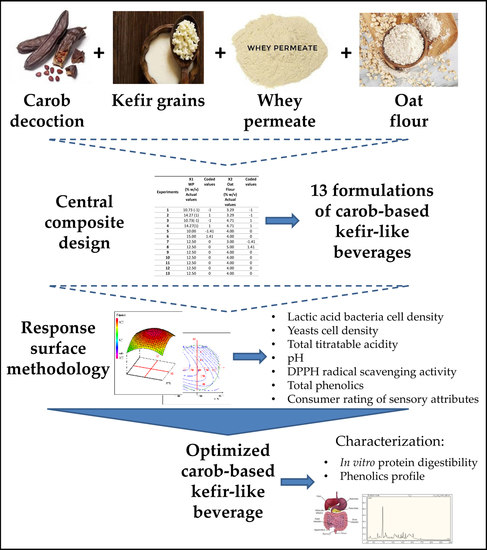
Functional Exploitation of Carob, Oat Flour, and Whey Permeate as Substrates for a Novel Kefir-Like Fermented Beverage: An Optimized Formulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and KEFIR Grains
2.2. KLB Preparation
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Determination of pH and TTA
2.5. Microbiological Analyses
2.6. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds (TPC)
2.7. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.8. Consumer Rating of Sensory Attributes
2.9. Analyses of Phenolics Profiles
2.10. In Vitro Protein Digestibility
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
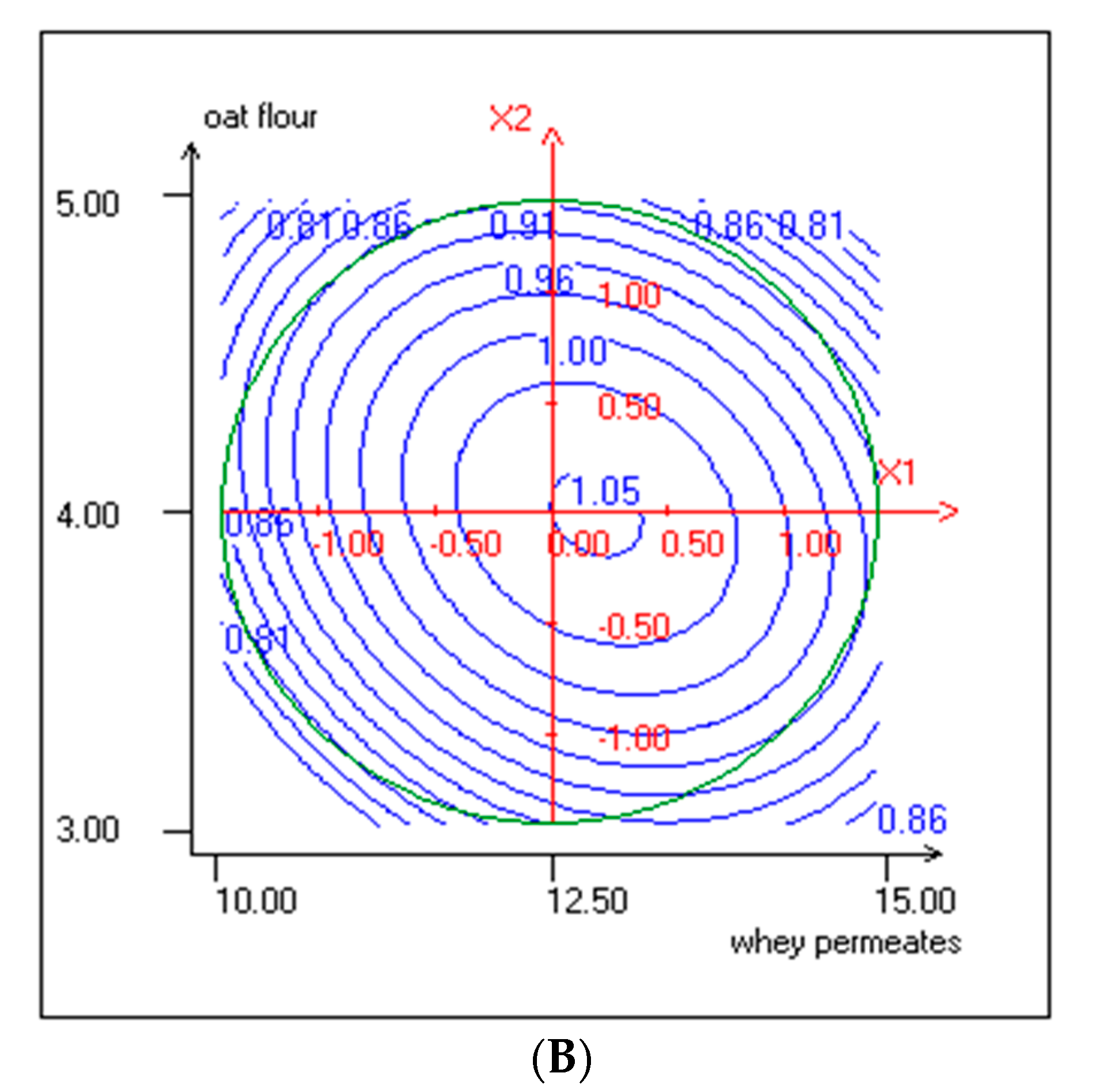
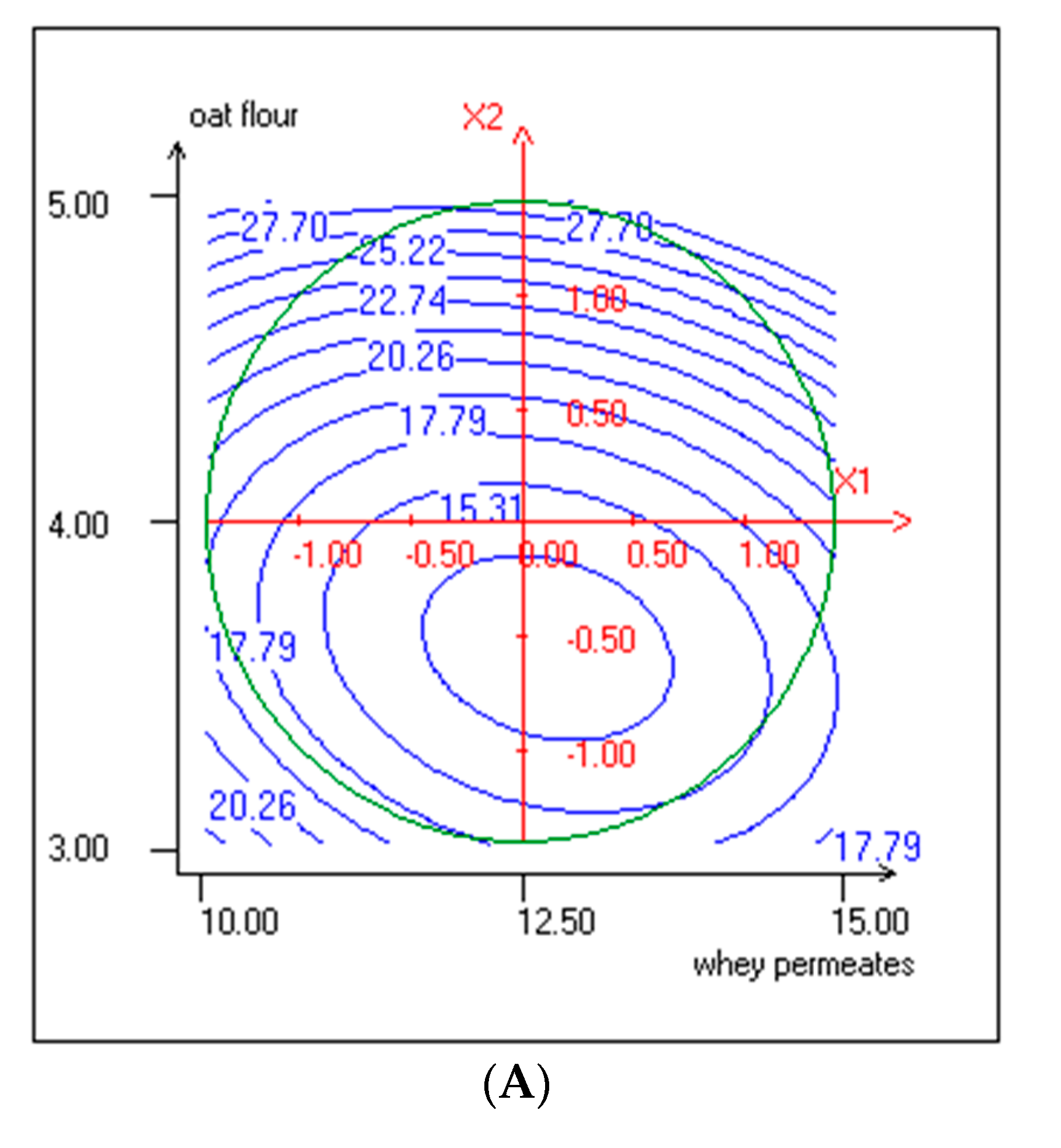
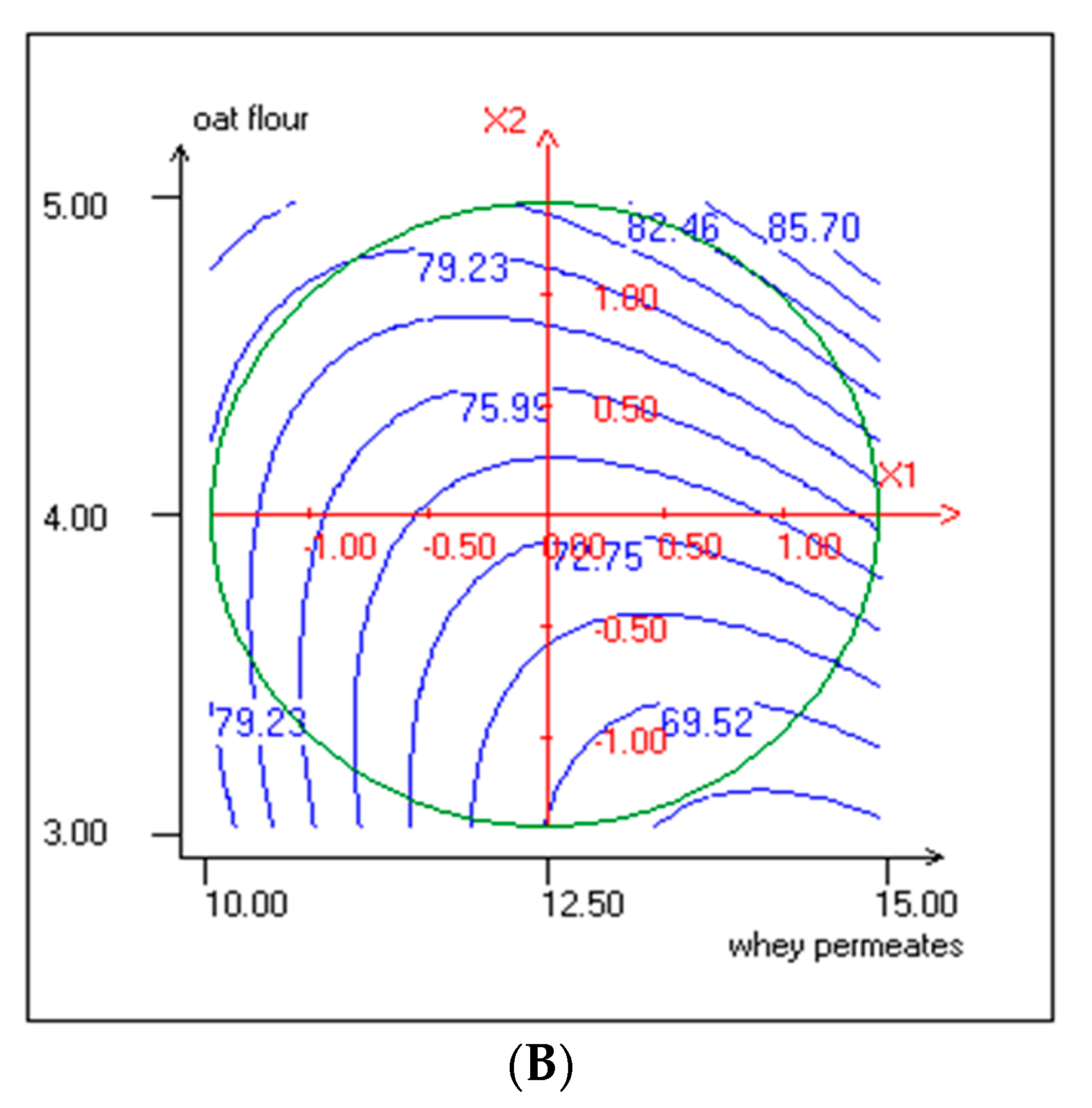
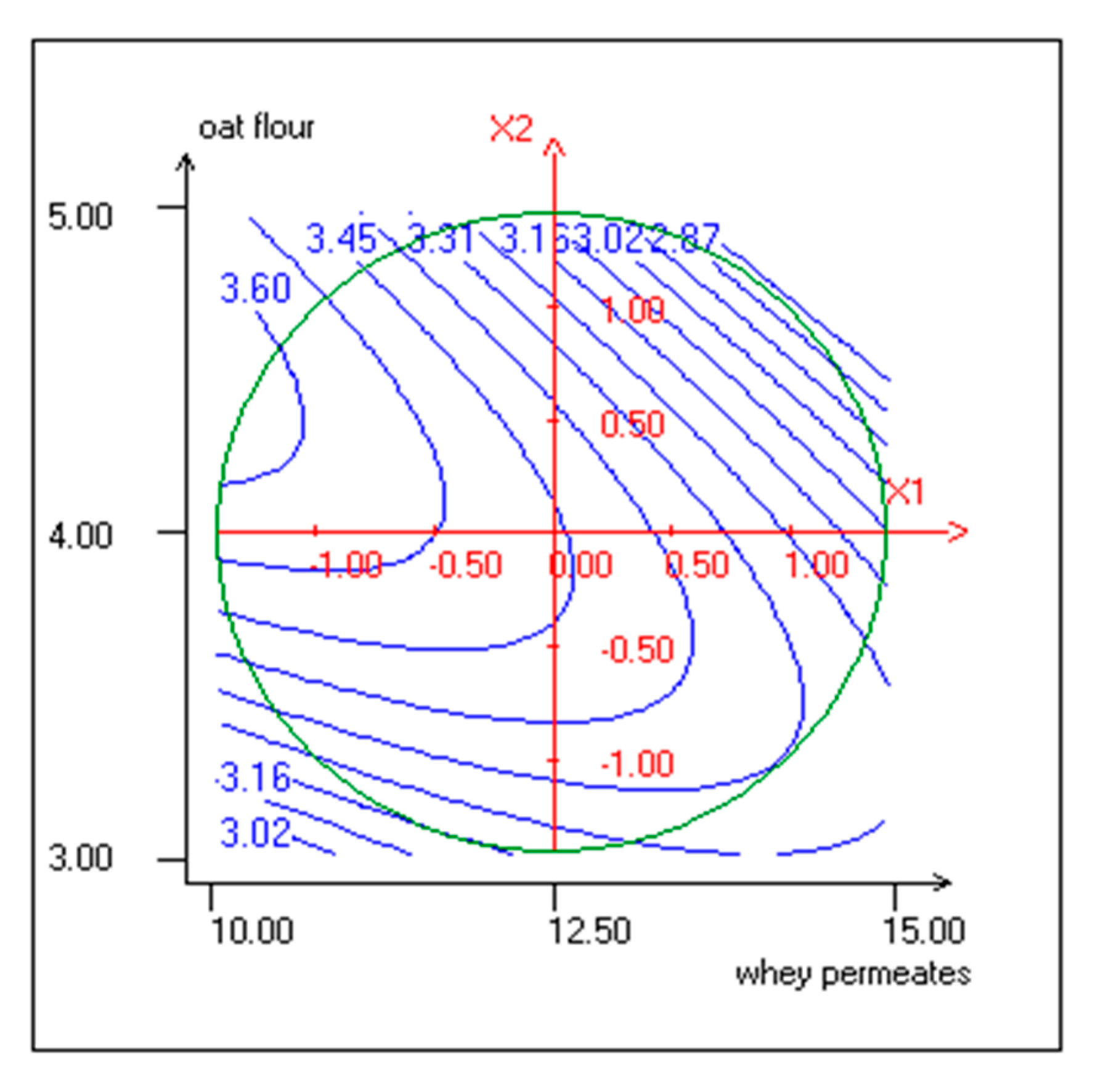
3.1. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Implementation
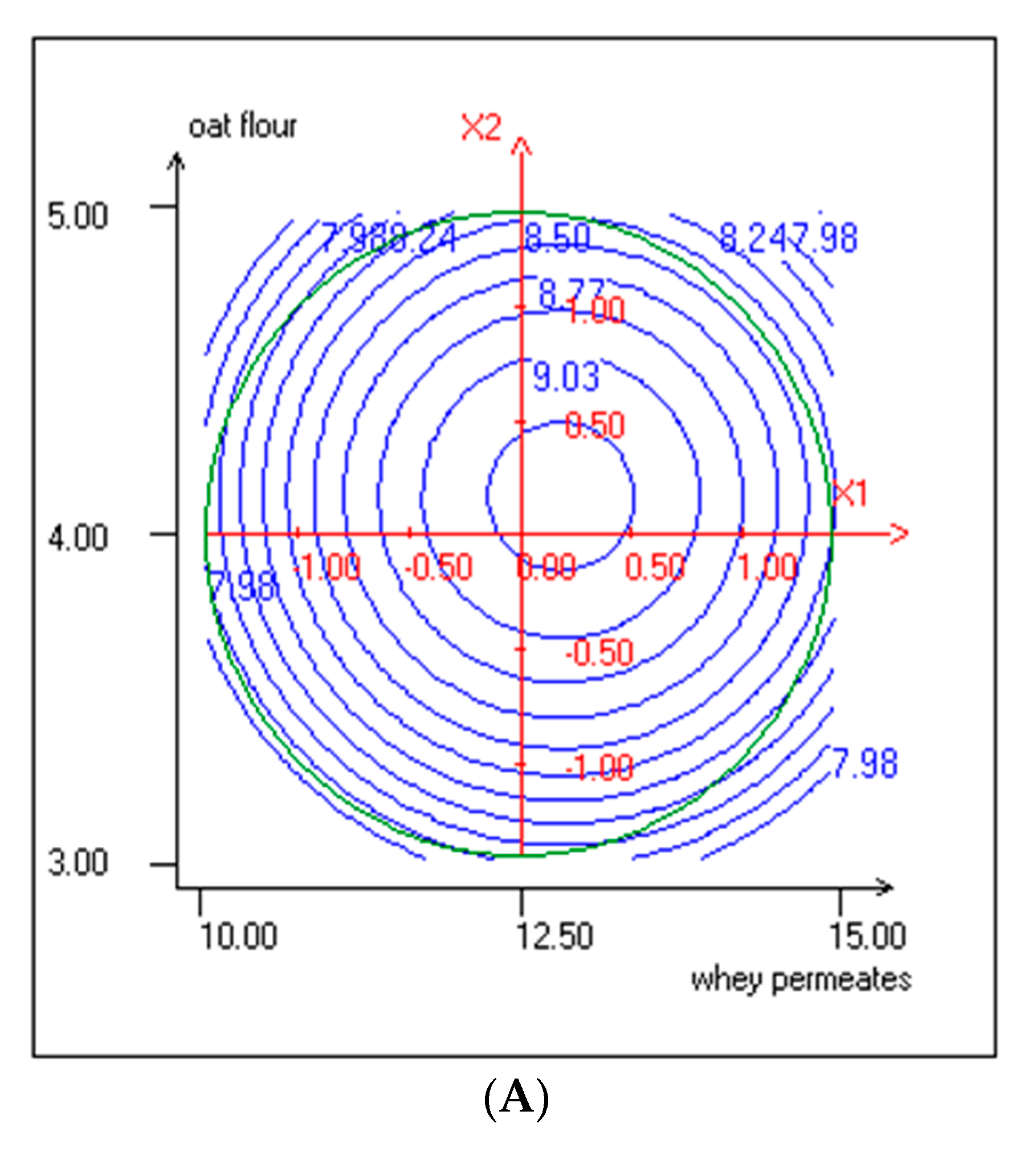
3.2. Effect of Independent Variables on Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeasts Growth
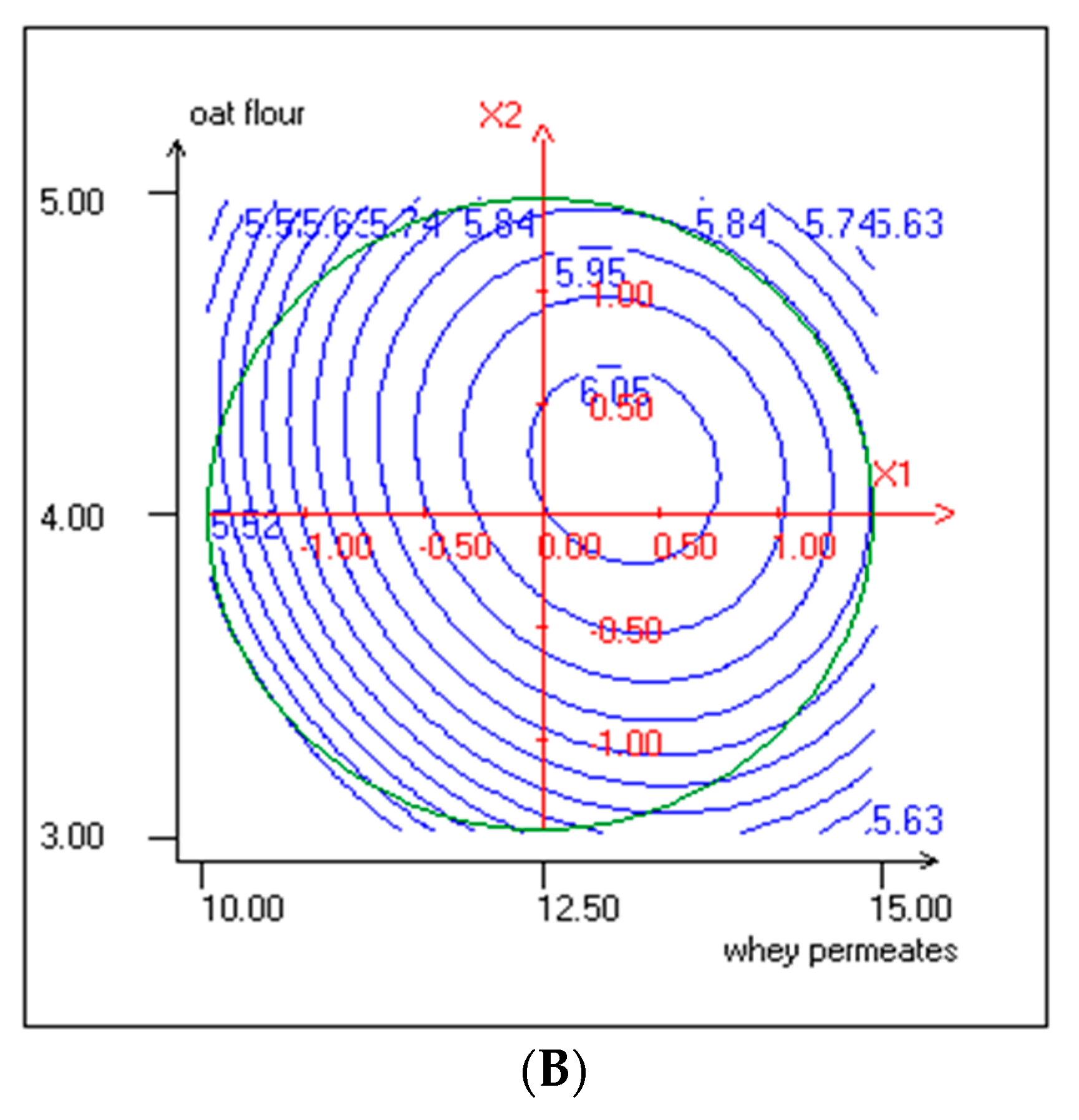
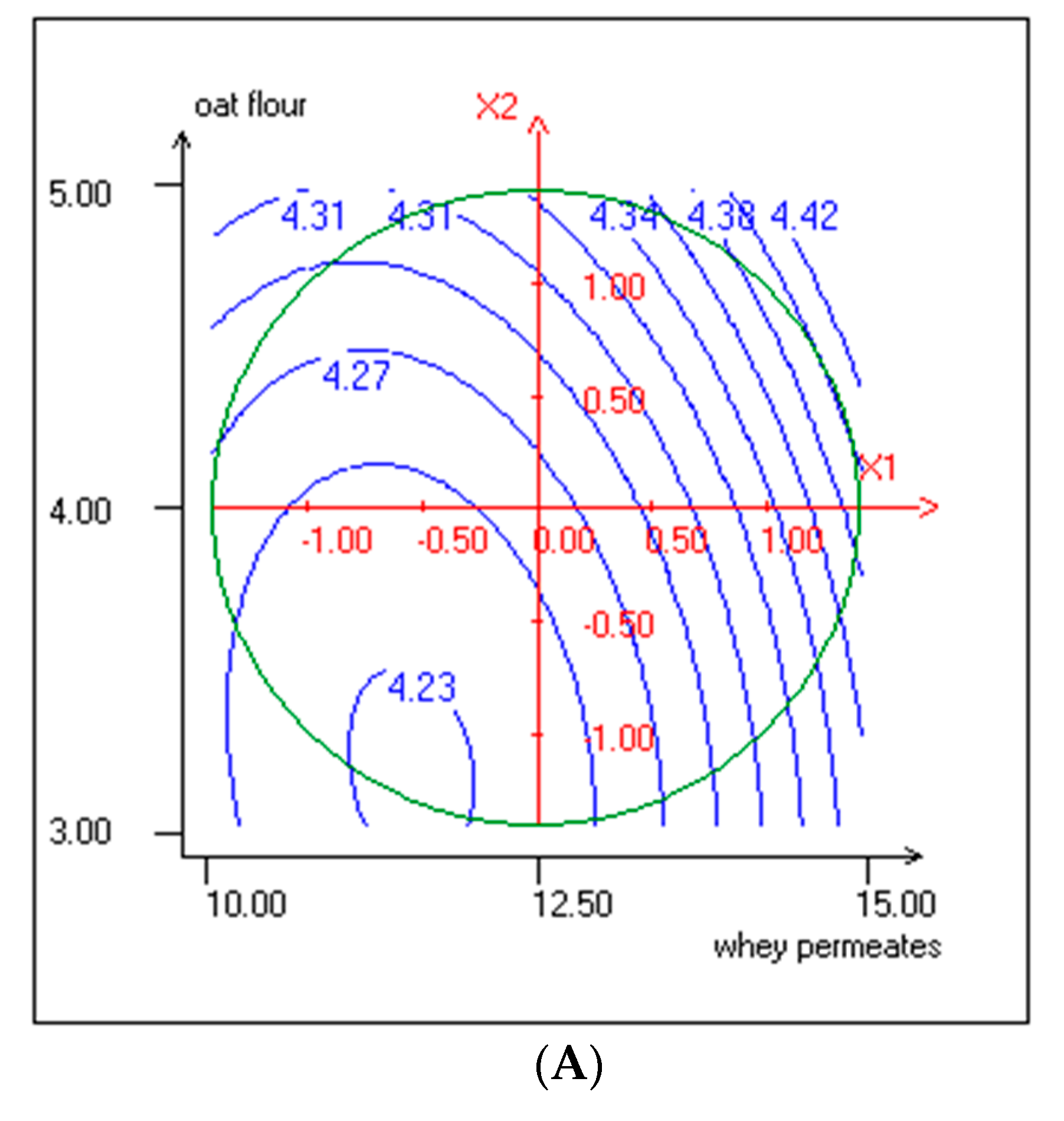
3.3. Effect of Independent Variables on pH and TTA
3.4. Effect of Independent Variables on TPC and Antiradical Activity
3.5. Effect of Independent Variables on CONSUMER Rating of Sensory Attributes
3.6. Verification of the Model
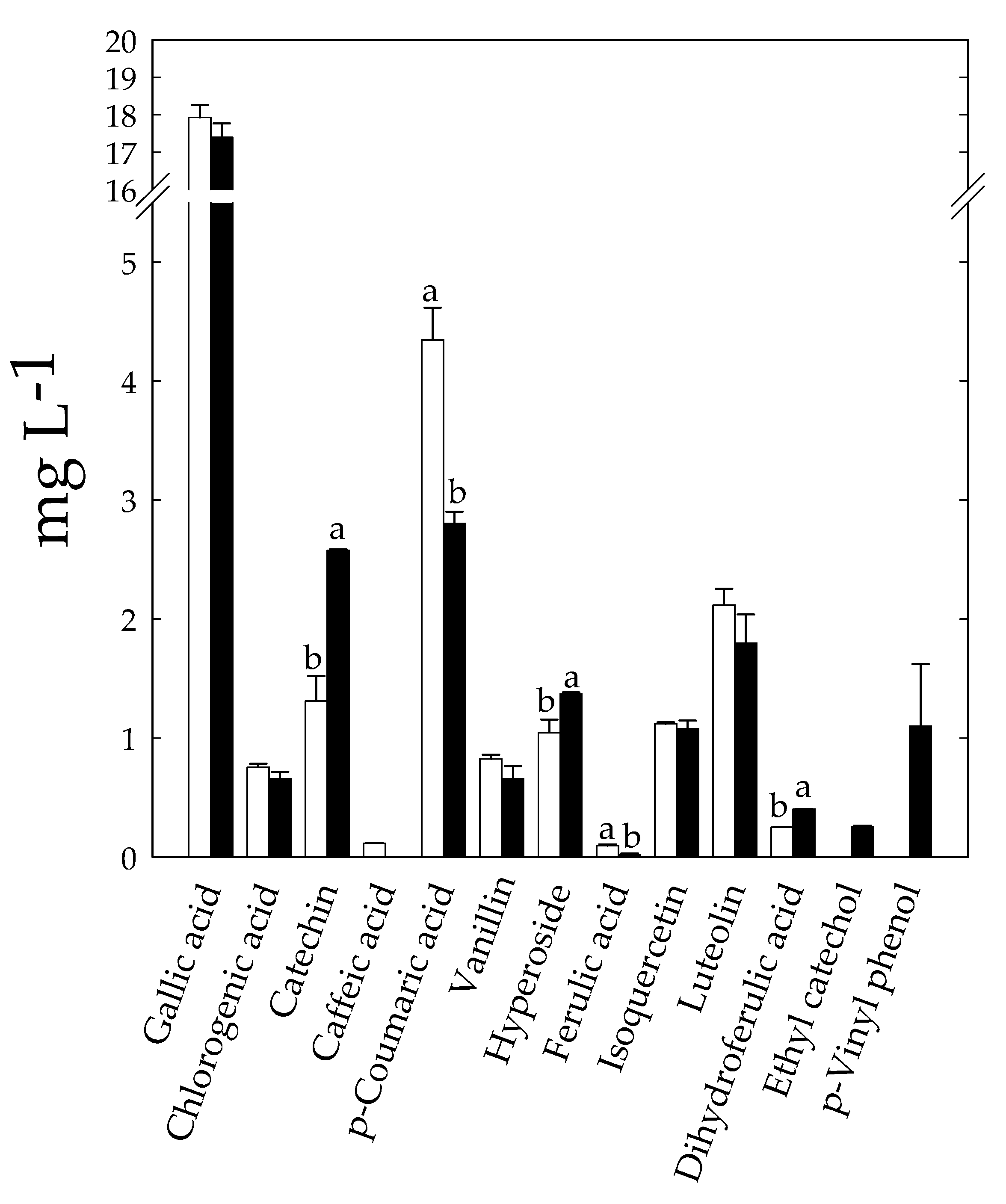
3.7. Effect of Fermentation on Bioactive and Nutritional Compounds of KLB
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nazir, M.; Arif, S.; Khan, R.S.; Nazir, W.; Khalid, N.; Maqsood, S. Opportunities and challenges for functional and medicinal beverages: Current and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorda, F.A.; De Melo Pereira, G.V.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Rakshit, S.K.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; De Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Soccol, C.R. Microbiological, biochemical, and functional aspects of sugary kefir fermentation—A review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnworth, E.R. Kefir—A complex probiotic. Food. Sci. Tech. Bull. Funct. Foods. 2005, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diosma, G.; Romanin, D.E.; Rey-Burusco, M.F.; Londero, A.; Garrote, G.L. Yeasts from kefir grains: Isolation, identification, and probiotic characterization. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanirati, S.B.F.; Abatemarco, M.J.; Sandes, S.H.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nunes, A.C.; Neumann, E. Selection of lactic acid bacteria from Brazilian kefir grains for potential use as starter or probiotic cultures. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T. Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and inflammation. Cell. 2014, 27, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.R.; Blandón, L.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Rodrigues, C.; Castro, G.