Simple Gain-Scheduled Control System for Dissolved Oxygen Control in Bioreactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
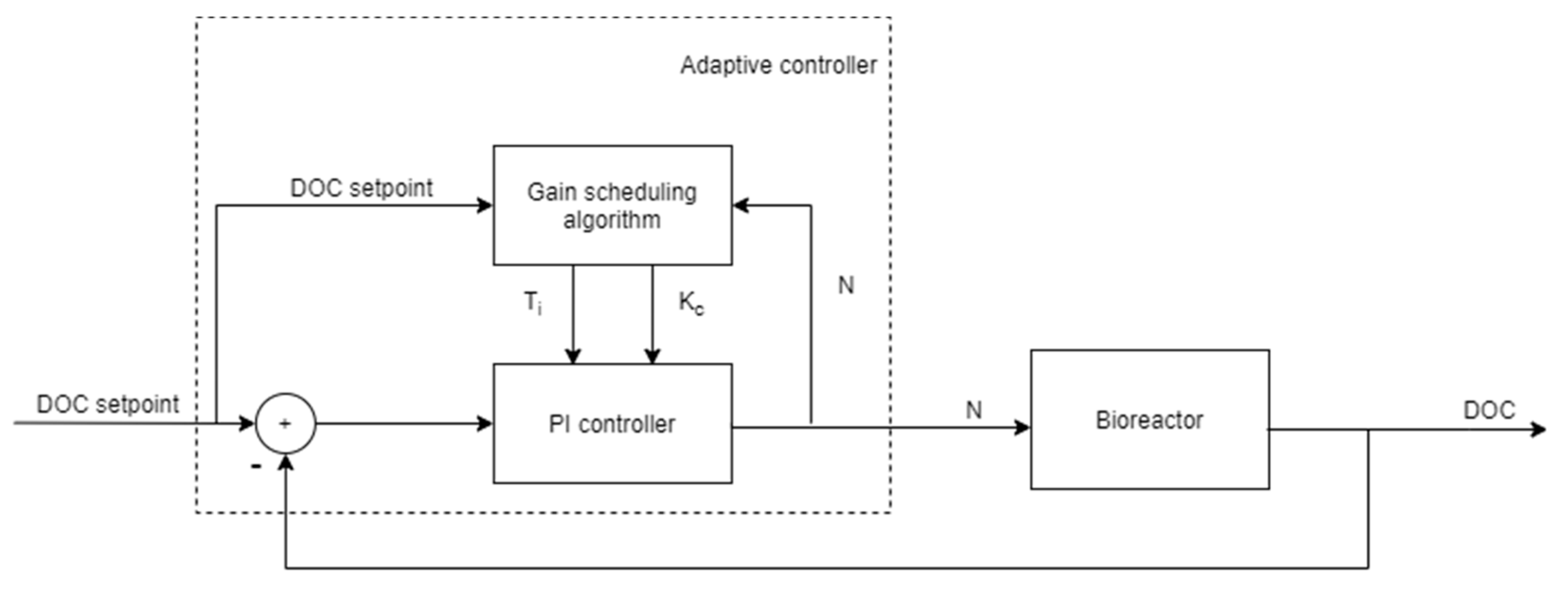
2.1. Development of Adaptation Algorithm for DOC Control
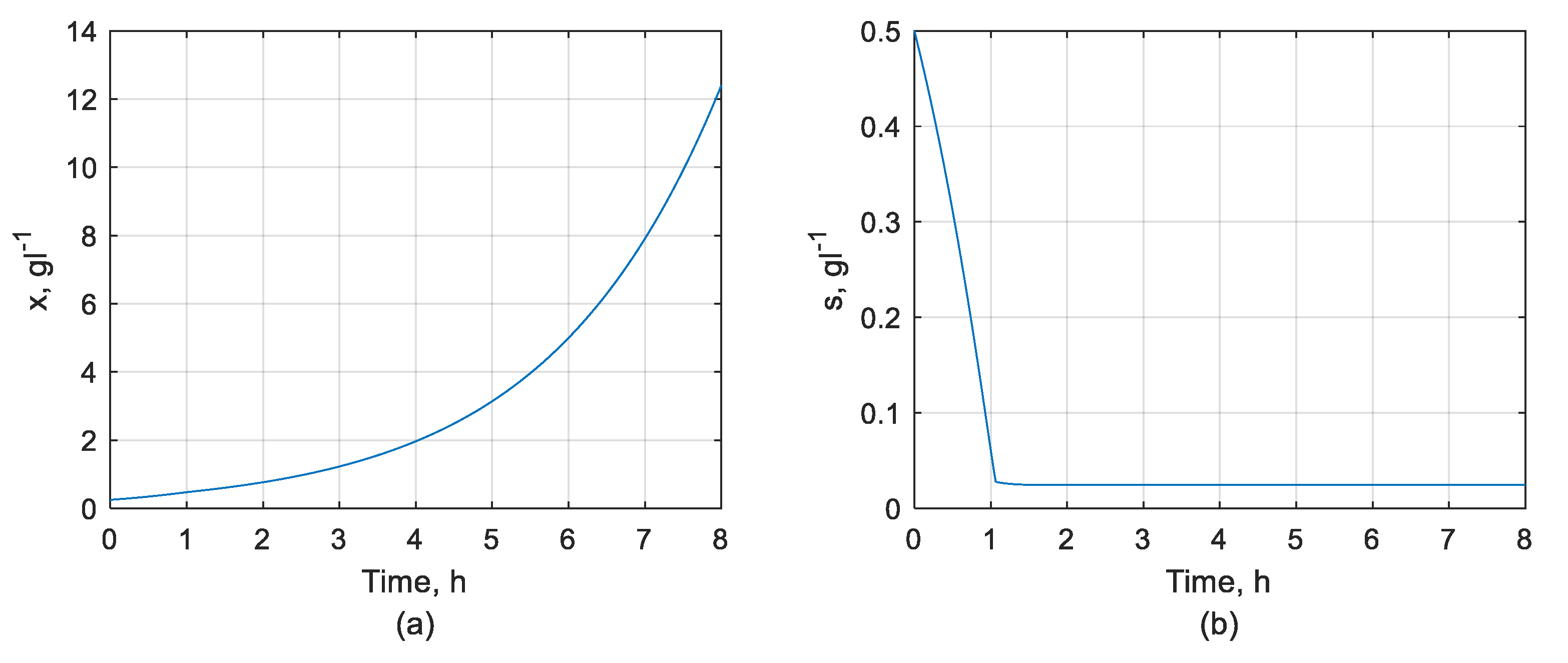
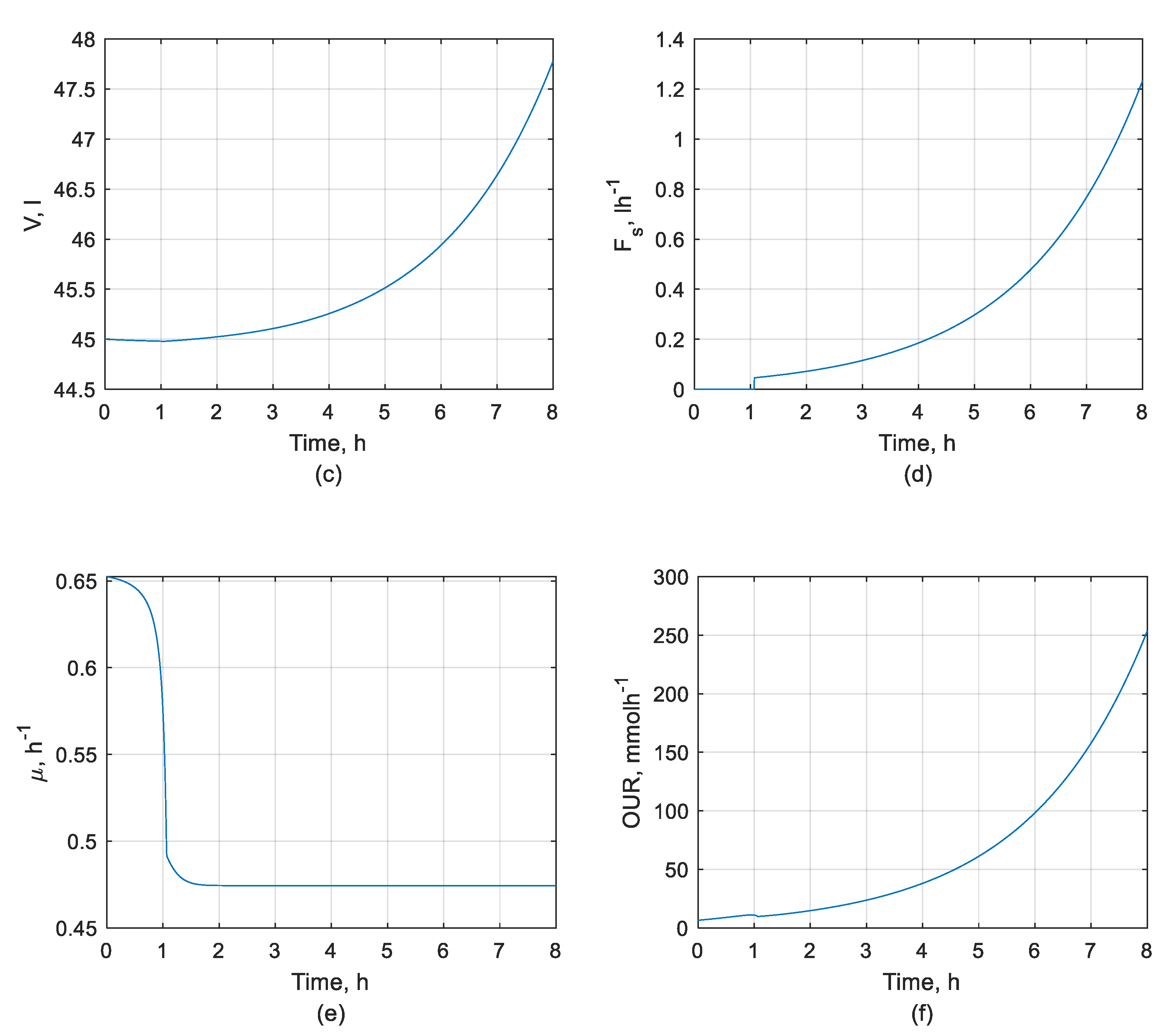
2.2. Mathematical Model of the Biotechnological Process
3. Results and Discussion
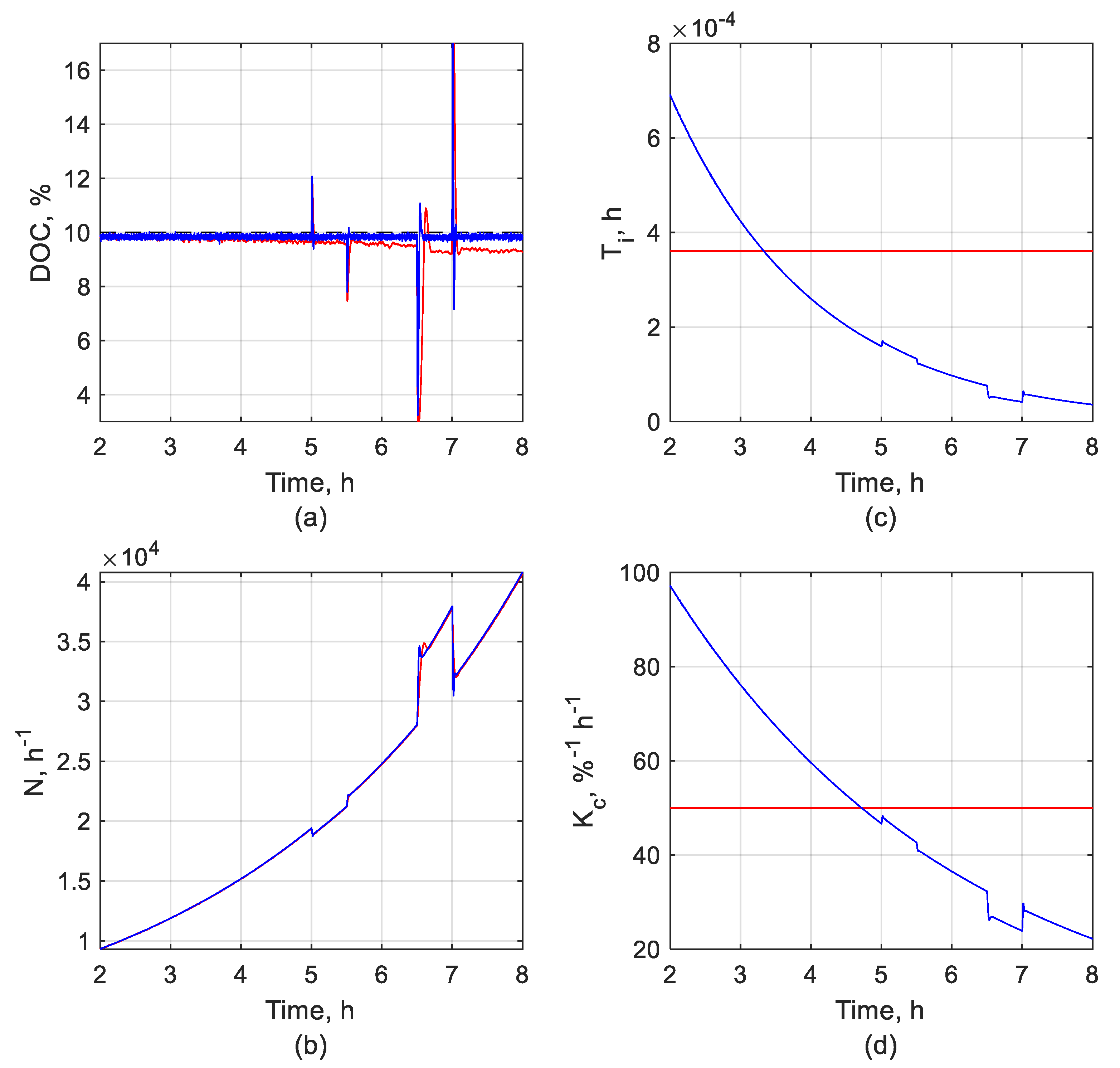
3.1. DOC Control System Performance
3.1.1. DOC Set-Point Tracking Performance
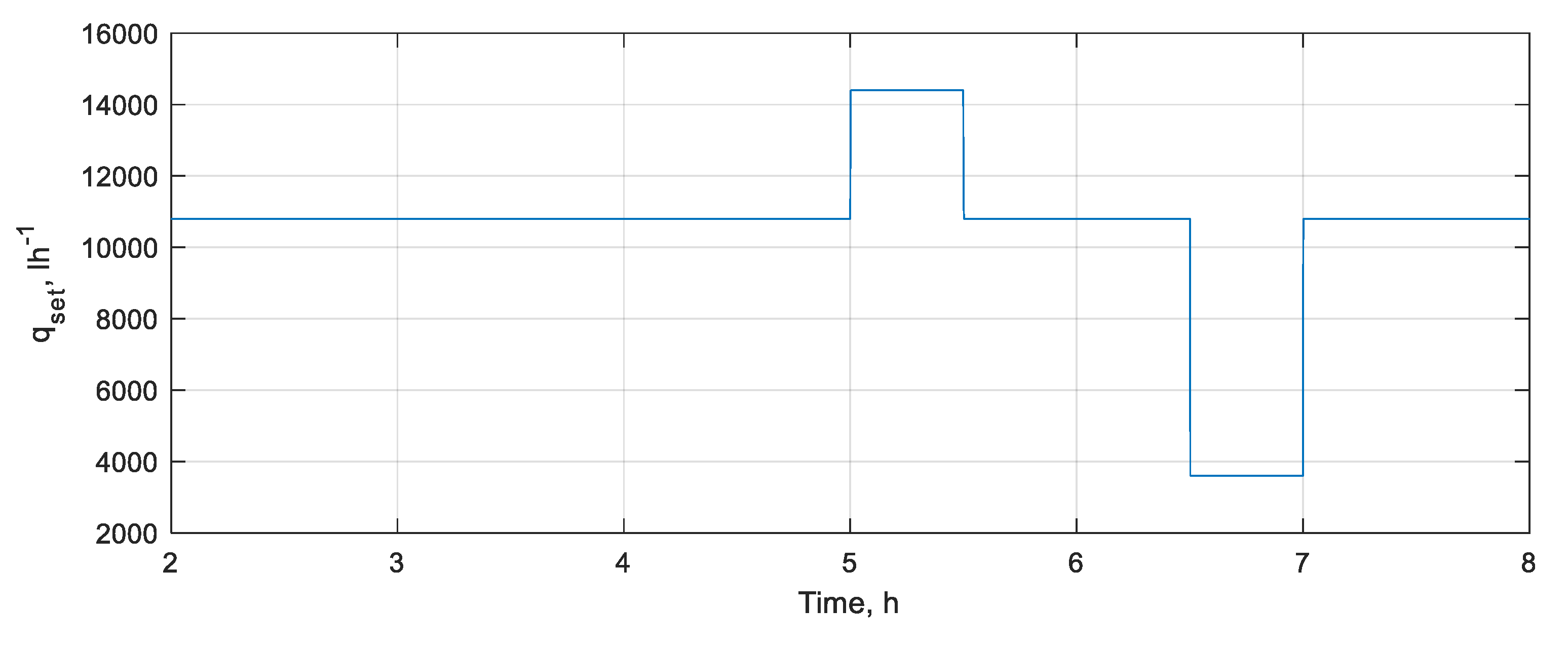
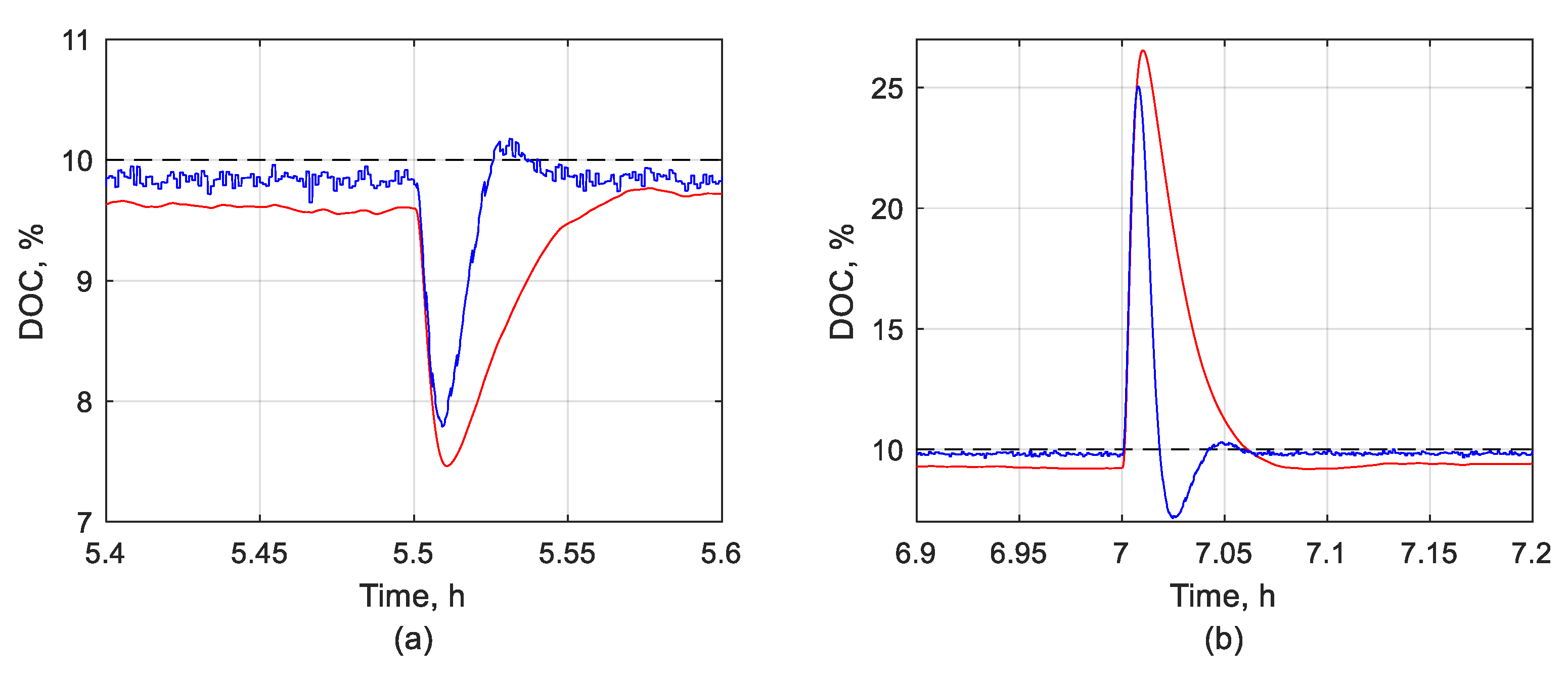
3.1.2. DOC Disturbance Rejection Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boudreau, M.A.; McMillan, G.K. New Directions in Bioprocess Modelling and Control: Maximizing Process Analytical Technology Benefits; ISA: Durham, NC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dochain, D. Bioprocess Control; ISTE: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.K.; Bhanot, S.; Mohanta, H.K.; Bansal, V. Design and implementation of adaptive fuzzy knowledge based control of pH for strong acid-strong base neutralization process. J. Engl. Res. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar]
