Evaluation of pH in Sausages Stuffed in a Modified Casing with Orange Extracts by Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The simultaneous effects of five variables (different concentrations of soy lecithin, soy oil, lactic acid, orange extracts, and treatment times) on the pH of sausages during 15 days of storage were elucidated by RSM.
- (2)
- The pH of sausages stuffed in modified casings after adding orange extracts was elaborated for the first time by HSI. The pH changes of each pixel in casings responding to different concentrations of orange extracts were clearly illustrated via prediction maps. The results can provide a better understanding of how pH reacts with orange extracts and provide useful information for future investigations.
- (3)
- The relationship between pH and spectra from the surface of cylindrical sausages with modified casings was established for the first time by PLSR.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soxhlet Extraction
2.2. Experiment Design and Casing Modification
2.3. Sausage Production
2.4. Hyperspectral Imaging System
2.5. pH Analysis
2.6. Spectral Pretreatment and Model Development
2.7. Feature Wavelengths Selection
2.8. Visualization of pH Distribution
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectral Characteristics and Simultaneous Effects on pH Analyzed by RSM
3.1.1. Spectra Overview
3.1.2. Simultaneous Effects on pH Analyzed by RSM
3.2. Calibration Models with Full Wavelengths
3.3. Calibration Models with Selected Feature Wavelengths
3.4. Visual Representation of Sausage pH Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, C.H.; Drummond, L.; Sun, D.W.; Zhang, Z.-H. Evaluation of natural hog casings modified by surfactant solutions combined with lactic acid by response surface methodology. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwata, L.; Feng, L.; Yian, N.; Yoshida, I.R.; Palihakkara, I.R.; Silva, N.D.; Tanaka, H.; Nga, N.T. Reduction of waste from beverage industry in Shizuoka prefecture. Available online: http://www.iai.ga.a.u-tokyo.ac.jp/mizo/lecture/noukoku-1/group-work/2012/G2_e.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Japanese Cabinet Approves Bill to Amend Food Recycling Law. Available online: https://www.japanfs.org/en/news/archives/news_id026664.html (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Ahmadi, A.; Shadboorestan, A. Oxidative stress and cancer; the role of hesperidin, a citrus natural bioflavonoid, as a cancer chemoprotective agent. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.H.; Otani, C.; García-Martín, J.F. Flavonoids as a starting point for therapeutics against COVID-19: Current state-of-the art research advances. In The Book of Flavonoids, 1st ed.; Feng, C.-H., García Martín, J.F., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Chapter 12; pp. 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.-Y.; Li, P.-J.; Xie, R.-S.; Cao, R.-S.; Su, D.-L.; Shan, Y. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle composites based on hesperidin and pectin and their synergistic antibacterial mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Zheng, M.; Li, X.Z.; Zhou, J.; Shang, Y.