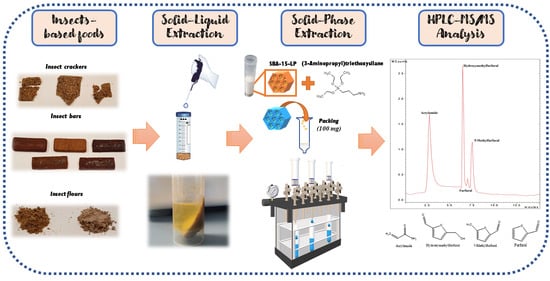
Simultaneous Determination of Furanic Compounds and Acrylamide in Insect-Based Foods by HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Employing a Functionalized Mesostructured Silica as Sorbent in Solid-Phase Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Samples
2.3. Synthesis of Functionalized Mesostructured Silica
2.4. Characterization of Mesostructured Silicas
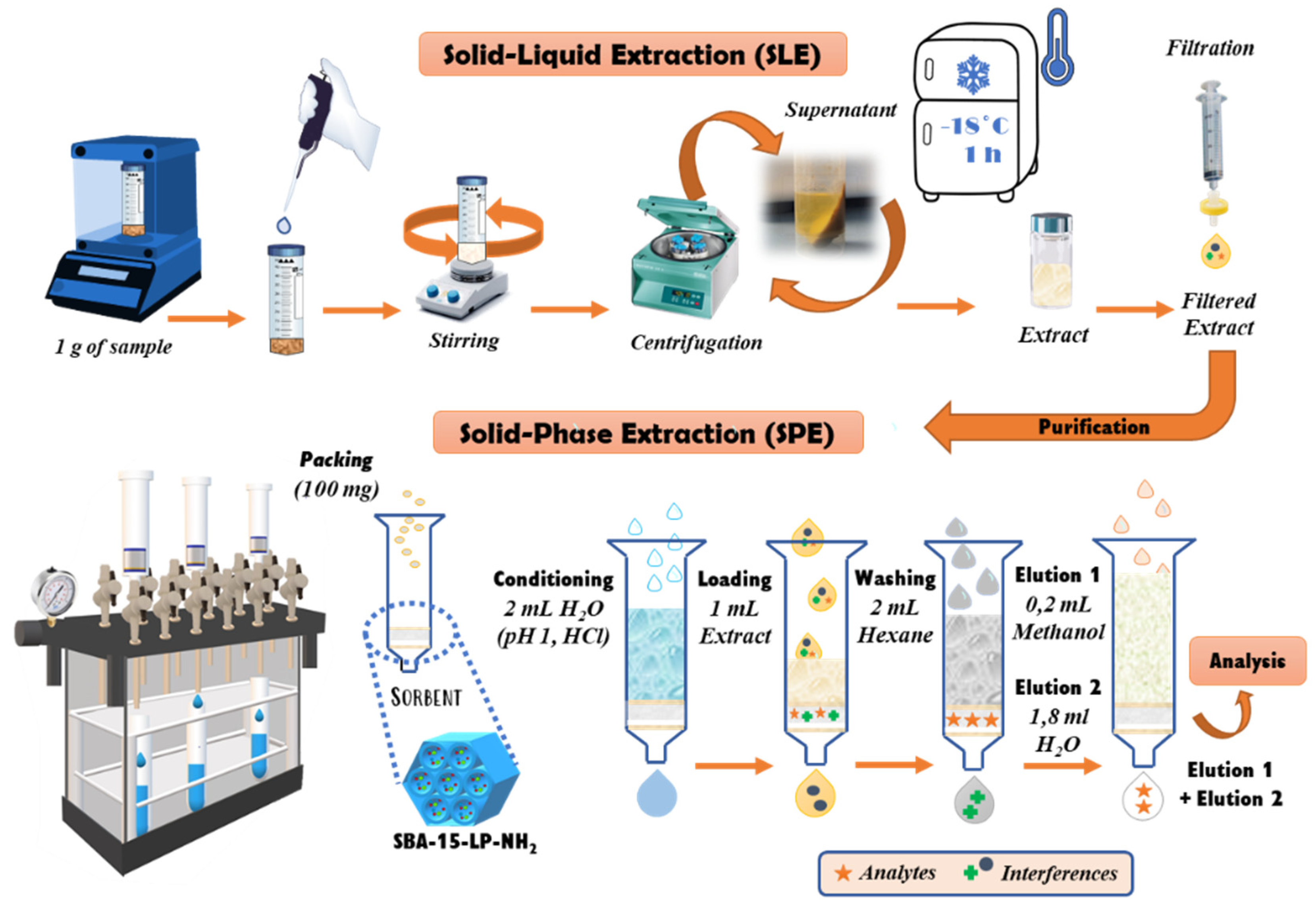
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Conditions
2.7. Instrumental Validation
2.8. Method Validation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Mesostructured Silicas
3.2. Optimization of HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Conditions
3.3. Optimization of Sample Extraction Procedure
3.3.1. Preliminary Studies
3.3.2. SPE Optimization
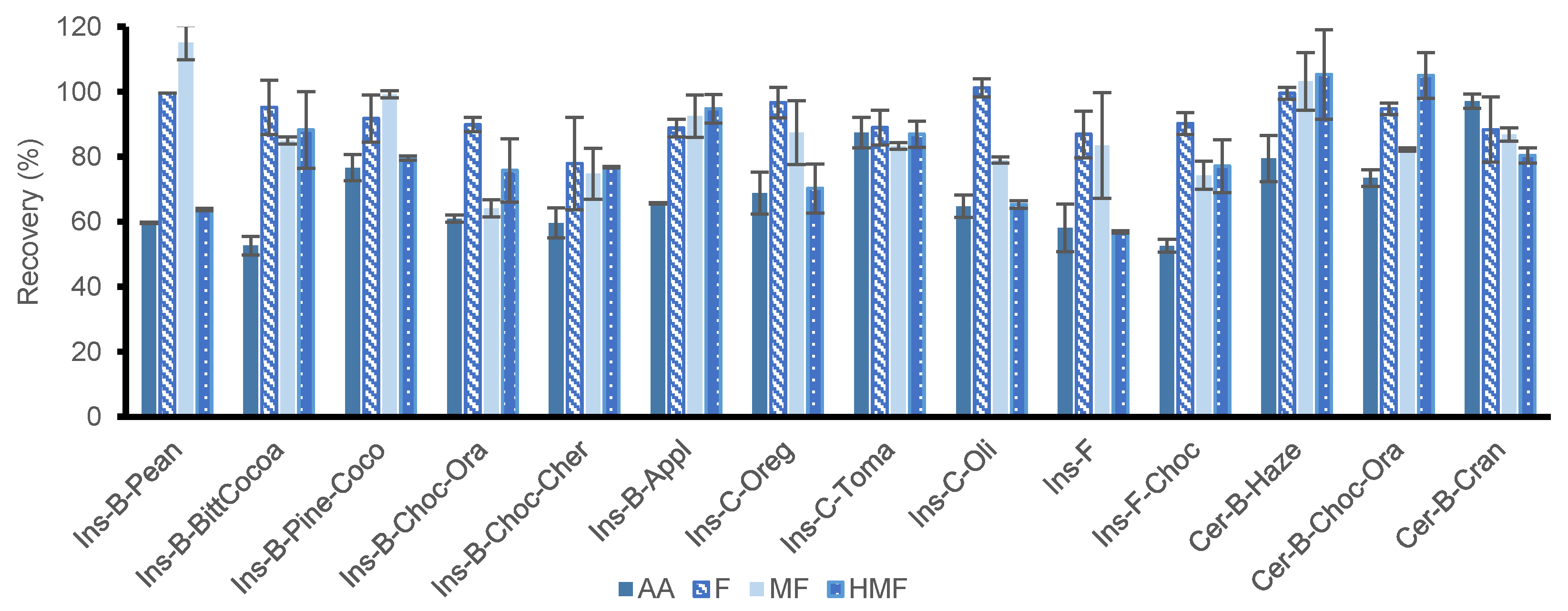
3.3.3. Application of the Optimized SLE-SPE Protocol
3.4. Instrumental Validation
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. Analysis of Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The Future of Food and Agriculture: Trends and Challenges; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2017; ISBN 9789251095515. [Google Scholar]
- Van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Mui, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; McDonald, D & Sarre, A.: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 171, ISBN 9789251075951. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, C.; Costa, A.; Balzaretti, C.M.; Russo, V.; Tedesco, D.E.A. Survey on food preferences of university students: From tradition to new food customs? Agriculture 2018, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S.A. Reducing the global environmental impact of livestock production: The minilivestock option. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez-Araque, R.; Egas-Montenegro, E. Edible insects: A food alternative for the sustainable development of the planet. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M.; Rybczyńska, K.; Jakubczyk, A. Selected species of edible insects as a source of nutrient composition. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (UE) 2015/2283 of the european parliament and of the coiuncil of 25 Novembrer 2015 on novel foods amending Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council and repealing Regulation (EC) No 258/97 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1852/2001. Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, L327, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cicatiello, C.; Vitali, A.; Lacetera, N. How does it taste? Appreciation of insect-based snacks and its determinants. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 21, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Risk profile related to production and consumption of insects as food and feed. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Looking at Edible Insects from a Food Safety Perspective. Challenges and Opportunities for the Sector; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; pp. 1–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on acrylamide in food. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 1–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs on the Evaluations of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Some Industrial Chemicals; IARC: Lyon, France, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 389–434. ISBN 9789283212607. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Shao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Co-extraction and co-purification coupled with HPLC-DAD for simultaneous detection of acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural in thermally processed foods. Molecules 2019, 24, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rufián-Henares, J.A.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Morales, F.J. Application of a fast high-performance liquid chromatography method for simultaneous determination of furanic compounds and glucosylisomaltol in breakfast cereals. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Jiménez, A.; García-Villanova, B.; Guerra-Hernández, E. Hydroxymethylfurfural and methylfurfural content of selected bakery products. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmen, V.; Morales, F.J. Processing Contaminants: Hydroxymethylfurfural. Encycl. Food Saf. 2014, 2, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Ameur, L.; Rega, B.; Giampaoli, P.; Trystram, G.; Birlouez-Aragon, I. The fate of furfurals and other volatile markers during the baking process of a model cookie. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Hydroxymethylfurfural determination in cereal and insect bars by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry employing a functionalized mesostructured silica as sorbent in solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 461124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheiner, L.; Schmidt, A.; Karpf, F.; Mayer, H.K. A novel UHPLC method for determining the degree of coffee roasting by analysis of furans. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesias, M.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Morales, F.J. Risk/benefit evaluation of traditional and novel formulations for nacking: Acrylamide and furfurals as process contaminants. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 79, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozinović, A.; Šarkanj, B.; Ačkar, D.; Balentić, J.P.; Šubarić, D.; Cvetković, T.; Ranilović, J.; Guberac, S.; Babić, J. Simultaneous determination of acrylamide and hydroxymethylfurfural in extruded products by LC-MS/MS method. Molecules 2019, 24, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, M.; Nie, S.; Chen, J.; Zeng, M.; Xie, M. Simultaneous Determination of Acrylamide and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Heat-Processed Foods Employing Enhanced Matrix Removal—Lipid as a New Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent Followed by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5017–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, C.J.; Tang, X.Y.; Yu, S.J. Determination of Four Bitter Compounds in Caramel Colors and Beverages Using Modified QuEChERS Coupled with Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detector-Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalá-Hurtado, S.