Abstract
Laser-spot-location detection technology based on photodetectors is widely used in the aerospace, medical, military and communication fields. However, most of the current research focuses on continuous laser detection in the visible and near-infrared bands, and the real-time high-precision position detection of a long-wave infrared pulsed laser is lacking. In this paper, a spot-position detection system based on a four-quadrant detector is designed for a 10.6 μm CO2-driven laser in extreme ultraviolet light source, and a second-order extended error compensation algorithm based on a Gaussian-spot model is proposed. Finally, the algorithm is verified and analyzed experimentally by a spot-position detection system under both focusing and defocusing conditions. The experimental results show that the root-mean-square error, maximum absolute error and average absolute error of the second-order error compensation algorithm are significantly reduced compared with the traditional algorithm, and the detection accuracy of the spot-position is better than 9 μm. The above results show that this spot-position detection system has obvious advantages and high accuracy, which can realize the high-precision real-time detection of a laser’s spot position to obtain accurate spot position information, provide feedback adjustments for subsequent beam pointing control, and provide a theoretical basis for the beam pointing stability of the extreme ultraviolet light source system.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, laser derivative technology has been applied to many scientific and technological fields, especially the lithography technology derived from the combination of laser technology and semiconductor technology, which has greatly promoted the development of human science and technology [1]. The emergence of Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography (EUVL) technology has injected new vitality into the semiconductor industry and is expected to promote its continued rapid development. EUVL is a projection lithography technology using extreme ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 13.5 nm as the working wavelength, with an extreme ultraviolet light source being one of the core technologies of EUVL, and it is also one of the last key tasks before the industrialization of EUVL technology [2,3,4,5].
In the EUVL process, the best way to produce extreme ultraviolet light is laser-produced plasma (LPP) [6], that is, a high-power, high repetition frequency, narrow-pulse width CO2 laser is used to bombard a droplet tin-target, which is filtered and collected to produce 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet monochromatic light [7,8,9]. This requires that the driving-laser pointing stability is accurate so that the CO2 laser energy is efficiently concentrated on a tin droplet with a diameter of tens of μm to improve the 13.5 nm optical conversion efficiency. In the extreme ultraviolet lithography light-source system, a CO2 laser can only meet the power requirements of target shooting through main oscillation power amplification (MOPA) technology. When the pulsed laser beam passes through the four-stage amplification system, it causes the laser directivity and the beam center to deviate from the optical axis due to various factors such as vibrations, gas circulation flow and a heat accumulation effect, which seriously affect the EUV conversion efficiency [10]. So, it is necessary to improve the beam pointing stability. The improvement of beam-pointing stability depends on the laser beam collimation technology, and the accurate acquisition of spot position information is a very important part of the laser beam collimation work [11,12]. Therefore, the high-precision position detection of the high repetition-frequency narrow-pulse CO2 laser spot is a key factor in ensuring the spatial accuracy on the tin target of laser-irradiated droplets and improving the EUV conversion efficiency [13].
In recent years, a number of research groups have carried out research on different types of laser-spot location detection technology to meet the needs of accurate spot location information acquisition in different application scenarios. In 2008, Kral L. et al. designed an automatic beam collimation system in which a four-quadrant detector was used to detect the position of a pulsed laser with a wavelength of 1315 nm, a pulse width of 5 ns and a pulse frequency of 10 Hz, making the beam-pointing error less than 10% of the beam diameter [14]. In 2014, Zarko P. et al. of Serbia proposed a new algorithm for obtaining spot shift signals based on the opposite sector of the four-quadrant detector’s photosensitive surface. Their simulation results show that the new algorithm improves the sensitivity of the four-quadrant detector to spot displacement detection, and the sensitivity of the detector center is improved by about √2 times [15]. In 2016, Wu et al. studied the position detection of a 1550 nm continuous laser spot with a four-quadrant detector and proposed an improved integral infinite solution model, which effectively reduced the position detection error for different radii [16]. In 2017, Tang et al. used a four-quadrant detector to detect the position of a 1064 nm continuous laser spot, and proposed a laser-spot-center location algorithm for a four-quadrant detector based on a Gaussian distribution. The experimental results show that the localization accuracy of the proposed algorithm is significantly improved compared with the traditional algorithm [17]. In 2019, Yu et al. used a four-quadrant detector to detect the spot position of a 1550 nm and 125 KHz pulsed laser. Compared with direct measurements, the improved measurement method reduced the root-mean-square error by 51.5% [18]. In 2020, Sun et al. used a spot location detection system based on a multi-unit array detector and a BP neural network position detection algorithm to detect the spot location of a 1550 nm continuous laser, and the experimental results reached the index requirements of the coarse tracking stage and the fine tracking stage of an APT system [19]. In 2020, the laser interference detection system designed by Zhang et al. selected near-, middle- and far-infrared cameras and two-dimensional PSD detectors as the imaging devices in a photoelectric imaging module to detect the position of infrared lasers in different bands, effectively improving the photoelectric detection and tracking accuracy, and achieving better photoelectric countermeasures [20].
In short, the current research on spot location detection mainly focuses on the short-wave or near-infrared band, and there are few studies on long-wave lasers. For the position detection of long-wave lasers, if the long-wave camera is used, there are disadvantages such as a large pixel interval, a low resolution of 10~20 μm, a low frame rate and high cost. At the same time, many studies are focused on continuous lasers, and pulsed lasers have higher requirements for noise suppression and signal extraction. In this paper, we will study the spot location detection technology of a 10.6 μm CO2 laser with a high repetition rate and a narrow pulse based on a four-quadrant detector. This work is a good supplement to the current situation of spot location detection without long-wave pulsed lasers.
In Section 2, the four-quadrant detector principle is introduced and a second-order error compensation algorithm based on a Gaussian spot model is proposed. The noise source and suppression method of the spot position detection system are discussed in Section 3. In Section 4, the synchronous acquisition and processing hardware of the multi-channel signals of the four-quadrant detector is designed to capture, collect and process the output signals of the four-quadrant detector. In Section 5, a spot detection system is built, and the improved spot location algorithm is verified and analyzed. The sixth section is the summary of this paper. The results show that this spot position detection system has obvious superiority, accuracy and practicability, and the accurate spot position information can provide feedback adjustments for the subsequent beam control system, and then provide a theoretical basis for improving the beam pointing stability.
