Analysis of Adhesion between Wet Clay Soil and Rotary Tillage Part in Paddy Field Based on Discrete Element Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Theoretical Model
2.3. Test Method
2.3.1. Simulation Parameters
2.3.2. Simulation Test Design
2.4. Simulation Model
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Simulation Test Results
3.1.1. Analysis of PB Test Results
3.1.2. Analysis of BBD Results
3.1.3. Interaction Effects of the Regression Model
3.1.4. Determination of Optimal Simulation Parameters
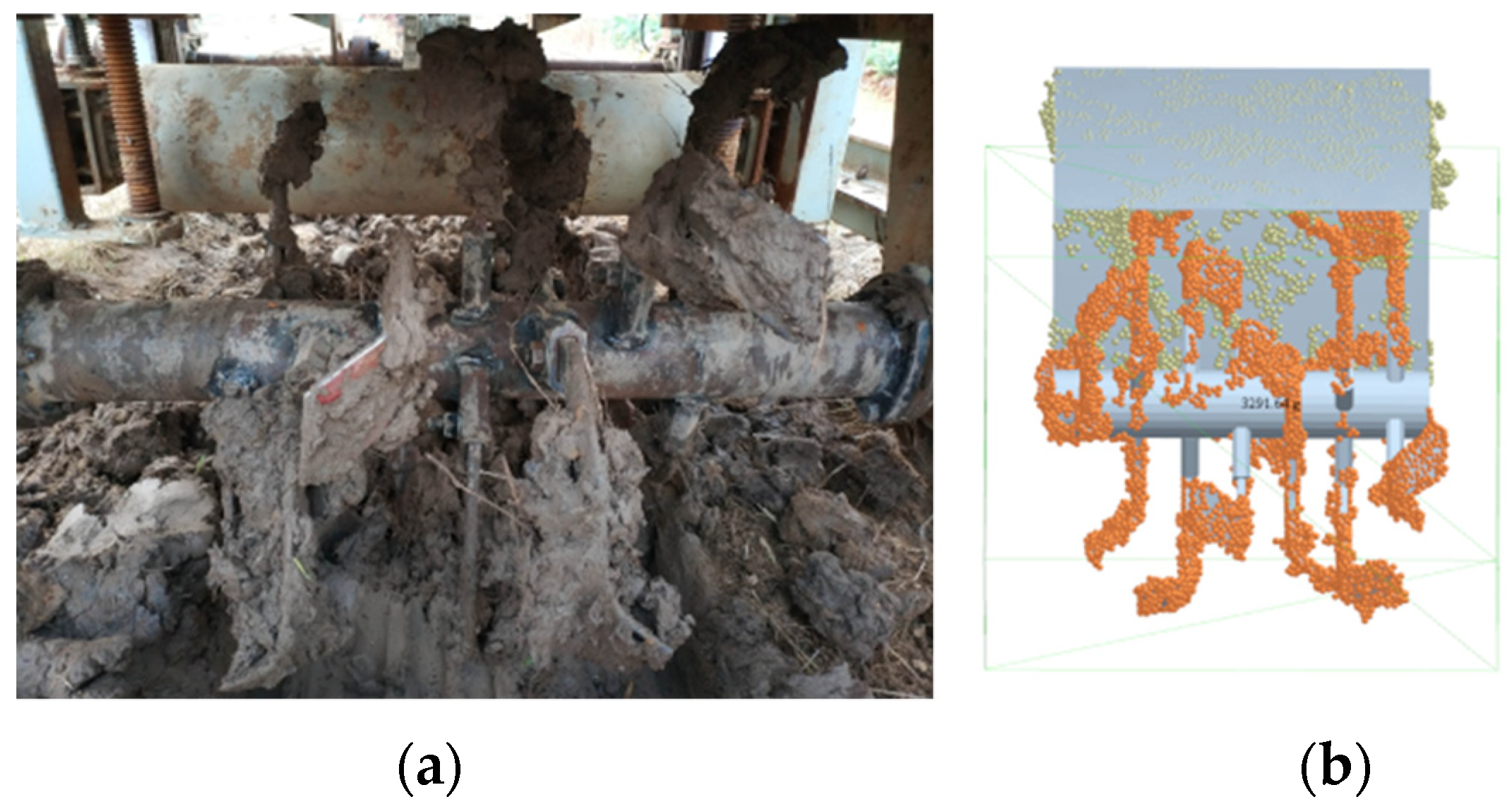
3.2. Analysis of Soil Adhesion Process
3.2.1. The Process of Soil Adhering to Rotary Tillage Part
3.2.2. Rotary Tillage Unit Soil Particles Distribution
3.2.3. Soil Particles Adhesion in Different Soil Zones
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Soil Moisture conTent and Straw on Soil Adhesion Mass
4.2. Measures to Reduce Soil Adhesion Mass of Rotary Tillage Part
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, J.P.; Carter, L.M.; Reicosky, D.C.; Shrestha, A.; Pettygrove, G.S.; Klonsky, K.M.; Marcum, D.B.; Chessman, D.; Roy, R.; Hogan, P.; et al. A history of tillage in California’s Central Valley. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 157, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Feng, J.; Zhai, S.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Bian, X.; Koide, R.T.; Liu, J. Long-term ditch-buried straw return alters soil water potential, temperature, and microbial communities in a rice-wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, P.; Jiang, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Cao, C. Evaluation of resource and energy utilization, environmental and eco-nomic benefits of rice water-saving irrigation technologies in a rice-wheat rotation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Z. Quantification of the soil stiffness constants using physical properties of paddy soils in Yangtze Delta Plain, China. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 200, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Liang, B.; Nan, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, W. Temporal physicochemical changes and transformation of biochar in a rice paddy: Insights from a 9-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, P.; Salokhe, V.M.; Nakashima, H. Modification of a mouldboard plough surface using arrays of polyethylene protuberances. J. Terramech. 2007, 44, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Cong, Q.; Tong, J.; Chen, B. Reducing adhesion of soil against loading shovel using bionic electro-osmosis method. J. Terramech. 2001, 38, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X. Theoretical analysis of the adhesion force of soil to solid materials. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 87, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massah, J.; Fard, M.R.; Aghel, H. An optimized bionic electro-osmotic soil-engaging implement for soil adhesion reduction. J. Terramech. 