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Determination of Free and Total Furfural Compounds in Infant Milk Formulas by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2128–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Ma, Y.; Fu, X.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; You, C. Effects of heat treatment, homogenization pressure, and overprocessing on the content of furfural compounds in liquid milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5276–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Qiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. Preparation of a Hydrophilic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Its Application in Solid-Phase Extraction to Determine of Trace Acrylamide in Foods Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A. Development of dummy molecularly imprinted based on functionalized silica nanoparticles for determination of acrylamide in processed food by matrix solid phase dispersion. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. Preparation and Application of Chitosan-Grafted Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Extraction for Determination of Trace Acrylamide in Foods Through High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, N.; Habibi, B.; Khataee, A.; Hassanzadeh, J. Application of surface molecular imprinted magnetic graphene oxide and high performance mimetic behavior of bi-metal ZnCo MOF for determination of atropine in human serum. Talanta 2019, 201, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Qiu, T.; Wang, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Xiong, H. Dummy-surface molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and selective quantification of acrylamide in heat-processed (including fried) foods. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, L.; Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 as Strong Cation-Exchange Sorbent for Solid-Phase Extraction of Atropine and Scopolamine in Gluten-Free Grains and Flours. Foods 2020, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Marina, M.L.; Sierra, I. One-pot synthesized functionalized mesoporous silica as a reversed-phase sorbent for solid-phase extraction of endocrine disrupting compounds in milks. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, N.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Evaluation of bi-functionalized mesoporous silicas as reversed phase/cation-exchange mixed-mode sorbents for multi-residue solid phase extraction of veterinary drug residues in meat samples. Talanta 2017, 165, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commision SANTE/11813/2017. Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues in Food and Feed. Available online: https://www.eurl-pesticides.eu/userfiles/file/EurlALL/AqcGuidance_SANTE_2019_12682.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- European Union. Council Directive 2001/110/EC of 20 December 2001 relating to honey. