Proteins from Microalgae: Nutritional, Functional and Bioactive Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microalgae Proteins
3. Protein Processing Methods
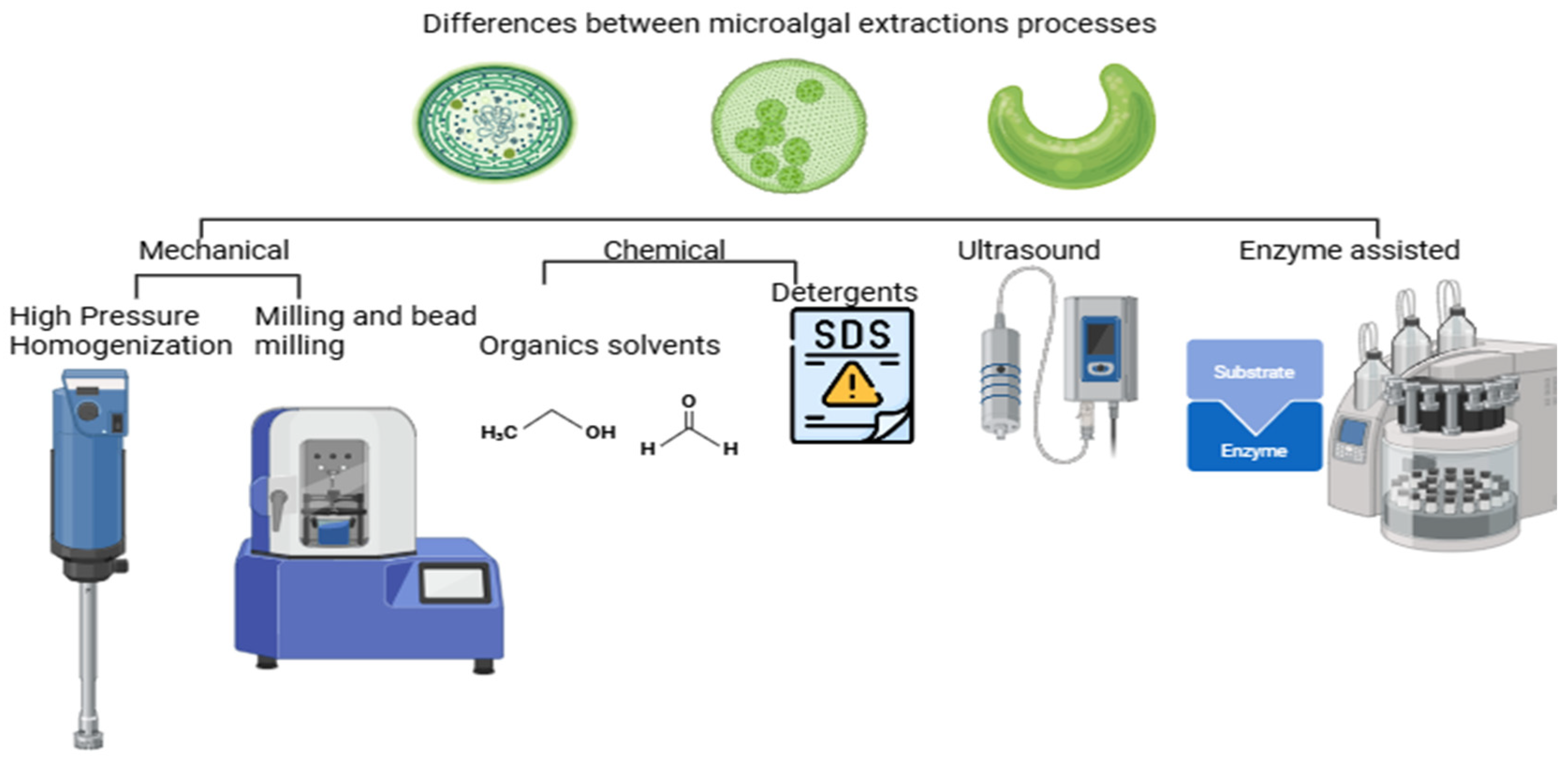
4. Protein Extraction Techniques
4.1. Mechanical Extraction
4.2. Chemical Extraction
4.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction
4.4. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction
5. Impact of Drying, Heating and Enzymatic Treatments
6. Techniques to Increase Protein Content in Microalgae
7. Nutritional Properties of Microalgae Proteins
7.1. Amino Acid Profile
7.2. Digestibility and Bioavailability
7.3. Functional Properties of Microalgae Proteins
8. Potential Applications in Food Products
9. Bioactive Properties of Microalgae Proteins
9.1. Antioxidant Activity
9.2. Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties
9.3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
10. Economic Feasibility
11. Environmental Impact
12. Research Gaps and Future Perspectives
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Tang, T.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, J. The potential and challenge of microalgae as promising future food sources. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rodrigues, M.M.; Estrada-Beristain, C.; Metri-Ojeda, J.; Pérez-lva, A.; Baigts-Allende, D.K. Spirulina platensis protein as sustainable ingredient for nutritional food products development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaró, S.; Morillas-España, A.; Acién, G.; Lafarga, T. Optimisation of operational conditions during the production of Arthrospira platensis using pilot-scale raceway reactors, protein extraction, and assessment of their techno-functional properties. Foods 2022, 11, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.C.; Almeida, T.; Colucci, G.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Manrique, Y.A.; Dias, M.M.; Barros, L.; Fernandes, A.; Colla, E.; Barreiro, M.F. Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) protein-rich extract as a natural emulsifier for oil-in-water emulsions: Optimization through a sequential experimental design strategy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozober, H.S.; Okun, A.; Shpigelman, A. The impact of high-pressure homogenization on thermal gelation of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) protein concentrate. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaa, F.; Wijesinghe, U.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Althobaiti, N.A.; Albalawi, A.E.; Khan, B.A.; Menaa, B. Marine Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds: A New Wave of Nanodrugs. Mar. Drugs. 2021, 19, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, H.; Xu, J.H.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, B.; Chen, K.W. Microalgae as a sustainable protein source: Key issues related to their production, application, and the way forward. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 17, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, V.S.; de Oliveira, D.R.B.; da Silva, C.A.S.; Santana, R.d.C.; Soares, N.d.F.F.; de Oliveira, E.B.; Martins, M.A.; Coimbra, J.S.d.R. Stabilization of oil–water emulsions with protein concentrates from the microalga Tetradesmus obliquus. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyande, A.K.; Chew, K.W.; Rambabu, K.; Tao, Y.; Chu, D.T.; Show, P.L. Microalgae: A potential alternative to health supplementation for humans. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Mehboob Nousheen, M.G.; Vasimalai, N.; Thajuddin, N.; Jung-Wan, K. An investigation of pepsin hydrolysate of short antibacterial peptides derived from Limnospira sp. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 5580–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Horsman, M.; Wang, B.; Wu, N.; Lan, C.Q. Effects of nitrogen sources on cell growth and lipid accumulation of green alga Neochloris oleoabundans. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 81, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Hao, X.; Tan, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of the enzymatic hydrolysates from Chlorella vulgaris protein and assessment of their antioxidant potential using Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón-Lee, T.; González-Mariño, G. Microalgae for “Healthy” Foods-Possibilities and Challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R. The amino-acid and sugar composition of 16 species of microalgae used in mariculture. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 145, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.W. Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, C.; Tibbetts, S.M.; Pan, S.; Udenigwe, C. Nutritional quality and bioactive properties of proteins and peptides from microalgae. In Handbook of Microalgae-Based Processes and Products; Jacob-Lopes, E., Maroneze, M.M., Queiroz, M.I., Zepka, L.Q., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 493–531. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshtipour, H.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Mohammadi, R.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Koshravi-Darani, K. Supplementation of Spirulina platensis and Chlorella vulgaris algae into probiotic fermented milks. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.N.; Evans, G.; Lease, H.J. The influence of product attributes, consumer attitudes and characteristics on the acceptance of: (1) Novel bread and milk, and dietary supplements and (2) fish and novel meats as dietary vehicles of long chain omega 3 fatty acids. Food Qual. Prefer. 2011, 22, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahl, S.; Strack, M.; Weinrich, R.; Mörlein, D. Consumer-oriented product development: The conceptualization of novel food products based on spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) and resulting consumer expectations. J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 1919482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urala, N.; Lähteenmäki, L. Attitudes behind consumers’ willingness to use functional foods. Food Qual. Prefer. 2004, 15, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, W. Functional foods: Consumer willingness to compromise on taste for health? Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.W.; Bruins, M.E.; Sanders, J.P.M. Enzyme assisted protein extraction from rapeseed, soybean, and microalgae meals. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, R.; Manickam, S.; Yap, Y.J.; Ling, T.C.; Chang, J.S.; Show, P.L. Extraction of proteins from microalgae using integrated method of sugaring-out assisted liquid biphasic flotation (LBF) and ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Costa, M.; Pinheiro Spínola, M.; Diogo Alves, V.; Mestre Prates, J.A. Improving protein extraction and peptide production from Chlorella vulgaris using combined mechanical/physical and enzymatic pre-treatments. Heliyon 2024, 10, 2405–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hosano, N.; Hosano, H. Recovering microalgal bioresources: A review of cell disruption methods and extraction technologies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safi, C.; Frances, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Laroche, C.; Pouzet, C.; Vaca-Garcia, C.; Pontalier, P.Y. Understanding the effect of cell disruption methods on the diffusion of Chlorella vulgaris proteins and pigments in the aqueous phase. Algal Res. 2015, 8, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, P.R.; Miron, T.L.; Olivieri, G.; Barbosa, M.J.; Wijffels, R.H.; Eppink, M.H.M. Mild disintegration of the green microalgae Chlorella vulgaris using bead milling. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günerken, E.; D’Hondt, E.; Eppink, M.H.; Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Elst, K.; Wijffels, R.H. Cell disruption for microalgae biorefineries. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.L.; de Vicente, M.; Galán, B. Microalgae, old sustainable food and fashion nutraceuticals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Laroche, C.; Zebib, B.; Merah, O.; Pierre-Yves, P.; Vaca-Garcia, C. Aqueous extraction of proteins from microalgae: Effect of different cell disruption methods. Algal Res. 2014, 3, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, G.; Poojary, M.; O’Donnell, C.; Lund, M.N.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound-assisted processing of Chlorella vulgaris for enhanced protein extraction. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Tavanandi, H.A.; Mantri, V.A.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S. Ultrasound assisted methods for enhanced extraction of phycobiliproteins from marine macro-algae, Gelidium pusillum (Rhodophyta). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Hosseini, S.E.; Asadi, G.; Khayambashi, B.; Abedinia, A. Optimization of microalgae protein extraction from Scenedesmus obliquus and investigating its functional properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 198, 116028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Mao, X.; Qi, P.; Zhang, X. Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging evaluation of pigment-protein complex extracted from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, F.; Wong, G.; Román, T.; Cárdenas, C.; Alvarez, C.; Schmitt, P.; Albericio, F.; Rojas, V. Identification of antimicrobial peptides from the microalgae Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butcher and bactericidal activity improvement. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, M.A.J.; Perera, C.O.; Hemar, Y. Production of bioactive proteins and peptides from the diatom Nitzschia laevis and comparison of their in vitro antioxidant activities with those from Spirulina platensis and Chlorella vulgaris. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquet, V.; Chérouvrier, J.R.; Farhat, F.; Thiéry, V.; Piot, J.M.; Bérard, J.B.; Kaas, R.; Serive, B.; Patrice, T.; Cadoret, J.P.; et al. Study on the microalgal pigments extraction process: Performance of microwave assisted extraction. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleakley, S.; Hayes, M. Algal proteins: Extraction, application, and challenges concerning production. Foods 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Nitrate concentration-shift cultivation to enhance protein content of heterotrophic microalga Chlorella vulgaris: Over-compensation strategy. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, P.S.C.; Barreira, L.A.; Pereira, H.G.C.; Perales, J.A.; Varela, J.C.S. Light emitting diodes (LEDs) applied to microalgal production. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, T.A.; Shariati, M. Dunaliella biotechnology: Methods and applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, N.T. Food and Industrial Bioproducts and Bioprocessing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mosibo, O.K.; Ferrentino, G.; Udenigwe, C.C. Microalgae Proteins as sustainable ingredients in novel foods: Recent developments and challenges. Foods 2024, 13, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gong, Z. Comprehensive insights into microalgae proteins: Nutritional profiles and innovative applications as sustainable alternative proteins in health and food sciences. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrikson, R. Earth Food Spirulina: The Complete Guide to a Powerful New Food That Can Help Rebuild Our Health and Restore our Environment; Ronore Enterprises, Inc.: Hana, HI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Niccolai, A.; Chini Zittelli, G.; Rodolfi, L.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R. Microalgae of interest as food source: Biochemical composition and digestibility. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Hinrichs, J.; Weiss, J. Emulsifying properties of acid-hydrolyzed insoluble protein fraction from Chlorella protothecoides: Formation and storage stability of emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.; Grossmann, L.; Hinrichs, J.; Weiss, J. Emulsifying properties of water-soluble proteins extracted from the microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, A.P.; Niccolai, A.; Bursic, I.