Abstract
As a kind of bioactive component in the rhizome of natural plant Curcuma longa L. (turmeric), curcumin is almost insoluble in water at neutral and acidic pH, which limits its further utilization and development. At the same time, traditional extraction and separation processes typically require the use of a large number of organic solvents. Ionic liquids (ILs) are organic molten salts with melting points below 100 °C. When an ionic liquid exists in a liquid state at or near room temperature, it is referred to as a room-temperature ionic liquid (RTIL). They have a temperature range, good physical and chemical stability, and good structural designability. They have a strong solubilization enhancement effect for many organic compounds. This study first explored the molecular forms of curcumin in ionic liquid aqueous solutions and the intermolecular interactions between curcumin and ionic liquids using spectral analysis and computational chemistry methods; furthermore, using an ionic liquid aqueous solution as an extraction agent, curcumin-like substances (curcuminoids) were extracted from turmeric powders under ultrasound assisted conditions, revealing the relationship between the structure of the ionic liquid and the extraction efficiency. After that, a kinetic study was conducted for the extraction of curcuminoids from turmeric powders, using second-order kinetics fitting to obtain the rate constant and initial extraction rate during the extraction process. Finally, the comparison with a ComplexGAPI tool and antioxidant experiment was performed on the extraction by using ionic liquids and traditional solvent. The full results can provide reference for the design of IL extractants and their application for natural products.
1. Introduction
From the current perspective, the micelle aggregation behavior of surfactants is of great significance for insoluble substances, including naturally active products [1]. In aqueous solution, when the concentration of surfactants reaches a certain value, they will aggregate to form micelles. The concentration at which surfactants begin to aggregate is called the critical micelle concentration (CMC) [2]. As the concentration of surfactants increases, the morphology of micelle aggregates gradually presents as follows: (1) relatively small spherical micelles; (2) slender cylindrical rod-shaped micelles with hemispherical ends; (3) larger flat-layered micelles; (4) a vesicle containing multiple spherical structures, composed of bilayer lamellar micelles arranged in one or more concentric spheres [3]. The solubilization effect of micelles is an important property of surfactants. Although both soluble and insoluble substances in solvents can be dissolved through the mechanism of micelle solubilization, from a practical application perspective, it is more meaningful that micelles can dissolve substances in typically insoluble solvents [4]. The solubilization ability of micelles towards target molecules is also influenced by intermolecular interactions. In the study of solubilization of ibuprofen and gefitolozil, the anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) has the lowest solubilization ability, while cationic and non-ionic surfactants have stronger solubilization ability. This is due to the dissociation of ibuprofen and gemfibrozil molecules into anions, which exhibit charge repulsion with the anionic head group of SDS [5]. In the solubilization of fenofibrate, danazol, and androstane, the solubility of danazol in ionic surfactants is much higher than that of fenofibrate and androstane. This is due to the ion–dipole interaction between polar danazol molecules and the charged head groups of ionic surfactants [6].
There are many factors that affect the solubilization of micelles, among which the most important are the structure of surfactants and solubilizers. As a kind of green solvent with excellent solubility, ionic liquids (ILs) exhibit good solubility for many organic and inorganic substances [7]. Those ILs with long carbon chains in cations often have properties similar to traditional surfactants, and those that can aggregate in water to form micelles can be called surface-active ionic liquids (SAILs) [8]. SAIL not only has good surface activity but also has a wide liquid temperature range and good “structural designability”. It has a wide range of application prospects in the fields of compound extraction and separation, drug delivery carrier construction, and micelle catalysis [9,10]. Generally speaking, as the carbon chain length of ionic liquids increases, CMC decreases, while the aggregation number increases. Table 1 summarizes the reported CMC and Nagg number of imidazolium bromide ILs in previous studies [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Although there is a certain research foundation on the micelle aggregation behavior of ionic liquids, there are still few reports on the micelle solubilization of ionic liquids. Previous studies have suggested that ionic liquids can enhance the water solubility of some insoluble organic compounds and biomolecules. For instance, a non-linear correlation of the concentration of ionic liquid with [Cnmim]+ cation and casein solubility was observed with a significant maximum at a concentration of approximately 40% [19]. In another case, the obviously increased solubility of glibenclamide (Glib) resulted from the formation of complex hydrogen bonds and the pi–pi interaction of the aromatic rings with the IL [20]. As a hydrophobic natural product, its solubility can be improved by non-ionic surfactant micelles induced by ionic liquids, which resulted from the formation of small sized mixed micelles (hydrodynamic diameter ≈ 10 nm) at a high number density [21]. When ionic liquid surfactants are used for extraction, the target substance micelle distribution coefficient is the driving force for successfully extracting it into ionic liquid micelles. That is to say, the greater the partition coefficient of a component from the aqueous phase to the ionic liquid micelles, the higher its extractability. Generally speaking, hydrophobic substances (octanol–water partition coefficient greater than 300) are more suitable for extraction with ionic liquid surfactants than polar substances, which provides the possibility for selective extraction [22].

Table 1.
Currently reported CMC and Nagg number of imidazolium bromide ILs.
Curcumin (Cur) and curcuminoids (e.g., demethoxycurcumin, DMC; bisdemethoxycurcumin, BDMC) are a kind of yellow pigments extracted from the rhizomes of ginger plants such as turmeric in the ginger family. Their structures belong to acidic polyphenols with an unsaturated aliphatic and aromatic main chain [23]. Curcumin is commonly used as a coloring agent and acid–base indicator for meat products and also has pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [24,25]. It is an orange yellow crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste, which is insoluble in water at neutral and acidic pH. This property limits its further utilization and development. In this study, curcumin and curcuminoids were chosen as the target molecules, and the solubilization enhancement effects of alkyl imidazolium bromine ionic liquids ([Cnmim]Br) were firstly explored through a series of experiments and computation for them. In addition, key conditions were investigated for the extraction of curcuminoids from turmeric powders, and classical kinetic models were applied to fit the whole process. Finally, a ComplexGAPI tool and an antioxidant experiment were performed for the comparison on the extraction by using ionic liquids and traditional solvent. The study was aimed to provide meaningful reference for the application of green extractants and assessment for natural products extraction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
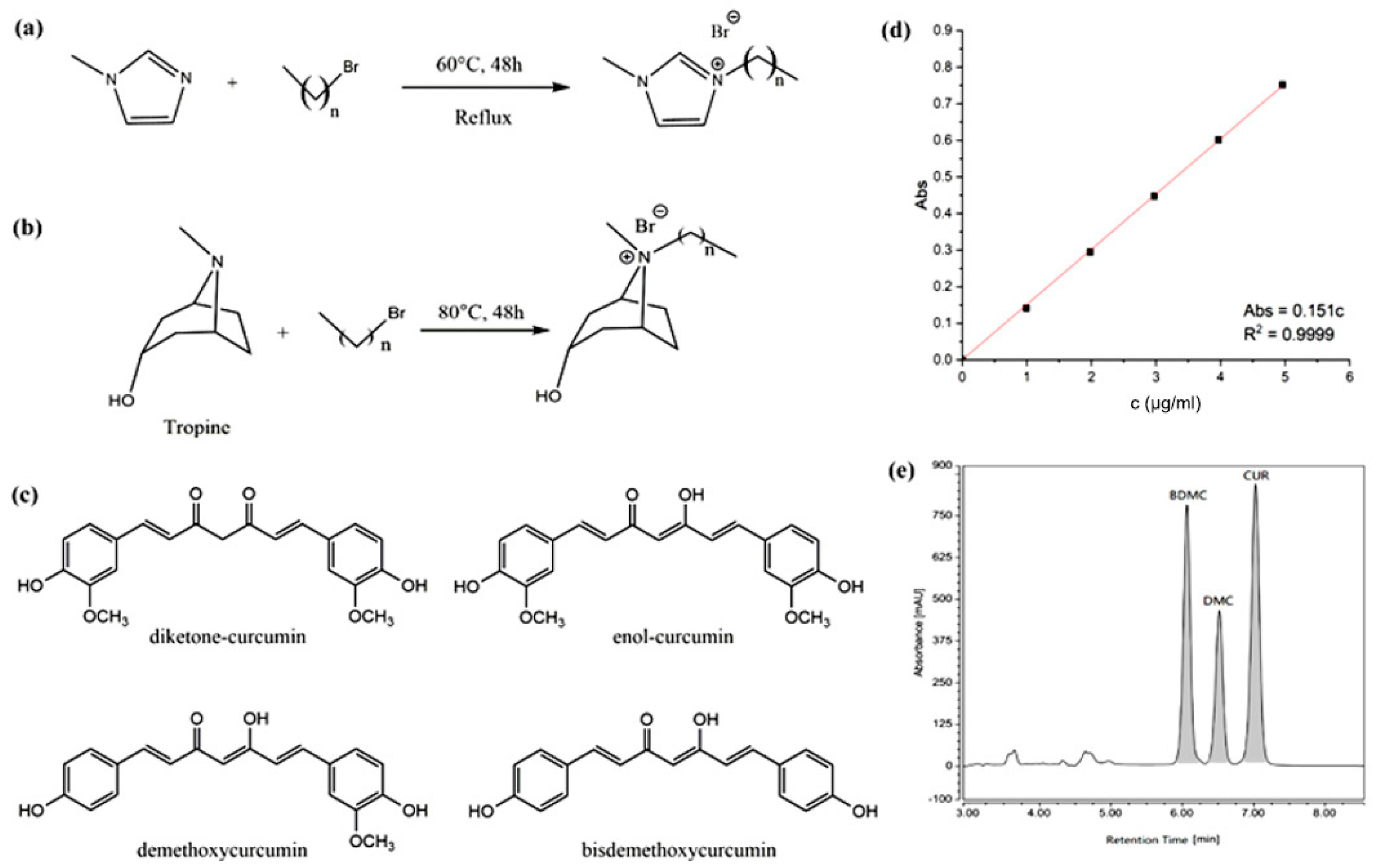
1-methylimidazole, 1-bromobutane, 1-bromohexane, 1-bromooctane, 1-bromodecane, 1-bromododecane, potassium hexafluorophosphate, sodium tetrafluoroborate, potassium hydrogen sulfate, anhydrous sodium acetate, dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide, methylene chloride, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl free radical (DPPH-D273092, 97%), and sodium lauryl sulfate were all purchased from Aladdin Chemical Reagent Company (Shanghai, China). Ultrapure (UP) water was obtained from a Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). The main ILs used in this study included 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bromine ([C8mim]Br), 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium bromine ([C10mim]Br), 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium bromine ([C12mim]Br), N-octyl tropine bromine ([C8Tr]Br), N-decyl tropine bromine ([C10Tr]Br), and N-dodecyl tropine bromine ([C12Tr]Br), which were synthesized according to the methods in the literature [26,27,28] (see Figure 1a,b), and their spectral purities of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) were above 96.5% (see Supplementary Materials). Curcumin and curcuminoids (99% purity) were purchased from MeilunBio (Dalian, China, see Figure 1c). Acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, and anhydrous ethanol were purchased from Kelong chemical factory (Chengdu, China).
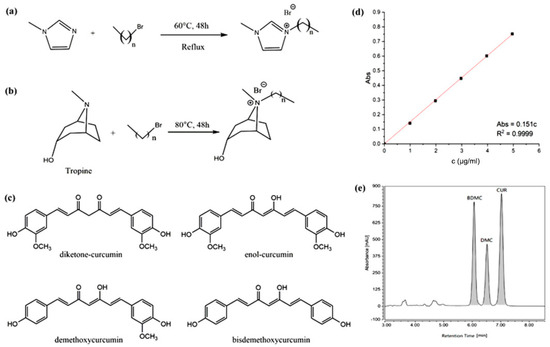
Figure 1.
