Immune-Mediated Neuropathies: Pathophysiology and Management
Abstract
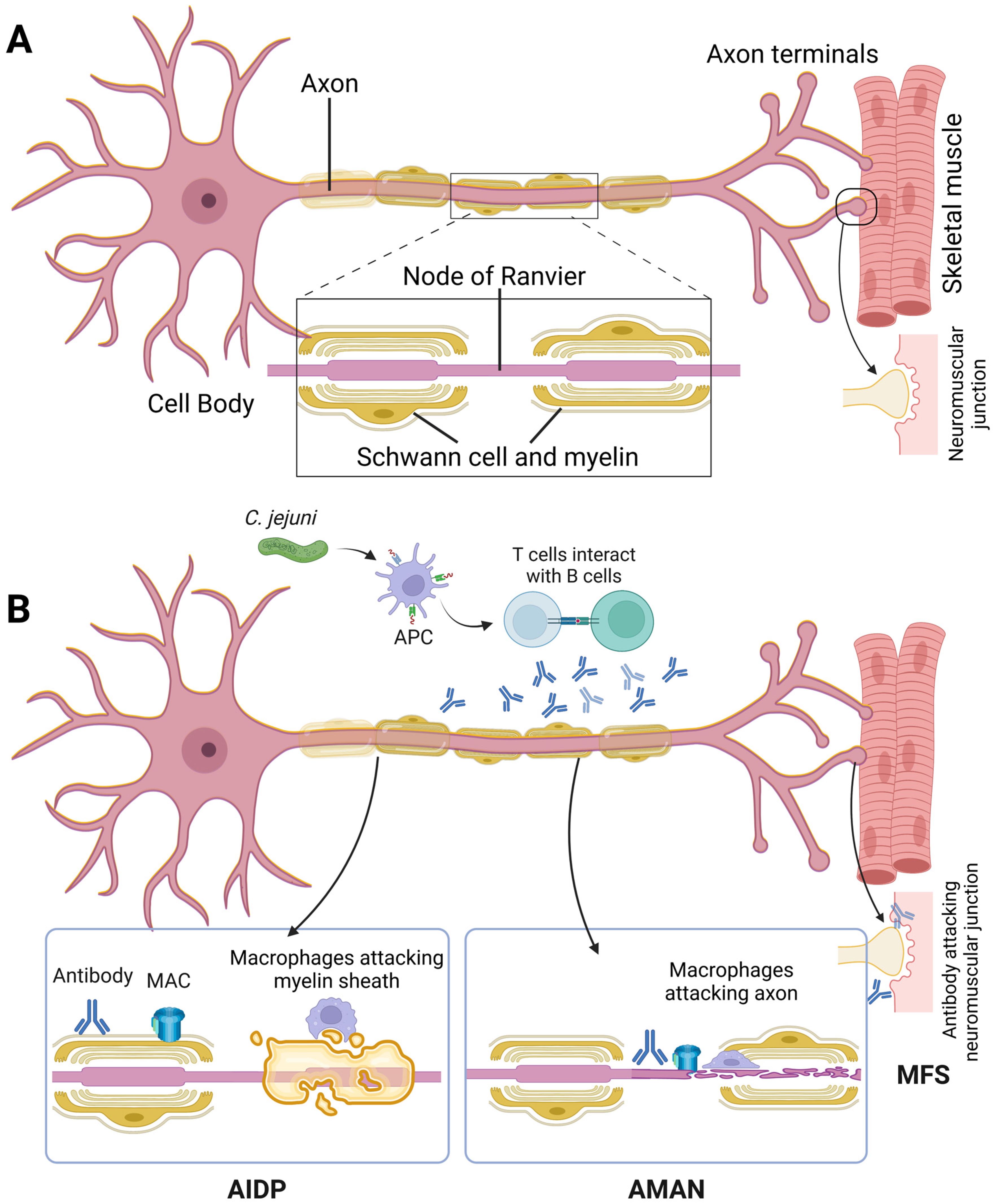
:1. Introduction
2. Guillain–Barre Syndrome
2.1. Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy
2.2. Axonal Types of Guillain–Barre Syndrome
2.2.1. Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy (AMAN)
2.2.2. Acute Motor Sensory Axonal Neuropathy (AMSAN)
2.3. Miller–Fisher Syndrome (MFS)
2.4. Roles of Ganglioside Complexes, Complement System and SARS-CoV-2 in Guillain–Barre Syndrome
2.5. Management
3. CIDP
4. Neuropathies with Conduction Blocks
5. Paraneoplastic Neuropathies
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asbury, A.K. Diagnostic Considerations in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9 (Suppl. 1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillain, G.; Barre, J.A.; Strohl, A. Radiculoneuritis Syndrome with Hyperalbuminosis of Cerebrospinal Fluid without Cellular Reaction. Notes on Clinical Features and Graphs of Tendon Reflexes. 1916. Ann. Med. Interne (Paris) 1999, 150, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sejvar, J.J.; Baughman, A.L.; Wise, M.; Morgan, O.W. Population Incidence of Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2011, 36, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Kohne, A.; Meyer zu Horste, G.; Kieseier, B.C. Incidence of Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Germany. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2007, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, I.M.; Rett, M.D.; Weintraub, E.; Marcy, M.; Amato, A.A.; Sheikh, S.I.; Ho, D.; Lee, G.M.; Yih, W.K.; Vaccine Safety Datalink Research Team. Guillain-Barre Syndrome Incidence in a Large United States Cohort (2000–2009). Neuroepidemiology 2012, 39, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.A.; Alentorn, A.; Martinez-Yelamos, S.; Martinez-Matos, J.A.; Povedano, M.; Montero, J.; Casasnovas, C. Very Early Electrodiagnostic Findings in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2011, 16, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijo-Barrientos, E.; Gonzalez, O.; Pastore-Olmedo, C. Presence of Repeater F-Waves in the Early Stage of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2012, 17, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, W.F.; Feasby, T.E. Conduction Block and Denervation in Guillain-Barre Polyneuropathy. Brain 1984, 107 Pt 1, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, S.; Sonoo, M.; Kadoya, A.; Chiba, A.; Shimizu, T. A-Waves in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Correlation with Electrophysiological Subtypes and Antiganglioside Antibodies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zochodne, D.W. Autonomic Involvement in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Review. Muscle Nerve 1994, 17, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, R.R.; McLeod, J.G. Autonomic Dysfunction in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1981, 44, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalos, N.P.; Borel, C.; Hanley, D.F. Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Therapeutic Implications of Swan-Ganz Monitoring. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flachenecker, P. Autonomic Dysfunction in Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2007, 254 (Suppl. 2), II96–II101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinstein, A.A. Paroxysmal Sympathetic Hyperactivity in the Neurological Intensive Care Unit. Neurol. Res. 2007, 29, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Hartung, H.P.; Kieseier, B.C.; Hughes, R.A. Guillain-Barre Syndrome After Exposure to Influenza Virus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, L.H.; Schmitz, P.I.; Meulstee, J.; van Doorn, P.A.; van der Meche, F.G. Prognostic Factors of Guillain-Barre Syndrome After Intravenous Immunoglobulin Or Plasma Exchange. Dutch Guillain-Barre Study Group. Neurology 1999, 53, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, A.; Press, R.; Holmqvist, L.W. Residual Disability 10 Years After Falling Ill in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Prospective Follow-Up Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 317, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshekhlee, A.; Hussain, Z.; Sultan, B.; Katirji, B. Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Incidence and Mortality Rates in US Hospitals. Neurology 2008, 70, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, A.B.; Taly, A.B.; Kulkarni, G.B.; Rao, U.G.; Rao, S. Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Patients of Guillain Barre Syndrome. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2011, 14, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, A.B.; Taly, A.B.; Kulkarni, G.B.; Uma Maheshwara Rao, G.S.; Rao, S. Prognosis of Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. Neurol. India 2011, 59, 707–711. [Google Scholar]
- Witsch, J.; Galldiks, N.; Bender, A.; Kollmar, R.; Bosel, J.; Hobohm, C.; Gunther, A.; Schirotzek, I.; Fuchs, K.; Juttler, E. Long-Term Outcome in Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakerley, B.R.; Uncini, A.; Yuki, N.; GBS Classification Group; GBS Classification Group. Guillain-Barre and Miller Fisher Syndromes—New Diagnostic Classification. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubun, N.; Nishibayashi, M.; Uncini, A.; Odaka, M.; Hirata, K.; Yuki, N. Conduction Block in Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy. Brain 2010, 133, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, T.; Prasad, K.; Lloyd, T.E. Peripheral Neuropathy: Clinical and Electrophysiological Considerations. Neuroimaging Clin. 2014, 24, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novello, B.J.; Pobre, T. Electrodiagnostic Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fokke, C.; van den Berg, B.; Drenthen, J.; Walgaard, C.; van Doorn, P.A.; Jacobs, B.C. Diagnosis of Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Validation of Brighton Criteria. Brain 2014, 137, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonhard, S.E.; Mandarakas, M.R.; Gondim, F.A.A.; Bateman, K.; Ferreira, M.L.B.; Cornblath, D.R.; van Doorn, P.A.; Dourado, M.E.; Hughes, R.A.C.; Islam, B.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Ten Steps. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, B.; Bunschoten, C.; van Doorn, P.A.; Jacobs, B.C. Mortality in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Neurology 2013, 80, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doets, A.Y.; Verboon, C.; van den Berg, B.; Harbo, T.; Cornblath, D.R.; Willison, H.J.; Islam, Z.; Attarian, S.; Barroso, F.A.; Bateman, K.; et al. Regional Variation of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Brain 2018, 141, 2866–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuitwaard, K.; Bos-Eyssen, M.E.; Blomkwist-Markens, P.H.; van Doorn, P.A. Recurrences, Vaccinations and Long-Term Symptoms in GBS and CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2009, 14, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, P.A.; Ruts, L.; Jacobs, B.C. Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and Treatment of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.H.; Soudain, S.E.; Gregson, N.A.; Hughes, R.A. Campylobacter Jejuni Infection and Guillain-Barre Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.A.; Cornblath, D.R. Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.C.; O’Brien, S.J.; Petersen, I.; Islam, A.; Hayward, A.; Rodrigues, L.C. Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Preceding Infection with Campylobacter, Influenza and Epstein-Barr Virus in the General Practice Research Database. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Jangouk, P.; Kierysch, E.K.; Meyer zu Horste, G.; Hartung, H.P.; Kieseier, B.C. Autoantibody-Mediated Dysfunction of Sympathetic Neurons in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, K.; Deng, F.; Xing, Y. Electrophysiological Subtypes and Prognosis of Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Northeastern China. Muscle Nerve 2012, 47, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbury, A.K.; Arnason, B.G.; Adams, R.D. The Inflammatory Lesion in Idiopathic Polyneuritis. its Role in Pathogenesis. Medicine 1969, 48, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.M. Pathogenesis of Immune-Mediated Neuropathies. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 33, S90–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WAKSMAN, B.H.; ADAMS, R.D. Allergic Neuritis: An Experimental Disease of Rabbits Induced by the Injection of Peripheral Nervous Tissue and Adjuvants. J. Exp. Med. 1955, 102, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Burns, J.B.; Brown, M.J.; Rosen, J.; Zweiman, B.; Lisak, R.P.; Pleasure, D.E. Transfer of Experimental Allergic Neuritis with P2-Reactive T-Cell Lines. Cell. Immunol. 1985, 91, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlubowski, M.; Hughes, R.A. Identification of the Neuritogen for Experimental Allergic Neuritis. Nature 1979, 277, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, P.; Lovelidge, C.A.; Taylor, W.A.; Hughes, R.A. P0 Myelin Protein Produces Experimental Allergic Neuritis in Lewis Rats. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 79, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, C.M.; Hughes, R.A.; Moore, S.E.; Smith, K.J.; Walsh, F.S. Induction of Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis with Peripheral Myelin Protein-22. Brain 1998, 121 Pt 10, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rostami, A.; Gregorian, S.K.; Brown, M.J.; Pleasure, D.E. Induction of Severe Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis with a Synthetic Peptide Corresponding to the 53-78 Amino Acid Sequence of the Myelin P2 Protein. