The Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Mung Bean Starch Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Mung Bean Flour
2.3. Extraction of Starch from Mung Bean Flour
2.4. Hydration Properties
2.5. Pasting Properties
2.6. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectra (FT-IR)
2.8. Amylose Determination
2.9. Distribution of Amylopectin Chain Length
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
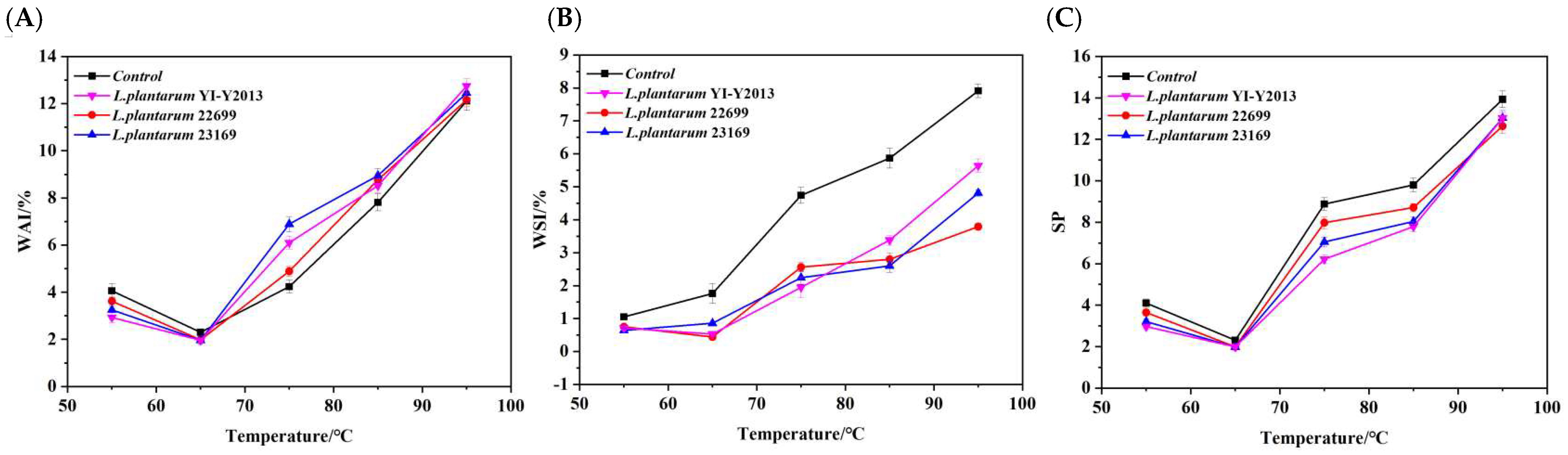
3.1. Gel Properties of Natural and Fermented Mung Bean Starch
3.1.1. Hydration Properties
3.1.2. Pasting Properties
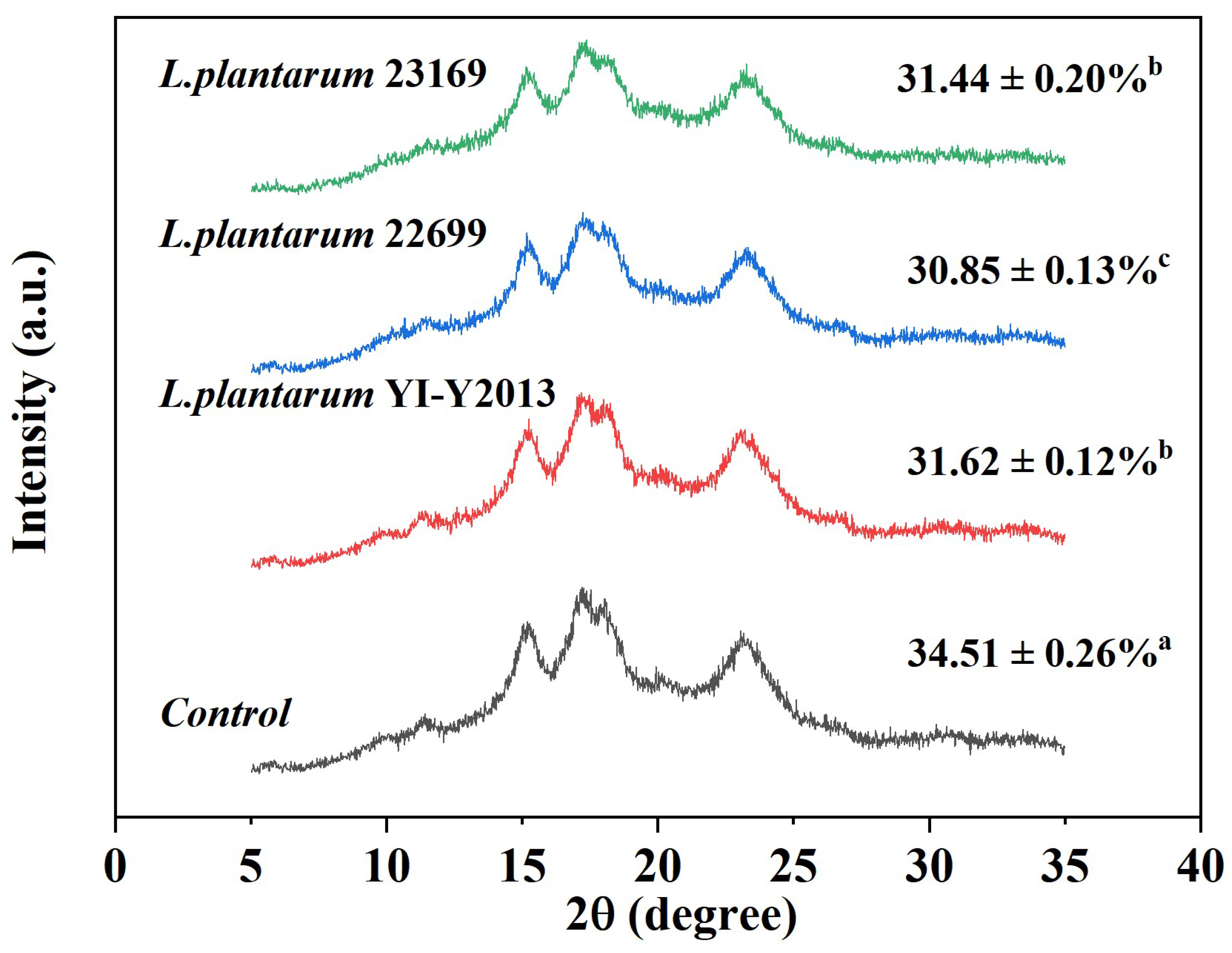
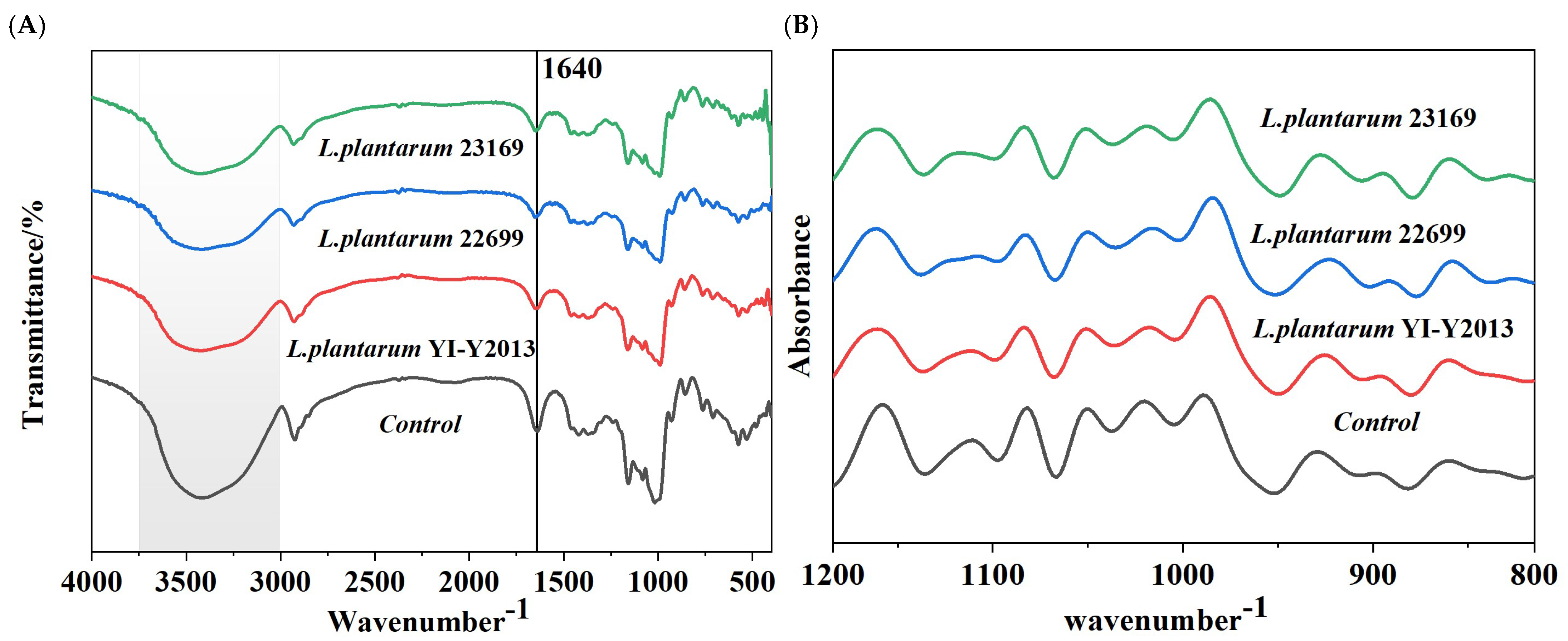
3.2. Ordered Structure of Natural and Fermented Mung Bean Starch
3.2.1. XRD Analysis
3.2.2. FT-IR Analysis
3.3. Fine Chain Structures of Natural and Fermented Mung Bean Starch
3.3.1. Amylose Content
3.3.2. Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution
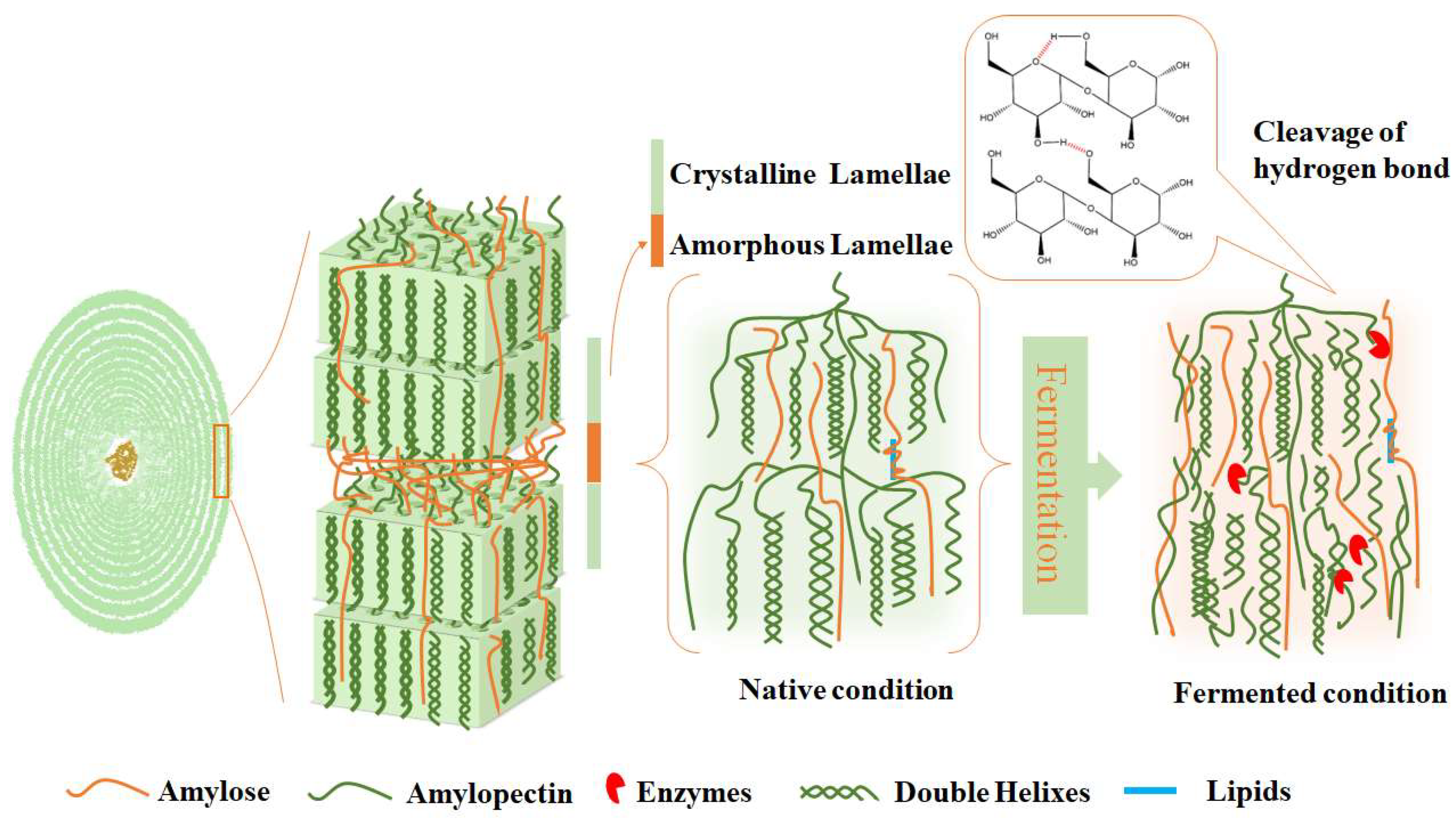
3.4. A Discussion of the Structural Alterations that Occur in Mung Bean Starch During Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, W. The multi-scale structure and physicochemical properties of mung bean starch modified by ultrasound combined with plasma treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Gong, B. Relations between rice starch fine molecular and lamellar/crystalline structures. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Meng, Y.; Yang, N.; Tao, H.; Xu, X. Effects of mung bean starch on quality of rice noodles made by direct dry flour extrusion. LWT 2015, 63, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, C.; Xing, B.; Ren, G.; Zhang, L. Investigating the effect of different contents of mung beans on the structure and function of extruded buckwheat noodles. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Thi Mai, H.; Phan Ngoc, H.; Pham Van, H. Varying amylose contents affect the structural and physicochemical characteristics of starch in mung bean. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Ma, C.; Xing, W.; Yang, Y.; Fan, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, N. Effect of lactobacillus acidophilus fermentation on the quality of glutinous rice products. Starch 2023, 75, 2200193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, J.C. Characteristics of mung bean starch isolated by using lactic acid fermentation solution as the steeping liquor. Food Chem 2006, 99, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, X.; Yin, J.; Xiong, T.