Synthesis routes of (a) imidazolium and (b) tropine-based ILs; (c) different structures of curcumin and related curcuminoids; (d) UV−Vis calibration curve of curcumin; and (e) HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) chromatogram of curcuminoids (CUR: curcumin, BDMC: bisdemethoxycurcumin, and DMC: demethoxycurcumin).
2.2. Instruments
A DF-101S oil bath pot and DZF-6050 vacuum-drying oven were procured from Yinyu-yuhua Instrument Co., Ltd. (Gongyi, China). The FA2004B electronic balance was sourced from Tianmei Balance Instrument Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The SHZ-D (III) circulation vacuum pump was from Dufu Instrument Factory (Zhengzhou, China). The RE-2000 rotary evaporator was from Yarong Biochemical Instrument Factory (Shanghai, China). The DC-2006 low-temperature constant temperature bath was from Hengping Instrument Factory (Shanghai, China). The 85-2 magnetic stirrer was from Sile Instrument Factory (Shanghai, China). The DDS-12A digital conductivity meter was from Hongyi Instrument Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The AOE 380 UV–Vis Spectrometer was from Aoyi Instrument Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The YM-031S ultrasonic generator was from Fangao Microelectronics Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China).
2.3. Determination of Critical Micelle Concentration of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids by Conductivity
According to the reported study [29], a certain amount of ionic liquid was accurately weighed to prepare a stock solution, which was then diluted to different concentrations of IL aqueous solutions. During measurement, 5 mL of the IL aqueous solution was taken and placed in a test tube. The probe of the conductivity meter was inserted into the test tube, ensuring that the electrode was fully submerged in the solution. After that, the test tube containing the probe was placed in a glass jacket, and the temperature was remained within the jacket at 25 °C using a constant temperature water bath circulator. Simultaneously, a magnetic stirrer was employed for agitation (300 rpm). Finally, the conductivity data were recorded once the values stabilized (see the details in Section S1 of Supplementary Materials).
2.4. UV–Vis Detection Method for Curcumin and Establishment of Its Standard Curve
In the study of enhanced solubility, UV–Vis was used for the quantitation of curcumin. The absorbance of IL exists in the far UV region, and the absorbance of curcumin was measured at visible region, which ensured the accurate measurement. On the basis of current method [30], 25.0 mg of curcumin was precisely weighed and dissolved in ethanol to prepare solutions with concentrations of solution with only ethanol added, 1.0 μg∙mL−1, 2.0 μg∙mL−1, 3.0 μg∙mL−1, 4.0 μg∙mL−1, and 5.0 μg∙mL−1. Ethanol was treated as the reference solution, and the absorbance was measured at 425 nm. With the concentration of curcumin as the x-axis and the absorbance as the y-axis, linear fitting was performed on the UV–Vis absorbance data to obtain the quantitative standard curve for curcumin. As illustrated in Figure 1, within the concentration range of 0.0 μg∙mL−1 to 5.0 μg∙mL−1, the absorbance of curcumin demonstrates a strong linear relationship with its concentration, with the linear equation being Abs = 0.151c and a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.9999 (see Figure 1d).
2.5. Establishing the Method for Determining Curcumin Solubility
Aqueous solutions of ionic liquid were prepared with concentrations of 10 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM, 300 mM, and 1000 mM; and 5 mL of each solution was placed in the separate test tubes. An excess amount of curcumin was added into each solution to ensure supersaturation. The system temperature was maintained at 25 °C using a thermostatic circulating water bath and the mixture was stirred with a magnetic stirrer. Stirred for 12 h to achieve dissolution equilibrium, the system was promptly sampled, and the solutions were filtered. The filtrate was then diluted with ethanol in appropriate ratios, followed by UV–Vis spectrophotometric analysis at a detection wavelength of 425 nm to determine the concentration of curcumin, thereby ascertaining its solubility in the various concentrations of ionic liquid aqueous solutions.
2.6. Extraction Conditions and Calculation of Extraction Yield
The details of the extraction experiment were introduced as in Section S2 of Supplementary Materials. Because of the complex composition of the extract, HPLC was used in the study of curcuminoid extraction from turmeric with ionic liquid. In the reverse-phase system under current HPLC conditions, the ionic liquid will not be effectively retained on the chromatographic column, which can be rapidly eluted as polar component and separated from the curcuminoids. Following the methods and conditions described in references [31,32], curcuminoids were analyzed using the following HPLC conditions: C18 reverse-phase chromatographic column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm; Welch materials, Shanghai, China) as stationary phase; acetonitrile—0.5% (v/v) aqueous acetic acid solution (60:40) as mobile phase; 430 nm of detection wavelength; 0.9 mL∙min−1 as flow rate; 20 μL of injection volume; 30 °C as column temperature. Figure 1e illustrates the HPLC chromatogram of the extracted curcuminoids, and it can be found that three compounds were well separated.
According to literature reports under identical HPLC conditions, the absorbance peaks at related retention time of 7.0 min, 6.5 min, and 6.1 min correspond to curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin, respectively. The calculation of the extraction yield of curcuminoids is shown in Equations (1)–(3).
where E is the extraction yield of curcuminoids (g∙100g−1), C is the concentration of curcuminoids in the extract determined by HPLC (mg∙mL−1), V is the total volume of the extract (mL), and m is the mass of the turmeric powders (mg).
2.7. Extraction Kinetics Fitting
To elucidate the behavior of the mass transfer of curcuminoids from turmeric powders to the extract, the following simplifications and assumptions were made as follows: (1) although the extraction process may involve various substances, only the extraction of curcuminoids is considered for simplicity; (2) the extraction process is assumed to commence with the diffusion of curcuminoids from the cell walls into the solution; (3) under identical extraction conditions, the concentration of curcuminoids at saturation is considered constant. The extraction process of curcuminoids can be modeled by a second-order kinetic equation (Equation (4)) [33,34].
where k is the extraction rate constant (mL∙mg−1min−1), CS (mg∙mL−1) represents the saturation concentration of curcuminoids at extraction equilibrium, signifying the maximum extraction capacity; and Ct (mg∙mL−1) is the concentration of curcuminoids at any given time t (min). By separating variables in Equation (4), Equation (5) can be obtained. Integrating Equation (5) and applying the initial and boundary conditions: at t = 0, Ct = 0, and at t = t, Ct = Ct, allows Equation (6) to be obtained. Ultimately, the functional relationship between Ct and t is established as Equation (8).
Transforming Equation (8) to Equation (9) yields a linear relationship between t/Ct and t. At t = 0, with Ct = 0, the initial extraction rate can be defined as Equation (11). In fitting the extraction kinetic data, t/Ct is used as the ordinate and t as the abscissa. Through linear fitting, CS, h, and k can be calculated.
2.8. Computational Chemistry Study
The structure optimization of ionic liquids and curcumin molecules was first carried out using Gaussian 09 W, and the selected optimization method was DFT B3LYP. Molecular electrostatic potential (ESP) is of great significance in investigating intermolecular electrostatic interactions, predicting reaction sites, and predicting molecular properties. It is widely used because molecules always approach each other in a complementary manner of electrostatic charges. ESP analysis was carried out on the van der Waals surface. A series of quantitative analyses of molecular van der Waals surface ESP was carried out with Multiwfn 3.6, using the 0.001 a.u. isoelectronic density surface as the van der Waals surface.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Critical Micelle Concentration of Imidazolium ILs in Aqueous Solutions
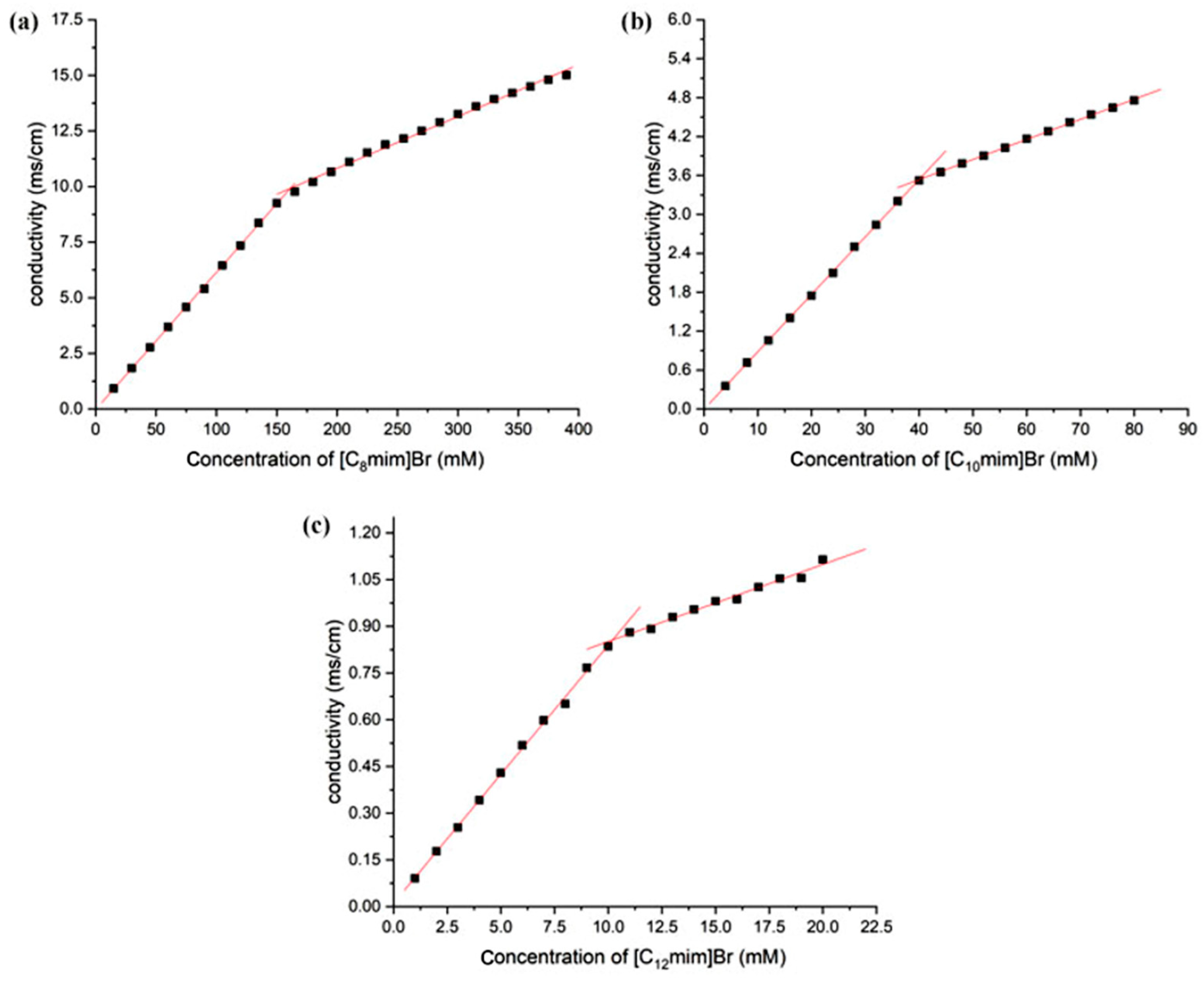
The methods for determining the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of surfactants include conductivity method, surface tension method, UV absorption method, fluorescence probe method, dynamic light scattering method, viscosity method, calorimetry method, and NMR method. The conductivity method for determining the CMC of ionic liquids is simple and accurate. When the concentration of ionic liquids with surface activity is lower than CMC, they are dispersed in water as monomers, and the conductivity of the solution shows a linear increase with the increase in ionic liquid concentration. Once the concentration reaches CMC, the added ionic liquid begins to associate to form micelles, and the degree of ionization of the micelle complex is usually lower than its monomer. At this point, the rate of increase in solution conductivity slows down, and the conductivity exhibits a “turning point” with the change of concentration. After performing segmented linear fitting on conductivity and concentration, the “inflection point” of the fitting corresponds to the CMC of the ionic liquid. The ratio of the slope after the “inflection point” to the slope before the “inflection point” is the ionization degree of the aggregate [35]. Here, Figure 2 shows the relationship between the conductivity and concentration of different types of imidazole ionic liquids in aqueous solutions. The longer the carbon chain of the ionic liquid, the smaller its CMC.
