Detection of Bioactive Peptides’ Signature in Podolica Cow’s Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Plan
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. LC-MS MS Analysis
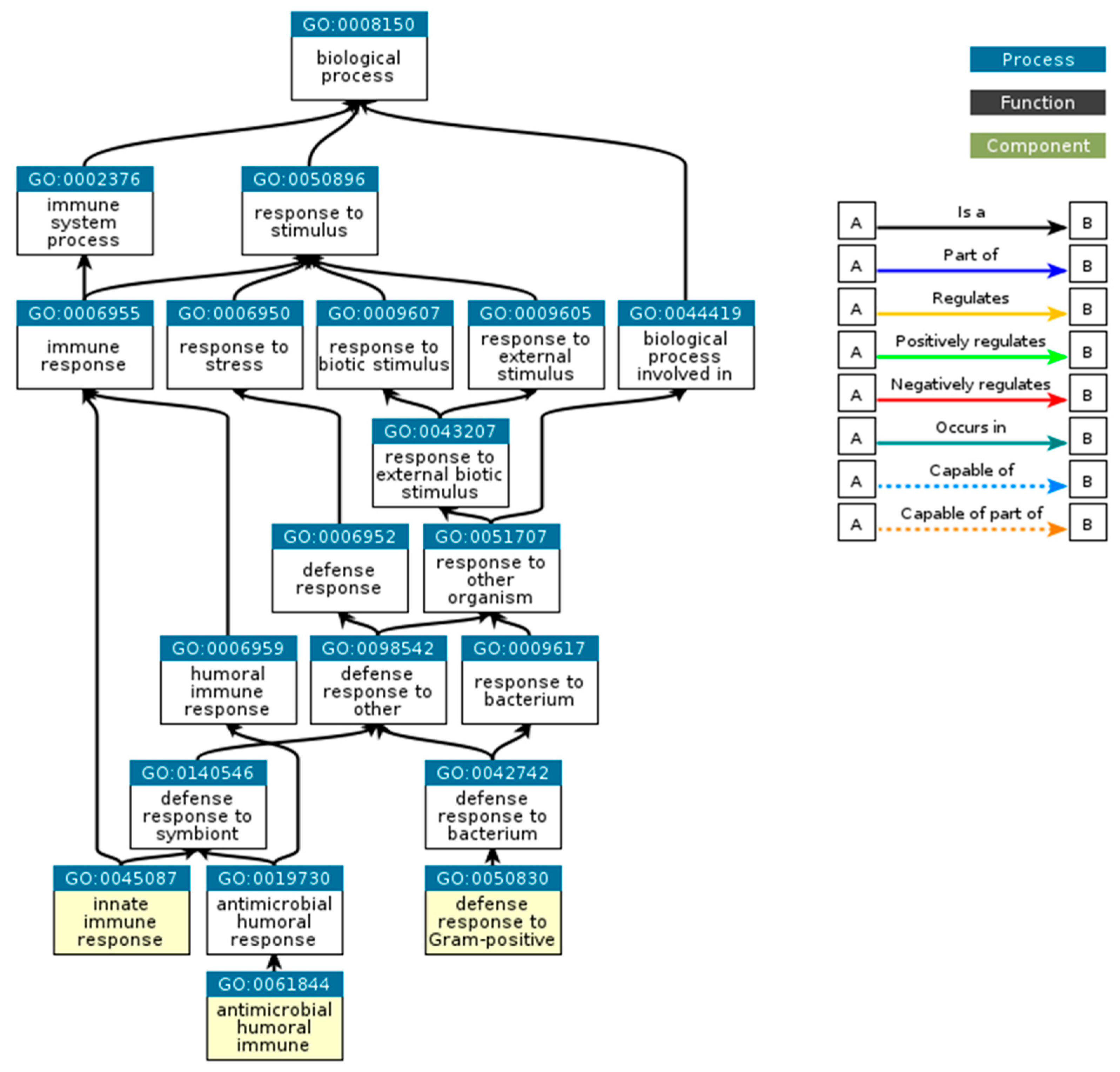
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
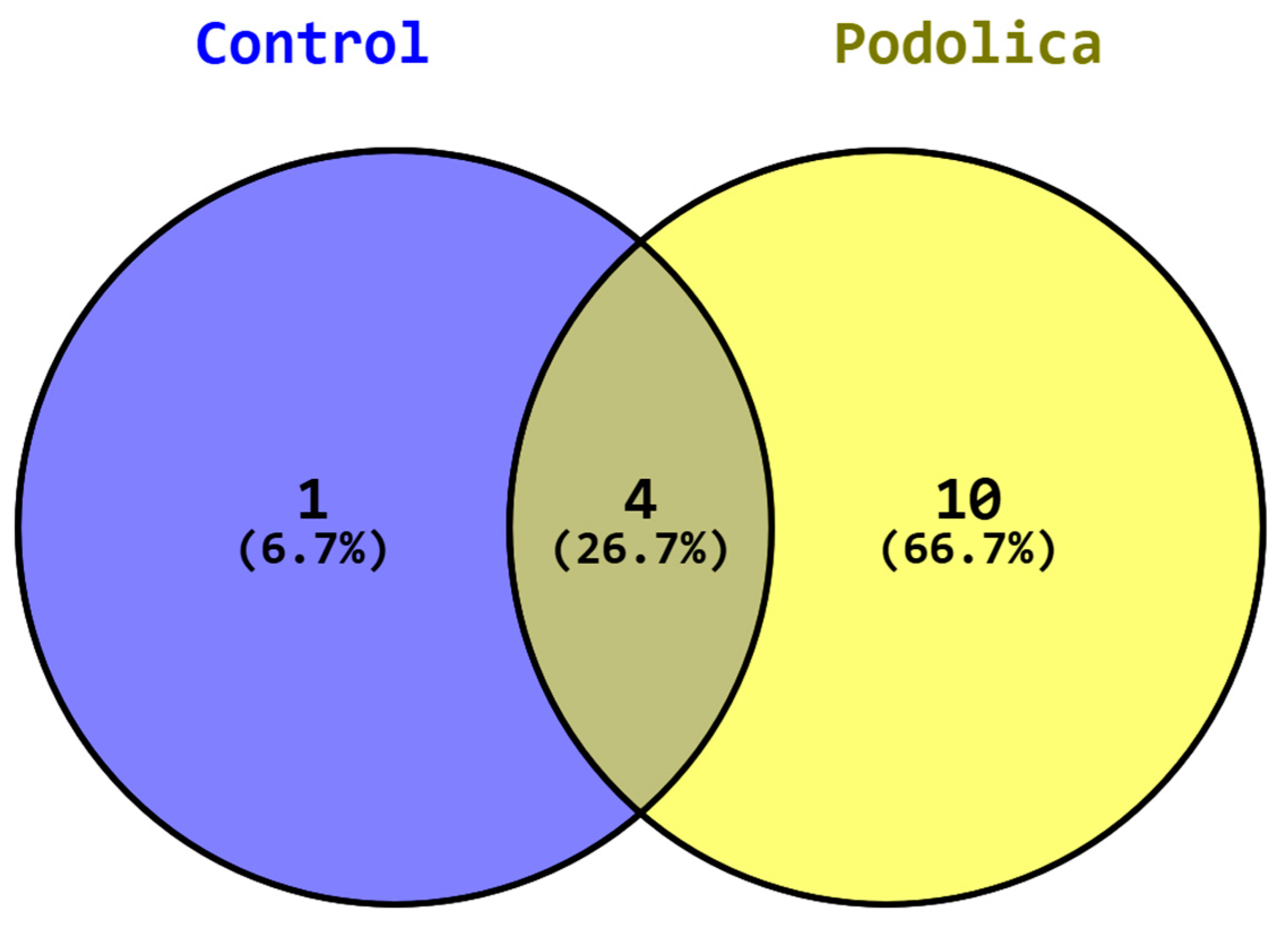
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costagliola, A.; Wojcik, S.; Pagano, T.B.; De Biase, D.; Russo, V.; Iovane, V.; Grieco, E.; Papparella, S.; Paciello, O. Age-related changes in skeletal muscle of cattle. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moioli, B.; Napolitano, F.; Catillo, G. Genetic diversity between Piedmontese, Maremmana, and Podolica cattle breeds. J. Hered. 2004, 95, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.A.; Ceniti, C.; Piras, C.; Tilocca, B.; Britti, D.; Morittu, V.M. Mid-Infrared (MIR) Spectroscopy for the quantitative detection of cow’s milk in buffalo milk. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2022, 64, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrella, G.; De Palo, P.; Maggiolino, A.; Faccia, M. A Study on Milk and Caciocavallo Cheese from Podolica Breed in Basilicata, Italy. Dairy 2023, 4, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinto, M.; Sevi, A.; Di Caterina, R.; Albenzio, M.; Muscio, A.; Rotunno, T. Quality of milk and Caciocavallo cheese from farms rearing Podolica and Italian Friesian cows. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2003, 15, 485–498. [Google Scholar]
- Spina, A.A.; Ceniti, C.; De Fazio, R.; Oppedisano, F.; Palma, E.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Raza, S.H.A.; Britti, D.; Piras, C. Spectral Profiling (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) and Machine Learning for the Recognition of Milk from Different Bovine Breeds. Animals 2024, 14, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, C.; De Fazio, R.; Di Francesco, A.; Oppedisano, F.; Spina, A.A.; Cunsolo, V.; Roncada, P.; Cramer, R.; Britti, D. Detection of antimicrobial proteins/peptides and bacterial proteins involved in antimicrobial resistance in raw cow’s milk from different breeds. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.W.S.; Camirand, W.M.; Pavlath, A.E.; Parris, N.; Friedman, M. Structures and functionalities of milk proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996, 36, 807–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanbacher, F.L.; Talhouk, R.S.; Murray, F.A. Biology and origin of bioactive peptides in milk. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1997, 50, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Technological options for the production of health-promoting proteins and peptides derived from milk and colostrum. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N. Antihypertensive peptides derived from food proteins. Pept. Sci. 1997, 43, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Cao, X.; Yue, X. Peptidomics as a tool to analyze endogenous peptides in milk and milk-related peptides. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucina, A.; Di Francesco, A.; Saletti, R.; Pittalà, M.G.G.; Zilberstein, G.; Zilberstein, S.; Tikhonov, A.; Bublichenko, A.G.; Righetti, P.G.; Foti, S. Meta-proteomic analysis of two mammoth’s trunks by EVA technology and high-resolution mass spectrometry for an indirect picture of their habitat and the characterization of the collagen type I, alpha-1 and alpha-2 sequence. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punginelli, D.; Catania, V.; Vazzana, M.; Mauro, M.; Spinello, A.; Barone, G.; Barberi, G.; Fiorica, C.; Vitale, M.; Cunsolo, V. A novel peptide with antifungal activity from red swamp crayfish procambarus clarkii. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinitcyn, P.; Hamzeiy, H.; Salinas Soto, F.; Itzhak, D.; McCarthy, F.; Wichmann, C.; Steger, M.; Ohmayer, U.; Distler, U.; Kaspar-Schoenefeld, S. MaxDIA enables library-based and library-free data-independent acquisition proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.W.; Alcock, B.P.; French, S.; Farha, M.A.; Raphenya, A.R.; Brown, E.D.; McArthur, A.G. A standardized nomenclature for resistance-modifying agents in the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02744-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bossche, T.; Verschaffelt, P.; Vande Moortele, T.; Dawyndt, P.; Martens, L.; Mesuere, B. Biodiversity analysis of metaproteomics samples with Unipept: A comprehensive tutorial. In Protein Bioinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 183–215. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.D.-H.; Liang, N.; Rathish, H.; Kim, B.J.; Lueangsakulthai, J.; Koh, J.; Qu, Y.; Schulz, H.-J.; Dallas, D.C. Bioactive milk peptides: An updated comprehensive overview and database. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 11510–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Qu, Y.; Dallas, D.C. Milk bioactive peptide database: A comprehensive database of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides and novel visualization. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Hussain, N.; Ujiroghene, O.J.; Pang, X.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Lv, J. Generation and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from trypsin-hydrolyzed α-lactalbumin-rich whey proteins. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlanto-Leppälä, A.; Koskinen, P.; Piilola, K.; Tupasela, T.; Korhonen, H. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of whey protein digests: Concentration and characterization of active peptides. J. Dairy Res. 2000, 67, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Sakurai, T.; Ochi, D.; Mitsuyama, E.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F. Antihypertensive effect of the bovine casein-derived peptide Met-Lys-Pro. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Suzuki, H. A peptide inhibitor of angiotensin I converting enzyme in the tryptic hydrolysate of casein. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1982, 46, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Tauzin, J.; Miclo, L.; Gaillard, J.-L. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from tryptic hydrolysate of bovine αS2-casein. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Mitachi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Tomizuka, N.; Suzuki, H. Studies on the active site and antihypertensive activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors derived from casein. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Phillips, J.G.; Renye, J.A., Jr. Measuring the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of an 8-amino acid (8mer) fragment of the C12 antihypertensive peptide. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3263–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mar Contreras, M.; Sanchez, D.; Sevilla, M.Á.; Recio, I.; Amigo, L. Resistance of casein-derived bioactive peptides to simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 32, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo, L.; Martínez-Maqueda, D.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. In silico and in vitro analysis of multifunctionality of animal food-derived peptides. Foods 2020, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.; Gómez-Ruiz, J.Á.; Recio, I.; Aleixandre, A. Changes in arterial blood pressure after single oral administration of milk-casein-derived peptides in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ruiz, J.