2. Laser Spot Location Algorithm
2.1. Four-Quadrant Detector Spot Detection Principle
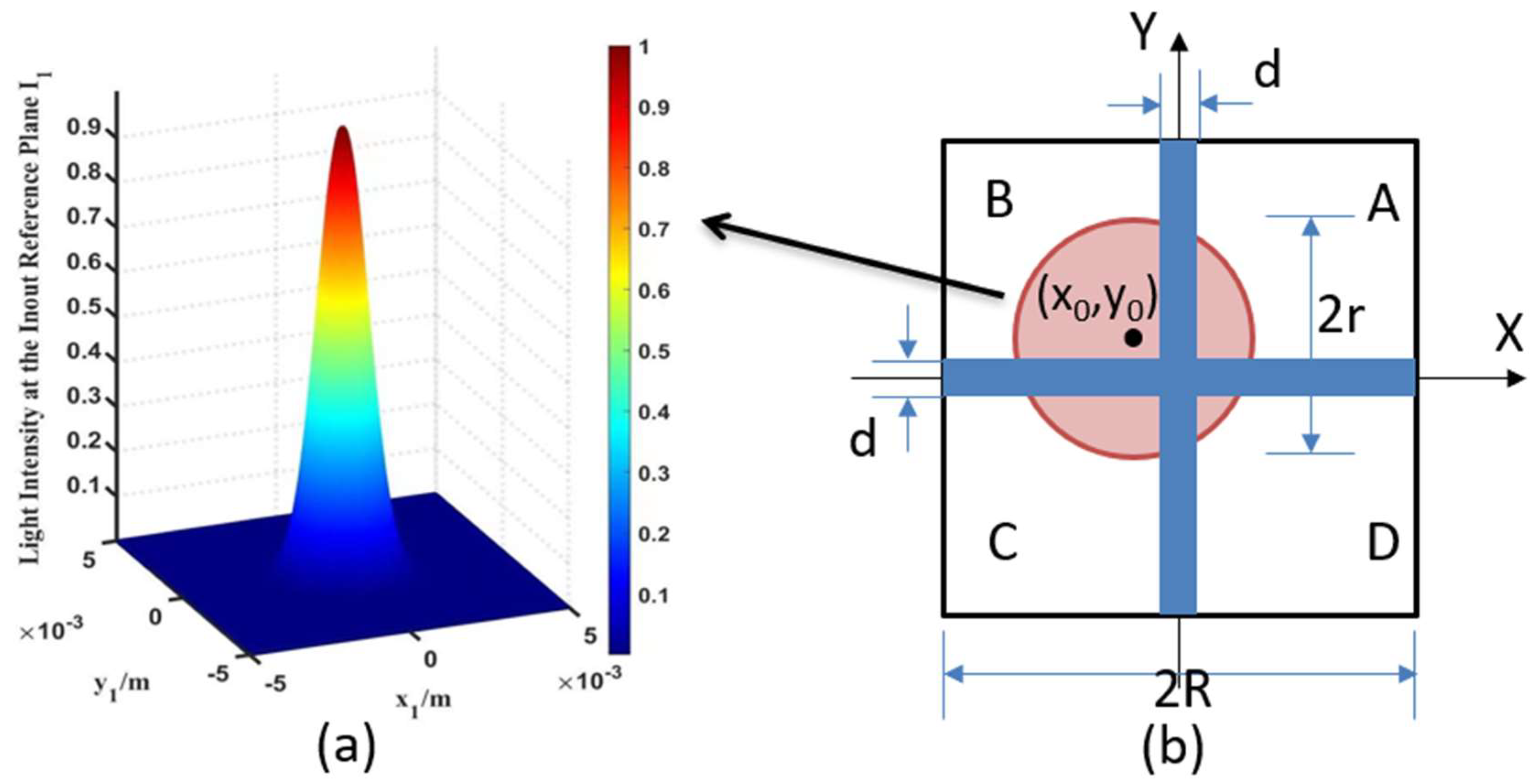
Generally speaking, the energy of the outgoing spot of a common laser has a Gaussian distribution, as shown in Figure 1a. The energy of the spot is strongest at its center, diffusing outward in a circular shape, and gradually weakening.
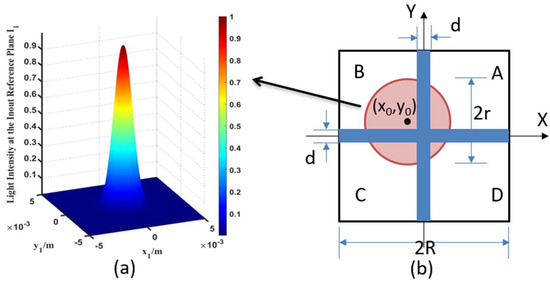
Figure 1.
(a) shows the spot model with a Gaussian energy distribution; (b) Schematic diagram of the photosensitive surface of the four-quadrant detector.
After the laser spot is converged by the optical system, it falls on the photosensitive surface of the detector, and the central position coordinate of the spot is , where represents the illuminance value at the photosensitive surface , then the equivalent probability density function of the spot energy in a two-dimensional Gaussian distribution is:
In this formula, is the illuminance, is the illuminance at the center of the spot, is the radius of the spot, which can reflect the energy decay rate of the Gaussian spot and the actual irradiation range of the spot, which needs to be verified and calibrated by experiments.
A four-quadrant detector is a common position measurement device, which is composed of four identical photodiodes in the form of a four-quadrant distribution. Compared with the other three kinds of photodetectors (a multi-element photodiode array [21], a charge-coupled device (CCD) and a position-sensitive detector (PSD)), the four-quadrant detector has the advantages of a small size, a wide spectral range, a fast response speed, a high position resolution, a high measurement accuracy, simple data processing, etc. It can measure the displacement on the nanoscale at a frequency of kHz. They are commonly used for position measurement and laser collimation, laser tracking and positioning, free-space optical communications, and laser-guided weapons [22].
A four-quadrant detector is a kind of photodetector which uses the photovoltaic effect to convert optical signals into electrical signals and extract information. The basic structure of the photosensitive surface is shown in Figure 1b, and the photosensitive surface is divided into four regions (A, B, C and D) by the dead zone. When the laser irradiates the detector, the four quadrants can independently output the photocurrent, and the current magnitude from each quadrant is proportional to the incident light spot energy. The initial solution of the spot position can be obtained by the normalization and difference algorithm as follows [23,24]:
where , , and are the photocurrents in each quadrant of the four-quadrant detector. is a normalized value, which represents the degree of shift of the spot relative to the center of the four-quadrant detector, but does not represent the actual position of the center of mass of the spot, and there is an S-shaped nonlinear relationship between the two.
In addition, because the energy distribution of the spot and the shape of the detector are symmetrical, the position relationship between the x-axis and the y-axis is relatively independent, and only the x-axis direction is discussed later.
2.2. Error Compensation Algorithm Based on Polynomial Fitting
When the laser is incident on the four-quadrant detector (detector size R, dead zone width d), the relationship between the solution value and the actual position of the centroid of the spot is [25,26,27]:
Equation (3) is a Gaussian spot centroid position detection model including the detector radius and the dead zone width. This equation is a transcendental equation and cannot be solved directly, but it can be rewritten as and expressed by an approximate decomposition as follows:
By combining this with Formula (1), the actual position of the centroid of the spot under the Gaussian spot model can be obtained as:
where is the inverse error function and is a function related to the size of the detector and the width of the dead zone, which plays the role of error compensation for the actual position of the centroid of the spot and is called the error compensation function. Moreover, the spot radius is a constant value in the system. Then, can be simplified as follows:
The error compensation factor is , which compensates the influence of the spot radius, the detector radius and the dead zone width on the actual position of the spot centroid.
The position residual model is constructed via the least-squares method, and the minimum residual between several groups of (, ) data is obtained through experiments. Then, the error compensation factor μ is derived by polynomial fitting, that is, , and then the expression for the spot centroid position based on the error compensation algorithm and based on polynomial fitting is obtained:
where is the fitting order, is the maximum of the fitting order, is the coefficient when the fitting order is and is the coefficient for fitting order . In order to take into account the accuracy of detection and the complexity of the position settlement, a second-order error compensation algorithm is selected for the experiment.
3. Noise Analysis and Suppression Methods
3.1. Noise Sources
The noise sources in the spot position detection system are mainly divided into three parts:
First, when the laser beam is incident on the photosensitive surface of the detector after passing through the optical system, the non-signal light in the working environment will be incident on the photosensitive surface of the four-quadrant detector at the same time as the laser beam, causing it to generate an induced photocurrent, eventually resulting in a larger voltage signal output by the signal acquisition circuit, thus affecting the spot location positioning accuracy of the spot detection system.
