Differential Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus When Inhibited by Bacillus velezensis Strain B2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strain
2.2. Isolation of Bacterial Isolates from Camellia sinensis
2.3. Screen for Potential Biocontrol Agents against A. flavus
2.4. Identification of Bacterial Isolates That Show Antagonism against A. flavus
2.5. Conidiation Assays of A. flavus Antagonized by B1 and B2
2.6. Transcriptomic Analysis of A. flavus Inhibited by B2 Using RNA-Seq
3. Results
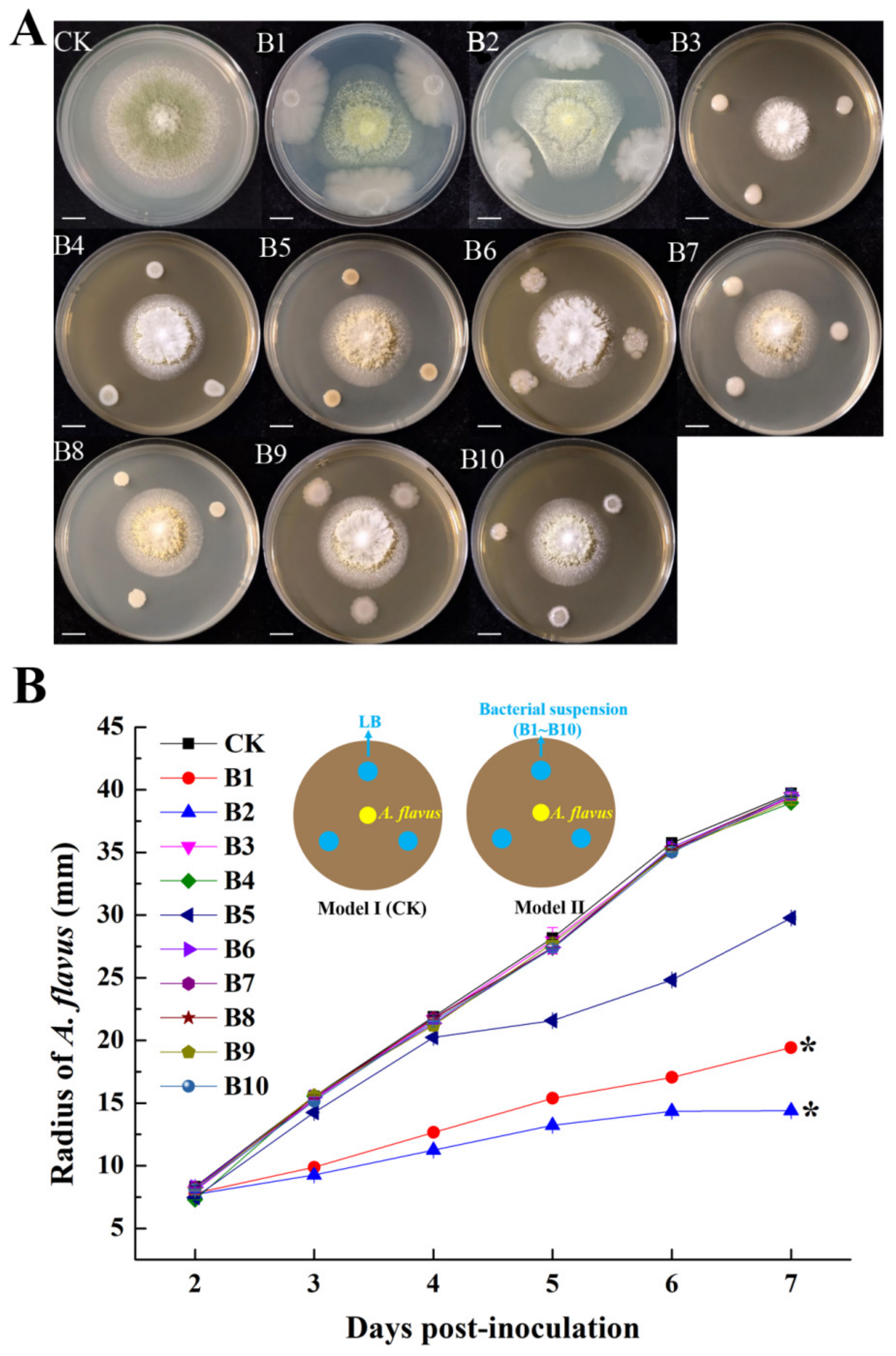
3.1. Screen for Potential Biocontrol Agents against A. flavus
3.2. Identification of Strains of B1 and B2
3.3. Conidiation of A. flavus Antagonized by B1 and B2
3.4. Overview of RNA-Seq Analysis and DEGs Identification of A. flavus Antagonized by B2
3.5. GO Terms Analysis of DEGs
3.6. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedayati, M.T.; Pasqualotto, A.C.; Warn, P.A.; Bowyer, P.; Denning, D.W. Aspergillus flavus: Human pathogen, allergen and mycotoxin producer. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1677–1692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.; Chen, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Aflatoxin Detoxification Using Microorganisms and Enzymes. Toxins 2021, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.P. Fungal secondary metabolism: Regulation, function and drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klich, M.A. Aspergillus flavus: The major producer of aflatoxin. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Amaike, S.; Affeldt, K.J.; Yin, W.; Franke, S.; Choithani, A.; Keller, N.P. The bZIP protein MeaB mediates virulence attributes in Aspergillus flavus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74030. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Bahuguna, A.; Ramalingam, S.; Lee, J.S.; Han, S.S.; Chun, H.S.; Kim, M. Aflatoxin Reduction and Retardation of Aflatoxin Production by Microorganisms in Doenjang during a One-Year Fermentation. Fungi 2022, 8, 190. [Google Scholar]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans and International Agency for Research on Cancer. Some traditional herbal medicines, some mycotoxins, naphthalene and styrene. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2002, 82, 171–249. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.; Lee, S.Y.; Woo, S.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Park, S.B.; Chun, H.S. Effect of plant-based compounds on the antifungal and antiaflatoxi-genic efficiency of strobilurins against Aspergillus flavus. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125663. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, H.N.; Das, C. A review on biological control and metabolism of aflatoxin. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 245–264. [Google Scholar]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Luo, X.Y. Molecular biology of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Health Res. 2003, 6, 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Global Burden of Aflatoxin-Induced Hepato cellular Carcinoma: A Risk Assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 818–824. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar-Mathur, P.; Sunkara, S.; Bhatnagar-Panwar, M.; Waliyar, F.; Sharma, K.K. Biotechnological advances for combating Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin contamination in crops. Plant Sci. 2015, 234, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hocking, A.D. Mycotoxins in Australia: Biocontral of aflatoxin in peanuts. Mycopathologia 2006, 162, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.Y.; Kang, Y.P.; Lei, Y. Studies on the Molecular Characteristics and Biological Control of Aspergillus Flavus in Peanut; Chinese Society of Plant Pathology: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cotty, P.J. Effect of atoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus on aflatoxin contamination of developing cottonseed. Plant Dis. 1990, 74, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorner, J.W.; Cole, R.J. Effect of application of nontoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus on subsequent aflatoxin contamination of peanuts in storage. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2002, 38, 329–339. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, G.; Singh, R.; Horn, B. Recombination and lineage specific gene loss in the aflatoxin gene cluster of Aspergillus flavus. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4870–4887. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, B.; Zhou, L.; Wei, D.D.; Xing, F.G.; Liu, Y. Prevention and Control of Peanut aflatoxin by non-toxic Aspergillus flavus. Chin. Soc. Fungi 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Fan, M.G. Research progress of aflatoxin removal technology. Food Mach. 2015, 31, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.W.; Zhang, D.H.; Yang, Y.; Cui, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.X.; Wang, X.P.; Jang, J. Prevention and Control of Peanut aflatoxin by non-toxic Aspergillus flavus. Chin. J. Oil Crops 2010, 32, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Run, P.S. Research Progress on Biological Control of aflatoxins in Peanut by antagonists. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 35, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lemfack, M.C.; Nickel, J.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R.; Piechulla, B. mVOC: Adatabase of microbial volatiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Morath, S.U.; Hung, R.; Bennett, J.W. Fxmgal volatile organic compounds: A review with emphasis on their biotechnollogical potential. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2012, 26, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.M.; Farag, M.A.; Hu, C.H.; Reddy, M.S.; Wei, H.X.; Paré, P.W.; Kloepper, J.W. Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Shang, Q.M.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.L. Analysis of Biomass production by Bacillus amylolyticus L-H15 and Optimization of fermentation process. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, W.D.; Ramarathnam, R.; Krishnamoorthy, A.S.; Savchuk, S.C. Identification and use of potential bacterial organic antifungal volatiles in biocontral. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 955–964. [Google Scholar]
- Zychowski, K.E.; Hoffmann, A.R.; Ly, H.J.; Pohlenz, C.; Buentello, A.; Romoser, A.; Gatlin, D.M.; Phillips, T.D. The effect of aflatoxin-B1 on red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) and assessment of dietary supplementation of NovaSil for the prevention of aflatoxicosis. Toxins 2013, 5, 1555–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Wochner, K.F.; Moreira, M.C.C.; Kalschne, D.L.; Colla, E.; Drunkler, D.A. Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 and M1 by Lactobacillus acidophilus and prebiotics in whole cow’s milk. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12670. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, O.L.; Suharoschi, R.; Gabbianelli, R. Biodetoxification and Protective Properties of Probiotics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1278. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, F.; Khalid, A.; Fu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Khan, S.; Wang, Z. Potential of Bacillus velezensis as a probiotic in animal feed: A review. Microbiology 2021, 59, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Song, Q.; Sun, W. Screening of Bacillus velezensis E2 and the inhibitory effect of its antifungal substances on Aspergillus flavus. Foods 2022, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Shan, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, F. Biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus on peanut kernels by use of a strain of marine Bacillus megaterium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Ni, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, S.; et al. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by cell-free extracts of Bacillus velezensis DY3108 with broad pH stability and excellent thermostability. Toxins 2018, 10, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Vahidinasab, M.