Characterizing the Contribution of Strain Specificity to the Microbiota Structure and Metabolites of Muqu and Fresh High-Temperature Daqu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Sampling of Fortified High-Temperature Daqu
2.1.1. Microorganism
2.1.2. Seed Preparation
2.1.3. Muqu Production
2.1.4. High-Temperature Daqu Production and Sampling
2.2. Determination of Physiochemical Properties
2.3. Detection of Volatile Metabolic Components
2.4. Detection of Non-Volatile Metabolic Components
2.4.1. Sample Preparation
2.4.2. UPLC Conditions
2.4.3. MS Conditions
2.5. Enumeration of Cultivable Microorganisms in Daqu
2.6. Analysis of Daqu Microbial Community Structure
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Differences in Physicochemical Properties between Muqu and HTD
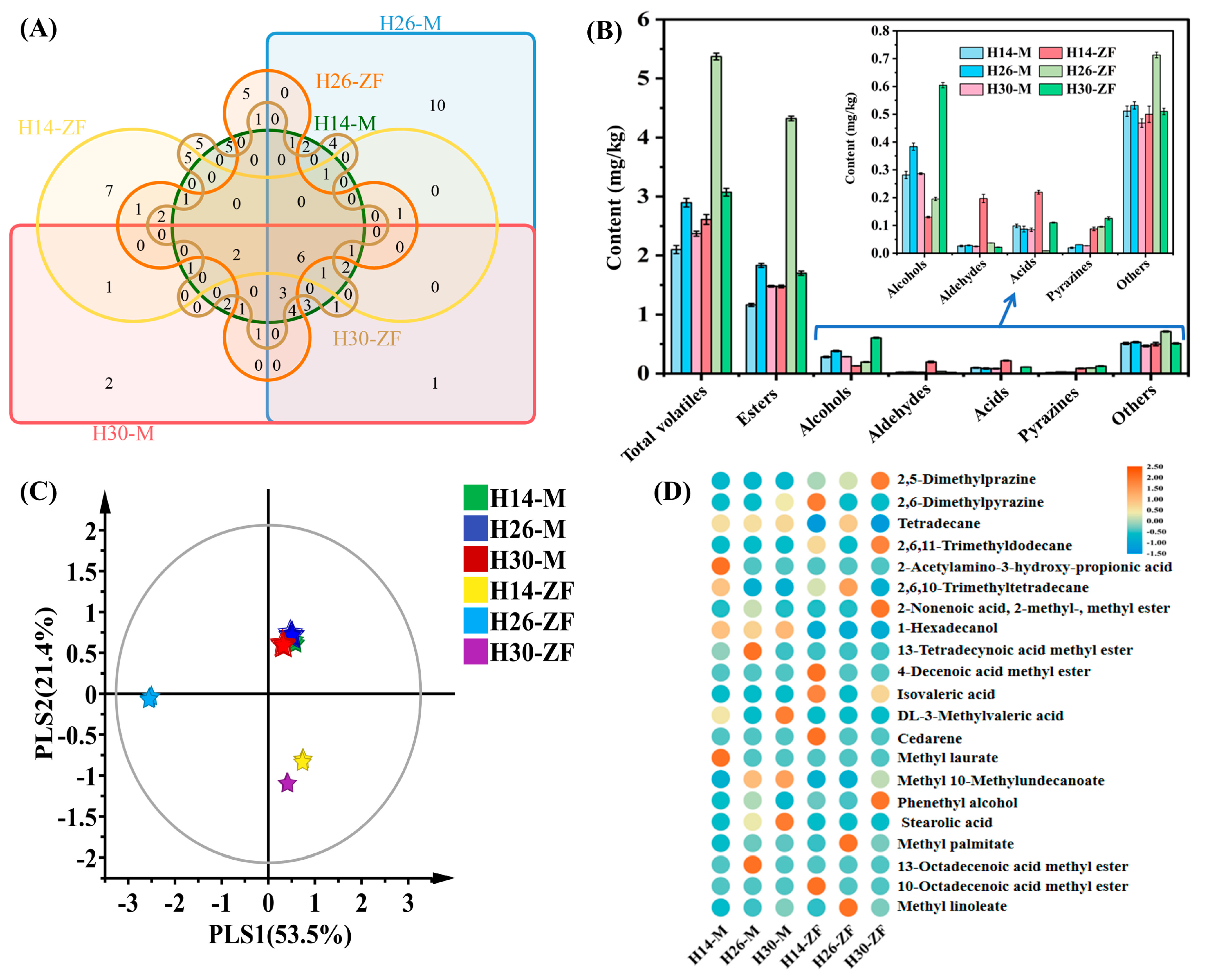
3.2. Differences in Volatile Metabolites
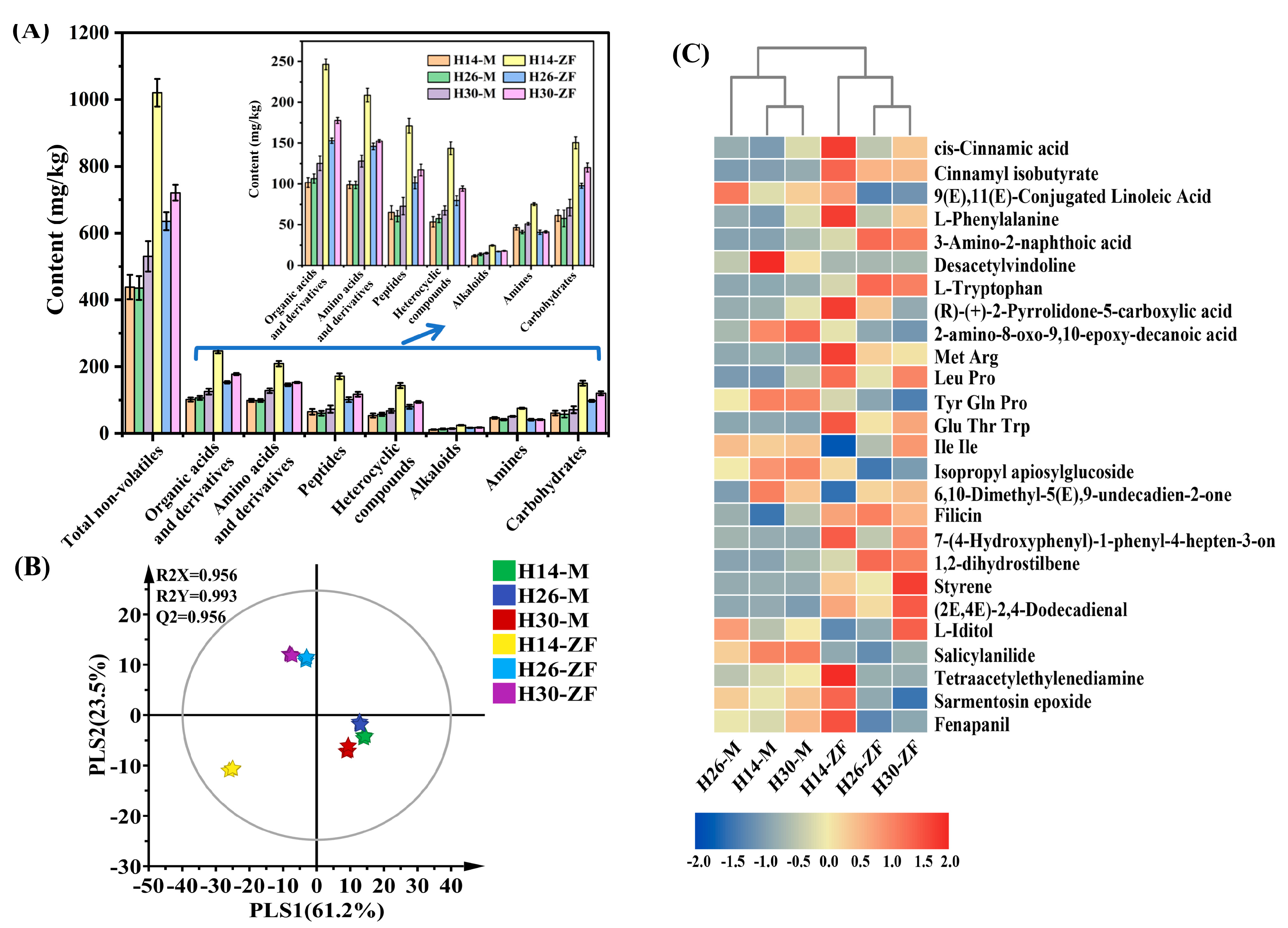
3.3. Variation of Non-Volatile Components
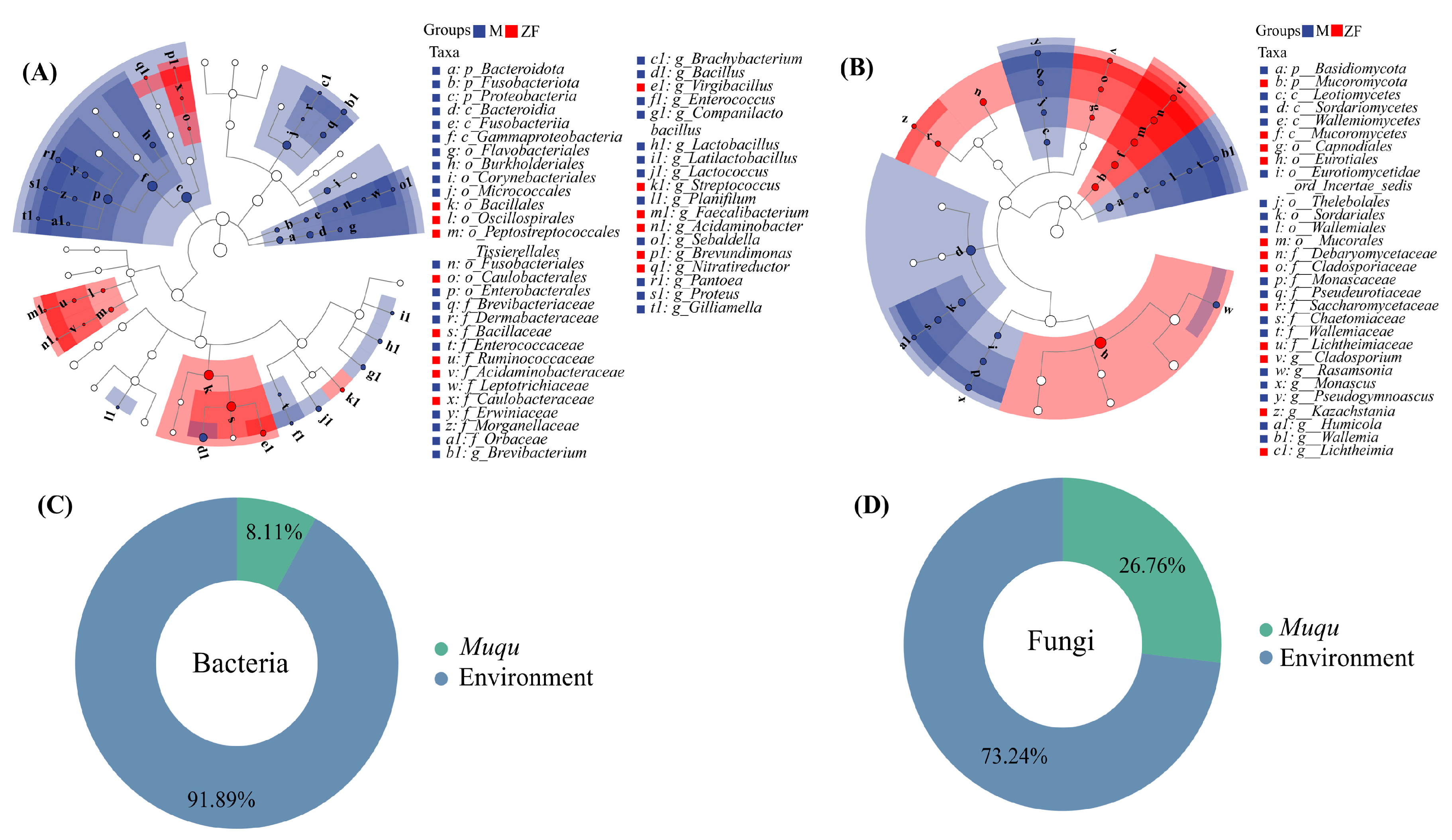
3.4. Differences in Microbial Community Structure
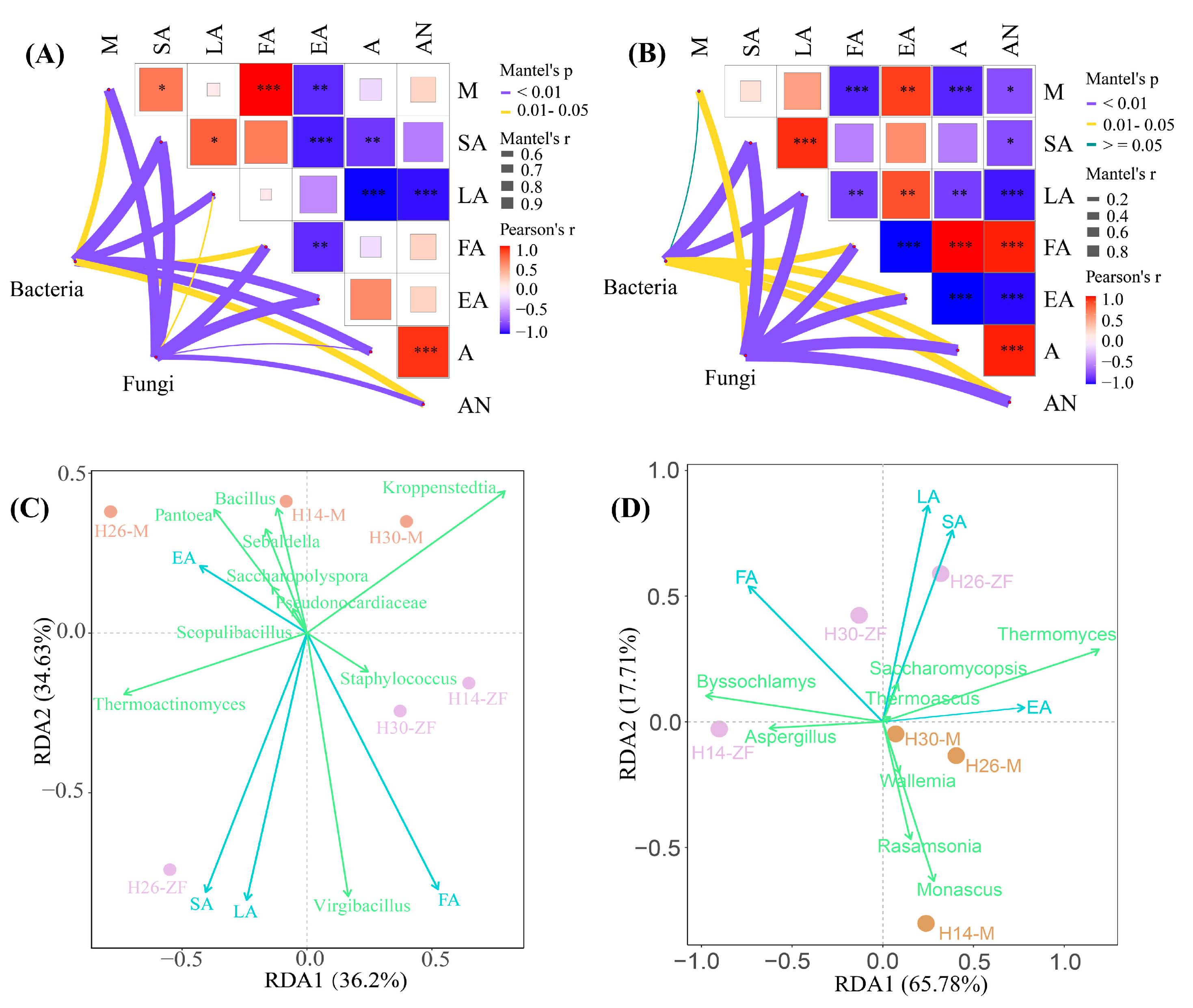
3.5. Correlation between Physicochemical Properties and Dominant Bacteria
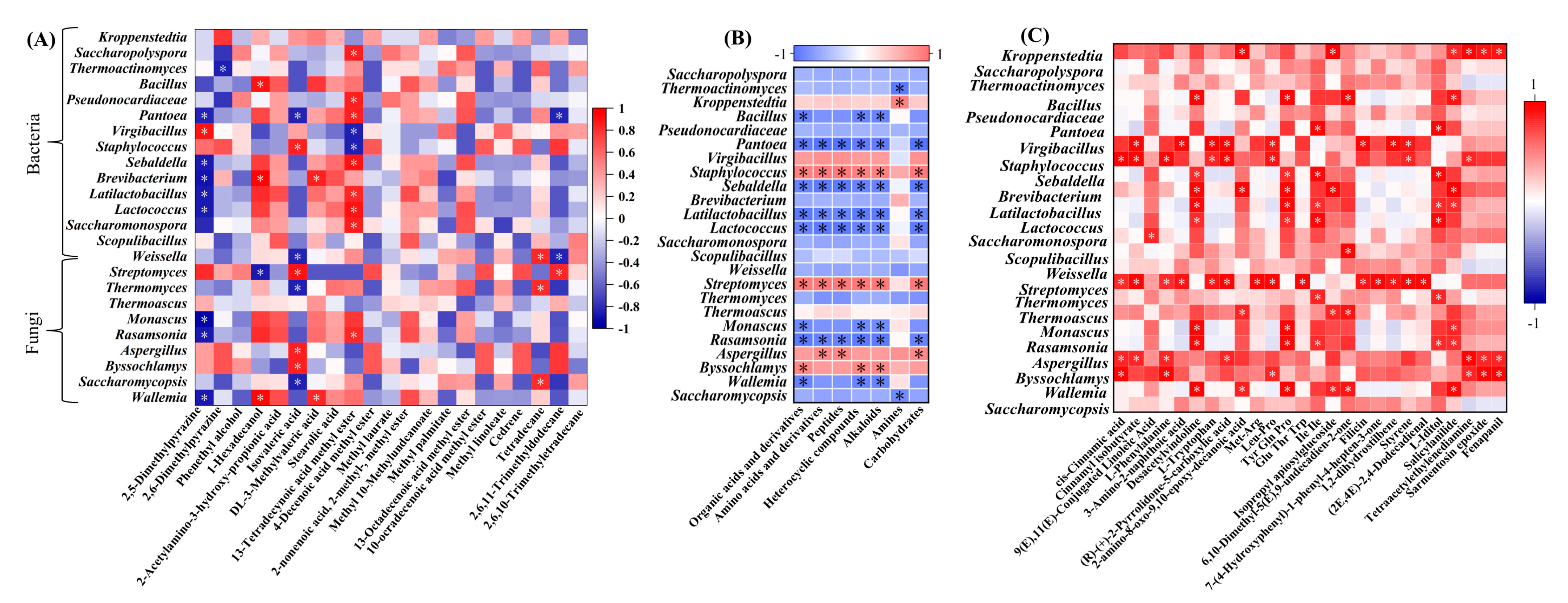
3.6. Differences in Correlations between Microorganisms and Metabolites
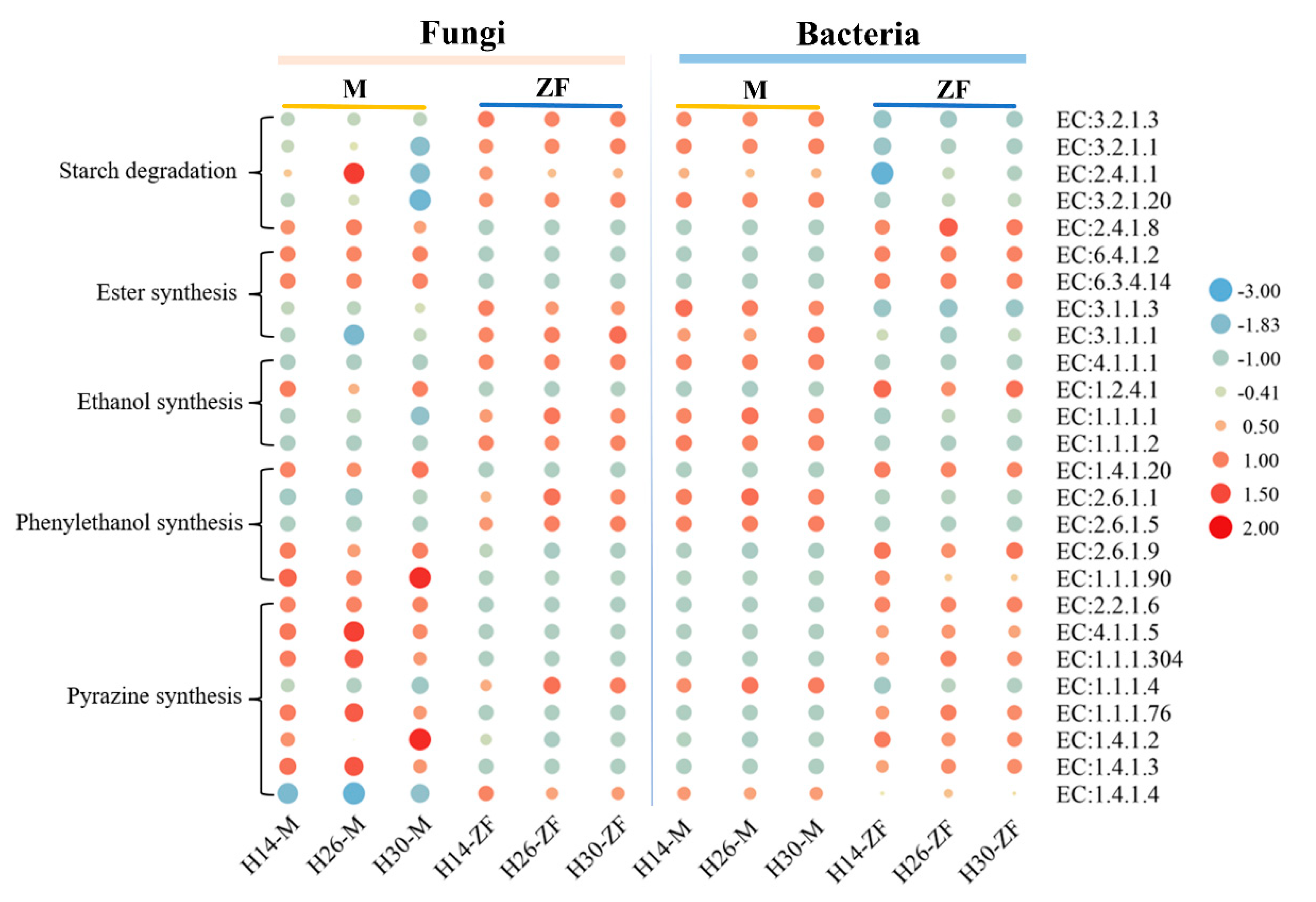
3.7. Function Prediction of Key Metabolic Pathways of Daqu