Second, when the four-quadrant detector is operating, it generates an induced current corresponding to the incident light signal and introduces some electrical noise. The thermal effect will also affect the generation and movement of carriers in the detector’s photosensitive surface, resulting in the detector’s output current being superimposed with some random current. There are mainly the following types of noise: 1/f noise, generation-compound noise, thermal noise and shot noise. The first two kinds of noise belong to low frequency noise, and with the improvement of the process, their impact can be almost ignored. The power spectral density of thermal noise and shot noise is uniformly distributed and is called white noise.
The output signal of the four-quadrant detector is the photocurrent signal. In order to realize the processing of the weak current pulse signal, it is necessary to use the trans-resistance amplifier to amplify the photocurrent signal. During the operation of the amplifier, the input current, voltage noise and thermal noise caused by the feedback resistance will affect the photocurrent signal output by the detector.
3.2. Noise Suppression Methods
3.2.1. Spot Signal Correction Algorithm Based on Compound Noise
The photosensitive surface of the detector receives the spot information and the photocurrent is generated by the photogenerated volt-effect, which is converted into a voltage signal through the back-end amplification circuit. The output signal of the detector can be expressed as:
where = A, B, C and D representing the four quadrants, is the light signal intensity, is the detector dark current, is the responsivity and is the gain coefficient. In order to eliminate the error introduced by the dark-current noise during position detection, the dark current needs to be calibrated as follows:
- (1)
- If the detector is installed in a dark room environment, then its output voltage can be considered to be generated only by the dark-current noise of the system:
- (2)
- Install the entire detection system in the working environment, but do not turn on the light source. At this point, each quadrant of the detector is illuminated only by ambient light so its output voltage is generated only by background light and dark current, which can be expressed as:
According to the calibration data, in the actual detection, the output voltage in each quadrant after the algorithm correction of the detector’s input signal is as follows:
Through the above calibration and correction process, the influence factors of the detection system can be calibrated quantitatively to suppress the influence of the detector’s dark current and background light.
3.2.2. Filtering Algorithm Based on Gaussian White Noise
The Kalman filter only needs to calculate the current state estimation according to the measurement variables of the previous moment. The amount of data required is small so the data collected can be updated and processed on the spot in real time. The Kalman filter is suitable for real-time processing and computer calculation, and it can be used to filter out the random noise introduced by the detector during operation, such as shot noise and thermal noise.
When the signal acquisition circuit collects the spot signal, noise will be introduced at the same time, so the state space model of the voltage signal is as follows:
Equation of state:
Equation of observation:
where is the voltage value at moment , is the voltage value at moment and is the observed voltage value at moment k. and represent the process excitation noise and observation noise, respectively, and are mainly caused by shot noise and thermal noise.
The main working process of Kalman filtering for spot signals is as follows:
Prediction process:
Calibration process:
where is the voltage value estimated previously, is the voltage at moment k predicted by the voltage at moment , is the further predicted value of the voltage, is the Kalman gain coefficient, is the prior prediction covariance, is the posterior prediction covariance, is the process excitation noise covariance matrix and R is the observation noise covariance matrix. In the process of collecting the output signal of the detector, the state process of the signal and the prediction process are independent of each other, so Q and R can be initialized into a diagonal matrix, and better filtering results can be obtained by optimizing the ratio of the two.
3.3. Noise Suppression Test
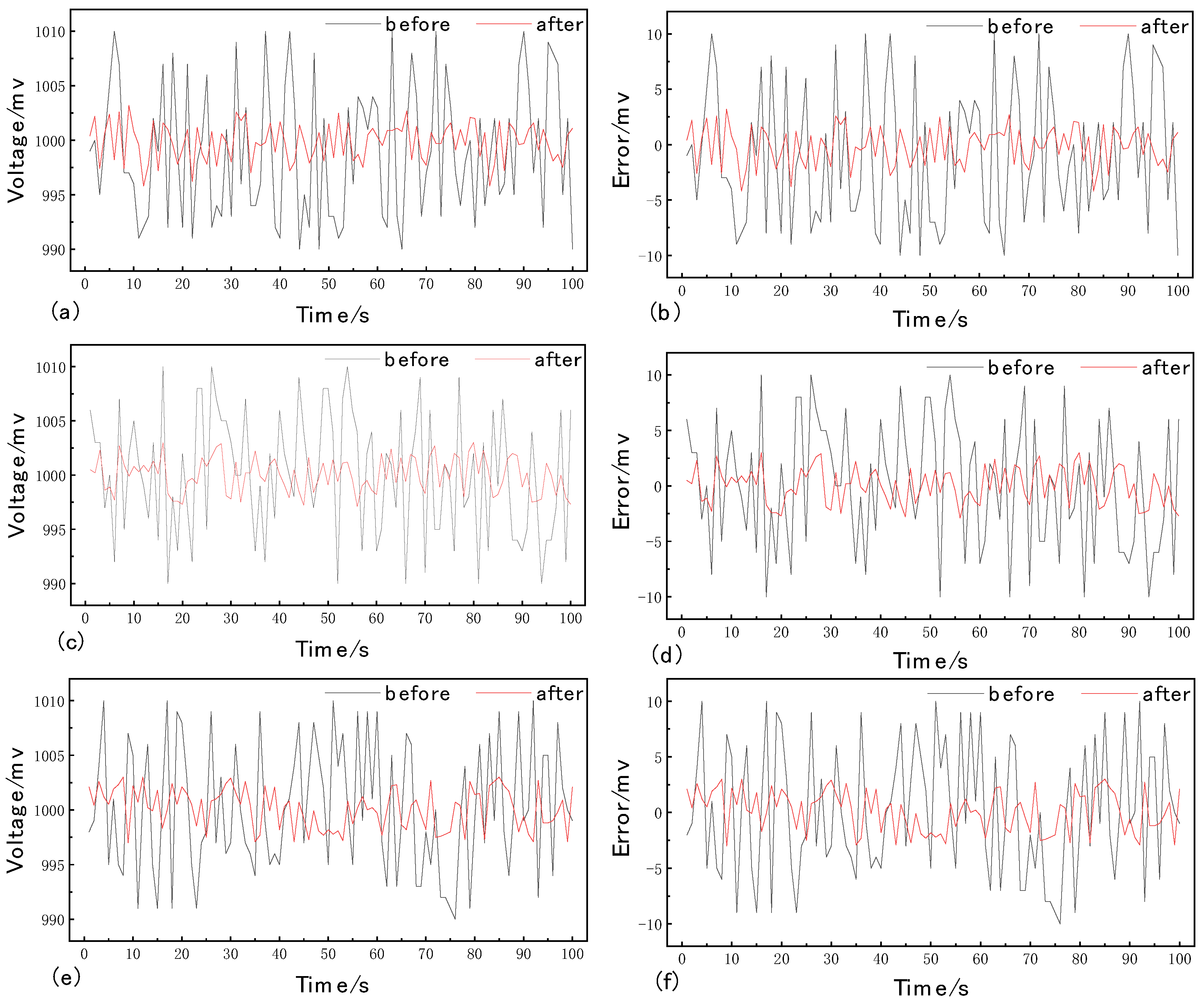
In order to test the effect of the spot signal correction algorithm and the Kalman filter on noise suppression, this paper tests the algorithm based on the experimental platform of spot position detection. After the appropriate laser spot parameters are adjusted, the laser spot is incident on the center of the detector’s photosensitive surface, and three sets of data are randomly collected for the output signal of the four-quadrant detector within 15 min, with 1000 data points selected for each group. The data processing results are shown in Figure 2: (a) and (b) are the first set of data results and errors; (c) and (d) are the second set of data results and errors; and (e) and (f) are the third set of data results and errors. Through the comparison of the experimental data curves, it can be seen that after the filtering algorithm, the root-mean-square error of the three groups of data is reduced by 71.76%, 71.27% and 68.30%, respectively, and the stability of the output signal of the four-quadrant detector has been significantly improved, and the signal can be kept stable for a long time.
