Enhancing the Functional and Emulsifying Properties of Potato Protein via Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Papain and Bromelain for Gluten-Free Cake Emulsifiers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Potato Protein Hydrolysate (PPH) Preparation and Characterization
2.2.1. PPH Preparation
2.2.2. Yield of PPH
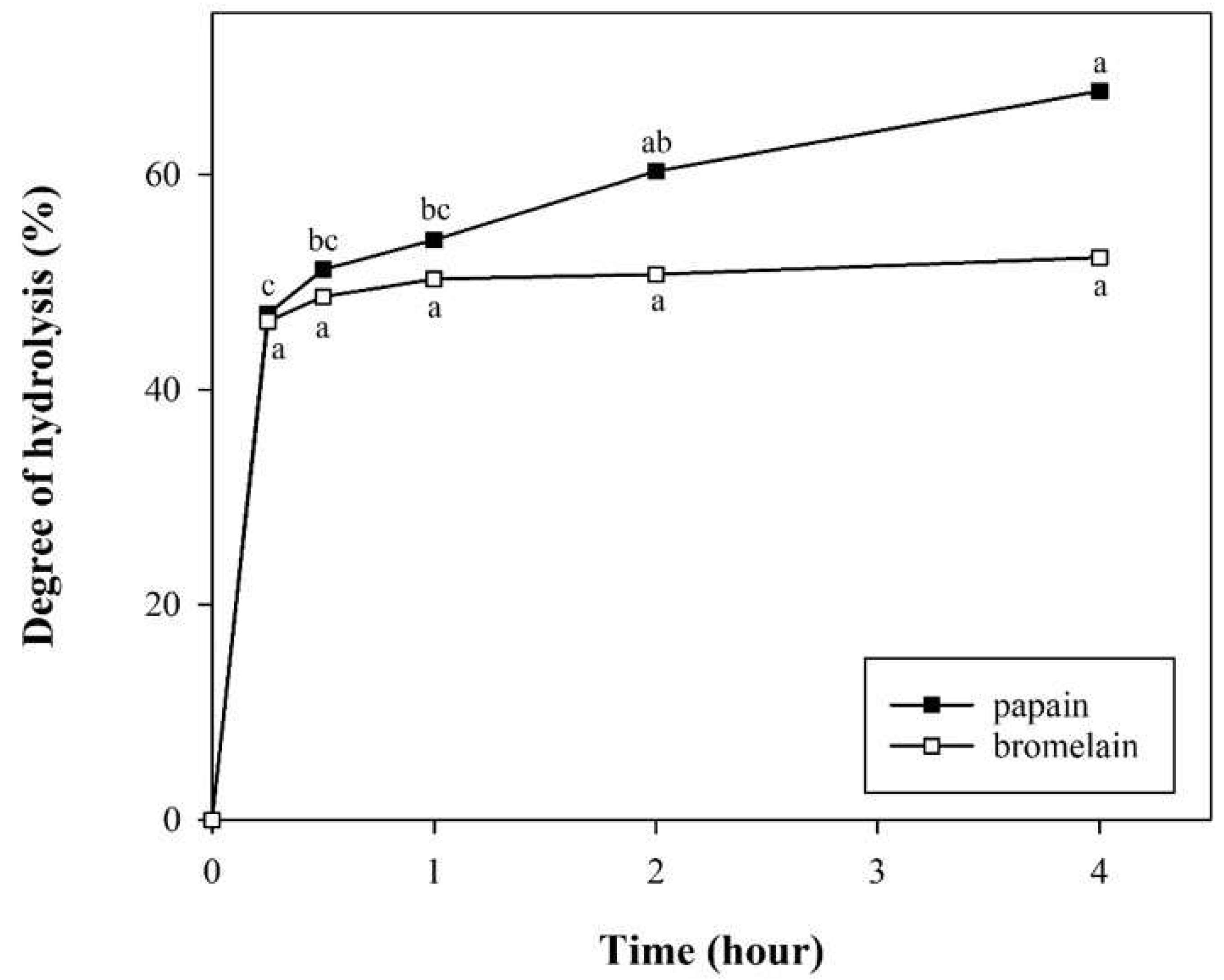
2.2.3. Degree of Hydrolysis
2.2.4. Molecular Weight
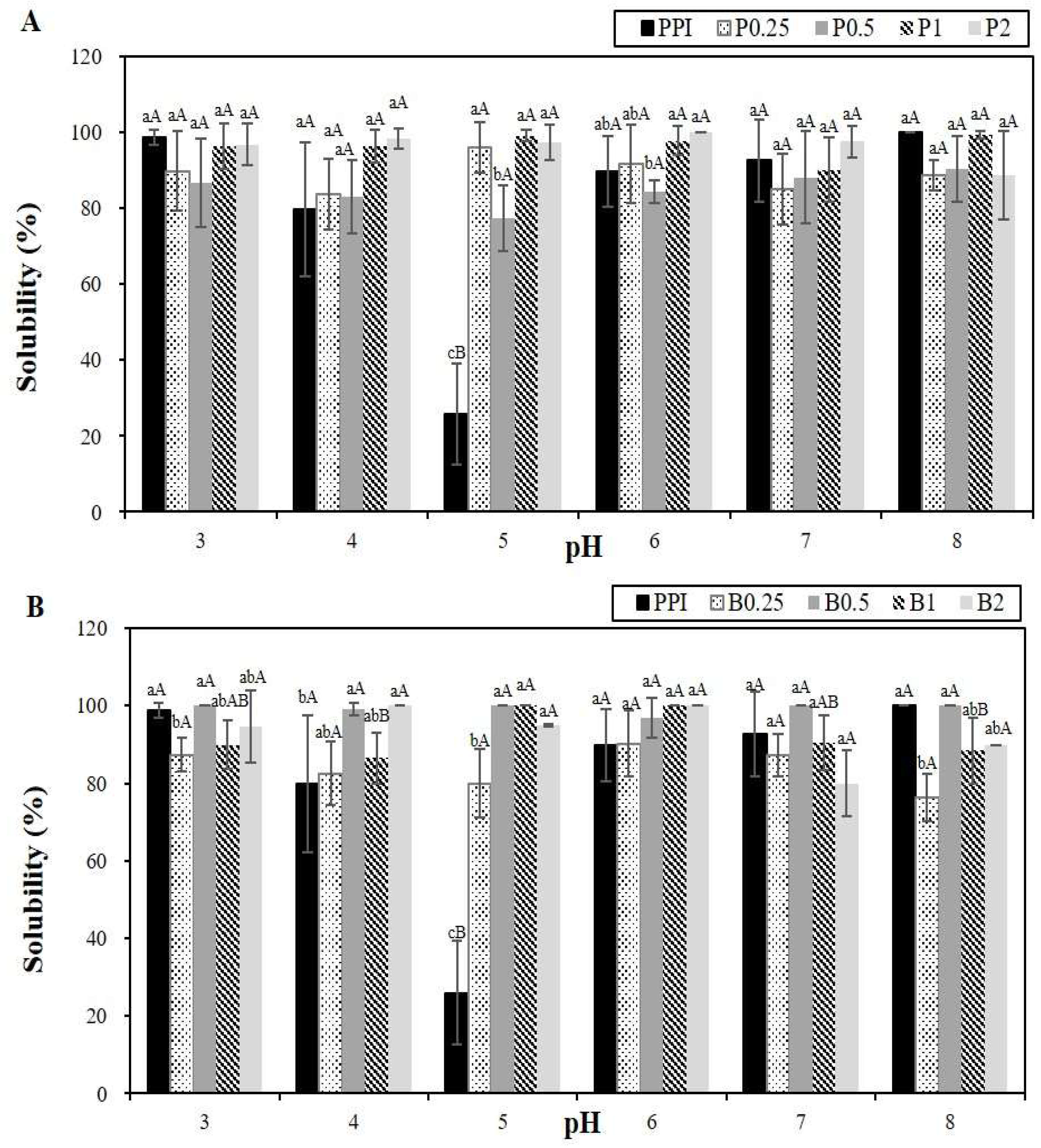
2.2.5. Solubility
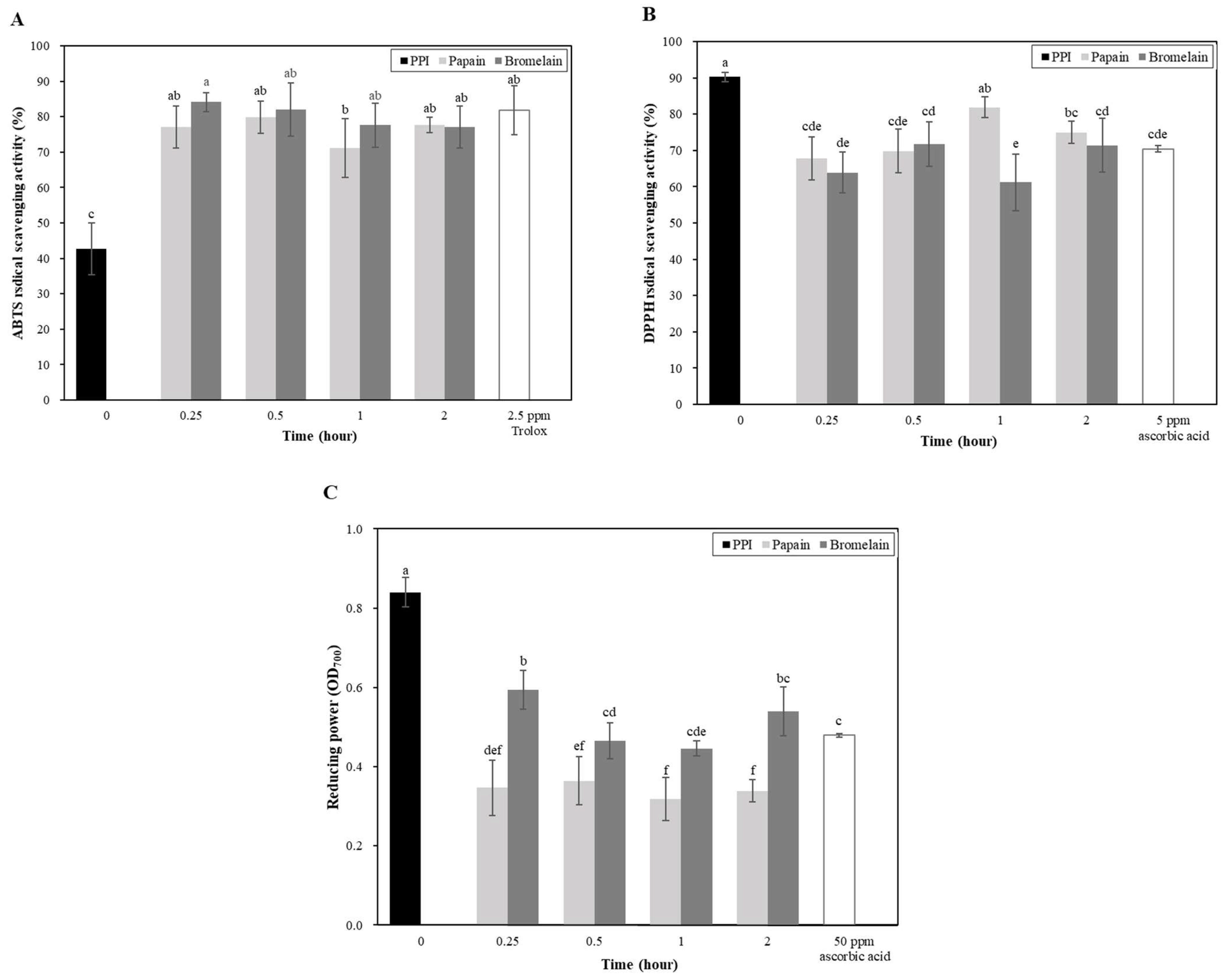
2.2.6. Antioxidant Activity
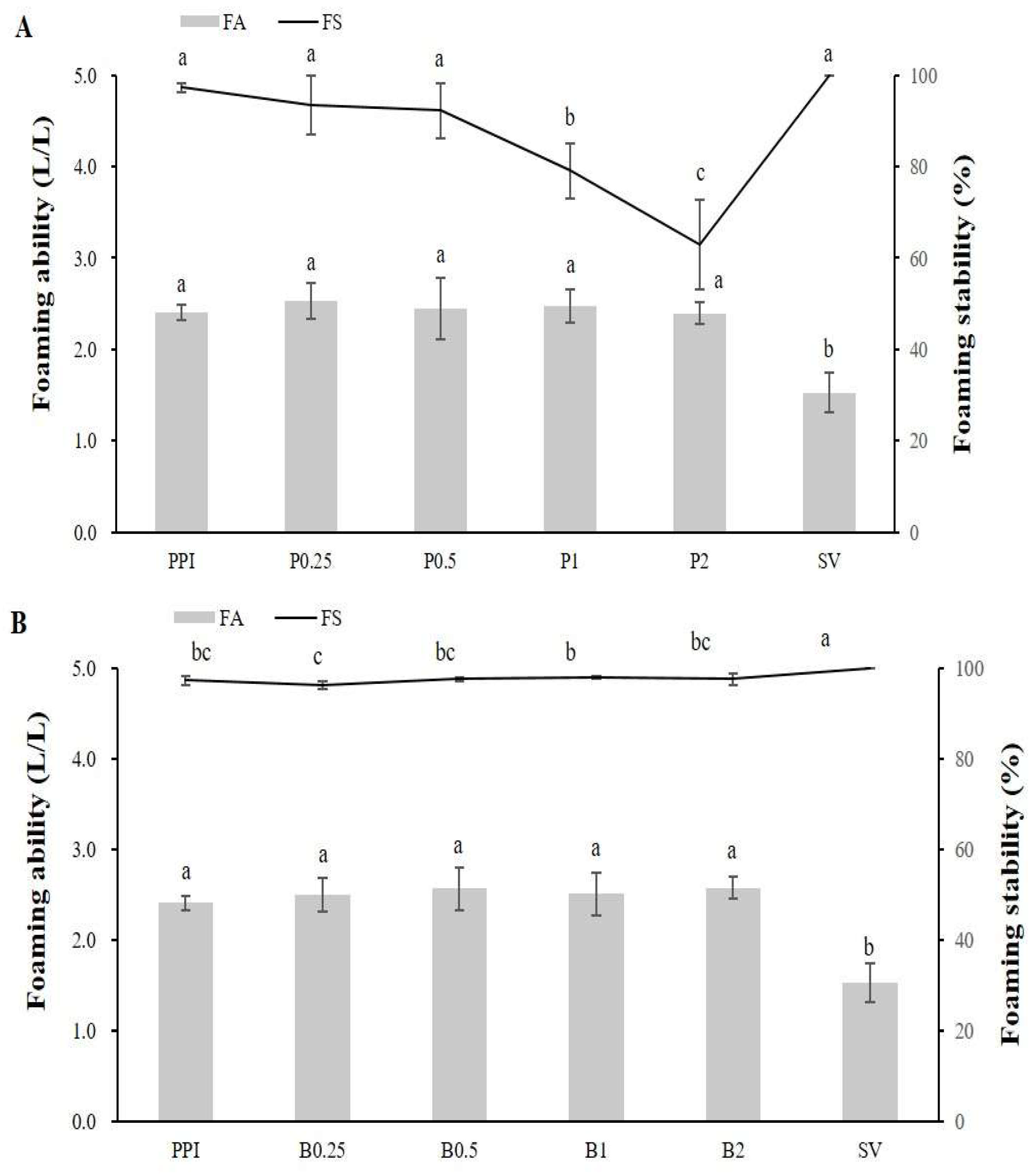
2.2.7. Foaming Ability and Stability
2.3. Emulsion Preparation and Characterization
2.3.1. Emulsion Preparation
2.3.2. Emulsion Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsion Stability Index (ESI)
2.3.3. Particle Characteristics
2.3.4. Viscosity Measurement
2.3.5. Emulsion Morphology
2.4. Chiffon Rice Cake Preparation and Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrolysis Yields, Degrees of Hydrolysis, and Molecular Weights of PPI and PPHs
3.2. Protein Solubility, Antioxidant Capacity, Foaming Stability, and Foaminging Ability
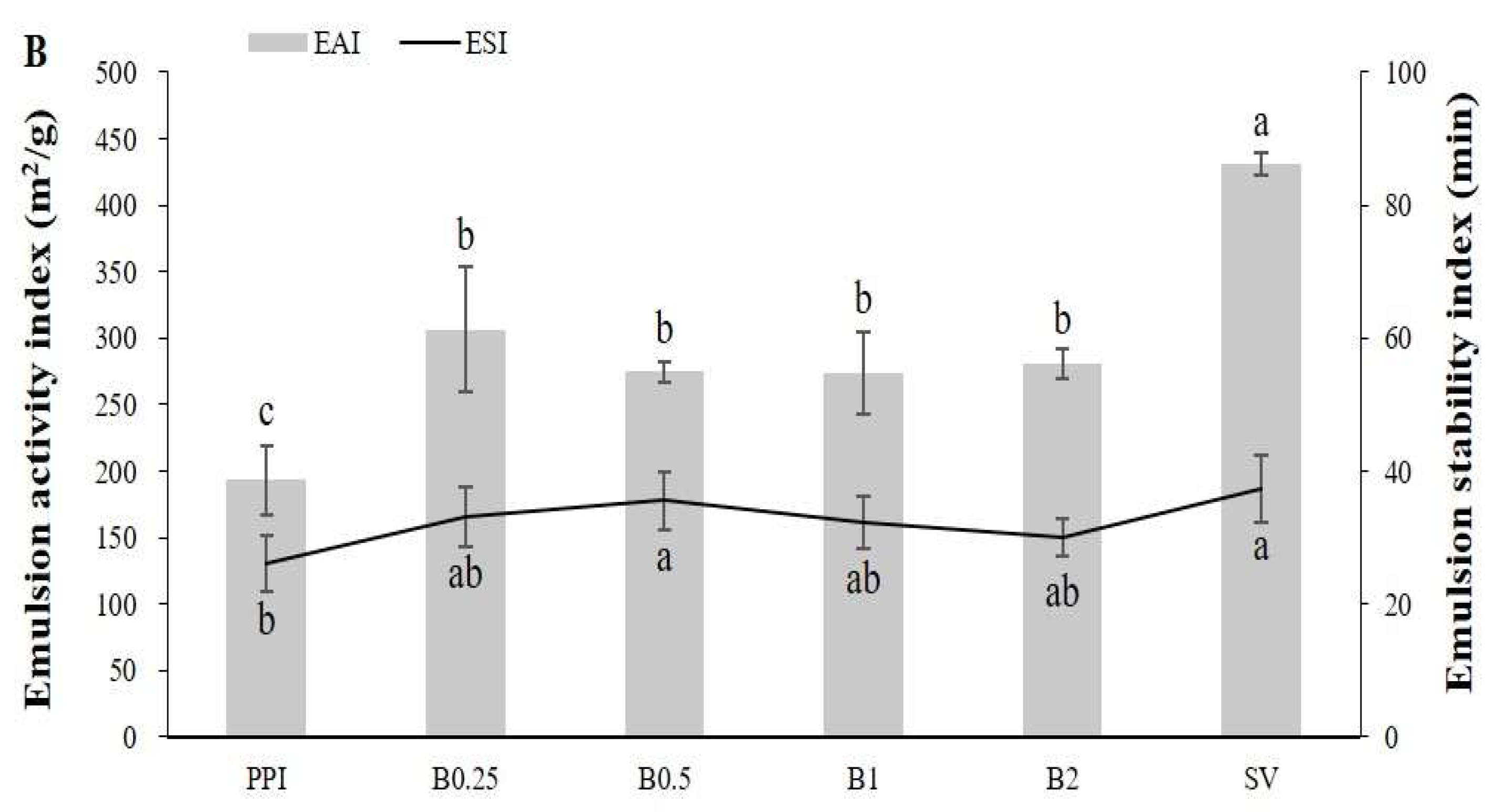
3.3. Emulsion Activity, Stability, and Characteristics of the Emulsions
3.4. Chiffon Rice Cake Batter Characteristics, Baking Performance, and Texture Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. The science of plant-based foods: Constructing next-generation meat, fish, milk, and egg analogs. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4049–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waqas, M.S.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Hussain, S.; Ullah, M.K.; Iqbal, M.M. Delayed irrigation: An approach to enhance crop water productivity and to investigate its effects on potato yield and growth parameters. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuszewska, B.; Tuśnio, A.; Taciak, M.; Mazurczyk, W. Variability in the composition of potato protein concentrate produced in different starch factories—A preliminary Survey. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2009, 154, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.; Bauw, G.; Welinder, K.G. Molecular properties and activities of tuber proteins from starch potato cv. Kuras. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9389–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, J.; Bártová, V. Patatin, the major protein of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers, and its occurrence as genotype effect: Processing versus table potatoes. Czech J. Food Sci. 2008, 26, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Qayum, A.; Xiuxiu, Z.; Liu, L.; Hussain, K.; Yue, P.; Yue, S.; Koko, M.Y.; Hussain, A.; Li, X. Potato protein: An emerging source of high quality and allergy-free protein, and its possible future-based products. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.H.; Kim, S.J.; Shimada, K.I.; Hashimoto, N.; Yamauchi, H.; Fukushima, M. Purple potato flake reduces serum lipid profile in rats fed a cholesterol-rich diet. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Behiry, S.I.; Younes, H.A.; Ashmawy, N.A.; Salem, M.Z.; Márquez-Molina, O.; Barbosa-Pilego, A. Antibacterial activity of three essential oils and some monoterpenes against Ralstonia solanacearum phylotype II isolated from potato. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuraiban, G.S.; Pertiwi, K.; Stamler, J.; Chan, Q.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Van Horn, L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Elliott, P.; Griep, L.M.O.; INTERMAP Research Group. Potato consumption, by preparation method and meal quality, with blood pressure and body mass index: The INTERMAP study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3042–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Guan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yang, X. Effect of cutting styles on quality, antioxidant activity, membrane lipid peroxidation, and browning in fresh-cut potatoes. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA GRAS. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/food-allergies (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Ralet, M.C.; Guéguen, J. Fractionation of potato proteins: Solubility, thermal coagulation and emulsifying properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, J.; Bártová, V.; Zdráhal, Z.; Sedo, O. Cultivar variability of patatin biochemical characteristics: Table versus processing potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4369–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, A.K.; Knorr, D. Influence of high isostatic pressure on structural and functional characteristics of potato protein. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Livney, Y.D. Potato protein-based nanovehicles for health-promoting hydrophobic bioactives in clear beverages. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Han, C.H.; Lee, M.H.; Hsu, F.L.; Hou, W.C. Patatin, the tuber storage protein of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), exhibits antioxidant activity in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koningsveld, G.A.; Walstra, P.; Voragen, A.G.; Kuijpers, I.J.; Van Boekel, M.A.; Gruppen, H. Effects of protein composition and enzymatic activity on formation and properties of potato protein stabilized emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6419–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waglay, A.; Karboune, S.; Alli, I. Potato protein isolates: Recovery and characterization of their properties. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn-Stoll, U.; Archut, A.; Eichhorn, M.; Kastner, H. Pectin-plant protein systems and their application. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Rao, G.N.; Rao, D.G.; Jyothirmayi, T. Protein hydrolysates from meriga (Cirrhinus mrigala) egg and evaluation of their functional properties. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.H.; Martin, A.M.; Saker-Sampaio, S.; Omar, S.; Goncalves, R.C. Studies on the enzymatic hydrolysis of Brazilian lobster (Panulirus spp.) processing wastes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1995, 69, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, F.M.; Martin, A.M. Optimization of nitrogen recovery in the enzymatic hydrolysis of dogfish (Squalus acanthias) protein. Composition of the hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 48, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Rasco, B.A. Fish protein hydrolysates: Production, biochemical, and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 43–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, S.D.A.; Martins, V.G.; Salas-Mellado, M.; Prentice, C. Evaluation of functional properties in protein hydrolysates from bluewing searobin (Prionotus punctatus) obtained with different microbial enzymes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavano, O.L. Protein hydrolysis using proteases: An important tool for food biotechnology. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzymatic 2013, 90, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.W.; Tang, C.H.; Wen, Q.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Li, L. Functional properties and in vitro trypsin digestibility of red kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolate: Effect of high-pressure treatment. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, X.Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate by various proteases and antioxidant properties of the resulting hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, M.; Yang, B.; Long, X.; Ren, J.; Zhao, H. Effects of limited proteolysis and high-pressure homogenisation on structural and functional characteristics of glycinin. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Kalapathy, U. Solubility and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolates modified by pancreatin. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Vij, S.; Hati, S. Functional significance of bioactive peptides derived from soybean. Peptides 2014, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Ramírez-Suarez, J.C.; Yada, R.Y. Plant proteases for bioactive peptides release: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, G.; Castillo, M.; Xiong, Y.L.; Álvarez, D.; Payne, F.A.; Garrido, M.D. Antioxidant and emulsifying properties of alcalase-hydrolyzed potato proteins in meat emulsions with different fat concentrations. Meat Sci. 2009, 83, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, N.; Mohammadzadeh Milani, J.; Biparva, P. Functional and conformational properties of proteolytic enzyme-modified potato protein isolate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Jin, J.D.; Chang, H.L.; Huang, K.C.; Chiang, Y.F.; Hsia, S.M. Physicochemical and antioxidative characteristics of potato protein isolate hydrolysate. Molecules 2020, 25, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, Z.I.M.; Amid, A.; Yusof, F.; Jaswir, I.; Ahmad, K.; Loke, S.P. Bromelain: An overview of industrial application and purification strategies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7283–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafid, K.; John, J.; Sayah, T.M.; Domínguez, R.; Becila, S.; Lamri, M.; Dib, A.L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gagaoua, M. One-step recovery of latex papain from Carica papaya using three-phase partitioning and its use as milk-clotting and meat-tenderizing agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamboya, E.A.F.; Amri, E. Papain, a plant enzyme of biological importance: A review. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, R.S.; Nickerson, M.T. Food proteins: A review on their emulsifying properties using a structure-function approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Advanced properties of gluten-free cookies, cakes, and crackers: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the structural, rheological, emulsifying and gelling properties of insoluble potato protein isolates. Ultrason. Sonochem 2022, 85, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Xiong, H. Structure, interfacial adsorption and emulsifying properties of potato protein isolate modified by chitosan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 638, 128314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Antioxidant and emulsifying properties of potato protein hydrolysate in soybean oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisaki, M. Egg-Free, Dairy-Free, Gluten-Free Safe Desserts; Liangpin Culture: Taipei, Taiwan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sangnark, A.; Noomhorm, A. Effect of particle sizes on functional properties of dietary fibre prepared from sugarcane bagasse. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, A.; Anagnostara, I.; Bezati, G.; Rizou, T.; Pavlidou, E.; Vouvoudi, E.; Kiosseoglou, V. Water extraction residue from maize milling by-product as a potential functional ingredient for the enrichment with fibre of cakes. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fan, F.; Wu, D.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Antioxidant and ACE inhibitory activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from Ruditapes philippinarum. Molecules 2018, 23, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachmann, E.; Nobis, V.; Kulozik, U.; Dombrowski, J. Surface and foaming properties of potato proteins: Impact of protein concentration, pH value and ionic strength. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbogouri, G.A.; Linder, M.; Fanni, J.; Parmentier, M. Influence of hydrolysis degree on the functional properties of salmon byproducts hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, C615–C622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, Z.; Sayyed-Alangi, S.Z.; Najafian, L. Effects of enzyme type and process time on hydrolysis degree, electrophoresis bands and antioxidant properties of hydrolyzed proteins derived from defatted Bunium persicum Bioss. Press Cake. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbroggio, M.F.; Montilha, M.S.; Figueiredo, V.R.G.; Georgetti, S.R.; Kurozawa, L.E. Influence of the degree of hydrolysis and type of enzyme on antioxidant activity of okara protein hydrolysates. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdar, S.N.; Rajalakshmi, V.; Pednekar, M.D.; Juan, F.; Yardi, V.; Sharma, A. Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant activity and ACE inhibitory activity of peanut protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intarasirisawat, R.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Wu, J. Antioxidative and functional properties of protein hydrolysate from defatted skipjack (Katsuwonous pelamis) roe. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagliani, L.; Silva, J.V.; Saffon, M.; Dombrowski, J. On the foaming properties of plant proteins: Current status and future opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Structure-modification by moderate oxidation in hydroxyl radical-generating systems promote the emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate. Food Struct. 2015, 6, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xue, S.W.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.L.; Bai, Y.H. Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve emulsifying properties of chicken myofibrillar protein and enhance the rheological properties and stability of the emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenke, K.D. Enzyme and chemical modification of proteins. In Food Proteins and Their Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; p. 395. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, S.K.; Saisivam, S.; Debanth, M.; Omri, A. Development and evaluation of chitosan nanoparticles based dry powder inhalation formulations of Prothionamide. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuacharoen, T.; Sabliov, C.M. Stability and controlled release of lutein loaded in zein nanoparticles with and without lecithin and pluronic F127 surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 503, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X. Oil density and viscosity affect emulsion stability and destabilization mechanism. J. Food Eng. 2024, 366, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiya, B.; Pongsawatmanit, R. Quality of batter and sponge cake prepared from wheat-tapioca flour blends. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2011, 45, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Y. Mechanical properties, microstructure, and in vitro digestion of transglutaminase-crosslinked whey protein and potato protein hydrolysate composite gels. Foods 2023, 12, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Yield (%) | |
|---|---|
| P0.25 | 29.21 ± 4.96 bc |
| P0.5 | 28.65 ± 3.31 c |
| P1 | 31.68 ± 0.09 bc |
| P2 | 34.88 ± 2.73 b |
| P4 | 41.30 ± 1.47 a |
| B0.25 | 11.58 ± 2.32 e |
| B0.5 | 14.50 ± 3.03 e |