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. GC × GC-TOF/MS and UPLC-Q-TOF/MS based untargeted metabolomics coupled with physicochemical properties to reveal the characteristics of different type daqus for making soy sauce aroma and flavor type baijiu. LWT 2021, 146, 111416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.T.; Cheng, Y.X.; Zuo, Q.C.; Huang, Y.G.; Wang, L. Exploring the impacts of traditional crafts on microbial community succession in Jiang-flavored Daqu. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Mao, X.; Liu, D.; Ning, X.Q.; Shen, Y.; Chen, B.; Nie, H.F.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.B. Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties and microbial composition in high-temperature Daqu with different colors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 588117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. Chameleon-like microbes promote microecological differentiation of Daqu. Food Microbiol. 2023, 109, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.M.; Deng, M.F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Wu, S.W.; Lin, P.; Huang, B.J.; Liu, C.M.; Wan, Y. Analysis of microbial community, physiochemical indices, and volatile compounds of Chinese te-flavor baijiu daqu produced in different seasons. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6525–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.W.; Yang, H.; Ou, M.Y.; Zhang, J.X. Storage period affecting dynamic succession of microbiota and quality changes of strong-flavor Baijiu Daqu. LWT 2021, 139, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Ban, S.D.; Hu, B.D.; Qiu, S.Y.; Zhou, H.X. Bacterial diversity of Moutai-flavour Daqu based on high-throughput sequencing method. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chai, L.J.; Fang, G.Y.; Mei, J.L.; Lu, Z.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; Shi, J.S.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity of the microbiome and metabolome profiles of high-temperature Daqu in the same workshop. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Luo, Y.; Yao, Y.Q.; Ji, W.; Xia, X.L. Multidimensional analysis of wheat original crucial endogenous enzymes driving microbial communities metabolism during high-temperature Daqu fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 413, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Wang, X.C.; Liu, X.; Li, X.T.; Zhang, C.N.; Li, W.W.; Sun, X.T.; Wang, W.H.; Sun, B.G. Discovery and development of a novel short-chain fatty acid ester synthetic biocatalyst under aqueous phase from Monascus purpureus isolated from Baijiu. Food Chem. 2020, 338, 128025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.J.; Liu, X.L.; Gao, T.; Gu, S.B.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.N.; Ma, J.L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Unraveling the correlations between bacterial diversity, physicochemical properties and bacterial community succession during the fermentation of traditional Chinese strong-flavor Daqu. LWT 2022, 154, 112764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.A.; Huang, X.N.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.X.; Han, B.Z. Contrasting the microbial community and metabolic profile of three types of light-flavor Daqu. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.Q.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wu, C.D.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R.Q. Alteration of microbial community for improving flavor character of Daqu by inoculation with Bacillus velezensis and Bacillus subtilis. LWT 2019, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Aroma characteristics of Moutai-flavour liquor produced with Bacillus licheniformis by solid-state fermentation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 57, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, X.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Tang, J.L.; Xu, Y. Bacillus licheniformis affects the microbial community and metabolic profile in the spontaneous fermentation of Daqu starter for Chinese liquor making. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 250, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Qin, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, C.D.; Jin, Y.; et al. Mechanism of Enhancing Pyrazines in Daqu via Inoculating Bacillus licheniformis with Strains Specificity. Foods 2023, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, M.; Qiu, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.D.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R.Q. Characterizing the microbial diversity and major metabolites of Sichuan bran vinegar augmented by Monascus purpureus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QB/T 4257–2011; General Methods of Analysis for DAQU. China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Stevenson, K.E.; Lembke, F. Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods, 5th ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 26408–2010; Method for Determination of Bacillus subtilis in Feeds. National Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Tong, W.H.; He, P.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, Z.W.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.B.; Feng, X.J. Occurrence, diversity, and character of bacillaceae in the solid fermentation process of strong aromatic liquors. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 811788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.J.; Meng, L.J.; Mei, Z.L.; Liu, Q.R.; Chai, L.J.; Zhong, X.Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G.Q.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; et al. Volatile compound abundance correlations provide a new insight into odor balances in sauce-aroma Baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.H.; Sheng, J.Y.; Zhao, H.M.; Feng, X.Y. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce 1-hexadecanol from xylose. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.G. Volatile Components and Aroma Characteristics of Fen-Maotai-Flavored Liquor. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.H. Analysis and Reconfiguration of Aromatic Substances in Medium-Temperature Daqu. Master’s Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.W.; Yang, B.Y.; Dai, M.Q.; Xu, Y.Q.; Li, X.T.; Sun, B.G. East meets west in alcoholic beverages: Flavor comparison, microbial metabolism and health effects. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Tang, P.; Zhang, P.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.F.; Xiao, D.G.; Guo, X.W. Unraveling the aroma profiling of Baijiu: Sensory characteristics of aroma compounds, analytical approaches, key odor-active compounds in different Baijiu, and their synthesis mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2024, 146, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Chen, L.Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lu, X.; Lu, J.J.; Hu, C.X.; Tu, H.B.; et al. High-sensitivity profiling of dipeptides in sauce-flavor Baijiu Daqu by chemical derivatization and ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, W.H.; Jin, Y. Peptidomics analysis of Jiang-flavor Daqu from high-temperature fermentation to mature and in different preparation season. J. Proteom. 2023, 273, 104804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhang, Y.D.; Jiang, Y.L.; Chen, B.; Chen, X.X.; Han, B.Z. Microbial communities and metabolites characteristics of high temperature Daqu with different grades. Chin. Brew. 2022, 41, 24–30. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Moisture (g/100 g) | Saccharification Ability (mg/g·h) | Liquefaction Ability (g/g·h) | Fermentation Ability (g/0.5 g·72 h) | Esterification Ability (mg/50 g·7 d) | Acidity (mmol/10 g) | Ammoniacal Nitrogen (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H14-M | 9.94 ± 0.15 d | 81.73 ± 1.65 d | 0.05 ± 0.00 d | 0.11 ± 0.00 d | 603.95 ± 5.29 c | 1.74 ± 0.01 a | 4.92 ± 0.02 d |