- US Food and Drug Administration: Guidance for Industry PAT—A Framework for Innovative Pharma-Ceutical Development, Manufacturing and Quality Assurance. 2004. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/pat-framework-innovative-pharmaceutical-development-manufacturing-and-quality-assurance (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. Bioreactor control improves bioprocess performance. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkus, M.; Repšytė, J.; Galvanauskas, V. Fuzzy logic-based adaptive control of specific growth rate in fed-batch biotechnological processes: A simulation study. Appl. Scien. 2020, 10, 6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levišauskas, D. An algorithm for adaptive control of dissolved oxygen concentration in batch culture. Biotechnol. Tech. 1995, 9, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levišauskas, D.; Simutis, R.; Galvanauskas, V. Adaptive set-point control system for microbial cultivation processes. Non. An. Mod. Cont. 2016, 21, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babuška, R.; Damen, M.R.; Hellinga, C.; Maarleveld, H. Intelligent adaptive control of bioreactors. J. Intell. Manuf. 2003, 14, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, A.; Andrášik, A.; Mizsey, P.; Fonyo, Z.; Illeová, V. Computer control of pH and DO in a laboratory fermenter using a neural network technique. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 26, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, J.; Jegatheesan, V.; Shi, G. Dissolved oxygen control in activated sludge process using a neural network-based adaptive PID algorithm. Appl. Scien. 2018, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palancar, M.C.; Aragón, J.M.; Miguéns, A.J.A.; Torrecilla, J.S. Application of a model reference adaptive control system to pH control. effects of lag and delay time. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1996, 35, 4100–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardello, R.J.; San, K.-Y. The design of controllers for batch bioreactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1988, 32, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprijanov, A.; Gnoth, S.; Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. Advanced