Functional Characterization of Different Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains Isolated from Chinese Traditional Sourdoughs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
2.2. Proteinase and Peptidase Activities
2.3. EPS Determination
2.4. Sourdough Fermentation
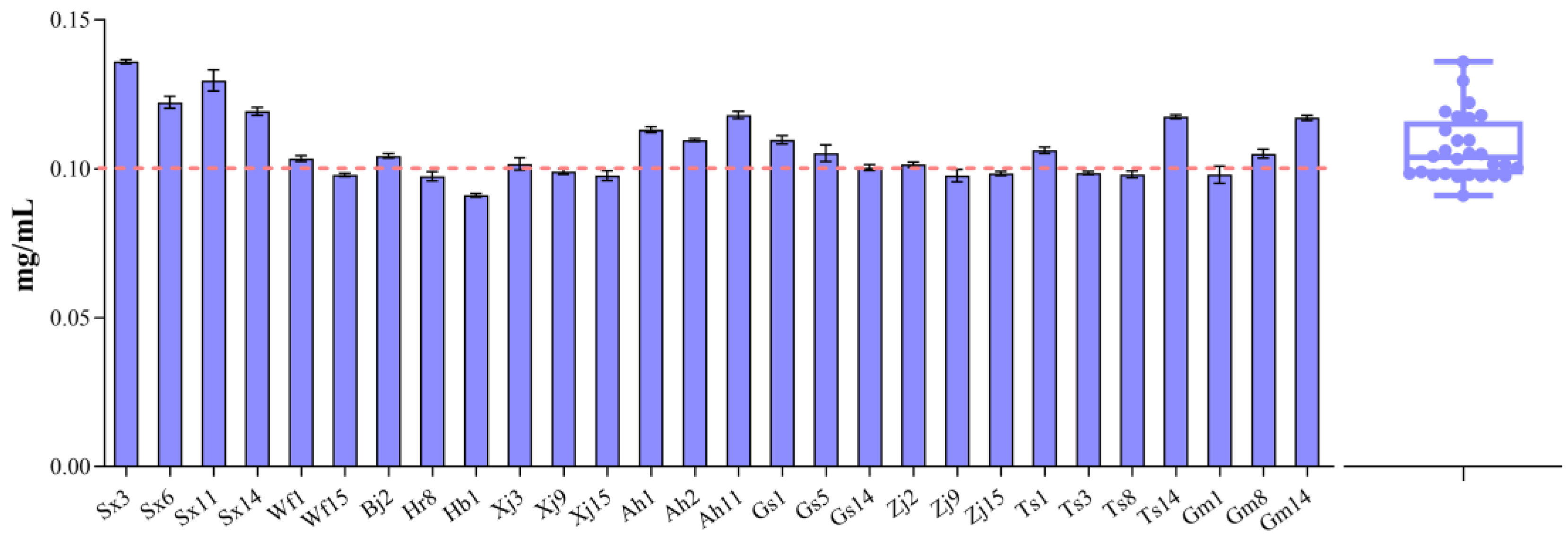
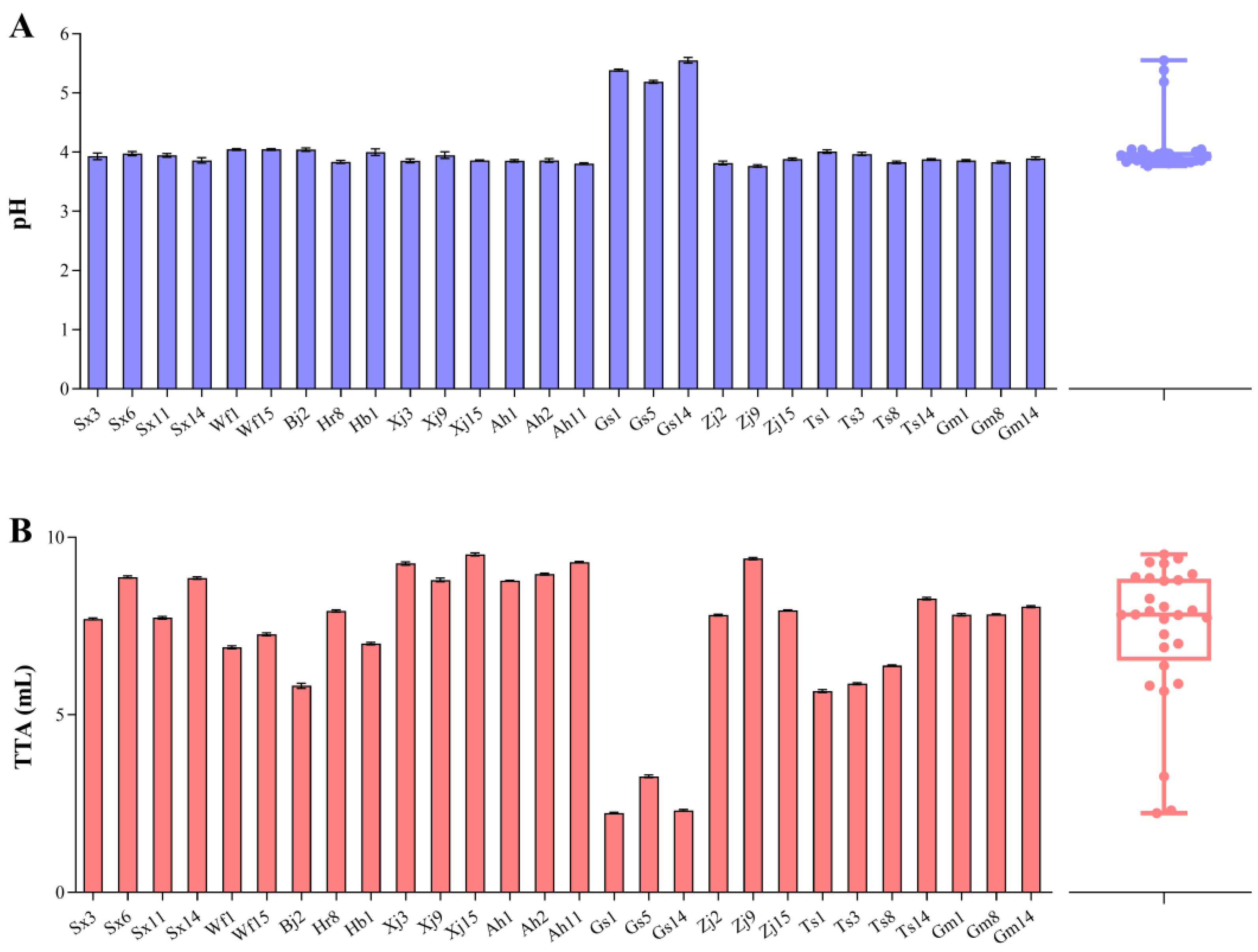
2.5. pH, Total Titratable Acidity, and Acid Content
2.6. Assessment of Sourdough’s Volatile Compounds
2.7. mRNA Sequencing
2.8. Statistical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proteolytic Activity of F. sanfranciscensis
3.2. EPS Production by F. sanfranciscensis
3.3. Acidification of F. sanfranciscensis during Sourdough Fermentation
3.4. Volatile Compound Profiles
3.5. Gene Expression Analysis of Different F. sanfranciscensis Strains during Sourdough Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gobbetti, M. The sourdough microflora: Interactions of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Ameur, H.; Polo, A.; Di Cagno, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. Thirty years of knowledge on sourdough fermentation: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Ecological parameters influencing microbial diversity and stability of traditional sourdough. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 171, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, R.S.; Huang, W.N.; Rayas-Duarte, P.; Wang, F.; Yao, Y. Effect of sourdough fermentation on the quality of Chinese Northern-style steamed breads. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, G.; He, G. Intraspecific diversity and fermentative properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae from Chinese traditional sourdough. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 124, 109195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, L.A.A.; Minervini, F.; Filannino, P.; Sardaro, M.L.S.; Gatti, M.; Lindner, J.D. Effects of Sourdough on FODMAPs in Bread and Potential Outcomes on Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients and Healthy Subjects. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 01972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, F.B.; Ripari, V.; Waszczynskyj, N.; Spier, M.R. Overview of Sourdough Technology: From Production to Marketing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 242–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Neysens, P. The sourdough microflora: Biodiversity and metabolic interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Rao, H.; Tian, Y.; Xue, W. Bacterial composition in sourdoughs from different regions in China and the microbial potential to reduce wheat allergens. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, L.A.A.; Sardaro, M.L.S.; Duarte, R.T.D.; Mazzon, R.R.; Neviani, E.; Gatti, M.; Lindner, J.D. Sourdough bacterial dynamics revealed by metagenomic analysis in Brazil. Food Microbiol. 2020, 85, 103302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.J.; Li, Y.; Sadiq, F.A.; Yang, H.Y.; Gu, J.S.; Yuan, L.; Lee, Y.K.; He, G.Q. Predominant yeasts in Chinese traditional sourdough and their influence on aroma formation in Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kerrebroeck, S.; Maes, D.; De Vuyst, L. Sourdoughs as a function of their species diversity and process conditions, a meta-analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tu, J.; Sadiq, F.A.