Á.; Ramos, M.; Recio, I. Identification of novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from ovine milk proteins by CE-MS and chromatographic techniques. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 4202–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hui, Y.; Gao, T.; Shu, G.; Chen, H. Function and characterization of novel antioxidant peptides by fermentation with a wild Lactobacillus plantarum 60. LWT 2021, 135, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Miao, J.; Liu, G.; Luo, Z.; Xia, Z.; Liu, F.; Yao, M.; Cao, X.; Sun, S.; Lin, Y. Bioactive peptides isolated from casein phosphopeptides enhance calcium and magnesium uptake in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, M.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Hill, C.; Stanton, C. Casein-derived antimicrobial peptides generated by Lactobacillus acidophilus DPC6026. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2260–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, R.M.; Guinane, C.M.; O’connor, P.M.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Hill, C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Production of the antimicrobial peptides Caseicin A and B by Bacillus isolates growing on sodium caseinate. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norberg, S.; O’Connor, P.M.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. Extensive manipulation of caseicins A and B highlights the tolerance of these antimicrobial peptides to change. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Eichler, J.; Pischetsrieder, M. Virtual screening of a milk peptide database for the identification of food-derived antimicrobial peptides. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides released by in vitro digestion of standard and hydrolyzed infant formulas. Peptides 2015, 73, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, S.; Shanmugam, V.P.; Tanedjeu, K.S.; Kapila, S.; Kapila, R. Effect of buffalo casein-derived novel bioactive peptides on osteoblast differentiation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Moriguchi, S.; Suganuma, H.; Shiota, A.; Tani, F.; Usui, H.; Kurahashi, K.; Sasaki, R.; Yoshikawa, M. Identification of casoxin C, an ileum-contracting peptide derived from bovine κ-casein, as an agonist for C3a receptors. Peptides 1997, 18, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz-Szłapka, E.; Jarmołowska, B.; Krawczuk, S.; Kostyra, E.; Kostyra, H.; Iwan, M. Contents of agonistic and antagonistic opioid peptides in different cheese varieties. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, H.; Tani, F.; Yoshikawa, M. Opioid antagonist peptides derived from κ-casein. J. Dairy Res. 1989, 56, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sequence | Mass | Protein | AA Residues | Protein Name | Charges | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSDGTFTSELSRLRDSARLQRLLQGLV | 3054.632 | P63296 | 27 | Secretin | 3 | 15.469 |
| VELQNRLSDESQ | 1416.685 | P60316 | 12 | Protein Hook homolog 3 | 1; 2; 3 | 22.339 |
| Hits | Functions | Protein IDs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grouped Results: | DPP-IV-inhibitory: 2 ACE-inhibitory: 6 Antioxidant: 2 Increase calcium uptake: 2 Antimicrobial: 3 Antianxiety: 1 Osteoanabolic: 1 Immunomodulatory: 1 Opioid: 1 | P00711: 4 P02662: 11 P02669: 2 P02668: 2 | |
| Total Counts: | 19 | 9 | 4 |
| Peptide | Protein ID | Protein Description | Intervals | Function | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDQWLCEKL | P00711 | Alpha-lactalbumin | 134–142 | DPP-IV-Inhibitory [20] | 59.6 |
| VGINYWLAHK | P00711 | Alpha-lactalbumin | 118–127 | DPP-IV-Inhibitory [20] | 13.8 |
| Peptide | Protein ID | Protein Description | Intervals | Function | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGINYWLAHK | P00711 | Alpha-lactalbumin | 118–127 | ACE-inhibitory [21] | 327 |
| FFVAPFPEVFGK | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 38–49 | ACE-inhibitory | (1) 52.0 [22] |
| (2) 77.0 [23] | |||||
| (3) 18.0 [24] | |||||
| FPEVFGK | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 43–49 | ACE-inhibitory | 140 [25] |
| PFPEVFGK | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 42–49 | ACE-inhibitory | 108 [26] |
| YLGY | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 106–109 | ACE-inhibitory | (1) 41.86 [27] |
| (2) 9.87 [28] | |||||
| HPHPHLSF | P02669 | Kappa-casein | 119–126 | ACE-inhibitory | (1) 28.9 [29] |
| (2) 28.9 [30] |
| Peptide | Protein ID | Protein Description | Intervals | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGINYWLAHK | P00711 | Alpha-lactalbumin | 118–127 | Antioxidant [31] |
| YLGY | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 106–109 | Antioxidant [27,28] |
| Peptide | Protein ID | Protein Description | Intervals | Function | PTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIGSESTEDQAMEDIK | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 58–73 | Increase calcium uptake [32] | 2 phosphorylations |