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Milk kefir: Composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Kok-Tas, T.; Ertekin-Filiz, B.; Seydim, A.C. Effect of different healing activity of kefir and kefiran extract. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 25, 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Worku, K.F.; Kurabachew, H.; Hassen, Y. Probiotication of Fruit Juices by Supplemented Culture of lactobacillus acidophilus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2019, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaefstathiou, E.; Agapiou, A.; Giannopoulos, S.; Kokkinofta, R. Nutritional characterization of carobs and traditional carob products. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulas, V.; Stylos, E.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Tzakos, A.G. Functional Components of Carob Fruit: Linking the Chemical and Biological Space. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rtibi, K.; Selmi, S.; Souli, A.; Sebai, H.; El-Benna, J.; Amri, M.; Marzouki, L. Gastroprotective effect of carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) against ethanol-inducedoxidative stress in rat. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markis, D.P.; Kefalas, P. Carob pods (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a source of polyphenolic antioxydants. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhadi, D.; Hariri, A.; Benattouche, Z.; Sahnouni, F.; Ould Yerou, K. Kinetic of batch production of lactic acid from carob pods syrup. Bull. Pharm. Res. 2017, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouis, N.; Hariri, A. Improving of lactic acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum from carob pods syrup. Wulfenia 2018, 25, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Saarela, M.; Virkajarvi, I.; Nohynek, L.; Vaari, A.; Matto, J. Fibres as carriers for Lactobacillus rhamnosus during freeze-drying and storage in apple juice and chocolate-coated breakfast cereals. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Robards, K.; Glennie-Holmes, M.; Helliwell, S. Oat lipids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Rui, X.; Lia, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J. Whole-grain oats (Avena sativa L.) as a carrier of lactic acid bacteria and a supplement rich in angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides through solid-state fermentation. Food Funct. 2018, 25, 2270–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Penas, E. Health benefits of oat: Current evidence and molecular mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luana, N.; Rossana, C.; Antonio, C.J.; Kaisa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Manufacture and characterization of a yogurt-like beverage made with oat flakes fermented by selected lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 185, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, A.A.; Bruno, F.; Golowczyc, M.A. Whey permeate containing galacto-oligosaccharides as a medium for biomass production and spray drying of Lactobacillus plantarum CIDCA 83114. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, D.M.; Hernández-Ledesma, M.; Amigo, B.; Martín-Álvarez, L.P.J.; Recio, I. Production of antioxidant hydrolyzates from a whey protein concentrate with thermolysin: Optimization by response surface methodology. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golowczyc, M.; Vera, C.; Santos, M.; Guerrero, C.; Carasi, P.; Illanes, A.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A.; Tymczyszyn, E. Use of whey permeate containing in situ synthesised galacto-oligosaccharides for the growth and preservation of Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’hir, S.; Ayed, L.; Hamdi, M. Microbialflora assiated with Tunisian household kefir. In Proceedings of the VIIème congrès International de Biotechnologie et Valorisation des Bio-Ressources, Tabarka, Tunisia, 20–23 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- M’hir, S.; Rtibi, K.; Ayed, L.; Hamdi, M.; Marzouki, L.; Sebai, H. Evaluation d el’effet protecteur du lait de chèvre fermenté par le kefir et enrichi à la caroube contre l’ulcère gastrique induit par l’étahnol chez le rat. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 7, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.; Montgomery, D. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sabokbar, N.; Khodaiyan, F. Characterization of pomegranate juice and whey based novel beverage fermented by kefir grains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karaaslan, M.; Ozden, M.; Vardin, H.; Turkoglu, H. Phenolic fortification of yogurt using grape and callus extracts. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hir, S.; Rtibi, K.; Mejri, A.; Ziadi, M.; Aloui, H.; Hamdi, M.; Ayed, L. Development of a Novel Whey Date Beverage Fermented with Kefir Grains Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1218058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlais, A.Z.; Da Ros, A.; Filannino, P.; Vincentini, O.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Biotechnological re-cycling of apple by-products: A reservoir model to produce a dietary supplement fortified with biogenic phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2020, 336, 127616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filannino, P.; Tlais, A.Z.; Morozova, K.; Cavoski, I.; Scampicchio, M.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Lactic acid fermentation enriches the profile of biogenic fatty acid derivatives of avocado fruit (Persea americana Mill.). Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeson, W.R.; Stahmann, M.A. A pepsin-pancreatin digest index of protein quality. J. Nutr. 1964, 83, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, C.G.; Lorusso, A.; Montemurro, M.; Gobbetti, M. Use of sourdough made with quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) flour and autochthonous selected lactic acid bacteria for enhancing the nutritional, textural and sensory features of white bread. Food Microbiol. 2016, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loullis, A.; Pinakoulaki, E. Carob as cocoa substitute: A review on composition, health benefits and food applications. Eur. Food. Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 959–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.R.; Walsh, G. The biotechnological potential of whey. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.L.; Erickson, J.M.; Hess, J.M.; Gould, T.J.; Slavin, J.L. Prebiotic Dietary Fiber and Gut Health: Comparing the in Vitro Fermentations of Beta-Glucan, Inulin and Xylooligosaccharide. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciecierska, A.; Ewa Drywień, M.; Hamulka, J.; Sadkowski, T. Nutraceurical functions of bêta-glucans. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2019, 70, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Bajaj, B.K. Development of fermented oat flour beverage as a potential probiotic vehicle. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Wan, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Rajashekara, G. Co-production of lactic acid and Lactobacillus rhamnosus cells from whey permeate with nutrient supplements. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2012, 5, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Ponce, A.; Nevarez-Morill, G.; Ortega-Rıvas, E.; Perez-Vega, S.; Salmeron, I. Fermentation adaptability of three probiotic Lactobacillus strains to oat, germinated oat and malted oat substrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabokbar, N.; Khodaiyan, F.; Moosavi-Nasab, M. Optimization of processing conditions to improve antioxidant activities of apple juice and whey based novel beverage fermented by kefir grains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3422–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lei, T.; Ren, X.; Pei, X.; Feng, Y. Response surface optimization of l-(+)- lactic acid roduction using corn steep liquor as an alternative nitrogen source by Lactobacillus rhamnosus CGMCC 1466. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, A.A.; Ghaly, M.F.; El-Naggar, A.K. Some physicochemical analyses of kefir produced under different fermentation conditions. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2013, 70, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Goulas, V.; Georgiou, E. Utilization of Carob Fruit as Sources of Phenolic Compounds with Antioxidant Potential: Extraction Optimization and Application in Food Models. Foods 2019, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, P.; Pihlava, J.M.; Hellström, J. Contents of phenolic acids, alkyl- and alkenylresorcinols, and avenanthramides in commercial grain products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8290–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, P.V. Phenolic compounds of cereals and their antioxidant capacity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soycana, G.; Schära, Y.M.; Kristeka, A.; Boberskaa, J.; Alsharifa, S.N.S.; Coronab, G.; Shewrya, P.R.; Spencera, J.P.E. Composition and content of phenolic acids and avenanthramides in commercial oat products: Are oats an important polyphenol source for consumers. Food Chem. X 2019, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Williamson, G.; Morand, C.; Scalbert, A.; Remesy, C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Sun, Y.S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Functional Properties of Polyphenols in Grains and Effects of Physicochemical Processing on Polyphenols. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 2793973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariken, J.T.J.A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Wilms, L.C.; Beetstra, S.A.J.N.; Heijnen, C.G.M.; Voss, H.P.; Bast, A. Interactions between Flavonoids and Proteins: Effect on the Total Antioxidant Capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Corona, O.; Guarcello, R.; Francesca, N.; Antonietta Germana, M.; Erten, H.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Development of new non-dairy beverages from Mediterranean fruit juices fermented with water kefir microorganisms. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, L.; M’hir, S.; Hamdi, M. Microbiological, Biochemical, and Functional Aspects of Fermented Vegetable and Fruit Beverages. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 5790432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, L.; Ben Abid, S.; Hamdi, M. Development of a beverage from red grape juice fermented with the Kombucha consortium. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, L.; Hamdi, M. Manufacture of a beverage from cactus pear juice using tea fungus fermentation. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorda, F.A.; Melo Pereira, G.V.; Omaz-Soccol, V.; Medeiros, A.P.; Rakshit, S.K.; Soccol, C.R. Development of kefir-based probiotic beverages with DNA protection and antioxidant activities using soybean hydrolyzed extract, colostrum and honey. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontonio, E.; Montemurro, M.; Pinto, D.; Marzani, B.; Trani, A.; Ferrara, G.; Mazzeo, A.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Lactic Acid Fermentation of Pomegranate Juice as a Tool to Improve Antioxidant Activity. Front. Microbiol 2019, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, P.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Metabolic and functional paths of lactic acid bacteria in plant foods: Get out of the labyrinth. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabokbar, N.; Khodaiyan, F. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of pomegranate juice and whey based novel beverage fermented by kefir grains. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydanek, M.G.; McGorrin, R.J. Gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy investigations on the flavor chemistry of oat groats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klensporf, D.; Jeleń, H. Effect of heat treatment on the flavor of oat flakes. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescuma, M.; Hébert, E.M.; Font de Valdez, G.; Mozzi, F. Functional Fermented Whey Foods: Their Role in Human Health. In Beneficial Microbes in Fermented and Functional Foods, 1st ed.; Ravishankar, R.V., Jamuna, A.B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 95–111. ISBN 9780429189746. [Google Scholar]
