Reactive Chromatography Applied to Ethyl Levulinate Synthesis: A Proof of Concept
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Chromatographic Reactor Setup
2.2.2. Take-up Test
3. Results and Discussion
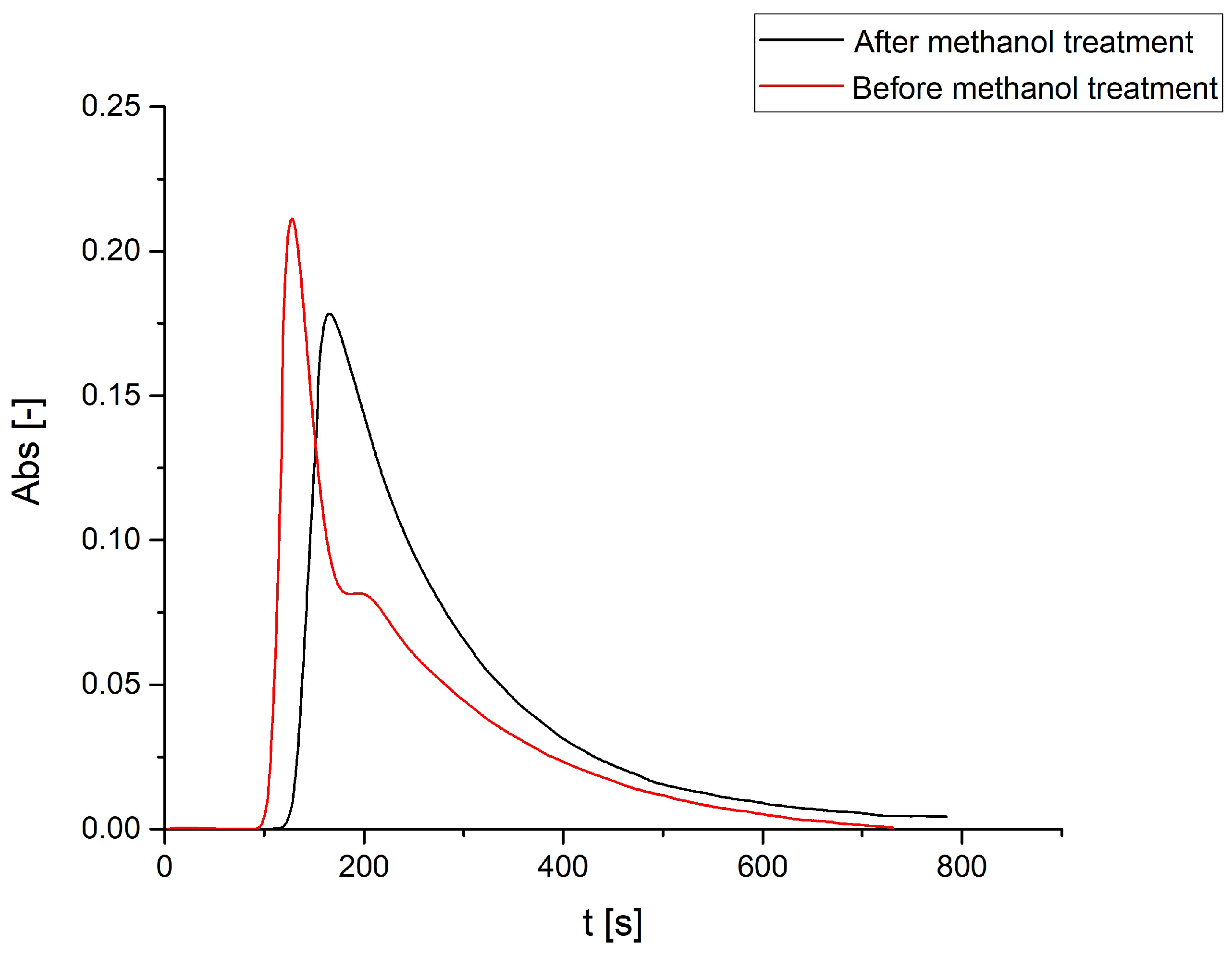
3.1. Dowex 50WX8 Take-up Tests
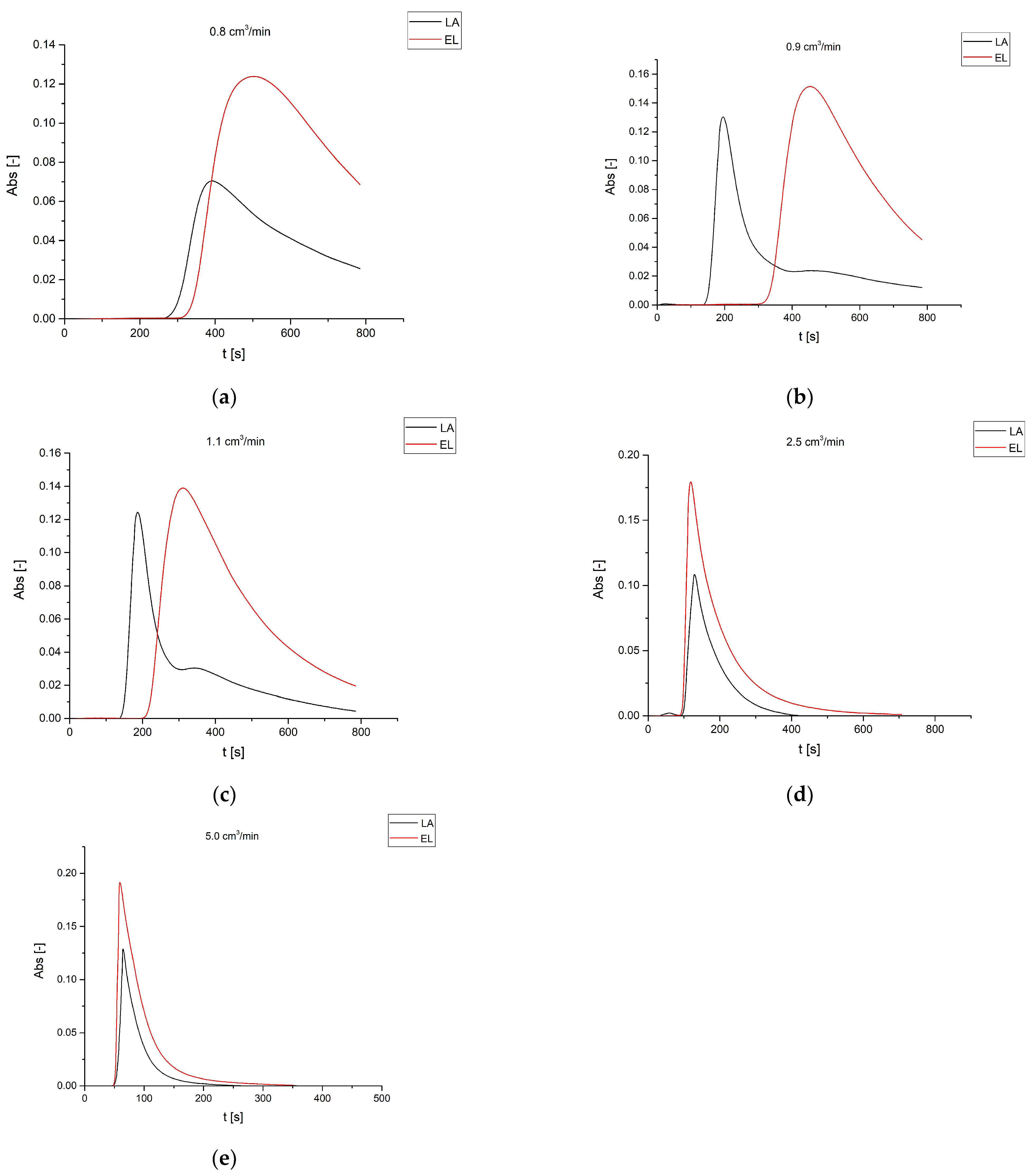
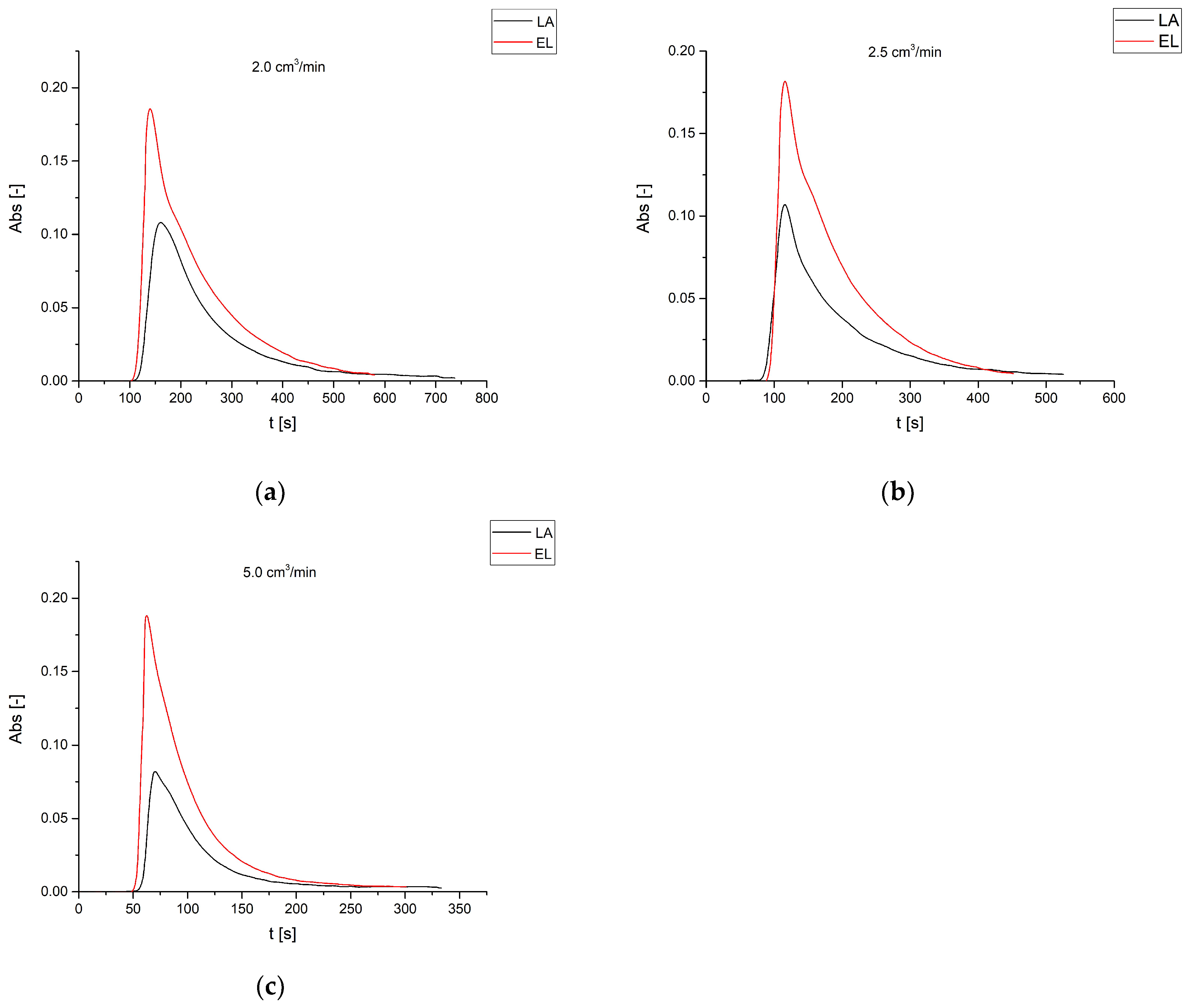
3.2. Reactive Chromatography Results
Effect of the Stream Flow Rate
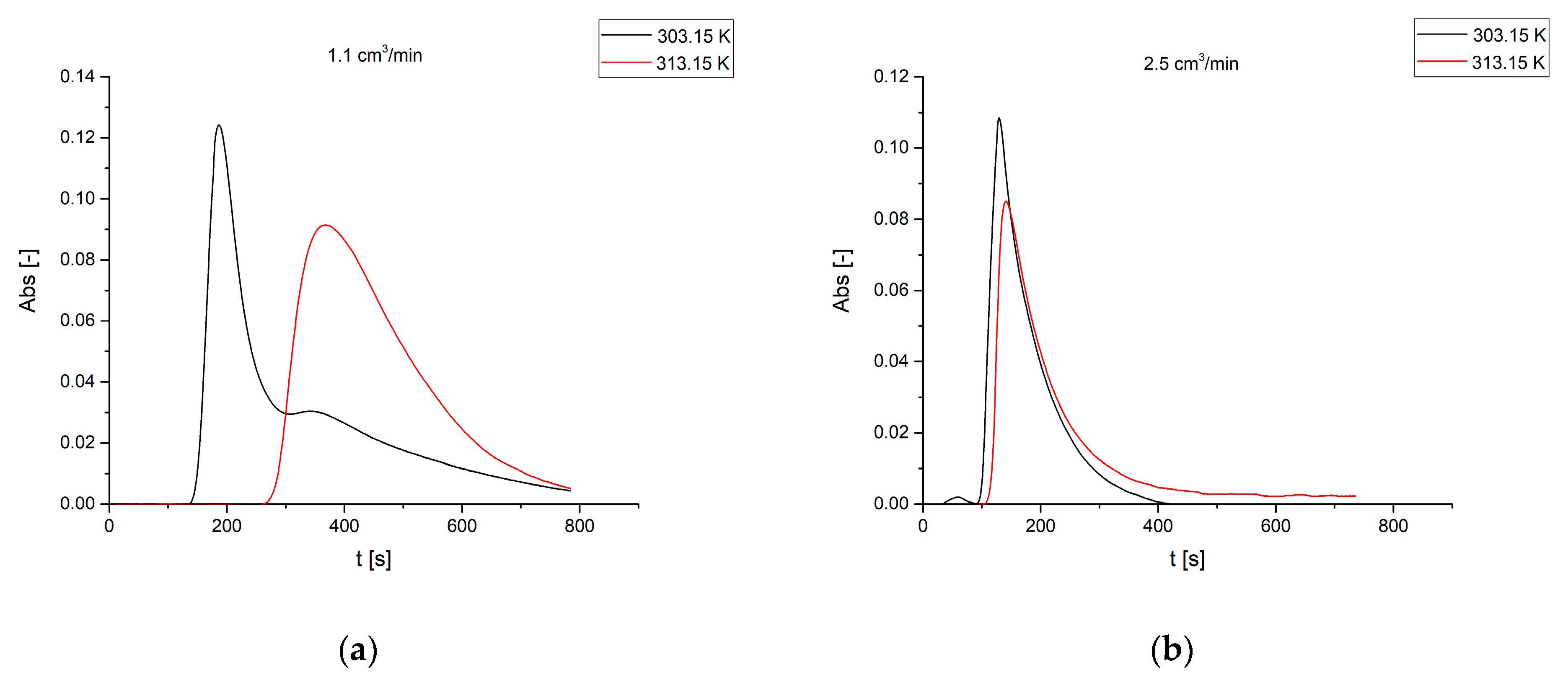
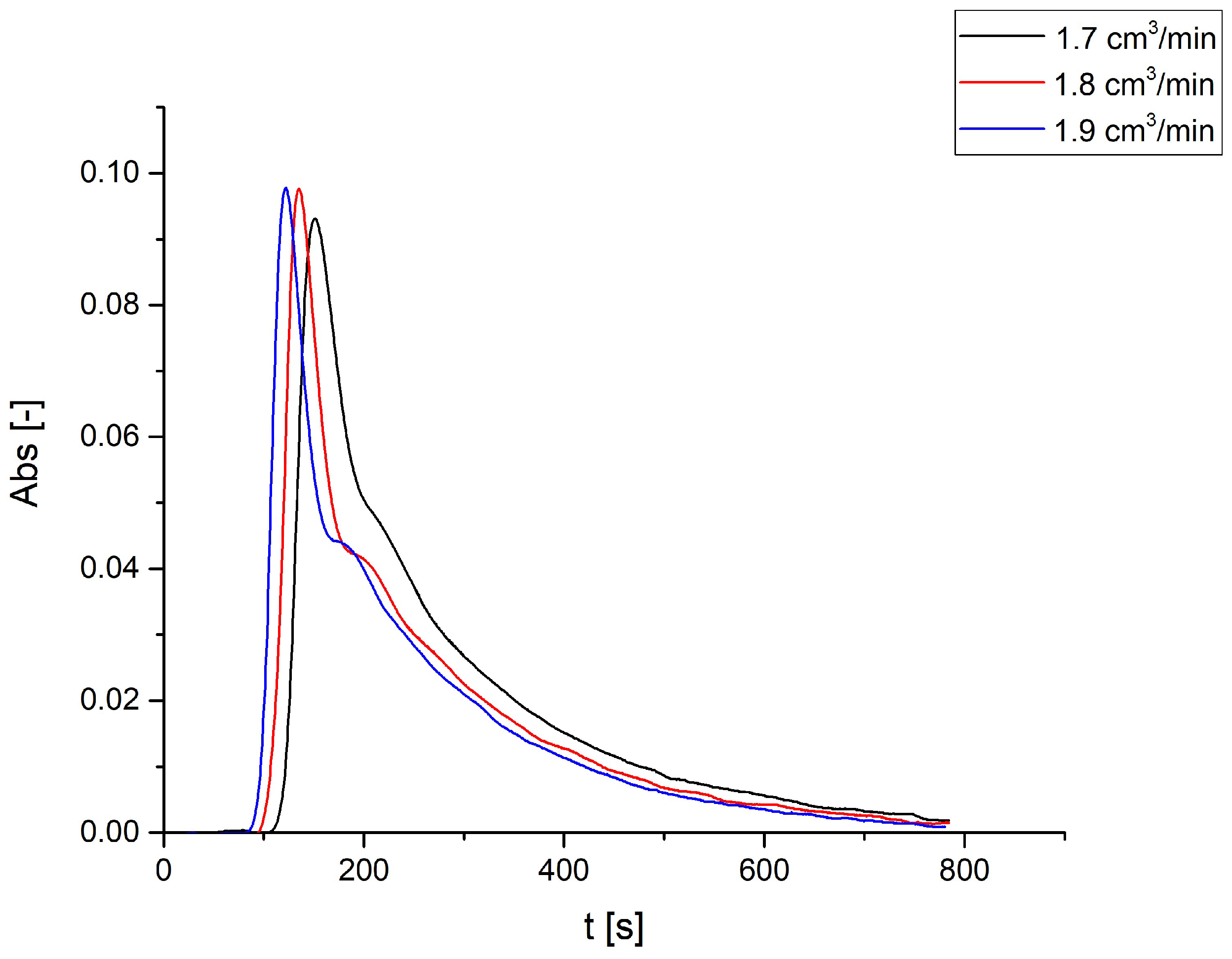
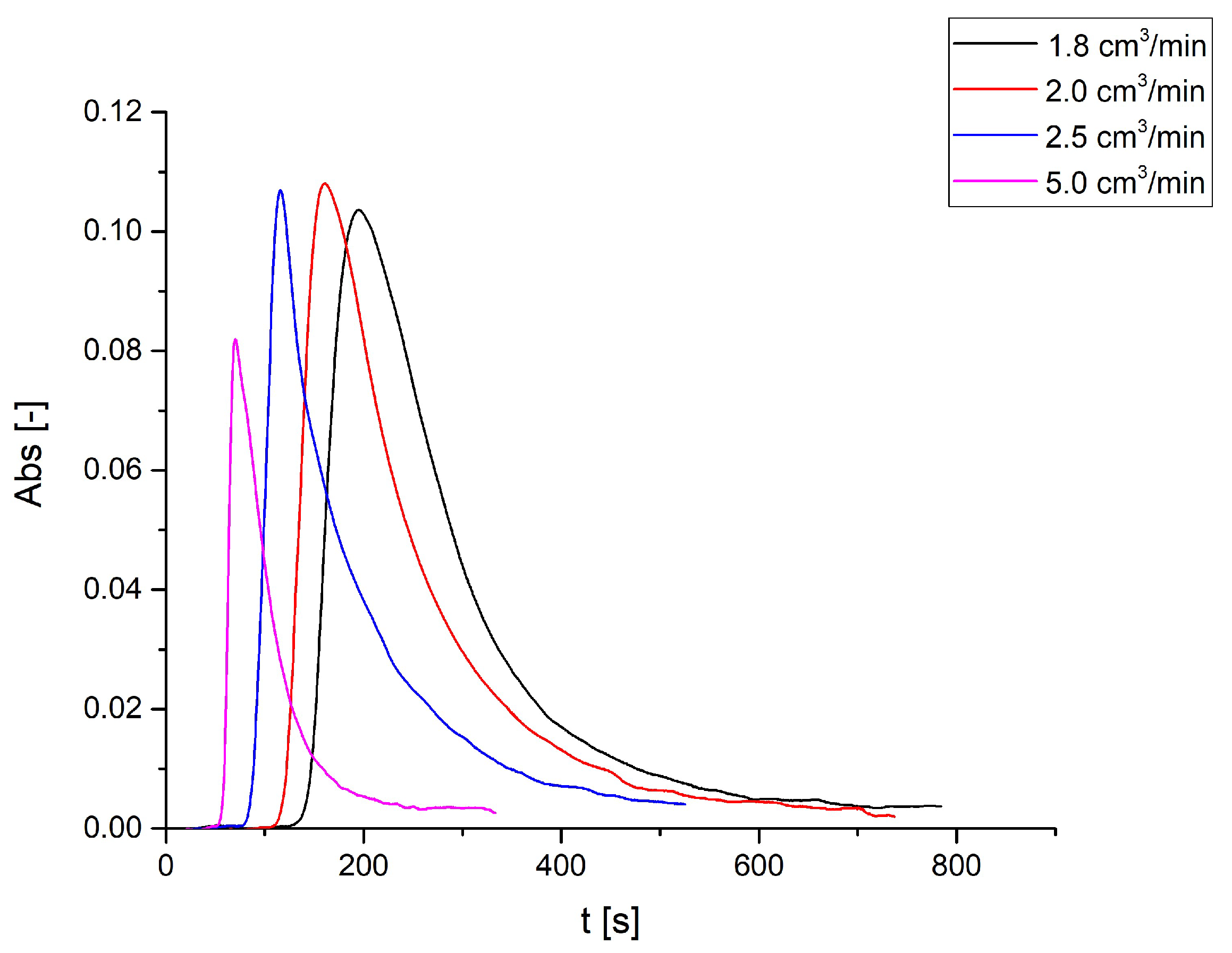
3.3. Effect of the Reactor Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LA | Levulinic acid |
| EL | Ethyl levulinate |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| H2O | Water |
| List of symbols | |
| T | Temperature [K] |
| t | Time [s] |
| Volume of dried resin [cm3] | |
| Volume of swelled resin [cm3] | |
| Swelling coefficient [%] | |
References
- Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Yu, Z.; Xiong, J.; Bai, H.; Zhang, R. Production of levulinic acid from cellulose and cellulosic biomass in different catalytic systems. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozell, J.J.; Petersen, G.R. Technology development for the production of biobased products from biorefinery carbohydrates—the US Department of Energy’s “Top 10” revisited. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Silva, J.; Grekin, R.; Mariano, A.; Filho, R. Making Levulinic Acid and Ethyl Levulinate Economically Viable: A Worldwide Technoeconomic and Environmental Assessment of Possible Routes. Energy Technol. 2017, 6, 613–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, H.; Moser, B.R.; Toler, J.; Smith, W.F.; Walker, T. Ethyl levulinate: A potential bio-based diluent for biodiesel which improves cold flow properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3262–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.W.; Floyd, A.J.; Kinsman, R.G.; Roshan-ali, Y. Dehydration Reactions of Fructose in Non-aqueous Media. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1982, 32, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuss, P.J.; Barta, K.; De Vries, J.G. Homogeneous catalysis for the conversion of biomass and biomass-derived platform chemicals. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1174–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuette, H.A.; Cowley, M.A. Levulinic acid. II. the vapor pressures of its alkyl esters (C1--C6. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1931, 53, 3485–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiwale, K.Y.; Sonar, S.K.; Niphadkar, P.S.; Joshi, P.N.; Deshpande, S.S.; Patil, V.S.; Bokade, V.V. Catalytic upgrading of renewable levulinic acid to ethyl levulinate biodiesel using dodecatungstophosphoric acid supported on desilicated H-ZSM-5 as catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 460–461, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, G.; Vázquez, P.; Romanelli, G.; Baronetti, G. Catalytic upgrading of levulinic acid to ethyl levulinate using reusable silica-included Wells-Dawson heteropolyacid as catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2012, 18, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, K.C.; Badgujar, V.C.; Bhanage, B.M. A review on catalytic synthesis of energy rich fuel additive levulinate compounds from biomass derived levulinic acid. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 197, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.R.; Rocha, A.S.; Mai, E.F.; Mota, C.J.A.; Teixeira da Silva, V. Levulinic acid esterification with ethanol to ethyl levulinate production over solid acid catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 425–426, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Rossano, C.; Salucci, E.; Tesser, R.; Salmi, T.; Di Serio, M. Intraparticle diffusion model to determine the intrinsic kinetics of ethyl levulinate synthesis promoted by Amberlyst-15. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 228, 115974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Tesser, R.; Rossano, C.; Cogliano, T.; Vitiello, R.; Leveneur, S.; Di Serio, M. Kinetic study of Amberlite IR120 catalyzed acid esterification of levulinic acid with ethanol: From batch to continuous operation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Kuddus, M. Use of Ion-Exchange Resin in Reactive Separation. In Applications of Ion Exchange Materials in Chemical and Food Industries; Inamuddin, T.A., Rangreez, M., Asiri, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 125–137. ISBN 978-3-030-06085-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzotti, M.; Kruglov, A.; Neri, B.; Gelosa, D.; Morbidelli, M. A continuous chromatographic reactor: SMBR. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.E.; Pereira, C.S.M.; Santos, J.C. Chromatographic Reactors. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.D.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A. Quantifying temperature and flow rate effects on the performance of a fixed-bed chromatographic reactor. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8097–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Tesser, R.; Rossano, C.; Vitiello, R.; Turco, R.; Salmi, T.; Di Serio, M. Chromatographic reactor modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 377, 119692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Catalyst | Particle Size [μm] | Crosslinking Degree [%] | Ionic Form | Total Exchange Capacity [meq/cm3] | Density [g/cm3] | Water Retention Capacity [%] | Max. Operative Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dowex 50WX8 | 150–300 | 8 | H+ | 1.7 | 0.8 | 50–56 | 120 |