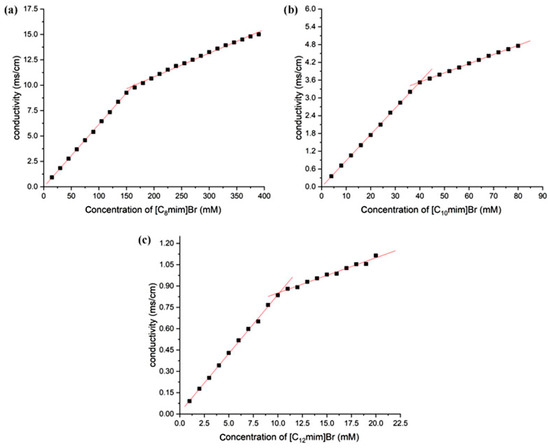
Figure 2.
The relationship between conductivity and concentration of imidazolium ILs in aqueous solution (25 °C, (a) [C8mim]Br, (b) [C10mim]Br, and (c) [C12mim]Br).
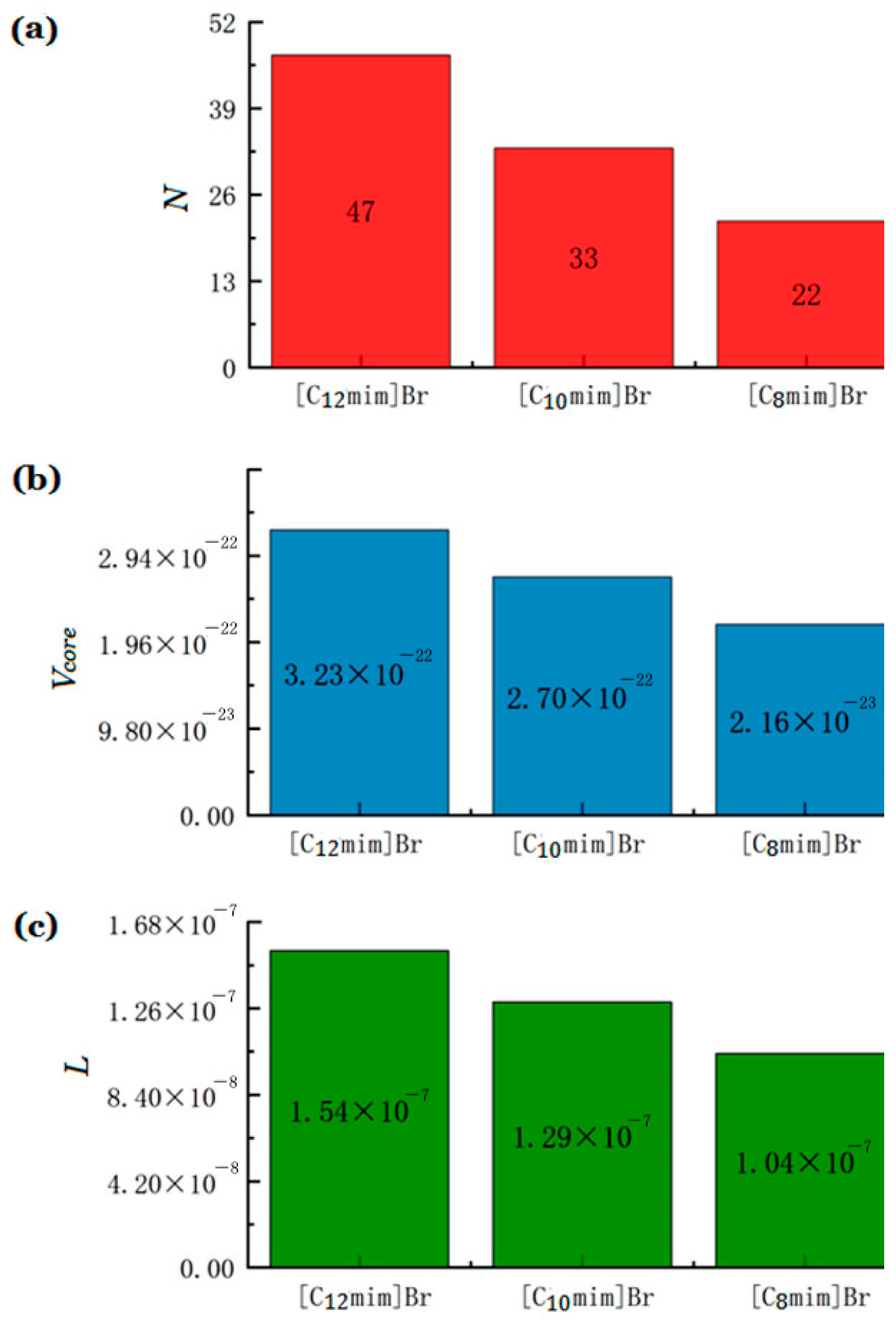
When the concentration is not too high, the aggregates of long-chain imidazolium ILs in water are spherical or nearly spherical, which are assumed to contain a hydrocarbon core consisting entirely of the hydrocarbon chain. The core of the micelle is composed of carbon chains on imidazole cations. According to the spherical volume formula, the volume of the micelle core (N•Vcore) is 4πL3/3. The micelle aggregation number of ionic liquids can be calculated by the following formula [36]:
where L is the length of the alkyl chain embedded in the core of the micelle; ncore is the carbon number in the core. For ionic liquids [Cnmim] Br (n = 8, 10, and 12), ncore ≈ nc − 1, where nc is the number of carbon atoms in the carbon chain [37]. The calculated aggregation number (N) and volume of single hydrocarbon core (Vcore) and the length of the carbon chain in the micelle core (L) of imidazole ionic liquids [Cnmim]Br (n = 12, 10, 8) are shown in Figure 3. The longer the carbon chain of ionic liquids, the greater the aggregation number of micelles, and the larger the micelle size. Here, the solvent is water as the polar component, and long alkyl-chain-substituted ILs represent less-polar component as surfactant. When the length of alkyl chain becomes longer, the degree of “dissimilarity” between solvent and surfactant is more significant. On the one hand, increasing the length of hydrophobic chains can lead to a decrease in the water solubility of surfactant monomers, thereby reducing the CMC of surfactant [38]. On the other hand, the surfactant with a longer hydrophobic chain has a higher aggregation number, resulting in larger micelle size and a greater space of the core [39].
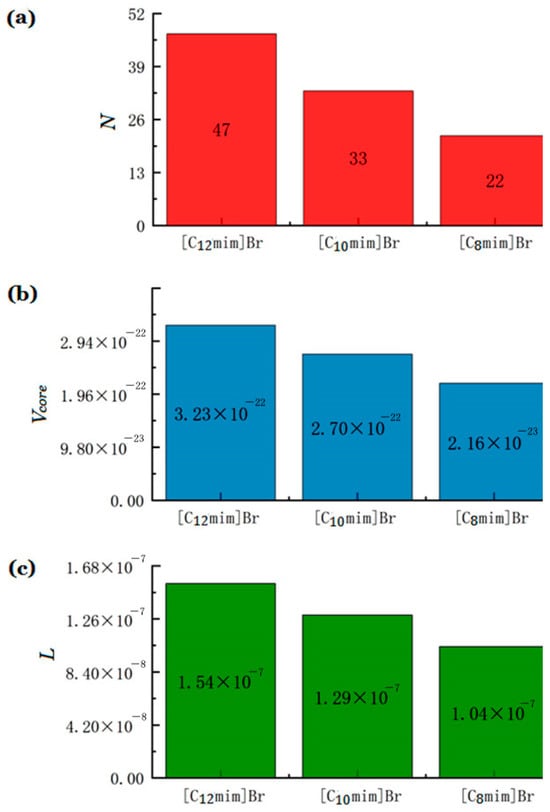
Figure 3.
(a) The calculated aggregation number (N), (b) the volume of single hydrocarbon core (Vcore), and (c) the length of the carbon chain in the micelle core (L) of three imidazolium ILs.
3.2. Effect of Imidazolium ILs on Curcumin Solubility
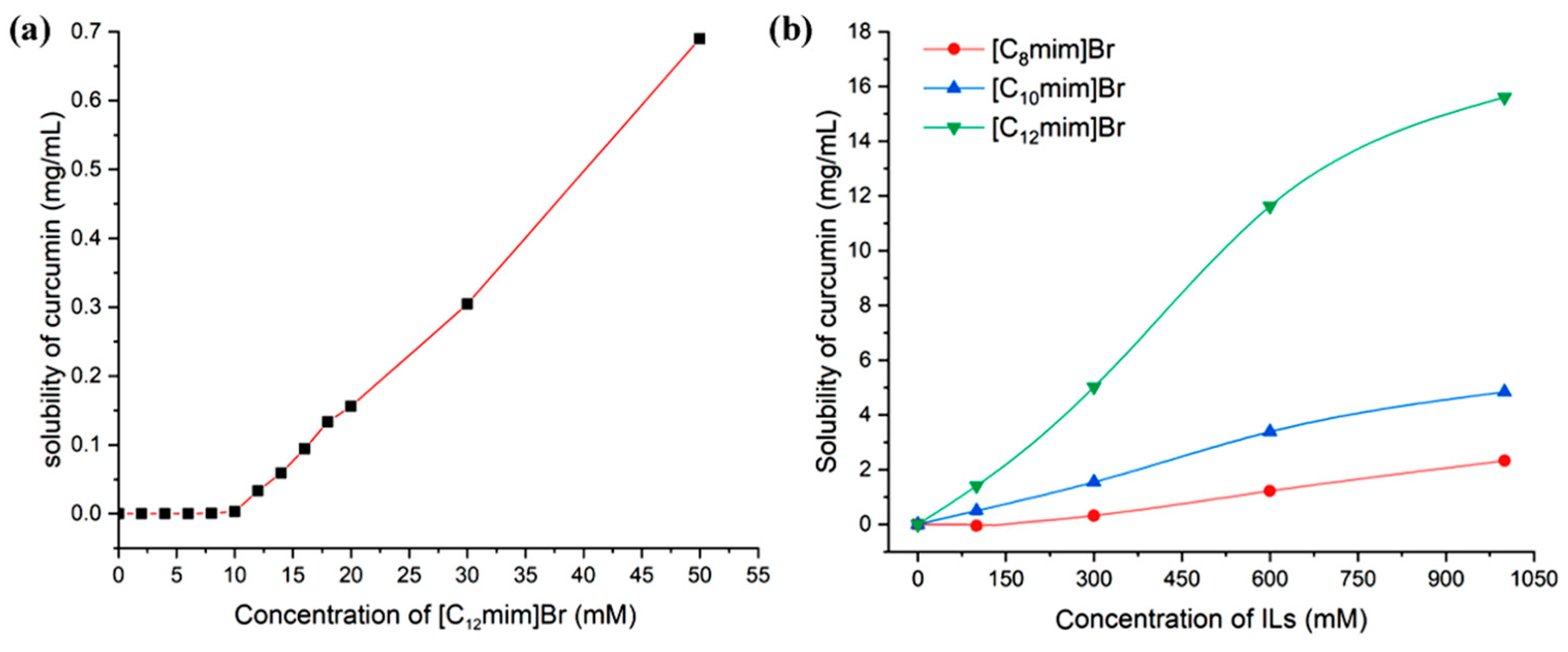
During the extraction process, using those solvents with a significant solubilization effect can reduce the volume of extractant used and decrease energy consumption and post-treatment burden, thereby improving extraction efficiency. The strengthened solubility of curcumin by ionic liquids is closely related to the aggregation behavior of the ionic liquids themselves. Therefore, the concentration of ionic liquids has a significant impact on the solubility of curcumin, as shown in Figure 4a. When the concentration of [C12mim]Br is below CMC (measured by conductivity method as 10.2 mM), curcumin is almost insoluble. When the concentration exceeds CMC, the solubility significantly increases. This indicates that the solubilization of curcumin by [C12mim]Br is a micelle phenomenon [39].