2021, 95, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, L.; Sun, J.; Tong, J. Earthworm epidermal mucus: Rheological behavior reveals drag-reducing characteristics in soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 158, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, K.; Kawanishi, K. Soil failure by introducing air under pressure. Trans. ASAE 1985, 27, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, R.L.; Gill, W.R.; Reaves, C.A. Experiences with lubricated plows. Trans. ASAE 1979, 22, 7–0012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, M.; Naderi-Boldaji, M.; Ghanbarian, D.; Ucgul, M.; Keller, T. DEM simulation of plate sinkage in soil: Calibration and experimental validation. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 203, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaf, Z.; Rubinstein, D.; Shmulevich, I. Determination of discrete element model parameters required for soil tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucgul, M.; Fielke, J.M.; Saunders, C. Three-dimensional discrete element modelling of tillage: Determination of a suitable contact model and parameters for a cohesionless soil. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 121, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, R. Effect of soil particle size on soil-subsoiler interactions using the discrete element method simulations. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 182, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tong, J.; Zhang, Z. DEM simulation of bionic subsoilers (tillage depth> 40 cm) with drag reduction and lower soil disturbance characteristics. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 119, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, R. Analysis of the movement behaviour of soil between subsoilers based on the discrete element method. J. Terramech. 2017, 74, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucgul, M.; Saunders, C.; Fielke, J.M. Comparison of the discrete element and finite element methods to model the interaction of soil and tool cutting edge. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 169, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.A.; Fielke, J.M.; Desbiolles, J.M.A. Torque and energy characteristics for strip-tillage cultivation when cutting furrows using three designs of rotary blade. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 129, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.A.; Hossain, M.I.; Gathala, M.K.; Timsina, J.; Krupnik, T.J. Optimal design and setting of rotary strip-tiller blades to intensify dry season cropping in Asian wet clay soil conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 207, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Ou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Duan, J. Study on plowing performance of EDEM low-resistance animal bionic device based on red soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, J. Design and application of performance test bench for rotary tiller components. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, O.; Gotteland, P. Modelling of sinkage tests in tilled soils for mobility study. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 80, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Kendall, K.; Roberts, A. Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids. Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1971, 324, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, C.; He, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Xu, H. Discrete element modelling of citrus fruit stalks and its verification. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 200, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katinas, E.; Chotěborský, R.; Linda, M.; Jankauskas, V. Wear modelling of soil ripper tine in sand and sandy clay by discrete element method. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 188, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Ru, S. Parameter calibration of discrete element simulation model for latosol particles in hot areas of Hainan Province. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tong, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, H.; Mao, C.; Ma, Y. Calibration of parameters of interaction between clayey black soil with different moisture content and soil-engaging component in northeast China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Wu, M.; Lu, J.; Quan, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, J. Calibration of simulation physical parameters of clay loam based on soil accumulation test. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, Z. Measurement and calibration of the discrete element parameters of wet bulk coal. Measurement 2019, 142, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Jena, H.M. Process optimization of butachlor bioremediation by Enterobacter cloacae using Plackett Burman design and response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2018, 119, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.N.; Portes, M.F.; e Moraes, H.M.F.; Junior, M.R.F.; Rosas, J.T.F.; Junior, W.D.A.O. Influence of tillage systems on soil physical properties, spectral response and yield of the bean crop. Remote Sens. Appl. 2021, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, X. Tillage practices affects the grain filling of inferior kernel of summer maize by regulating soil water content and photosynthetic capacity. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, J.V.; Tanner, D.W. The frictional characteristics of steel sliding on soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1977, 28, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhai, S.; Liu, J. The impacts of ditch-buried straw layers on the interface soil physicochemical and microbial properties in a rice-wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 202, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Xia, J. Evaluation of straw spatial distribution after straw incorporation into soil for different tillage tools. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, G.T.; Kätterer, T.; Munkholm, L.J.; Parvage, M.M.; Keller, T.; Rychel, K.; Kirchmann, H. Short-term effects of loosening and incorporation of straw slurry into the upper subsoil on soil physical properties and crop yield. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 184, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



