Dynamics Changes in Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity, and Non-Volatile Metabolites During Bulang Pickled Tea Fermentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Tea Processing and Sample Collection
2.3. Taste Evaluation
2.4. Enumeration of Viable Microbes
2.5. Determination of pH and Total Titratable Acidity
2.6. Analysis of Chemical Composition
2.6.1. Determination of Total Soluble Sugar
2.6.2. Determination of Soluble Protein
2.6.3. Determination of Total Free Amino Acids
2.6.4. Determination of Total Phenolics and Total Flavonoids
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activities
2.8. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis by UPLC-QTOF-MS
2.8.1. Sample Preparation and Treatment
2.8.2. UPLC Conditions
2.8.3. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.8.4. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Data Processing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
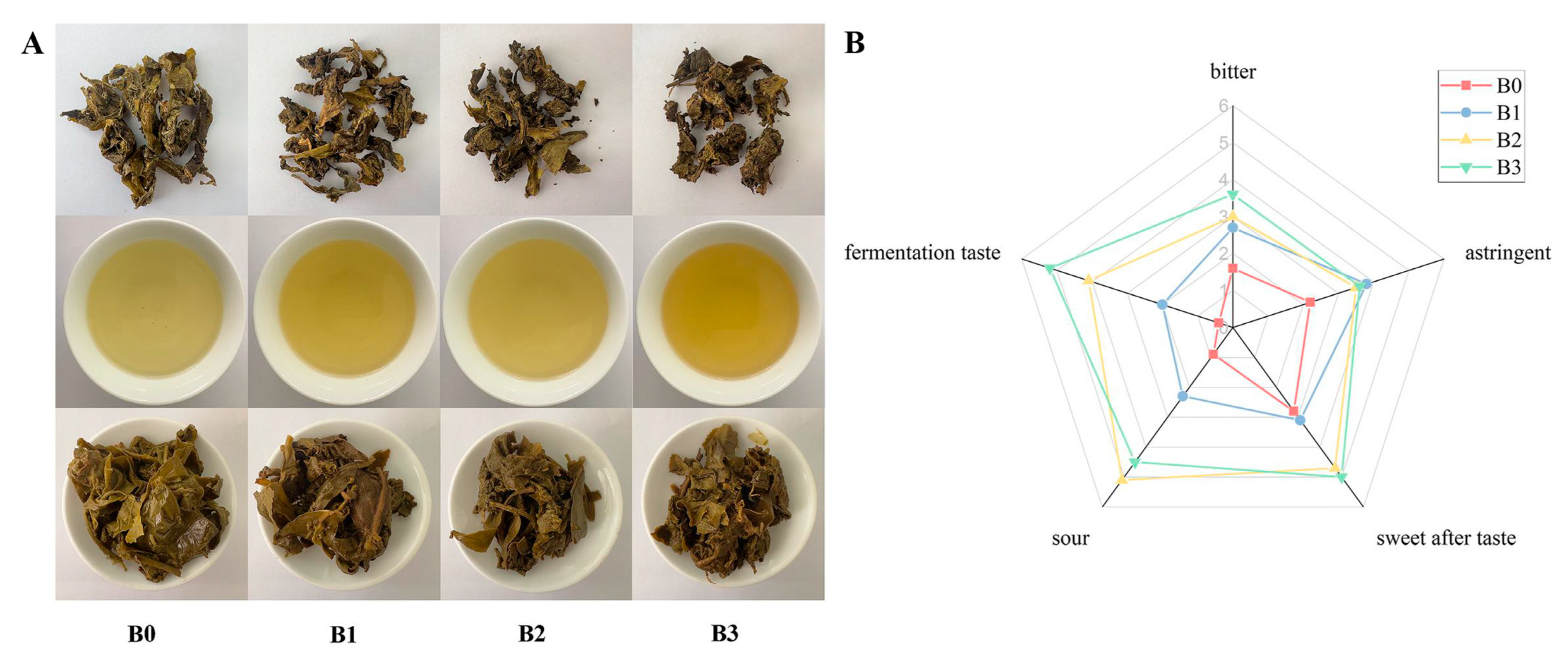
3.1. Taste Characteristics
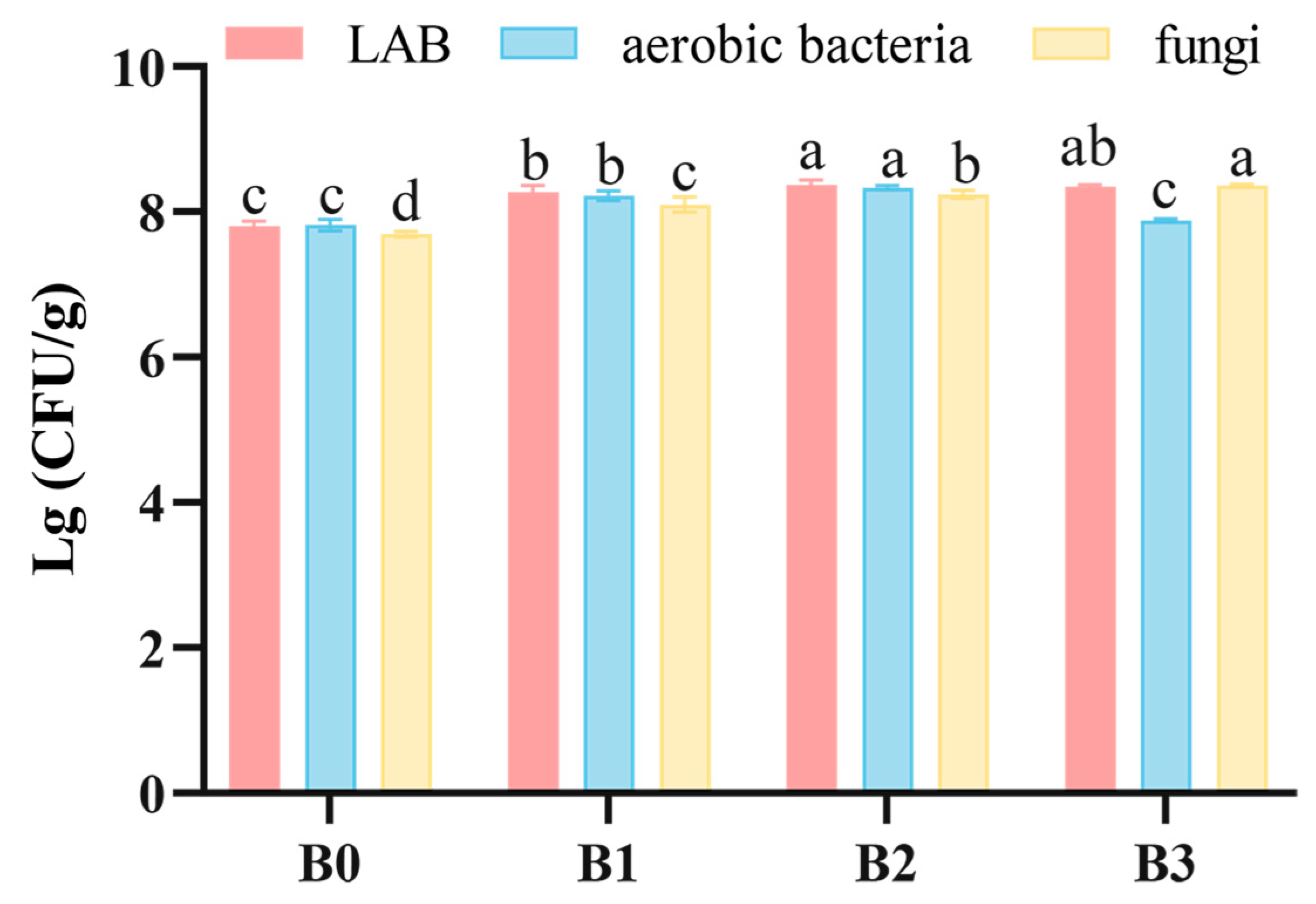
3.2. Culturable Microbes Counting
3.3. Physiochemical Parameters
3.4. Phytochemical Contents
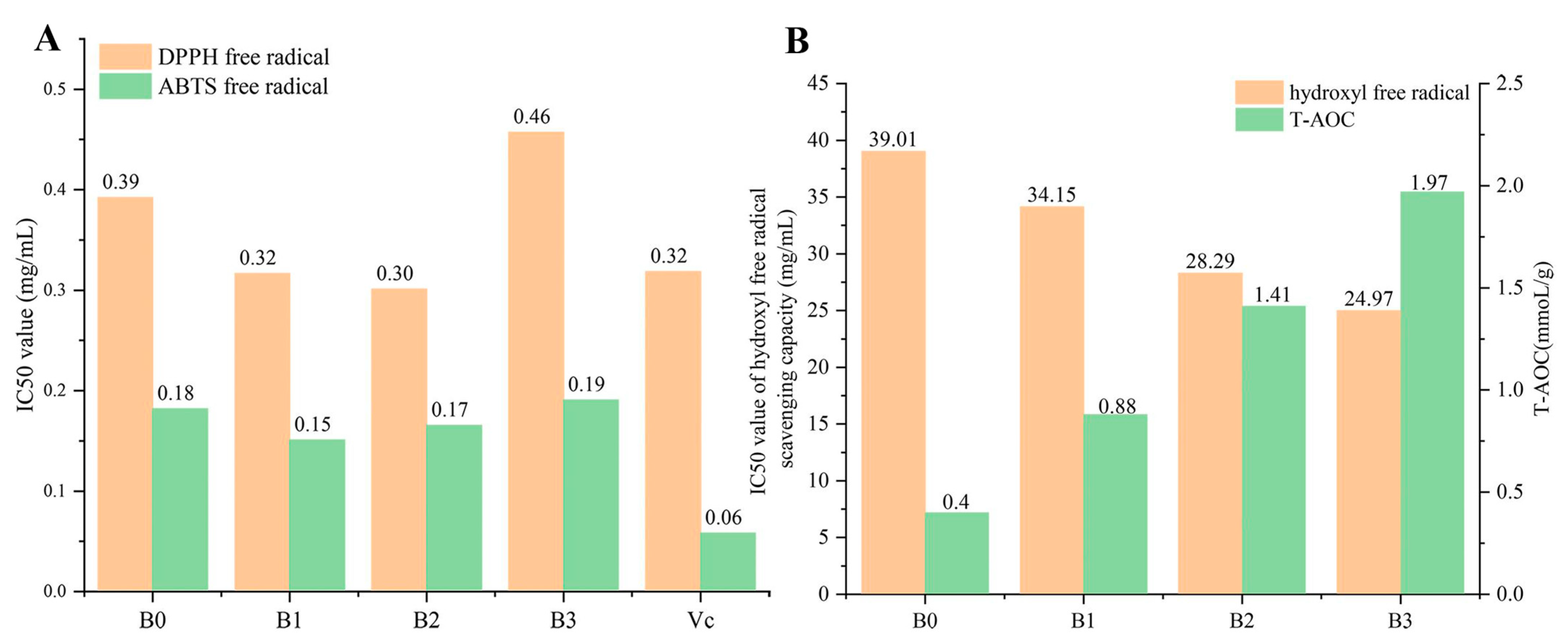
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
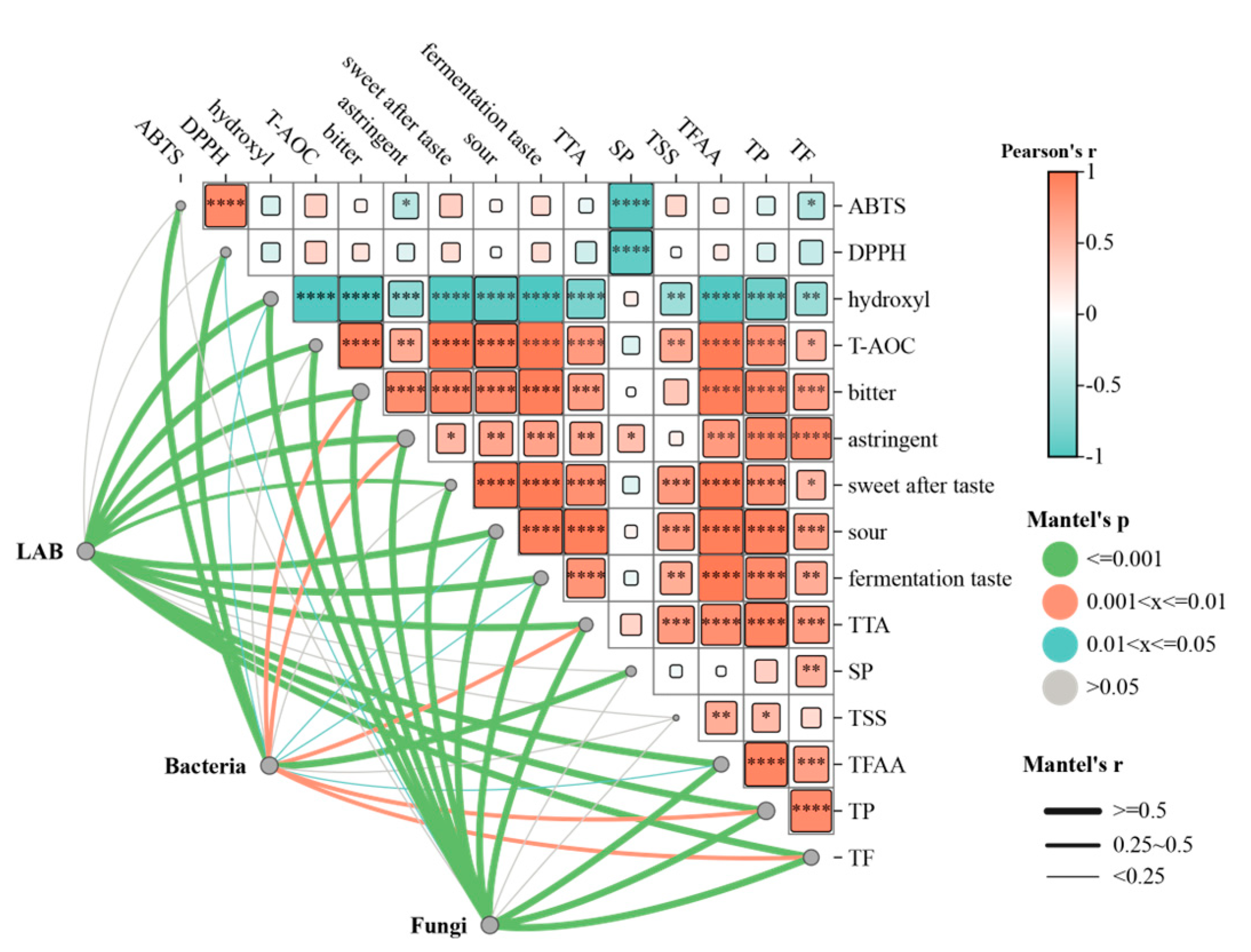
3.6. Mantel Test Analysis of Culturable Microbes, Physiochemical Parameters, Physiochemical Parameters, and Antioxidant Measures
3.7. Metabolomics Analysis of Changes in Non-Volatile Metabolites
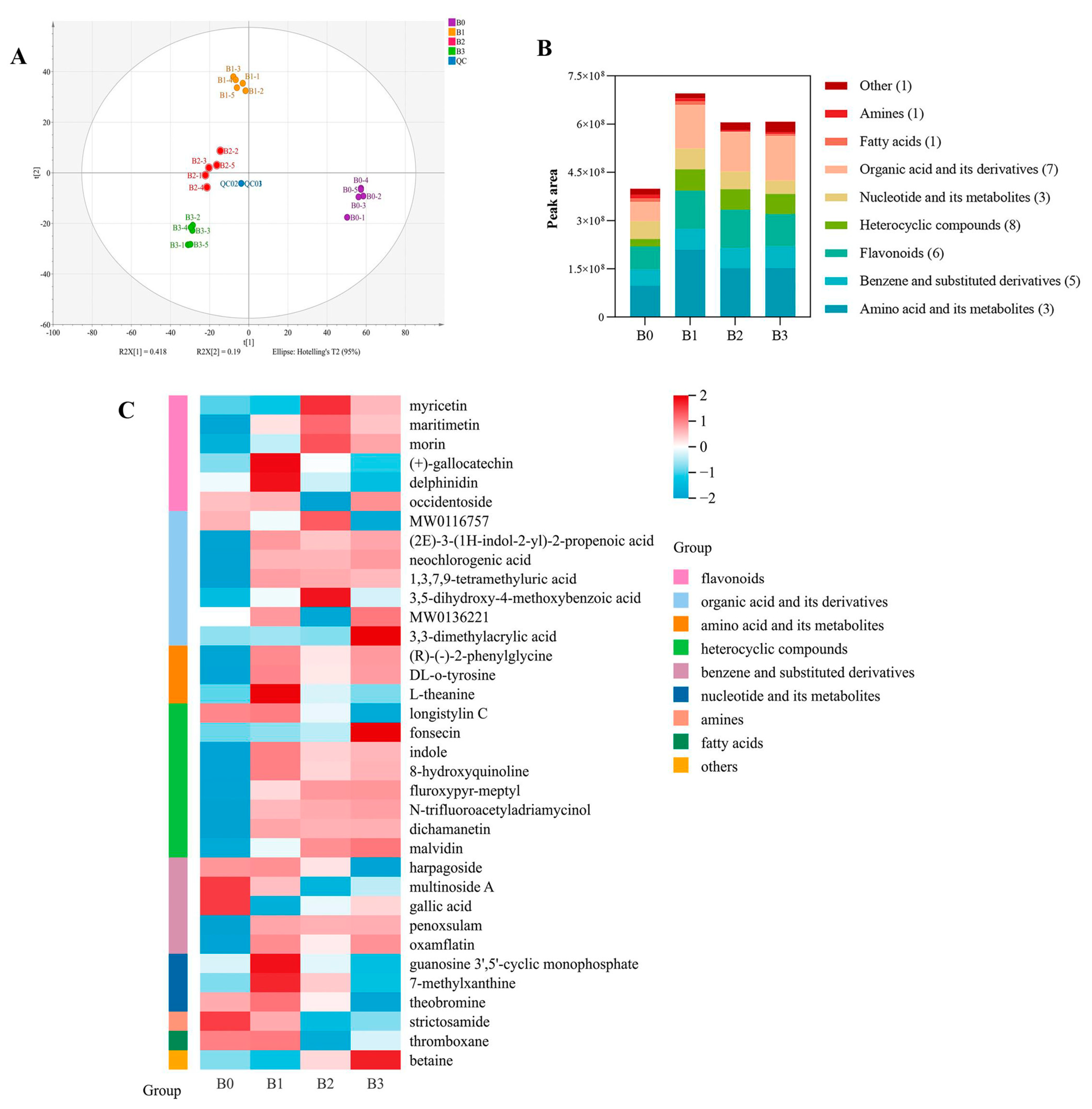
3.7.1. Analysis of Non-Volatile Metabolites
3.7.2. Dynamic Changes in Differential Non-Volatile Metabolites
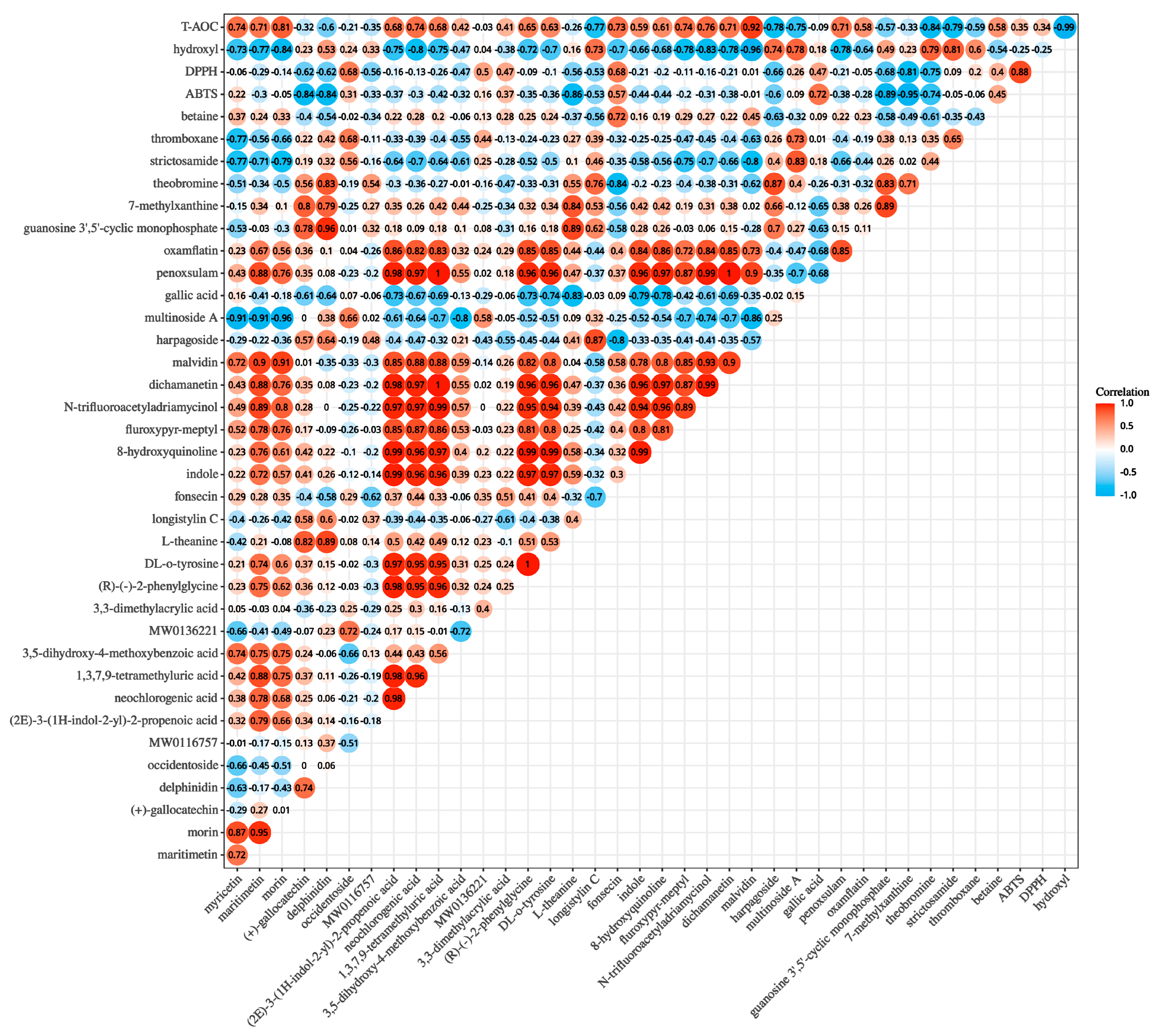