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A.; Rodolfi, L.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R. Microalgae as functional ingredients in savory food products: Application to wheat crackers. Foods 2019, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T. Effect of microalgal biomass incorporation into foods: Nutritional and sensorial attributes of the end products. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 178–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelhadj, S.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Degraeve, P.; Attia, H.; Ghorbel, D. Effect of pH on the functional properties of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis protein isolate. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Extraction, structural and functional properties of Haematococcus pluvialis protein after pigment removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronakis, I.S. Gelation of edible blue-green algae protein isolate (Spirulina platensis strain pacifica): Thermal transitions, rheological properties, and molecular forces involved. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez Garcia, E.; van Leeuwen, J.J.; Safi, C.; Sijtsma, L.; van den Broek, L.A.M.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Wijffels, R.H.; van den Berg, C. Techno-functional properties of crude extracts from the green microalga Tetraselmis suecica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7831–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, L.; Hinrichs, J.; Goff, H.D.; Weiss, J. Heat-Induced Gel Formation of a Protein-Rich Extract from the Microalga Chlorella sorokiniana. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 56, 102176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draaisma, R.B.; Wijffels, R.H.; Slegers, P.M.; Brentner, L.B.; Roy, A.; Barbosa, M.J. Food commodities from microalgae. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Amorim, M.; Soares, J.; Vieira, B.B.; Batista-Silva, W.; Martins, M.A. Extraction of proteins from the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus BR003 followed by lipid extraction of the wet deproteinized biomass using hexane and ethyl acetate. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafyra, M.; Papadaki, S.; Chronis, M.; Krokida, M. Microalgae based innovative animal fat and proteins replacers for application in functional baked products. Open Agric. 2018, 3, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, V.O. Carbohidratos y proteínas en microalgas: Potenciales alimentos funcionales. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2019, 22, e2019043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashandy, S.A.; El Awdan, S.A.; Ebaid, H.; Alhazza, I.M. Antioxidant potential of Spirulina platensis mitigates oxidative stress and reprotoxicity induced by sodium arsenite in male rats. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 7174351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Qian, Z.J.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. Characterization of growth and protein contents from microalgae Navicula incerta with the investigation of antioxidant activity of enzymatic hydrolysates. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Llanos, M.; Lagumersindez-Denis, N.; Marín-Prida, J.; Pavón-Fuentes, N.; Falcon-Cama, V.; Piniella-Matamoros, B.; Camacho-Rodríguez, H.; Fernández-Massó, J.R.; Valenzuela-Silva, C.; Raíces-Cruz, I.; et al. Benefcial efects of oral administration of C-Phycocyanin and phycocyanobilin in rodent models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Life Sci. 2018, 194, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, L.; Aggarwal, A. Astaxanthin inhibits cytokines production and infammatory gene expression by suppressing IκB kinase-dependent nuclear factor κB activation in pre and postpartum Murrah bufaloes during diferent seasons. Vet. World 2018, 11, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheih, I.C.; Fang, T.J.; Wu, T.