- Mosele, J.I.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.P.; Motilva, M.J. Stability and metabolism of Arbutus unedo bioactive compounds (phenolics and antioxidants) under in vitro digestion and colonic fermentation. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Díaz-Rubio, M.E.; Saura-Calixto, F. Non-extractable polyphenols, a major dietary antioxidant: Occurrence, metabolic fate and health effects. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2013, 26, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filannino, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R. Hydroxycinnamic acids used as external acceptors of electrons: An energetic advantage for strictly heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7574–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, T.M.; Romano, D.; Vigentini, I.; Foschino, R.C.; Monti, D.; Mamone, G.; Molinari, F. New insights on the features of the vinyl phenol reductase from the wine-spoilage yeast Dekkera/Brettanomyces bruxellensis. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, S.; Palomero, F.; Morata, A.; Calderón, F.; Suárez-Lepe, J.A. Factors affecting the hydroxycinnamate decarboxylase/vinylphenol reductase activity of Dekkera/Brettanomyces: Application for Dekkera/Brettanomyces control in red wine making. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, M15–M22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, R.; De Las Rivas, B.; De Felipe, F.L.; Reverón, I.; Santamaría, L.; Esteban-Torres, M.; Landete, J.M. Biotransformation of phenolics by Lactobacillus plantarum in fermented foods. In Fermented Foods in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Verni, M.; Demarinis, C.; Rizzello, C.G.; Baruzzi, F. Design and Characterization of a Novel Fermented Beverage from Lentil Grains. Foods 2020, 9, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.; Coda, R.; Montemurro, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Use of selected lactic acid bacteria and quinoa flour for manufacturing novel yogurt-like beverages. Foods 2018, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Parameter (%, w/v) | Ranges and Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.41 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 1.41 | ||
| X1 | WP | 10 | 10.73 | 12.5 | 14.27 | 15 |
| X2 | OF | 3 | 3.29 | 4 | 4.71 | 5 |
| ExpN° | Coded Variables | Responses Variables | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP (% w/v) Actual Values | Coded Values | Oat Flour (% w/v) Actual values | Coded Values | LAB Cells Count (log CFU/mL) | Yeasts Cells Count (log CFU/mL) | pH | TTA (%) | TPC (mg EGA/mL) | DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity (%) | OA (5 Point Hedonic Scale) | |
| X1 | X2 | (Y1) | (Y2) | (Y3) | (Y4) | (Y5) | (Y6) | ||||