-X.; Li, Z.S.; Qu, L.M. A consecutive extraction of pectin and hesperidin from Citrus aurantium L.: Process optimization, extract mechanism, characterization and bioactivity analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 182, 114849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavite, P.; Donzelli, A. Hesperidin and SARS-CoV-2: New light on the healthy function of citrus fruits. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-H.; Otani, C.; Ogawa, Y. Innovatively identifying naringin and hesperidin by using terahertz spectroscopy and evaluating flavonoids extracts from waste orange peels by coupling with multivariate analysis. Food Control. 2022, 137, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, J.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Sendra, E.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Navarro, C.; Pérez-Alvarez, J. Orange fibre as potential functional ingredient for dry-cured sausages. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 226, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ginés, J.M.; Fernández-López, J.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Sendra, E.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. Effect of storage conditions on quality characteristics of bologna sausages made with citrus fiber. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichan, T.; Kijpatanasilp, I.; Asadatorn, N.; Assatarakul, K. Optimization of ultrasound extraction of functional compound from making seed by response surface methodology and antimicrobial activity of optimized extract with its application in orange juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 83, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Fang, Q.; Zhong, L.; Wei, Q. Preparation, optimization, and characterization of inclusion complexes of Cinnamomum longepaniculatum essential oil in β-cyclodextrin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.A.; Zaidel, D.N.A.; Muhamad, I.I.; Hamid, M.A.; Yaakob, H.; Jusoh, Y.M.M. Optimization of the amtopxodamt-rich xanthone extract from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) pericarp via microwave-assisted extraction. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.H.; Sun, D.W. Optimisation of immersion vacuum cooling operation and quality of Irish cooked sausages by using response surface methodology. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Hu, J.G.; Fu, L.D.; Zhang, L.J. Optimization of enzymolysis-ultrasonic assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Momordica charabtia L. by response surface methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.H. Optimizing procedures of ultrasound-assisted extraction of waste orange peels by response surface methodology. Molecules 2022, 27, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.M.; Dornelles, R.C.P.; Vidal, A.R.; Fontoura, A.; Kubota, E.H.; Mello, R.O.; Kempka, A.P.; Deminate, I.M. Development of cooked and smoked chicken sausage with reduced sodium and fat. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2017, 26, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; Possas, A.; Rincon, F.; Garcia-Gimeno, R.M.; Martinez, B. Model for Listeria monocytogenes inactivation by high hydrostatic pressure processing in Spanish chorizo sausage. Food Microbiol. 