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W. Prevalence, Genetic Diversity, and Technological Functions of the Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis in Sourdough: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1209–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gallo, G.; Curci, M.; Siragusa, S.; Crecchio, C.; Parente, E.; Gobbetti, M. Molecular and functional characterization of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis strains isolated from sourdoughs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 114, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Sadiq, F.A.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; He, G. Prevalence and diversity of lactic acid bacteria in Chinese traditional sourdough revealed by culture dependent and pyrosequencing approaches. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Gu, J.; Yuan, L.; He, G. Genotyping of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis isolates from Chinese traditional sourdoughs by multilocus sequence typing and multiplex RAPD-PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 258, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Corsetti, A. Lactobacillus sanfrancisco a key sourdough lactic acid bacterium: A review. Food Microbiol. 1997, 14, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, G.; Tavman, Ş. Functional and technological aspects of sourdough fermentation with Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Baek, H.; Lib, S.B.; Hur, J.S.; Shim, S.; Shin, S.Y.; Han, N.S.; Seo, J.H. Development of species-specific PCR primers and polyphasic characterization of isolated from Korean sourdough. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 200, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picozzi, C.; Bonacina, G.; Vigentini, I.; Foschino, R. Genetic diversity in Italian strains assessed by multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analyses. Microbiol. SGM 2010, 156, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhomme, E.; Onno, B.; Chuat, V.; Durand, K.; Orain, S.; Valence, F.; Dousset, X.; Jacques, M.A. Genotypic diversity of strains isolated from French organic sourdoughs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 226, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yu, Y.; Kemperman, R.; Jimenez, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Zhang, G. Comparative Genomics Reveals Genetic Diversity and Variation in Metabolic Traits in Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, L.; Sugihara, T. Microorganisms of the San Francisco sour dough bread process II. Isolation and characterization of undescribed bacterial species responsible for the souring activity. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 21, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Görg, A. Electrophoretic characterization of wheat grain allergens from different cultivars involved in bakers’ asthma. Electrophoresis 1993, 14, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, C.L.; Rollan, G.C.; de Valdez, G.F. Gluten breakdown by lactobacilli and pediococci strains isolated from sourdough. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, E.; Shibata, D.; Matoba, T. Modified colorimetric ninhydrin methods for peptidase assay. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 118, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xu, L.; Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Diversity of isolated lactic acid bacteria in Ya’an sourdoughs and evaluation of their exopolysaccharide production characteristics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 95, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sadiq, F.A.; Liu, T.; Zhang, G.; He, G. Use of physiological and transcriptome analysis to infer the interactions between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis isolated from Chinese traditional sourdoughs. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 126, 109268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Loponen, J.; Gobbetti, M. Proteolysis in sourdough fermentations: Mechanisms and potential for improved bread quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guédon, E.; Renault, P.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Delorme, C. Transcriptional pattern of genes coding for the proteolytic system of Lactococcus lactis and evidence for coordinated regulation of key enzymes by peptide supply. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savijoki, K.; Ingmer, H.; Varmanen, P. Proteolytic systems of lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, N.; Pavlovic, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Ganzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Functional Characterization of the Proteolytic System of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis DSM 20451T during Growth in Sourdough. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6260–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, O.; Villani, F.; Oliviero, D.; Greco, T.; Coppola, S. Effect of proteolytic starter cultures as leavening agents of pizza dough. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 84, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, C.; Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Contribution of sourdough lactobacilli, yeast, and cereal enzymes to the generation of amino acids in dough relevant for bread flavor. Cereal Chem. 2002, 79, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunji, E.R.; Mierau, I.; Hagting, A.; Poolman, B.; Konings, W.N. The proteotytic systems of lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1996, 70, 187–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Pobiega, K.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M. Characteristics of the proteolytic enzymes produced by lactic acid bacteria. Molecules 2021, 26, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Smacchi, E.; Corsetti, A. The proteolytic system of Lactobacillus sanfrancisco CB1: Purification and characterization of a proteinase, a dipeptidase, and an aminopeptidase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Vermeulen, N.; Vogel, R.F. Carbohydrate, peptide and lipid metabolism of lactic acid bacteria in sourdough. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hu, Y.; Wu, F.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X.; Gänzle, M.G. Comparison of the functionality of exopolysaccharides produced by sourdough lactic acid bacteria in bread and steamed bread. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8907–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitter, M.; Fleig, M.; Schmidt, H.; Hertel, C. Effect of exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis on the processing properties of wheat doughs. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korakli, M.; Pavlovic, M.; Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Exopolysaccharide and kestose production by Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis LTH2590. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieking, M.; Gänzle, M.G. Exopolysaccharides from cereal-associated lactobacilli. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, H.; Zhang, L.; He, G. The influence of different lactic acid bacteria on sourdough flavor and a deep insight into sourdough fermentation through RNA sequencing. Food Chem. 2020, 307, 125529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleukx, W.; Delcour, J.A. A Second Aspartic Proteinase Associated with Wheat Gluten. J. Cereal Sci. 2000, 32, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M.; Corsetti, A.; Di Cagno, R. Biochemistry and physiology of sourdough lactic acid bacteria. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, A.; Settanni, L. Lactobacilli in sourdough fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 539–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Pepe, O.; Mauriello, G. Effect of leavening microflora on pizza dough properties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 85, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pico, J.; Bernal, J.; Gomez, M. Wheat bread aroma compounds in crumb and crust: A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhu, H.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Spontaneous sourdough processing of Chinese Northern-style steamed breads and their volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, T.; Sadiq, F.A.; Yang, H.; Liu, T.; Ruan, H.; He, G. A study revealing the key aroma compounds of steamed bread made by Chinese traditional sourdough. J. Zhejiang Univ. SCIENCE B 2016, 17, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Hansen, S. Volatile compounds in wheat sourdoughs produced by lactic acid bacteria and sourdough yeasts. Z. Fuer Lebensm. Unters. Und Forsch. 1994, 198, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, A.; Chrysanthou, A.; Koutidou, M. Characterisation of volatile compounds of lupin protein isolate-enriched wheat flour bread. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétel, C.; Onno, B.; Prost, C. Sourdough volatile compounds and their contribution to bread: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, N.; Czerny, M.; Ganzle, M.G.; Schieberle, P.; Vogel, R.F. Reduction of (E)-2-nonenal and (E,E)-2,4-decadienal during sourdough fermentation. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 45, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quílez, J.; Ruiz, J.A.; Romero, M.P. Relationships Between Sensory Flavor Evaluation and Volatile and Nonvolatile Compounds in Commercial Wheat Bread Type Baguette. J. Food Sci. 2010, 71, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, E.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. Intraspecies diversity and genome-phenotype-associations in. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 243, 126625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, E.; Ferreira-Cerca, S.; Hurt, E. Eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4815–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Organism | Strains | Isolation Source | Genetic Clusters * |
|---|---|---|---|
| F. sanfranciscensis | Wf1 | Sourdough, Shandong China | 1 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Wf15 | Sourdough, Shandong China | 1 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Gm1 | Sourdough, Shandong China | 2 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Gm8 | Sourdough, Shandong China | 3 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Gm14 | Sourdough, Shandong China | 4 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ah1 | Sourdough, Anhui China | 4 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ah2 | Sourdough, Anhui China | 3 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ah11 | Sourdough, Anhui China | 5 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Sx3 | Sourdough, Shanxi China | 6 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Sx6 | Sourdough, Shanxi China | 7 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Sx11 | Sourdough, Shanxi China | 8 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Sx14 | Sourdough, Shanxi China | 9 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Gs1 | Sourdough, Gansu China | 10 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Gs5 | Sourdough, Gansu China | 11 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Gs14 | Sourdough, Gansu China | 12 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Bj2 | Sourdough, Shannxi China | 1 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Zj2 | Sourdough, Zhejiang China | 13 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Zj9 | Sourdough, Zhejiang China | 13 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Zj15 | Sourdough, Zhejiang China | 14 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Hb1 | Sourdough, Hebei China | 1 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ts1 | Sourdough, Hebei China | 15 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ts3 | Sourdough, Hebei China | 16 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ts8 | Sourdough, Hebei China | 17 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Ts14 | Sourdough, Hebei China | 16 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Hr8 | Sourdough, Heilongjiang China | 14 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Xj3 | Sourdough, Xinjiang China | 18 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Xj9 | Sourdough, Xinjiang China | 19 |
| F. sanfranciscensis | Xj15 | Sourdough, Xinjiang China | 20 |
| Gene_ID | Description | Fold Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | |||
| malL | oligo-1,6-glucosidase | 207.63 | <0.001 |
| glf | UDP-galactopyranose mutase | 72.07 | <0.001 |
| gntK | gluconokinase | 13.59 | <0.001 |
| gpo | glutathione peroxidase | 12.92 | <0.001 |
| clpE | ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit | 8.30 | <0.001 |
| LSA_RS04355 | class I SAM-dependent methyltransferase | 8.04 | <0.001 |
| pepDA | dipeptidase | 7.55 | <0.001 |
| dnaI | primosomal protein DnaI | 7.41 | <0.001 |
| nrdI | ribonucleotide reductase assembly protein NrdI | 7.16 | <0.001 |
| plsC | 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase | 6.51 | <0.001 |
| ysgA | RNA methyltransferase | 6.13 | <0.001 |
| ecsA | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 5.96 | <0.001 |
| thyA | thymidylate synthase | 5.77 | <0.001 |
| gor | glutathione reductase | 5.26 | <0.001 |
| npdA | NAD-dependent protein deacylase | 4.98 | <0.001 |
| guaA | glutamine-hydrolyzing GMP synthase | 4.63 | <0.001 |
| ackA | acetate kinase | 4.30 | <0.001 |
| pyrD | dihydroorotate dehydrogenase | 3.93 | <0.001 |
| rluD | RluA family pseudouridine synthase | 3.75 | <0.001 |
| citD | citrate lyase subunit gamma (acyl carrier protein) | 3.74 | <0.001 |
| ybeY | rRNA maturation RNase YbeY | 3.61 | <0.001 |
| LSA_RS04400 | DUF948 domain-containing protein | 3.17 | <0.001 |
| ldh | L-lactate dehydrogenase | 3.08 | <0.001 |
| gntR | GntR family transcriptional regulator | 3.04 | <0.001 |
| map | type I methionyl aminopeptidase | 3.01 | <0.001 |
| Downregulated | |||
| glnM | aspartate/glutamate/glutamine transport system permease protein | 23.65 | <0.001 |
| glnH | aspartate/glutamate/glutamine transport system substrate-binding protein | 18.84 | <0.001 |
