Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on Physical Stability of Lily Juice: Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Microstructure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Lily Juice
2.3. Ultrasonic Setting
2.4. Rheological Properties of Lily Juice
2.5. Particle Size Measurement
2.6. Zeta Potential
2.7. Cloud Stability
2.8. Color Parameters
2.9. pH and TSS
2.10. Microstructure Observation
2.11. Stability Assessment of the Ultrasonicated Juice
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Steady-State Rheological Properties
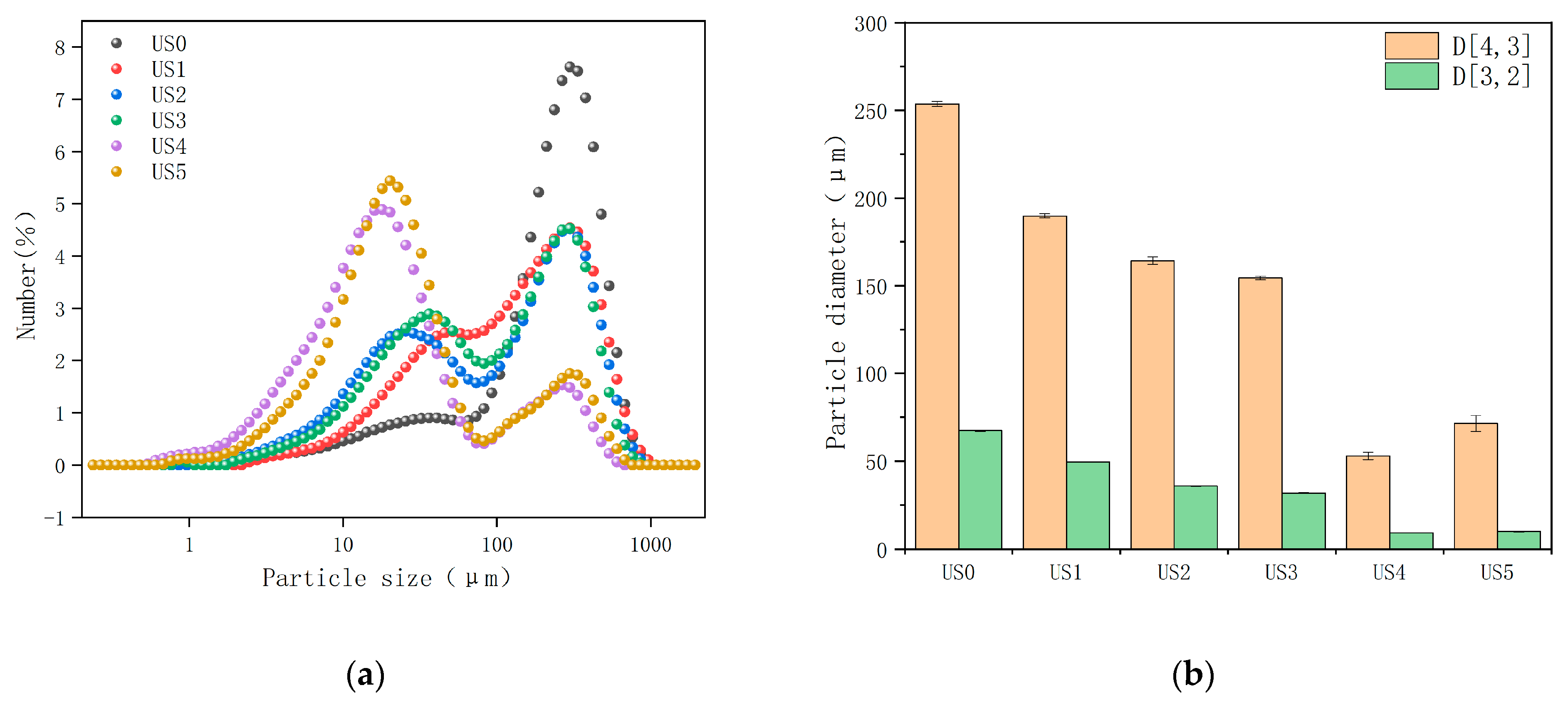
3.2. Particle Size Analysis
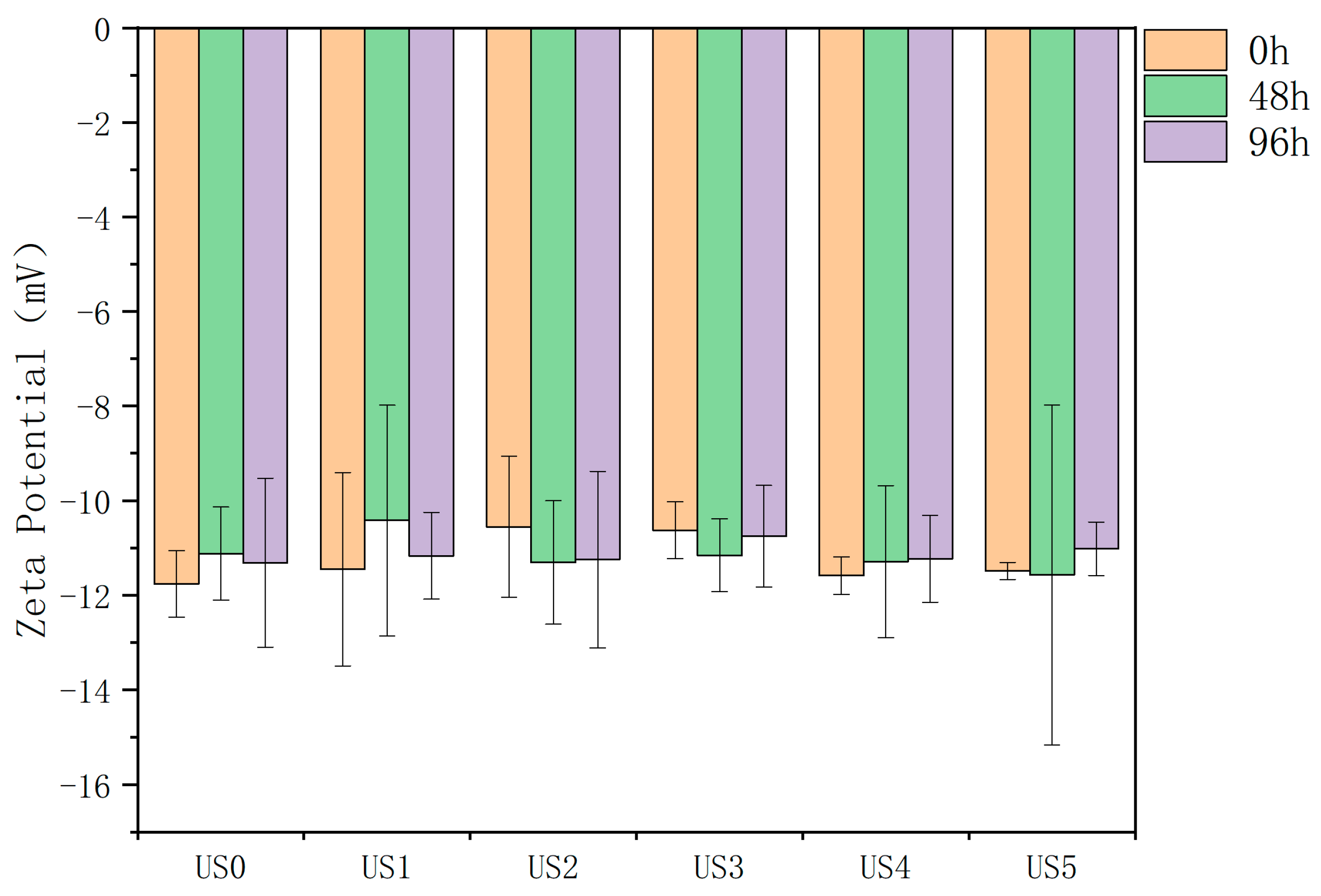
3.3. Zeta Potential
3.4. Color Value
3.5. pH and TSS
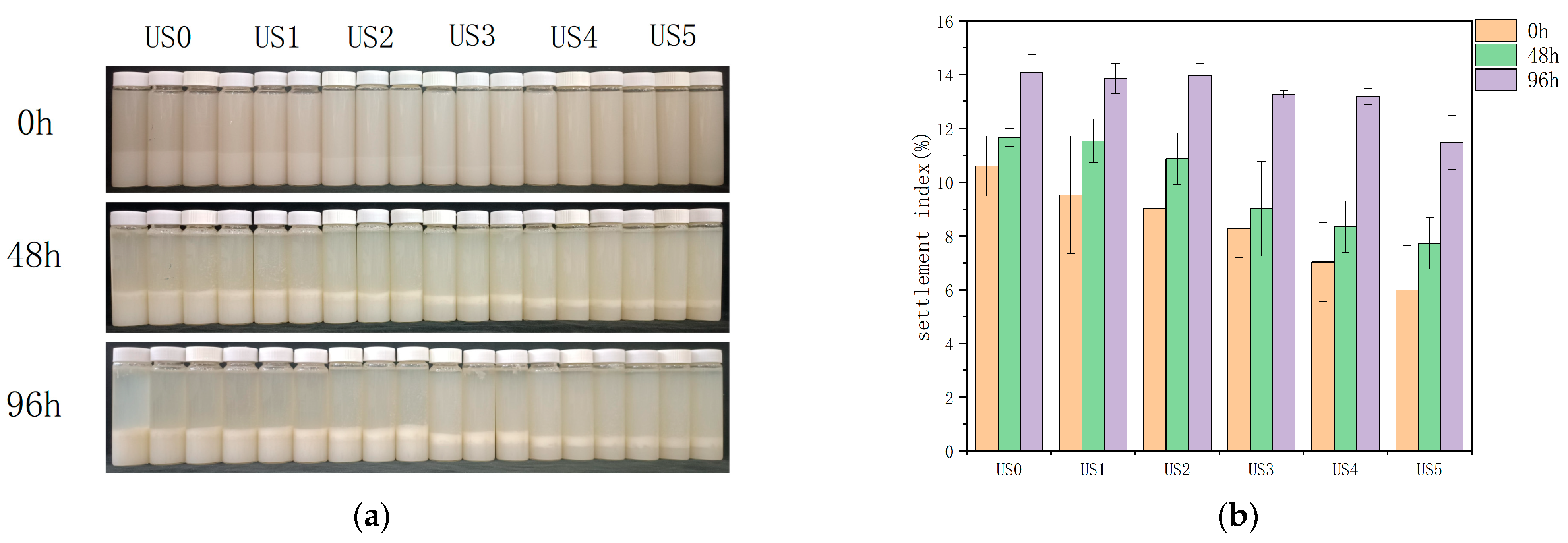
3.6. Cloud Value
3.7. Optical Microstructure
3.8. Stability Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Penha, C.B.; Santos, V.D.P.; Speranza, P.; Kurozawa, L.E. Plant-based beverages: Ecofriendly technologies in the production process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 72, 102760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, Y.; Ding, S. Comparison of the biochemical properties and thermal inactivation of polyphenol oxidase from three lily bulb cultivars. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of nutrition components in Lanzhou lily bulb by confocal Raman microscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 244, 118837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Yan, L.; Yan, Z.; Du, W.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, B.; Wu, Z. Review on preservation techniques of edible lily bulbs in China. CyTA-J. Food 2022, 20, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Chen, J.; Yue, C.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, H. Modification of lily polysaccharide by selenylation and the immune-enhancing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 142, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, R.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, R.; Mhatre, P.; Sonawane, S.; Sharma, S.; Gat, Y.; Chandran, D.; Hasan, M.; Dey, A. Application of ultrasonication as pre-treatment for freeze drying: An innovative approach for the retention of nutraceutical quality in foods. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafudoulla, M.; Ulrich, M.S.; Toushik, S.H.; Nahar, S.; Roy, P.K.; Mizan, F.R.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.-D. Challenges and opportunities of non-conventional technologies concerning food safety. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2023, 79, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Okonkwo, C.E.