2018, 69, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, H.; Hosseini, H.; Kamankesh, M.; Ghasemzadeh-Mohammadi, V.; Mohammadi, A. Rapid determination of nitrosamines in sausage and salami using microwave-assisted extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; Makino, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Thuyet, D.C.; García-Martín, J.F. Hyperspectral imaging in tandem with R statistics and image processing for detection and visualisation of pH in Japanese big sausages under different storage conditions. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, Y. Rapid and nondestructive classification of Cantonese sausage degree using hyperspectral images. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, S.B.; Guo, Z.M.; Huang, X.W.; Hu, X.T.; Holmes, M.; Zou, X.B. Noise-free microbial colony counting method based on hyperspectral features of agar plates. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamrruzzaman, M.; Kalita, D.; Ahmed, M.T.; ElMasry, G.; Makino, Y. Effect of variable selection algorithms on model performance for predicting moisture content in biological materials using spectral data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1202, 339390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripatrawan, U.; Makino, Y. Simultaneous assessment of various quality attributes and shelf life of packaged bratwurst using hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2018, 146, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Z.; Yoon, S.-C.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.F.; Lu, C.J.; Li, N. Non-destructive assessment of final color and pH attributes of broiler breast fillets using visible and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging: A preliminary study. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 92, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; Makino, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Rodríguez-Pulido, F.J. Real-time prediction of pre-cooked Japanese sausages color with different storage days using hyperspectral imaging. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.H.; Makino, Y. Colour analysis in sausages stuffed in modified casings with different storage days using hyperspectral imaging—A feasibility study. Food Control. 2020, 111, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; Makino, Y.; García-Martín, J.F. Hyperspectral imaging coupled with multivariate analysis and image processing for detection and visualisation of colour in cooked sausages stuffed with different modified casings. Foods 2020, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; Makino, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Rodríguez-Pulido, F.J. Estimation of adenosine triphosphate content in ready-to-eat sausages with different storage days, using hyperspectral imaging coupled with R statistics. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdolec, N.; Hadžiosmanović, M.; Kozačinski, L.; Cvrtila, Ž.; Filipović, I.; Škrivanko, M.; Leskovar, K. Microbial and physicochemical succession in fermented sausages produced with bacteriocinogenic culture of Lactobacillus sakei and semi-purified bacteriocin mesenterocin Y. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Sun, D.-W.; Allen, P. Prediction of moisture, colour and pH in cooked, pre-sliced turkey hams by NIR hyperspectral imaging system. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.L.; Cai, F.H.; Zhu, P.Y.; Fang, H.X.; Li, J.W.; He, S.L. Non-invasive and rapid pH monitoring for meat quality assessment using a low-cost portable hyperspectral scanner. Meat Sci. 2019, 152, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Makino, Y.; Oshita, S. Parsimonious model development for real-time monitoring of moisture in red meat using hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; Sun, D.W.; García-Martín, J.F.; Zhang, Z.-H. Effects of different cooling methods on shelf-life of cooked jumbo plain sausages. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokić, S.; Molnar, M.; Cikoš, A.-M.; Jakovljević, M.; Šafranko, S.; Jerković, I. Separation of selected bioactive compounds from orange peel using the sequence of supercritical CO2 extraction and ultrasound solvent extraction: Optimization of limonene and hesperidin content. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2799–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; García-Martín, J.F.; Lavado, M.B.; López-Barrera, M.C.; Álvarez-Mateos, P. Evaluation of different solvents on flavonoids extraction efficiency from sweet oranges and ripe and immature Seville oranges. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 55, 3123–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.S.; López, B.G.-C.; Diniz, S.N.; Antunes, A.A.; Garcia, D.M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Marcucci, M.C. Quantification of flavonoids in brazilian orange peels and industrial orange juice processing wastes. Agric. Sci. 2017, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjelvareid, M.H.; Heia, K.; Olsen, S.H.; Stormo, S.K. Detection of blood in fish muscle by constrained spectral unmixing of hyperspectral images. J. Food Eng. 2017, 212, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnay, L.; Králik, F.; Oros, G.; Koncz, Á.; Firtha, F. Monitoring the effect of transglutaminase in semi-hard cheese during ripening by hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Eng. 2017, 196, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Yang, D.; Ying, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, T. Discrimination between Shaoxing wines and other Chinese rice wines by near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pu, H.B.; Sun, D.-W.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.-A. Combination of spectra and texture data of hyperspectral imaging for prediction of pH in salted meat. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.B.; Sun, D.-W.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Cheng, J.-H. Using wavelet textural features of visible and near infrared hyperspectral image to differentiate between fresh and frozen-thawed pork. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3088–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMasry, G.M.; Nakauchi, S. Image analysis operations applied to hyperspectral images for non-invasive sensing of food quality—A comprehensive review. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 142, 53–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.Y.; Oshita, S.; Makino, Y.; Han, D. Influence of sampling component on determination of soluble solids content of Fuji apple by near-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 71, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.L.; Riccioli, C.; Sun, D.