3.8. Correlation Analysis of Non-Volatile Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nanba, A.; Miyagawa, K.; Omori, M.; Kato, M.; Tamura, A.; Saito, H. Non-salted pickled tea (sour tea) in south-east Yunnan in China. Jpn. Soc. Home Econ. 1998, 49, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Shu, P. Research and reflection on the tea drinking customs of the Bulang ethnic group: Taking Mangjing village in Lancang as an Example. Tea Fujian 2020, 42, 294–296. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Foo, H.L.; Cao, Z.; Lin, Q. Changes in microbial diversity and volatile metabolites during the fermentation of Bulang pickled tea. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phovisay, S.; Abdullahi, A.D.; Kham, N.N.; Unban, K.; Shetty, K.; Khanongnuch, C. Microbial population and physicochemical properties of miang fermented in bamboo tubes by the luar ethnic group in lao PDR. Foods 2024, 13, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Q.-Q.; Granato, D.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Ho, C.-T. Association between chemistry and taste of tea: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Cong, L.; Wu, M.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y. A fermented tea with high levels of gallic acid processed by anaerobic solid-state fermentation. LWT 2016, 71, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Guan, M.; Yuan, X.; Li, S.; Ren, D.; Gu, Y.; Liang, M.; Yi, L. Aroma and taste analysis of pickled tea from spontaneous and yeast-enhanced fermentation by mass spectrometry and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unban, K.; Khatthongngam, N.; Pattananandecha, T.; Saenjum, C.; Shetty, K.; Khanongnuch, C. Microbial community dynamics during the non-filamentous fungi growth-based fermentation process of Miang, a traditional fermented tea of north Thailand and their product characterizations. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiasa, M.; Kurokawa, M.; Ohta, K.; Esumi, T.; Akita, H.; Niki, K.; Yagi, Y.; Echigo, N.; Hatakeyama, D.; Kuzuhara, T. Identification and purification of resorcinol, an antioxidant specific to Awa-ban (pickled and anaerobically fermented) tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Mao, H.; Lu, F.; Ma, C.; Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, C.; Xiao, R. Widely targeted metabolomics and HPLC analysis elaborated the quality formation of Yunnan pickled tea during the whole process at an industrial scale. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 135716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, M.; Han, Z.; Lai, G.; Jiang, Z.; Long, P.; Zhang, L. Monitoring of pickled tea during processing: From LC-MS based metabolomics analysis to inhibitory activities on α-amylase and α-glycosidase. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Wang, Z.; Peng, H.; Li, W.; Yang, P. UPLC–QTOF/MS-based non-targeted metabolomics coupled with the quality component, QDA, to reveal the taste and metabolite characteristics of six types of Congou black tea. LWT 2023, 185, 115197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T23776-2018; Methodology for Sensory Evaluation of Tea. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Fan, F.-Y.; Huang, C.-S.; Tong, Y.-L.; Guo, H.-W.; Zhou, S.-J.; Ye, J.-H.; Gong, S.-Y. Widely targeted metabolomics analysis of white peony teas with different storage time and association with sensory attributes. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Mai, Y.; Guo, H.; He, X.-Q.; Xia, Y.; Li, H.; Zhuang, Q.-G.; Gan, R.