| B1 | 15.36 ± 4.94 e |
| B2 | 16.99 ± 0.14 de |
| B4 | 21.64 ± 4.16 d |
| Z-Average (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPI | 1205 ± 34.28 d | 0.701 ± 0.036 a | −5.48 ± 0.48 f |
| P0.25 | 954 ± 64.63 e | 0.612 ± 0.024 bc | −8.71 ± 0.47 b |
| P0.5 | 944 ± 97.42 e | 0.662 ± 0.008 ab | −7.75 ± 0.25 bcd |
| P1 | 1125 ± 36.25 d | 0.645 ± 0.032 ab | −7.07 ± 0.32 de |
| P2 | 1192 ± 30.92 d | 0.649 ± 0.023 ab | −7.66 ± 0.65 bcde |
| B0.25 | 1203 ± 46.87 d | 0.557 ± 0.002 c | −8.28 ± 0.17 bc |
| B0.5 | 1272 ± 97.17 cd | 0.614 ± 0.109 bc | −7.31 ± 0.64 cde |
| B1 | 1662 ± 86.49 b | 0.620 ± 0.049 abc | −6.69 ± 0.38 e |
| B2 | 1406 ± 158.0 c | 0.628 ± 0.018 abc | −8.00 ± 0.41 bcd |
| SV | 1851 ± 50.15 a | 0.620 ± 0.037 abc | −10.01 ± 0.60 a |
| 1 s−1 | 10 s−1 | 20 s−1 | 40 s−1 | 60 s−1 | 80 s−1 | 100 s−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPI | 152 ± 40.69 bc | 24.20 ± 6.52 ab | 14.85 ± 4.80 ab | 9.43 ± 2.14 ab | 6.63 ± 1.77 ab | 5.09 ± 1.11 ab | 4.26 ± 0.85 a |
| P0.25 | 0.18 ± 0.03 d | 0.16 ± 0.02 c | 0.13 ± 0.02 c | 0.11 ± 0.04 c | 0.09 ± 0.05 c | 0.09 ± 0.03 d | 0.08 ± 0.03 d |
| P0.5 | 0.12 ± 0.09 d | 0.10 ± 0.05 c | 0.09 ± 0.04 c | 0.08 ± 0.03 c | 0.06 ± 0.03 c | 0.06 ± 0.02 d | 0.06 ± 0.02 d |
| P1 | 0.20 ± 0.02 d | 0.17 ± 0.01 c | 0.14 ± 0.00 c | 0.13 ± 0.01 c | 0.11 ± 0.01 c | 0.10 ± 0.01 d | 0.10 ± 0.01 d |
| P2 | 0.21 ± 0.03 d | 0.18 ± 0.02 c | 0.17 ± 0.02 c | 0.14 ± 0.01 c | 0.12 ± 0.01 c | 0.11 ± 0.00 d | 0.10 ± 0.00 d |
| B0.25 | 97.82 ± 56.08 cd | 14.24 ± 7.12 bc | 7.54 ± 4.02 bc | 3.91 ± 1.51 c | 2.70 ± 1.36 c | 2.22 ± 0.86 cd | 1.89 ± 0.81 cd |
| B0.5 | 98.06 ± 58.50 cd | 13.67 ± 5.76 bc | 7.49 ± 3.75 bc | 5.04 ± 1.34 bc | 3.46 ± 1.70 bc | 2.76 ± 0.53 bc | 2.22 ± 0.40 bc |
| B1 | 277 ± 93.00 a | 37.42 ± 11.00 a | 20.39 ± 5.71 a | 10.44 ± 3.64 a | 7.38 ± 2.46 a | 5.47 ± 1.73 a | 4.61 ± 1.43 a |
| B2 | 248 ± 48.48 ab | 32.02 ± 5.70 a | 17.87 ± 3.20 a | 9.09 ± 1.25 ab | 6.54 ± 1.33 ab | 4.81 ± 0.73 ab | 3.97 ± 0.67 ab |
| SV | 204 ± 97.82 abc | 33.54 ± 10.50 a | 19.45 ± 5.76 a | 9.93 ± 2.65 ab | 7.41 ± 2.37 a | 5.97 ± 1.47 a | 5.23 ± 1.14 a |
| Batter Density (g/cm3) | Specific Volume (mL/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| PPI | 0.451 ± 0.017 a | 3.21 ± 0.42 a |
| P0.25 | 0.429 ± 0.012 ab | 3.36 ± 0.25 a |
| P0.5 | 0.423 ± 0.015 ab | 3.25 ± 0.11 a |
| P1 | 0.422 ± 0.020 ab | 3.73 ± 0.46 a |
| P2 | 0.419 ± 0.012 b | 3.38 ± 0.59 a |
| B0.25 | 0.398 ± 0.011 b | 3.14 ± 0.10 a |
| B0.5 | 0.405 ± 0.020 b | 3.16 ± 0.18 a |