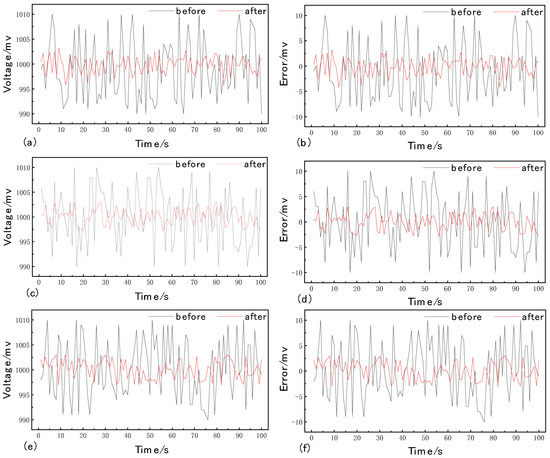
Figure 2.
Statistics of the noise suppression results.
4. Building the Spot Position Detection System Platform
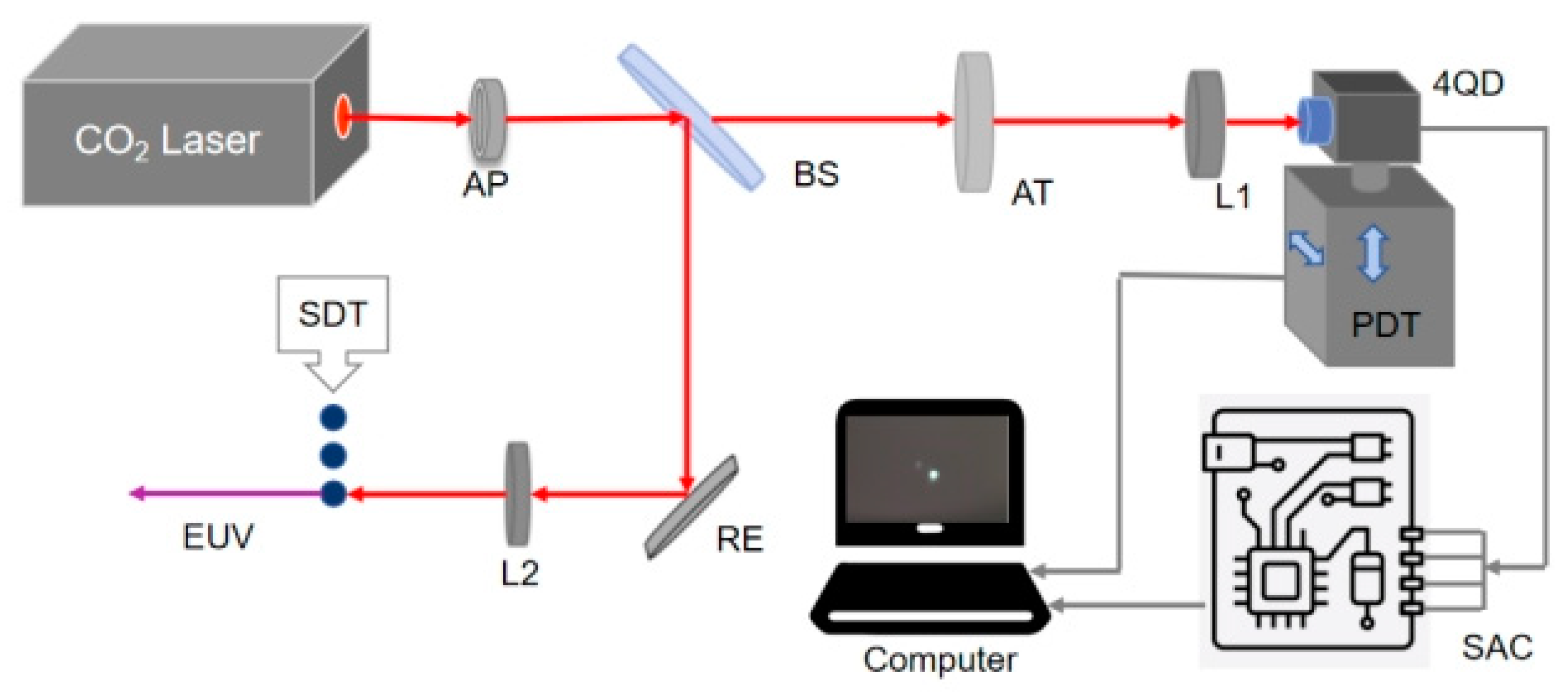
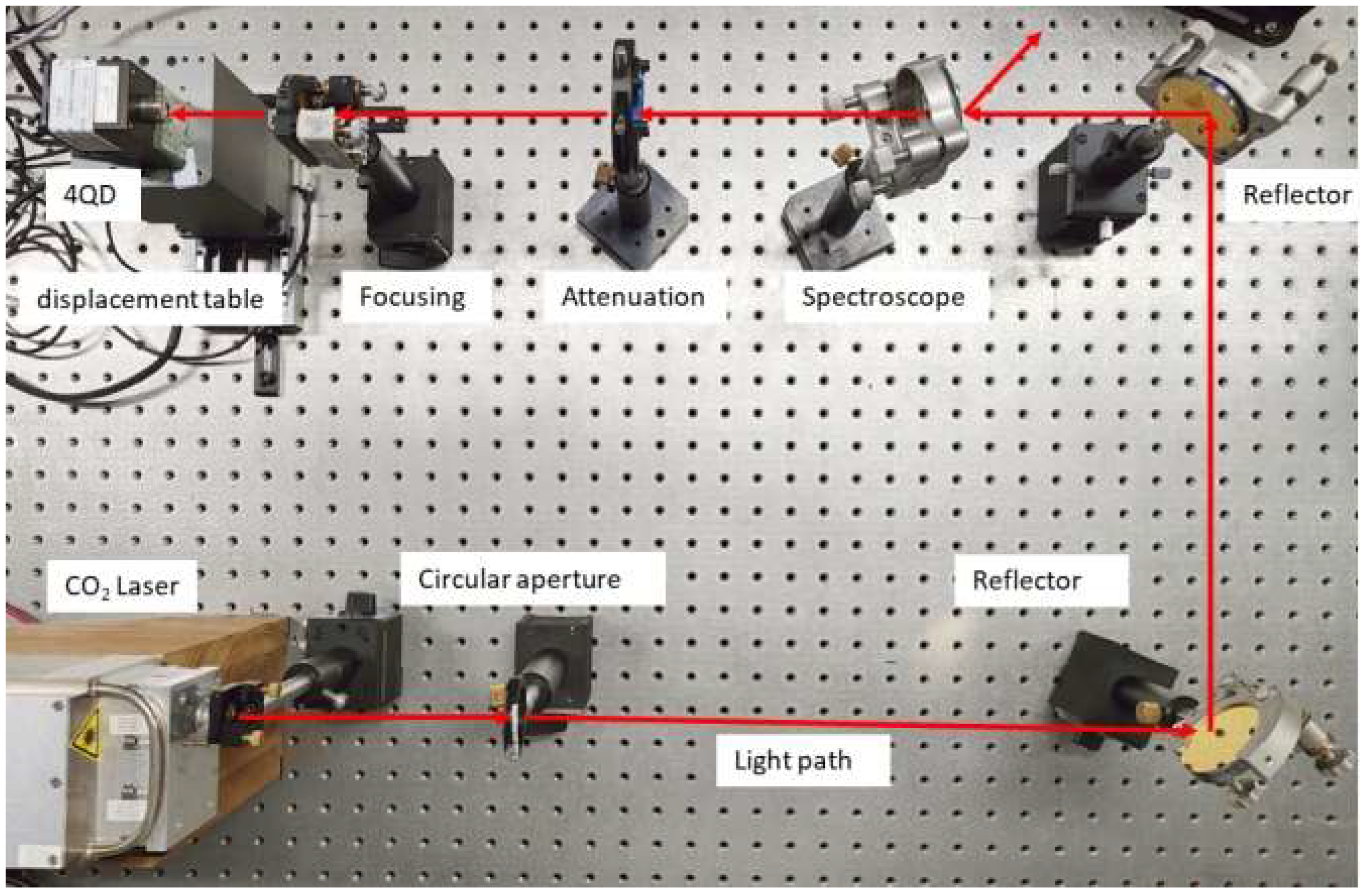
In order to verify the accuracy and practicability of the spot position resolution algorithm, a spot position detection system based on a four-quadrant detector is built in this paper. The optical circuit schematic diagram is shown in Figure 3, where the red signal line represents the transmission of optical signals and the black signal line represents the transmission of electrical signals. The detection system mainly consists of a light source, an optical convergence system and a spot acquisition and position solving system. Of these, the optical convergence system mainly includes a circular aperture (AP), a beam splitter (BS), an attenuator (AT) and a focusing mirror (L1). The spot acquisition and position calculation system includes a four-quadrant detector (4QD), a precision displacement table (PDT), a signal acquisition circuit (SAC), a DSP controller and a computer. The light source used in the experiment is a pumped CO2 laser in the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source system, with a wavelength of 10.6 μm. It is produced by Nanjing Chenrui Tengjing Laser Technology Co., LTD and its model is CR60L. The lens material used in this band experiment is ZnSe. The spectroscope, as the main optical system, has a splitting ratio of R:T = 99:1, which ensures that 99% of the beam is used for the subsequent target work of the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source, and 1% of the transmitted beam is used for real-time spot location detection. In total, 99% of the beam passes through a 10.6 μm reflector (RE) and an optical lens (L2), and then accurately irradiates the Sn droplet target (SDT) to produce extreme ultraviolet light. In the