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Olaniran, A.F. Ultrasound, infrared and its assisted technology, a promising tool in physical food processing: A review of recent developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1587–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munekata, P.E.; Domínguez, R.; Budaraju, S.; Roselló-Soto, E.; Barba, F.J.; Mallikarjunan, K.; Roohinejad, S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Effect of innovative food processing technologies on the physicochemical and nutritional properties and quality of non-dairy plant-based beverages. Foods 2020, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.J.; Paniwnyk, L.; Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A. Ultrasonic food processing. Altern. Conv. Food Process. 2011, 19, 387–414. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Flores, H.E.; Garnica-Romo, M.G.; Bermúdez-Aguirre, D.; Pokhrel, P.R.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Physico-chemical parameters, bioactive compounds and microbial quality of thermo-sonicated carrot juice during storage. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.D.R.C.; Barros, Z.M.P.; de Carvalho, C.B.O.; Honorato, F.A.; Guerra, N.B.; Azoubel, P.M. Effect of sonication on soursop juice quality. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Juárez, J.; Graff, K.; Lucas, M. Introduction to power ultrasonics. In Power Ultrasonics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, M.L.; Miano, A.C.; Augusto, P.E. Ultrasound processing of fruit and vegetable juices. In Ultrasound: Advances for Food Processing and Preservation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 181–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.; Goh, K.M. Sonication treatment convalesce the overall quality of hand-pressed strawberry juice. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, G.; Zhou, C.; Su, W.; Hu, X. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on color, carotenoid content, enzyme activity, rheological properties, and microstructure of pumpkin juice during storage. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoli, S.S.; Rojas, M.L.; do Amaral, J.E.P.G.; Canniatti-Brazaca, S.G.; Augusto, P.E.D. Ultrasound processing of guava juice: Effect on structure, physical properties and lycopene in vitro accessibility. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Vanga, S.K.; Raghavan, V. High-intensity ultrasound processing of kiwifruit juice: Effects on the microstructure, pectin, carbohydrates and rheological properties. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.L.; Leite, T.S.; Cristianini, M.; Alvim, I.D.; Augusto, P.E. Peach juice processed by the ultrasound technology: Changes in its microstructure improve its physical properties and stability. Food Res. Int. 2016, 82, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Liu, H. Ultrasonic treatment maintains the flavor of the melon juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kou, C.; Xi, P.; Liu, H. Ultrasonic and other sterilization methods on nutrition and flavor of cloudy apple juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menelli, G.S.; Fracalossi, K.L.; Lepaus, B.M.; De São José, J.F.B. Effects of high-intensity ultrasonic bath on the quality of strawberry juice. CyTA-J. Food 2021, 19, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, S. Effects of high-pressure homogenization on the structural, physical, and rheological properties of lily pulp. Foods 2019, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.