Effects of Extraction Methods on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Common Vetch Starch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
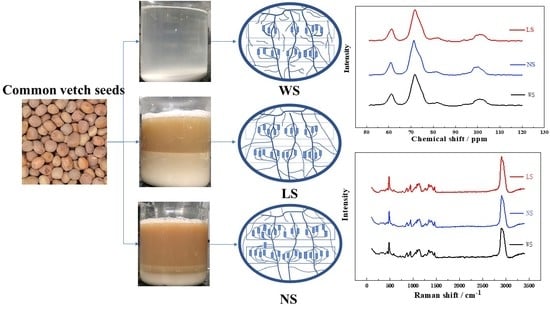
2.2. Starch Extraction
2.3. Chemical Composition
2.4. Morphological Characteristics
2.5. Particle Size Distribution
2.6. Molecular Weight and Amylopectin Chain-Length Distributions
2.7. X-ray Diffraction
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Raman Spectroscopy
2.9. 13C CP/MAS NMR Analysis
2.10. Pasting Property
2.11. Thermal Property
2.12. Starch Solubility and Swelling Power
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Compositions
3.2. Morphology Structure and Particle Size Distribution of Starch Granules
3.3. Molecular Weight and Chain Length Distribution of the Starches
3.4. Crystalline Structure
3.5. Pasting and Thermal Properties
3.6. Starch Solubility (SA) and Swelling Power (SP)
3.7. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santiago-Ramos, D.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.d.D.; Véles-Medina, J.J.; Salazar, R. Physicochemical properties of nixtamalized black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flours. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Han, J.A.; Liu, Q.; Chung, H.J. Effect of processing, storage, and modification on in vitro starch digestion characteristics of food legumes: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egharevba, H.O. Chemical Properties of Starch and Its Application in the Food Industry. In Chemical Properties of Starch; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Effects of hydrothermal-alkali and freezing-thawing pre-treatments on modification of corn starch with octenyl succinic anhydride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Hedayati, S.; Shahidi, F. Effects of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata) Protein Isolate on Rheological, Textural, and Structural Properties of Native Corn Starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Shahidi, F.; Hedayati, S. A novel starch from bitter vetch (Vicia ervilia) seeds: A comparison of its physicochemical, structural, thermal, rheological, and pasting properties with conventional starches. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, W.; Huang, Y.; Coulter, J.A.; Nan, Z. Common vetch cultivars improve yield of oat row intercropping on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau by optimizing photosynthetic performance. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 117, 126088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırıncıoğlu, H.K.; Ünal, S.; Erbektaş, E.; Doğruyol, L. Relationships between seed yield and yield components in common vetch (Vicia sativa ssp. sativa) populations sown in spring and autumn in central Turkey. Field Crops Res. 2010, 116, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.J.; Stout, D.G.; Moore, T. Forage production by four annual cropping sequences emphasizing barley under irrigation in southern interior British Columbia. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1992, 72, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vasilakoglou, I.B.; Dhima, K.V.; Dordas, C.A.; Yiakoulaki, M.D. Forage yield and quality of common vetch mixtures with oat and triticale in two seeding ratios. Field Crops Res. 2006, 99, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Q.; Shen, Y. Seed mixture of oats and common vetch on fertilizer and water-use reduction in a semi-arid alpine region. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 219, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Tian, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, M.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X. The multi-scale structure, thermal and digestion properties of mung bean starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Shen, Q.; Zheng, W.; Tan, B. Properties and qualities of vermicelli made from sour liquid processing and centrifugation starch. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, J.C. Characteristics of mung bean starch isolated by using lactic acid fermentation solution as the steeping liquor. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Whiteside, W.S.; Singh, A.; Ozogul, F.; Gupta, A.; Gahlawat, S.K. Properties, preparation methods, and application of sour starches in the food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.S.; Neves, G.; Caliari, M.; Júnior, M.S.S. Waxy maize starch modified by sun-drying after spontaneous or backslopping fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, T.P.R.; Leonel, M.; Mischan, M.M.; Cabello, C. Study and application of photo-modified cassava starch with lactic acid and UV-C irradiation. LWT 2020, 139, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Gong, S.; Li, M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J. Physicochemical properties of potato starch fermented by amylolytic Lactobacillus plantarum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Chen, J.R.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.H.; Ma, Z.Q.; Ren, L.K.; Wu, N.; Chen, F.L.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, B.; et al. Effects of fermentation on the structure and physical properties of glutinous proso millet starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 123, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayemi, O.E.; Ojokoh, A.O. The Effect of Different Fermentation Techniques on the Nutritional Quality of the Cassava Product (fufu). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2014, 38, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, J.; Ji, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Endogenous protein and lipid facilitate the digestion process of starch in cooked quinoa flours. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Guo, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wei, C. Comparative structure of starches from high-amylose maize inbred lines and their hybrids. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, J.; Hong, Y.; Liu, G.; Zheng, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, P. Impact of amylose content on starch physicochemical properties in transgenic sweet potato. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zou, F.; Guo, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. The relationship between linear chain length distributions of amylopectin and the functional properties of the debranched starch-based films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 279, 119012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, R.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, X. Effect of natural fermentation on the structure and physicochemical properties of wheat starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chao, C.; Yu, J.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S. New insight into starch retrogradation: The effect of short-range molecular order in gelatinized starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Boye, J.I. Molecular rearrangement of Laird lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) starch during different processing treatments of the seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atichokudomchai, N.; Varavinit, S.; Chinachoti, P. A study of ordered structure in acid-modified tapioca starch by 13C CP/MAS solid-state NMR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.H.; Lin, Z.; Liu, L.; Qin, W.; Wang, A.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.T. Effects of ultrasound-assisted cellulase enzymatic treatment on the textural properties and in vitro starch digestibility of brown rice noodles. LWT 2021, 146, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of pregelatinized starch on the characteristics, microstructures, and quality attributes of glutinous rice flour and dumplings. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvere, P.O.; Onyekwere, E.U.; Ngoddy, P.O. Production of maize-bambara groundnut complementary foods fortified pre-fermentation with processed foods rich in calcium, iron, zinc and provitamin A. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shen, Q. Studies on the physicochemical properties of mung bean starch from sour liquid processing and centrifugation. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, R.; Dewanti-Hariyadi, R.; Hariyadi, P.; Fardiaz, D. Profile of Microorganisms and Amylose Content of White Corn Flours of Two Local Varieties as Affected by Fermentation Process. In Proceedings of the 2014 2nd International Conference on Food and Agricultural Sciences, Auckland, New Zealand, 12–13 November 2014; Volume 77, pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Q.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Combinatorial effect of fermentation and drying on the relationship between the structure and expansion properties of tapioca starch and potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 145, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, M.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T.; Jin, Z.; Mu, W. Impact of mild acid hydrolysis on structure and digestion properties of waxy maize starch. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 506–513. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Zou, J.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Duan, R.; Yang, B. Effect of lactobacteria fermentation on structure and physicochemical properties of Chinese yam starch (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.). Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Xu, B.; Qin, F.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Meng, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. C-type starch from high-amylose rice resistant starch granules modified by antisense RNA inhibition of starch branching enzyme. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2010, 58, 7383–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, J.; Jin, F. Granular structure and allomorph position in C-type Chinese yam starch granule revealed by SEM, 13C CP/MAS NMR and XRD. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Qin, F.; Zhou, W.; Yu, H.; Xu, B.; Chen, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. Granule Structure and Distribution of Allomorphs in C-Type High-Amylose Rice Starch Granule Modified by Antisense RNA Inhibition of Starch Branching Enzyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11946–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, R.; Strappe, P.; Blanchard, C.; Zhou, Z. Insights into the multi-scale structure of wheat starch following acylation: Physicochemical properties and digestion characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Fang, G.; Luo, Z.; Gao, Q. Effect of granule size on the structure and digestibility of jackfruit seed starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gao, J.; Wu, G.; Zheng, J.; Ouyang, S.