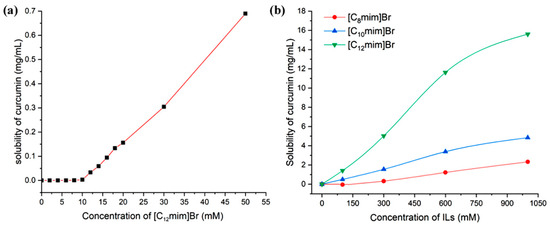
Figure 4.
The relationship of curcumin solubility with the concentration of imidazolium ILs (25 °C, (a) [C12mim]Br in the range of 0–50 mM, (b) three ILs within 1000 mM).
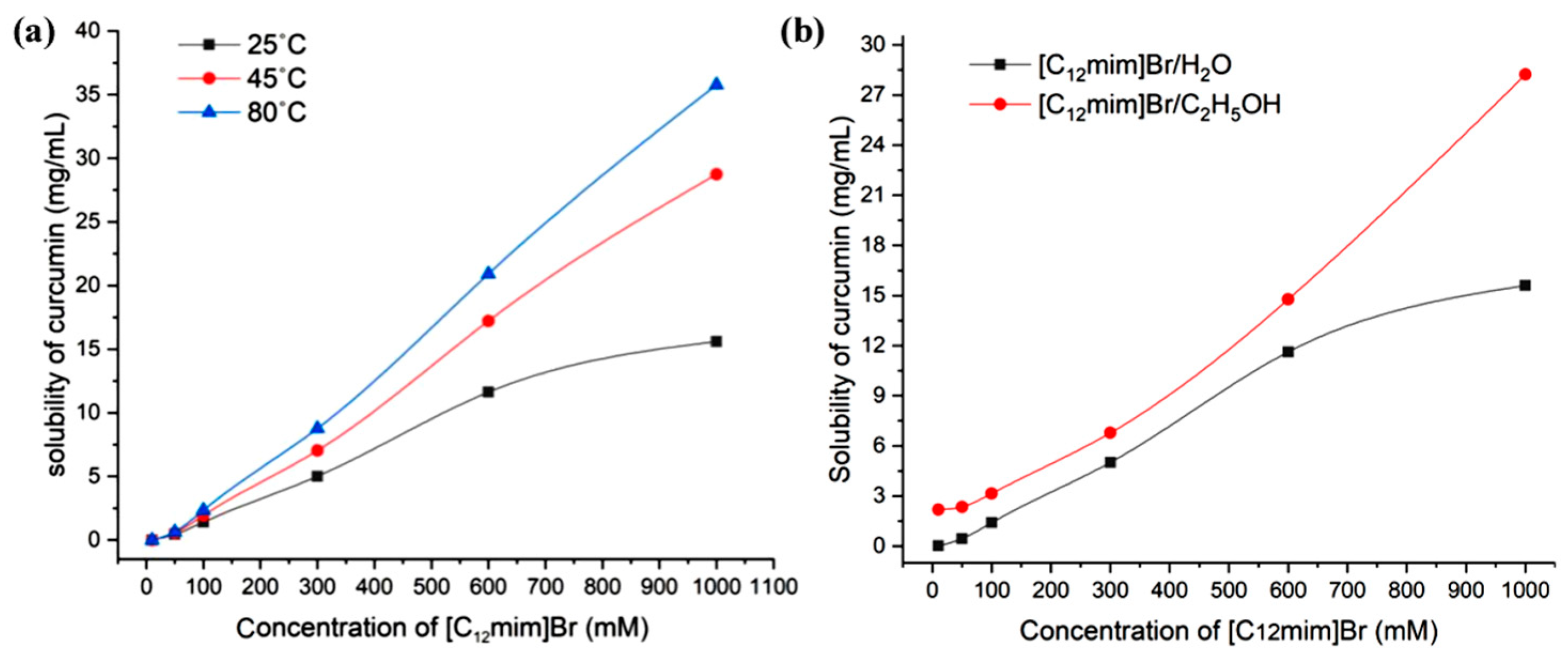
The relationship between the concentration of ionic liquids and the solubility of curcumin in the range of 0–1000 mM is shown in Figure 4b. Through the results, it can be found that with the increase in ionic liquid concentration, the solubilization ability of curcumin significantly increases. This is because as the concentration of ionic liquids increases, on the one hand, the number of micelle aggregates rapidly increases, and more and more curcumin molecules can enter the micelles from the external aqueous phase; on the other hand, the morphology of micelle aggregates began to transform from smaller spherical micelles to larger rod-shaped and layered micelles. The solubilizing space available inside the micelles significantly increased, and the number of soluble curcumin molecules in a single micelle significantly increased. However, when the concentration of the ionic liquid reaches 1000 mM, the water content in the system is already very low, and the viscosity of the system becomes large. The time required for curcumin to reach dissolution equilibrium in the system becomes very long, making the determination of equilibrium solubility more difficult. Figure 5a exhibits the solubility of curcumin in aqueous solutions of [C12mim]Br at different concentrations at 25 °C, 45 °C, and 80 °C. It can be proved that the higher the temperature, the greater the solubility of curcumin. This is due to the increase in temperature leading to an increase in the soluble space in the micelle [28].
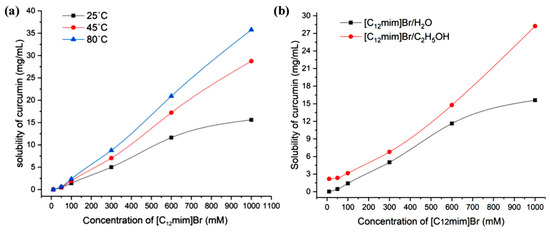
Figure 5.
(a) The relationship of curcumin solubility with the concentration of [C12mim]Br at different temperatures and (b) curcumin solubility in different concentrations of [C12mim]Br aqueous solution and ethanolic solution (25 °C).
On the basis of the above research, considering that ethanol is often used in combination with ionic liquids, we also investigated the solubility of curcumin in imidazole-type ionic liquid ethanol solutions. Due to the good dissolution effect of ethanol on curcumin, using ethanol instead of water to prepare [C12mim]Br ethanolic solution may achieve a better solubilization effect. The relevant experimental results are shown in Figure 5b. At low concentrations, the solubility of curcumin in [C12mim]Br ethanol solution is similar to that in pure ethanol. When the concentration of [C12mim]Br exceeds 50 mM, the solubility begins to significantly increase. Overall, the solubility of curcumin in [C12mim]Br ethanolic solution is higher than that in [C12mim]Br aqueous solution.
3.3. Comparison with the Effect of Tropine-Based ILs on Curcumin Solubility
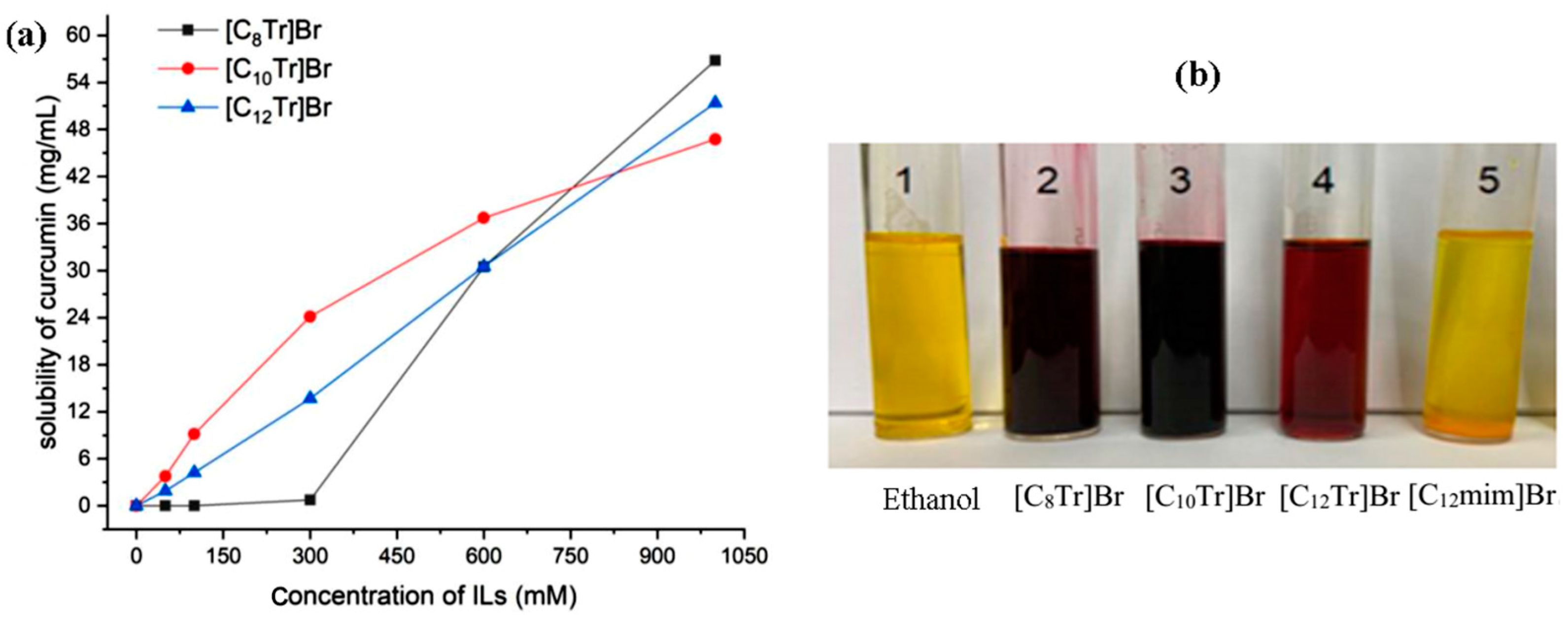
The solubilization mechanism of Tropinol-based ionic liquids on curcumin is more complex, and it is not only a single effect of micelle solubilization. The aqueous solution of tropine-based ionic liquids has a certain alkalinity, especially when the carbon chain length is less than 10 carbon atoms, its alkalinity is strong [39]. Under strong alkaline conditions, the phenolic hydroxyl groups of curcumin molecules undergo ionization, resulting in a significant increase in molecular polarity and water solubility. Therefore, for Tropine-based ionic liquids with a carbon chain length of 12, the solubilization mechanism is still mainly micelle solubilization, and the solubilization amount of curcumin basically increases linearly with the concentration of the ionic liquid. For Tropine-based ionic liquids with carbon chain lengths of 10 and 8, an increase in their concentration leads to an increase in the alkalinity of the solution, an increase in the ionization degree of curcumin, and, therefore, an increase in solubilization. From Figure 6a, it can be seen that at some concentrations, ionic liquids with short carbon chains actually have greater solubilization. However, under alkaline conditions, curcumin undergoes rapid degradation so the application of such solubilization may be limited. Generally speaking, when curcumin is dissolved in organic solvents, the solution turns yellow. However, in environments with high pH values, the phenolic hydroxyl groups of curcumin undergo ionization, and the solution changes from yellow to red. As shown in Figure 6b, curcumin exhibits different colors when dissolved in different types of ionic liquid aqueous solutions (with curcumin concentrations of 0.5 mg∙mL−1 and ionic liquid concentrations of 200 mM). In the aqueous solutions of [C8Tr]Br and [C10Tr]Br (sample 2 and 3), the curcumin solution shows a dark red color, indicating that these two ionic liquid aqueous solutions have strong alkalinity. In the aqueous solution of [C12Tr]Br (sample 4), the curcumin solution appears brownish red, indicating that this ionic liquid aqueous solution has weak alkalinity. In ethanol (sample 1) and [C12mim]Br aqueous solutions (sample 5), the curcumin solution appears yellow, and the solution is neutral.