| YKVPQLEIVPNSAEER | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 119–134 | Increase calcium uptake [32] | 1 phosphorylation |
| Peptide | Protein ID | Protein Description | Intervals | Function | Inhibition Type | Inhibited Microorganisms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDIPNPIGSENSEK | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 195–208 | Antimicrobial [33] | MIC | L. innocua |
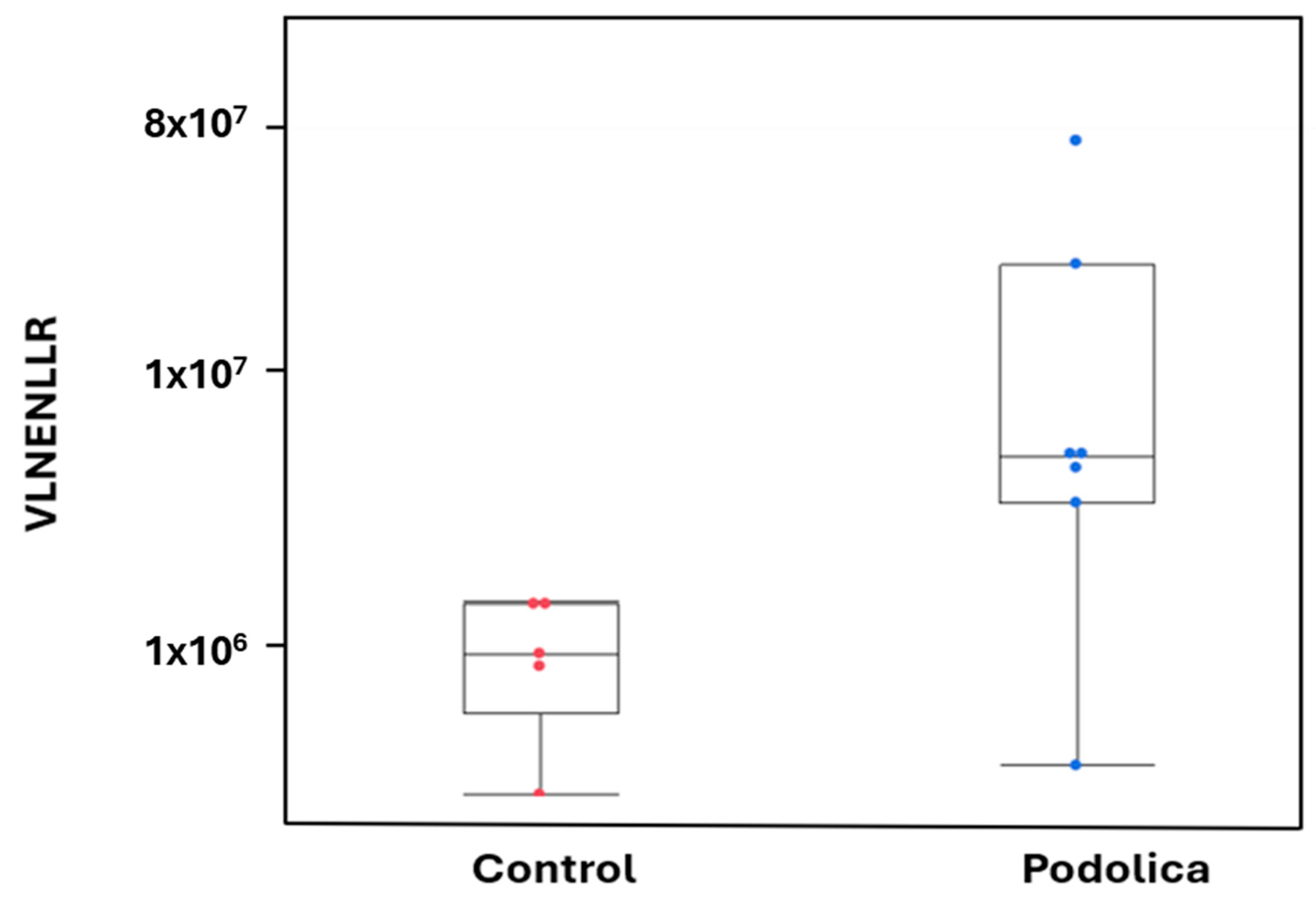
| VLNENLLR | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 30–37 | Antimicrobial | (1) MIC, | (1) E. coli C. sakazakii L. innocua L. bulgaricus S. mutans [33] |
| (2) MIC, | (2) C. sakazakii [34] | |||||
| (3) MIC | (3) C. sakazakii C. muytjensii [35] | |||||
| YLEQLLR | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 109–115 | Antimicrobial | MIC | B. subtilis—53.6 E. coli NEB 5α—241 E. coli ATCC 25,922—40.2 [36] |
| Peptide | Protein ID | Protein Description | Intervals | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YLGYLEQLLR | P02662 | Alpha-S1-casein | 106–115 | Antianxiety [37] |
| HPHPHLSF | P02669 | Kappa-casein | 119–126 | Osteoanabolic [38] |
| YIPIQYVLSR | P02668 | Kappa-casein | 46–55 | Immunomodulatory [39] |
| YIPIQYVLSR | P02668 | Kappa-casein | 46–55 | Opioid [40,41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Fazio, R.; Di Francesco, A.; Di Ciccio, P.A.; Cunsolo, V.; Britti, D.; Lomagistro, C.; Roncada, P.; Piras, C. Detection of Bioactive Peptides’ Signature in Podolica Cow’s Milk. Foods 2025, 14, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050877
De Fazio R, Di Francesco A, Di Ciccio PA, Cunsolo V, Britti D, Lomagistro C, Roncada P, Piras C. Detection of Bioactive Peptides’ Signature in Podolica Cow’s Milk. Foods. 2025; 14(5):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050877
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Fazio, Rosario, Antonella Di Francesco, Pierluigi Aldo Di Ciccio, Vincenzo Cunsolo, Domenico Britti, Carmine Lomagistro, Paola Roncada, and Cristian Piras. 2025. "Detection of Bioactive Peptides’ Signature in Podolica Cow’s Milk" Foods 14, no. 5: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050877
APA StyleDe Fazio, R., Di Francesco, A., Di Ciccio, P. A., Cunsolo, V., Britti, D., Lomagistro, C., Roncada, P., & Piras, C. (2025). Detection of Bioactive Peptides’ Signature in Podolica Cow’s Milk. Foods, 14(5), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050877