-W. Development of an alternative technique for rapid and accurate determination of fish caloric density based hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Eng. 2016, 190, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.B.; Yoon, S.-C.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, C.Y. Prediction of pH of fresh chicken breast fillets by VNIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Eng. 2017, 208, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolamo, A.D.; Lippolis, V.; Nordkvist, E.; Visconti, A. Rapid and non-invasive analysis of deoxynivalenol in durum and common wheat by Fourier-Transform Near Infrared (FT-NIR) spectroscopy. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2009, 26, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
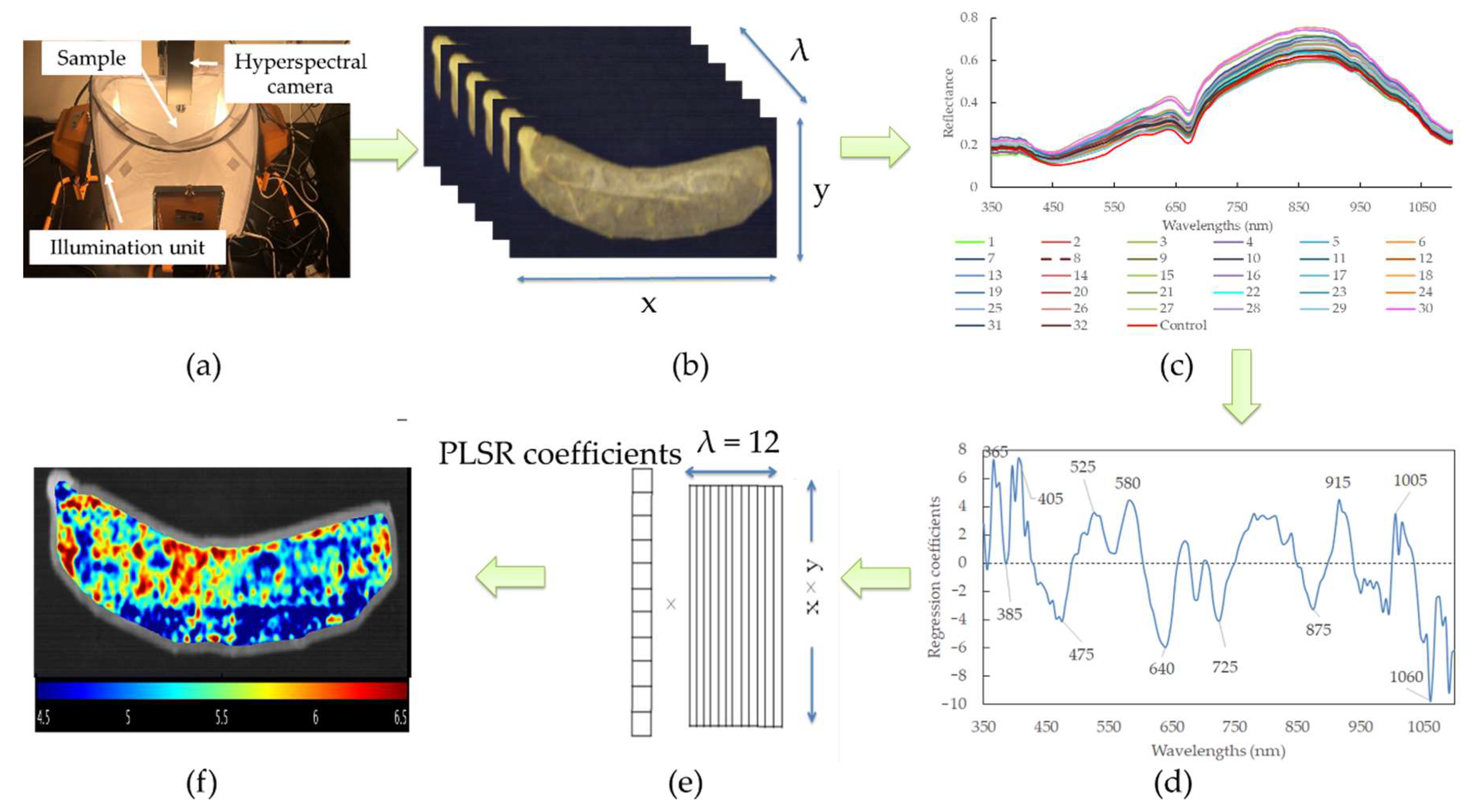
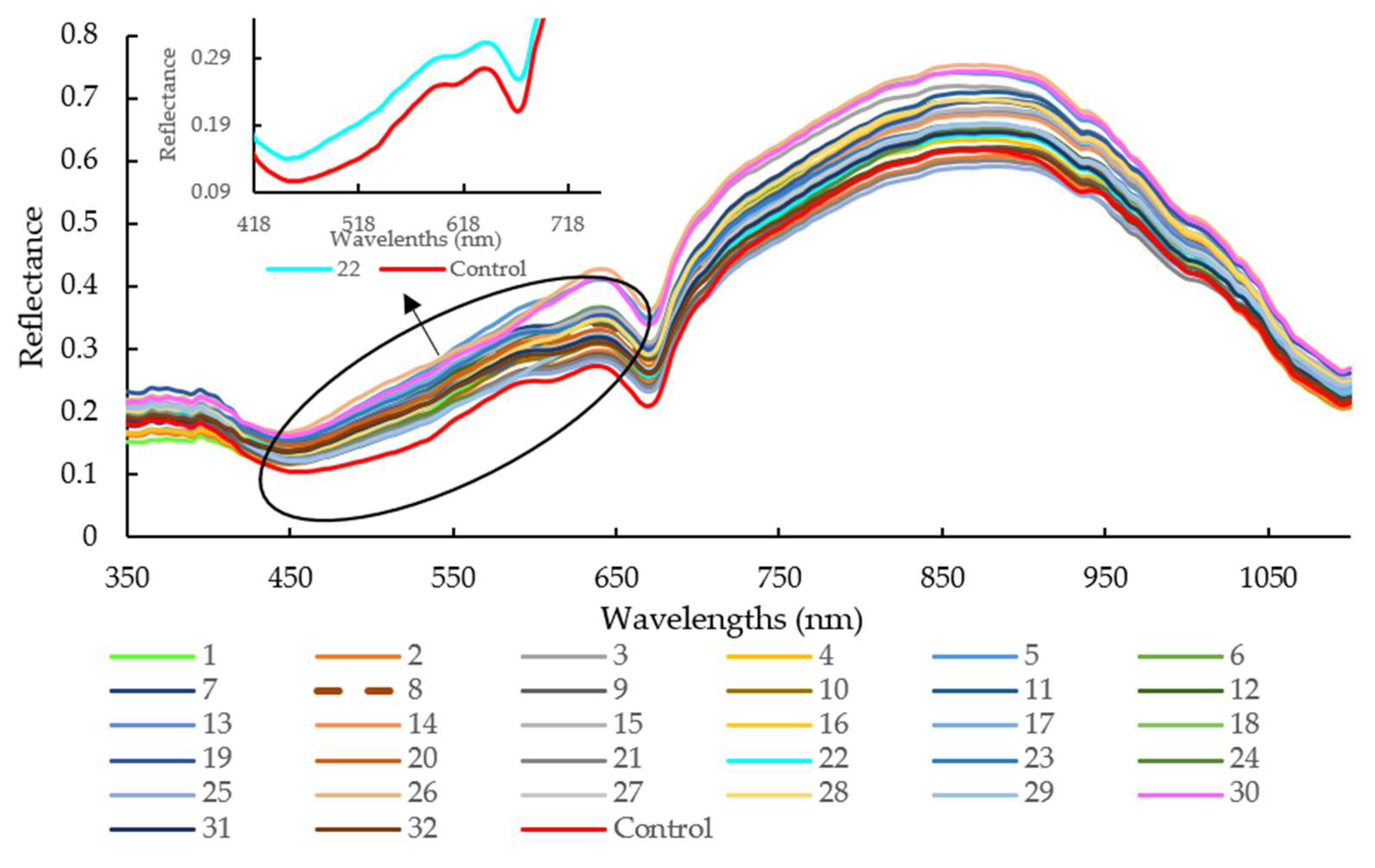




| Treatments | Surfactant Solution with Orange Extracts | Slush Slat with Lactic Acid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soy Lecithin Concentration (X1, %, w/w) | Soy Oil Concentration (X2,%, w/w) | Orange Extracts (X3, %, w/w) | Treatment Time (X5, min) | Lactic Acid (ml/kg NaCl, X4) | Treatment Time (X5, min) | |
| 1 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 2 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 22.50 (A, +α) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 3 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 1.18 (F,−1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) | 18.00 (F,−1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 4 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 16.50 (A, -α) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 5 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 6 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 7 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 8 | 1.07 (A, -α) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 9 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 105 (A, +α) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 105 (A, +α) |
| 10 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 45 (A, -α) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 45(A, -α) |
| 11 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 12 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 13 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 14 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 15 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 16 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 17 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 2.93(A, +α) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 18 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 19 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 20 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) | 21.00 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 21 | 2.11(F, −1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 60 (F, −1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 22 | 4.20(F, +1) | 1.18 (F, −1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) |
| 23 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.53(A, +α) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 24 | 5.16 (A, +α) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 25 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.40 (F, +1) | 90 (F, +1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 26 | 3.16(C, 0) | 1.78(C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 27 | 4.20 (F, +1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 90 (F, +1) |