| rpsL | small subunit ribosomal protein S12 | 13.42 | <0.001 |
| rpsG | small subunit ribosomal protein S7 | 9.23 | <0.001 |
| ltaS | LTA synthase family protein | 8.90 | <0.001 |
| typA | translational GTPase TypA | 8.82 | <0.001 |
| metQ | D-methionine transport system substrate-binding protein | 8.12 | <0.001 |
| LSA_RS06240 | membrane protein | 7.63 | <0.001 |
| accD | acetyl-CoA carboxylase subunit beta | 7.11 | <0.001 |
| fusA | elongation factor G | 6.57 | <0.001 |
| lytR | LytR family transcriptional regulator | 6.04 | <0.001 |
| rplC | 50S ribosomal protein L3 | 5.63 | <0.001 |
| rplK | large subunit ribosomal protein L11 | 5.08 | <0.001 |
| minD | septum site-determining protein MinD | 4.90 | <0.001 |
| LSA_RS01620 | threonine/serine exporter | 4.63 | 0.005 |
| rplL | large subunit ribosomal protein L7/L12 | 4.41 | <0.001 |
| LSA_RS01505 | cation:proton antiporter | 4.25 | 0.008 |
| rplV | 50S ribosomal protein L22 | 4.05 | <0.001 |
| ecfA1 | energy-coupling factor transport system ATP-binding protein | 3.94 | <0.001 |
| adk | adenylate kinase | 3.64 | <0.001 |
| rplB | large subunit ribosomal protein L2 | 3.47 | <0.001 |
| prsA | peptidylprolyl isomerase | 3.33 | 0.015 |
| rplN | large subunit ribosomal protein L14 | 3.13 | <0.001 |
| scrK | fructokinase | 3.11 | <0.001 |
| LSA_RS05375 | gfo/Idh/MocA family oxidoreductase | 3.08 | <0.001 |
| adh2 | bifunctional acetaldehyde-CoA/alcohol dehydrogenase | 3.02 | <0.001 |
| Catergory | GO_Term | Cluster Frequency | Corrected p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| molecular_function | GO:0019843 rRNA binding | 7.0% | <0.001 |
| cellular_component | GO:0005840 ribosome | 8.5% | 0.003 |
| cellular_component | GO:0030529 intracellular ribonucleoprotein complex | 8.5% | 0.005 |
| cellular_component | GO:1990904 ribonucleoprotein complex | 8.5% | 0.006 |
| cellular_component | GO:0044391 ribosomal subunit | 2.7% | 0.01 |
| molecular_function | GO:0005198 structural molecule activity | 8.0% | 0.03 |
| Pathway | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Ribosome | <0.001 |
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | 0.014 |
| Galactose metabolism | 0.021 |
| Two-component system | 0.028 |
| ABC transporters | 0.035 |
| Arginine biosynthesis | 0.041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Lin, J.; Han, X.; Bi, J.; Dong, L.; Sun, J.; Shen, C.; Xu, Y. Functional Characterization of Different Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains Isolated from Chinese Traditional Sourdoughs. Foods 2024, 13, 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172670
Yang H, Lin J, Han X, Bi J, Dong L, Sun J, Shen C, Xu Y. Functional Characterization of Different Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains Isolated from Chinese Traditional Sourdoughs. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172670
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Huanyi, Jiaqi Lin, Xueyuan Han, Juguo Bi, Lijia Dong, Jianqiu Sun, Chi Shen, and Ying Xu. 2024. "Functional Characterization of Different Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains Isolated from Chinese Traditional Sourdoughs" Foods 13, no. 17: 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172670
APA StyleYang, H., Lin, J., Han, X., Bi, J., Dong, L., Sun, J., Shen, C., & Xu, Y. (2024). Functional Characterization of Different Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains Isolated from Chinese Traditional Sourdoughs. Foods, 13(17), 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172670




