Health Risk Exposure Assessment of Migration of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Perfluorooctanoic Acid from Paper and Cardboard in Contact with Food under Temperature Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
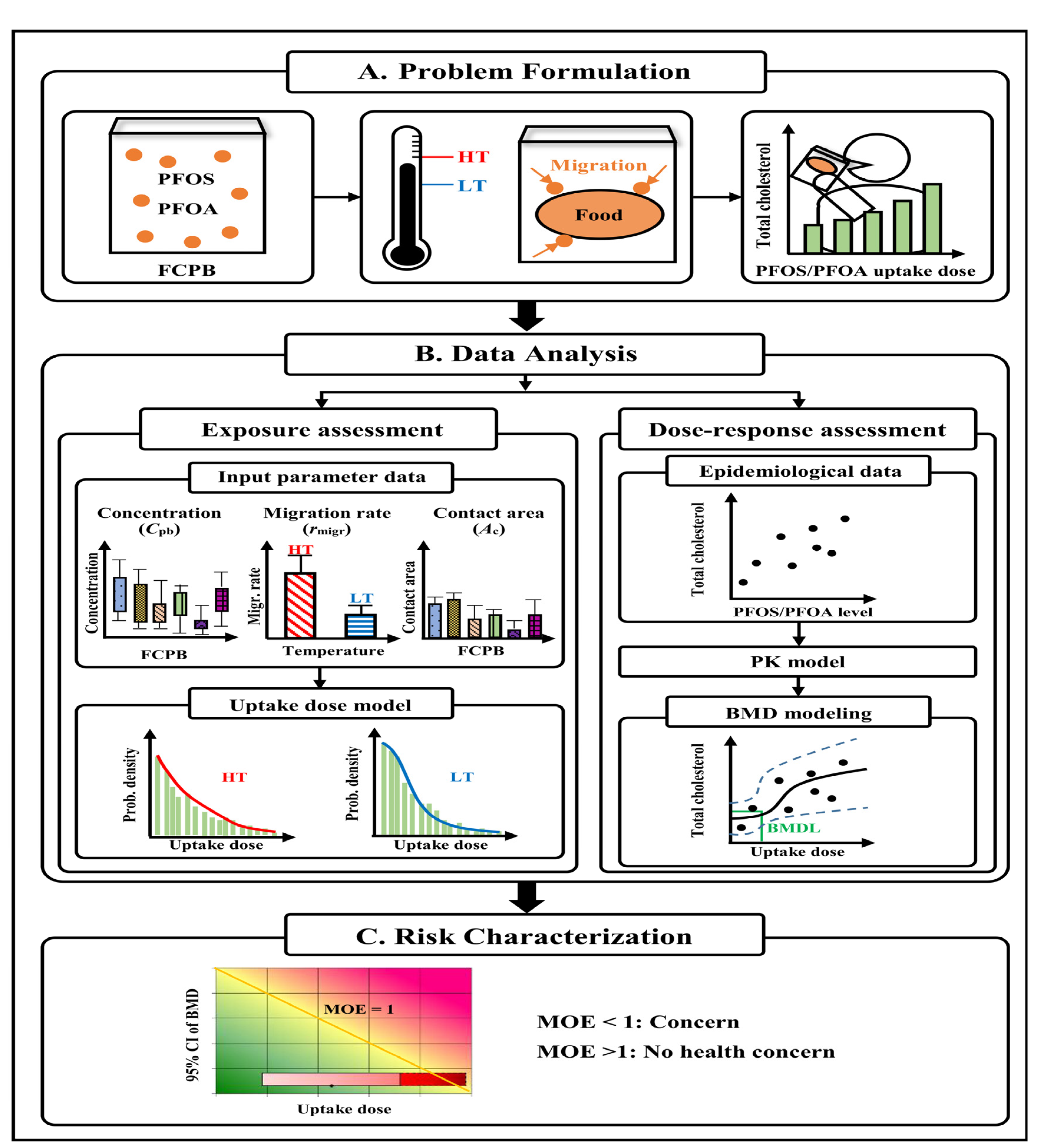
2.1. Study Framework
2.2. Study Data
2.3. Exposure Assessment
2.4. Dose–Response Assessment
2.5. Risk Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
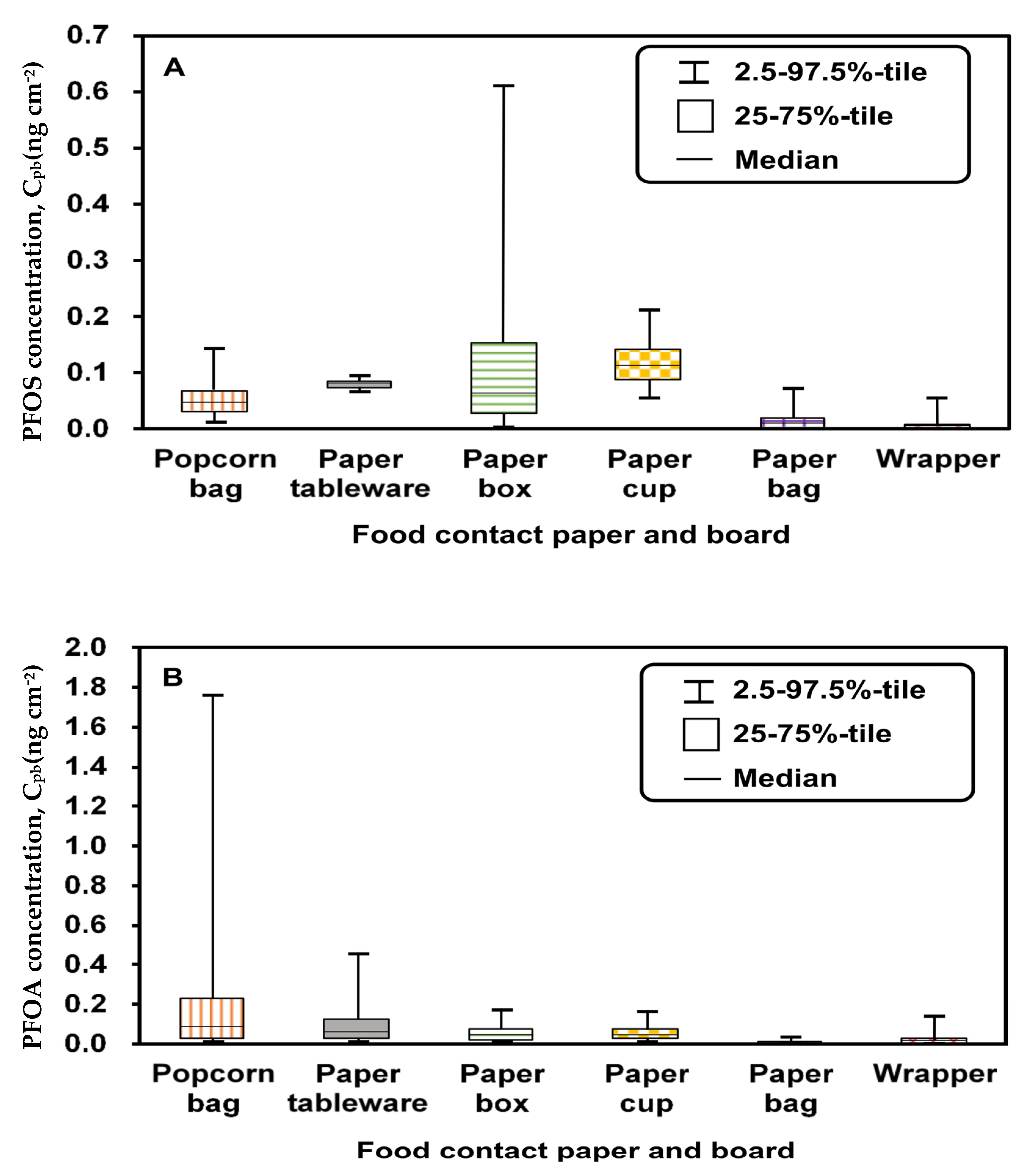
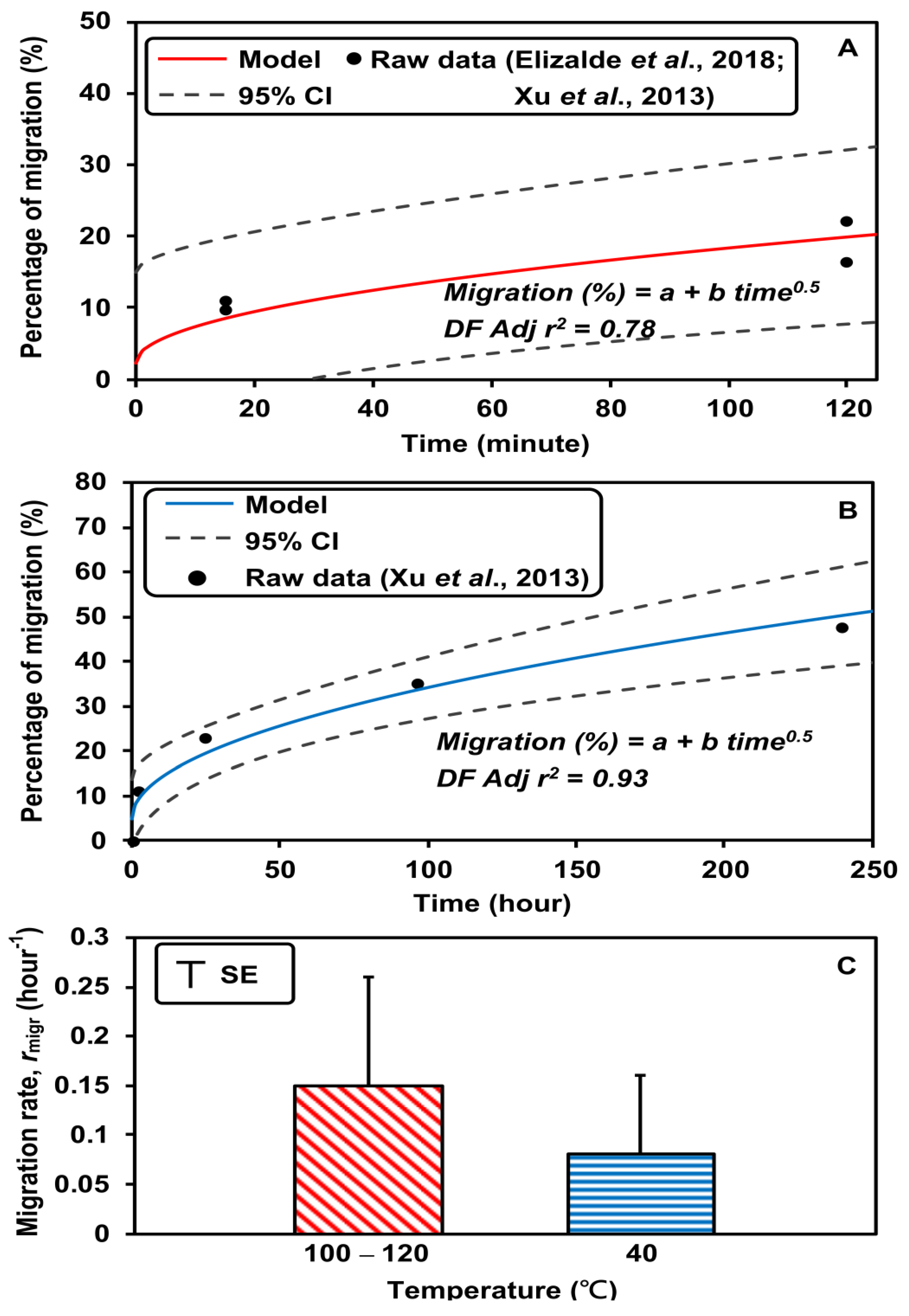
3.1. Input Parameters
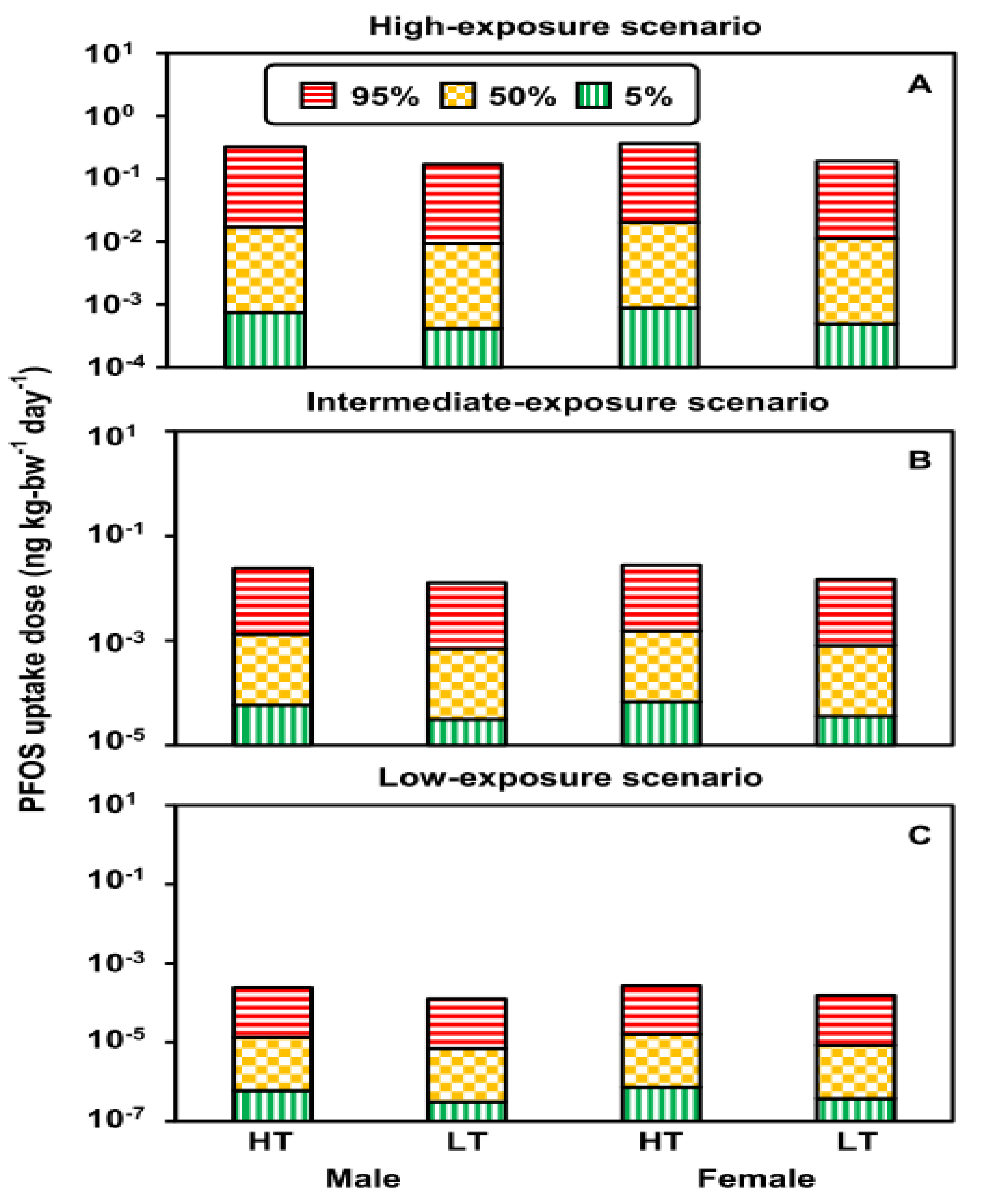
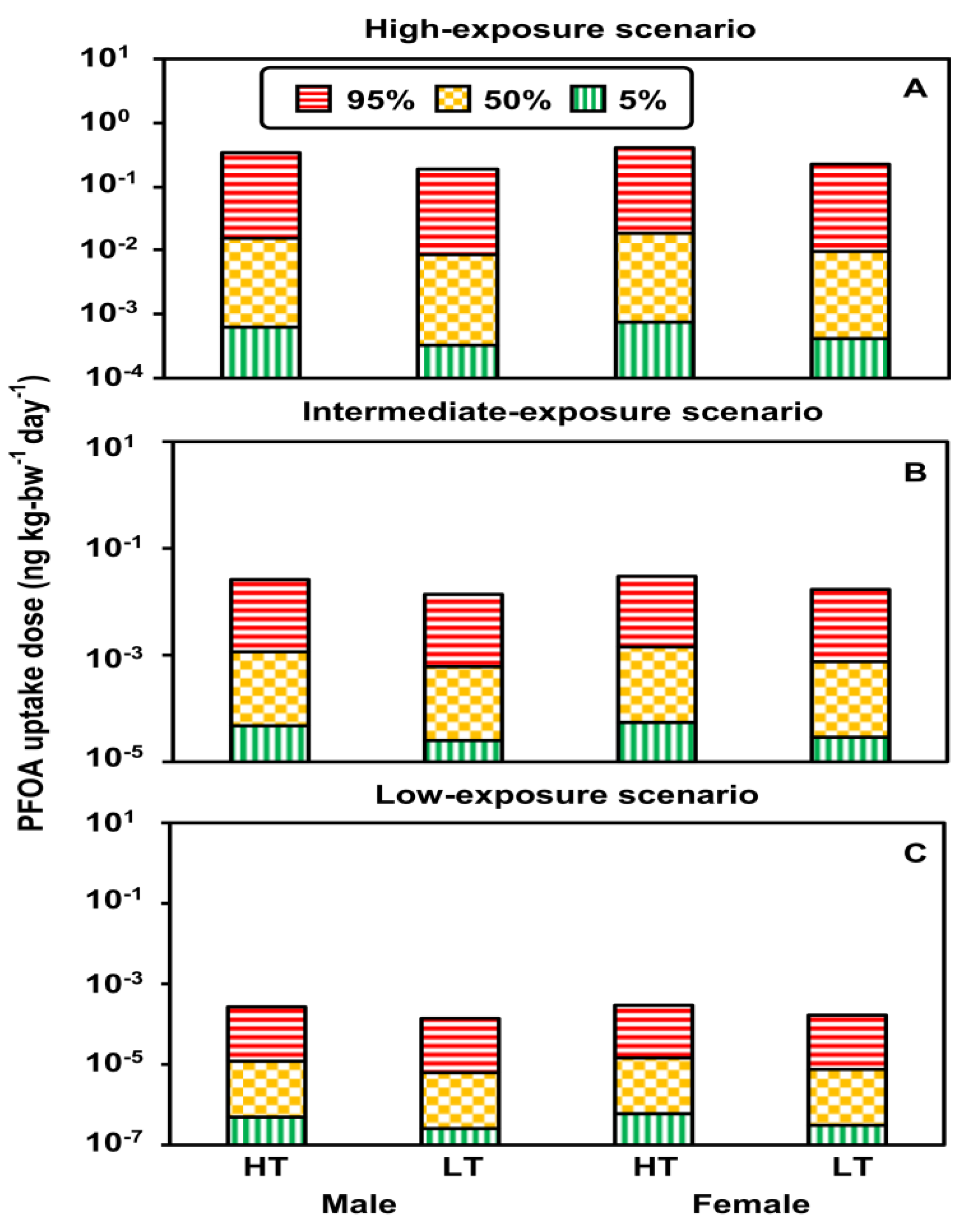
3.2. Uptake Doses under Exposure Scenarios
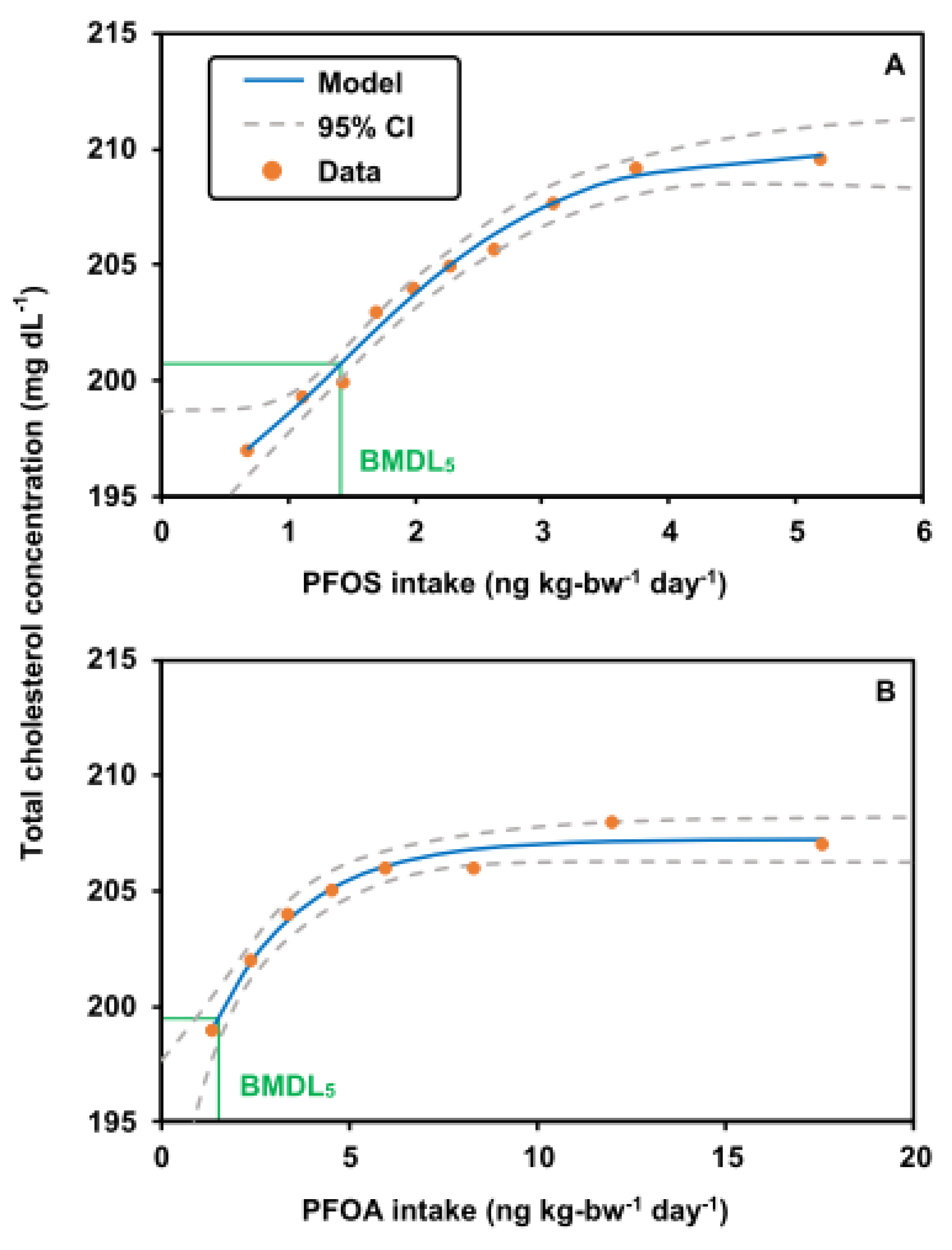
3.3. BMDL5 of PFOS and PFOA
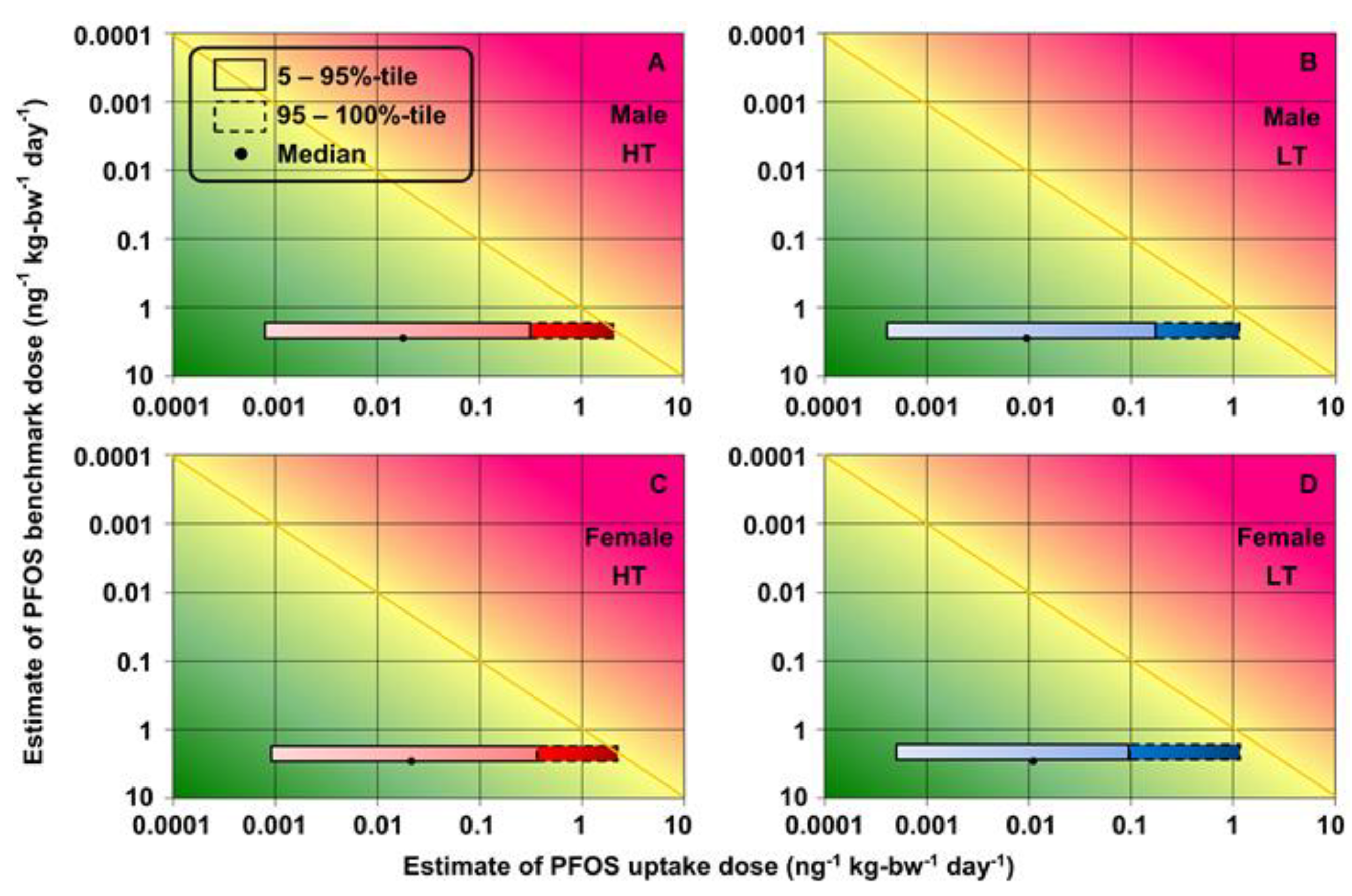
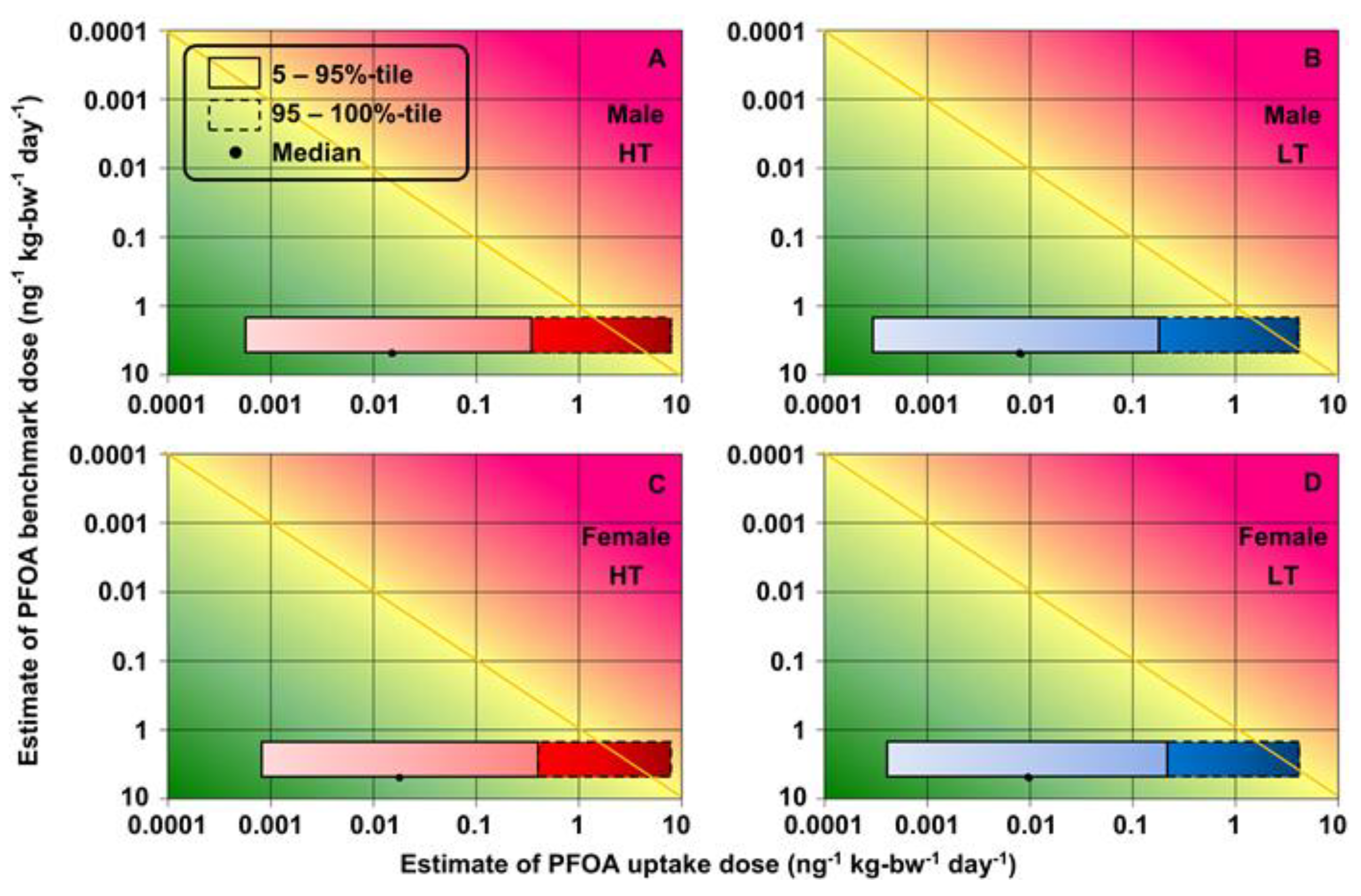
3.4. Health Risk Assessment of Increased Total Cholesterol
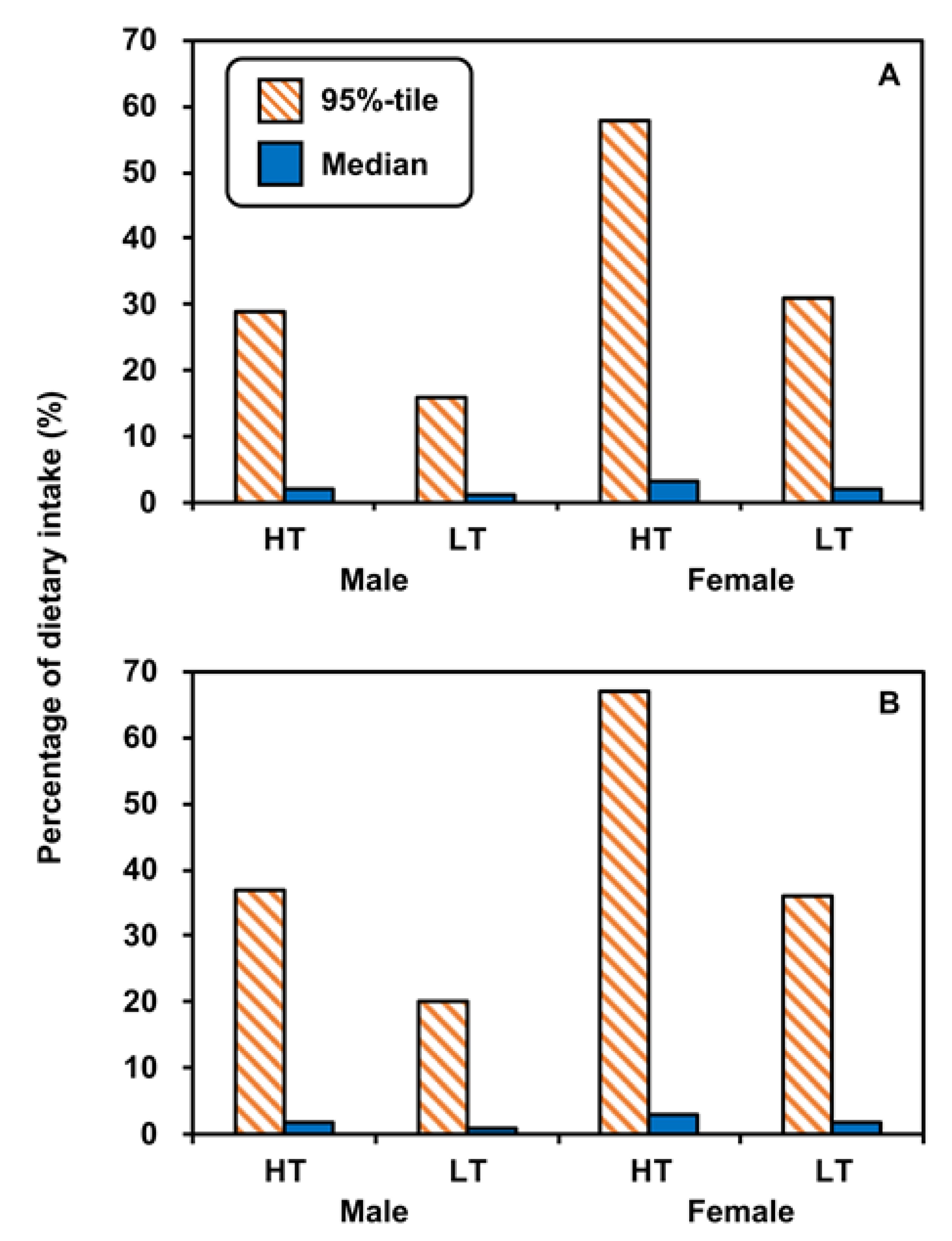
3.5. Percentages in Dietary Intakes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viberg, H.; Eriksson, P. Chapter 43—Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Perfluorooctanoic Acid. In Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 811–827. ISBN 978-0-12-804239-7. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Technical Fact Sheet-Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2017-12/documents/ffrrofactsheet_contaminants_pfos_pfoa_11-20-17_508_0.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Kannan, K.; Corsolini, S.; Falandysz, J.; Fillmann, G.; Kumar, K.S.; Loganathan, B.G.; Mohd, M.A.; Olivero, J.; Van Wouwe, N.; Yang, J.H.; et al. Perfluorooctanesulfonate and Related Fluorochemicals in Human Blood from Several Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4489–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartell, S.