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. A review: Effects of microbial fermentation on the structure and bioactivity of polysaccharides in plant-based foods. Food Chem 2024, 440, 137453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Quan, K. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on the volatile flavors of mung beans. LWT 2021, 146, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Chen, J.-R.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.-H.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Ren, L.-K.; Wu, N.; Chen, F.-L.; Liu, X.-F.; Wang, B.; et al. Effects of fermentation on the structure and physical properties of glutinous proso millet starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Sung, J.M.; Choi, Y.S.; Park, J.D. Effect of natural fermentation on milled rice grains: Physicochemical and functional properties of rice flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, H.; Yi, C. Soybean protein isolate affects in vitro digestion properties of fermented indica rice starch by regulating its gel characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sharp, P.; Copeland, L. Structural and functional properties of starches from field peas. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, C.; Zhu, H.; Bao, J.; Quan, K.; Yang, R. The texture of fresh rice noodles as affected by the physicochemical properties and starch fine structure of aged paddy. LWT 2020, 130, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiga, B.H.; Kumcuoglu, S.; Vatansever, M.; Tavman, S. Thermal and pasting properties of Quinoa—Wheat flour blends and their effects on production of extruded instant noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 97, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC International. Methods 61-03.01. Amylograph Method for Milled Rice. In Approved Methods of Analysis, 10th ed.; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Xu, X. Microstructure, gelatinization and pasting properties of rice starch under acid and heat treatments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S.; Kumar, M.; Siroha, A.K.; Kennedy, J.F.; Dhull, S.B.; Whiteside, W.S. Pearl