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Henkel, M.; Hausmann, R.; Heravi, K.M. Bacillus velezensis UTB96 is an antifungal soil isolate with a reduced genome size compared to that of Bacillus velezensis FZB42. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00667-19. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Patlan, D.; Solis-Cruz, B.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G. The use of probiotics in poultry production for the control of bacterial infections and aflatoxins. In Prebiotics and Probiotics-Potential Benefits in Human Nutrition and Health; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Liu, Q.Z.; Yu, F.G.; Wang, X.D.; Shan, S.H. Study on inhibition of growth and toxin synthesis of Aspergillus flavus by a marine Bacillus strain. Agric. Life Sci. Ed. 2010, 36, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, M.M.; Jang, J.; Fan, L.P.; Li, J. Study on the germicidal effect and mechanism of far infrared on Aspergillus flavus spores. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fang, W. Duplication of a Pks gene cluster and subsequent functional diversification facilitate environmental adaptation in Metarhizium species. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Chen, X.X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Mi, W.B.; Guo, N.; Zhao, H.; Yue, Y.; Dryburgh, F.; et al. Genome-wide identification of pathogenicity, conidiation and colony sectorization genes in Metarhizium robertsii. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3896–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Drai, D.; Elmer, G.; Kafkafi, N.; Golani, I. Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 125, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, A.M.; Wilson, R.A.; Bok, J.W. Relationship between secondary metabolism and fungal development. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 447–459. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, K.C.; Cotty, P.J. An isolate of Aspergillus flavus used to reduce aflatoxin contamination in cottonseed has a defective polyketide synthase gene. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piechulla, B.; Degenhardt, J. The emerging importance of microbial volatile organic compounds. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’alessandro, M.; Erb, M.; Ton, J.; Brandenburg, A.; Karlen, D.; Zopfi, J.; Turlings, T.C.J. Volatiles produced by soil-borne endophytic bacteria increase plant pathogen resistance and affect tritrophic interactions. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ongena, M.; Jacques, P. Bacillus lipopeptides: Versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rauscher, S.; Pacher, S.; Hedtke, M.; Kniemeyer, O.; Fischer, R. A phosphorylation code of the Aspergillus nidulans global regulator VelvwtA (VeA) determines specific functions. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somashekar, D.; Rati, E.R.; Chandrashekar, A. PCR-restriction fragment length analysis of aflR gene for differentiation and detection of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in maize. Food Microbiol. 2004, 93, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Yao, Y.; Xu, S.; Xie, X. Fusion expression and anti-Aspergillus flavus activity of a novel inhibitory protein DN-AflR. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Fedorova, N.D.; Montalbano, B.G.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E.; Bennett, J.W.; Nierman, W.C. Tight control of mycotoxinbiosynthesis gene expression in Aspergillus flavus by temperature as revealed by RNA-Seq. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 322, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Li, B.; Yin, R.; Weng, Q.; Chen, Q. Development and evaluation of ITS- and aflP-based LAMP assays for rapid detection of Aspergillus flavus in food samples. Can. J. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh, M.; Shi, Z.Q.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Hu, L.B.; Ghassempour, A. Inhibition of the Aspergillus flavus grouth and aflatoxin B1 contamination on pistachio nut by fengycin and surfactin-producing Bacillus subtilis UTBSP1. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Dorner, J.W. Biological control of aflatoxin contamination of crops. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2008, 9, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Screening of Non-Toxin-Producing Aspergillus Flavus Strain and Its Application in Peanut Planting; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.K.; Weaver, M.A.; Horn, B.W.; Carbone, I.; Monacell, J.T.; Shier, W.T. Selection of Aspergillus flavus isolates for biological control of aflatoxins in corn. Toxin Rev. 2011, 30, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.L. Study on the inhibitory effect of volatile compounds produced by Bacillus on Aspergillus flavus. Cent. South Univ. For. Sci. Technol. 2008, 9, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, J.W.; Qu, S.Y.; Qi, X.Z.; Wang, G.X.; Ling, F. Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus velezensis K2 on growth, immunity and resistance to Vibrio harveyi infection of hybrid grouper. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Thurlow, C.M.; Williams, M.A.; Carrias, A.; Ran, C.; Newman, M.; Tweedie, J.; Allison, E.; Jescovitch, L.N.; Wilson, A.E.; Terhune, J.S.; et al. Bacillus velezensis AP193 exerts probiotic effects in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and reduces aquaculture pond eutrophication. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, Y.; Ke, X.; Yi, M.; Liu, Z.; Han, X.; Shi, C.; Lu, M. Bacillus velezensis LF01: In vitro antimicrobial activity against fish pathogens, growth performance enhancement, and disease resistance against streptococcosis in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 9023–9035. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Tang, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Tao, F.; Li, F.; Wang, Z. Characteristics and application of a novel species of Bacillus: Bacillus velezensis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 500–505. [Google Scholar]




| Pathway | Gene ID | Gene Description | Log2FC | Style |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aflatoxin biosynthetic process | AFLA_3422 | Aldo/keto reductase family | 9.50 | up |
| AFLA_860 | Cytochrome P450 | 8.23 | up | |
| Ribosome synthesis | AFLA_23553 | 50s ribosome-binding GTPase | 11.03 | up |
| AFLA_19265 | 50s ribosome-binding GTPase | 11.05 | up | |
| AFLA_7027 | 50s ribosome-binding GTPase | 9.39 | up | |
| Biosynthetic process | AFLA_1792 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | −2.56 | down |
| AFLA_2285 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | −2.24 | down | |
| Energy metabolism | AFLA_2285 | Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | −2.24 | down |
| Folding, sorting and degradation | AFLA_18974 | Protein processing in Endoplasmic reticulum | −2.17 | down |
| AFLA_12766 | Protein processing in Endoplasmic reticulum | −1.81 | down | |
| Catabolism | AFLA_3999 | Carbon metabolism | −1.65 | down |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, T.; Hu, X.; Zeng, G. Differential Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus When Inhibited by Bacillus velezensis Strain B2. Foods 2022, 11, 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223620
Wu Q, Li H, Wang S, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Jin T, Hu X, Zeng G. Differential Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus When Inhibited by Bacillus velezensis Strain B2. Foods. 2022; 11(22):3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223620
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qiaoyun, Huanhuan Li, Sunxing Wang, Zhongnian Zhang, Zhipeng Zhang, Tuwei Jin, Xiufang Hu, and Guohong Zeng. 2022. "Differential Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus When Inhibited by Bacillus velezensis Strain B2" Foods 11, no. 22: 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223620
APA StyleWu, Q., Li, H., Wang, S., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., Jin, T., Hu, X., & Zeng, G. (2022). Differential Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus When Inhibited by Bacillus velezensis Strain B2. Foods, 11(22), 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223620