| H26-M | 9.59 ± 0.20 e | 46.72 ± 0.43 e | 0.05 ± 0.00 d | 0.08 ± 0.00 f | 617.23 ± 1.93 b | 1.74 ± 0.01 a | 4.52 ± 0.01 e |
| H30-M | 9.81 ± 0.05 d | 108.93 ± 2.23 c | 0.07 ± 0.00 c | 0.10 ± 0.00 e | 602.64 ± 2.10 c | 1.62 ± 0.01 c | 3.81 ± 0.01 f |
| H14-ZF | 11.85 ± 0.19 c | 21.05 ± 0.26 f | 0.03 ± 0.00 e | 0.23 ± 0.02 a | 190.08 ± 2.04 e | 1.70 ± 0.01 b | 6.20 ± 0.01 a |
| H26-ZF | 13.09 ± 0.08 b | 439.86 ± 1.56 a | 0.36 ± 0.00 a | 0.20 ± 0.00 b | 529.09 ± 7.58 d | 1.29 ± 0.01 d | 5.35 ± 0.01 b |
| H30-ZF | 18.11 ± 0.09 a | 219.04 ± 2.21 b | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 0.17 ± 0.00 c | 742.09 ± 16.45 a | 1.00 ± 0.01 e | 5.18 ± 0.02 c |
| Sample | Bacteria (CFU/g) | Mesophilic Bacteria (CFU/g) | Fungi (CFU/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H14-M | (1.16 ± 0.01) × 109 b | (1.13 ± 0.03) × 108 a | (1.07 ± 0.22) × 104 e |
| H26-M | (9.72 ± 0.21) × 108 c | (3.63 ± 0.13) × 107 d | (1.60 ± 0.22) × 104 d |
| H30-M | (1.24 ± 0.02) × 109 a | (3.97 ± 0.15) × 107 c | (6.22 ± 0.13) × 103 f |
| H14-ZF | (5.74 ± 0.12) × 107 f | (3.35 ± 0.19) × 107 d | (4.62 ± 0.45) × 105 a |
| H26-ZF | (7.28 ± 0.20) × 107 e | (4.01 ± 0.09) × 107 c | (4.80 ± 0.58) × 104 c |
| H30-ZF | (1.38 ± 0.03) × 108 d | (1.08 ± 0.02) × 108 b | (2.31 ± 0.13) × 105 b |
| Number of Daqu | Bacteria | Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Shannon | Chao1 | Shannon | |