control of dissolved oxygen concentration in fed batch cultures during recombinant protein production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnoth, S.; Kuprijanov, A.; Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. Simple adaptive pH control in bioreactors using gain-scheduling methods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.B.; Lee, S.C.; Chang, H.N.; Chang, Y.K. Dissolved oxygen concentration regulation using auto-tuning proportional-integral-derivative controller in fermentation process. Biotechnol. Tech. 1991, 5, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levisauskas, D.; Simutis, R.; Galvanauskas, V.; Urniezius, R. Simple control systems for set-point control of dissolved oxygen concentration in batch fermentation processes. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Smets, I.Y.; Claes, J.; November, E.J.; Bastin, G.P.; Van Impe, J.F. Optimal adaptive control of (bio) chemical reactors: Past, present and future. J. Process. Control. 2004, 14, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastin, G.; Impe, J.F. Nonlinear and adaptive control in biotechnology: A tutorial. Eur. J. Control 1995, 1, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkus, M.; Simutis, R.; Galvanauskas, V. Unified structure of adaptive system for control of basic process variables in biotechnological cultivation processes: Ph control system case study. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Galvanauskas, V.; Simutis, R.; Vaitkus, V. Adaptive control of biomass specific growth rate in fed-batch biotechnological processes. A comparative study. Process 2019, 7, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brignoli, Y.; Freeland, B.; Cunningham, D.; Dabros, M. Control of specific growth rate in fed-batch bioprocesses: Novel controller design for improved noise management. Process 2020, 8, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, W.S. (Ed.) The Control. Handbook; IEEE/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Villadsen, J.; Nielsen, J.; Liden, G. Bioreaction Engineering Principles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Levisauskas, D.; Galvanauskas, V.; Henrich, S.; Wilhelm, K.; Volk, N.; Lübbert, A. Model-based optimization of viral capsid protein production in fed-batch culture of recombinant Escherichia coli. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 25, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedeking, R.; Piret, E.L. A kinetic study of the lactic acid fermentation. Batch process at controlled pH. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 67, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| H = 0.7906 L mmol−1 | ε = 0.15 | Tel1 = 10 s |
| Tel2 = 2 s | Tq = 2 s | Tu = 1 s |
| α = 0.8·10−7 | β = 2 | γ = 0.2 |
| vmol = 0.0224 l mmol−1 | ||
| Initial Conditions | ||
| cel(0) = 10% | q(0) = 2 s−1 | u(0) = 2.5 s−1 |
| ca(0) = 0.0266 mmol L−1 | yO2(0) = 0.2099 | ael (0) = 10% |
| Model Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Y = 0.8646 gg−1 | m = 0.018 gg−1 h−1 | Yxs = 0.52 gg−1 |
| µmax = 0.737 1 h−1 | Ki = 93.8 gl−1 | S0 = 450 gl−1 |
| Ks = 0.02 gl−1 | kc = 0.00265 mmol L−1 | Fsmp = 0.025 lh−1 |
| Initial Conditions | ||
| V(0) = 45 L | x(0) = 0.25 gl−1 | s(0) = 0.5 gl−1 |
| Fixed Parameter Values | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kc | Ti | |
| DOC control | 50%−1 h−1 | 3.6 × 10−4 h |
| Control Type | Tuning Parameters | Mean Absolute Error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disturbance Rejection | Set-Point Tracking | ||
| Standard DOC | Kc = 50%−1 h−1, Ti = 3.6 × 10−4 h | 0.166 | 0.071 |
| Adaptive DOC | KTi = 0.6 × 105, KKc = 1.5 × 105 | 0.063 | 0.028 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butkus, M.; Levišauskas, D.; Galvanauskas, V. Simple Gain-Scheduled Control System for Dissolved Oxygen Control in Bioreactors. Processes 2021, 9, 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091493
Butkus M, Levišauskas D, Galvanauskas V. Simple Gain-Scheduled Control System for Dissolved Oxygen Control in Bioreactors. Processes. 2021; 9(9):1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091493
Chicago/Turabian StyleButkus, Mantas, Donatas Levišauskas, and Vytautas Galvanauskas. 2021. "Simple Gain-Scheduled Control System for Dissolved Oxygen Control in Bioreactors" Processes 9, no. 9: 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091493
APA StyleButkus, M., Levišauskas, D., & Galvanauskas, V. (2021). Simple Gain-Scheduled Control System for Dissolved Oxygen Control in Bioreactors. Processes, 9(9), 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091493






