Research Progress on Shrimp Allergens and Allergenicity Reduction Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Prevalence and Epidemiology of Shrimp Allergy
3. Molecular Characterization of Shrimp Allergens
3.1. TM
3.2. AK
3.3. SCP
3.4. MLC
3.5. TnC
3.6. HC
3.7. Triosephosphate Isomerase (TPI)
3.8. Other Allergens
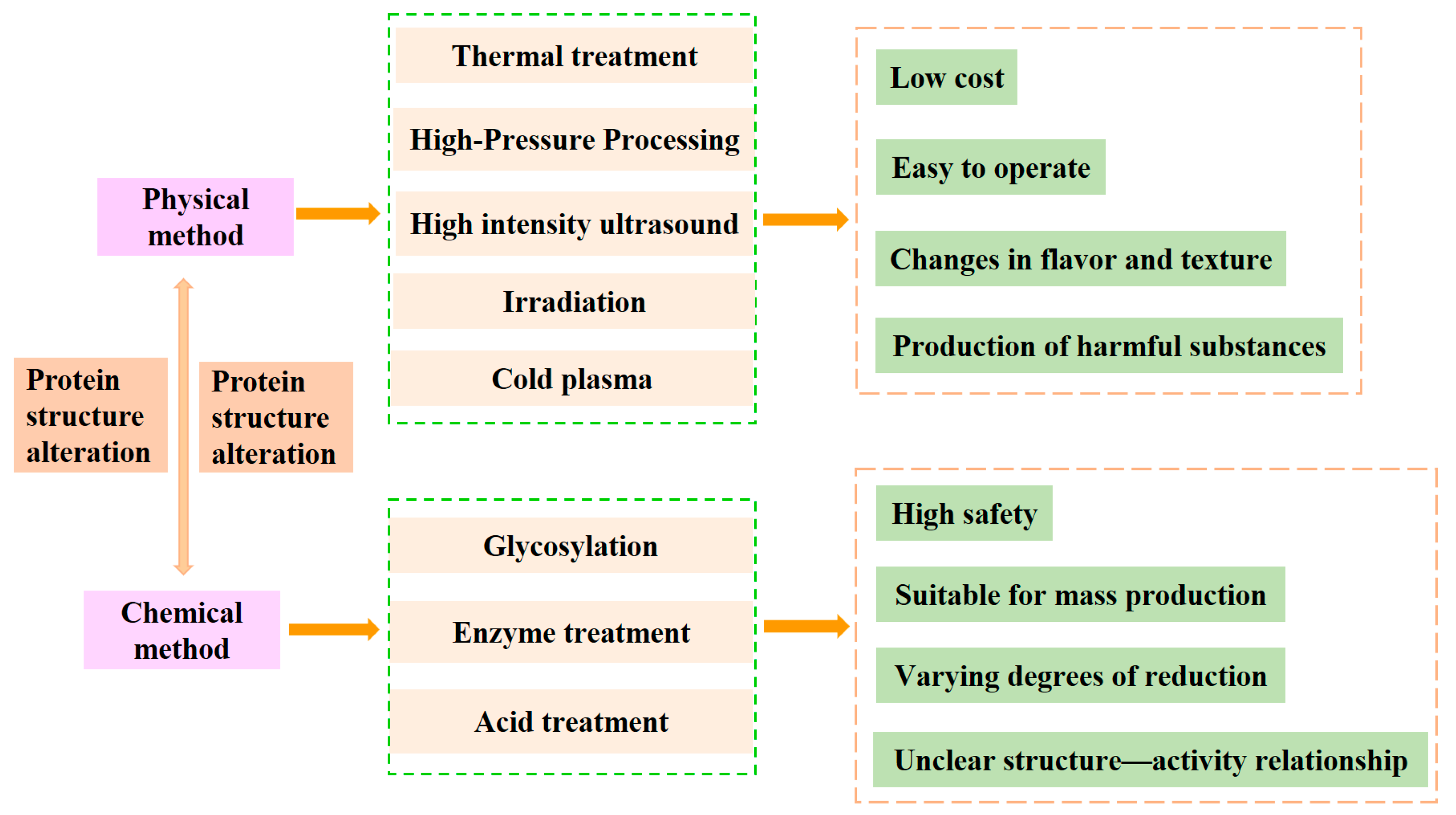
4. Effect of Processing Technologies on Shrimp Allergenicity
4.1. Physical Method
4.1.1. Thermal Treatment
4.1.2. High-Pressure Processing (HPP)
4.1.3. High-Intensity Ultrasound (HIU)
4.1.4. Irradiation
4.1.5. Cold Plasma (CP)
4.1.6. Other Physical Methods
4.2. Chemical Method
4.2.1. Glycosylation
4.2.2. Enzyme Treatment
4.2.3. Acid Treatment
4.2.4. Other Chemical Treatments
4.3. Biological Method
4.4. Synergistic Reduction Techniques
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, J.; Mishra, H.N. A comprehensive review of the spoilage of shrimp and advances in various indicators/sensors for shrimp spoilage monitoring. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173 Pt 1, 113270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.; Eilertsen, K.; Elvevoll, O.E. Health benefits of marine foods and ingredients. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, F.; Artaria, C. Astaxanthin in cardiovascular health and disease: Mechanisms of action, therapeutic merits, and knowledge gaps. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.B. Seafood allergy: Occurrence, mechanisms and measures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chu, X.L.; Dong, C.M. Research progress and immunological insights of shrimp allergens. Fish Shellfish. Immu. 2025, 156, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, M.; Boyano-Martnez, T.; Garcia-Ara, C.; Quirce, S. Shellfish allergy: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immu. 2015, 49, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Qiu, H.; Wei, S.; Sun, Q.X.; Xia, Q.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Han, Z.Y.; Ji, H.W.; Liu, S.C. Research progress of allergenicity reduction methods targeting shrimp tropomyosin. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.; Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.N. Potential efficacy of processing technologies for mitigating crustacean allergenicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 2807–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Freeland, D.M.H.; Nadeau, K.C. Food allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khora, S.S. Seafood-Associated Shellfish Allergy: A Comprehensive Review. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 504–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, T.; Vasiljevic, T.; Ramchandran, L. Effect of processing on conformational changes of food proteins related to allergenicity. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.; Abramson, M.; Bailey, M.; Walters, E. International prevalences of reported food allergies and intolerances. Comparisons arising from the European Community Respiratory Health Survey (ECRHS) 1991–1994. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 55, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Orson, F.; Ogawa, Y.; Parker, C.; Davis, C.M. Adult seafood allergy in the Texas Medical Center: A 13-year experience. Allergy Rhinol. 2011, 2, e71–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indolfi, C.; Dinardo, G.; Klain, A.; Salvatori, A.; Esposito, M.; Vela, V.; Decimo, F.; Ciprandi, G.; del Giudice, M.M. Evaluation of Der p 10 in a cohort of European children: Role of molecular diagnostics and clinical features. J. Immunol. Res. 2023, 2023, 5551305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Giudice, M.M.; Dinardo, G.; Klain, A.; D’Addio, E.; Bencivenga, C.L.; Decimo, F.; Indolfi, C. Anaphylaxis after shrimp intake in a European pediatric population: Role of molecular diagnostics and implications for novel foods. Children 2023, 10, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, N.Y.; Maskatia, Z.; Miller, S.; Guffey, D.; Minard, C.G.; Davis, C.M. Risk factors in pediatric shrimp allergy. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2015, 36, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuso, R.; Sánchez-Garcia, S.; Lin, J.; Fu, Z.Y.; Ibáñez, M.D.; Carrillo, T.; Blanco, C.; Goldis, M.; Bardina, L.; Sastre, J.; et al. Greater epitope recognition of shrimp allergens by children than by adults suggests that shrimp sensitization decreases with age. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1286–1293.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, P.; Summers, C.; Chinn, S.; Hooper, R.; Van Ree, R.; Lidholm, J. Prevalence and distribution of sensitization to foods in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey: A EuroPrevall analysis. Allergy 2010, 65, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, B.K.; Pradhan, D.D.; Mahar, J.; Sahu, S.K. Prevalence of allergic sensitization in childhood asthma. Cureus 2021, 13, e15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daul, C.B.; Slattery, M.; Reese, G.; Lehrer, S.B. Identification of the major brown shrimp (Penaeus aztecus) as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Int. Arch. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 105, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanti, K.N.; Martin, B.M.; Nagpal, S.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Rao, P.V. Identification of tropomyosin as the major shrimp allergen and characterization of its IgE binding epitopes. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 5354–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortea, I.; Canas, B.; Gallardo, J.M. Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Species-Specific Peptides from Arginine Kinase for the Identification of Commercially Relevant Shrimp Species. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5356–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gillen, C.M.; Wheatly, M.G. Molecular characterization of the sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein (SCP) from crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 144, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, H.L.; Maleki, S.J.; Cao, M.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Su, W.J.; Liu, G.M. Purification, Characterization, and Analysis of the Allergenic Properties of Myosin Light Chain in Procambarus clarkii. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Kalic, T.; McLean, T.R.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Seafood allergy: A comprehensive review of fish and shellfish allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piboonpocanun, S.; Jirapongsananuruk, O.; Tipayanon, T.; Boonchoo, S.; Goodman, R.E. Identification of hemocyanin as a novel non-cross-reactive allergen from the giant freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.D.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Voskamp, A.; Komoda, T.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Lopata, A.L. Effect of heat processing on antibody reactivity to allergen variants and fragments of black tiger prawn: A comprehensive allergenomic approach. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, M.; Maleki, S.; Zhang, M.L.; Liu, Q.M.; Cao, M.J.; Su, W.J.; Liu, G.M. Triosephosphate isomerase and filamin C share common epitopes as novel allergens of Procambarus clarkii. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Wu, C.C.; Tyan, Y.C.; Yu, W.T.; Huang, E.S.; Yu, H.-S. Identification of pyruvate kinase as a novel allergen in whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) by specific-IgE present in patients with shrimp allergy. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnaneedi, S.; Huerlimann, R.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Kamath, S.D.; Wade, N.M.; Jerry, D.R.; Lopata, A.L. Novel Allergen Discovery through Comprehensive De Novo Transcriptomic Analyses of Five Shrimp Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R.; Day, E.D., Jr.; Miller, J.S. The major heat-stable allergen of shrimp. Ann. Allergy 1981, 47, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leung, P.S.C.; Chu, K.H.; Chow, W.K.; Ansari, A.; Bandea, C.I.; Kwan, H.S.; Nagy, S.M.; Gershwin, M.E. Cloning, expression, and primary structure of Metapenaeus ensis tropomyosin, the major heat-stable shrimp allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, G.; Schicktanz, S.; Lauer, I.; Randow, S.; Lüttkopf, D.; Vogel, L.; Lehrer, S.B.; Vieths, S. Structural, immunological and functional properties of natural recombinant Pena l, the major allergen of brown shrimp Penaeu saztecus. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2006, 36, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.D.; Rahman, A.; Komoda, T.; Lopata, A.L. Impact of heat processing on the detection of the major shellfish allergen tropomyosin in crustaceans and molluscs using specific monoclonal antibodies. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4031–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.H.; Shao, H.M.; Hu, X.; Hua, X.W.; Meng, X.Y.; Chen, H.B. Characterization of systemic allergenicity of tropomyosin from shrimp (Macrobrachium nipponense) and anaphylactic reactions in digestive tract. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, W.; Rynkiewicz, M.J.; Moore, J.R. A new twist on tropomyosin binding to actin filaments: Perspectives on thin filament function, assembly and biomechanics. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2020, 41, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, K.; Suma, Y.; Ishizaki, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Molecular cloning of tropomyosin identified as allergens in six species of crustaceans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Rao, X.M.; Yu, Z.H. Alkaline unfolding and salt-induced folding of arginine kinase from shrimp Feneropenaeus chinensis under high pH conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 38, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalayasingam, M.; Gerez, I.F.A.; Yap, G.C.; Llanora, G.V.; Chia, I.P.; Chua, L.; Lee, C.J.A.O.; Ta, L.D.H.; Cheng, Y.K.; Thong, B.Y.H.; et al. Clinical and immunochemical profiles of food challenge proven or anaphylactic shrimp allergy in tropical Singapore. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.L.; Wu, C.G.; Xiang, J.H.; Dong, B. Molecular cloning and response to laminarin stimulation of arginine kinase in haemolymph in Chinese shrimp, Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2005, 19, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Mao, H.Y.; Cao, M.J.; Cai, Q.F.; Su, W.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, G.M. Purification, physicochemical and immunological characterization of arginine kinase, an allergen of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamez, C.; Zafra, M.; Boquete, M.; Sanz, V.; Mazzeo, C.; Ibanez, M.D.; Sanchez-Garcia, S.; Sastre, J.; del Pozo, V. New shrimp IgE-binding proteins involved in mite-seafood cross-reactivity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.; Northcutt, M.J.; Rohrback, S.E.; Carpenter, R.O.; Niehaus-Sauter, M.M.; Gao, Y.; Wheatly, M.G.; Gillen, C.M. Characterization of sarcoplasmic calcium binding protein (SCP) variants from freshwater crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 160, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Cao, M.J.; Cai, Q.F.; Su, W.J.; Mao, H.Y.; Liu, G.M. Purification and characterisation of sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein, a novel allergen of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Food Chem. 2013, 139, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morii, A.; Mita, H.; Ishizaki, S.; Shiomi, K. Importance of conformation for the IgE reactivity of sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein from the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 236, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laly, S.J.; Sankar, T.V.; Panda, S.K. Identification of allergic proteins of Flower tail shrimp (Metapenaeus dobsonii). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 5415–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Jin, T.C.; Li, M.S.; Yun, X.; Huan, F.; Liu, Q.M.; Hu, M.J.; Wei, X.F.; Zheng, P.Y.; Liu, G.M. Crystal Structure analysis of sarcoplasmic-calcium-binding protein: An Allergen in Scylla paramamosain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuso, R.; Grishina, G.; Bardina, L.; Carrillo, T.; Blanco, C.; Ibanez, M.D.; Sampson, H.A.; Beyer, K. Myosin light chain is a novel shrimp allergen, Lit v 3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, H.; Koketsu, A.; Ishizaki, S.; Shiomi, K. Molecular cloning and functional expression of allergenic sarcoplasmic calcium-binding proteins from Penaeus shrimps. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Zhu, W.Y.; Zeng, J.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X. Insight into the mechanism of allergenicity decreasing in recombinant sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein from shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) with thermal processing via spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulation techniques. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.J.; Huan, F.; Liu, M.; Li, M.S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.X.; Lai, D.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. IgE epitope analysis of sarcoplasmic-calcium-binding protein, a heat-resistant allergen in Crassostrea angulata. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8570–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Characterization of myosin light chain in shrimp hemocytic phagocytosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, H.-F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, H.L.; Cao, M.J.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, M.L.; He, X.R.; Liu, G.M. Expression and epitope identification of myosin light chain isoform 1, an allergen in Procambarus clarkii. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.; Zhu, L.; Landim-Vieira, M.; Pinto, J.R.; Chalovich, J.M. Basic residues within the cardiac troponin T C terminus are required for full inhibition of muscle contraction and limit activation by calcium. JBC 2019, 294, 19535–19545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauermeister, K.; Wangorsch, A.; Garoffo, L.P.; Reuter, A.; Conti, A.; Taylor, S.L.; Lidholm, J.; Dewitt, A.M.; Enrique, E.; Vieths, S.; et al. Generation of a comprehensive panel of crustacean allergens from the North Sea Shrimp Crangon crangon. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanasundaram, A.; Santiago, T.C. Identification and characterization of new allergen troponin C (Pen m 6.0101) from Indian black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 240, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, M.; Grishina, G.; Yang, A.C.; Sanchez-Garcıa, S.; Lin, J.; Towle, D.; Ibanez, M.D.; Sastre, J.; Sampson, H.A.; Ayuso, R. Molecular diagnosis of shrimp allergy: Efficiency of several allergens to predict clinical reactivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Prac. 2015, 3, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, P.; Chen, C.D.; Liu, S.J.; Huang, R.Q.; Zhong, M.Q.; Wei, C.J.; Zhang, Y.L. Hemocyanin from Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei has antiproliferative effect against HeLa cell in vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanaruksombat, S.; Srisomsap, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Punyarit, P.; Phiriyangkul, P. Identification of a novel allergen from muscle and various organs in banana shrimp (Fenneropenaeus merguiensis). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 113, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinroch, C.; Srisomsap, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Punyarit, P.; Phiriyangkul, P. Identification of novel allergen in edible insect, Gryllus bimaculatus and its cross-reactivity with Macrobrachium spp. allergens. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.B.; Kamath, S.D.; Iyer, S.P.; Pratap, K.; Karnaneedi, S.; Taki, A.C.; Nugraha, R.; Schaeffer, P.M.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; et al. Defining specific allergens for improved component-resolved diagnosis of shrimp allergy in adults. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zhang, H.J.; Shen, N.X.; Guo, C.; Ren, Y.J.; Xie, Y.; Gu, X.B.; Lai, W.M.; Peng, X.R.; Yang, G.Y. Molecular characterization and allergenicity potential of triosephosphate isomerase from Sarcoptes scabiei. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 257, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Hurlburt, B.K.; Li, G.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Fei, D.X.; Shen, H.W.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Identification of triosephosphate isomerase as a novel allergen in Octopus fangsiao. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 85, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Carrasco-Miranda, J.S.; Ramirez-Aguirre, C.D.; López-Hidalgo, M.; Benitez-Cardoza, C.G.; Ochoa-Leyva, A.; Cardona-Felix, C.S.; Diaz-Quezada, C.; Rudiño-Piñera, E.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; et al. Structural insights from a novel invertebrate triosephosphate isomerase from Litopenaeus vannamei. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2016, 1864, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, M.A.; Pascal, M.; El Kharbouchi, O.; Sabato, V.; Hagendorens, M.M.; Decuyper, I.I.; Bridts, C.H.; Ebo, D.G. Shellfish allergens: Tropomyosin and beyond. Allergy 2017, 72, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laly, S.J.; Sankar, T.V.; Panda, S.K. Effect of extended period of boiling on allergic protein of flower tail shrimp Metapenaeus dobsoni. Indian J. Fish. 2019, 66, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejrhit, N.; Azdad, O.; Chda, A.; El Kabbaoui, M.; Bousfiha, A.; Bencheikh, R.; Tazi, A.; Aarab, L. Evaluation of the sensitivity of Moroccans to shrimp tropomyosin and effect of heating and enzymatic treatments. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, H.; Yamamura, A.; Kimijima, T.; Ishizaki, S.; Ochiai, Y. Elimination of the major allergen tropomyosin from shrimp muscle by boiling treatment. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Cao, M.J.; Cai, Q.F.; Weng, W.Y.; Su, W.J.; Liu, G.M. Effects of different processing methods on digestibility of Scylla paramamosain allergen (tropomyosin). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, M.; Buckow, R.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O.P. Effect of simulated digestion on antigenicity of banana prawn (Fenneropenaeus merguiensis) after high pressure processing at different temperatures. Food Control. 2019, 104, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.R.; Hu, X.S.; Chen, F. Effects of combined high pressure and thermal treatments on the allergenic potential of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) tropomyosin in a mouse model of allergy. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, Z.X.; Lin, H.; Samee, H. Effect of power ultrasound on the immunoactivity and texture changes of shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Lin, H.; Cao, L.M.; Khalid, J. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on the allergenicity of shrimp. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2006, 7, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound processing on the physiochemical and allergenic properties of shrimp. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 65, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muanghorn, W.; Konsue, N.; Sham, H.; Othman, Z.; Mohamed, F.; Noor, N.M.; Othman, N.; Akmal, N.; Fauzi, N.A.; Solomen, M.; et al. Effects of gamma irradiation on tropomyosin allergen, proximate composition and mineral elements in giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, A.Y.; Mei, K.L.; Lv, M.C.; Lu, J.F.; Lou, Q.M.; Yang, W.G. The effect of electron beam irradiation on IgG binding capacity and conformation of tropomyosin in shrimp. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Li, Z.J.; Pavase, T.; Li, Z.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, N. Evaluation of electron beam irradiation to reduce the IgE binding capacity of frozen shrimp tropomyosin. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekezie, F.G.C.; Sun, D.W.; Cheng, J.H. Altering the IgE binding capacity of king prawn (Litopenaeus Vannamei) tropomyosin through conformational changes induced by cold argon-plasma jet. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Li, J.L.; Sun, D.W. In vivo biological analysis of cold plasma on allergenicity reduction of tropomyosin in shrimp. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Li, J.L.; Sun, D.W. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on structure, surface hydrophobicity and allergenic properties of shrimp tropomyosin. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.B.; Ni, S.Q.; Wang, Y.B. Maillard reaction with ribose, galacto-oligosaccharide or chitosan-oligosaccharide reduced the allergenicity of shrimp tropomyosin by inducing conformational changes. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.T.; Ahmed, I.; Qu, X.; Ju, G.X.; Yang, N.; Guo, Y.M.; Li, Z.X. Effect of the structure and potential allergenicity of glycated tropomyosin, the shrimp allergen. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.M.; Huang, Y.Y.; Cai, Q.F.; Weng, W.Y.; Su, W.J.; Cao, M.J. Comparative study of in vitro digestibility of major allergen, tropomyosin and other proteins between Grass prawn (Penaeus monodon) and Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Ni, S.Q.; Wang, C.; Li, X.T.; Fu, L.L. Cross-linking of shrimp tropomyosin catalyzed by transglutaminase and tyrosinase produces hypoallergens for potential immunotherapy. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, P.E.; Madeleine, S.; Benigno, A. Shrimp allergy: Effect of vinegar soaking on allergenicity. World Allergy Organ. J. 2007, 11, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasekan, A.; Cao, H.J.; Maleki, S.; Nayak, B. Shrimp tropomyosin retains antibody reactivity after exposure to acidic condition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3623–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.N.; Li, Z.X.; Gao, Q.; Pavase, T.R.; Lin, H. Effect of malonaldehyde cross-linking on the ability of shrimp tropomyosin to elicit the release of inflammatory mediators and cytokines from activated RBL-2H3 cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4263–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.N.; Li, Z.X.; Lin, H.; Du, S.Y.; Hao, Z.N.; Lin, H.X.; Zhu, Z. Effect of malondialdehyde treatment on the IgE binding capacity and conformational structure of shrimp tropomyosin. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Xie, M.H.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Huang, J.J.; Sun, Z.H.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, Y.B. Lactobacillus Casei Zhang alleviates shrimp tropomyosin-induced food allergy by switching antibody isotypes through the NF-κB-dependent immune tolerance. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1900496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Hu, Z.H.; Yan, Y.L. Litopenaeus vannamei fermentation using selected Lactobacillus spp. to reduce its allergenicity. Food Agric. Immunol. 2023, 34, 2210267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.M.; Cheng, H.; Nesbit, J.B.; Su, W.J.; Cao, M.J.; Maleki, S.J. Effects of Boiling on the IgE-Binding Properties of Tropomyosin of Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, T1–T5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O.N. Effects of selected processing treatments on antigenicity of banana prawn (Fenneropenaeus merguiensis) tropomyosin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, M.; Harada, A.; Ishimaru, T.; Sakumichi, E.; Saratani, F.; Sato-Minami, C.; Azakami, H.; Miyasaki, T.; Hanaoka, K. Contribution of structural reversibility to the heat stability of the tropomyosin shrimp allergen. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingham, T.; Ye, M.; Chen, H.Q.; Chintapenta, L.K.; Handy, E.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.Q.; Ozbay, G. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on the physical, microbial, and chemical attributes of Oysters (Crassostrea virginica). J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M1158–M1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Ren, Y.Y.; Bi, Y.G.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, K.W.; Chen, F. Review: Seafood allergy and potential application of high hydrostatic pressure to reduce seafood allergenicity. Int. J. Food Eng. 2019, 15, 20180392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Bi, Y.G.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, K.W.; Chen, F. Application of high pressure processing to improve digestibility, reduce allergenicity, and avoid protein oxidation in cod (Gadus morhua). Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, L.L.; Ji, Y.; Zeng, J.H.; Timira, V.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, G.Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X. Insight into IgG/IgE binding ability, in vitro digestibility and structural changes of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) soluble extracts with thermal processing. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasekan, A.O.; Nayak, B. Effects of buffer additives and thermal processing methods on the solubility of shrimp (Penaeus monodon) proteins and the immunoreactivity of its major allergen. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.X.; Lin, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.Z.; Sun, K.Y.; Sun, N. Mechanism of the reduced allergenicity of shrimp (Macrobrachium nipponense) by combined thermal/pressure processing: Insight into variations in protein structure, gastrointestinal digestion and immunodominant linear epitopes. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Tu, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tian, M. High-intensity ultrasound enhances the immunoglobulin (Ig)G and IgE binding of ovalbumin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Tu, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.D. Glycation of ovalbumin after high-intensity ultrasound pretreatment: Effects on conformation, immunoglobulin (Ig)G/IgE binding ability and antioxidant activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Chen, W.; Zhou, P. Conformation stability, in vitro digestibility and allergenicity of tropomyosin from shrimp (Exopalaemon modestus) as affected by high intensity ultrasound. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, K.X.; Du, J.Y.; Tan, Z.F.; Xu, Y.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhou, D.Y.; Li, D.Y. High-intensity ultrasound improved the physicochemical and gelling properties of Litopenaeus vannamei myofibrillar protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 90, 106217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Cao, L.H.; Jamil, K. Reduction of allergenic properties of shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) allergens by high intensity ultrasound. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 223, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakiyeh, B.Z.; Asma, A.; Seyyed, M.A.N.; Behrooz, J.; Mohammad, H. The effects of X-Rayirradiation on safety and nutritional value of food: A systematic review article. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.W.; Park, J.W.; Hong, C.S.; Kang, I.J. Effects of Gamma Radiation on the Conformational and Antigenic Properties of a Heat-Stable Major Allergen in Brown Shrimp. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Lin, H.; Cao, L.M.; Jamil, K. The influence of gamma irradiation on the allergenicity of shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoux, C.M.G.; Patange, A.; Lamba, S.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Tiwari, B.K.; Scannell, A.G.M. Applications of nonthermal plasma technology on safety and quality of dried food ingredients. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangapani, C.; Patange, A.; Bourke, P.; Keener, K.; Cullen, P.J. Recent Advances in the Application of Cold Plasma Technology in Foods. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, S.K. Effect of Selected Nonthermal Processing Methods on the Allergen Reactivity of Atlantic White Shrimp (Litopenaeus setiferus); University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.H.; Wang, H.F.; Sun, D.W. Insight into the IgE-binding sites of allergenic peptides of tropomyosin in shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) induced by cold plasma active particles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plagemann, R.; von Langermann, J.; Kragl, U. Microwave-assisted covalent immobilization of enzymes on inorganic surfaces. Eng. Life Sci. 2014, 14, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Impact of microwave processing on the secondary structure, in-vitro protein digestibility and allergenicity of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) proteins. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriver, S.; Yang, W.; Chung, S.Y.; Percival, S. Pulsed Ultraviolet Light Reduces Immunoglobulin E Binding to Atlantic White Shrimp (Litopenaeus setiferus) Extract. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediga, H.H.; Hester, P.; Yepuri, A.; Reddy, G.B.; Madala, S.K. Nε-Carboxymethyl-Lysine Modification of Extracellular Matrix Proteins Augments Fibroblast Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, X.M.; Xiao, H.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Zhou, P. Insight into the allergenicity of shrimp tropomyosin glycated by functional oligosaccharides containing advanced glycation end products. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, P. Glycation by saccharides of different molecular sizes affected the allergenicity of shrimp tropomyosin via epitope loss and the generation of advanced glycation end products. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7042–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Yang, H.; Rao, S.T.; Liu, G.-Y.; Hu, M.J.; Zeng, B.C.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. The Maillard reaction reduced the sensitization of tropomyosin and arginine kinase from Scylla paramamosain, simultaneously. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2934–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, P. Insight into the effects of deglycosylation and glycation of shrimp tropomyosin on in vivo allergenicity and mast cell function. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3934–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.Z.; Lv, L.T.; Li, Z.X.; Mi, N.; Chen, H.R.; Lin, H. Effect of transglutaminase-catalyzed glycosylation on the allergenicity and conformational structure of shrimp (Metapenaeus ensis) tropomyosin. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.Y.; Cheng, J.F.; Hu, Y.X.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, A.