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, L10, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Oracz, J.; Nebesny, E.; Zyzelewicz, D. New trends in quantification of acrylamide in food products. Talanta 2011, 86, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrarca, M.H.; Rosa, M.A.; Queiroz, S.C.N.; Godoy, H.T. Simultaneous determination of acrylamide and 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone in baby food by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1522, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petisca, C.; Henriques, A.R.; Pérez-Palacios, T.; Pinho, O.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O. Assessment of hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural in commercial bakery products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 33, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (UE) 2017/2158 of 20 November 2017 establishing mitigation measures and benchmark levels for the reduction of the presence of acrylamide in food. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, L304, 24–44. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, A.; Kamankesh, M.; Hosseini, H.; Hadian, Z.; Ghasemi, J.; Mohammadi, A. Investigation and determination of acrylamide in 24 types of roasted nuts and seeds using microextraction method coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry: Central composite design. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.A.G.; Andrzejewski, D.; Gay, M.L.; Nortrup, D.; Musser, S.M. Rugged LC-MS/MS Survey Analysis for Acrylamide in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7547–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateo, F.; Bononi, M.; Andreoli, G. Acrylamide levels in cooked rice, tomato sauces and some fast food on the Italian market. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analyte | Ionization Mode | Precursor Ions m/z | MS2 Product Ions m/z (CE, V) | Dwell Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | ESI (+) | 72.0 | 53.5 (6.5), 54.8 * (5) | 0.5 |
| F | ESI (+) | 97.0 | 40.7 (11.5), 69.3 (7), 95.7 * (5) | 0.5 |
| MF | ESI (+) | 110.9 | 53.0 (14), 54.9 (12), 81.0 (12), 109.6 *(5) | 0.5 |
| HMF | ESI (+) | 127.0 | 53.0 (22), 80.6 (14), 108.8 *(10) | 0.5 |
| Material | SBET a (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (Å) | L0 b (mmol NH2 Groups/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15-LP | 482 | 1.7 | 38 91 | - |
| SBA-15-LP-NH2 | 357 | 1.3 | 36 89 | 0.96 |
| Analyte a | Sample | Linear Range (µg/mL) | Matrix Matched Calibration (R2) | MDL (µg/g) b | MQL (µg/g) b | ME (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | Ins-B-Pine-Coco | 0.1–10 | y = 9.4 × 107x + 1.7 × 106 (0.999) | 0.4 | 1.3 | 112 |
| Ins-C-Toma | 0.1–10 | y = 1.1 × 108x + 5.6 × 106 (0.998) | 0.8 | 1.4 | 142 | |
| Ins-F | - | - | - | - | - | |
| F | Ins-B-Pine-Coco | 0.5–10 | y = 5.7 × 106x + 8.5 × 105 (0.998) | 2.4 | 7.9 | 15 |
| Ins-C-Toma | 0.5–10 | y = 5.0 × 106x + 6.1 × 105 (0.997) | 2.7 | 8.8 | 2 | |
| Ins-F | 0.5–10 | y = 4.7 × 106x + 3.3 × 106 (0.999) | 2.6 | 8.5 | −6 | |
| MF | Ins-B-Pine-Coco | 0.2–10 | y = 3.3 × 107x + 4.0 × 106 (0.996) | 0.9 | 3.1 | 19 |
| Ins-C-Toma | 0.5–10 | y = 2.9 × 107x + 1.6 × 106 (0.998) | 1.9 | 6.5 | 5 | |