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, G. Physicochemical and structural properties of A- and B-starch isolated from normal and waxy wheat: Effects of lipids removal. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Oyedeji, A.B.; Ogundele, O.M.; Adebo, O.A.; Kayitesi, E.; Njobeh, P.B. Infrared heating under optimized conditions enhanced the pasting and swelling behaviour of cowpea starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Shang, Z.; Man, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, C.; Wei, C. Comparison of molecular structures and functional properties of high-amylose starches from rice transgenic line and commercial maize. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Combined molecular and supramolecular structural insights into pasting behaviors of starches isolated from native and germinated waxy brown rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 283, 119148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chi, C. Impact of long-term storage on multi-scale structures and physicochemical properties of starch isolated from rice grains. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.-F.; Lu, F.; Yang, Z.; Tao, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.-L. Physical modification of waxy maize starch: Combining SDS and freezing/thawing treatments to modify starch structure and functionality. Food Struct. 2022, 32, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabot, G.L.; Silva, E.K.; Emerick, L.B.; Felisberto, M.H.F.; Clerici, M.T.P.S.; Meireles, M.A.A. Physicochemical, morphological, thermal and pasting properties of a novel native starch obtained from annatto seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Content | WS | LS | NS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total starch | 91.37 ± 0.53 a | 92.56 ± 0.39 a | 91.98 ± 0.18 a |
| Moisture | 4.85 ± 0.05 a | 4.85 ± 0.05 a | 4.83 ± 0.18 a |
| Lipid | 0.86 ± 0.05 a | 0.77 ± 0.12 a | 0.52 ± 0.01 b |
| Protein | 1.07 ± 0.12 a | 0.83 ± 0.12 a | 0.93 ± 0.01 a |
| Amylose | 30.25 ± 0.65 c | 35.69 ± 0.54 a | 32.34 ± 0.33 b |
| Content | WS | LS | NS |
|---|---|---|---|
| D (3,2) | 27.77 ± 0.09 a | 26.44 ± 0.02 b | 12.95 ± 0.17 c |
| D10 | 18.31 ± 0.26 a | 18.25 ± 0.02 a | 12.74 ± 0.37 b |
| D50 | 28.30 ± 0.02 a | 27.85 ± 0.02 b | 23.58 ± 0.18 c |
| D90 | 43.56 ± 0.59 a | 42.42 ± 0.04 b | 38.60 ± 0.21 c |
| SSA (m2/kg) | 224 ± 1 c | 297 ± 2 b | 463 ± 13 a |
| Mw (kDa) | 52339 ± 977 a | 44042 ± 149 b | 35573 ± 372 c |
| Mn(kDa) | 13416 ± 350 a | 12309 ± 128 b | 9294 ± 55 c |
| Mw/Mn | 3.90 ± 0.11 a | 3.58 ± 0.03 b | 3.83 ± 0.06 a |
| DP 6–12 (%) | 42.04 ± 0. 04 a | 37.62 ± 0. 04 b | 25.47 ± 0.16 c |
| DP 13–24 (%) | 35.98 ± 0.21 c | 40.84 ± 0.05 b | 48.21 ± 0.18 a |
| DP 25–36 (%) | 12.35 ± 0.12 b | 11.96 ± 0.01 b | 15.20 ± 0.18 a |
| DP > 37 (%) | 9.64 ± 0.14 b | 9.58 ± 0.01 b | 11.01 ± 0.13 a |
| Content | WS | LS | NS |
|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | |||
| Crystal type | C | C | C |
| RC (XRD, %) | 30.22 ± 0.13 c | 34.16 ± 0.20 b | 39.43 ± 0.41 a |
| FT-IR | |||
| DO (1047 cm−1/1022 cm−1) | 1.34 ± 0.00 c | 1.41 ± 0.01 b | 1.48 ± 0.00 a |
| DD (995 cm−1/1022 cm−1) | 0.80 ± 0.00 c | 0.87 ± 0.01 b | 0.94 ± 0.00 a |
| Raman spectrum | |||
| FWHM (480 cm−1) | 28.50 ± 0.52 a | 24.19 ± 0.60 b | 19.59 ± 0.13 c |
| 13C-NMR | |||
| RC (NMR, %) | 47.32 ± 0.9 c | 51.29 ± 1.11 b | 55.65 ± 1.23 a |
| DH (%) | 58.97 ± 0.86 c | 62.88 ± 1.03 b | 69.81 ± 0.77 a |
| PPA (%) | 5.91 ± 0.22 a | 4.72 ± 0.22 b | 2.60 ± 0.12 c |
| SH (%) | 1.93 ± 0.02 a | 1.73 ± 0.04 b | 1.27 ± 0.11 c |
| Content | WS | NS | LS |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV (cP) | 1812 ± 9 c | 2055 ± 10 a | 1905 ± 17 b |
| TV (cP) | 1518 ± 10 c | 1691 ± 21 a | 1553 ± 14 b |
| BD (cP) | 295 ± 1 b | 364 ± 19 a | 352 ± 3 a |
| FV (cP) | 2635 ± 37 c | 3126 ± 23 a | 2762 ± 25 b |
| SB (cP) | 1118 ± 28 c | 1435 ± 2 a | 1208 ± 11 b |
| PT (°C) | 77.27 ± 0.29 a | 74.47 ± 0.17 c | 75.60 ± 0.12 b |
| To (°C) | 63.46 ± 1.16 a | 59.93 ± 0.13 b | 57.46 ± 0.14 c |
| Tp (°C) | 68.39 ± 0.66 a | 68.78 ± 1.16 a | 67.59 ± 0.99 a |
| Tc (°C) | 75.24 ± 0.51 c | 77.09 ± 0.64 b | 80.50 ± 0.19 a |
| ΔH (J/g) | 15.61 ± 0.15 c | 17.69 ± 0.10 b | 20.17 ± 0.31 a |
| SA (%) | 12.47 ± 0.25 b | 13.72 ± 0.16 a | 14.03 ± 0.23 a |
| SP | 7.17 ± 0.11 c | 8.74 ± 0.01 a | 8.11 ± 0.07 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, X.; Geng, D.; Bian, X.; Tang, N. Effects of Extraction Methods on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Common Vetch Starch. Foods 2022, 11, 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182920
Zhang X, Cheng Y, Jia X, Geng D, Bian X, Tang N. Effects of Extraction Methods on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Common Vetch Starch. Foods. 2022; 11(18):2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182920
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaojun, Yongqiang Cheng, Xin Jia, Donghui Geng, Xiaojia Bian, and Ning Tang. 2022. "Effects of Extraction Methods on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Common Vetch Starch" Foods 11, no. 18: 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182920
APA StyleZhang, X., Cheng, Y., Jia, X., Geng, D., Bian, X., & Tang, N. (2022). Effects of Extraction Methods on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Common Vetch Starch. Foods, 11(18), 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182920