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, H. A composite enzyme derived from papain and chymotrypsin reduces the Allergenicity of Cow’s Milk allergen casein by targeting T and B cell epitopes. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.D.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Man, C.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.J. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis combined with processing on allergenicity of food allergens. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laly, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Sankar, T.V.; Panda, S.K. In vitro characterisation of tropomyosin from flower tail shrimp, Metapenaeus dobsoni and effect of hydrolysis on allergenicity of tropomyosin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7434–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Xu, L.L.; Li, S.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I.; Chen, G.Z.; Cao, X.; Li, Z.X. Immunomodulatory effect of laccase/caffeic acid and transglutaminase in alleviating shrimp tropomyosin (met e 1) allergenicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7765–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Hu, M.J.; Sun, L.C.; Sun, L.C.; Han, X.Y.; Liu, Q.M.; Alcocer, M.; Fei, D.X.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Allergenicity and oral tolerance of enzymatic cross-linked tropomyosin evaluated using cell and mouse models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.L.; Ni, S.Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.B. Transglutaminase-catalysed cross-linking eliminates Penaeus chinensis tropomyosin allergenicity by altering protein structure. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X.; Xu, L.L.; Qazi, I.M.; Luo, C.; Gao, X.; Khan, M.U.; Iqbal, A.; Guo, Y.M.; et al. Tyrosinase/caffeic acid cross-linking alleviated shrimp (Metapenaeus ensis) tropomyosin-induced allergic responses by modulating the Th1/Th2 immunobalance. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Lv, L.T.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X.; Ma, J.J.; Chen, G.Z.; Sun, L.R.; Xu, L.L. Effect of tyrosinase-aided crosslinking on the IgE binding potential and conformational structure of shrimp (Metapenaeus ensis) tropomyosin. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhao, J.L. Research progress in crustacean allergens and their mitigation technologies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.T.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X.; Ahmed, I.; Mi, N.S.; Chen, G.Z. Allergenicity of acrolein-treated shrimp tropomyosin evaluated using RBL-2H3 cell and mouse model. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4374–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.T.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, J.; Ahmed, I.; Chen, H.R. Changes of structure and IgE binding capacity of shrimp (Metapenaeus ensis) tropomyosin followed by acrolein treatment. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.T.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X.; Nayak, B.; Ahmed, I.; Tian, S.L.; Chen, G.Z.; Lin, H.; Zhao, J.X. Structural changes of 2,2′-azobis (2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) treated shrimp tropomyosin decrease allergenicity. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Xu, L.L.; Sun, L.R.; Chen, G.Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X. Influence of linoleic acid on the immunodetection of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) tropomyosin and the mechanism investigation via multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling techniques. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.T.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X.; Ahmed, I.; Chen, G.Z. Determining the effect of malondialdehyde on the IgE-binding capacity of shrimp tropomyosin upon in vitro digestion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 4588–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Han, Y.Y.; Yang, B.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.X. The natural substances with anti-allergic properties in food allergy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.T.; Qu, X.; Yang, N.; Liu, Z.G.; Wu, X.L. Changes in structure and allergenicity of shrimp tropomyosin by dietary polyphenols treatment. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.X.; Li, X.-M.; Wang, H.; Lin, H. Insight into the conformational and allergenicity alterations of shrimp tropomyosin induced by Sargassum fusiforme polyphenol. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.Y.; Ju, G.X.; Lv, X.J.; Sui, X.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liang, L.F.; Yang, Q.L.; Wu, W.; Lv, L.T. Reducing the allergenicity of tropomyosin in shrimp by covalent conjugation with quercetin and chlorogenic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 130099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.W.; Yang, Y.L.; Sun, Y.X.; Cui, Q.; Wan, Y.; Fu, G.M.; Chen, H.B.; Cheng, J.J. Recent advances in alleviating food allergenicity through fermentation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7255–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, U.; Shimizu, Y.; Joe, G.