Effects of Different Degrees of Gelatinization on Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Kudzu Starch Samples with Different DG
2.3. Particle Size Distribution
2.4. Apparent Amylose Content
2.5. Amylose Leaching
2.6. Digestive Properties
2.6.1. Digestive Properties of Raw Starch
2.6.2. Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch with Different DG
2.7. Thermal Properties
2.8. Iodine-Binding Capacity (IBC)
2.9. Determination of DG
2.9.1. Enzymatic Method
2.9.2. DSC Method
2.9.3. Iodine-Binding Method
2.10. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.11. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.12. Fourier Transforms Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.13. Rheology
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
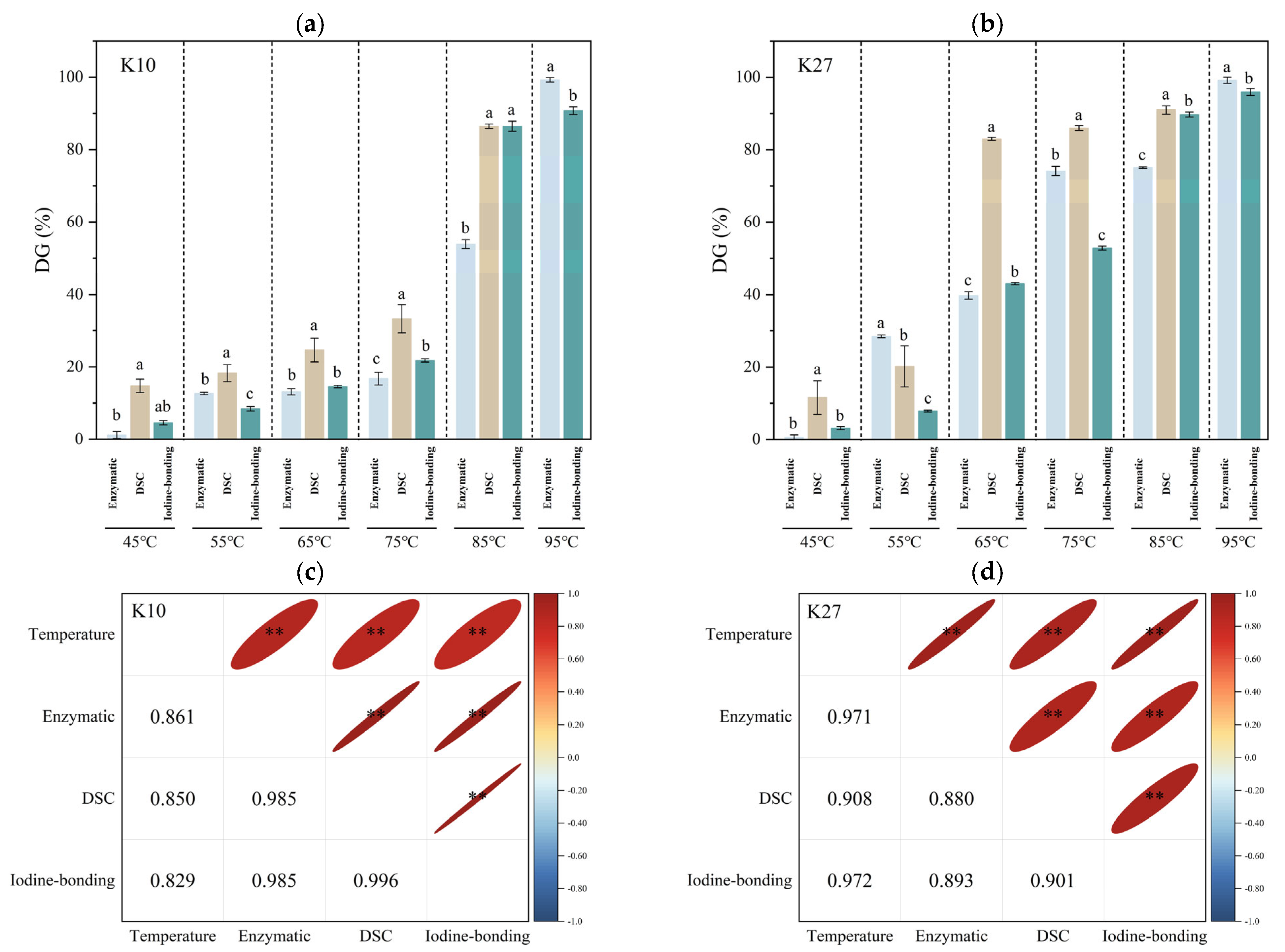
3.1. Starch DG Determined by Three Different Methods and Their Correlations
3.1.1. Enzymatic Method
3.1.2. DSC Method
3.1.3. Iodine-Bonding Method
3.1.4. Comparison of Three Methods for Determining Starch DG
3.1.5. Correlation of Three Methods for Determination of Starch DG
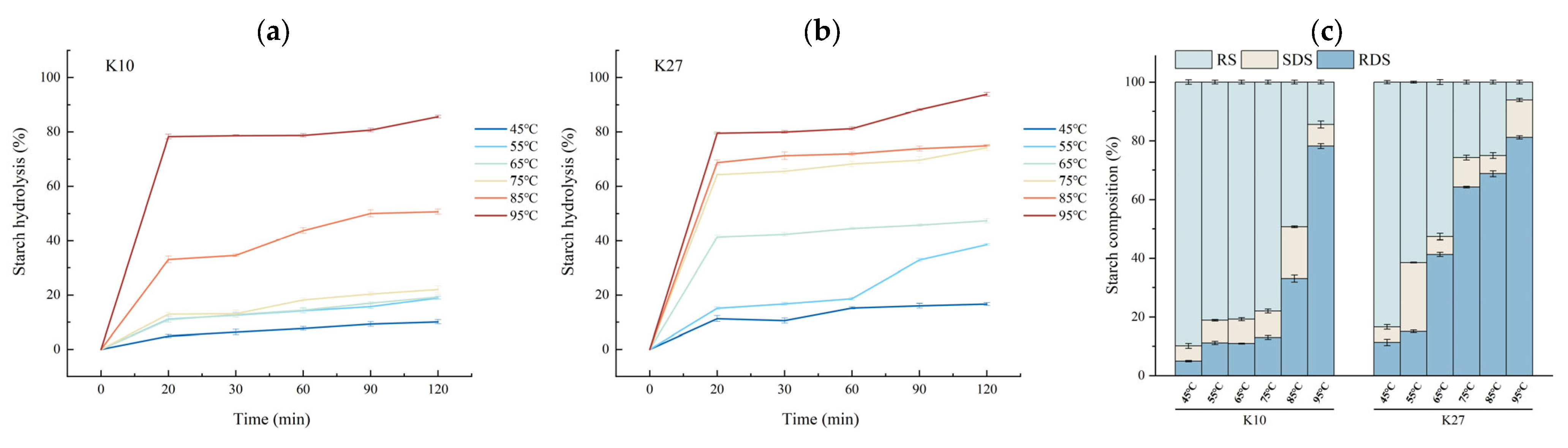
3.2. In Vitro Digestive Properties
3.2.1. Digestive Properties of Raw Starch
3.2.2. Effects of Different DG on the Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch
3.3. Effects of Different DG on the Thermal Properties of Kudzu Starch
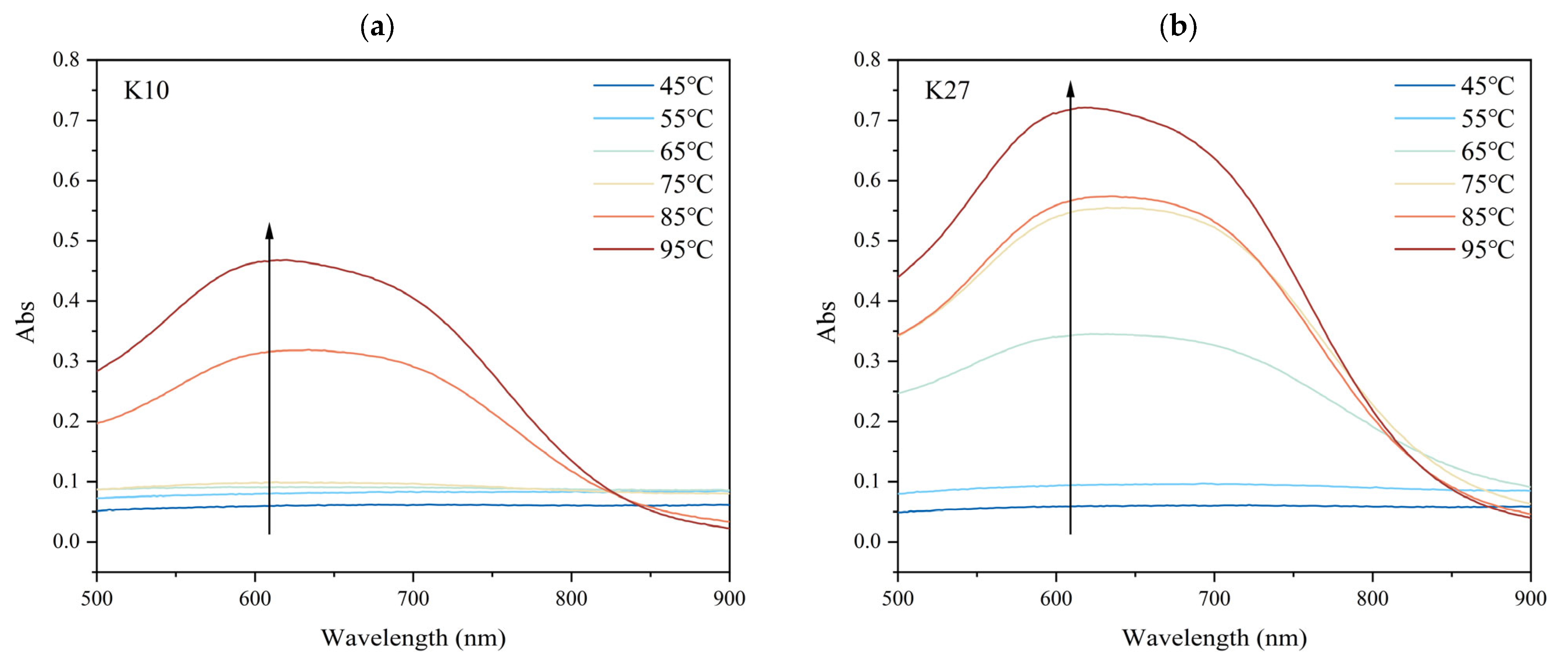
3.4. Effects of Different DG on the Iodine-Binding Capacity of Kudzu Starch
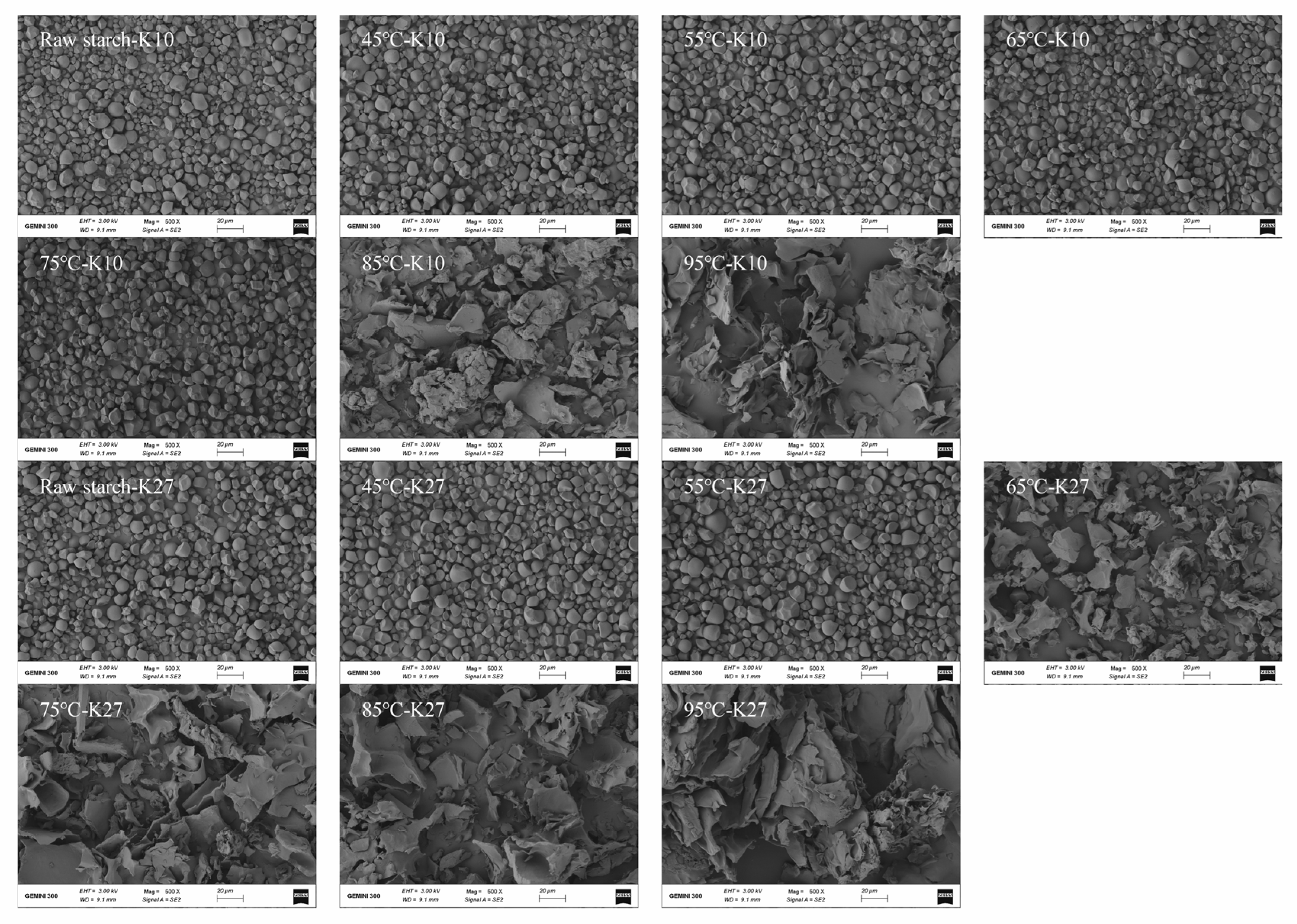
3.5. Effects of Different DG on the Morphology of Kudzu Starch
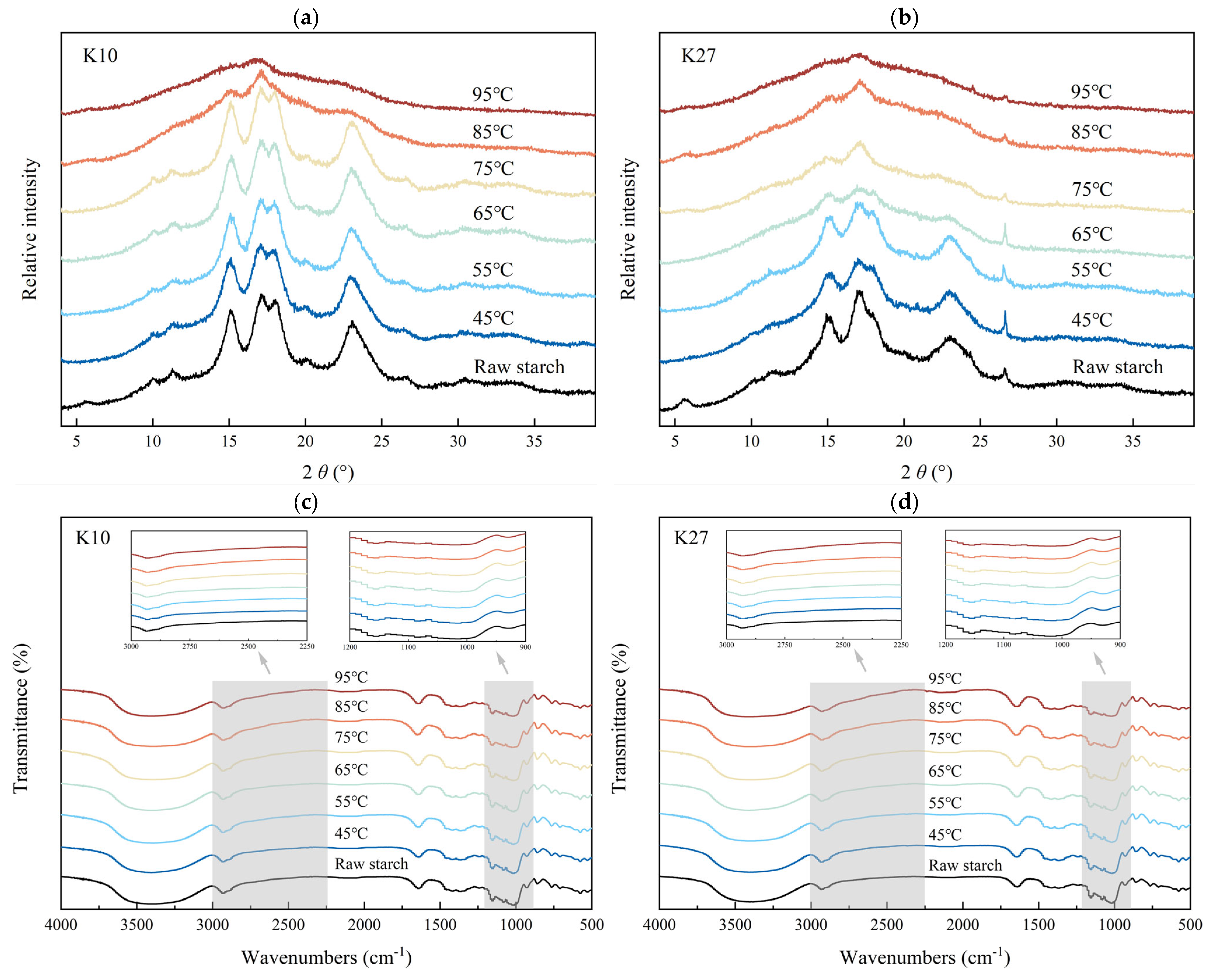
3.6. Effects of Different DG on the Long-Range Ordered Structure of Kudzu Starch
3.7. Effects of Different DG on the Short-Range Ordered Structure of Kudzu Starch
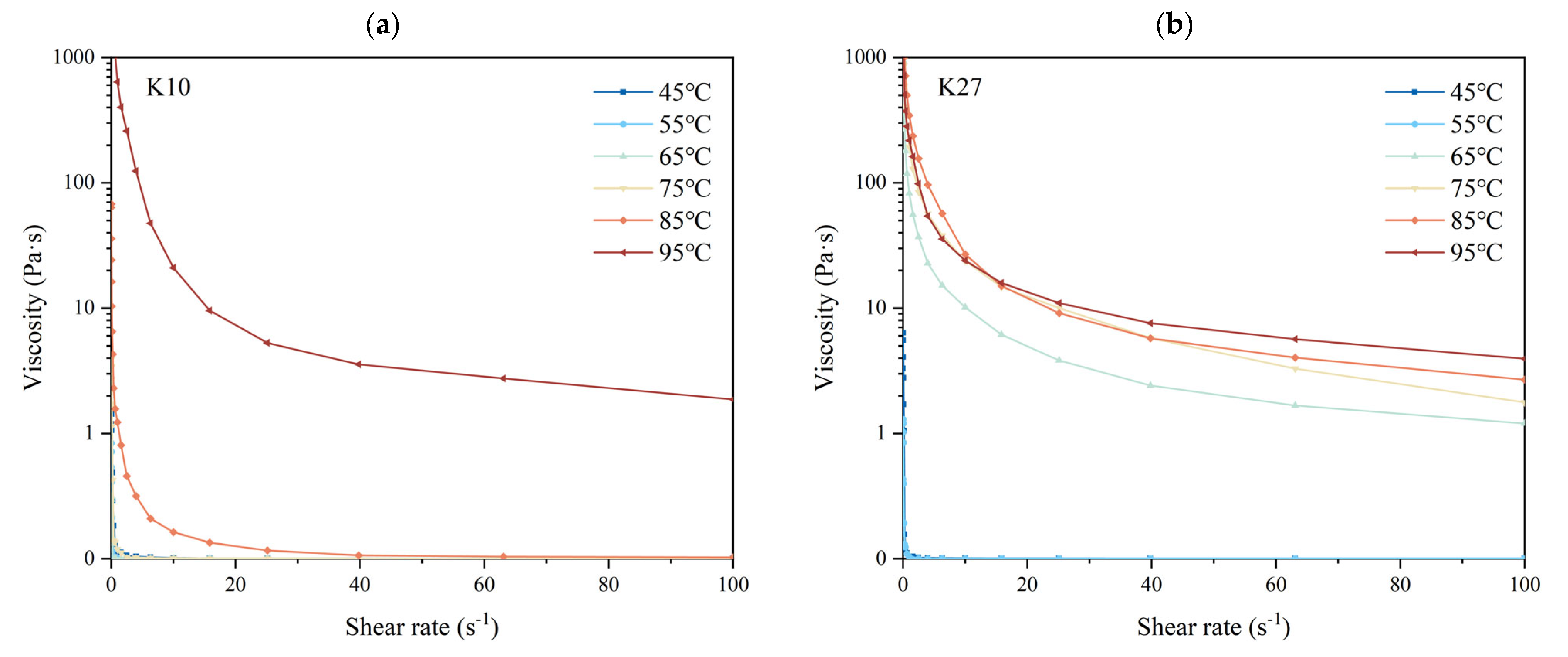
3.8. Effects of Different DG on the Apparent Viscosity of Kudzu Starch
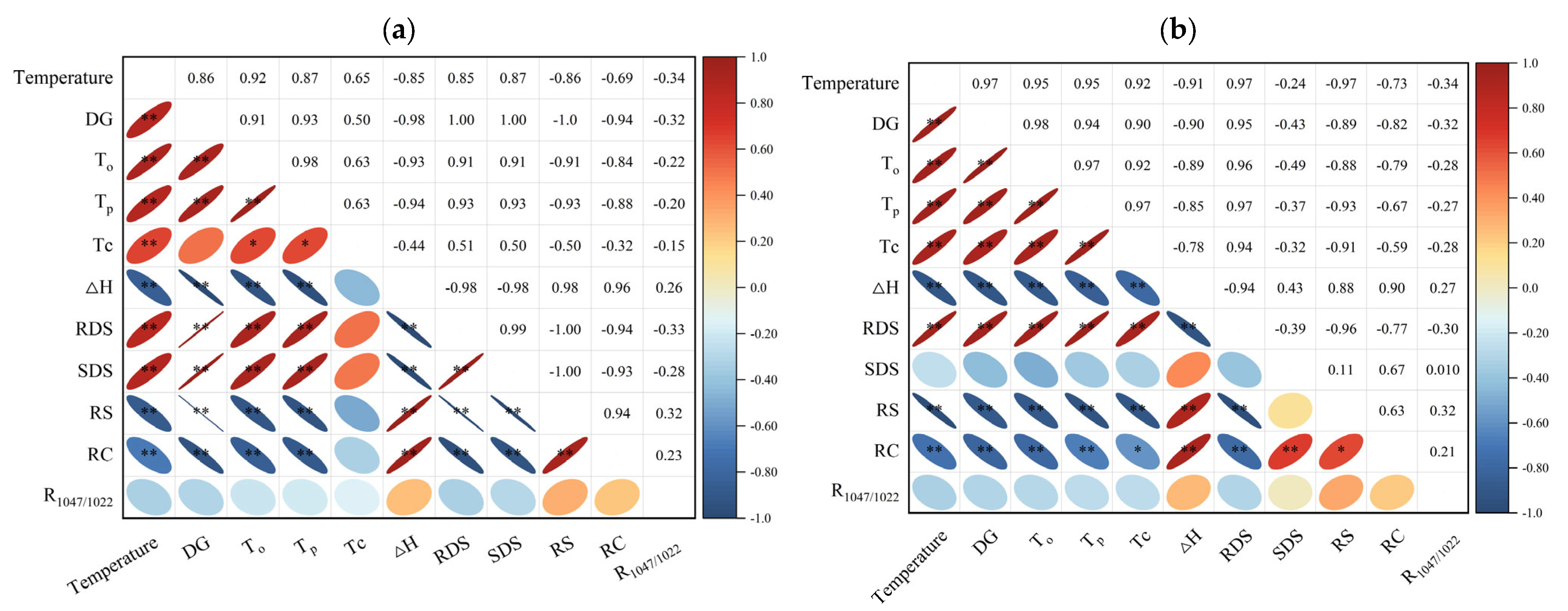
3.9. DG as a Key Determinant of the Multifunctional Properties of Kudzu Starch
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Miao, M.; Sun, J.; Fang, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lai, Q.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure and physicochemical properties of starches from six accessions of the genus Pueraria in China. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Huang, F.; Guo, J.; Song, K.; He, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X. Unveiling the hidden potential of Pueraria lobata: A comprehensive analysis based on fiber morphology and physicochemical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 20824–20839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fang, Y. Structure, properties and applications of kudzu starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Li, M.; Huang, B.; Zou, X.; Li, S.; Sang, X.; Yang, L. Comparative analysis of multi-angle structural alterations and cold-water solubility of kudzu starch modifications using different methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Li, M.; Hou, X.; Qiao, D.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B. Shortening growth year improves functional features of kudzu starch by tailoring its multi-scale structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Jekle, M.; Becker, T. Starch gelatinization and its complexity for analysis. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, D.; Pinho, L.; Patel, B.; Desam, P.; Campanella, O.H. Characterization of starch-water interactions and their effects on two key functional properties: Starch gelatinization and retrogradation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Lin, Q.; Fang, Y. Effects of reheating methods on rheological and textural characteristics of rice starch with different gelatinization degrees. Foods 2022, 11, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, H.; Cornacchia, L.; Sala, G.; Scholten, E. Effect of gelatinization and swelling degree on the lubrication behavior of starch suspensions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, J.; Aguilera, J.M. In vitro digestibility and glycemic response of potato starch is related to granule size and degree of gelatinization. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, E34–E38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Feng, D.; Pan, Y.; Li, E.; Wang, J.; Li, C. The important role of starch fine molecular structures in starch gelatinization property with addition of sugars/sugar alcohols. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 330, 121785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; McClements, D.J.; Luo, S.; Liu, C.; Ye, J. Recent advances in the impact of gelatinization degree on starch: Structure, properties and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 340, 122273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.D.; da Silveira, N.P.; Bondam, A.F.; Hoffmann, J.F. Starch gelatinization behavior: The impact of granular structure. Starch-Stärke 2024, 76, 2300143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.; Singh, B.; Singh, P.; Sharma, S. Functional, rheological, morphological, and micro-structural properties of extrusion-processed corn and potato starches. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2000140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, S.; Fang, G.