| 28 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78(C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 29 | 3.16 (C, 0) | 1.78(C, 0) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 30 | 2.11 (F, −1) | 2.38 (F, +1) | 0.12 (F, −1) | 60 (F, −1) | 18.00 (F, −1) | 60(F, −1) |
| 31 | 3.16(C, 0) | 1.78 (C, 0) | 0.00 (A, -α) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| 32 | 3.20(C, 0) | 0.60 (A, -α) | 0.26 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) | 19.50 (C, 0) | 75 (C, 0) |
| Analysis of Variance | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Df | Adj SS | F-Value |
| Model | 20 | 14.45 | 1.12 |
| Linear | 5 | 3.54 | 1.10 |
| X1 | 1 | 1.64 | 2.56 |
| X2 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| X3 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| X4 | 1 | 0.00 | 0 |
| X5 | 1 | 1.88 | 2.93 |
| Square | 5 | 2.55 | 0.79 |
| X1 × X1 | 1 | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| X2 ×X2 | 1 | 0.81 | 1.27 |
| X3 ×X3 | 1 | 0.64 | 1.00 |
| X4 ×X4 | 1 | 0.60 | 0.93 |
| X5 × X5 | 1 | 0.71 | 1.10 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 10 | 8.37 | 1.30 |
| X1 × X2 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| X1 × X3 | 1 | 3.98 | 6.19 * |
| X1 × X4 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| X1 × X5 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| X2 × X3 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.78 |
| X2 × X4 | 1 | 1.04 | 1.62 |
| X2 × X5 | 1 | 0.66 | 1.02 |
| X3 × X4 | 1 | 0.68 | 1.06 |
| X3 × X5 | 1 | 0.84 | 1.30 |
| X4 × X5 | 1 | 0.60 | 0.93 |
| Error | 11 | 7.07 | |
| Lack of Fit | 6 | 3.30 | 0.73 |
| Pure Error | 5 | 3.78 | |
| Total | 31 | 21.52 |
| Treatments | Calibration Group (n = 110) | Prediction Group (n = 55) | Cross-Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectance (R) | Rc2 | RMSEC (%) | Rp2 | RMSEP (%) | Rcv2 | RMSECV (%) | |
| Raw | 0.6849 | 0.4628 | 0.6485 | 0.4709 | 0.7496 | 0.4063 | |
| 1st Derivative | 0.5342 | 0.5626 | 0.6401 | 0.4766 | 0.8756 | 0.2864 | |
| 2nd Derivative | 0.6291 | 0.502 | 0.3843 | 0.6233 | 0.7431 | 0.4115 | |
| MSC | 0.5569 | 0.5488 | 0.6416 | 0.4756 | 0.6524 | 0.4787 | |
| SNV | 0.5570 | 0.5487 | 0.6416 | 0.4756 | 0.6528 | 0.4785 | |
| Normalization | 0.6770 | 0.4685 | 0.6855 | 0.4455 | 0.7194 | 0.4301 | |
| Normalization + 1st Derivative | 0.6813 | 0.4654 | 0.6503 | 0.4698 | 0.7152 | 0.4333 | |
| 1st Derivative + Normalization | 0.5692 | 0.5411 | 0.5524 | 0.5314 | 0.6197 | 0.5007 | |
| Normalization + 2nd Derivative | 0.7282 | 0.4298 | 0.4091 | 0.6106 | 0.7534 | 0.4032 | |
| 2nd Derivative + Normalization | 0.3417 | 0.6688 | 0.1309 | 0.7406 | 0.3447 | 0.6573 | |
| Absorbance (A) | Raw | 0.7025 | 0.4496 | 0.6626 | 0.4614 | 0.7305 | 0.4216 |
| 1st Derivative | 0.7300 | 0.4283 | 0.6789 | 0.4501 | 0.7798 | 0.3810 | |
| 2nd Derivative | 0.5257 | 0.5677 | 0.3710 | 0.63 | 0.6544 | 0.4733 | |
| MSC | 0.5479 | 0.5543 | 0.5677 | 0.5223 | 0.6384 | 0.4883 | |
| SNV | 0.5476 | 0.5545 | 0.5680 | 0.5221 | 0.6384 | 0.4883 | |
| Normalization | 0.5021 | 0.5817 | 0.6015 | 0.5015 | 0.5927 | 0.5182 | |
| Normalization + 1st Derivative | 0.5324 | 0.5637 | 0.6560 | 0.4659 | 0.5706 | 0.5321 | |