| 1 | 10.73 (−1) | −1 | 3.29 | −1 | 7.85 ± 0.08 | 5.47 ± 0.27 | 4.21 ± 0.01 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 19.365 ± 0.24 | 74.27 ± 0.33 | 3.20 ± 0.52 |
| 2 | 14.27 (1) | 1 | 3.29 | −1 | 8.17 ± 0.1 | 5.73 ± 0.24 | 4.29 ± 0.02 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 17.369 ± 0.53 | 67.90 ± 0.023 | 3.30 ± 0.57 |
| 3 | 10.73 (−1) | −1 | 4.71 | 1 | 8.25 ± 011 | 5.70 ± 0.28 | 4.31 ± 0.03 | 0.86 ± 0.02 | 25.317 ± 0.28 | 81.84 ± 0.51 | 3.50 ± 0.61 |
| 4 | 14.27 (1) | 1 | 4.71 | 1 | 8.55 ± 0.09 | 5.79 ± 0.26 | 4.42 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 27.697 ± 0.98 | 85.70 ± 0.39 | 2.80 ± 0.62 |
| 5 | 10.00 | −1.41 | 4.00 | 0 | 8.02 ± 0.12 | 5.51 ± 0.29 | 4.26 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 15.625 ± 0.33 | 78.36 ± 0.29 | 3.60 ± 0.68 |
| 6 | 15.00 | 1.41 | 4.00 | 0 | 8.55 ± 0.1 | 6.00 ± 0.25 | 4.39 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 16.328 ± 0.3 | 75.30 ± 0.62 | 3.10 ± 0.52 |
| 7 | 12.50 | 0 | 3.00 | −1.41 | 8.09 ± 0.09 | 5.69 ± 0.27 | 4.27 ± 0.04 | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 14.259 ± 0.38 | 71.65 ± 0.42 | 3.20 ± 0.41 |
| 8 | 12.50 | 0 | 5.00 | 1.41 | 8.45 ± 0.12 | 5.94 ± 0.29 | 4.29 ± 0.03 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 24.617 ± 0.28 | 77.28 ± 0.25 | 3.10 ± 0.64 |
| 9 | 12.50 | 0 | 4.00 | 0 | 9.10 ± 0.10 | 6.05 ± 0.26 | 4.25 ± 0.02 | 1.05 ± 0.03 | 14.070 ± 0.41 | 74.61 ± 0.34 | 3.40 ± 0.50 |
| 10 | 12.50 | 0 | 4.00 | 0 | 9.11 ± 0.09 | 6.05 ± 0.29 | 4.27 ± 0.03 | 1.05 ± 0.05 | 14.780 ± 0.65 | 72.44 ± 0.29 | 3.45 ± 0.60 |
| 11 | 12.50 | 0 | 4.00 | 0 | 9.21 ± 0.10 | 6.04 ± 0.25 | 4.25 ± 0.02 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 14.680 ± 0.52 | 73.38 ± 0.35 | 3.42 ± 0.53 |
| 12 | 12.50 | 0 | 4.00 | 0 | 9.19 ± 0.11 | 6.05 ± 0.28 | 4.27 ± 0.03 | 1.05 ± 0.03 | 14.680 ± 0.44 | 72.93 ± 0.22 | 3.55 ± 0.60 |
| 13 | 12.50 | 0 | 4.00 | 0 | 9.29 ± 0.09 | 6.05 ± 0.24 | 4.25 ± 0.01 | 1.07 ± 0.04 | 14.570 ± 0.32 | 72.69 ± 0.41 | 3.50 ± 0.61 |
| SourceTitle | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | Y5 | Y6 | Y7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Signif.% | Coefficient | Signif.% | Coefficient | Signif.% | Coefficient | Signif.% | Coefficient | Signif.% | Coefficient | Signif.% | Coefficient | Signifi.% | |
| Model | ||||||||||||||
| b0 | 9.180 | *** | 6.051 | *** | 4.258 | *** | 1.054 | *** | 14.556 | *** | 73.211 | *** | 3.464 | *** |
| Linear | ||||||||||||||
| b1 | 0.171 | *** | 0.131 | *** | 0.047 | *** | 0.029 | ** | 0.172 | 15.8 | −0.855 | * | −0.163 | *** |
| b2 | 0.161 | *** | 0.080 | *** | 0.032 | ** | 0.006 | 14.7 | 3.866 | *** | 4.167 | *** | −0.043 | 6.6 |
| Quadratic | ||||||||||||||
| b11 | −0.466 | *** | -0.175 | *** | 0.035 | ** | −0.078 | *** | 1.893 | *** | 2.255 | ** | −0.070 | * |
| b22 | −0.473 | *** | -0.146 | *** | 0.012 | * | −0.080 | *** | 3.624 | *** | 1.072 | * | −0.170 | *** |
| Interaction | ||||||||||||||
| b12 | −0.005 | 90.1 | -0.043 | *** | 0.008 | 24.2 | −0.032 | ** | 1.094 | ** | 2.557 | ** | −0.200 | *** |
| R2 | 0.986 | 0.925 | 0.861 | 0.920 | 0.835 | 0.816 | 0.965 | |||||||