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Q. Study on internal structure and digestibility of jackfruit seed starch revealed by chemical surface gelatinization. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, Q. Enzymatic determination of total starch and degree of starch gelatinization in various products. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Pueraria lobata starch regulates gut microbiota and alleviates high-fat high-cholesterol diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, A.; Hoover, R. Effect of heat-moisture treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, S.; Sui, Z.; Kong, X. Structural, physicochemical, and digestive properties of starch-tannic acid complexes modulated by co-heating temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z. Structure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of extruded starch-lauric acid complexes with different amylose contents. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Effects of preparation methods on potato microstructure and digestibility: An in vitro study. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, I.; GarciaAlonso, A.; SauraCalixto, F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahama, U.; Hirota, S. Fatty Acids, Epicatechin-dimethylgallate, and rutin interact with buckwheat starch inhibiting its digestion by amylase: Implications for the decrease in glycemic index by buckwheat flour. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12431–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, J.; Branzani, R.S.; Franco, C.M.L. Behavior of Peruvian carrot (Arracacia xanthorrhiza) and cassava (Manihot esculenta) starches subjected to heat-moisture treatment. Starch-Stärke 2014, 66, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shen, M.; Luo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Han, X.; Xie, J. Effect of Mesona chinensis polysaccharide on the pasting, rheological, and structural properties of tapioca starch varying in gelatinization temperatures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskaybas-Emlek, B.; Ozbey, A.; Aydemir, L.Y.; Kahraman, K. Production of buckwheat starch-myristic acid complexes and effect of reaction conditions on the physicochemical properties, X-ray pattern and FT-IR spectra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Li, L.; Huang, Q. Structure, physicochemical and in vitro digestion properties of ternary blends containing swollen maize starch, maize oil and zein protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, I.M.; Smith, A.M.; Morris, G.A.; Ghori, M.U.; Carnachan, S.M. Structural and rheological studies of a polysaccharide mucilage from lacebark leaves (Hoheria populnea A. Cunn.