experiment, the laser beam passes through a circular diaphragm with a diameter of 3 mm to control the incidence range of the light, avoid the scattering and interference of the light, and make the light propagate in the optical system according to the requirements for improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the system, and to adjust the shape of the spot to be close to the circle to improve the accuracy of the four-quadrant detector. The four-quadrant detector in the spot position detection system is made by Vigo System S.A., with model number PCQ-4TE-12/QIP-10k-100M-M4. The precision displacement table used in the experiment is produced by Sanying Precision Control Instrument Equipment Co., LTD., which includes an ETSL-100G micro-precision electronic control translation table and an EVSL-50G micro-precision electronic control lifting table. The resolution of the PDT is 0.1 μm and the repeated positioning accuracy is ±0.3 μm.
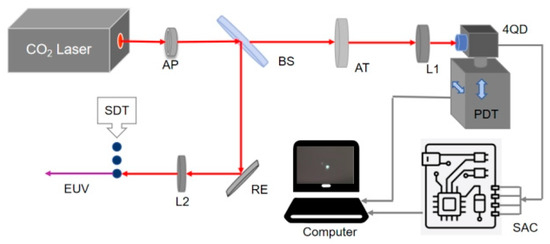
Figure 3.
Optical path principle of the high precision position detection system based on a driven laser spot of extreme ultraviolet light source.
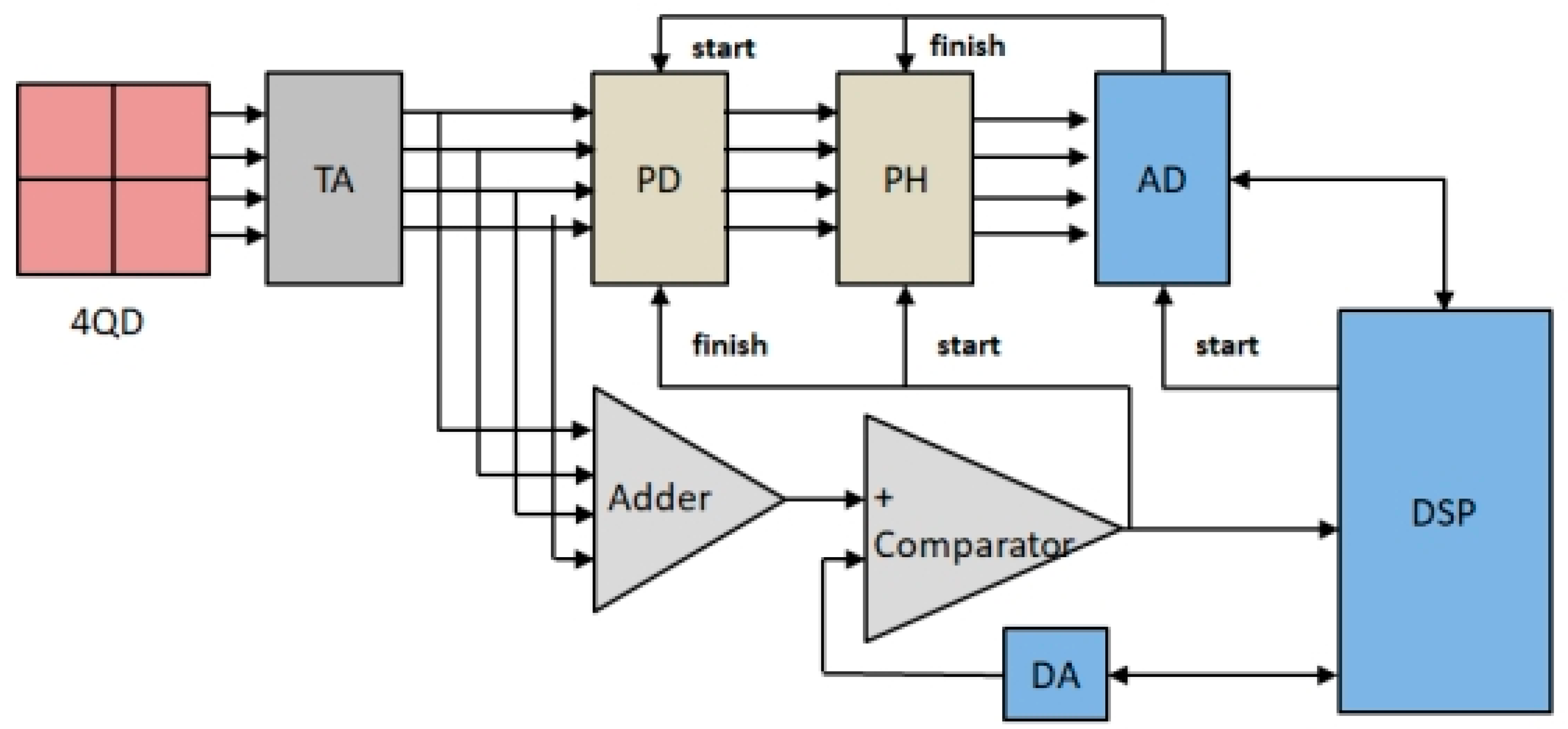
According to the detection principle of the four-quadrant detector, it is necessary to ensure that the output electrical signals from the four quadrants of the detector are obtained at the same time as the collection of the output electrical signals from each quadrant affects the resolution accuracy of the spot position. Therefore, this paper designs a multi-channel synchronous acquisition and processing circuit for the acquisition of detector output signals to ensure the accuracy and real-time performance of the acquisition signals. The multi-channel synchronous acquisition and processing circuit mainly includes a control circuit, a pulse detection and holding circuit, a comparison circuit, etc. The hardware block diagram is shown in Figure 4.