| Ins-F | 0.5–10 | y = 2.8 × 107x + 5.0 × 106 (0.995) | 1.7 | 5.7 | 0 | |
| HMF | Ins-B-Pine-Coco | 0.1–10 | y = 3.6 × 107x + 9.2 × 106 (0.991) | 0.5 | 1.5 | 27 |
| Ins-C-Toma | 0.2–10 | y = 1.0 × 107x + 4.5 × 105 (0.998) | 1.0 | 3.3 | −65 | |
| Ins-F | 0.2–10 | y = 1.1 × 107x + 2.9 × 106 (0.997) | 0.6 | 2.1 | −60 |
| Analyte | Level a | Recovery (% ± SD) b | Intra-Day Precision (% RSD) b | Inter-Day Precision (% RSD) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | Low | 70 ± 6 | 8 | 11 |
| High | 70 ± 8 | 11 | 10 | |
| F | Low | 91 ± 10 | 11 | 13 |
| High | 83 ± 5 | 8 | 14 | |
| MF | Low | 94 ± 7 | 7 | 11 |
| High | 79 ± 6 | 8 | 11 | |
| HMF | Low | 101 ± 3 | 3 | 5 |
| High | 96 ± 3 | 5 | 8 |
| Sample | AA (µg/g ± SD) | F (µg/g ± SD) | MF (µg/g ± SD) | HMF (µg/g ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ins-B-Pean | n.d | 37 ± 1 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | n.d |
| Ins-B-BittCocoa | n.d | 107 ± 3 | 17 ± 1 | n.d |
| Ins-B-Pine-Coco | n.d | <MQL | <MQL | 15 ± 2 |
| Ins-B-Choc-Ora | n.d | n.d | 6.9 ± 0.8 | <MQL |
| Ins-B-Choc-Cher | n.d | 9 ± 2 | 14 ± 4 | 41 ± 13 |
| Ins-B-Appl | n.d | n.d | <MQL | 2.5 ± 0.4 |
| Ins-C-Oreg | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 9 ± 1 | 13 ± 1 | n.d |
| Ins-C-Toma | <MQL | 20 ± 6 | 6.8 ± 0.6 | n.d |
| Ins-C-Oli | <MQL | 11 ± 2 | 8 ± 1 | n.d |
| Ins-F | n.d | 8 ± 1 | n.d | n.d |
| Ins-F-Choc | n.d | 40 ± 1 | 10 ± 1 | 7 ± 2 |
| Cer-B-Haze | n.d | 10 ± 3 | <MQL | 333 ± 38 |
| Cer-B-Choc-Ora | n.d | n.d | <MQL | 402 ± 30 |
| Cer-B-Cran | n.d | n.d | n.d | 706 ± 51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Gómez, L.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Simultaneous Determination of Furanic Compounds and Acrylamide in Insect-Based Foods by HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Employing a Functionalized Mesostructured Silica as Sorbent in Solid-Phase Extraction. Foods 2021, 10, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071557
González-Gómez L, Morante-Zarcero S, Pérez-Quintanilla D, Sierra I. Simultaneous Determination of Furanic Compounds and Acrylamide in Insect-Based Foods by HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Employing a Functionalized Mesostructured Silica as Sorbent in Solid-Phase Extraction. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071557
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Gómez, Lorena, Sonia Morante-Zarcero, Damián Pérez-Quintanilla, and Isabel Sierra. 2021. "Simultaneous Determination of Furanic Compounds and Acrylamide in Insect-Based Foods by HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Employing a Functionalized Mesostructured Silica as Sorbent in Solid-Phase Extraction" Foods 10, no. 7: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071557
APA StyleGonzález-Gómez, L., Morante-Zarcero, S., Pérez-Quintanilla, D., & Sierra, I. (2021). Simultaneous Determination of Furanic Compounds and Acrylamide in Insect-Based Foods by HPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Employing a Functionalized Mesostructured Silica as Sorbent in Solid-Phase Extraction. Foods, 10(7), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071557