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Molecular disassembly of starch granules during gelatinization and its effect on starch digestibility: A review. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1564–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Okouchi, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takechi, T.; Hatanaka, Y.; Kitsuda, K.; Mannari, T.; Takamura, H. Effect of the addition of high-temperature water on the properties of batter and bread made from gluten-free rice flour. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmura, M.; Matsumiya, K.; Tatsuro, M.; Fujita, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Matsumura, Y. Change in surface structure and inner microstructure of durum wheat pasta during the boiling process. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliaderis, C.G. Differential scanning calorimetry in food research: A review. Food Chem. 1983, 10, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Changes of multi-scale structure during mimicked DSC heating reveal the nature of starch gelatinization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Ma, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Ren, F.; Tian, Y.; Jin, Z. A review of structural transformations and properties changes in starch during thermal processing of foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Li, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhai, L.; Qin, P.; Yang, L. Starch modification with molecular transformation, physicochemical characteristics, and industrial usability: A state-of-the-art review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, S.; Lehene, M.; Branzanic, A.M.V.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R. On the origin of the blue color in the iodine/iodide/starch supramolecular complex. Molecules 2022, 27, 8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chao, C.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Copeland, L. New insights into gelatinization mechanisms of cereal endosperm starches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguleswaran, S.; Vasanthan, T.; Hoover, R.; Bressler, D. Amylolysis of amylopectin and amylose isolated from wheat, triticale, corn and barley starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, R.D.; Asis, R.; Aldao, M.A.J. Evaluation of the degree of starch gelatinization by a new enzymatic method. Starch-Stärke 2003, 55, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Miao, S. Basic principles in starch multi-scale structuration to mitigate digestibility: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Zha, F.; Yang, Z.