| Test | cLA [mol/L] | cEL [mol/L] | T [K] | Q [cm3/min] | P [bar] | ΔP [kg/cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 6 | - | 303 | 0.8 | 2 | 9 |
| C2 | 6 | - | 303 | 0.9 | 2 | 10 |
| C3 | 6 | - | 303 | 1.1 | 2 | 13 |
| C4 | 6 | - | 303 | 2.5 | 2 | 30 |
| C5 | 6 | - | 303 | 5 | 2 | 54 |
| C6 | - | 6 | 303 | 0.8 | 2 | 9 |
| C7 | - | 6 | 303 | 0.9 | 2 | 10 |
| C8 | - | 6 | 303 | 1.1 | 2 | 13 |
| C9 | - | 6 | 303 | 2.5 | 2 | 30 |
| C10 | - | 6 | 303 | 5 | 2 | 54 |
| C11 | 6 | - | 313 | 1.1 | 2 | 13 |
| C12 | 6 | - | 313 | 1.7 | 2 | 21 |
| C13 | 6 | - | 313 | 1.8 | 2 | 23 |
| C14 | 6 | - | 313 | 1.9 | 2 | 24 |
| C15 | 6 | - | 313 | 2.5 | 2 | 30 |
| C16 | - | 6 | 313 | 1.1 | 2 | 13 |
| C17 | - | 6 | 313 | 1.7 | 2 | 21 |
| C18 | - | 6 | 313 | 1.8 | 2 | 23 |
| C19 | - | 6 | 313 | 1.9 | 2 | 24 |
| C20 | - | 6 | 313 | 2.5 | 2 | 30 |
| C21 | 6 | - | 323 | 1.8 | 2 | 23 |
| C22 | 6 | - | 323 | 2.0 | 2 | 26 |
| C23 | 6 | - | 323 | 2.5 | 2 | 30 |
| C24 | 6 | - | 323 | 5.0 | 2 | 54 |
| C25 | - | 6 | 323 | 1.8 | 2 | 23 |
| C26 | - | 6 | 323 | 2.0 | 2 | 26 |
| C27 | - | 6 | 323 | 2.5 | 2 | 30 |