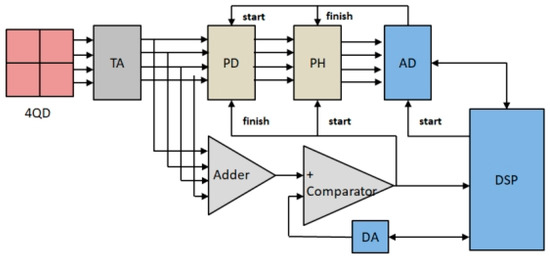
Figure 4.
Hardware schematic diagram of the multi-channel synchronous acquisition and processing circuit.
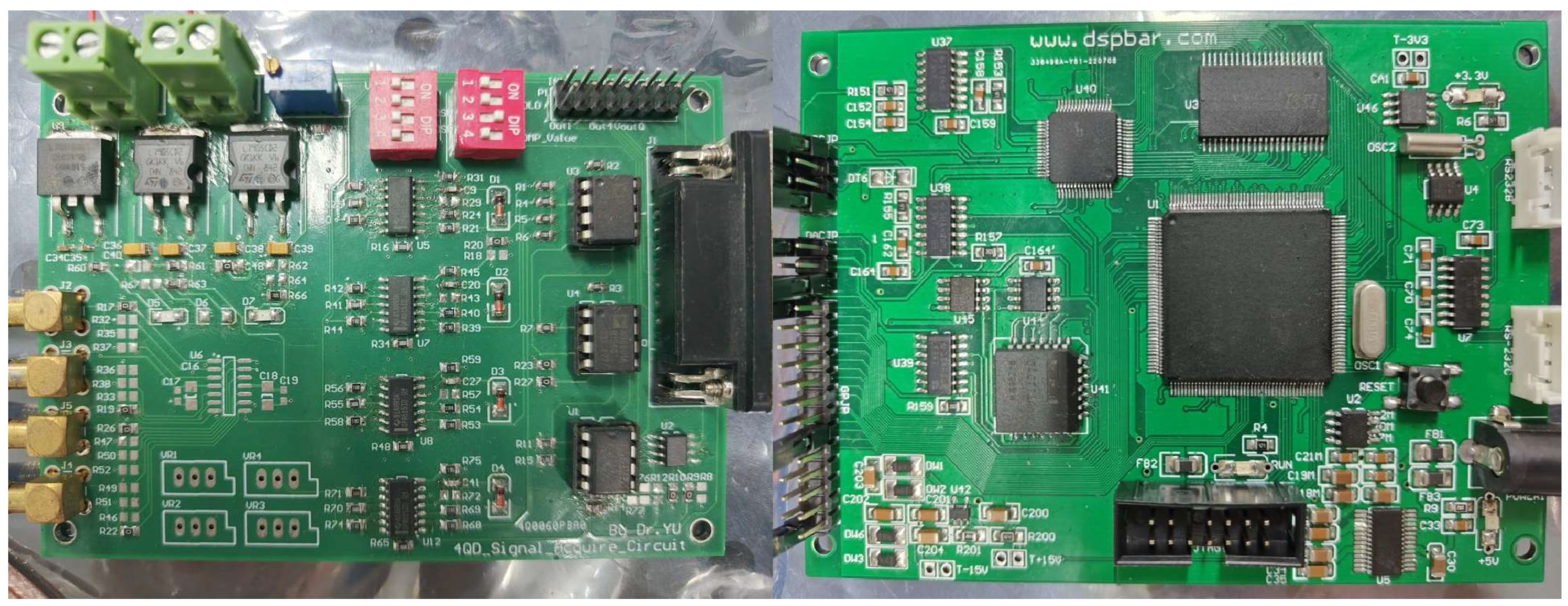
A physical image of the multi-channel synchronous acquisition and processing circuit is shown in Figure 5. The four-quadrant detector multi-channel synchronous signal acquisition and processing process begins with the four-channel transimpedance amplification (TA) circuit integrated within the four-quadrant detector converting the charge generated by the laser signal detected in each quadrant into a voltage signal. After amplifying each signal with the multi-channel operational amplifier, each signal is summed up and compared with the voltage set at the negative end of the high-speed comparator. When the control terminal detects that the accumulated voltage value of the four detection signals exceeds the set threshold, the pulse detection (PD) circuit stops operating, and the pulse hold (PH) circuit starts to maintain the pulse signal state. Then, the four-channel synchronous analog-to-digital conversion (AD) chip starts to convert the analog pulse signal into a digital signal. When the conversion on the AD chip is detected, the pulse holding circuit will discharge the stored charge and start to detect and hold the next pulse signal. Finally, the digital information of the collected spot position is uploaded to the DSP, and the spot centroid position of the laser beam is calculated by the spot position solving algorithm.

Figure 5.
Physical picture of the multi-channel synchronous acquisition hardware.
