally, the authors suggested great potential of this generated edible film for food packaging [99].
4.3. Zein as a Carrier of Pesticides
Zein has been proposed for a wide variety of uses [85], including the packing of pesticides and fertilizers. The increasing population results in an increasing demand for agri-food products, requiring large quantities of pesticide for protection. Although there are well-documented pesticides, there is still a concern about exposure to these. In order to avoid harmful side effects, it is necessary to design pesticides with a well-controlled delivery. The zein-based nanocarriers of pesticides can be administrated by adhesion to the root system and foliage, together with the minimization of water and soil pollution [100].
Avermectins are a group of 16-membered macrocyclic lactones which owns properties to attack nematodes, acarus and insects while their toxicity is low for mammals [101]. The nanocarriers can also protect pesticides from high temperatures and radiation. Their encapsulation implies a series of steps. The first is to phosphorylate the zein with the aid of sodium caseinate, leading to improvement of the hydrophilicity. Then, avermectin must be loaded to the phosphorylated zein by stirring them in ethanol solution. The last step is to add a solution of modified carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) by diallyldimethylammonium chloride (DMDAAC). This last step aims to improve the stability, ultraviolet (UV) resistance, and adhesion of the phosphorylated zein loaded with avermectin with the aid of CMC. However, the CMC cannot be combined with the phosphorylated zein, and thus DMDAAC is used to modify the CMC and achieve this combination [89].
Natamycin is a compound produced by a soil bacterium and used in low concentration against yeasts and molds, and it prevents the production of mycotoxins. Natamycin can also be used on fruits after harvesting. The main drawback of this compound is its low photostability, which results in it being expensive, minimizing its availability and application. The zein can encapsulate the natamycin and provide photostability, while a shell of carboxymethyl chitosan may enhance the stability of the zein core. The coated natamycin has a stable pH range from 2.0 to 8.0. Also, its photostability has been improved by an increase 3.12-fold [102].
4.4. Zein as a Potential Material for Bandages
Zein has been applied in the design of a zein/chitosan composite bandage loaded with ellagic acid [88]. This acid is a derivative of gallic acid which is commonly found on raspberry and red fruits. Its applications imply anti-carcinogenic and antioxidant activities and it can be used against inflammatory processes [103]. Tavares and co-workers developed a preparation protocol consisting of diluting chitosan on 3% acetic acid solution and 6.25% of glycerol. Subsequently, the zein was immersed in a solution of 70% ethanol and 1.2% of ellagic acid. This solution was then stirred and allowed to evaporate the solvent at a temperature of 25 °C for a period of 5 days. The results were a successful bandage with anti-bacterial properties, specifically against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus [88]. Finally, zein played a significant role and influence on the release of ellagic acid.
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Trends
Through this review, the exploration of the physicochemical parameters of zein, as well as its role in applications for TE and nanotechnology, have been addressed and discussed. Zein has been identified as a biopolymer that mostly possesses two functions, (i) it gives support to the cells providing them with a scaffold, and (ii) it is useful as a wall material for encapsulating compounds that are sensitive to certain environmental parameters. When dealing with TE applications, the scaffolds are excellent providers of environmental cellular growth and proliferation, however, there are still some compounds that can be encapsulated to give an additional feature. Notably, zein can provide stability to some molecules the in terms of environmental parameters, as well as controlled delivery [88,89,91,93,94,95,102]. The scaffolds or ECM have been upgraded in terms of mechanical properties when combined with other synthetic polymers, natural polymers, or inorganic compounds. Initially, the scaffold was designed to give support to the cell, but the scaffolds can now be loaded with biological factors in order to make easier the growth of cells. Moreover, the trends show a significant increase in scaffolds tailored via the electrospinning technique rather than the 3D printing technique.