| C28 | - | 6 | 323 | 5.0 | 2 | 54 |
| Molar Fractions [–] | α [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | EtOH | EL | H2O | |
| 1 | - | - | - | 51.6 |
| - | 1 | - | - | 58.5 |
| - | - | 1 | - | 45.7 |
| - | - | - | 1 | 57.5 |
| 0.8 | 0.2 | - | - | 45.7 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - | 49.0 |
| 0.2 | 0.8 | - | - | 52.8 |
| 0.8 | - | 0.2 | - | 45.1 |
| 0.5 | - | 0.5 | - | 36.1 |
| 0.2 | - | 0.8 | - | 45.1 |
| 0.8 | - | - | 0.2 | 49.2 |
| 0.5 | - | - | 0.5 | 51.0 |
| 0.2 | - | - | 0.8 | 56.2 |
| - | 0.8 | 0.2 | - | 52.1 |
| - | 0.5 | 0.5 | - | 44.2 |
| - | 0.2 | 0.8 | - | 47.7 |
| - | 0.8 | - | 0.2 | 54.9 |
| - | 0.5 | - | 0.5 | 52.8 |
| - | 0.2 | - | 0.8 | 57.9 |
| - | - | 0.8 | 0.2 | 45.1 |
| - | - | 0.5 | 0.5 | 50.6 |
| - | - | 0.2 | 0.8 | 57.4 |
| Test | T [K] | Q [cm3/min] | XLA [%] * |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 303 | 0.8 | 100 |
| C2 | 303 | 0.9 | 87 |
| C3 | 303 | 1.1 | 58 |
| C4 | 303 | 2.5 | 0 |
| C5 | 303 | 5.0 | 0 |
| C11 | 313 | 1.1 | 100 |
| C12 | 313 | 1.7 | 65 |
| C13 | 313 | 1.8 | 67 |
| C14 | 313 | 1.9 | 68 |
| C15 | 313 | 2.5 | 0 |
| C21 | 323 | 1.8 | 100 |
| C22 | 323 | 2.0 | 100 |
| C23 | 323 | 2.5 | 0 |
| C24 | 323 | 5.0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossano, C.; Pizzo, C.L.; Tesser, R.; Di Serio, M.; Russo, V. Reactive Chromatography Applied to Ethyl Levulinate Synthesis: A Proof of Concept. Processes 2021, 9, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091684
Rossano C, Pizzo CL, Tesser R, Di Serio M, Russo V. Reactive Chromatography Applied to Ethyl Levulinate Synthesis: A Proof of Concept. Processes. 2021; 9(9):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091684
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossano, Carmelina, Claudio Luigi Pizzo, Riccardo Tesser, Martino Di Serio, and Vincenzo Russo. 2021. "Reactive Chromatography Applied to Ethyl Levulinate Synthesis: A Proof of Concept" Processes 9, no. 9: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091684
APA StyleRossano, C., Pizzo, C. L., Tesser, R., Di Serio, M., & Russo, V. (2021). Reactive Chromatography Applied to Ethyl Levulinate Synthesis: A Proof of Concept. Processes, 9(9), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091684