millet grain as an emerging source of starch: A review on its structure, physicochemical properties, functionalization, and industrial applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, C.; Cong, X.; Wu, T.; Song, Y.S.; Zhang, M. Effects of oligomeric procyanidins on the retrogradation properties of maize starch with different amylose/amylopectin ratios. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Effects of different crop starches on the cooking quality of Chinese dried noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2080–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, C.; Liu, M.; Cai, D.; Liu, J. Influence of multiple freezing/thawing cycles on a structural, rheological, and textural profile of fermented and unfermented corn dough. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Tangsrianugul, N.; Suphantharika, M. A review on isolation, characterization, modification, and applications of proso millet starch. Foods 2023, 12, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Guo, W.; Chen, P.; Liu, C.; Wei, J.; Zheng, X.; Omer, S.H.S. Effects of bifidobacteria fermentation on physico-chemical, thermal and structural properties of wheat starch. Foods 2022, 11, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhu, K.; Li, S.; Tan, L.; Wu, G.; Dong, W. Effect of degree of polymerization of amylopectin on the gelatinization properties of jackfruit seed starch. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zou, J.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Duan, R.; Yang, B. Effect of lactobacteria fermentation on structure and physicochemical properties of Chinese yam starch (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.). Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Gong, S.; Li, M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J. Physicochemical properties of potato starch fermented by amylolytic Lactobacillus plantarum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Bao, J.; Corke, H.; Sui, Z. Starch granule-associated proteins affect the physicochemical properties of rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adeloye, A.A.; Olaomo, O.O.; Kayitesi, E. Effect of fermentation time on physicochemical properties of starch extracted from cassava root. Food Biosci. 