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lyu, C.; Kato, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Steenland, K. Rate of decline in serum PFOA concentrations after granular activated carbon filtration at two public water systems in Ohio and West Virginia. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 118, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, A.; Toyoshima, M.; Fujimiya, M.; Harada, K.; Ataka, K.; Inoue, K.; Koizumi, A. Perfluorooctane sulfonate influences feeding behavior and gut motility via the hypothalamus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and perfluorooctanoic acid in food. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05194. [Google Scholar]
- Grasty, R.C.; Bjork, J.A.; Wallace, K.B.; Lau, C.S.; Rogers, J.M. Effects of prenatal perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure on lung maturation in the perinatal rat. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasty, R.C.; Grey, B.E.; Lau, C.S.; Rogers, J.M. Prenatal window of susceptibility to perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced neonatal mortality in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2003, 68, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, N.; Fredriksson, A.; Eriksson, P. Neonatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) causes neurobehavioural defects in adult mice. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Hanson, R.G.; Narotsky, M.G.; Rogers, J.M.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J. Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure during Pregnancy in the Mouse. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Jin, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, L. Effect of gestational and lactational exposure to perfluorooctanesulfonate on calcium-dependent signaling molecules gene expression in rats’ hippocampus. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist, E.M.; Filgo, A.J.; Cummings, C.A.; Kissling, G.E.; Hoenerhoff, M.J.; Fenton, S.E. Hepatic Mitochondrial Alteration in CD-1 Mice Associated with Prenatal Exposures to Low Doses of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibodeaux, J.R.; Hanson, R.G.; Rogers, J.M.; Grey, B.E.; Barbee, B.D.; Richards, J.H.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Stevenson, L.A.; Lau, C. Exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate during pregnancy in rat and mouse. I: Maternal and prenatal evaluations. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity and human health review: Current state of knowledge and strategies for informing future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.-W.; Qian, Z.; Emo, B.; Vaughn, M.; Bao, J.; Qin, X.-D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Lee, Y.L.; Dong, G.-H. Association of polyfluoroalkyl chemical exposure with serum lipids in children. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Wang, C.; Sung, F.-C.; Su, T.-C. Association between serum per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and thrombograms in young and middle-aged Taiwanese populations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, T.H.; Hsu, W.; Noonan, G.; Diachenko, G. Migration of fluorochemical paper additives from food-contact paper into foods and food simulants. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 25, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, T.H.; White, K.; Honigfort, P.; Twaroski, M.L.; Neches, R.; Walker, R.A. Perfluorochemicals: Potential sources of and migration from food packaging. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, S.; Pelzing, M. An optimized method for the determination of perfluorooctanoic acid, perfluorooctane sulfonate and other perfluorochemicals in different matrices using liquid chromatography/ion-trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Moral, M.P.; Tena, M.T. Determination of perfluorocompounds in popcorn packaging by pressurised liquid extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 101, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreta, C.; Tena, M.T. Fast determination of perfluorocompounds in packaging by focused ultrasound solid-liquid extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1302, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poothong, S.; Boontanon, S.K.; Boontanon, N. Determination of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in food packaging using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 205–206, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeib, T.; Hassan, Y.; Rauert, C.; Harner, T. Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in indoor dust and food packaging materials in Egypt: Trends in developed and developing countries. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, E.; Kim, S.K.; Akinleye, H.B.; Kannan, K. Quantitation of gas-phase perfluoroalkyl surfactants and fluorotelomer alcohols released from nonstick cookware and microwave popcorn bags. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surma, M.; Wiczkowski, W.; Zieliński, H.; Cieślik, E. Determination of Selected Perfluorinated Acids (PFCAs) and Perfluorinated Sulfonates (PFASs) in Food Contact Materials Using LC-MS/MS. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2015, 28, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Peng, H.; Huang, C.; Hu, J. Ubiquitous Occurrence of Fluorotelomer Alcohols in Eco-Friendly Paper-Made Food-Contact Materials and Their Implication for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaleta, I.; Negreira, N.; Bizkarguenaga, E.; Prieto, A.; Covaci, A.; Zuloaga, O. Screening and identification of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in microwave popcorn bags. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiraki, E.; Costopoulou, D.; Vassiliadou, I.; Bakeas, E.; Leondiadis, L. Determination of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in various foodstuff packaging materials used in the Greek market. Chemosphere 2014, 94, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Noonan, G.; Begley, T. Migration of perfluoroalkyl acids from food packaging to food simulants. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muncke, J. Migration. Food Packaging Forum. Available online: https://www.foodpackagingforum.org/food-packaging-health/migration (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Elizalde, M.P.; Gómez-Lavín, S.; Urtiaga, A.M. Migration of perfluorinated compounds from paperbag to Tenax® and lyophilised milk at different temperatures. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, D.; Horowitz, L.; Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Hungerbühler, K. Estimating consumer exposure to PFOS and PFOA. Risk Anal. 2008, 28, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L. Health risks of dietary exposure to perfluorinated compounds. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. EU Regulation 10/2011 Outlines the Regulatory Requirements for the Food Contact Testing of Plastic Articles or Materials. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/cs_fcm_legis_pm-guidance_brochure_engl.