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Structure characteristics and functionality of water-soluble fraction from high-intensity ultrasound treated pea protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, L.; Qu, J.; Blennow, A.; Hansen, A.R.; Wu, Y.; Guo, D.; Liu, X. Amylose content and specific fine structures affect lamellar structure and digestibility of maize starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, P.J.; Warren, F.J.; Grassby, T.; Patel, H.; Ellis, P.R. Analysis of starch amylolysis using plots for first-order kinetics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corgneau, M.; Gaiani, C.; Petit, J.; Nikolova, Y.; Banon, S.; Ritie-Pertusa, L.; Doan Thanh Lam, L.; Scher, J. Digestibility of common native starches with reference to starch granule size, shape and surface features towards guidelines for starch-containing food products. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham Van, H.; Huynh Thi, C.; Nguyen Thi Lan, P. In vitro digestibility and in vivo glucose response of native and physically modified rice starches varying amylose contents. Food Chem. 2016, 191, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Mackie, A.; Farina, F.; Aponte, M.; Sarghini, F.; Masi, P. Characterisation, in vitro digestibility and expected glycemic index of commercial starches as uncooked ingredients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 4126–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisbert, M.; Castell, A.-L.; Vinoy, S.; Nazare, J.-A. The impact of slowly digestible and resistant starch on glucose homeostasis and insulin resistance. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2024, 27, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tan, L.; Kong, L. Multiple levels of health benefits from resistant starch. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 10, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Resistant starch formation in rice: Genetic regulation and beyond. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Kitamura, R.; Saito, T.; Mikami, A.; Susaki, K.; Kobayashi, H. Structural characteristics determining starch digestibility in cooked rice complexed with an emulsion formulation. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 141913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, F.S.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Foster-Powell, K.; Buyken, A.E.; Goletzke, J. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values 2021: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, C. Application of first-order kinetics modeling to reveal the nature of starch digestion characteristics. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6652–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zuo, J.; Chen, B.; Fu, Z.; Lin, X.; Wu, J.; Zheng, B.; Lu, X. Structural, properties and digestion in vitro changes of starch subjected to high pressure homogenization: An update review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E. Observations on the impact of amylopectin and amylose structure on the swelling of starch granules. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, W.; Kang, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, P.; Yan, S.; Yu, B.; Guo, L.; Cui, B.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Structural changes in corn starch granules treated at different temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Jia, M.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, G.; Qin, P.; et al. Amylopectin chain length distributions and amylose content are determinants of viscoelasticity and digestibility differences in mung bean starch and proso millet starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E.; Soldatov, D.V.; Seetharaman, K. Impact on molecular organization of amylopectin in starch granules upon annealing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, B.E.; Janaswamy, S.; Yao, Y. Properties of starch subjected to partial gelatinization and β-amylolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Kong, S.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, J. Insight into characteristics in rice starch under heat- moisture treatment: Focus on the structure of amylose/amylopectin. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, B.; Bartz, J.; Radunz, M.; do Evangelho, J.A.; Pinto, V.Z.; Zavareze, E.d.R.; Guerra Dias, A.R. Impact of heat-moisture treatment on rice starch, applied directly in grain paddy rice or in isolated starch. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Annor, G.; Vamadevan, V.; Lin, A.H.-M. On the architecture of starch granules revealed by iodine binding and lintnerization. Part 2: Molecular structure of lintnerized starches. Biopolymers 2025, 116, e23636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesek, S.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R. The iodine/iodide/starch supramolecular complex. Molecules 2024, 29, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C. Recent progress in understanding starch gelatinization-An important property determining food quality. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 293, 119735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Pooja, N.; Mal, S.S.; Paul, U.C.; Rahman, M.H.; Mazumder, N. An insight into the gelatinization properties influencing the modified starches used in food industry: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 1195–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Wu, H.