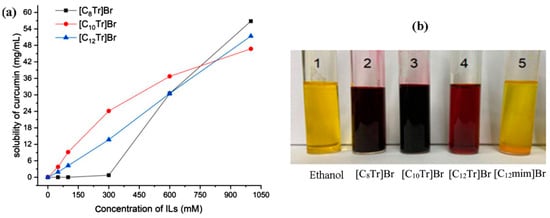
Figure 6.
(a) The relationship of curcumin solubility with the concentration of three tropine-based ILs (25 °C) and (b) color comparison of curcumin solubilized in different solvents.
3.4. Computation for Intermolecular Interactions
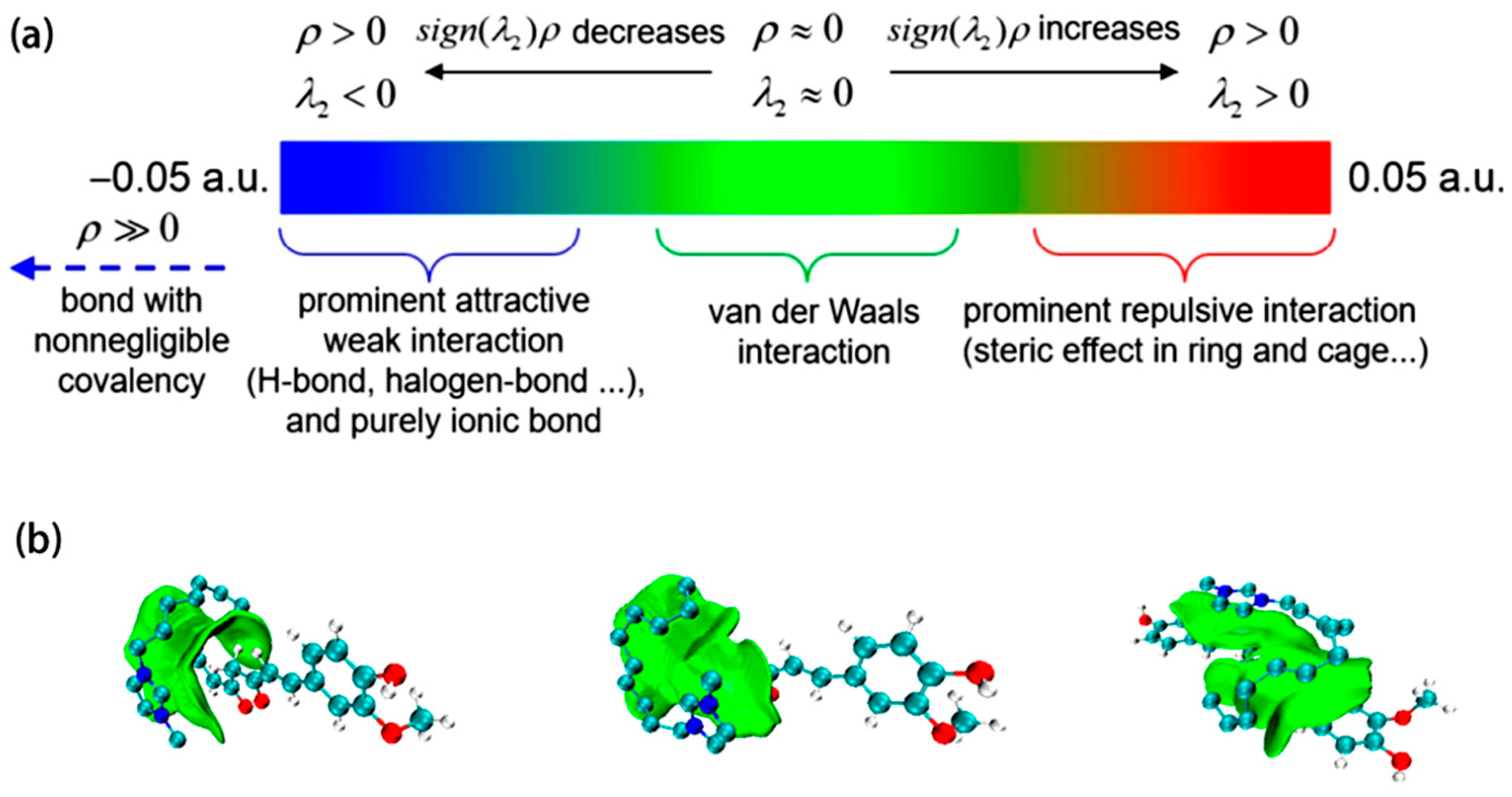
In order to further understand the intermolecular interactions between the tested ILs and Cur, Gaussian09W was used to optimize the structures of curcumin and three ionic liquids—[C8mim]Br, [C10mim]Br, and [C12mim]Br. Initially, the molecular structures of curcumin and the ionic liquid cation were constructed using GaussianView. Subsequently, the DFT-B3LYP method with the 6-31G(d,p) basis set was applied. The system charge was set to +1 to execute the structural optimization. Analyses of weak interactions were performed using the IGMH method implemented in the Multiwfn software (version 3.8) [40,41]. This quantum chemistry-based approach employs the second-largest eigenvalue (λ2) of the electronic density Hessian matrix, projecting it onto wavefunction eigenvalues that characterize interactions between atoms, among fragments, and within fragments. This procedure generates a color-coded interaction trend map, as illustrated in Figure 7a [42]. The resulting wavefunction data were visualized using VMD software (version 1.9.4a53), producing the depiction shown in Figure 7b. The analysis preliminarily indicates that van der Waals forces are the primary interactions between curcumin and the three ionic liquids, while hydrogen bonds are relatively weaker or nonexistent.
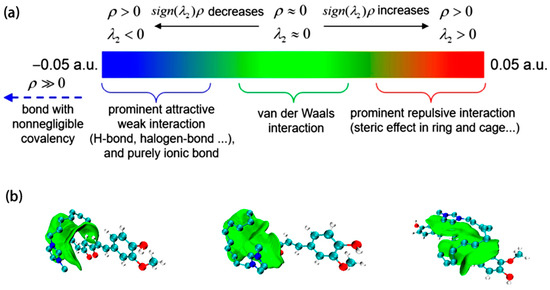
Figure 7.
(a) IGMH method colorimetric relation; (b) VMD visualization IGMH method after the weak interaction analysis results (from left to right: curcumin and C8mim+, C10mim+, and C12mim+).
3.5. Electrostatic Potential Distribution of Ionic Liquids and Curcumin Molecules
Molecular electrostatic potential (ESP, V) reflects the overall charge distribution of the system, including both nuclear and electronic charges. It is a true physical property that can be measured experimentally or calculated. ESP is of great significance in investigating intermolecular electrostatic interactions, predicting reaction sites, and predicting molecular properties. By analyzing the ESP distribution on the van der Waals surface, the strength and orientation of many non-covalent interactions can be well predicted and explained, such as hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, and π-hole bonding [43]. Table 2 exhibits the results from the General Interaction Property Function (GIPF) based on ESP to quantitatively analyze the ESP distribution of ionic liquids and curcumin molecule, respectively, including the highest electrostatic potential (VS, max), the lowest electrostatic potential (VS, min), and the average deviation of the distribution of the molecular van der Waals surface (Π) and the variance of the distribution (σ2). It should be noted that curcumin has two isomers: a diketone structure and an enol structure. The data in Table 2 indicate that the length of the carbon chain of ionic liquids has little effect on the maximum and minimum values of ESP but has a certain impact on the overall distribution of electrostatic potential: (1) For the same type of ionic liquids, the longer the hydrophobic carbon chain is, the more ESP distribution on the van der Waals surface Π. The smaller the carbon chain, the smaller the polarity of ionic liquids with longer carbon chains. (2) When the side chain carbon atoms of the tested imidazole-type ionic liquids exceed 8, σ2 of the ESP distribution significantly increases, indicating a stronger ability to interact with other molecules through its own charge region. (3) The cationic head group of ionic liquids has the maximum positive charge, while the enol structure of curcumin has the maximum negative charge, and electrostatic interactions may occur between the two. This electrostatic effect may cause damage to the intramolecular hydrogen bonds in the enol structure, causing curcumin molecules to transform from enol-like structures to diketone-like structures.

Table 2.
GIPF parameters of ESP distribution on the van der Waals surface of ILs and curcumin.
3.6. Effects of Main Extraction Conditions
Solubilizing enhancement makes some compounds that are originally difficult to extract easier to extract. In addition, it can ensure that the extracted compounds maintain high solubility in the solvent, thereby improving the quality and stability of the product. Strengthened solubilization can also affect the mass transfer rate and equilibrium state during the extraction process, which is of great significance for basic research. In order to achieve rapid extraction, the solvent’s ability to dissolve the extract and the rapid mass transfer ability of the substance in the solvent are very important. On the one hand, the solubility of curcumin increases with the increase in ionic liquid concentration. If the concentration of ionic liquid in the extraction agent is too low, the extraction effect will obviously not be good. On the other hand, the viscosity of the extraction agent will also increase with the increase in ionic liquid concentration, and a too-high viscosity will hinder mass transfer and be unfavorable for extraction. Choosing the appropriate conditions is crucial for the extraction of turmeric-like substances.