-Y. Phenolic content, main flavonoids, and antioxidant capacity of instant sweet tea (Lithocarpus litseifolius [Hance] Chun) prepared with different raw materials and drying methods. Foods 2021, 10, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlotterbeck, J.; Cebo, M.; Kolb, A.; Lämmerhofer, M. Quantitative analysis of chemoresistance-inducing fatty acid in food supplements using UHPLC–ESI-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of rape bee pollen after fermentation and their correlation with chemical components by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetkovic, D.; Markov, S.; Djuric, M.; Savic, D.; Velicanski, A. Specific interfacial area as a key variable in scaling-up Kombucha fermentation. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, F.; Huang, D.; Chen, X. Alternations in the multilevel structures of chickpea protein during fermentation and their relationship with digestibility. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. Metaproteomics insights into traditional fermented foods and beverages. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2506–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, D.L.; Su, X.Q.; Duan, S.M.; Wan, J.Q.; Yuan, W.X.; Liu, B.Y.; Ma, Y.; Pan, Y.H. An integrated metagenomics/metaproteomics investigation of the microbial communities and enzymes in solid-state fermentation of Pu-erh tea. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam Abu, H.; Ni Putu Vidya, P.; Sasangka, P.; Anna, S.; Tri, A.; Arie, S. The effect of variations in sugar types and fermentation time on enzyme activity and total titrated acid on eco-enzyme results of fermentation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Biological Science (ICBS 2021), Online, 14–15 October 2021; pp. 585–589. [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuka, M.; Goto, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Shimada, Y. Evaluation of pure antioxidative capacity of antioxidants: ESR spectroscopy of stable radicals by DPPH and ABTS assays with singular value decomposition. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. DPPH radical scavenging assay. Processes 2023, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, L.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B. Extraction and characterization of polysaccharides from Schisandra sphenanthera fruit by Lactobacillus plantarum CICC 23121-assisted fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Lin, L. Process optimization and quality components analysis of γ-aminobutyric acid pickled tea. Foods 2024, 13, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Hou, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Dynamics changes in volatile profile, non-volatile metabolites and antioxidant activities of dark tea infusion during submerged fermentation with Eurotium cristatum. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ma, S.; Ou, C.; Fan, F.; Gong, S.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q. Yellow tea: More than turning green leaves to yellow. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 7836–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Fermentation and complex enzyme hydrolysis for improving the total soluble phenolic contents, flavonoid aglycones contents and bio-activities of guava leaves tea. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Mu, B.; Ge, C.; Chen, S.; Cui, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Piao, C.; Li, G.-h. Exploring the novel antioxidant peptides in low-salt dry-cured ham: Preparation, purification, identification and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Ma, C.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B.; Xia, T. Comparative analysis of chemical constituents and antioxidant activity in tea-leaves microbial fermentation of seven tea-derived fungi from ripened Pu-erh tea. LWT 2021, 142, 111006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chang, N.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yao, C.; Wan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. K-solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus) promote theanine synthesis in tea roots (Camellia sinensis) by activating CsTSI activity. Tree Physiol. 2022, 42, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Luo, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Wu, P.; Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Ni, L.; et al. The investigation on the characteristic metabolites of Lactobacillus plantarum RLL68 during fermentation of beverage from by-products of black tea manufacture. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Deng, W.; Ning, J. Effects of microbial action and moist-heat action on the nonvolatile components of Pu-erh tea, as revealed by metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15602–15613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kang, S.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Park, J.J.; Yun, H.S. Cyanidin and malvidin in aqueous extracts of black carrots fermented with Aspergillus oryzae prevent the impairment of energy, lipid and glucose metabolism in estrogen-deficient rats by AMPK activation. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Q.; Yin, J.; Shi, J.; Xue, S.; Xu, Y. Improving the taste of autumn green tea with tannase. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, F.