The future perspective is focused on scaffolds, which potentially provide a controlled administration of drugs, as well as a huge improvement in their design with the aid of 3D printing. It is quite possible that the use of scaffolds could be implemented in the major clinical procedures in the near future. However, new sustainable and environmentally friendly materials (like zein) are still needed in these kinds of application. Importantly, an improvement of software will be needed in order to have more precise and accurate scaffolds that allow mimicking of the cell environment, and thus optimal cellular growth and proliferation. The future trends also aim to increase the few actual structural designs and improve the already existing fabrication methods. Thus, researchers have adopted computational methods to mix 3D printing techniques for the new scaffold design. Today, a new term has appeared, named computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE), which refers to the use of the computational tools to design scaffolds, considering the geometry of the scaffold structure, as well as the size of the pores and the loading conditions of the scaffold stress distributions [104], as observed in Figure 5.
Figure 5.
Computerized models for optimized scaffolds [104].
Also, the current increasing demand of innovation for efficient drug-loading scaffolds requires an improvement in the design, material blending, and control of the drug-releasing pattern, as well as the formulation of a porous scaffold with an improvement on the mechanical stability by adding inorganic biomaterial particle. In addition, another challenge to overcome is the improvement of the seeding technique of mesenchymal stem cells to preserve the survival affected by the composition of the scaffold, as well as an optimization of the nanofibrous scaffold for clinical applications. Furthermore, it is important to maintain the survival of the stem cells after insertion into the human body. At this point, the cell affinity towards synthetic polymers is also an important factor; herein, there is a clear research gap on improving the hydrophilicity of the well-known hydrophobic zein. It is likely that researchers will be focused on implementing chemical modification techniques towards the enhancement of this property. Finally, it is essential to develop a sterilization technique for scaffolds [105,106].
Author Contributions
C.J.P.-G. wrote the paper and R.C.-M. edited and contributed to writing the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
R. Castro-Muñoz acknowledges the School of Engineering and Science and the FEMSA-Biotechnology Center at Tecnológico de Monterrey for their support through the Bioprocess (0020209I13) Focus Group.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goranov, V.; Shelyakova, T.; De Santis, R.; Haranava, Y.; Makhaniok, A.; Gloria, A.; Tampieri, A.; Russo, A.; Kon, E.; Marcacci, M.; et al. 3D Patterning of cells in Magnetic Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladapo, B.I.; Obisesan, O.B.; Oluwole, B.; Adebiyi, V.A.; Usman, H.; Khan, A. Mechanical characterization of a polymeric scaffold for bone implant. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 9057–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrian, M.; Lambrechts, T.; Papantoniou, I.; Geris, L. Computational Modeling of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Proliferation and Extra-Cellular Matrix Production in 3D Porous Scaffolds in a Perfusion Bioreactor: The Effect of Growth Factors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pan, S.; Xia, P.; Chang, Y.; Fu, C.; Kong, W.; Yu, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Qi, Z. Advances in the application of gold nanoparticles in bone tissue engineering. J. Biol. Eng. 2020, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhivya, S.; Keshav Narayan, A.; Logith Kumar, R.; Viji Chandran, S.; Vairamani, M.; Selvamurugan, N. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds containing chitosan, calcium polyphosphate and pigeonite for bone tissue engineering. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhan, X.; Lan, F.; He, J.; Gu, Z.; Wu, Y. Protein Corona of Magnetic Hydroxyapatite Scaffold Improves Cell Proliferation via Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3690–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cícero, A.M.; Mardegan, P.J.I.; Feldman, S. Matrices de tercera generación en la ingeniería de tejidos óseos. Actual. Osteol. 2017, 13, 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Lv, Y. Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croisier, F.; Jérôme, C. Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; González-Valdez, J.; Ahmad, M.Z. High-performance pervaporation chitosan-based membranes: New insights and perspectives. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2020, 20190051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, N.A.; Hefni, H.H.H.; Abd-Elaal, A.A.A.; Badr, E.A.; Abou Kana, M.T.H. Advancement on modification of chitosan biopolymer and its potential applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 681–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Lin, X. Electrospun zein/gelatin scaffold-enhanced cell attachment and growth of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Materials 2017, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhannejhad, L.; Abdouss, M.; Nikfarjam, N.; Mazinani, S.; Heydari, V. Electrospinning of zein/propolis nanofibers; antimicrobial properties and morphology investigation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuenmayor, C.; Cosio, M. Encapsulation of Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds in Zein Ultra-Thin Fibers Via Electrospinning. Rev. EIA 2016, 3, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashdorj, U.; Reyes, M.K.; Unnithan, A.R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Tumurbaatar, B.