3.6.1. Effects of Particle Size and Solid-to-Liquid Ratio
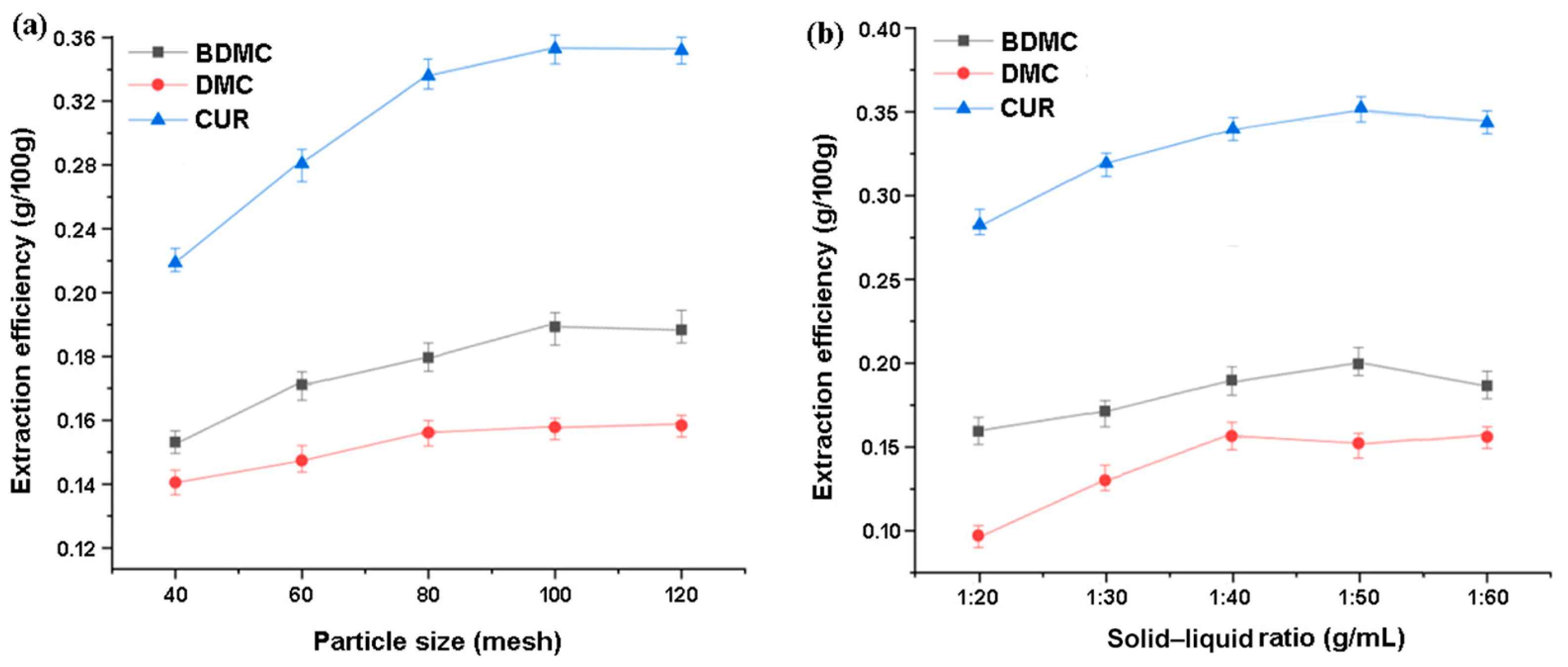
Firstly, an ultrasound-assisted extraction of curcuminoids was carried out using ionic liquids with raw materials with different particle sizes (40–120 mesh) under the same conditions. The ionic liquid concentration was 300 mM, the solid–liquid ratio was 1:50 (g∙mL−1), the extraction temperature was 30 °C, and the ultrasonic extraction time was 30 min at 100 W. The results are shown in Figure 8a. It can be seen that the total changing trend is to rise first and then gradually reach a level. Usually, a sufficient crushing of raw material particles is necessary, especially for objects such as turmeric that are not easily crushed as small particles are conducive to mass transfer. During crushing, plant cells undergo varying degrees of damage under the action of shear force. Generally, the larger the mesh size, the more obvious the degree of damage, and, at this point, the components within the cell are more likely to detach from the raw material and dissolve in the extraction solvent. However, if crushed too fine, the particles tend to aggregate and float on the surface of the extraction solution without being fully soaked. On the other hand, there are more impurities that can be dissolved. Based on the results of this study, a particle size of 100 mesh is suitable for a sufficient extraction of raw materials.
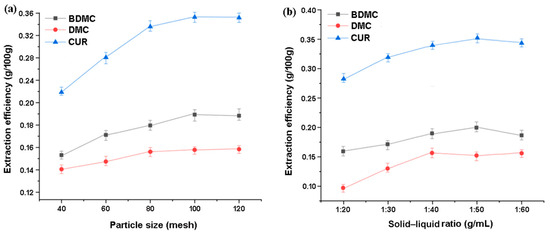
Figure 8.
(a) The effects of the raw material size and (b) solid−liquid ratio on the extraction of curcuminoids.
Moreover, Figure 8b shows the comparison of the different solid–liquid ratios on the target extraction under the conditions including 100 mesh of raw material, 300 mM IL concentration, 30 °C of the extraction temperature, and the 100 W ultrasonic extraction for 30 min. On the one hand, insufficient solvent is hard to achieve thorough extraction; and the increased volume of extractant will result in a greater concentration difference between the solid and liquid phases, which strengthens the driving force of mass transfer in turn. On the other hand, excessive extractant would result in unnecessary wastage and more consumption in post-treatment after extraction; at the same time, voluminous extraction solvents will absorb too much ultrasonic energy, which is not conducive to improving the extraction efficiency. The experimental results indicate that all three components reach high levels at a solid–liquid ratio of 1:50; and the improvement extent of DMC and CUR is more obvious than that of BDMC.
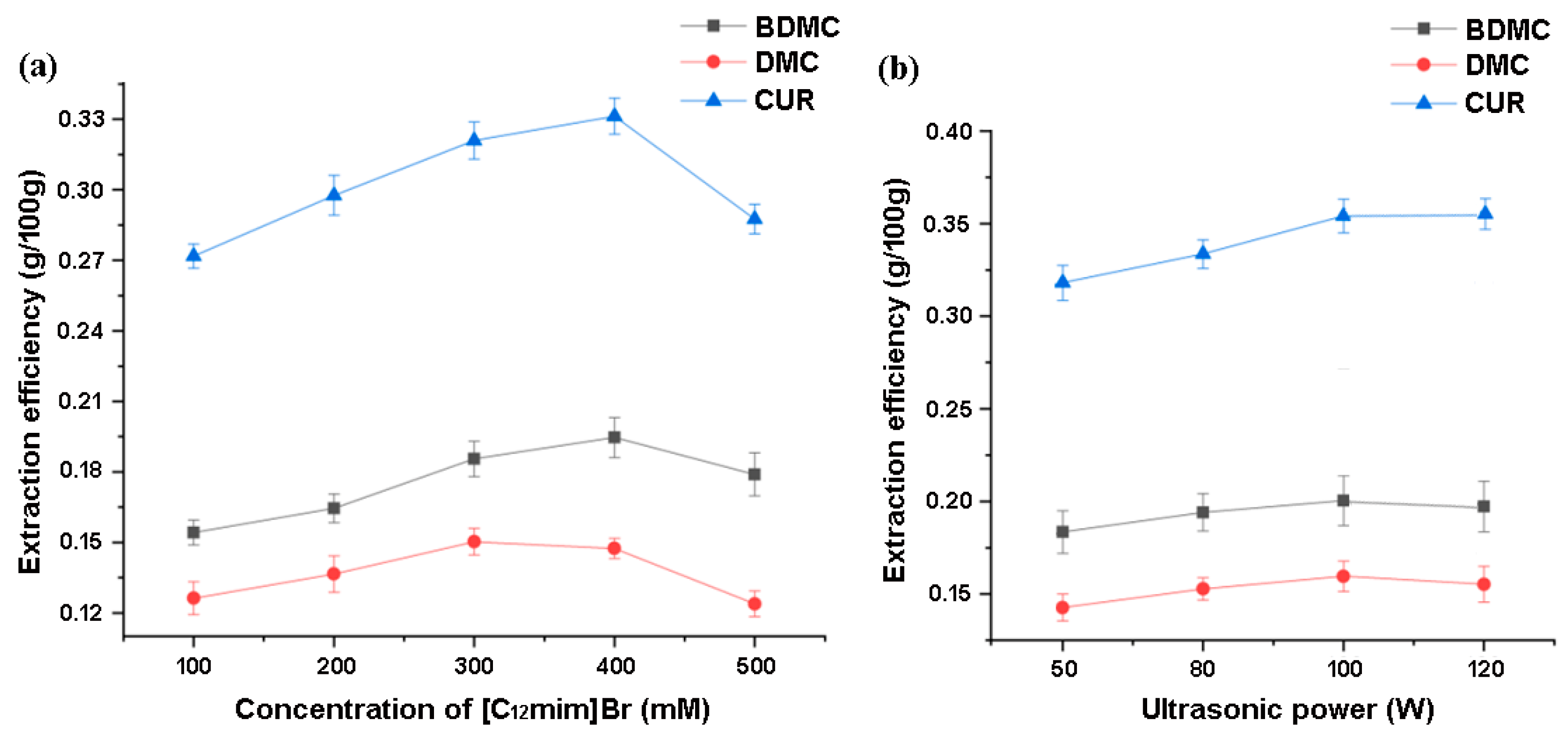
3.6.2. Effects of IL Concentration and Ultrasonic Power
To achieve rapid extraction, the solvent’s ability to dissolve the extract and the rapid mass transfer ability of the target substance in the solvent are very important. On the one hand, the solubility of curcumin increases with the increase in ionic liquid concentration. If the concentration of the ionic liquid in the extraction agent is too low, the extraction effect will obviously not be good. On the other hand, the viscosity of the extraction agent will also increase with the increase in ionic liquid concentration, and a too-high viscosity will hinder mass transfer and be unfavorable for extraction. Choosing the appropriate concentration of ionic liquids is crucial for the extraction of curcuminoid substances. Under the same conditions, different concentrations (100–500 mM) of ionic liquids were used as extractants for extraction comparison. In the investigation on IL concentration, the extraction temperature was 30 °C, and the 100 W ultrasonic extraction time was 30 min. Figure 9a shows the trend of the extraction efficiency of curcuminoids with the concentration of ionic liquid [C12mim]Br. It can be proved that 400 mM of [C12mim]Br is enough to achieve the satisfied extraction for the targets.
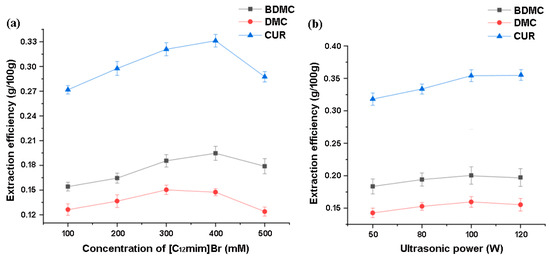
Figure 9.
The effects of (a) the concentration of [C12mim]Br and (b) ultrasonic power on the extraction of curcuminoids.
Ionic liquid ultrasonic extraction method is an extraction method that utilizes the cavitation, mechanical, and thermal effects of ultrasound to accelerate the release, diffusion, and dissolution of intracellular effective substances in ionic liquids, significantly improving extraction efficiency; the cavitation effect is the main driving force for the ultrasonic extraction of ionic liquids. There are often some small bubbles in liquids. When a certain frequency of ultrasound acts on the liquid, small bubbles of appropriate size can resonate. They quickly expand during the sparse stage of ultrasonic wave and are suddenly adiabatic compressed and burst during the compression stage of sound waves. During the process of bursting, small bubbles can generate high-temperature and high-pressure shock waves, which can cooperate with the action of ionic liquids to cause the rupture of materials and even biological cell walls, thereby accelerating the dissolution of intracellular substances. As shown in Figure 9b, an appropriate increase in ultrasound power is beneficial for improving the extraction efficiency, but when the target substances have been fully extracted, excessive power can lead to more coexisting impurities being dissolved. In this study, 100 W is sufficient for the extraction of curcuminoids compounds, which is much lower than the commonly used 200–500 W [44,45] in existing ultrasonic extraction studies by using ionic liquid. This also proves that the selected ionic liquid has a very obvious solubilization effect on the targets, and further increasing the power can only lead to unnecessary energy consumption.