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Catechins: Protective mechanism of antioxidant stress in atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1144878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, A.; Cirri, P.; Santi, A.; Paoli, P. Morin: A promising natural drug. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 774–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alla, N.; Palatheeya, S.; Challa, S.R.; Kakarla, R. Morin attenuated the global cerebral ischemia via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2024, 39, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Omara, T.; Kahwa, I.; Khan, U.M. Anticancer potential of delphinidin and its derivatives: Therapeutic and mechanistic insights. Med. Chem. Res. 2024, 33, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharma, D.; Almulla, A. A Review: Biological Importance of Heterocyclic Compounds. Der Pharma Chem. 2017, 2017, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Rashad, M.M.; Mahmoud, A.E.; Ali, M.; Nooman, M.; Alkashef, A. Antioxidant and anticancer agents produced from pineapple waste by solid state fermentation. Int. J. Toxicol. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 7, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Ku, X.; Cheng, L.-L.; Pan, S.-A.; Fan, L.; Deng, W.-W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.-Z. Metabolite and transcriptome profiling on xanthine alkaloids-fed tea plant (camellia sinensis) shoot tips and roots reveal the complex metabolic network for caffeine biosynthesis and degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 551288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Ma, C.; Ren, X.; Xia, T.; Li, X. LC–MS/MS-based metabolomic analysis of caffeine-degrading fungus Aspergillus sydowii during tea fermentation. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, A.G.; Das, P.R.; Ismail, A.; Gajjar, P.; Balasubramani, S.P.; Sheikh, M.B.; Tsolova, V.; Sherif, S.M.; El-Sharkawy, I. Untargeted metabolomics and antioxidant capacities of muscadine grape genotypes during berry development. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, M.; Hou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Shen, H.; Ao, J.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Luo, A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial characteristics of ethyl acetate polar fractions from walnut green husk. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Foo, H.; Cao, Z.; Lin, Q. Dynamics Changes in Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity, and Non-Volatile Metabolites During Bulang Pickled Tea Fermentation. Foods 2025, 14, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050878
Zhou J, Chen L, Zhang F, Foo H, Cao Z, Lin Q. Dynamics Changes in Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity, and Non-Volatile Metabolites During Bulang Pickled Tea Fermentation. Foods. 2025; 14(5):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050878
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jinping, Laifeng Chen, Fan Zhang, Hooiling Foo, Zhenhui Cao, and Qiuye Lin. 2025. "Dynamics Changes in Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity, and Non-Volatile Metabolites During Bulang Pickled Tea Fermentation" Foods 14, no. 5: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050878
APA StyleZhou, J., Chen, L., Zhang, F., Foo, H., Cao, Z., & Lin, Q. (2025). Dynamics Changes in Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity, and Non-Volatile Metabolites During Bulang Pickled Tea Fermentation. Foods, 14(5), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050878