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Hundley, S.G.; Sarrif, A.M.; Kennedy, G.L. Absorption, distribution, and excretion of ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFO) after oral administration to various species. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 29, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, K.T.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Lipworth, L.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Sørensen, M. Association between Plasma PFOA and PFOS Levels and Total Cholesterol in a Middle-Aged Danish Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.W.; Hatch, E.E.; Webster, T.F. Exposure to Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals and Cholesterol, Body Weight, and Insulin Resistance in the General U.S. Population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 118, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Tinker, S.; Frisbee, S.; Ducatman, A.; Vaccarino, V. Association of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate with serum lipids among adults living near a chemical plant. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Hsu, J.F.; Ho, H.H.; Chiang, C.F.; Liao, P.C. Background levels of persistent organic pollutants in humans from Taiwan: Perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeghy, P.P.; Lorber, M. An assessment of the exposure of Americans to perfluorooctane sulfonate: A comparison of estimated intake with values inferred from NHANES data. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Schlummer, M.; Möller, A.; Gruber, L.; Wolz, G.; Ungewiss, J.; Böhmer, S.; Dekant, W.; Mayer, R.; Liebl, B.; et al. Exposure of an adult population to perfluorinated substances using duplicate diet portions and biomonitoring data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7928–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, L.S.; Huber, S.