| Adj-R2 | 0.975 | 0.872 | 0.762 | 0.862 | 0.717 | 0.684 | 0.940 | |||||||
| Independant Variables | DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity (%) | TPC (mg GAE/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfermented | Fermented | Unfermented | Fermented | |
| Exp 1 | 68.49 ef ± 0.67 | 74.27 de ± 0.46 | 9.59 a ± 0.34 | 19.36 e ± 0.55 |
| Exp 2 | 65.60 a ± 0.44 | 67.90 a ± 0.55 | 14.04 f ± 0.44 | 17.36 d ± 0.37 |
| Exp 3 | 70.53 g ± 0.61 | 81.84 g ± 0.89 | 10.73 b ± 0.52 | 25.31 f ± 0.63 |
| Exp 4 | 68.84 ef ± 0.55 | 85.70 h ± 0.77 | 12.55 e ± 0.66 | 27.69 g ± 0.34 |
| Exp 5 | 75.12 h ± 0.41 | 78.36 f ± 0.69 | 14.33 f ± 0.48 | 15.62 bc ± 0.62 |
| Exp 6 | 68.43 de ± 0.52 | 75.30 e ± 0.55 | 11.75 cde ± 0.33 | 16.32 c ± 0.87 |
| Exp 7 | 66.41 ab ± 0.52 | 71.65 b ± 0.73 | 10.88 bc ± 0.42 | 14.25 a ± 0.60 |
| Exp 8 | 69.40 f ± 0.65 | 77.28 f ± 0.62 | 9.22 a ± 0.49 | 24.61 f ± 0.68 |
| Exp 9 | 66.91 bc ± 0.43 | 74.61 e ± 0.51 | 11.50 bcd ± 0.68 | 14.07 a ± 0.34 |
| Exp 10 | 66.86 bc ± 0.35 | 72.44 bc ± 0.87 | 11.60 bcd ± 0.55 | 14.78 ab ± 0.67 |
| Exp 11 | 67.57 cd ± 0.63 | 73.38 cd ± 0.69 | 11.92 de ± 0.46 | 14.68 ab ± 0.47 |
| Exp 12 | 67.17 bc ± 0.73 | 72.93 c ± 0.49 | 11.88 de ± 0.77 | 14.68 ab ± 0.72 |
| Exp13 | 66.81 bc ± 0.45 | 72.69 bc ± 0.67 | 11.64 cd ± 0.62 | 14.57 a ± 0.56 |
| Response Variable | Optimum Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Predicted | |
| pH | 4.32 ± 0.02 | 4.29 |
| TTA (%) | 0.95 ± 0.04 | 0.96 |
| Lactic acid bacteria cells count (Log CFU/mL) | 8.62 ± 0.15 | 8.57 |
| Yeasts cells count (Log CFU/mL) | 5.80 ± 0.26 | 5.87 |
| DPPH radical scavenging activity (%) | 79.80 ± 0.46 | 78.59 |
| TPC mg GAE/mL | 21.40 ± 0.53 | 22.76 |
| OA (5 point hedonic scale) | 3.44 ± 0.46 | 3.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
M’hir, S.; Filannino, P.; Mejri, A.; Tlais, A.Z.A.; Di Cagno, R.; Ayed, L. Functional Exploitation of Carob, Oat Flour, and Whey Permeate as Substrates for a Novel Kefir-Like Fermented Beverage: An Optimized Formulation. Foods 2021, 10, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020294
M’hir S, Filannino P, Mejri A, Tlais AZA, Di Cagno R, Ayed L. Functional Exploitation of Carob, Oat Flour, and Whey Permeate as Substrates for a Novel Kefir-Like Fermented Beverage: An Optimized Formulation. Foods. 2021; 10(2):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020294
Chicago/Turabian StyleM’hir, Sana, Pasquale Filannino, Asma Mejri, Ali Zein Alabiden Tlais, Raffaella Di Cagno, and Lamia Ayed. 2021. "Functional Exploitation of Carob, Oat Flour, and Whey Permeate as Substrates for a Novel Kefir-Like Fermented Beverage: An Optimized Formulation" Foods 10, no. 2: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020294
APA StyleM’hir, S., Filannino, P., Mejri, A., Tlais, A. Z. A., Di Cagno, R., & Ayed, L. (2021). Functional Exploitation of Carob, Oat Flour, and Whey Permeate as Substrates for a Novel Kefir-Like Fermented Beverage: An Optimized Formulation. Foods, 10(2), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020294