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Jing, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Su, C.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, H.; Li, W. Effects of repeated and continuous dry heat treatments on properties of sweet potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, H.; Zhang, D.; Lue, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, J.; et al. Insights into the regulation mechanisms of dual hydrothermal treatment on the structure and digestive characteristics of A- and B-type wheat starch granules. Food Res. Int. 2025, 200, 115448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Mai, S.; Li, C. Effects of extrusion on starch molecular degradation, order-disorder structural transition and digestibility: A review. Foods 2022, 11, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, S.; Chao, C.; Yu, J.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S. Changes of starch during thermal processing of foods: Current status and future directions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Li, X.; Lu, P.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Dry heating and annealing treatment synergistically modulate starch structure and digestibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Geng, D.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, N. Characterization of dynamic of the structural changes of legume starches during gelatinization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Pu, H.; Keipper, W. The effects of temperature on starch molecular conformation and hydrogen bonding. Starch-Stärke 2022, 74, 2100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, S. Molecular order and functional properties of starches from three waxy wheat varieties grown in China. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhai, C.; Sun, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, W. Insight into microstructure evolution during starch retrogradation by infrared and Raman spectroscopy combined with two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy analysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Luo, X.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Shao, X.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Influence of sodium alginate on the gelatinization, rheological, and retrogradation properties of rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H. Effects of particle properties, intermolecular forces, and molecular structure on the shear-thickening behavior of waxy starch dispersions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimonie, D.; Grigorescu, R.