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linington, C.; Engelhardt, B.; Kapocs, G.; Lassman, H. Induction of Persistently Demyelinated Lesions in the Rat Following the Repeated Adoptive Transfer of Encephalitogenic T Cells and Demyelinating Antibody. J. Neuroimmunol. 1992, 40, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linington, C.; Mann, A.; Izumo, S.; Uyemura, K.; Suzuki, M.; Meyermann, R.; Wekerle, H. Induction of Experimental Allergic Neuritis in the BN Rat: P2 Protein-Specific T Cells Overcome Resistance to Actively Induced Disease. J. Immunol. 1986, 137, 3826–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.F.; Feasby, T.E.; Lovgren, D.; Wilkie, L. Adoptive Transfer of Experimental Allergic Neuritis in the Immune Suppressed Host. Acta Neuropathol. 1993, 86, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Mix, E.; Olsson, T.; Link, H. Cellular mRNA Expression of Interferon-Gamma, IL-4 and Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-Beta) by Rat Mononuclear Cells Stimulated with Peripheral Nerve Myelin Antigens in Experimental Allergic Neuritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 98, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Stoll, G.; van der Meide, P.; Jung, S.; Hartung, H.P. Transient Cellular Expression of Gamma-Interferon in Myelin-Induced and T-Cell Line-Mediated Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis. Brain 1992, 115 Pt 6, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.O.; Hamilton, T.A. Molecular Transductional Mechanisms by which IFN Gamma and Other Signals Regulate Macrophage Development. Immunol. Rev. 1987, 97, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, H.P.; Schafer, B.; van der Meide, P.H.; Fierz, W.; Heininger, K.; Toyka, K.V. The Role of Interferon-Gamma in the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Disease of the Peripheral Nervous System. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, H.P.; Toyka, K.V. T-Cell and Macrophage Activation in Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis and Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27 (Suppl. 1), S57–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collart, M.A.; Belin, D.; Vassalli, J.D.; de Kossodo, S.; Vassalli, P. Gamma Interferon Enhances Macrophage Transcription of the Tumor Necrosis Factor/Cachectin, Interleukin 1, and Urokinase Genes, which are Controlled by Short-Lived Repressors. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 164, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msheik, Z.; El Massry, M.; Rovini, A.; Billet, F.; Desmouliere, A. The Macrophage: A Key Player in the Pathophysiology of Peripheral Neuropathies. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainaghi, P.P.; Collimedaglia, L.; Alciato, F.; Leone, M.A.; Naldi, P.; Molinari, R.; Monaco, F.; Avanzi, G.C. The Expression Pattern of Inflammatory Mediators in Cerebrospinal Fluid Differentiates Guillain-Barre Syndrome from Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Cytokine 2010, 51, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, K.; Mix, E.; Wang, X.; Adem, A.; Zhu, J. Differential Susceptibility to Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis in Lewis Rat Strains is Associated with T-Cell Immunity to Myelin Antigens. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunn, A.; Utermohlen, O.; Sanchez-Ruiz, M.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Blau, T.; Schluter, D.; Deckert, M. Dual Role of B Cells with Accelerated Onset but Reduced Disease Activity in P0106−125-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis of IgH0/0 Mice. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, W.; Hua-bing, W.; Wei-zhi, W. A Study of Associated Cell-Mediated Immune Mechanisms in Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis Rats. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 185, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ray, A.; Miller, N.M.; Hartwig, D.; Pritchard, K.A.; Dittel, B.N. Inhibition of Myeloperoxidase at the Peak of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Restores Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Ameliorates Disease Severity. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.C.; Latchman, Y.E.; Buhlmann, J.E.; Tomczak, M.F.; Horwitz, B.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. Regulation of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 Expression during Normal and Autoimmune Responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 2706–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaupt, A.; Bruck, W.; Hartung, T.; Toyka, K.V.; Gold, R. Schwann Cell Apoptosis in Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis of the Lewis Rat and the Functional Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 306, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Lindgren, J.U.; Zhu, Y.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Zhu, J. Exogenous Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type I Ameliorates Murine Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2003, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, H.L.; Quezada, H.C.; Mix, E.; Yang, X.; Winblad, B.; Adem, A.; Zhu, J. TNF-Alpha Receptor 1 Deficiency Reduces Antigen-Presenting Capacity of Schwann Cells and Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis in Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 470, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.O.; Duan, R.S.; Quezada, H.C.; Chen, Z.G.; Mix, E.; Jin, T.; Yang, X.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Zhu, J. Aggravation of Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis in TNF-Alpha Receptor 1 Deficient Mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 186, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzu, G.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Bouvier-Labit, C.; Liprandi, A.; Bianco, N.; Pellissier, J.F. Immunohistochemical Localization of Cytokines, C5b-9 and ICAM-1 in Peripheral Nerve of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 174, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.O.; Zhu, J. The Role of Cytokines in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharief, M.K.; Ingram, D.A.; Swash, M.; Thompson, E.J. I.V. Immunoglobulin Reduces Circulating Proinflammatory Cytokines in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Neurology 1999, 52, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarini, M.; Angelucci, E.; Foglietta, T.; Vernia, P. Guillain-Barre Syndrome After Treatment with Human Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factoralpha (Adalimumab) in a Crohn’s Disease Patient: Case Report and Literature Review. J. Crohns Colitis 2011, 5, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patwala, K.; Crump, N.; De Cruz, P. Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Association with Antitumour Necrosis Factor Therapy: A Case of Mistaken Identity. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.; Moon, C.; Jeong, C.; Matsumoto, Y.; Koh, C.S.; Shin, T. Upregulation of Erythropoietin in Rat Peripheral Nervous System with Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis. Brain Res. 2010, 1333, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausberg, A.K.; Meyer Zu Horste, G.; Dehmel, T.; Stettner, M.; Lehmann, H.C.; Sheikh, K.A.; Kieseier, B.C. Erythropoietin Ameliorates Rat Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis by Inducing Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Press, R.; Pashenkov, M.; Jin, J.P.; Link, H. Aberrated Levels of Cerebrospinal Fluid Chemokines in Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 23, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieseier, B.C.; Krivacic, K.; Jung, S.; Pischel, H.; Toyka, K.V.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Hartung, H.P. Sequential Expression of Chemokines in Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 110, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieseier, B.C.; Clements, J.M.; Pischel, H.B.; Wells, G.M.; Miller, K.; Gearing, A.J.; Hartung, H.P. Matrix Metalloproteinases MMP-9 and MMP-7 are Expressed in Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis and the Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 43, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, P.M.; Wells, G.M.; Clements, J.M.; Gearing, A.J.; Redford, E.J.; Davies, M.; Smith, K.J.; Hughes, R.A.; Brown, M.C.; Miller, K.M. Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression during Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis. Brain 1998, 121 Pt 3, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Creange, A.; Sharshar, T.; Planchenault, T.; Christov, C.; Poron, F.; Raphael, J.C.; Gherardi, R.K. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 is Increased and Correlates with Severity in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Neurology 1999, 53, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieseier, B.C.; Kiefer, R.; Gold, R.; Hemmer, B.; Willison, H.J.; Hartung, H.P. Advances in Understanding and Treatment of Immune-Mediated Disorders of the Peripheral Nervous System. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyati, K.