| B1 | 0.421 ± 0.013 b | 3.71 ± 0.48 a |
| B2 | 0.420 ± 0.020 b | 3.62 ± 0.13 a |
| SV | 0.422 ± 0.011 ab | 3.37 ± 0.24 a |
| Hardness (N) | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Resilience | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPI | 0.49 ± 0.10 c | 0.777 ± 0.011 c | 0.763 ± 0.022 b | 0.262 ± 0.008 c |
| P0.25 | 0.70 ± 0.05 bc | 0.815 ± 0.026 b | 0.779 ± 0.012 ab | 0.278 ± 0.016 bc |
| P0.5 | 1.01 ± 0.30 a | 0.861 ± 0.002 a | 0.786 ± 0.002 ab | 0.317 ± 0.010 a |
| P1 | 0.77 ± 0.06 abc | 0.849 ± 0.013 a | 0.793 ± 0.019 a | 0.307 ± 0.006 a |
| P2 | 0.89 ± 0.20 ab | 0.853 ± 0.013 a | 0.797 ± 0.012 a | 0.304 ± 0.004 a |
| B0.25 | 0.91 ± 0.10 ab | 0.848 ± 0.022 a | 0.782 ± 0.007 ab | 0.301 ± 0.016 ab |
| B0.5 | 0.83 ± 0.08 ab | 0.855 ± 0.007 a | 0.784 ± 0.002 ab | 0.306 ± 0.010 a |
| B1 | 0.73 ± 0.21 abc | 0.841 ± 0.032 ab | 0.789 ± 0.005 ab | 0.302 ± 0.027 ab |
| B2 | 0.81 ± 0.13 ab | 0.850 ± 0.003 a | 0.787 ± 0.008 ab | 0.314 ± 0.011 a |
| SV | 0.89 ± 0.11 ab | 0.866 ± 0.016 a | 0.792 ± 0.008 a | 0.320 ± 0.010 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, W.-C.; Tan, C.-X.; Lai, P.-H.; Wang, S.-T.; Chiou, T.-Y.; Lee, W.-J. Enhancing the Functional and Emulsifying Properties of Potato Protein via Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Papain and Bromelain for Gluten-Free Cake Emulsifiers. Foods 2025, 14, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060978
Sung W-C, Tan C-X, Lai P-H, Wang S-T, Chiou T-Y, Lee W-J. Enhancing the Functional and Emulsifying Properties of Potato Protein via Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Papain and Bromelain for Gluten-Free Cake Emulsifiers. Foods. 2025; 14(6):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060978
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Wen-Chieh, Chui-Xuan Tan, Pei-Hsuan Lai, Shang-Ta Wang, Tai-Ying Chiou, and Wei-Ju Lee. 2025. "Enhancing the Functional and Emulsifying Properties of Potato Protein via Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Papain and Bromelain for Gluten-Free Cake Emulsifiers" Foods 14, no. 6: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060978
APA StyleSung, W.-C., Tan, C.-X., Lai, P.-H., Wang, S.-T., Chiou, T.-Y., & Lee, W.-J. (2025). Enhancing the Functional and Emulsifying Properties of Potato Protein via Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Papain and Bromelain for Gluten-Free Cake Emulsifiers. Foods, 14(6), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060978