2020, 33, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.N.P.; Mal, S.S.; Paul, U.C.; Rahman, H.; Mazumder, N. An insight into the gelatinization properties influencing the modified starches used in food industry: A review. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2022, 15, 1195–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.L.; Li, X.P.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.Z. Effect of kansui addition on dough rheology and quality characteristics of chickpea-wheat composite flour-based noodles and the underlying mechanism. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Tian, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, M.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X. The multi-scale structure, thermal and digestion properties of mung bean starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Huang, S.; Chi, C.; Lu, P.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Li, X. Digestibility and structure changes of rice starch following co-fermentation of yeast and Lactobacillus strains. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.X.; Li, X.X.; Chen, L.; Situ, W.B. Digestibility and structural changes of waxy rice starch during the fermentation process for waxy rice vinasse. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fan, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, N. Effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the physicochemical and structural characteristics of starch in blends of glutinous and japonica rice. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.J.; Yao, W.; Gao, F.F.; Zheng, D.Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, J.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Physicochemical properties comparative analysis of corn starch and cassava starch, and comparative analysis as adhesive. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfarzad, A.; Yousefi, A.; Ako, K. Steady/dynamic rheological characterization and FTIR study on wheat starch-sage seed gum blends. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Combinatorial effect of fermentation and drying on the relationship between the structure and expansion properties of tapioca starch and potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansi, W.; Mushtaq, B.S.; Mahdi, A.A.; Al-Maqtari, Q.A.; Al-Adeeb, A.; Ahmed, A.; Fan, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Jinxin, L.; et al. Molecular structure, morphological, and physicochemical properties of highlands barley starch as affected by natural fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashogbon, A.O.; Akintayo, E.T.; Oladebeye, A.O.; Oluwafemi, A.D.; Akinsola, A.F.; Imanah, O.E. Developments in the isolation, composition, and physicochemical properties of legume starches. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2938–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumoro, A.C.; Widiyanti, M.; Ratnawati, R.; Retnowati, D.S. Nutritional and functional properties changes during facultative submerged fermentation of gadung (Dioscorea hispida Dennst) tuber flour using Lactobacillus plantarum. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonghui, Y.; Kumar, G.G.; Linyue, Z.; Jingjie, Z.; Jing, W.; Baoguo, S. The classical and potential novel healthy functions of rice bran protein and its hydrolysates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 8454–8466. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, F.; Xiao, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G. Spontaneous fermentation tunes the physicochemical properties of sweet potato starch by modifying the structure of starch molecules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, B.Y.; Yin, R.M.; Li, X.S.; Cui, S.S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.X.; Chen, W. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum isolated from different niches. Genes 2021, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Du, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Cao, C. Grain starch, fatty acids, and amino acids determine the pasting properties in dry cultivation plus rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Samples | PV/cP | TV/cP | FV/cP | BD/cP | SB/cP | PT/min | GT/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5088 ± 0.71 c | 1607 ± 9.19 c | 4428 ± 164.05 c | 2345 ± 4.95 b | 1703 ± 10.61 c | 4.57 ± 0.05 a | 75.20 ± 0.07 b |
| L. Plantarum YI-Y2013 | 5364 ± 17.68 b | 3019 ± 12.73 b | 4722 ± 2.12 b | 3481 ± 9.90 a | 2822 ± 173.24 a | 4.60 ± 0.00 a | 78.75 ± 0.49 a |