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Verma, A.; Paliwal, V.K. Correlation of Matrix Metalloproteinases-2 and -9 with Proinflammatory Cytokines in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 3540–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Kohne, A.; Bernal, F.; Jangouk, P.; Meyer Zu Horste, G.; Dehmel, T.; Hartung, H.P.; Previtali, S.C.; Kieseier, B.C. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 is Involved in Myelination of Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons. Glia 2009, 57, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijf, M.L.; Samsom, J.N.; van Rijs, W.; Bax, M.; Huizinga, R.; Heikema, A.P.; van Doorn, P.A.; van Belkum, A.; van Kooyk, Y.; Burgers, P.C.; et al. TLR4-Mediated Sensing of Campylobacter Jejuni by Dendritic Cells is Determined by Sialylation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gries, M.; Davies, L.; Liu, Y.; Bachhuber, A.; Spiegel, J.; Dillmann, U.; Hartmann, T.; Fassbender, K.; Walter, S. Response of Toll-Like Receptors in Experimental Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Kinetic Analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 518, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Liang, Q.H.; Ramkalawan, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhou, W.B.; Tian, F.F.; Li, J.; Yang, H. Expression of Toll-Like Receptors 2, 4 and 9 in Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, L. T Cells: TLRs Deliver a Direct Hit to TH17 Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.L.; Wang, W.Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.K.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Th17 Helper Cell and T-Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain 3 Involvement in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Tagawa, Y.; Handa, S. Autoantibodies to Peripheral Nerve Glycosphingolipids SPG, SLPG, and SGPG in Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, K.; Ariga, T.; Yu, R.K. Antiganglioside Antibodies and their Pathophysiological Effects on Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Related Disorders—A Review. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahrizaila, N.; Yuki, N. Antiganglioside Antibodies in Guillain-Barre Syndrome and its Related Conditions. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Uncini, A.; Yuki, N.; Misawa, S.; Notturno, F.; Nasu, S.; Kanai, K.; Noto, Y.; Fujimaki, Y.; Shibuya, K.; et al. Antiganglioside Antibodies are Associated with Axonal Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Japanese-Italian Collaborative Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2012, 83, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.W.; Jacobs, B.C.; Laman, J.D. The Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A True Case of Molecular Mimicry. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Leon, A.; Toffano, G. Ganglioside Function in the Development and Repair of the Nervous System. from Basic Science to Clinical Application. Mol. Neurobiol. 1989, 3, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susuki, K.; Baba, H.; Tohyama, K.; Kanai, K.; Kuwabara, S.; Hirata, K.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; Rasband, M.N.; Yuki, N. Gangliosides Contribute to Stability of Paranodal Junctions and Ion Channel Clusters in Myelinated Nerve Fibers. Glia 2007, 55, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Kryzer, T.J.; Griesmann, G.E.; Kim, K.; Benarroch, E.E.; Lennon, V.A. CRMP-5 Neuronal Autoantibody: Marker of Lung Cancer and Thymoma-Related Autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 49, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawara, K.; Kuwabara, S.; Mori, M.; Hattori, T.; Koga, M.; Yuki, N. Axonal Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Relation to Anti-Ganglioside Antibodies and Campylobacter Jejuni Infection in Japan. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willison, H.J.; Yuki, N. Peripheral Neuropathies and Anti-Glycolipid Antibodies. Brain 2002, 125, 2591–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Taki, T.; Inagaki, F.; Kasama, T.; Takahashi, M.; Saito, K.; Handa, S.; Miyatake, T. A Bacterium Lipopolysaccharide that Elicits Guillain-Barre Syndrome has a GM1 Ganglioside-Like Structure. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 178, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aspinall, G.O.; McDonald, A.G.; Pang, H.; Kurjanczyk, L.A.; Penner, J.L. Lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter Jejuni Serotype O:19: Structures of Core Oligosaccharide Regions from the Serostrain and Two Bacterial Isolates from Patients with the Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall, G.O.; Fujimoto, S.; McDonald, A.G.; Pang, H.; Kurjanczyk, L.A.; Penner, J.L. Lipopolysaccharides from Campylobacter Jejuni Associated with Guillain-Barre Syndrome Patients Mimic Human Gangliosides in Structure. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuki, N. Infectious Origins of, and Molecular Mimicry in, Guillain-Barre and Fisher Syndromes. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Taki, T.; Takahashi, M.; Saito, K.; Yoshino, H.; Tai, T.; Handa, S.; Miyatake, T. Molecular Mimicry between GQ1b Ganglioside and Lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter Jejuni Isolated from Patients with Fisher’s Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 36, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Gilbert, M.; Mohammad, Q.D.; Klaij, K.; Li, J.; van Rijs, W.; Tio-Gillen, A.P.; Talukder, K.A.; Willison, H.J.; van Belkum, A.; et al. Guillain-Barre Syndrome-Related Campylobacter Jejuni in Bangladesh: Ganglioside Mimicry and Cross-Reactive Antibodies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, M.; Kuijf, M.L.; Heikema, A.P.; van Rijs, W.; Bruijns, S.C.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Crocker, P.R.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Vliet, S.J.; van Kooyk, Y. Campylobacter Jejuni Lipooligosaccharides Modulate Dendritic Cell-Mediated T Cell Polarization in a Sialic Acid Linkage-Dependent Manner. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Lehmann, H.C.; Manoharan, S.; Hashmi, M.; Shim, S.; Ming, G.L.; Schnaar, R.L.; Lopez, P.H.; Bogdanova, N.; Sheikh, K.A. Anti-Ganglioside Antibody-Mediated Activation of RhoA Induces Inhibition of Neurite Outgrowth. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodfellow, J.A.; Bowes, T.; Sheikh, K.; Odaka, M.; Halstead, S.K.; Humphreys, P.D.; Wagner, E.R.; Yuki, N.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; et al. Overexpression of GD1a Ganglioside Sensitizes Motor Nerve Terminals to Anti-GD1a Antibody-Mediated Injury in a Model of Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halstead, S.K.; Humphreys, P.D.; Zitman, F.M.; Hamer, J.; Plomp, J.J.; Willison, H.J. C5 Inhibitor rEV576 Protects Against Neural Injury in an in Vitro Mouse Model of Miller Fisher Syndrome. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2008, 13, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenshields, K.N.; Halstead, S.K.; Zitman, F.M.; Rinaldi, S.; Brennan, K.M.; O’Leary, C.; Chamberlain, L.H.; Easton, A.; Roxburgh, J.; Pediani, J.; et al. The Neuropathic Potential of Anti-GM1 Autoantibodies is Regulated by the Local Glycolipid Environment in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, P.H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Lehmann, H.C.; Griffin, J.W.; Schnaar, R.L.; Sheikh, K.A. Passive Transfer of IgG Anti-GM1 Antibodies Impairs Peripheral Nerve Repair. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9533–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.M.; Rogart, R.B. Density of Sodium Channels in Mammalian Myelinated Nerve Fibers and Nature of the Axonal Membrane Under the Myelin Sheath. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takigawa, T.; Yasuda, H.; Kikkawa, R.; Shigeta, Y.; Saida, T.; Kitasato, H. Antibodies Against GM1 Ganglioside Affect K+ and Na+ Currents in Isolated Rat Myelinated Nerve Fibers. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 37, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, K.A.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Griffin, J.W. The Distribution of Ganglioside-Like Moieties in Peripheral Nerves. Brain 1999, 122 Pt 3, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Susuki, K.; Rasband, M.N.; Tohyama, K.; Koibuchi, K.; Okamoto, S.; Funakoshi, K.; Hirata, K.; Baba, H.; Yuki, N. Anti-GM1 Antibodies Cause Complement-Mediated Disruption of Sodium Channel Clusters in Peripheral Motor Nerve Fibers. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3956–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakatani, Y.; Kawakami, K.; Nagaoka, T.; Utsunomiya, I.; Tanaka, K.; Yoshino, H.; Miyatake, T.; Hoshi, K.; Taguchi, K. Ca Channel Currents Inhibited by Serum from Select Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 57, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, Y.; Hotta, S.; Utsunomiya, I.; Tanaka, K.; Hoshi, K.; Ariga, T.; Yu, R.K.; Miyatake, T.; Taguchi, K. Cav2.1 Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channel Current is Inhibited by Serum from Select Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruss, H.; Schwab, J.M.; Derst, C.; Gortzen, A.; Veh, R.W. Neurofascin as Target of Autoantibodies in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Brain 2011, 134, e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devaux, J.J.; Odaka, M.; Yuki, N. Nodal Proteins are Target Antigens in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2012, 17, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, J.J. Antibodies to Gliomedin Cause Peripheral Demyelinating Neuropathy and the Dismantling of the Nodes of Ranvier. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fewou, S.N.; Rupp, A.; Nickolay, L.E.; Carrick, K.; Greenshields, K.N.; Pediani, J.; Plomp, J.J.; Willison, H.J. Anti-Ganglioside Antibody Internalization Attenuates Motor Nerve Terminal Injury in a Mouse Model of Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, J.W.; Li, C.Y.; Macko, C.; Ho, T.W.; Hsieh, S.T.; Xue, P.; Wang, F.A.; Cornblath, D.R.; McKhann, G.M.; Asbury, A.K. Early Nodal Changes in the Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy Pattern of the Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neurocytol. 1996, 25, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.W.; Li, C.Y.; Ho, T.W.; Xue, P.; Macko, C.; Gao, C.Y.; Yang, C.; Tian, M.; Mishu, B.; Cornblath, D.R. Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Northern China. the Spectrum of Neuropathological Changes in Clinically Defined Cases. Brain 1995, 118 Pt 3, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafer-Macko, C.; Hsieh, S.T.; Li, C.Y.; Ho, T.W.; Sheikh, K.; Cornblath, D.R.; McKhann, G.M.; Asbury, A.K.; Griffin, J.W. Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy: An Antibody-Mediated Attack on Axolemma. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, A.; Mori, M.; Ogawara, K.; Hattori, T.; Kuwabara, S. Differences in Patterns of Progression in Demyelinating and Axonal Guillain-Barre Syndromes. Neurology 2003, 61, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.W.; Li, C.Y.; Cornblath, D.R.; Gao, C.Y.; Asbury, A.K.; Griffin, J.W.; McKhann, G.M. Patterns of Recovery in the Guillain-Barre Syndromes. Neurology 1997, 48, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncini, A.; Kuwabara, S. Electrodiagnostic Criteria for Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Critical Revision and the Need for an Update. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, A.; Morrison, I.; Barrie, J.A.; Halstead, S.K.; Townson, K.H.; Greenshields, K.N.; Willison, H.J. Motor Nerve Terminal Destruction and Regeneration Following Anti-Ganglioside Antibody and Complement-Mediated Injury: An in and Ex Vivo Imaging Study in the Mouse. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencioni, M.T.; Notturno, F.; Caporale, C.M.; Creati, B.; Prencipe, V.; Battistini, L.; Uncini, A. T Cell Response in Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sorge, N.M.; Yuki, N.; Jansen, M.D.; Nishimoto, Y.; Susuki, K.; Wokke, J.H.; van de Winkel, J.G.; van den Berg, L.H.; van der Pol, W.L. Leukocyte and Complement Activation by GM1-Specific Antibodies is Associated with Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy in Rabbits. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 182, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.W.; Willison, H.J.; Nachamkin, I.; Li, C.Y.; Veitch, J.; Ung, H.; Wang, G.R.; Liu, R.C.; Cornblath, D.R.; Asbury, A.K.; et al. Anti-GD1a Antibody is Associated with Axonal but Not Demyelinating Forms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Kuwabara, S.; Koga, M.; Hirata, K. Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy and Acute Motor-Sensory Axonal Neuropathy Share a Common Immunological Profile. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 168, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesell, J. Inflammatory Neuropathies. Semin. Neurol. 2010, 30, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, Y.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, Y.; Na, S. A Case of Acute Motor and Sensory Axonal Neuropathy Following Hepatitis a Infection. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 1839–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimachkie, M.M.; Barohn, R.J. Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Variants. Neurol. Clin. 2013, 31, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capasso, M.; Notturno, F.; Manzoli, C.; Uncini, A. Involvement of Sensory Fibres in Axonal Subtypes of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuki, N.; Shahrizaila, N. Keeping it Simple: Is there a Need for the various Subtyping of Axonal Forms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FISHER, M. An Unusual Variant of Acute Idiopathic Polyneuritis (Syndrome of Ophthalmoplegia, Ataxia and Areflexia). N. Engl. J. Med. 1956, 255, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, A.; Kusunoki, S.; Shimizu, T.; Kanazawa, I. Serum IgG Antibody to Ganglioside GQ1b is a Possible Marker of Miller Fisher Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 31, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willison, H.J.; Veitch, J.; Paterson, G.; Kennedy, P.G. Miller Fisher Syndrome is Associated with Serum Antibodies to GQ1b Ganglioside. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aranyi, Z.; Kovacs, T.; Sipos, I.; Bereczki, D. Miller Fisher Syndrome: Brief Overview and Update with a Focus on Electrophysiological Findings. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 15–20, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathi, T.; Tan, E.Y.; Kokubun, N.; Verma, K.; Yuki, N. Non-Demyelinating, Reversible Conduction Failure in Fisher Syndrome and Related Disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, T.; Hughes, R.A.; Nobile-Orazio, E.; Leger, J.M. Immunosuppressant and Immunomodulatory Treatments for Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 3, CD003217. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, S.E.; Park, S.H. Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in Fisher Syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.L.; Fook-Chong, S.; Chan, L.L.; Ong, W.Y.; Ratnagopal, P. Electrophysiological Evidence of Cerebellar Fiber System Involvement in the Miller Fisher Syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 288, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Kuwabara, S.; Fukutake, T.; Yuki, N.; Hattori, T. Clinical Features and Prognosis of Miller Fisher Syndrome. Neurology 2001, 56, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Kuwabara, S.; Fukutake, T.; Hattori, T. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy for Miller Fisher Syndrome. Neurology 2007, 68, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Tagawa, Y.; Lunn, M.P.T.; Laroy, W.; Heffer-Lauc, M.; Li, C.Y.; Griffin, J.W.; Schnaar, R.L.; Sheikh, K.A. Localization of Major Gangliosides in the PNS: Implications for Immune Neuropathies. Brain 2002, 125, 2491–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGonigal, R.; Campbell, C.I.; Barrie, J.A.; Yao, D.; Cunningham, M.E.; Crawford, C.L.; Rinaldi, S.; Rowan, E.G.; Willison, H.J. Schwann Cell Nodal Membrane Disruption Triggers Bystander Axonal Degeneration in a Guillain-Barre Syndrome Mouse Model. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusunoki, S.; Kaida, K.; Ueda, M. Antibodies Against Gangliosides and Ganglioside Complexes in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: New Aspects of Research. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, G.; Kaida, K.; Kusunoki, S.; Ueda, M.; Kimura, F.; Kamakura, K. Antibodies to Ganglioside Complexes Consisting of Asialo-GM1 and GQ1b Or GT1a in Fisher and Guillain-Barre Syndromes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 214, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, K.; Morita, D.; Kanzaki, M.; Kamakura, K.; Motoyoshi, K.; Hirakawa, M.; Kusunoki, S. Anti-Ganglioside Complex Antibodies Associated with Severe Disability in GBS. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 182, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notturno, F.; Luciani, M.; Caporale, C.M.; Ciarelli, A.; Uncini, A. Antibodies to Ganglioside Complexes in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Clinical Correlates, Fine Specificity and Complement Activation. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunoki, S.; Kaida, K. Antibodies Against Ganglioside Complexes in Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Related Disorders. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, K.; Kamakura, K.; Ogawa, G.; Ueda, M.; Motoyoshi, K.; Arita, M.; Kusunoki, S. GD1b-Specific Antibody Induces Ataxia in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Neurology 2008, 71, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijf, M.L.; Godschalk, P.C.; Gilbert, M.; Endtz, H.P.; Tio-Gillen, A.P.; Ang, C.W.; van Doorn, P.A.; Jacobs, B.C. Origin of Ganglioside Complex Antibodies in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 188, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, R.R.; van Schaik, I.N.; Vreijling, J.P.; Troost, D.; Baas, F. Expression of Complement Components in the Peripheral Nervous System. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dashiell, S.M.; Vanguri, P.; Koski, C.L. Dibutyryl Cyclic AMP and Inflammatory Cytokines Mediate C3 Expression in Schwann Cells. Glia 1997, 20, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaglia, V.; Daha, M.R.; Baas, F. The Complement System in the Peripheral Nerve: Friend Or Foe? Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koski, C.L.; Estep, A.E.; Sawant-Mane, S.; Shin, M.L.; Highbarger, L.; Hansch, G.M. Complement Regulatory Molecules on Human Myelin and Glial Cells: Differential Expression Affects the Deposition of Activated Complement Proteins. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedeler, C.A.; Matre, R. Complement Receptors CR1 on Human Peripheral Nerve Fibres. J. Neuroimmunol. 1988, 17, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koski, C.