-K.; Lin, P.H. Anticancer and antioxidant activities of the peptide fraction from algae protein waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Antibiotic resistance and its cost: Is it possible to reverse resistance? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilhelmelli, F.; Vilela, N.; Albuquerque, P.; Derengowski, L.d.S.; Silva-Pereira, I.; Kyaw, C.M. Antibiotic development challenges: The various mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and of bacterial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.J.; Desbois, A.P.; Dyrynda, E.A. Conventional and unconventional antimicrobials from fish, marine invertebrates and microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1213–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.B.; Ebersole, J.L. A novel bioactivity of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their ester derivatives. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2010, 25, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, G. Obtención de un Hidrolizado Enzimático Bioactivo de Proteína Microalgal con Potencial Antimicrobiano. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.S.; Salomon, P.; Hamerski, L.; Walter, J.; Menezes, R.B.; Siqueira, J.E.; Santos, A.; Santos, J.A.M.; Ferme, N.; Guimarães, T.; et al. Inhibitory effect of microalgae and cyanobacteria extracts on influenza virus replication and neuraminidase activity. PeerJ 2018, 2018, e5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, I.S.; Park, S.J. A Spirulina maxima-derived peptide inhibits HIV-1 infection in a human T cell line MT4. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Serrano, B.V.; Cabanillas-Salcido, S.L.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; Jiménez-Camacho, R.; Norzagaray-Valenzuela, C.D.; Calderón-Zamora, L.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Farfán-Morales, C.N.; Romero-Utrilla, A.; et al. Efecto antiviral de los hidrolizados proteicos de la microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum contra el serotipo 2 del virus del dengue. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkia, I.; Saari, N.; Manning, S.R. microalgae for high-value products towards human health and nutrition. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, H. Microalgal metabolic engineering facilitates precision nutrition and dietary regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Luo, S.; He, R.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; An, Y.; Lu, Y. Utilization of microalgae and duckweed as sustainable protein sources for food and feed: Nutritional potential and functional applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 4466–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Encinas, J.P.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Juárez, J.; Ornelas-Paz, J.d.J.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Proteins from Microalgae: Nutritional, Functional and Bioactive Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060921
García-Encinas JP, Ruiz-Cruz S, Juárez J, Ornelas-Paz JdJ, Del Toro-Sánchez CL, Márquez-Ríos E. Proteins from Microalgae: Nutritional, Functional and Bioactive Properties. Foods. 2025; 14(6):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060921
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Encinas, Juan Pablo, Saul Ruiz-Cruz, Jousé Juárez, José de Jesús Ornelas-Paz, Carmen Lizette Del Toro-Sánchez, and Enrique Márquez-Ríos. 2025. "Proteins from Microalgae: Nutritional, Functional and Bioactive Properties" Foods 14, no. 6: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060921
APA StyleGarcía-Encinas, J. P., Ruiz-Cruz, S., Juárez, J., Ornelas-Paz, J. d. J., Del Toro-Sánchez, C. L., & Márquez-Ríos, E. (2025). Proteins from Microalgae: Nutritional, Functional and Bioactive Properties. Foods, 14(6), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060921