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun zein/Ag nanocomposite mats for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turasan, H.; Cakmak, M.; Kokini, J. Fabrication of zein-based electrospun nanofiber decorated with gold nanoparticles as a SERS platform. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8872–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, S.; Asadi, H.; Ghalei, B. Zein nanoparticle-embedded electrospun PVA nanofibers as wound dressing for topical delivery of anti-inflammatory diclofenac. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Lin, M.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J. Characterization of the protein and peptide of excipient zein by the multi-enzyme digestion coupled with nano-LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.J.; Weng, Y.M. Novel edible composite films fabricated with whey protein isolate and zein: Preparation and physicochemical property evaluation. LWT 2019, 101, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T. Zein/fucoidan-based composite nanoparticles for the encapsulation of pterostilbene: Preparation, characterization, physicochemical stability, and formation mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Effect of α-tocopherol antioxidant on rheological and physicochemical properties of chitosan/zein edible films. LWT 2020, 118, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, P.; Vaseeharan, B.; Vijayakumar, S.; Balan, B.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Biopolymer zein-coated gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial potential, toxicity and histopathological effects against the Zika virus vector Aedes aegypti. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momany, F.A.; Sessa, D.J.; Lawton, J.W.; Selling, G.W.; Hamaker, S.A.H.; Willett, J.L. Structural Characterization of α-Zein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Hayat, U.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Wang, J.Y. Zein-based micro- and nano-constructs and biologically therapeutic cues with multi-functionalities for oral drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, R.; Xu, H. Physicochemical properties of zein-based films by electrophoretic deposition using indium tin oxide electrodes: Vertical and horizontal electric fields. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E.; Curti, P.S.; Meniqueti, A.B.; Martins, A.F.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Recent advances in food-packing, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of zein and zein-based materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22438–22470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Xin, Z.; Meng, X.; Sun, S.; Qiao, Q.; Deng, H. Recovering high value-added substances from corn distillers dried grains with solubles: A semi-continuous countercurrent downstream processing method. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, M.; Ramos-Rivera, L.; Silva, R.; Nazhat, S.N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Zein-based composites in biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Wilson, B.W.; Vadlani, P.V. Evaluation of green solvents for a sustainable zein extraction from ethanol industry DDGS. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 85, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabueng, N.; Napathorn, S.C. Toward non-toxic and simple recovery process of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) using the green solvent 1,3-dioxolane. Process Biochem. 2018, 69, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchene, K.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Ksibi, M. Types, occurrence, and distribution of microplastics and metals contamination in sediments from south west of Kerkennah archipelago, Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, Y.S.; Alrumman, S.A.; Alamri, S.A.; Ot, K.A. Bioplastic ( poly-3-hydroxybutyrate ) production by the marine bacterium Pseudodonghicola xiamenensis through date syrup valorization and structural assessment of the biopolymer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.; Fathi, M.; Soleimanian-zad, S. Incorporation of zein nanofibers produced by needle-less electrospinning within the casted gelatin film for improvement of its physical properties. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 122, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospinning of multilevel structured functional micro-/nanofibers and their applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7290–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, W.; Ma, D.; Ma, Q.; Bridges, D.; Ma, Y.; Hu, A. Electrospinning of Nanofibers and Their Applications for Energy Devices. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 140716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhan, L.; Shao, P.; Xiang, N.; Sun, P.; Chen, H.; Gao, H. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Electrospinning of zein-ethyl cellulose hybrid nanofibers with improved water resistance for food preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebschner, M.A.K. Biomechanical considerations of animal models used in tissue engineering of bone. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1697–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Gimble, J.M.; Lee, K.; Marra, K.G.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoo, J.J.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Adipose tissue engineering for soft tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2010, 16, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, V.; Boland, T.; Trusk, T.; Forgacs, G.; Markwald, R.R. Organ printing: Computer-aided jet-based 3D tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.B.; Pacelli, S.; El Haj, A.J.; Dua, H.S.; Hopkinson, A.; White, L.J.; Rose, F.R.A.J. Gelatin-based materials in ocular tissue engineering. Materials 2014, 7, 3106–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, K.; Kai, D.; Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. Polyester elastomers for soft tissue engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4545–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomater. Silver Jubil. Compend. 2000, 21, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L. Recent advances in additive manufacturing technology for bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 3591–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, R.; Bhatt, V.D.; Dhot, P.S. Tissue Engineering; Current Status & Futuristic Scope. J. Med. Life 2019, 12, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Filardo, G.; Andriolo, L.; Soler, F.; Berruto, M.; Ferrua, P.; Verdonk, P.; Rongieras, F.; Crawford, D.C. Treatment of unstable knee osteochondritis dissecans in the young adult: Results and limitations of surgical strategies—The advantages of allografts to address an osteochondral challenge. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiarwut, S.; Niyompanich, J.; Ekabutr, P.; Chuysinuan, P.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Development and characterization of antibacterial hydroxyapatite coated with mangosteen extract for bone tissue engineering. Polym. Bull. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A. Reinforced polymers for connective tissue. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, P.Y.; Teh, T.K.H.; Tay, A.S.R.; Asuncion, M.C.T.; Png, S.N.; Toh, S.L.; Goh, J.C.H. Stem cell-derived cell-sheets for connective tissue engineering. Connect. Tissue Res. 2016, 57, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielli, A.; Bernardini, R.; Varvaras, D.; Rossi, P.; Di Blasi, G.; Petrella, G.; Buonomo, O.C.; Mattei, M.; Orlandi, A. Characterization of a new decellularized bovine pericardial biological mesh: Structural and mechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 78, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Jia, Y.Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, J. Tissue engineering in female pelvic floor reconstruction. Eng. Life Sci. 2020, 20, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liao, S.; Ngiam, M.; Chan, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Degradation behaviors of electrospun resorbable polyester nanofibers. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2009, 15, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeley, W.L.; Redenti, S.; Klassen, H.; Tao, S.; Desai, T.; Young, M.J.; Langer, R. A microfabricated scaffold for retinal progenitor cell grafting. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Hacker, M.C.; Haesslein, A.; Jo, S.; Ammon, D.M.; Borazjani, R.; Kunzler, J.; Mikos, A. Injectable, in situ forming poly(propylene fumarate)-based ocular drug delivery systems. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 79, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, J.A.; Bandello, F.; Belfort, R.; Blumenkranz, M.S.; Gillies, M.; Heier, J.; Loewenstein, A.; Yoon, Y.H.; Jacques, M.L.; Jiao, J.; et al. Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial of Dexamethasone Intravitreal Implant in Patients with Macular Edema Due to Retinal Vein Occlusion. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1134–1146.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, M.; Mills, D.K.; Urbanska, A.M.; Saeb, M.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.P.K.; Stevens, M.M. Using Remote Fields for Complex Tissue Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, R.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Living cardiac patch: The elixir for cardiac regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, I.C.P.; Kaasi, A.; Maciel Filho, R.; Jardini, A.L.; Gabriel, L.P. Cardiac tissue engineering: Current state-of-the-art materials, cells and tissue formation. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2018, 16, eRB4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-X.; Han, N.; Kou, Y.-H.; Zhu, Q.-T.; Liu, X.-L.; Quan, D.-P.; Chen, J.-G.; Jiang, B.-G. Tissue engineering for the repair of peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Vig, K.; Chaudhari, A.; Tripathi, S.; Dixit, S.; Sahu, R.; Pillai, S.