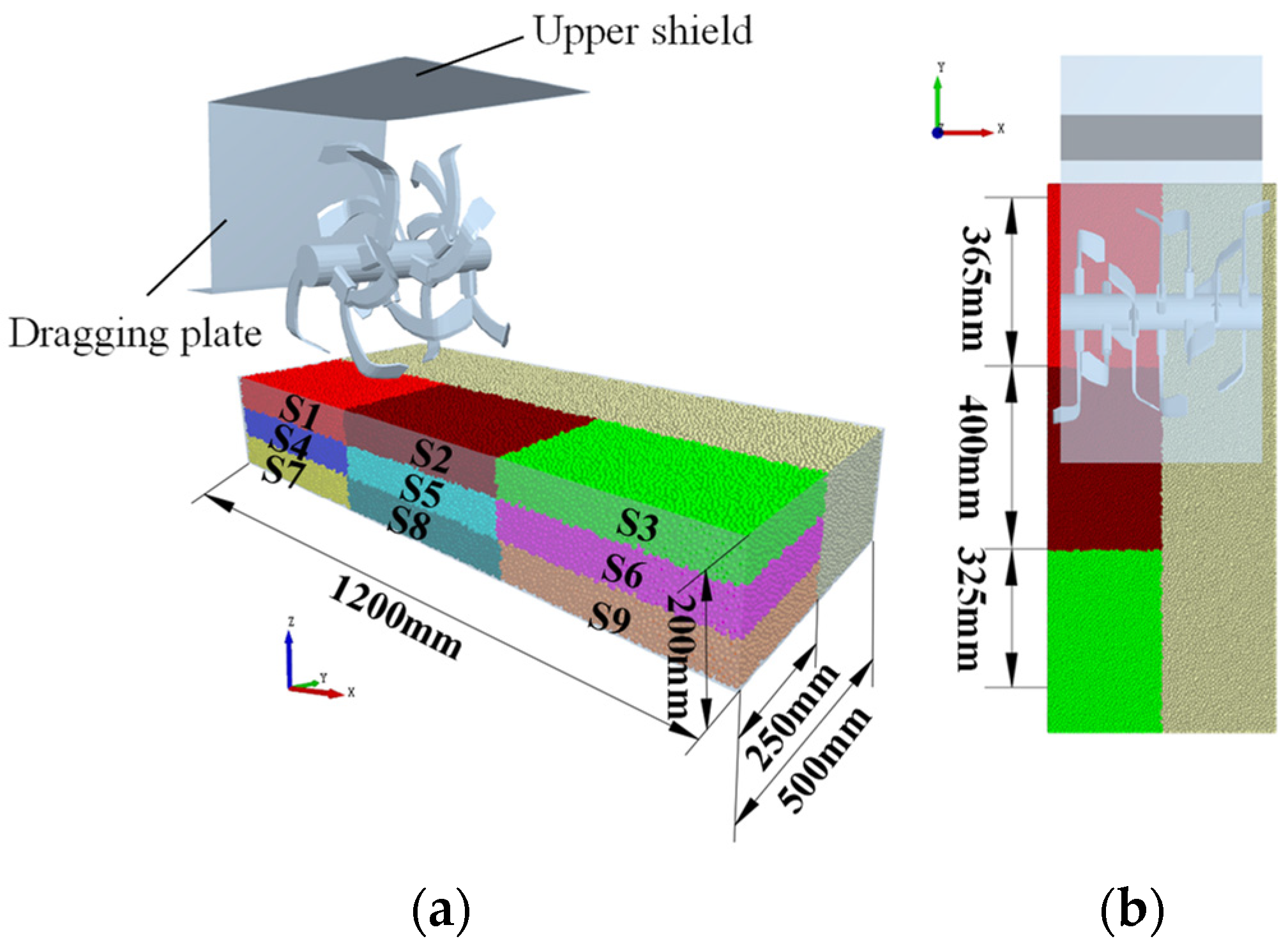





| Bulk Density/(g∙cm−3) | Moisture Content/% | Organic Matter Content/(g∙kg−1) | Particle Composition/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value | Standard Deviation | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Clay <0.002 mm | Silt 0.05~2.0 mm | Sand 0.05~2.0 mm |
| 1.15 | 0.15 | 35.75 | 1.35 | 15.26 | 2.34 | 42.46 | 49.29 | 8.25 |
| Simulation Parameters | Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Level (−1) | Middle Level (0) | High Level (1) | |||
| Material contact parameters | Particle-particle | Coefficient of restitution (A) | 0.1 | 0.45 | 0.8 |
| Coefficient of static friction (B) | 0.01 | 0.505 | 1 | ||
| Coefficient of rolling friction (C) | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.41 | ||
| Particle-geometry | Coefficient of restitution (D) | 0.05 | 0.375 | 0.7 | |
| Coefficient of static friction (E) | 0.1 | 0.6 | 1.1 | ||
| Coefficient of rolling friction (F) | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.45 | ||
| Contact model parameters | Particle-particle | JKR surface energy (G) | 50 | 75 | 100 |
| Particle-geometry | Energy density (H) | 4 × 105 | 5 × 105 | 6 × 105 | |
| Test Serial Number | Parameter Notations | Soil Adhesion Mass Q/kg | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 3.08929 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 3.16071 |
| 3 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 2.57697 |
| 4 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 4.26519 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1.89305 |
| 6 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.80082 |
| 7 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 3.28965 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 3.44142 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 3.81288 |
| 10 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 3.45382 |
| 11 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 2.30370 |
| 12 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 3.82330 |
| Parameters | Effect | Sum of Squares | Contribution/% | p-Value | Significance Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | −0.48 | 0.69 | 9.47 | 0.0592 | 4 |
| B | 0.42 | 0.54 | 7.33 | 0.0797 | 5 |
| C | −0.92 | 2.53 | 34.57 | 0.0109 * | 1 |
| D | 0.18 | 0.095 | 1.30 | 0.3516 | 8 |
| E | −0.65 | 1.27 | 17.39 | 0.0276 * | 2 |
| F | −0.33 | 0.33 | 4.49 | 0.1334 | 7 |
| G | 0.65 | 1.27 | 17.34 | 0.0277 * | 3 |
| H | −0.35 | 0.36 | 4.88 | 0.1228 | 6 |
| R2 = 0.9678, R2adj = 0.8818, CV = 8.43%, adequate precision = 11.294 | |||||