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Swoveland, P.T.; Lawley, T.J.; Shin, M.L.; Frank, M.M.; Joiner, K.A. Activation of Terminal Components of Complement in Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Other Demyelinating Neuropathies. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 80, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartung, H.P.; Schwenke, C.; Bitter-Suermann, D.; Toyka, K.V. Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Activated Complement Components C3a and C5a in CSF. Neurology 1987, 37, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafer-Macko, C.E.; Sheikh, K.A.; Li, C.Y.; Ho, T.W.; Cornblath, D.R.; McKhann, G.M.; Asbury, A.K.; Griffin, J.W. Immune Attack on the Schwann Cell Surface in Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparounas, K.; O’Hanlon, G.M.; O’Leary, C.P.; Rowan, E.G.; Willison, H.J. Anti-Ganglioside Antibodies can Bind Peripheral Nerve Nodes of Ranvier and Activate the Complement Cascade without Inducing Acute Conduction Block in Vitro. Brain 1999, 122 Pt 5, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Susuki, K.; Yuki, N.; Schafer, D.P.; Hirata, K.; Zhang, G.; Funakoshi, K.; Rasband, M.N. Dysfunction of Nodes of Ranvier: A Mechanism for Anti-Ganglioside Antibody-Mediated Neuropathies. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanguri, P.; Koski, C.L.; Silverman, B.; Shin, M.L. Complement Activation by Isolated Myelin: Activation of the Classical Pathway in the Absence of Myelin-Specific Antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 3290–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koski, C.L.; Humphrey, R.; Shin, M.L. Anti-Peripheral Myelin Antibody in Patients with Demyelinating Neuropathy: Quantitative and Kinetic Determination of Serum Antibody by Complement Component 1 Fixation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silverman, B.A.; Carney, D.F.; Johnston, C.A.; Vanguri, P.; Shin, M.L. Isolation of Membrane Attack Complex of Complement from Myelin Membranes Treated with Serum Complement. J. Neurochem. 1984, 42, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, G.; Schmidt, B.; Jander, S.; Toyka, K.V.; Hartung, H.P. Presence of the Terminal Complement Complex (C5b-9) Precedes Myelin Degradation in Immune-Mediated Demyelination of the Rat Peripheral Nervous System. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 30, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedeler, C.A.; Conti, G.; Fujioka, T.; Scarpini, E.; Rostami, A. The Expression of CD59 in Experimental Allergic Neuritis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 165, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant-Mane, S.; Piddlesden, S.J.; Morgan, B.P.; Holers, V.M.; Koski, C.L. CD59 Homologue Regulates Complement-Dependent Cytolysis of Rat Schwann Cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 69, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongsisay, V.; Susuki, K.; Matsuno, K.; Yamahashi, T.; Okamoto, S.; Funakoshi, K.; Hirata, K.; Shinoda, M.; Yuki, N. Complement Inhibitor Prevents Disruption of Sodium Channel Clusters in a Rabbit Model of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 205, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hanlon, G.M.; Plomp, J.J.; Chakrabarti, M.; Morrison, I.; Wagner, E.R.; Goodyear, C.S.; Yin, X.; Trapp, B.D.; Conner, J.; Molenaar, P.C.; et al. Anti-GQ1b Ganglioside Antibodies Mediate Complement-Dependent Destruction of the Motor Nerve Terminal. Brain 2001, 124, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halstead, S.K.; Humphreys, P.D.; Goodfellow, J.A.; Wagner, E.R.; Smith, R.A.; Willison, H.J. Complement Inhibition Abrogates Nerve Terminal Injury in Miller Fisher Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitman, F.M.; Todorov, B.; Verschuuren, J.J.; Jacobs, B.C.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; Willison, H.J.; Plomp, J.J. Neuromuscular Synaptic Transmission in Aged Ganglioside-Deficient Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willison, H.J.; Halstead, S.K.; Beveridge, E.; Zitman, F.M.; Greenshields, K.N.; Morgan, B.P.; Plomp, J.J. The Role of Complement and Complement Regulators in Mediating Motor Nerve Terminal Injury in Murine Models of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 201–202, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansita, J.A.; Mease, K.M.; Qiu, H.; Yednock, T.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Kramer, S. Nonclinical Development of ANX005: A Humanized Anti-C1q Antibody for Treatment of Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidson, A.I.; Halstead, S.K.; Goodfellow, J.A.; Chavada, G.; Mallik, A.; Overell, J.; Lunn, M.P.; McConnachie, A.; van Doorn, P.; Willison, H.J. Inhibition of Complement in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: The ICA-GBS Study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2017, 22, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misawa, S.; Kuwabara, S.; Sato, Y.; Yamaguchi, N.; Nagashima, K.; Katayama, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Iwai, Y.; Amino, H.; Suichi, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Eculizumab in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, G.; Palmerini, F.; Ravaglia, S.; Ruiz, L.; Invernizzi, P.; Cuzzoni, M.G.; Franciotta, D.; Baldanti, F.; Daturi, R.; Postorino, P.; et al. Guillain-Barre Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2574–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. Guillain-Barre Syndrome: The First Documented COVID-19-Triggered Autoimmune Neurologic Disease: More to Come with Myositis in the Offing. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7, e781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladawi, M.; Elfil, M.; Abu-Esheh, B.; Abu Jazar, D.; Armouti, A.; Bayoumi, A.; Piccione, E. Guillain Barre Syndrome as a Complication of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 49, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abara, W.E.; Gee, J.; Marquez, P.; Woo, J.; Myers, T.R.; DeSantis, A.; Baumblatt, J.A.G.; Woo, E.J.; Thompson, D.; Nair, N.; et al. Reports of Guillain-Barre Syndrome After COVID-19 Vaccination in the United States. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2253845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Chahinian, H.; Yahi, N. Leveraging Coronavirus Binding to Gangliosides for Innovative Vaccine and Therapeutic Strategies Against COVID-19. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 538, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Ghosh, R.; Mandal, A.; Pandit, A.; Roy, D.; Sengupta, S.; De, K.; Swaika, B.C.; Benito-Leon, J. COVID-19 Induced Miller Fisher Syndrome Presenting with Autonomic Dysfunction: A Unique Case Report and Review of Literature. Neurohospitalist 2022, 12, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.A.C.; Swan, A.V.; van Doorn, P.A. Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD002063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, B.; Walgaard, C.; Drenthen, J.; Fokke, C.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Doorn, P.A. Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Hartung, H.; Hetzel, G.R.; Stuve, O.; Kieseier, B.C. Plasma Exchange in Neuroimmunological Disorders: Part 1: Rationale and Treatment of Inflammatory Central Nervous System Disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Efficiency of Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Role of Replacement Fluids. French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1987, 22, 753–761. [Google Scholar]
- Raphael, J.C.; Chevret, S.; Hughes, R.A.; Annane, D. Plasma Exchange for Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 7, CD001798. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.A.; Swan, A.V.; van Doorn, P.A. Corticosteroids for Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2, CD001446. [Google Scholar]
- Oczko-Walker, M.; Manousakis, G.; Wang, S.; Malter, J.S.; Waclawik, A.J. Plasma Exchange After Initial Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment in Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Critical Reassessment of Effectiveness and Cost-Efficiency. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2010, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.; Swan, A.V.; Raphael, J.C.; Annane, D.; van Koningsveld, R.; van Doorn, P.A. Immunotherapy for Guillain-Barre Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Brain 2007, 130, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalakas, M.C. Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Autoimmune Neuromuscular Diseases. JAMA 2004, 291, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Spaeth, P.J. The Importance of FcRn in Neuro-Immunotherapies: From IgG Catabolism, FCGRT Gene Polymorphisms, IVIg Dosing and Efficiency to Specific FcRn Inhibitors. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2021, 14, 1756286421997381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.; Rajabally, Y.A. Current Proposed Mechanisms of Action of Intravenous Immunoglobulins in Inflammatory Neuropathies. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartung, H.P. Advances in the Understanding of the Mechanism of Action of IVIg. J. Neurol. 2008, 255 (Suppl. 3), 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacca, F.; Barnett, C.; Vu, T.; Peric, S.; Phillips, G.A.; Zhao, S.; Qi, C.Z.; Gelinas, D.; Chiroli, S.