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Advances in Skin Regeneration Using Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongi, T.; Tirinato, L.; Pagliari, F.; Giugni, A.; Allione, M.; Perozziello, G.; Candeloro, P.; Di Fabrizio, E. Fabrication and Applications of Micro/Nanostructured Devices for Tissue Engineering. NanoMicro Lett. 2016, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, Z. Enhanced mechanical and osteogenic differentiation performance of hydroxyapatite/zein composite for bone tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Ramazani, S. Aloe vera-loaded nanofibrous scaffold based on Zein/Polycaprolactone/Collagen for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.-M. Co-electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes of Collagen and Zein for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-W.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.-F.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.-Y. Design and optimization of a biodegradable porous zein conduit using microtubes as a guide for rat sciatic nerve defect repair. Biomaterials 2017, 131, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, R.; Palakurthi, S. Zein in controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram Rad, Z.; Mokhtari, J.; Abbasi, M. Calendula officinalis extract/PCL/Zein/Gum arabic nanofibrous bio-composite scaffolds via suspension, two-nozzle and multilayer electrospinning for skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, S.; Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. A novel bilayer zein/MMT nanocomposite incorporated with H. perforatum oil for wound healing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 31, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Antunes, M.; da Silva Dannenberg, G.; Fiorentini, Â.M.; Pinto, V.Z.; Lim, L.-T.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Antimicrobial electrospun ultrafine fibers from zein containing eucalyptus essential oil/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Huang, R.; Vaze, N.; Xu, T.; Eitzer, B.D.; Krol, W.; MacQueen, L.A.; Chang, H.; Bousfield, D.W.; Chan-Park, M.B.; et al. Development of Biodegradable and Antimicrobial Electrospun Zein Fibers for Food Packaging. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram Rad, Z.; Mokhtari, J.; Abbasi, M. Fabrication and characterization of PCL/zein/gum arabic electrospun nanocomposite scaffold for skin tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 93, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Caetano, G.; Ambler, W.S.; Blaker, J.J.; Frade, M.A.; Mandal, P.; Diver, C.; Bártolo, P. Enhancing the hydrophilicity and cell attachment of 3D printed PCL/graphene scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials 2016, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.X.; Wang, Y.S.; Ma, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Electrospinning of PLGA/gelatin randomly-oriented and aligned nanofibers as potential scaffold in tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-Hay, A.; Hussein, K.H.; Casettari, L.; Khalil, K.A.; Hamdy, A.S. Fabrication of novel high performance ductile poly(lactic acid) nanofiber scaffold coated with poly(vinyl alcohol) for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 60, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero Aguilar, L.M.; Silva, S.M.; Moulton, S.E. Growth factor delivery: Defining the next generation platforms for tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2019, 306, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhao, X.-R.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Yu, J.-K. 3D- Printed Poly(ε-caprolactone) Scaffold Integrated with Cell-laden Chitosan Hydrogels for Bone Tissue Engineering. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, L.; Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Roether, J.A. Electrospun zein fibers incorporating poly(glycerol sebacate) for soft tissue engineering. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, M.; Ghaee, A.; Nourmohammadi, J. Poly (sodium 4-styrene sulfonate)-modified hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in zein-based scaffold as a drug carrier for vancomycin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazarab, Z.; Teimouri, A.; Chermahini, A.N.; Azadi, M. Fabrication and characterization of nanobiocomposite scaffold of zein/chitosan/nanohydroxyapatite prepared by freeze-drying method for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, Y.; Sun, D.; Ma, W.; Yao, J.; Zhang, M. Preparation and characterization of coaxial electrospinning rhBMP2-loaded nanofiber membranes. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Romo, I.L.; Leija Gutiérrez, H.M.; Barrera, E.V.; Elías-Zúñiga, A. Development of forcespun fiber-aligned scaffolds from gelatin-zein composites for potential use in tissue engineering and drug release. MRS Commun. 2018, 8, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Buera-González, J.; de la Iglesia, Ó.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Malankowska, M.; Rubio, C.; Figoli, A.