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
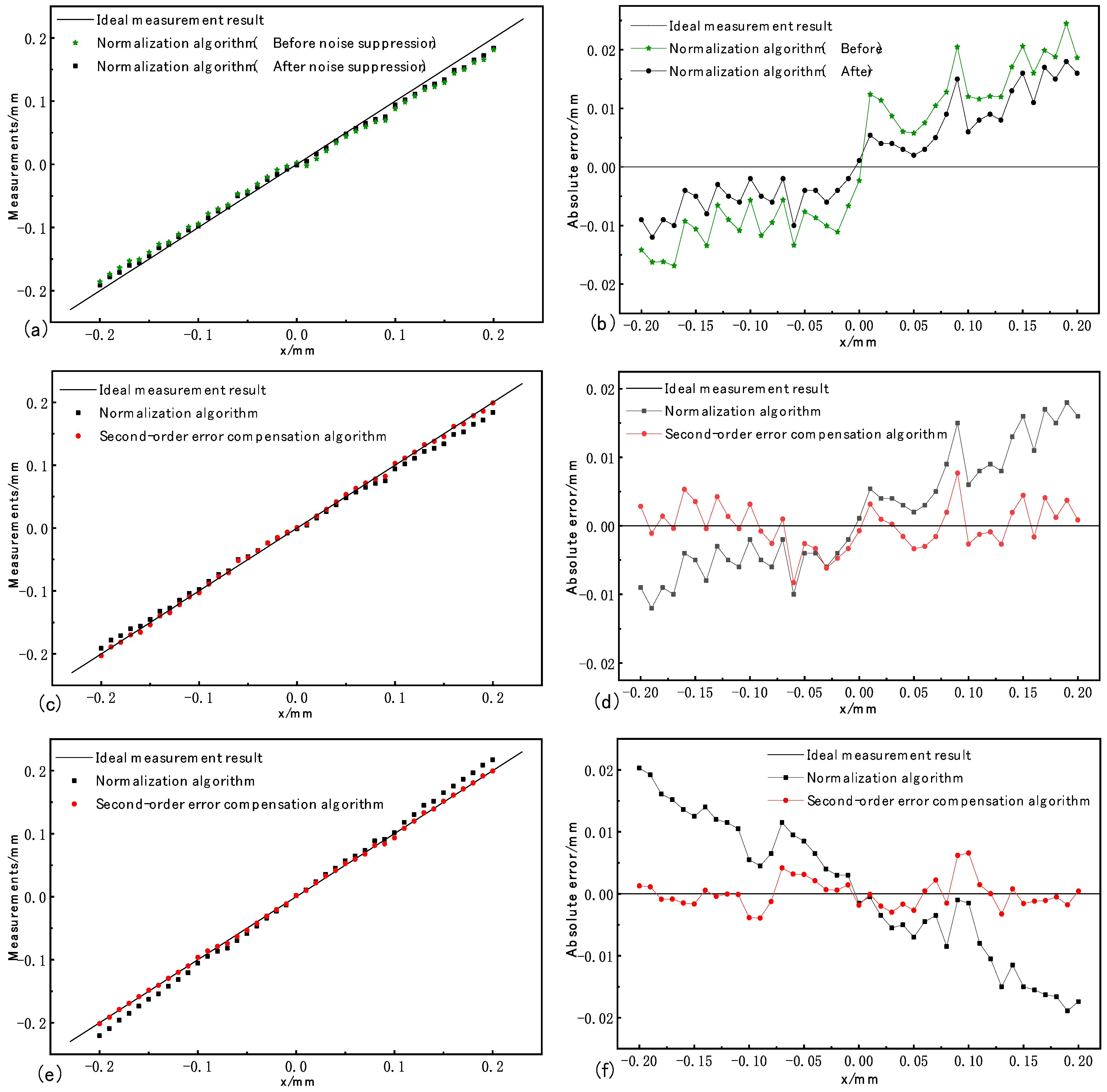
The actual optical path diagram of the spot position detection system is shown in Figure 6. The specific parameters of the emitting laser light source are: wavelength, 10.6 μm; frequency, 1 KHz; pulse width, 200 ns; power, 1.9 w; and spot diameter, 3 mm. The attenuation rate of the attenuator is 1/10. Since the size of each pixel of the four-quadrant detector is 0.25 mm × 0.25 mm, a focusing mirror with a size of 2.54 cm and a focal length of 50 mm is added. In the focus position, the spot diameter is adjusted to 0.28 mm, and the laser power is 0.01 w. At 2 mm of positive defocus, the spot diameter is adjusted to 0.32 mm and the laser power to 0.008 w. The incident laser of the detector meets the requirement. After the adjustment of the spot position detection system, experiments were carried out under the conditions of zero focus and defocus. By moving the displacement table, the four-quadrant detector was controlled to move from −0.20 mm ≤ x ≤ 0 mm to 0 mm ≤ x ≤ 0.20 mm with a moving interval of 0.01 mm. By collecting the output voltage of the four-quadrant detector, the one-to-one corresponding value between the actual displacement of the spot position and the initial solution of the spot position of the normalized algorithm can be obtained. Meanwhile, the second-order error compensation algorithm is used to solve the initial solution of the spot position, and the measured value of the spot position analysis algorithm can be obtained. The above experimental results are shown in Figure 7.
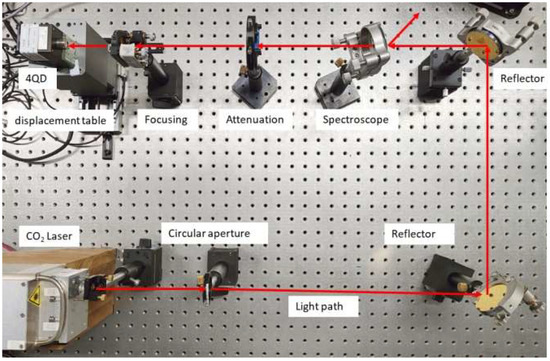
Figure 6.
Actual optical path diagram of the spot position detection system.
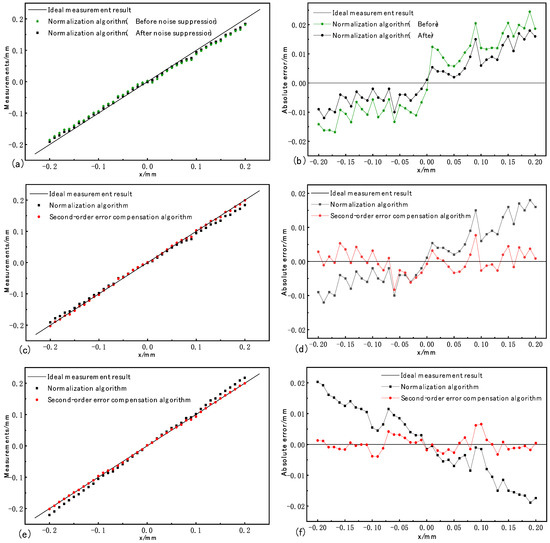
Figure 7.
Statistics of the experimental results.
The spot position detection results are analyzed as follows: Figure 7a,b show the comparison of measurement results and errors before and after filtering using the normalization algorithm at the focal point; (c) and (d) represent the measurement results and errors obtained at the first group of focal points; and (e) and (f) correspond to the measurement results and errors acquired at the second set of defocuses. It can be seen from (c) and (e) that the second-order error compensation algorithm has significantly improved the linearity compared with the normalized algorithm.
At the focal point, the spot position detection error obtained by the normalization algorithm before and after the noise suppression is shown in Figure 7b. The root-mean-square error before noise suppression is 0.0129, and the root-mean-square error after noise suppression is 0.0087, a reduction of 32.56%. The maximum absolute error before noise suppression is 0.024 mm and after noise suppression is 0.018 mm, which is reduced by 25%. The average absolute error before noise suppression is 0.0123 mm, and the average absolute error after noise suppression is 0.0074 mm, a reduction of 39.84%.
The spot position detection errors obtained by the normalization algorithm and the second-order error compensation algorithm at the focal point are shown in Figure 7d. The root-mean-square error of the normalized algorithm and the second-order error compensation algorithm are 0.0087 and 0.0032, respectively, which are reduced by 63.21% compared with the original result. The maximum absolute error of the normalized algorithm is 0.018 mm, and that of the second-order error compensation algorithm is 0.0083 mm, which is reduced by 53.89% compared with the original result. The average absolute error of the normalized algorithm is 0.0074 mm, while the average absolute error of the second-order error compensation algorithm is reduced by 0.0018 mm, which is 75.68% lower than the original result.