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M. Efgartigimod Improved Health-Related Quality of Life in Generalized Myasthenia Gravis: Results from a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Study (ADAPT). J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y. Efgartigimod: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.A.; Gorson, K.C.; Cros, D.; Griffin, J.; Pollard, J.; Vallat, J.M.; Maurer, S.L.; Riester, K.; Davar, G.; Dawson, K.; et al. Intramuscular Interferon Beta-1a in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 2010, 74, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.; Mehndiratta, M.M. Corticosteroids for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002, 1, CD002062, Updated in Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 8, CD002062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, M.M.; Pinter, M.J.; Kraner, S.D.; Barchi, R.L. Loss of Electrical Excitability in an Animal Model of Acute Quadriplegic Myopathy. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 43, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, M.M.; Pinter, M.J. Sodium Channel Inactivation in an Animal Model of Acute Quadriplegic Myopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J. Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Clin. Med. 2010, 10, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; O’Brien, P.C.; Oviatt, K.F.; Dinapoli, R.P.; Daube, J.R.; Bartleson, J.D.; Mokri, B.; Swift, T.; Low, P.A.; Windebank, A.J. Prednisone Improves Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy More than no Treatment. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bergh, P.Y.; Hadden, R.D.; Bouche, P.; Cornblath, D.R.; Hahn, A.; Illa, I.; Koski, C.L.; Leger, J.M.; Nobile-Orazio, E.; Pollard, J.; et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on Management of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Report of a Joint Task Force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—First Revision. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.D.; McKelvey, R.; Durcan, L.; Carpenter, S.; Karpati, G. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) in Diabetics. J. Neurol. Sci. 1996, 142, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research Criteria for Diagnosis of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP). Report from an Ad Hoc Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Neurology 1991, 41, 617–618. [Google Scholar]
- Vallat, J.M.; Sommer, C.; Magy, L. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges for a Treatable Condition. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saperstein, D.S.; Katz, J.S.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J. Clinical Spectrum of Chronic Acquired Demyelinating Polyneuropathies. Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koski, C.L.; Baumgarten, M.; Magder, L.S.; Barohn, R.J.; Goldstein, J.; Graves, M.; Gorson, K.; Hahn, A.F.; Hughes, R.A.; Katz, J.; et al. Derivation and Validation of Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 277, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.A.; Ney, J.; Lewis, R.A. Electrodiagnostic Errors Contribute to Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Misdiagnosis. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, P.Y.K.; van Doorn, P.A.; Hadden, R.D.; Avau, B.; Vankrunkelsven, P.; Allen, J.A.; Attarian, S.; Blomkwist-Markens, P.H.; Cornblath, D.R.; Eftimov, F.; et al. European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Report of a Joint Task Force-Second Revision. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3556–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Lais, A.C.; Karnes, J.L.; Sparks, M.; Hunder, H.; Low, P.A.; Windebank, A.J. Permanent Axotomy, a Model of Axonal Atrophy and Secondary Segmental Demyelination and Remyelination. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, C.; Lacroix, C.; Plante, V.; Adams, D.; Chedru, F.; Guglielmi, J.M.; Said, G. Clinicopathologic Findings and Prognosis of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Neurology 1999, 52, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, A.F. Experimental Allergic Neuritis (EAN) as a Model for the Immune-Mediated Demyelinating Neuropathies. Rev. Neurol. 1996, 152, 328–332. [Google Scholar]
- Csurhes, P.A.; Sullivan, A.A.; Green, K.; Pender, M.P.; McCombe, P.A. T Cell Reactivity to P0, P2, PMP-22, and Myelin Basic Protein in Patients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, L.J.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, W.Z. Impairment of Circulating CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2008, 13, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.; Hughes, S.; Cooper, J.; Ben-Smith, A.; Savage, C. Gamma Delta T Cells Infiltrating Sensory Nerve Biopsies from Patients with Inflammatory Neuropathy. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Hohendorf, T.; Schwab, N.; Uceyler, N.; Gobel, K.; Sommer, C.; Wiendl, H. CD8+ T-Cell Immunity in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 2012, 78, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausberg, A.K.; Dorok, M.; Stettner, M.; Muller, M.; Hartung, H.P.; Dehmel, T.; Warnke, C.; Meyer Zu Horste, G.; Kieseier, B.C. Recovery of the T-Cell Repertoire in CIDP by IV Immunoglobulins. Neurology 2013, 80, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, I.; Keller, C.W.; Hiepe, F.; Tackenberg, B.; Lunemann, J.D. Terminal Complement Activation is Increased and Associated with Disease Severity in CIDP. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.W.; Quast, I.; Dalakas, M.C.; Lunemann, J.D. IVIG Efficacy in CIDP Patients is Not Associated with Terminal Complement Inhibition. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 330, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, N.; Akiguchi, I.; Nagao, M.; Nishio, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Kimura, J. Expression of Endothelial Leukocyte Adhesion Molecule-1 (ELAM-1) in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Neurology 1994, 44, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahad, D.J.; Howell, S.J.; Woodroofe, M.N. Expression of Chemokines in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum of Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kieseier, B.C.; Tani, M.; Mahad, D.; Oka, N.; Ho, T.; Woodroofe, N.; Griffin, J.W.; Toyka, K.V.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Hartung, H.P. Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Inflammatory Demyelinating Neuropathies: A Central Role for IP-10. Brain 2002, 125, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartung, H.P.; Reiners, K.; Schmidt, B.; Stoll, G.; Toyka, K.V. Serum Interleukin-2 Concentrations in Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Chronic Idiopathic Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Comparison with Other Neurological Diseases of Presumed Immunopathogenesis. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 30, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, S.; Kuwabara, S.; Mori, M.; Kawaguchi, N.; Yoshiyama, Y.; Hattori, T. Serum Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Neurology 2001, 56, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzos, M.; Angeli, A.V.; Rombos, A.; Kyrozis, A.; Nikolaou, C.; Zouvelou, V.; Dimitriou, A.; Zoga, M.; Evangelopoulos, M.E.; Tsatsi, A.; et al. Proinflammatory Cytokines in Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid of CIDP Patients. Neurol. Res. 2012, 34, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. B Cells as Therapeutic Targets in Autoimmune Neurological Disorders. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2008, 4, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmire, J.K.; Asano, M.S.; Kaech, S.M.; Sarkar, S.; Hannum, L.G.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Ahmed, R. Requirement of B Cells for Generating CD4+ T Cell Memory. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGaha, T.L.; Sorrentino, B.; Ravetch, J.V. Restoration of Tolerance in Lupus by Targeted Inhibitory Receptor Expression. Science 2005, 307, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerenwaldt, A.; Lux, A.; Danzer, H.; Spriewald, B.M.; Ullrich, E.; Heidkamp, G.; Dudziak, D.; Nimmerjahn, F. Fcgamma Receptor IIB (FcgammaRIIB) Maintains Humoral Tolerance in the Human Immune System in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18772–18777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, H.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. The Inhibitory Fcgamma Receptor Modulates Autoimmunity by Limiting the Accumulation of Immunoglobulin G+ Anti-DNA Plasma Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackenberg, B.; Jelcic, I.; Baerenwaldt, A.; Oertel, W.H.; Sommer, N.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Lunemann, J.D. Impaired Inhibitory Fcgamma Receptor IIB Expression on B Cells in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4788–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Lunemann, J.D. Expression and Function of the Inhibitory Fcgamma-Receptor in CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2011, 16 (Suppl. 1), 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.A. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanvito, L.; Makowska, A.; Mahdi-Rogers, M.; Hadden, R.D.; Peakman, M.; Gregson, N.; Nemni, R.; Hughes, R.A. Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses to Myelin Protein Peptides in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.X.; Archelos, J.J.; Hartung, H.P.; Pollard, J.D. P0 Protein is a Target Antigen in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, C.G.; Jensen, M.A.; Dukala, D.; Soliven, B. Targeting of Myelin Protein Zero in a Spontaneous Autoimmune Polyneuropathy. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8753–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, D.; Giannopoulos, K.; Gray, I.; Gregson, N.; Makowska, A.; Pritchard, J.; Hughes, R.A. Antibodies to Peripheral Nerve Myelin Proteins in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.X.; Taylor, J.; Andrias-Kauba, S.; Pollard, J.D. Passive Transfer of Demyelination by Serum Or IgG from Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Patients. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Goni, E.; Fehmi, J.; Lleixa, C.; Martin-Aguilar, L.; Devaux, J.; Hoftberger, R.; Delmont, E.; Doppler, K.; Sommer, C.; Radunovic, A.; et al. Antibodies to the Caspr1/Contactin-1 Complex in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Brain 2021, 144, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncini, A.; Vallat, J. Autoimmune Nodo-Paranodopathies of Peripheral Nerve: The Concept is Gaining Ground. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehmi, J.; Vale, T.; Keddie, S.; Rinaldi, S. Nodal and Paranodal Antibody-Associated Neuropathies. Pract. Neurol. 2021, 21, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, N.; Misu, K.; Koike, H.; Ichimura, M.; Nagamatsu, M.; Hirayama, M.; Sobue, G. Age of Onset Influences Clinical Features of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 184, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehndiratta, M.M.; Hughes, R.A. Plasma Exchange for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 9, CD003906. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimov, F.; Winer, J.B.; Vermeulen, M.; de Haan, R.; van Schaik, I.N. Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 1, CD001797. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.; Krishnan, A.V.; Park, S.B.; Kiernan, M.C. Modulatory Effects on Axonal Function After Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaebel, K.; Blackhouse, G.; Campbell, K.; Robertson, D.; Xie, F.; Assasi, N.; Chalk, C.; Levine, M.; Goeree, R. Intravenous Immunoglobulin for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Med. 2010, 4, e154–e166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.A.; Swan, A.V.; van Doorn, P.A. Cytotoxic Drugs and Interferons for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, 4, CD003280. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi-Rogers, M.; Swan, A.V.; van Doorn, P.A.; Hughes, R.A. Immunomodulatory Treatment Other than Corticosteroids, Immunoglobulin and Plasma Exchange for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 11, CD003280. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.; Dalakas, M.C.; Merkies, I.; Latov, N.; Leger, J.; Nobile-Orazio, E.; Sobue, G.; Genge, A.; Cornblath, D.; Merschhemke, M.; et al. Oral Fingolimod for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (FORCIDP Trial): A Double-Blind, Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile-Orazio, E.; Cocito, D.; Jann, S.; Uncini, A.; Beghi, E.; Messina, P.; Antonini, G.; Fazio, R.; Gallia, F.; Schenone, A.; et al. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Versus Intravenous Methylprednisolone for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schaik, I.N.; Bril, V.; van Geloven, N.; Hartung, H.; Lewis, R.A.; Sobue, G.; Lawo, J.; Praus, M.; Mielke, O.; Durn, B.L.; et al. Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin for Maintenance Treatment in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (PATH): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Schaik, I.N.; Mielke, O.; Bril, V.; van Geloven, N.; Hartung, H.; Lewis, R.A.; Sobue, G.; Lawo, J.; Praus, M.; Durn, B.L.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin IgPro20 in CIDP: PATH Extension Study. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2019, 6, e590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.A.; Sumner, A.J.; Brown, M.J.; Asbury, A.K. Multifocal Demyelinating Neuropathy with Persistent Conduction Block. Neurology 1982, 32, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saperstein, D.S.; Amato, A.A.; Wolfe, G.I.; Katz, J.S.; Nations, S.P.; Jackson, C.E.; Bryan, W.W.; Burns, D.K.; Barohn, R.J. Multifocal Acquired Demyelinating Sensory and Motor Neuropathy: The Lewis-Sumner Syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1999, 22, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezaki, T.; Kaji, R.; Akiguchi, I.; Kimura, J. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1994, 34, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viala, K.; Renie, L.; Maisonobe, T.; Behin, A.; Neil, J.; Leger, J.M.; Bouche, P. Follow-Up Study and Response to Treatment in 23 Patients with Lewis-Sumner Syndrome. Brain 2004, 127, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parry, G.J.; Clarke, S. Multifocal Acquired Demyelinating Neuropathy Masquerading as Motor Neuron Disease. Muscle Nerve 1988, 11, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestronk, A.; Cornblath, D.R.; Ilyas, A.A.; Baba, H.; Quarles, R.H.; Griffin, J.W.; Alderson, K.; Adams, R.N. A Treatable Multifocal Motor Neuropathy with Antibodies to GM1 Ganglioside. Ann. Neurol. 1988, 24, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, H.; Kieseier, B.C.; Jander, S.; Hartung, H.P. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlam, L.; van der Pol, W.L.; Cats, E.A.; Straver, D.C.; Piepers, S.; Franssen, H.; van den Berg, L.H. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy: Diagnosis, Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 8, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, S.; Cascella, M. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Loewenbruck, K.F.; Liesenberg, J.; Dittrich, M.; Schafer, J.; Patzner, B.; Trausch, B.; Machetanz, J.; Hermann, A.; Storch, A. Nerve Ultrasound in the Differentiation of Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Predominant Lower Motor Neuron Disease (ALS/LMND). J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronlage, M.; Knop, K.C.; Schwarz, D.; Godel, T.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Baumer, P. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Versus Multifocal Motor Neuropathy: Utility of MR Neurography. Radiology 2019, 292, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muley, S.A.; Parry, G.J. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.S.; Wolfe, G.I.; Bryan, W.W.; Jackson, C.E.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J. Electrophysiologic Findings in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Neurology 1997, 48, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiernan, M.C.; Guglielmi, J.M.; Kaji, R.; Murray, N.M.; Bostock, H. Evidence for Axonal Membrane Hyperpolarization in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy with Conduction Block. Brain 2002, 125, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestronk, A.; Choksi, R. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Serum IgM Anti-GM1 Ganglioside Antibodies in most Patients Detected using Covalent Linkage of GM1 to ELISA Plates. Neurology 1997, 49, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schaik, I.N.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Brand, A.; Vermeulen, M. Diagnostic Value of GM1 Antibodies in Motor Neuron Disorders and Neuropathies: A Meta-Analysis. Neurology 1995, 45, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, R. Physiology of Conduction Block in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy and Other Demyelinating Neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cats, E.A.; Jacobs, B.C.; Yuki, N.; Tio-Gillen, A.P.; Piepers, S.; Franssen, H.; van Asseldonk, J.T.; van den Berg, L.H.; van der Pol, W.L. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy: Association of Anti-GM1 IgM Antibodies with Clinical Features. Neurology 2010, 75, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlam, L.; Cats, E.A.; Harschnitz, O.; Jansen, M.D.; Piepers, S.; Veldink, J.H.; Franssen, H.; Stork, A.C.J.; Heezius, E.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; et al. Complement Activity is Associated with Disease Severity in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2015, 2, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budding, K.; Johansen, L.E.; Van de Walle, I.; Dijkxhoorn, K.; de Zeeuw, E.; Bloemenkamp, L.M.; Bos, J.W.; Jansen, M.D.; Curial, C.A.D.; Silence, K.; et al. Anti-C2 Antibody ARGX-117 Inhibits Complement in a Disease Model for Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2021, 9, e1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azulay, J.P.; Blin, O.; Pouget, J.; Boucraut, J.; Bille-Turc, F.; Carles, G.; Serratrice, G. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment in Patients with Motor Neuron Syndromes Associated with Anti-GM1 Antibodies: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Neurology 1994, 44, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuth, S.G.; Kleinschnitz, C. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy: Update on Clinical Characteristics, Pathophysiological Concepts and Therapeutic Options. Eur. Neurol. 2010, 63, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schaik, I.N.; van den Berg, L.H.; de Haan, R.; Vermeulen, M. Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 2, CD004429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepers, S.; Jansen, M.D.; Cats, E.A.; van Sorge, N.M.; van den Berg, L.H.; van der Pol, W.L. IVIg Inhibits Classical Pathway Activity and Anti-GM1 IgM-Mediated Complement Deposition in MMN. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 229, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuki, N.; Watanabe, H.; Nakajima, T.; Spath, P.J. IVIG Blocks Complement Deposition Mediated by Anti-GM1 Antibodies in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Mann, C.A.; Barry, S.; Brennan, K.; Overell, J.R.; Willison, H.J. An Open Label Clinical Trial of Complement Inhibition in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2011, 16, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbo, T.; Andersen, H.; Hess, A.; Hansen, K.; Sindrup, S.H.; Jakobsen, J. Subcutaneous Versus Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy: A Randomized, Single-Blinded Cross-Over Trial. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; Manley, G.T.; Posner, J.B. Immunization with the Paraneoplastic Encephalomyelitis Antigen HuD does Not Cause Neurologic Disease in Mice. Neurology 1995, 45, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Posner, J.B. Anti-Hu--Associated Paraneoplastic Encephalomyelitis/Sensory Neuronopathy. A Clinical Study of 71 Patients. Medicine 1992, 71, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntzer, T.; Antoine, J.C.; Steck, A.J. Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis of Sensory Neuronopathies (Ganglionopathies). Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanschitz, J.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Kristoferitsch, W.; Drlicek, M.; Budka, H. Ganglionitis in Paraneoplastic Subacute Sensory Neuronopathy: A Morphologic Study. Neurology 1997, 49, 1156–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Kimmel, D.W.; Lennon, V.A. Paraneoplastic and Oncologic Profiles of Patients Seropositive for Type 1 Antineuronal Nuclear Autoantibodies. Neurology 1998, 50, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschernatsch, M.; Stolz, E.; Strittmatter, M.; Kaps, M.; Blaes, F. Antinuclear Antibodies Define a Subgroup of Paraneoplastic Neuropathies: Clinical and Immunological Data. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mutoh, T.; Tachi, M.; Yano, S.; Mihara, T.; Yamamoto, H. Impairment of Trk-Neurotrophin Receptor by the Serum of a Patient with Subacute Sensory Neuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoine, J.C.; Absi, L.; Honnorat, J.; Boulesteix, J.M.; de Brouker, T.; Vial, C.; Butler, M.; De Camilli, P.; Michel, D. Antiamphiphysin Antibodies are Associated with various Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes and Tumors. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalmau, J.; Gultekin, S.H.; Voltz, R.; Hoard, R.; DesChamps, T.; Balmaceda, C.; Batchelor, T.; Gerstner, E.; Eichen, J.; Frennier, J.; et al. Ma1, a Novel Neuron- and Testis-Specific Protein, is Recognized by the Serum of Patients with Paraneoplastic Neurological Disorders. Brain 1999, 122 Pt 1, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.H.; Vernino, S.; Lennon, V.A. ANNA-3 Anti-Neuronal Nuclear Antibody: Marker of Lung Cancer-Related Autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toni, L.; Marconi, S.; Nardelli, E.; Alberti, D.; Borsellino, G.; Fracasso, G.; Bach, S.; Bertolasi, L.; Santo, A.; Bassi, A.; et al. Gangliosides Act as Onconeural Antigens in Paraneoplastic Neuropathies. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 156, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keime-Guibert, F.; Graus, F.; Fleury, A.; Rene, R.; Honnorat, J.; Broet, P.; Delattre, J.Y. Treatment of Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes with Antineuronal Antibodies (Anti-Hu, Anti-Yo) with a Combination of Immunoglobulins, Cyclophosphamide, and Methylprednisolone. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voltz, R.; Graus, F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Paraneoplastic Neurological Disorders. Onkologie 2004, 27, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Lieshout, J.J.; Wieling, W.; van Montfrans, G.A.; Settels, J.J.; Speelman, J.D.; Endert, E.; Karemaker, J.M. Acute Dysautonomia Associated with Hodgkin’s Disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1986, 49, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, C.; Vital, A.; Julien, J.; Rivel, J.; deMascarel, A.; Vergier, B.; Henry, P.; Barat, M.; Reiffers, J.; Broustet, A. Peripheral Neuropathies and Lymphoma without Monoclonal Gammopathy: A New Classification. J. Neurol. 1990, 237, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kato, K.; Funakoshi, K.; Watanabe, S.; Toyoshima, I. Neuropathology of Paraneoplastic Neuropathy with Anti-Disialosyl Antibody. Muscle Nerve 2005, 32, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognvaldsson, S.; Steingrimsson, V.; Turesson, I.; Bjorkholm, M.; Landgren, O.; Yngvi Kristinsson, S. Peripheral Neuropathy and Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance: A Population-Based Study Including 15,351 Cases and 58,619 Matched Controls. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2679–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, H.M.; Mauermann, M.L.; Rajkumar, S.V. Monoclonal Gammopathy-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy: Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosselin, S.; Kyle, R.A.; Dyck, P.J. Neuropathy Associated with Monoclonal Gammopathies of Undetermined Significance. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 30, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, G.B.; Mahadevan, A.; Taly, A.B.; Yasha, T.C.; Seshagiri, K.S.; Nalini, A.; Satishchandra, P.; Veerendrakumar, M.; Shankar, S.K. Clinicopathological Profile of Polyneuropathy, Organomegaly, Endocrinopathy, M Protein and Skin Changes (POEMS) Syndrome. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwait, R.; O’Regan, K.; Campigotto, F.; Harris, B.; Yarar, D.; Bagshaw, M.; Leleu, X.; Leduc, R.; Ramaiya, N.; Weller, E.; et al. The Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging in Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Ginsberg, L. POEMS Syndrome: Clinical Update. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascual-Goni, E.; Martin-Aguilar, L.; Lleixa, C.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; Simon-Talero, M.J.; Diaz-Manera, J.; Cortes-Vicente, E.; Rojas-Garcia, R.; Moga, E.; Juarez, C.; et al. Clinical and Laboratory Features of Anti-MAG Neuropathy without Monoclonal Gammopathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kieseier, B.C.; Mathey, E.K.; Sommer, C.; Hartung, H. Immune-Mediated Neuropathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Neuropathy | Variants | Ab or Immune-Complex Targets | Antibodies | Preceding Infections/Associations | Treatment Options | Diagnostic Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guillain–Barre syndrome | (1) Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP) | Schwann cell plasmalemma | none | Campylobacter jejuni, Mycoplasma, EBV, CMV, Varicella zoster, HIV, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma | Intravenous immunoglobulin Plasma exchange | (1) Clinical presentation plateaus at 4 weeks (2) Increased CSF protein (3) Acellular CSF (4) Neurophysiological findings:
|
| (2) Acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN) | Axolemma | Anti-GM1, Anti-GM2, Anti-GQ1b, Anti-GT1a, Anti-GD1a, Anti-GD1b | ||||
| (3) Acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy (AMSAN) | Axolemma | As in (2) | ||||
| (4) Sensory variant | Axolemma | As in (2) | ||||
| (5) Miller–Fisher | Cranial motor nerves | Anti-GQ1b | ||||
| CIDP | Relapsing | As for GBS | Anti-gangliosides as for GBS (presumed to be involved in CIDP as well, but not yet documented). In a small proportion of patients, antibodies against proteins located at the node of Ranvier are detected (antibodies target neurofascin, contactin and contactin-associated protein 1) | Diabetes mellitus; Connective tissue diseases; infections; dysproteinaemias | Intravenous immunoglobulin; Plasma exchange; corticosteroids; immunosuppression | Same as in GBS but clinical presentation is more progressive and prolonged |
| Chronic monophasic | ||||||
| Slow progressive | ||||||
| Neuropathy with conduction block | MMN | Probably the nodes of Ranvier are a major target but also the axolemma and Schwann cell plasmalemma | Anti-GM1 | None | Intravenous immunoglobulin | Multifocal conduction abnormalities with conduction blocks and no sensory features electrophysiologically |
| MADSAM | Negative for anti-GM1 | None | Intravenous immunoglobulin and corticosteroids | Multifocal conduction abnormalities with conduction blocks and sensory abnormalities |
| Paraneoplastic Neuropathy | |
|---|---|
| Variants |
|
| Antibody or immune-complex targets |
|
| Antibodies |
|
| Preceding infections/associations |
|
| Treatments |
|
| Diagnostic criteria |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shastri, A.; Al Aiyan, A.; Kishore, U.; Farrugia, M.E. Immune-Mediated Neuropathies: Pathophysiology and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087288
Shastri A, Al Aiyan A, Kishore U, Farrugia ME. Immune-Mediated Neuropathies: Pathophysiology and Management. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087288
Chicago/Turabian StyleShastri, Abhishek, Ahmad Al Aiyan, Uday Kishore, and Maria Elena Farrugia. 2023. "Immune-Mediated Neuropathies: Pathophysiology and Management" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087288
APA StyleShastri, A., Al Aiyan, A., Kishore, U., & Farrugia, M. E. (2023). Immune-Mediated Neuropathies: Pathophysiology and Management. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087288