-H.; Saeki, H. Hiroki Saeki. Food safety evaluation of commercial Terasi, Indonesian fermented shrimp paste, from the viewpoint of food allergy. Fish. Sci. 2023, 89, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, U.; Shimizu, Y.; Joe, G.H.; Saeki, H. Impact of backslopping in TERASI manufacture, as an improving method to reduce shrimp allergenicity. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Saeki, H.; Nakamura, A.; Kim, K.B.W.R.; Lee, J.W.; Byun, M.W.; Kim, S.M.; Lim, S.M.; Ahn, D.H. Allergenicity Changes in Raw Shrimp (Acetes japonicus) and Saeujeot (Salted and Fermented Shrimp) in Cabbage Kimchi due to Fermentation Conditions. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 16, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.L.; Qu, X.; Wang, X.D.; Che, H.X.; Huang, Z.Q.; Ge, X.Y.; Lv, L.T. Effects of methylglyoxal on shrimp tropomyosin structure and allergenicity during thermal processing. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.X.; Lin, S.Y.; Gao, X.C.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.Z.; Sun, N. Reduced allergenicity of shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) by altering the protein fold, digestion susceptibility, and allergen epitopes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9120–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huan, F.; Han, T.-J.; Liu, S.H.; Li, M.-S.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, G.X.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Combination processing method reduced IgE-Binding activity of Litopenaeus vannamei by modifying Lysine, Arginine, and Cysteine on multiple allergen epitopes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4865–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Q.; Cheng, J.H.; Keener, K.M. Changing the IgE binding capacity of tropomyosin in shrimp through structural modification induced by cold plasma and glycation treatment. Foods 2023, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biochemical Names | MW (kDa) | Function | Source | Heat Resistance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tropomyosin | 34–38 kDa | Regulates muscle contraction | Penaeus aztecus (Pen a l) Penaeus indiana (Pen I 1) | Yes | [20,21] |
| Arginine kinase | 40 kDa | Cellular energy metabolism | Penaeus monodon (Pen m 2) Litopenaeus vannamei (Lit v 2) | No | [22] |
| Sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein | 20–22 kDa | Regulates muscle relaxation | Penaeus monodon (Pen m 4) Litopenaeus vannamei (Lit v 4) | Yes | [23] |
| Myosin light chain | 18–20 kDa | Material transport, muscle contraction, and cell division | Procambarus clarkii | Yes | [24] |
| Troponin C | 18 kDa | Calcium-dependent contraction in both skeletal and cardiac muscle | North Sea Shrimp (Cra c 6) | no data | [25] |
| Hemocyanin | 60–80 kDa | Animal respiration and physiological activities | Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Mac ro 2) | Yes | [26] |
| Triosephosphate isomerase | 26–29 kDa | Engage in glycolysis, lipid metabolism, gluconeogenesis | black tiger prawn | No | [27] |
| Filamin C | 90 kDa | Stabilizes the cytoskeleton | Procambarus clarkii | No | [28] |
| pyruvate kinase | 63 kDa | Catalytic enzyme | Litopenaeus vannamei | no data | [29] |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 37 kDa | Catalytic enzyme | Fenneropenaeus merguiensis | no data | [30] |
| Enolase (EA) | 50 kDa | Enzyme protein | Melicertus latisulcatus Fenneropenaeus merguiensis | no data | [30] |
| Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ A Tpase | 113 kDa | Enzyme protein | Melicertus latisulcatus Fenneropenaeus merguiensis | no data | [30] |
| Myosin heavy chain | 18–20 kDa | Provide energy, muscle contraction | Melicertus latisulcatus Fenneropenaeus merguiensis | no data | [30] |
| Processing Method | Mechanism | Effect on Allergenicity | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal treatment |
|
|
|
| [66,67,68] |
| High-pressure processing |
|
|
|
| [69,70,71] |
| High-intensity ultrasound |
|
|
|
| [72,73,74] |
| Irradiation |
|
|
|
| [75,76,77] |
| Cold plasma |
|
|
|
| [78,79,80] |
| Glycosylation |
|
|
|
| [81,82] |
| Enzyme treatment |
|
|
|
| [83,84] |
| Acid treatment |
|
|
|
| [85,86] |
| Malondialdehyde crosslinking |
|
|
|
| [87,88] |
| Biological method |
|
|
|
| [89,90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, H. Research Progress on Shrimp Allergens and Allergenicity Reduction Methods. Foods 2025, 14, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050895
Chen B, He H, Wang X, Wu S, Wang Q, Zhang J, Qiao Y, Liu H. Research Progress on Shrimp Allergens and Allergenicity Reduction Methods. Foods. 2025; 14(5):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050895
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bingjie, Hui He, Xiao Wang, Songheng Wu, Qiankun Wang, Jinglin Zhang, Yongjin Qiao, and Hongru Liu. 2025. "Research Progress on Shrimp Allergens and Allergenicity Reduction Methods" Foods 14, no. 5: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050895
APA StyleChen, B., He, H., Wang, X., Wu, S., Wang, Q., Zhang, J., Qiao, Y., & Liu, H. (2025). Research Progress on Shrimp Allergens and Allergenicity Reduction Methods. Foods, 14(5), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050895