-M.; Trica, B.; Raduly, M.; Damian, C.-M.; Trusca, R.; Mustatea, A.-E.; Dima, S.-O.; Oancea, F. De- and re-structuring of starch to control the melt and solid state visco-elasticity as method for getting new multi component compounds with scalable properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, S.; Larrea-Wachtendorff, D.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Ferrari, G. In vitro digestibility of rice and tapioca starch-based hydrogels produced by high-pressure processing (HPP). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 93, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satusap, P.; Chavasit, V.; Kriengsinyos, W.; Judprasong, K. Development of cereal and legume based food products for the elderly. Springerplus 2014, 3, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ∆H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K10 | ||||
| 45 °C | 79.85 ± 0.39 d | 84.85 ± 0.39 c | 89.05 ± 2.61 b | 17.64 ± 0.38 d |
| 55 °C | 80.42 ± 0.45 cd | 85.53 ± 0.35 c | 91.52 ± 0.56 ab | 16.91 ± 0.48 c |
| 65 °C | 80.50 ± 0.30 c | 85.09 ± 0.42 c | 90.66 ± 0.74 ab | 15.58 ± 0.68 b |
| 75 °C | 83.25 ± 0.20 b | 86.85±0.16 b | 92.65 ± 1.38 a | 13.80 ± 0.81 a |
| 85 °C | 85.69 ± 0.22 a | 89.18 ± 0.54 a | 92.48 ± 0.22 a | 2.79 ± 0.13 a |
| 95 °C | - | - | - | - |
| K27 | ||||
| 45 °C | 61.08 ± 0.30 d | 66.52 ± 2.35 d | 76.62 ± 1.04 d | 13.26 ± 0.70 d |
| 55 °C | 58.67 ± 0.28 d | 66.76 ± 2.28 d | 76.78 ± 0.65 d | 11.97 ± 0.85 cd |
| 65 °C | 72.48 ± 0.05 c | 76.77 ± 0.46 c | 81.47 ± 2.94 c | 2.55 ± 0.06 c |
| 75 °C | 79.93 ± 0.83 b | 95.63 ± 0.91 b | 102.06 ± 3.79 b | 2.10 ± 0.11 b |
| 85 °C | 90.96 ± 4.12 a | 102.07 ± 3.93 a | 107.59 ± 1.77 a | 1.35 ± 0.18 a |
| 95 °C | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Zhu, F.; Li, M.; Kong, X. Effects of Different Degrees of Gelatinization on Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch. Foods 2025, 14, 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213614
He Z, Zhu F, Li M, Kong X. Effects of Different Degrees of Gelatinization on Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213614
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zirui, Fan Zhu, Mei Li, and Xiangli Kong. 2025. "Effects of Different Degrees of Gelatinization on Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch" Foods 14, no. 21: 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213614
APA StyleHe, Z., Zhu, F., Li, M., & Kong, X. (2025). Effects of Different Degrees of Gelatinization on Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Kudzu Starch. Foods, 14(21), 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213614