| L. Plantarum 22699 | 5818 ± 47.38 a | 3433 ± 65.76 a | 5176 ± 61.52 a | 2367 ± 43.84 b | 1743 ± 4.24 c | 4.50 ± 0.04 a | 76.40 ± 0.49 b |
| L. Plantarum 23169 | 5464 ± 72.12 b | 2966 ± 185.97 b | 5069 ± 26.87 a | 2499 ± 258.09 b | 2104 ± 159.12 b | 4.57 ± 0.05 a | 77.98 ± 0.53 a |
| Sample | Short-Ordered Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| DO (R1047/1022) | DD (R995/1022) | |
| Control | 0.848 ± 0.056 b | 1.150 ± 0.080 c |
| L. Plantarum YI-Y2013 | 0.981 ± 0.020 a | 1.700 ± 0.020 a |
| L. Plantarum 22699 | 0.970 ± 0.034 a | 1.508 ± 0.089 b |
| L. Plantarum 23169 | 0.941 ± 0.034 ab | 1.633 ± 0.014 ab |
| Sample | Amylose Content | Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP (6–12) (FA) | DP (13–24) (Fb1) | DP (25–36) (Fb2) | DP (37–60) (Fb3) | ||
| Control | 23.61 ± 0.21 c | 43.02 ± 0.86 b | 29.28 ± 1.08 a | 13.02 ± 0.08 a | 14.68 ± 0.14 a |
| L. Plantarum YI-Y2013 | 35.36 ± 0.10 ab | 45.94 ± 0.35 ab | 27.98 ± 1.02 a | 12.92 ± 0.24 a | 13.16 ± 0.44 b |
| L. Plantarum 22699 | 37.82 ± 0.33 a | 46.22 ± 1.77 a | 28.03 ± 1.11 a | 12.83 ± 0.26 a | 12.99 ± 0.31 b |
| L. Plantarum 23169 | 33.01 ± 0.23 b | 46.66 ± 1.74 a | 28.31 ± 1.03 a | 12.68 ± 0.06 a | 13.37 ± 0.86 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, T.; Xu, L.; Yuan, J.; Li, Z.; Yi, C. The Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Mung Bean Starch Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum. Foods 2024, 13, 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213409
Huang Z, Li Y, Guo T, Xu L, Yuan J, Li Z, Yi C. The Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Mung Bean Starch Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum. Foods. 2024; 13(21):3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213409
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhen, Yisi Li, Tian Guo, Li Xu, Jieyao Yuan, Zuyin Li, and Cuiping Yi. 2024. "The Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Mung Bean Starch Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum" Foods 13, no. 21: 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213409
APA StyleHuang, Z., Li, Y., Guo, T., Xu, L., Yuan, J., Li, Z., & Yi, C. (2024). The Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Mung Bean Starch Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum. Foods, 13(21), 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13213409