The spot position detection errors obtained by the normalization algorithm and the second-order error compensation algorithm at the focal point are shown in Figure 7f. The root-mean-square error of the normalized algorithm and the second-order error compensation algorithm are 0.0111 and 0.0023, respectively, which are reduced by 79.28% compared with the original result. The maximum absolute error of the normalized algorithm is 0.0203 mm, and that of the second-order error compensation algorithm is 0.0066 mm, which is reduced by 67.49% compared with the original result. The average absolute error of the normalized algorithm is 0.0096 mm, while the average absolute error of the second-order error compensation algorithm is reduced by 0.0026 mm, which is 72.92% lower than the original result.
Through the above experimental results, we can summarize as follows:
- (1)
- The noise suppression method used in this paper has a good suppression effect on the noise in the spot detection system, and the detection error is significantly reduced.
- (2)
- Compared with the defocusing case, the spot position detection error obtained by the normalization algorithm in the case of focusing is smaller, which is consistent with the conclusion that the spot diameter is smaller when it is close to the radius of the photosensitive surface.
- (3)
- Under both focusing and defocusing conditions, the detection error obtained by the second-order error compensation algorithm is significantly reduced compared with the normalized algorithm, which shows the superiority of the second-order error compensation algorithm.
- (4)
- It can be concluded that when the spot center is within the detection range of −0.20 mm ≤ x ≤ 0.20 mm, the detection accuracy of the spot position detection system is lower than 9 μm under both focusing and defocusing conditions.
6. Conclusions
In summary, aiming at the current situation where there is little research on real-time high-precision position detection based on long-wave infrared pulsed lasers, this paper carried out a high-precision position detection research based on 10.6 μm CO2 driven laser in extreme ultraviolet light source. In this paper, a second-order error compensation algorithm for laser spot position detection based on a Gaussian distribution is proposed, and a spot location detection system based on a four-quadrant detector is built. The experimental verification and analysis of this algorithm under both focusing and defocusing conditions shows that compared with the traditional normalization algorithm, the second-order error compensation algorithm proposed in this paper greatly improves the positioning accuracy, and the detection accuracy of the spot position is lower than 9 μm. Moreover, the increase in algorithmic complexity is small, and the DSP controller can realize real-time processing. The spot solution algorithm and spot location detection system have obvious advantages and practicability.
In conclusion, the spot position detection system designed in this paper based on the four-quadrant detector can realize the high-precision detection of a CO2 laser, address the lack of research on far-infrared pulsed lasers in the current spot position detection research, and provide an accurate adjustment amount for the subsequent beam pointing control, which is of great significance for improving the beam pointing stability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Y.; methodology, R.B. and D.Y.; software, R.B. and J.X.; validation, R.B., J.X. and R.Z.; formal analysis, R.B.; investigation, R.B.; resources, F.C., D.Y. and Q.P.; data curation, R.B.; writing—original draft preparation, R.B.; writing—review and editing, R.B. and D.Y.; visualization, R.B. and Z.L.; supervision, F.C., D.Y. and Q.P.; project administration, D.Y. and Q.P.; funding acquisition, F.C., D.Y. and Q.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62104223, Grant No. 62335016).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Li, J.; Yan, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J.; Guo, H.; Qu, L. Nanoscale multi-beam lithography of photonic crystals with ultrafast laser. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.P.; Sun, C.K.; Lin, J.Q. Laser-produced plasma light source for extreme ultraviolet lithography. Chin. Opt. 2013, 6, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante, C.; Principi, E.; Marini, A.; Batignani, G.; Fumero, G.; Virga, A.; Foglia, L.; Mincigrucci, R.; Simoncig, A.; Spezzani, C.; et al. Non-linear self-driven spectral tuning of Extreme Ultraviolet Femtosecond Pulses in monoatomic materials. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, N.; Hu, W.M.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, S.J.; Bo, Y.; Peng, Q.J.; Xu, Z.Y. Research progress on laser produced plasma light source for 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet lithography. Chin. Opt. 2020, 13, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Peng, Y.; Leng, Y. Research progress and development trend of extreme ultraviolet lithography sources. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2022, 59, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, F. Experimental Study on the Temporal Evolution Parameters of Laser–Produced Tin Plasma under Different Laser Pulse Energies for LPP–EUV Source. Photonics 2023, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.Y.; Deng, C.M.; Wu, Y.Q. Research progress of extreme ultraviolet lithography materials. Infrared Laser Eng. 2014, 43, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.R. Research on Short Pulse CO2 Laser Amplification and Noise Light Isolation Technology; Changchun Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Changchun, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, T. Development progress of extreme ultraviolet lithography. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2002, 12, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tuitje, F.; Gil, P.M.; Helk, T.; Gautier, J.; Tissandier, F.; Goddet, J.-P.; Guggenmos, A.; Kleineberg, U.; Sebban, S.; Oliva, E.; et al. Nonlinear ionization dynamics of hot dense plasma observed in a laser-plasma amplifier. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boge, R.; Horáček, J.; Mazůrek, P.; Naylon, J.A.; Green, J.T.; Hubka, Z.; Šobr, V.; Novák, J.; Batysta, F.; Antipenkov, R.; et al. Robust method for long-term energy and pointing stabilization of high energy, high average power solid state lasers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 023113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Yu, D.Y.; Pan, Q.K. Beam pointing stability of extreme ultraviolet lithography light source system. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 58, 1714004. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Florian, C.; Arnold, C.B. Single-lens dynamic z-scanning for simultaneous in situ position detection and laser processing focus control. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, L. Automatic beam alignment system for a pulsed infrared laser. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 013102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarić, Ž.P.; Manojlović, S.M.; Bondžulić, B.P.; Andrić, M.S.; Mitrović, S.T. New relationship of displacement signal at quadrant photodiode: Control signal analysis and simulation of a laser tracker. Optik 2014, 125, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, Z. Research on high-precision near-infrared spot location detection model. Infrared Laser Eng. 2016, 45, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Gu, G.; Qian, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J. Laser spot center location algorithm based on Gaussian distribution for four-quadrant detector. Infrared Laser Eng. 2017, 46, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, G.; He, D.; Xu, S.; Xia, Y.; Huang, Y. High-Precision Light Spot Position Detection in Low SNR Condition Based on Quadrant Detector. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Research on Spot Location Detection Technology of Space Laser Communication Based on Array Detector; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, CAS): Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Based on PSD and Laser Interference Detection and Assessment of the CCD; Xi’an University of Electronic Science and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Zheng, Q.; Yu, C.; Huang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Xiong, Y.; Kong, C.; Ye, L.; et al. A High-Performance ε-Ga2O3-Based Deep-Ultraviolet Photodetector Array for Solar-Blind Imaging. Materials 2022, 16, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.Y.; Liang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, X. Principle and research progress of spot detection with four-quadrant detector. J. Appl. Opt. 2023, 44, 927–942. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.Y. Research on Key Technologies of Laser Positioning System Based on Four-Quadrant Detector; Xi’an University of Technology: Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Song, Y.H. Laser direction finding device and application. Electro-Opt. Technol. Appl. 2017, 32, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Luan, X.; Wang, F.; Xue, Q. An improvement to the infinite integration method Based on quadrant detector. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167, 109681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. High-precision spot positioning algorithm based on four-quadrant detector. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1633, 012122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Mao, C.; Wu, C.; Peng, X.; Wan, M.; Ren, K.; Gu, G.; Chen, Q.; Qian, W. A calibration and correction method for the measurement system based on four-quadrant detector. Optik 2020, 204, 164226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).