3.7. Study on the Extraction Kinetics of Ionic Liquids
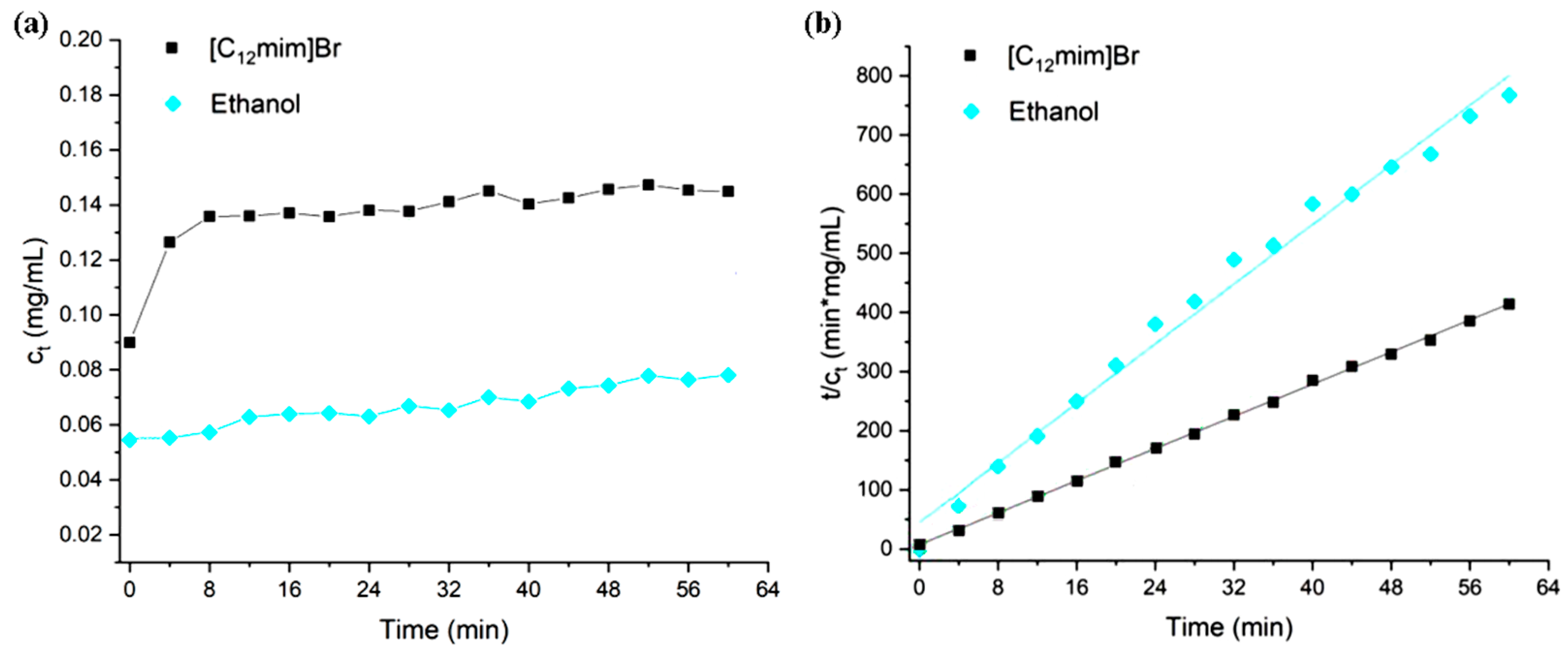
In order to further investigate the impact of extractants on extraction kinetics, different types of ionic liquids and ethanol were used for extraction kinetics studies under the same conditions. The concentration of ionic liquid is 300 mM, and the extraction temperature is 30 °C. During the extraction process, samples are taken every 4 min. The process of extracting turmeric-like substances using ionic liquids can be assumed as two consecutive stages: (1) under the action of ionic liquids, a portion of turmeric-like substances on or near the surface of turmeric powder quickly diffuse and dissolve in the extraction agent; (2) under the dual effects of ionic liquids and ultrasound assistance, more turmeric-like substances are extracted from the inside of turmeric powders. The external diffusion of objects is even slower during this stage [33]. The trend of the concentration of total curcumin substances in the extraction solution (total concentration of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and dideoxycurcumin) over time is shown in Figure 10. Before starting ultrasonic extraction (extraction time 0), a certain concentration of turmeric-like substances had already been dissolved in the solution, which corresponds to the first stage mentioned above. In the initial stage of ionic liquid extraction, the extraction rate is the fastest, gradually decreasing over time, and the concentration of turmeric substances eventually approaches saturation.
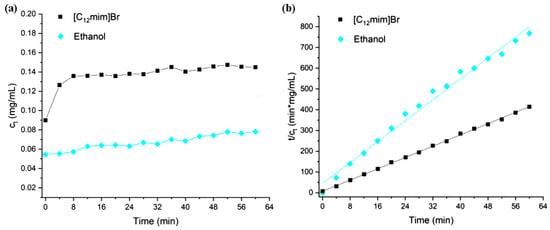
Figure 10.
(a) Curcuminoid concentration as a function of time in the extraction process with different solvents and (b) second-order kinetic fitting for the curcuminoid extraction with different solvents.
From Figure 10a, it can be seen that the ultrasound-assisted extraction of turmeric-like substances is very important. In the process of extracting turmeric substances using ionic liquids, with the increase in ultrasound time, the concentration of turmeric substances in the extraction solution initially increases rapidly and finally tends to flatten out. Without ultrasound assistance, the extraction efficiency of ionic liquids will significantly decrease. When the extraction time is 0, the concentration of turmeric substances dissolved in [C12mim] Br is higher than that in ethanol. The first stage is related to the type of ionic liquid but not to the length of the carbon chain. It may be due to the stronger hydrogen bonding effect of imidazolium ionic liquids compared to quaternary ammonium ionic liquids, which have a stronger ability to dissolve and destroy cellulose in the cell wall. The second stage is not only related to the type of ionic liquid but also to the carbon chain length of the ionic liquid as the mass transfer process is dominant in this stage. Increasing the carbon chain length of the ionic liquid leads to an increase in viscosity, and slowing down the mass transfer leads to a slower extraction rate. In the process of ethanol extraction, the concentration of turmeric substances shows a relatively gentle trend over time, and the final extraction effect is not as good as that of ionic liquids. Due to the poor penetration of ethanol compared to ionic liquids, the extraction ability of turmeric-like substances in turmeric powder is poor, and the extraction efficiency in the second stage is poor. Simulate the second stage of the extraction process using a second-order kinetic model of extraction. The simulated linear fitting results are shown in Figure 10b. Moreover, the extraction saturation concentration (CS), extraction rate constant (k), initial extraction rate (h), and correlation coefficient (R2) obtained through fitting calculation are shown in Table 3. It can be observed that the initial extraction rate and rate constant of ionic liquids are higher than those of ethanol. As comparison, the R2 of first-order kinetics was 0.89861, indicating the latter was not suitable for the fitting data here.

Table 3.
Second-order kinetic fitting data of the curcuminoid extraction with different solvents.
3.8. ComplexGAPI Analysis and Product Antioxidant Activity
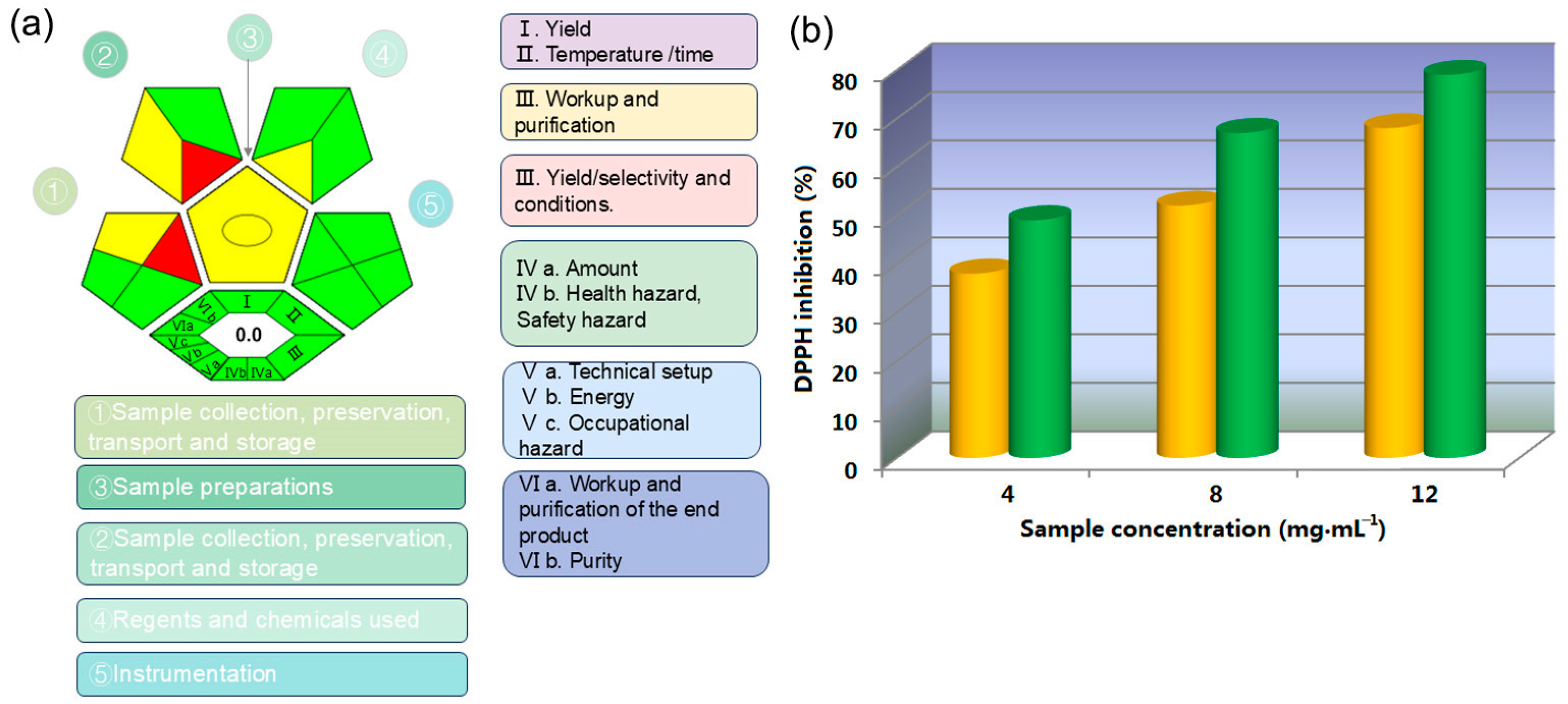
A prominent approach in chemistry is the philosophy of green chemistry, which aims to conduct chemical processes in accordance with the principles of sustainable development. Greenness is a crucial parameter for evaluating experimental methods. The degree of greenness can be assessed through various tools, such as Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and the Green Analytical Procedure Index (GAPI). The ComplexGAPI is a tool that encompasses all aspects of the analytical process, from sample collection, transportation, preservation, and storage to sample preparation and final analysis, also including those aspects and processes conducted prior to general separation methods [46,47]. The creation of ComplexGAPI is based on the same principles that guided the development of GAPI. The analytical results illustrated in Figure 11a demonstrate the eco-friendliness of the entire extraction and separation process, encompassing sample preparation, reagent and chemical usage, and the collection, preservation, transportation, and storage of samples. It can be intuitively observed that this work aligns with the principles of green chemistry under most conditions. Compared to GAPI, ComplexGAPI features an additional hexagonal region at the base of its diagram, symbolizing the “green” attributes of the pre-analytical process. This region encompasses factors such as yield, conditions, reagents, solvents, instrumentation, and the processing and purification of the product. The tool employs a color scale to evaluate the environmental impact at each stage, ranging from green to yellow to red, with green indicating compliance with predefined numerical standards. For instance, when the yield exceeds 89%, its corresponding position in the diagram is displayed in green; for yields between 70% and 89%, the color appears yellow; and for yields below 70%, it is represented in red. The specific evaluation criteria can be found in Table 1 in [46]. By employing green assessment methods, an experimental design can be utilized to minimize or eliminate the use or generation of hazardous substances, facilitating the discovery of techniques and approaches to accelerate chemical reactions with minimal reagent use while achieving equivalent results at the same cost. Additionally, evaluating the life cycle of chemical products—including their design, manufacturing, usage, and ultimate disposal—can help to reduce synthesis steps, increase yields, and enhance plant capacity, all while lowering energy and water consumption. The use of toxic and/or hazardous reagents and solvents can be avoided by substituting them with low-toxicity or non-toxic alternatives, thereby reducing chemical waste generation. In essence, green chemistry analytical tools enable researchers to swiftly identify shortcomings in the processes under consideration and pinpoint critical areas that require attention to mitigate environmental harm and ensure personal safety. In our work, the experimental design was also guided by the principles of green chemistry. We used a method that operates under green solvent conditions at room temperature, featuring high atom economy and recyclability. This approach effectively minimizes environmental pollution and reduces potential impacts on operators. Furthermore, the extracted products using ethanol and [C12mim]Br were compared with their antioxidant activity based on DPPH method [48] (see the details in Section S3 of Supplementary Materials), and the extract using the latter was obtained by back-extraction with methylene chloride and concentration under vacuum. At the levels of three concentrations, the antioxidant activity of [C12mim]Br-based extract is better than that of ethanol-based extract in the high, medium, and low concentrations below 12 mg∙mL−1, which can further prove the significance of IL-enhanced process. In summary, the solubilization effect of ionic liquids has multiple significance and roles in the field of extraction. By the rational utilization of enhanced solubilization, extraction efficiency can be improved and extraction conditions can be optimized, and then application scope can be expanded; as the results, it is beneficial for improving product quality and stability, as well as promoting environmental protection and sustainable development.