| H14-M | 211.96 | 4.56 | 59.02 | 2.71 |
| H26-M | 209.20 | 4.65 | 43.90 | 1.65 |
| H30-M | 159.09 | 4.22 | 63.00 | 2.42 |
| H14-ZF | 173.06 | 3.95 | 68.00 | 2.28 |
| H26-ZF | 274.24 | 3.85 | 66.05 | 1.60 |
| H30-ZF | 216.08 | 3.84 | 49.00 | 1.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Tang, Q.; Jin, Y. Characterizing the Contribution of Strain Specificity to the Microbiota Structure and Metabolites of Muqu and Fresh High-Temperature Daqu. Foods 2024, 13, 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193098
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Huang J, Zhou R, Tang Q, Jin Y. Characterizing the Contribution of Strain Specificity to the Microbiota Structure and Metabolites of Muqu and Fresh High-Temperature Daqu. Foods. 2024; 13(19):3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193098
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Zhu Zhang, Jun Huang, Rongqing Zhou, Qiuxiang Tang, and Yao Jin. 2024. "Characterizing the Contribution of Strain Specificity to the Microbiota Structure and Metabolites of Muqu and Fresh High-Temperature Daqu" Foods 13, no. 19: 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193098
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Huang, J., Zhou, R., Tang, Q., & Jin, Y. (2024). Characterizing the Contribution of Strain Specificity to the Microbiota Structure and Metabolites of Muqu and Fresh High-Temperature Daqu. Foods, 13(19), 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193098