-Y.; Jiang, S.-W.; Cai, J.; Cao, X.-M.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, S.-T.; Wang, H.-L.; Pan, L.-J. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on the rheological properties of taro (Colocasia esculenta (L). Schott) pulp. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 50, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; He, W.-Q. Effect of high pressure homogenization on sugar beet pulp: Rheological and microstructural properties. LWT 2020, 125, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, L. Comparative studies on the stabilization of Flos Sophorae Immaturus beverages by various hydrocolloids. LWT 2020, 123, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, C.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Y. Impact of pH, freeze–thaw and thermal sterilization on physicochemical stability of walnut beverage emulsion. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanzadeh, S.; Ziaiifar, A.M.; Kashaninejad, M. Influence of thermal treatment, homogenization and xanthan gum on physicochemical properties of watermelon juice: A response surface approach. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalerao, P.P.; Mahale, S.A.; Dhar, R.; Chakraborty, S. Optimizing the formulation for a pomegranate-amla-muskmelon based mixed fruit beverage using sensory analysis and evaluating its thermal stability. LWT 2020, 133, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; Li, P.; Luo, D.; Guo, J. Physical stability of chestnut lily beverages (CLB): Effects of shear homogenization on beverage rheological behavior, particle size, and sensory properties. Foods 2022, 11, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, B.; Decker, E.; Panya, A. The influence of flaxseed gum on the microrheological properties and physicochemical stability of whey protein stabilized β-carotene emulsions. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Xu, B.; Khan, S.; Shukat, R.; Ahmad, N.; Imran, M.; Rehman, A.; Karrar, E.; Aadil, R.M.; Korma, S.A. Impact of high-intensity thermosonication treatment on spinach juice: Bioactive compounds, rheological, microbial, and enzymatic activities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 78, 105740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.E.; Ibarz, A.; Cristianini, M. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on the rheological properties of tomato juice: Time-dependent and steady-state shear. J. Food Eng. 2012, 111, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.M.; Sato, A.C.K.; Barbosa, G.; Dacanal, G.; Ciro-Velásquez, H.J.; Cunha, R.L. The effect of homogenisation on the stability of pineapple pulp. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.S.; Augusto, P.E.; Cristianini, M. Using high pressure homogenization (HPH) to change the physical properties of cashew apple juice. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogi, D.; Oberoi, D.; Malik, S. Effect of particle size, temperature, and total soluble solids on the rheological properties of watermelon juice: A response surface approach. Int. J. Food Prop. 2010, 13, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Cui, J.; Zhao, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J. Effects of high-pressure homogenization on pectin structure and cloud stability of not-from-concentrate orange juice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 647748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelter, T.; Wientjes, R.; Vreeker, R.; Klaffke, W. Enzymatic modifications of pectins and the impact on their rheological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 47, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Lu, Z.; Ye, F.; Zhao, G. Effects of breaking methods on the viscosity, rheological properties and nutritional value of tomato paste. Foods 2021, 10, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Fu, X. Effect of guar gum on stability and physical properties of orange juice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellala, C.K.D.; Bi, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M. Effect of high pressure homogenization on mixed juice stability, rheology, physicochemical properties and microorganism reduction. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, P.; Svelander, C.; Bialek, L.; Schumm, S.; Langton, M. Rheology and microstructure of carrot and tomato emulsions as a result of high-pressure homogenization conditions. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, E130–E140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, L.; Yi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, X.; Decker, E.A. Impact of high-intensity ultrasound on the chemical and physical stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by almond protein isolate. LWT 2021, 149, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patist, A.; Bates, D. Ultrasonic innovations in the food industry: From the laboratory to commercial production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.S.; Augusto, P.E.; Cristianini, M. The use of high pressure homogenization (HPH) to reduce consistency of concentrated orange juice (COJ). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 26, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xi, P.; Cai, T.; Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Effects of temperature-controlled ultrasound treatment on sensory properties, physical characteristics and antioxidant activity of cloudy apple juice. LWT 2021, 142, 111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohtani, S.; Yoshii, H. Microstructure, composition, and their relationship with emulsion stability. In Food Microstructure and Its Relationship with Quality and Stability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Tang, X.; Fan, L. Improvement in physical and thermal stability of cloudy ginkgo beverage during autoclave sterilization: Effects of microcrystalline cellulose and gellan gum. LWT 2021, 135, 110062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croak, S.; Corredig, M. The role of pectin in orange juice stabilization: Effect of pectin methylesterase and pectinase activity on the size of cloud particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Genovese, D.; Lozano, J. Zeta-potential as a way to determine optimal conditions during fruit juice clarification. In Food Engineering: Integrated Approaches; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Xu, E.; Liu, D. Ultrasonication of Thawed Huyou Juice: Effects on cloud stability, physicochemical properties and bioactive compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Guan, Y.; Bi, J.; Liu, X.; Yi, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhou, M. Change of the rheological properties of mango juice by high pressure homogenization. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, S.; Calvo, C.; Costell, E.; Durán, L. Influence of color on perception of sweetness and fruit flavor of fruit drinks. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2001, 7, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.W.; Streaker, C.B.; Zhang, Q.H.; Min, D.B. Effects of pulsed electric fields on the quality of orange juice and comparison with heat pasteurization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4597–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.F.R.; Gomes, A.D.S.; Castro, D.R.G.; Souza, F.D.C.D.A.; Mar, J.M.; da Silva, L.S.; Sanches, E.A.; Bezerra, J.D.A.; Bakry, A.M.; Campelo, P.H. Ultrasound-assisted homogenization and gum Arabic combined to physicochemical quality of cupuaçu juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. Effects of ultrasound processing on physicochemical parameters, antioxidants, and color quality of bayberry juice. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 7917419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepaus, B.M.; Santos, A.K.P.D.O.; Spaviero, A.F.; Daud, P.S.; de São José, J.F.B. Stability parameters during refrigerated storage and changes on the microstructure of orange-carrot blend juice processed by high-power ultrasound. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 891662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteles, T.V.; Costa, M.G.M.; de Jesus, A.L.T.; de Miranda, M.R.A.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Rodrigues, S. Power ultrasound processing of cantaloupe melon juice: Effects on quality parameters. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Soh, C.; Liew, S.; Teh, F. Effects of sonication and carbonation on guava juice quality. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| US0 | US1 | US2 | US3 | US4 | US5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 0.00739 ± 3.27318 × 10−4 a | 0.0061 ± 2.56015 × 10−4 b | 0.00442 ± 1.33271 × 10−4 c | 0.00338 ± 2.70179 × 10−4 d | 0.00282 ± 9.7261 × 10−5 e | 0.00253 ± 1.49411 × 10−4 e |
| n | 0.86803 ± 0.0097 a | 0.89714 ± 0.01097 b | 0.93504 ± 0.00899 c | 0.94858 ± 0.01648 cd | 0.96742 ± 0.00921d e | 0.97564 ± 0.01424 e |
| R2 | 0.998 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| L* | a* | b* | ∆E | TSS | pH | Cloud Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US0 | 20.27 ± 0.07 a | 2.9 ± 0.19 a | 5.87 ± 0.25 a | 0 | 1.87 ± 0.06 a | 6.72 ± 0.03 a | 0.19 ± 0.002 a |
| US1 | 19.90 ± 0.07 ab | 2.95 ± 0.05 a | 6.84 ± 0.82 a | 1.18 ± 0.77 b | 1.9 ± 0.1 ab | 6.7 ± 0.02 a | 0.196 ± 0.001 a |
| US2 | 19.84 ± 0.4 b | 4.15 ± 0.16 b | 6.94 ± 1.1 a | 1.85 ± 0.32 bc | 1.93 ± 0.06 ab | 6.66 ± 0.04 a | 0.219 ± 0.008 b |
| US3 | 19.86 ± 0.12 ab | 5.14 ± 0.08 c | 6.02 ± 0.32 a | 2.32 ± 0.2 cd | 2.03 ± 0.06 bc | 6.66 ± 0.03 a | 0.244 ± 0.002 c |
| US4 | 19.79 ± 0.25 b | 5.29 ± 0.44 c | 6.04 ± 0.36 a | 2.46 ± 0.65 cd | 2.1 ± 0.1 cd | 6.68 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.003 d |
| US5 | 19.71 ± 0.07 b | 5.98 ± 0.31 d | 5.94 ± 0.26 a | 3.14 ± 0.39 d | 2.2 ± 0.1 e | 6.72 ± 0.03 a | 0.283 ± 0.003 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.-H.; Zhu, J.-K.; Shao, L.; Yue, C.-H.; Li, P.-Y.; Bai, Z.-Y.; Luo, D.-L. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on Physical Stability of Lily Juice: Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Microstructure. Foods 2024, 13, 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081276
Han S-H, Zhu J-K, Shao L, Yue C-H, Li P-Y, Bai Z-Y, Luo D-L. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on Physical Stability of Lily Juice: Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Microstructure. Foods. 2024; 13(8):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081276
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Si-Hai, Jun-Kun Zhu, Lei Shao, Chong-Hui Yue, Pei-Yan Li, Zhou-Ya Bai, and Deng-Lin Luo. 2024. "Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on Physical Stability of Lily Juice: Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Microstructure" Foods 13, no. 8: 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081276
APA StyleHan, S.-H., Zhu, J.-K., Shao, L., Yue, C.-H., Li, P.-Y., Bai, Z.-Y., & Luo, D.-L. (2024). Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on Physical Stability of Lily Juice: Rheological Behavior, Particle Size, and Microstructure. Foods, 13(8), 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081276