| 1st Derivative + Normalization | 0.4812 | 0.5938 | 0.4831 | 0.5711 | 0.6123 | 0.5056 | |
| Normalization + 2nd Derivative | 0.6149 | 0.5116 | 0.2514 | 0.6873 | 0.6240 | 0.4979 | |
| 2nd Derivative + Normalization | 0.0179 | 0.8170 | 0.0217 | 0.7857 | 0.0183 | 0.8045 | |
| Treatments | Calibration Group (n = 110) | Prediction Group (n = 55) | Cross-Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectance | Rc2 | RMSEC (%) | Rp2 | RMSEP (%) | Rcv2 | RMSECV (%) | |
| Raw | 0.6876 | 0.4608 | 0.6648 | 0.4599 | 0.6844 | 0.4561 | |
| 1st Derivative | 0.5881 | 0.5291 | 0.6257 | 0.486 | 0.6373 | 0.4890 | |
| 2nd Derivative | 0.5560 | 0.5493 | 0.6640 | 0.4604 | 0.6001 | 0.5135 | |
| MSC | 0.5370 | 0.5609 | 0.6530 | 0.4680 | 0.6319 | 0.4926 | |
| SNV | 0.5369 | 0.5610 | 0.6532 | 0.4678 | 0.6229 | 0.4986 | |
| Normalization | 0.6860 | 0.4619 | 0.6896 | 0.4426 | 0.6954 | 0.4482 | |
| Normalization + 1st Derivative | 0.6695 | 0.4739 | 0.6613 | 0.4623 | 0.6705 | 0.4661 | |
| 1st Derivative + Normalization | 0.6124 | 0.5132 | 0.6189 | 0.4904 | 0.6021 | 0.5122 | |
| Normalization + 2nd Derivative | 0.6603 | 0.4805 | 0.6688 | 0.4571 | 0.6730 | 0.4643 | |
| 2nd Derivative + Normalization | 0.5427 | 0.5574 | 0.6393 | 0.4771 | 0.5956 | 0.5164 | |
| Absorbance | Raw | 0.6996 | 0.4518 | 0.6706 | 0.4559 | 0.7050 | 0.4410 |
| 1st Derivative | 0.6553 | 0.4840 | 0.6835 | 0.4469 | 0.7026 | 0.4428 | |
| 2nd Derivative | 0.6608 | 0.4801 | 0.6653 | 0.4596 | 0.6654 | 0.4697 | |
| MSC | 0.5564 | 0.549 | 0.5824 | 0.5133 | 0.5709 | 0.5319 | |
| SNV | 0.5209 | 0.5706 | 0.6267 | 0.4854 | 0.5912 | 0.5191 | |
| Normalization | 0.5719 | 0.5394 | 0.5315 | 0.5437 | 0.5956 | 0.5163 | |
| Normalization + 1st Derivative | 0.5331 | 0.5633 | 0.5782 | 0.5159 | 0.5616 | 0.5376 | |
| 1st Derivative + Normalization | 0.5517 | 0.5519 | 0.5307 | 0.5442 | 0.5413 | 0.5499 | |
| Normalization + 2nd Derivative | 0.5899 | 0.5279 | 0.5822 | 0.5135 | 0.5973 | 0.5153 | |
| 2nd Derivative + Normalization | 0.5892 | 0.5284 | 0.5728 | 0.5192 | 0.5977 | 0.515 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, C.-H.; Arai, H.; Rodríguez-Pulido, F.J. Evaluation of pH in Sausages Stuffed in a Modified Casing with Orange Extracts by Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with Response Surface Methodology. Foods 2022, 11, 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182797
Feng C-H, Arai H, Rodríguez-Pulido FJ. Evaluation of pH in Sausages Stuffed in a Modified Casing with Orange Extracts by Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with Response Surface Methodology. Foods. 2022; 11(18):2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182797
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Chao-Hui, Hirofumi Arai, and Francisco J. Rodríguez-Pulido. 2022. "Evaluation of pH in Sausages Stuffed in a Modified Casing with Orange Extracts by Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with Response Surface Methodology" Foods 11, no. 18: 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182797
APA StyleFeng, C.-H., Arai, H., & Rodríguez-Pulido, F. J. (2022). Evaluation of pH in Sausages Stuffed in a Modified Casing with Orange Extracts by Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with Response Surface Methodology. Foods, 11(18), 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182797