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C. Characterisation of human exposure pathways to perfluorinated compounds—Comparing exposure estimates with biomarkers of exposure. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergren, R.; Cousins, I.T. Tracking the pathways of human exposure to perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5565–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Inoue, K.; Morikawa, A.; Yoshinaga, T.; Saito, N.; Koizumi, A. Renal clearance of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in humans and their species-specific excretion. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.A.; Gift, J.S.; Zhao, Q.J. Introduction to benchmark dose methods and U.S. EPA’s benchmark dose software (BMDS) version 2.1.1. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embry, M.R.; Bachman, A.; Bell, D.R.; Boobis, A.R.; Cohen, S.M.; Dellarco, M.; Dewhurst, I.C.; Doerrer, N.G.; Hines, R.; Moretto, A.; et al. Risk assessment in the 21st century: Roadmap and matrix. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOHW (Ministry of Health and Welfare). Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan 2013–2016. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=3828&pid=10443 (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Chen, W.L.; Bai, F.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, C.Y. Concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances in foods and the dietary exposure among Taiwan general population and pregnant women. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Exposure Scenario | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Unit | Low | Intermediate | High | Reference |
| Cpb | ng cm−2 | Collecting dataa | This study | ||
| rmigr | hour−1 | HT: 0.15 (100–120 °C) b LT: 0.08 (40 °C) b | This study | ||
| MFpb | % | 10 | 50 | 100 | Trudel et al. [33] |
| ffood_pb | day−1 | 0.03 | 0.3 | 1 | Trudel et al. [33] |
| Ac | cm2 | Measuring c | This study | ||
| tc | hour | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | Trudel et al. [33] |
| Fuptake | % | Simulating d | This study | ||
| mbw | kg-bw | 70.4 19.79 e (Male) 58.017.51 e (Female) | MOHW [48] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, S.-H.; Yu, C.-C. Health Risk Exposure Assessment of Migration of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Perfluorooctanoic Acid from Paper and Cardboard in Contact with Food under Temperature Variations. Foods 2023, 12, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091764
You S-H, Yu C-C. Health Risk Exposure Assessment of Migration of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Perfluorooctanoic Acid from Paper and Cardboard in Contact with Food under Temperature Variations. Foods. 2023; 12(9):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091764
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Shu-Han, and Chun-Chieh Yu. 2023. "Health Risk Exposure Assessment of Migration of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Perfluorooctanoic Acid from Paper and Cardboard in Contact with Food under Temperature Variations" Foods 12, no. 9: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091764
APA StyleYou, S.-H., & Yu, C.-C. (2023). Health Risk Exposure Assessment of Migration of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Perfluorooctanoic Acid from Paper and Cardboard in Contact with Food under Temperature Variations. Foods, 12(9), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091764






