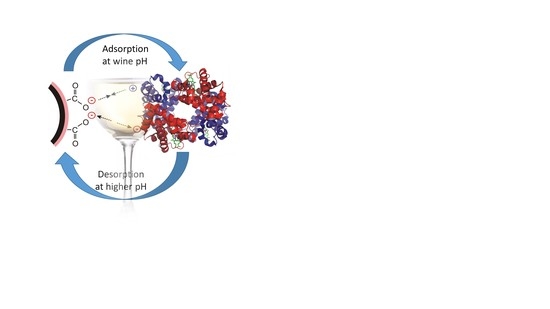
Regeneration of Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in the Removal of Pathogenesis-Related Proteins from White Wines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wines
2.2. Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.3. Adsorption and Desorption of Haze-Forming Proteins in Wine by Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.4. Wine Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Protein Content in Wines before and after Treatment with Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.2. Effect of Magnetic Nanoparticles on Metal Content
3.3. Desorption of Wine Proteins from Magnetic Nanoparticle Surface as a Function of the Cleaning Solvent and Wash Cycle
3.4. Effect of the Cleaning Solvent Used for Regeneration on Performance of MNPs in Wine Protein Removal
3.5. Phenolic Composition of the Wines
3.6. Concentration of Organic Acids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrasco, A.; Siebert, K.J. Human visual perception of haze and relationships with instrumental measurements of turbidity. Thresholds, magnitude estimation and sensory descriptive analysis of haze in model systems. Food Qual. Prefer. 1999, 10, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, J. Human Visual Perception of Haze in White Wine and Model Solutions and Relationships with Instrumental Turbidity and Imaging Models. Master’s Thesis, Lincoln University, Lincoln, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, E.J.; Shirley, N.J.; Williams, P.J. Nuisance proteins of wine are grape pathogenesis-related proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, E.J.; Alexander, G.; Muhlack, R.; Pocock, K.F.; Colby, C.; O’Neill, B.K.; Hoj, P.B.; Jones, P. Preventing protein haze in bottled white wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2005, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, J. Flawless: Understanding Faults in Wine; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- DKT Driver Knowledge Tests. Available online: https://www.driverknowledgetests.com/resources/what-temperature-can-it-reach-inside-your-car-in-summer/ (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- Marangon, M.; Van Sluyter, S.C.; Haynes, P.A.; Waters, E.J. Grape and wine proteins: Their fractionation by hydrophobic interaction chromatography and identification by chromatographic and proteomic analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, M.; Van Sluyter, S.C.; Waters, E.J.; Menz, R.I. Structure of Haze Forming Proteins in White Wines: Vitis vinifera Thaumatin-Like Proteins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Høj, P.B.; Tattersall, D.B.; Adams, K.; Pocock, K.F.; Hayasaka, Y.; van Heeswijck, R.; Waters, E. The ’Haze Proteins’ of Wine-A Summary of Properties, Factors Affecting their Accumulation in grapes, and the Amount of Bentonite Required for their Removal from Wine. In Proceedings of the ASEV 50th Anniversary Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 19–23 June 2000; American Society of Enology and Viticulture: Davis, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall, D.B.; Pocock, K.F.; Hayasaka, Y.; Adams, K.; van Heeswijck, R.; Waters, E.J.; Høj, P.B. Pathogenesis related proteins-Their accumulation in grapes during berry growth and their involvement in white wine heat instability. Current knowledge and future perspectives in relation to winemaking practices. In Molecular Biology and Biotechnology of the Grapevine; Dordrecht, N., Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Majewski, P.; Barbalet, A.; Waters, E. $1 billion hidden cost of bentonite fining. Aust. N. Z. Grapegrow. Winemak. 2011, 569, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmento, M.R.; Oliveira, J.C.; Boulton, R.B. Selection of low swelling materials for protein adsorption from white wines. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, S.; Polesani, M.; Curioni, A. Removal of specific protein components by chitin enhances protein stability in a white wine. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2005, 56, 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- Esti, M.; Benucci, I.; Liburdi, K.; Garzillo, A.M. Effect of wine inhibitors on free pineapple stem bromelain activity in a model wine system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3391–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, M.; Lucchetta, M.; Duan, D.; Stockdale, V.J.; Hart, A.; Rogers, P.J.; Waters, E.J. Protein removal from a chardonnay juice by addition of carrageenan and pectin. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2012, 18, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, M.; Van Sluyter, S.C.; Robinson, E.M.C.; Muhlack, R.A.; Holt, H.E.; Haynes, P.A.; Godden, P.W.; Smith, P.A.; Waters, E.J. Degradation of white wine haze proteins by aspergillopepsin i and ii during juice flash pasteurization. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocock, K.F.; Hoj, P.B.; Adams, K.S.; Kwiatkowski, M.J.; Waters, E.J. Combined heat and proteolytic enzyme treatment of white wines reduces haze forming protein content without detrimental effect. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2003, 9, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierczynska-Vasilev, A.; Boyer, P.; Vasilev, K.; Smith, P.A. A novel technology for the rapid, selective, magnetic removal of pathogenesis-related proteins from wines. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierczynska-Vasilev, A.; Mierczynski, P.; Maniukiewicz, W.; Visalakshan, R.M.; Vasilev, K.; Smith, P.A. Magnetic separation technology: Functional group efficiency in the removal of haze-forming proteins from wines. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierczynska-Vasilev, A.; Wahono, S.K.; Smith, P.A.; Bindon, K.; Vasilev, K. Using zeolites to protein stabilize white wines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12240–12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, M.; Lucchetta, M.; Waters, E.J. Protein stabilisation of white wines using zirconium dioxide enclosed in a metallic cage. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2011, 17, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss, C.; Cuénat, P. Stabilisation tartrique des vins par traitement aux zéolithes. Revue Suisse Vitic. Arboric. Hortic. 2005, 37, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Ibanez, J.G.; Carreon-Alvarez, A.; Barcena-Soto, M.; Casillas, N. Metals in alcoholic beverages: A review of sources, effects, concentrations, removal, speciation, and analysis. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2008, 21, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, F.; Grass, S.; Umanskaya, N.; Scheibe, C.; Müller-Renno, C.; Davoudi, N.; Hannig, M.; Ziegler, C. Cleaning of biomaterial surfaces: Protein removal by different solventsfabian. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierczynska, A.; Michelmore, A.; Tripathi, A.; Goreham, R.V.; Sedev, R.; Vasilev, K. Ph-Tunable gradients of wettability and surface potential. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 8399–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, H.; Boyes, S.; Keene, J.; Heatherbell, D. Protein instability of wines-influence of protein isoelectric point. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1994, 45, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio, M.D.; Dambergs, R.G.; Herderich, M.J.; Smith, P.A. High throughput analysis of red wine and grape phenolics-adaptation and validation of methyl cellulose precipitable tannin assay and modified somers color assay to a rapid 96 well plate format. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4651–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verette, E.; Noble, A.C.; Somers, T.C. Hydroxycinnamates of vitis-vinifera: Sensory assessment in relation to bitterness in white wines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1988, 45, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element (mg/L) * | Control SAB (pH 3.39) | SAB + Bare MNPs | SAB + AcrA/MNPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | 829 ± 50 a | 86 ± 15 b | 84 ± 16 b |
| Ca | 53 ± 5 a | <30 b | <30 b |
| Mg | 94 ± 5 a | <50 b | <50 b |
| Na | 19 ± 1 a | <10 b | <10 b |
| Mn | 1.4 ± 0.2 c | 3.2 ± 0.5 b | 4.4 ± 0.8 a |
| Cu | <0.1 a | 0.1 a | 0.1 a |
| Zn | 0.89 ± 0.1 a | 0.32 ± 0.2 b | 0.31 ± 0.1 b |
| Fe | 0.6 ± 0.2 b | 0.9 ± 0.5 a | 0.8 ± 0.2 a |
| Sr | 1.43 ± 0.3 a | 0.16 ± 0.1 b | 0.15 ± 0.1 b |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mierczynska-Vasilev, A.; Qi, G.; Smith, P.; Bindon, K.; Vasilev, K. Regeneration of Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in the Removal of Pathogenesis-Related Proteins from White Wines. Foods 2020, 9, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010001
Mierczynska-Vasilev A, Qi G, Smith P, Bindon K, Vasilev K. Regeneration of Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in the Removal of Pathogenesis-Related Proteins from White Wines. Foods. 2020; 9(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMierczynska-Vasilev, Agnieszka, Geridi Qi, Paul Smith, Keren Bindon, and Krasimir Vasilev. 2020. "Regeneration of Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in the Removal of Pathogenesis-Related Proteins from White Wines" Foods 9, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010001
APA StyleMierczynska-Vasilev, A., Qi, G., Smith, P., Bindon, K., & Vasilev, K. (2020). Regeneration of Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in the Removal of Pathogenesis-Related Proteins from White Wines. Foods, 9(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010001