| Test Serial Number | Particle-Particle Coefficient of Rolling Friction (X1) | Particle-Geometry Coefficient of Static Friction (X2) | Particle-Particle JKR Surface Energy (X3) | Soil Adhesion Mass Q/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 4.18287 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 3.83967 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 4.22254 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3.56838 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 3.17658 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 2.59036 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 4.34951 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3.50291 |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 3.44985 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 2.80660 |
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 4.49234 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3.90811 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.16467 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.20683 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.35562 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.35264 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.21725 |
| Source of Variation | Sum of Square | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 4.49 | 9 | 0.50 | 0.0004 ** |
| X1 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.74 | 0.0010 ** |
| X2 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.27 | 0.0146 ** |
| X3 | 2.24 | 1 | 2.24 | <0.0001 ** |
| X1 × 2 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.024 | 0.3640 |
| X1 × 3 | 0.017 | 1 | 0.017 | 0.4431 |
| X2 × 3 | 8.71 × 10−4 | 1 | 8.71 × 10−4 | 0.8590 |
| X12 | 0.20 | 1 | 0.20 | 0.0271 * |
| X22 | 0.96 | 1 | 0.96 | 0.0005 ** |
| X32 | 0.022 | 1 | 0.022 | 0.3879 |
| Residual | 0.18 | 7 | 0.026 | - |
| Lack of fit | 0.15 | 3 | 0.049 | 0.0541 |
| Pure error | 0.031 | 4 | 7.87 × 10−3 | - |
| Total | 4.67 | 16 | - | - |
| R2 = 0.9616, R2adj = 0.9121, CV = 4.51%, adequate precision = 14.037 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Zheng, K.; Xia, J.; Liu, G.; Jiang, L.; Li, D. Analysis of Adhesion between Wet Clay Soil and Rotary Tillage Part in Paddy Field Based on Discrete Element Method. Processes 2021, 9, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050845
Cheng J, Zheng K, Xia J, Liu G, Jiang L, Li D. Analysis of Adhesion between Wet Clay Soil and Rotary Tillage Part in Paddy Field Based on Discrete Element Method. Processes. 2021; 9(5):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050845
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jian, Kan Zheng, Junfang Xia, Guoyang Liu, Liu Jiang, and Dong Li. 2021. "Analysis of Adhesion between Wet Clay Soil and Rotary Tillage Part in Paddy Field Based on Discrete Element Method" Processes 9, no. 5: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050845
APA StyleCheng, J., Zheng, K., Xia, J., Liu, G., Jiang, L., & Li, D. (2021). Analysis of Adhesion between Wet Clay Soil and Rotary Tillage Part in Paddy Field Based on Discrete Element Method. Processes, 9(5), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050845