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Towards the dehydration of ethanol using pervaporation cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijiang, C.; Qin, Z.; Xianyou, S.; Yuanpei, L. Zein/Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) electrospun blend fiber scaffolds: Preparation, characterization and cytocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, C.E.; Ramos-Rivera, L.; Conti, B.; Boccaccini, A.R. Zein-Based Electrospun Fibers Containing Bioactive Glass with Antibacterial Capabilities. Macromol. Biosci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. Zein and zein -based nano-materials for food and nutrition applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.G.; Das, R.P.; Kunwar, A. Protein: A versatile biopolymer for the fabrication of smart materials for drug delivery. J. Chem. Sci. 2019, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguer, M.P.; Borne, M.; Chalier, P.; Gontard, N.; Morel, M.H.; Peyron, S.; Gavara, R.; Hernandez-Munoz, P. Retention and release of cinnamaldehyde from wheat protein matrices. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, W.S.; Tavares-júnior, A.G.; Otero-espinar, F.J.; Martín-pastor, M.; Sousa, F.F.O. Design of ellagic acid-loaded chitosan/zein films for wound bandaging. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Lin, G.; Lian, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zhou, X. Carboxymethyl cellulose capsulated zein as pesticide nano-delivery system for improving adhesion and anti-UV properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; Elgohary, M.M.; Kamel, N.M. Implications of Protein- and Peptide-Based Nanoparticles as Potential Vehicles for Anticancer Drugs, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, W.; Guan, S.; Fan, L.; Cai, D. Targeted delivery of honokiol by zein/hyaluronic acid core-shell nanoparticles to suppress breast cancer growth and metastasis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, G. Overview on zein protein: A promising pharmaceutical excipient in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Yi, J.Z.; Xie, M.; Zhang, L.M. Long-circulating zein-polysulfobetaine conjugate-based nanocarriers for enhancing the stability and pharmacokinetics of curcumin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Han, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, T. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded zein nanoparticles stabilized by sodium caseinate/sodium alginate: Curcumin solubility, thermal properties, rheology, and stability. Process Biochem. 2020, 94, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Leena, M.; Yoha, K.S.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Edible coating with resveratrol loaded electrospun zein nanofibers with enhanced bioaccessibility. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Aman mohammadi, M.; Delavar, M.; Tabibiazar, M.; Ramezani, S. Development of resveratrol loaded chitosan-gellan nanofiber as a novel gastrointestinal delivery system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Encapsulation of resveratrol in zein/pectin core-shell nanoparticles: Stability, bioaccessibility, and antioxidant capacity after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Fathi, M.; Soleimanian-Zad, S. Nanoencapsulation of cinnamic aldehyde using zein nanofibers by novel needle-less electrospinning: Production, characterization and their application to reduce nitrite in sausages. J. Food Eng. 2020, 288, 110140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, F.; Zi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, J. Development and characterization of a hydroxypropyl starch/zein bilayer edible film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacsó, T.; Neaga, I.O.; Erincz, A.; Astete, C.E.; Sabliov, C.M.; Oprean, R.; Bodoki, E. Perspectives in the design of zein-based polymeric delivery systems with programmed wear down for sustainable agricultural applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 155, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Gao, F.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhao, X.; Guo, L.; Shen, Y.; Liu, G.; et al. Construction and characterization of avermectin B2 solid nanodispersion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Fang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liang, X.; Wu, D. Natamycin-loaded zein nanoparticles stabilized by carboxymethyl chitosan: Evaluation of colloidal/chemical performance and application in postharvest treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahieh, K.H.; Falahieh, K.H.; Sarkaki, A.; Sarkaki, A.; Edalatmanesh, M.; Naseri, M.K.G.; Farbood, Y. Ellagic acid attenuates post-cerebral ischemia and reperfusion behavioral deficits by decreasing brain tissue inflammation in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Lu, W.F.; Fuh, J.Y.H. A review on the use of computational methods to characterize, design, and optimize tissue engineering scaffolds, with a potential in 3D printing fabrication. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 1329–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani, Z.; Venugopal, J.R.; Urbanska, A.M.; Mills, D.K.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. A bird’s eye view on the use of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Current state-of-the-art, emerging directions and future trends. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 2181–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkasabgy, N.A.; Mahmoud, A.A. Fabrication Strategies of Scaffolds for Delivering Active Ingredients for Tissue Engineering. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).