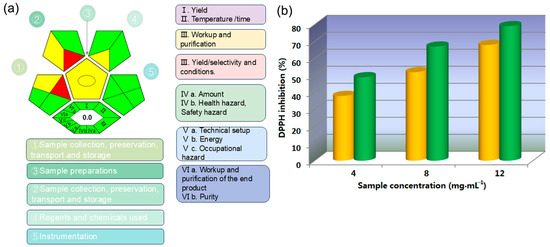
Figure 11.
(a) The greenness of extraction evaluated by ComplexGAPI and (b) antioxidant activities of different extracts (yellow: ethanol extract; green: IL extract).
4. Conclusions
In this study, we determined the critical micelle concentration of imidazolium ionic liquids in water using a conductivity method and calculated the micelle aggregation number using a geometric method. Secondly, the solubility of curcumin in ionic liquid aqueous solution was determined, and the structure of the ionic liquid and the effect of ionic liquid concentration on the solubility of curcumin were explored. The results indicate that the solubilization ability of ionic liquids for curcumin is closely related to their micelle aggregation behavior. The longer the carbon chain and higher the concentration of ionic liquids, the higher the solubility of curcumin. In addition, the size and charge type of the hydrophilic structure of ionic liquid cations also have a certain impact on the solubility of curcumin. At concentrations below the critical micelle concentration, there is an electrostatic interaction between the monomeric ionic liquid and curcumin, leading to the transformation of curcumin from an enol structure to a diketone structure. After reaching the critical micelle concentration, the ionic liquid aggregates to form micelles. Computational chemistry further reveals the key interactions between the two. In ultrasonic extraction, the extraction rate of turmeric-like substances showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase in ionic liquid concentration. The optimal extraction concentrations of [C12mim] Br were 400 mM and 500 mM, respectively. In addition, ideal results were obtained by fitting with the second-order kinetic model, and the rate constant and initial extraction rate during the extraction process were obtained. Finally, ComplexGAPI analysis and product antioxidant activity have also proved the advantage of IL-based extraction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations12020029/s1. Figure S1: 1H NMR profile of [Cnmim]Br (300 MHz, D2O), Figure S2: 1H NMR profile of [CnTr]Br (300 MHz, D2O).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L. and Y.Q.; methodology, D.L.; software, Y.C.; validation, Y.C. and J.L.; formal analysis, J.L.; investigation, D.L.; data curation, Y.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.; writing—review and editing, S.Y.; visualization, J.S.; supervision, S.Y.; project administration, S.Y. and Y.C.; funding acquisition, S.Y. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC1604) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities/Sichuan University-Luzhou Science and Technology Innovation Platform Construction Project (2022CDLZ-20).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
All the authors’ affiliations provided the convenience for related studies, respectively. Special thanks to the Engineering Experimental Teaching Center, School of Chemical Engineering, Sichuan University for related measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Perinelli, D.R.; Cespi, M.; Lorusso, N.; Palmieri, G.F.; Bonacucina, G.; Blasi, P. Surfactant Self-Assembling and Critical Micelle Concentration: One Approach Fits All? Langmuir 2020, 36, 5745–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.D.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, S.A.; Shanker, R.M.; Charman, W.N.; Pouton, C.W.; Porter, C.J.H. Strategies to Address Low Drug Solubility in Discovery and Development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Yagui, C.O.; Pessoa, A.; Tavares, L.C. Micellar solubilization of drugs. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 8, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fayyaz, S.; Talat, R.; Ali, S.; Khalid, N.; Shah, A.; Ullah, F. Synthesis, Characterization, and Micellization Behavior of Cationic Surfactants: N-Alkyl-3-Methylpyridinium Bromides and Their Drug Interaction Study by UV–Visible Spectroscopy and Conductometry. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 22, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M.; Teymoori, F. An insight into effect of micelle-forming surfactants on aqueous solubilization and octanol/water partition coefficient of the drugs gemfibrozil and ibuprofen. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 262, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarov, Z.; Katev, V.; Radeva, D.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D. Micellar solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs: Effect of surfactant and solubilizate molecular structure. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Y.; Cheng, H.L.; Zhao, Y.G.; Cui, H.R. Ionic Liquids in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, C.S.; Cognigni, A.; Schroder, C.; Bica-Schroder, K. Surface-active ionic liquids: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, B.; Medos, Z.; Cognigni, A.; Bica, K.; Chen, L.J.; Bešter-Rogač, M. Thermodynamic study for micellization of imidazolium based surface active ionic liquids in water: Effect of alkyl chain length and anions. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 532, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, D.A.; Gabdrakhmanov, D.R.; Lukashenko, S.S.; Voloshina, A.D.; Sapunova, A.S.; Kulik, N.V.; Nizameev, I.R.; Kadirov, M.K.; Kashapov, R.R.; Zakharova, L.Y. Supramolecular systems based on cationic imidazole-containing amphiphiles bearing hydroxyethyl fragment: Aggregation properties and functional activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zheng, L.Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Inoue, T. Aggregation behavior of long-chain imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution: Micellization and characterization of micelle microenvironment. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar, Q.Q.; Chandawalla, J.; Sawyer, K.; Anderson, J.L. Interfacial and micellar properties of imidazolium-based monocationic and dicationic ionic liquids. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanyur, R.; Biczok, L.; Miskolczy, Z. Micelle formation of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 299, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Ebina, H.; Dong, B.; Zheng, L.Q. Electrical conductivity study on micelle formation of long-chainimidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Li, N.; Zheng, L.Q.; Li, Y.; Inoue, T. Surface adsorption and micelle formation of surface active ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, S.J.; Wang, J.J.; Tang, J.M. Aggregation of ionic liquids [C(n)mim]Br (n = 4, 6, 8, 10, 12) in D2O: A NMR study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirieix-Plenet, J.; Gaillon, L.; Letellier, P. Behaviour of a binary solvent mixture constituted by an amphiphilic ionic liquid, 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide and water Potentiometric and conductimetric studies. Talanta 2004, 63, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, I.; Collier, L.; Millar, S.L.; Prokeš, I.; Lord, J.C.D.; Butts, C.P.; Bowers, J.; Webster, J.R.P.; Heenan, R.K. Structural studies of the phase, aggregation and surface behaviour of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium halide plus water mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 307, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, P.; Wagner, M.; Rossmanith, P. Ionic liquids designed as chaotrope and surfactant for use in protein chemistry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawi, M.A.; Hamdan, I.I.; Sallam, A.A.; Heshmeh, N.A. Solubility enhancement of glibenclamide in choline–tryptophan ionic liquid: Preparation, characterization and mechanism of solubilization. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, H.; Patil, R.; Ray, D.; Aswal, V.K.; Bahadur, P.; Tiwari, S. Structural changes in non-ionic surfactant micelles induced by ionic liquids and application thereof for improved solubilization of quercetin. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, V.; German-Hernandez, M.; Martin-Perez, A.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic Liquid-Based Surfactants in Separation Science. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Pius, A.; Gopi, S.; Gopi, S. Biological activities of curcuminoids, other biomolecules from turmeric and their derivatives—A review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 15, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. The Golden Spice for Life: Turmeric with the Pharmacological Benefits of Curcuminoids Components, Including Curcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin, and Demethoxycurcumins. Curr. Org. Synth. 2024, 21, 665–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Sun, J.; Choe, U.; Chen, P.; Blaustein, R.A.; et al. Chemical Composition of Turmeric (Curcuma longa L. ) Ethanol Extract and Its Antimicrobial Activities and Free Radical Scavenging Capacities. Foods 2024, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar]
- Cornellas, A.; Perez, L.; Comelles, F.; Ribosa, I.; Manresa, A.; Garcia, M.T. Self-aggregation and antimicrobial activity of imidazolium and pyridinium based ionic liquids in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 355, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterno, A.; Fiorenza, R.; Marullo, S.; Musumarra, G.; Scire, S. Prediction of ionic liquid’s heat capacity by means of their in silico principal properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G.F.; Nie, L.R.; Yao, S. Synthesis and characterization of novel hexafluorophosphate salts with tropine-type cations. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Chaudhary, S. Ionic liquids effect on critical micelle concentration of SDS: Conductivity, fluorescence and NMR studies. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 327, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. Development of UV spectrophotometric method for estimation of curcumin in bulk drug and nanogel formulation: A hydrolytic degradation studies. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Anal. 2022, 9, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.Y. Optimization of ionic liquid based ultrasonic assisted extraction of antioxidant compounds from Curcuma longa L. using response surface methodology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Li, Q. Optimization of ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction technique for curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 104, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, M.G.; Svinyarov, I. Ionic liquid-supported solid–liquid extraction of bioactive alkaloids. II. Kinetics, modeling and mechanism of glaucine extraction from Glaucium flavum Cr. (Papaveraceae). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Lim, X.Y.; Chong, C.H.; Mah, S.H.; Chua, B.L. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of natural antioxidants from betel leaves (Piper betle): Extraction kinetics and modeling. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2192–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Del Castillo, J.L.; Czapkiewicz, J.; Rodriguez, J.R. Conductivity, density, and adiabatic compressibility of dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Micelle Shape and Size. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, H.C.; Zhao, Y. Conductivities, volumes, fluorescence, and aggregation behavior of ionic liquids [C(4)mim][BF4] and [C(n)mim]Br(n = 4, 6, 8, 10, 12) in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 6181–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, D. Interfaces and the driving force of hydrophobic assembly. Nature 2005, 437, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Kunjappu, J.T. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F.W. Multiwfn: A Multifunctional Wavefunction Analyzer. J. Comput. Chem 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T. A comprehensive electron wavefunction analysis toolbox for chemists, Multiwfn. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 082503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, Q.X. Independent gradient model based on Hirshfeld partition: A new method for visual study of interactions in chemical systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2022, 43, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhou, Z.L.; Zou, L.; Chi, R. Imidazolium-based ionic liquids with inorganic anions in the extraction of salidroside and tyrosol from Rhodiola: The role of cations and anions on the extraction mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Liu, J.C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, Y. Ultrasonic-enhanced surface-active ionic liquid-based extraction and defoaming for the extraction of psoralen and isopsoralen from Psoralea corylifolia seeds. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Yi, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhou, W.-L.; Li, F.-F. Ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside from Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) with Further Purification by an Aqueous Two-Phase System. Molecules 2015, 20, 17929–17943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Wojnowski, W. Complementary green analytical procedure index (ComplexGAPI) and software. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 8657–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eryan, R.T.; Toubar, S.S.; Ashour, A.A.; Elshahed, M.S. Application of analytical Eco-Scale and Complex-GAPI tools for green assessment of a new simple nanoparticle modified carbon paste electrode method for voltammetric determination of mosapride citrate in pharmaceutical dosage form and human plasma. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, T.; Gülçin, I. Antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of curcumin. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 174, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).