1H NMR Spectroscopy to Characterize Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oil Blends, Using Statistical Models and Databases Based on Monocultivar Reference Oils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation for NMR Analyses
2.3. Acquisition and Processing of 1H NMR Spectra
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis Applied to NMR Spectroscopy Data
3. Results and Discussion
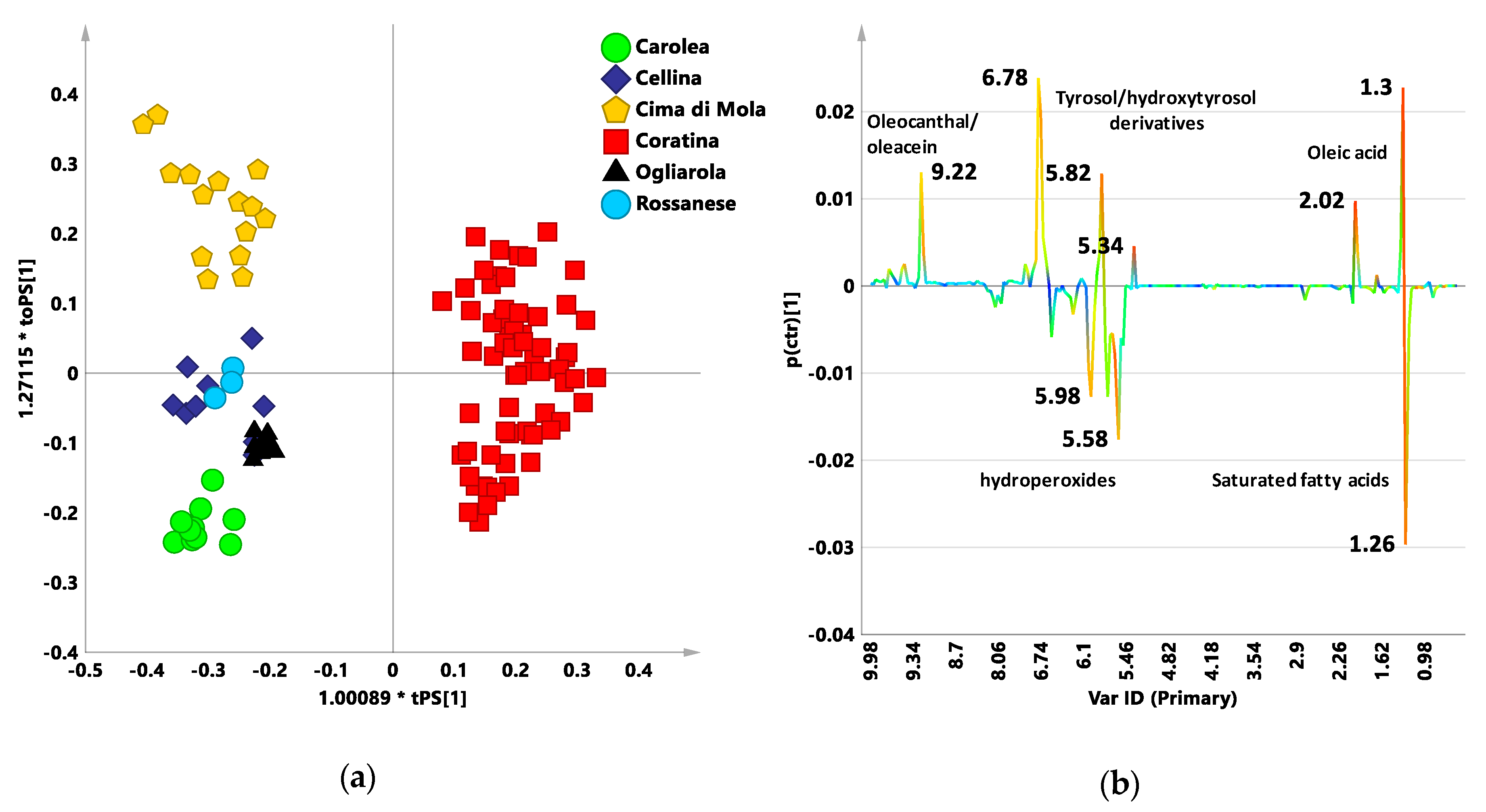
3.1. New Reference Model: PLS-DA Analysis
3.1.1. 2016/2017 Harvesting Year
3.1.2. 2017/2018 Harvesting Year
3.1.3. 2018/2019 Harvesting Year
3.1.4. 2019/2020 Harvesting Year
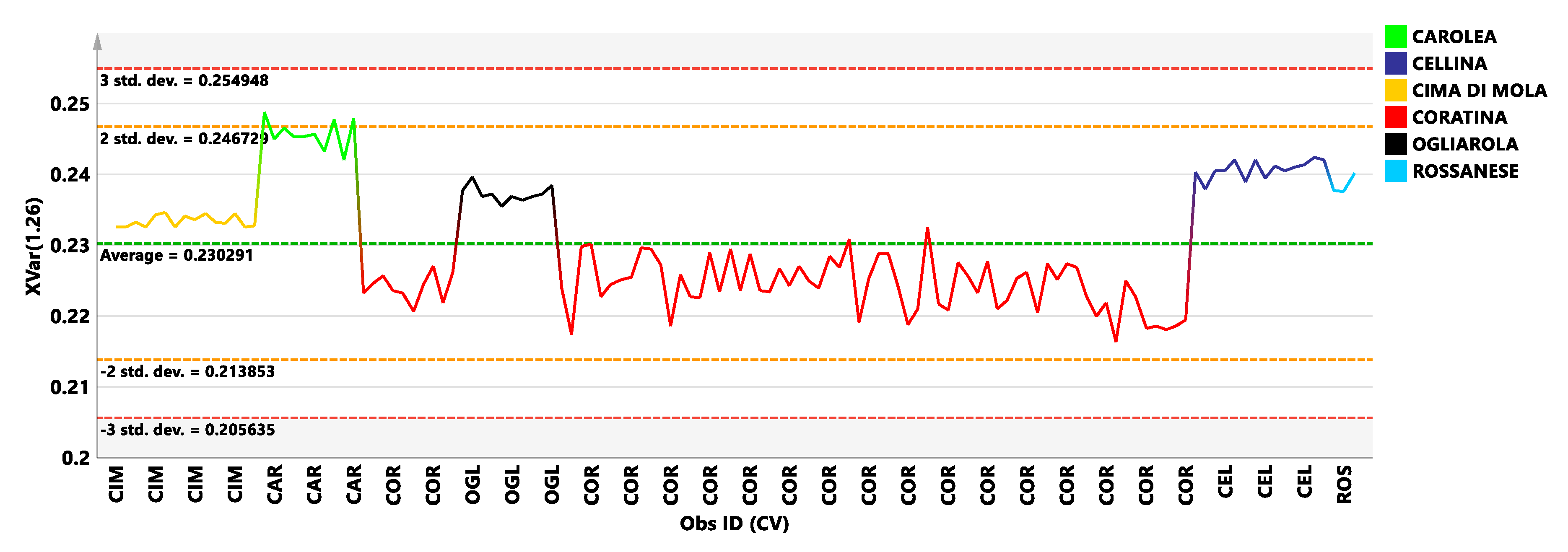
3.2. Coratina vs. Sweetners Cultivars: OPLS-DA Pairwise Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Monaco, G.; Officioso, A.; D’Angelo, S.; La Cara, F.; Ionata, E.; Marcolongo, L.; Squillaci, G.; Maurelli, L.; Morana, A. Characterization of extra virgin olive oils produced with typical Italian varieties by their phenolic profile. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Q. Determination of adulteration content in extra virgin olive oil using FT-NIR spectroscopy combined with the BOSS–PLS algorithm. Molecules 2019, 24, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cicerale, S.; Lucas, L.; Keast, R. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory phenolic activities in extra virgin olive oil. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISMEA. Istituto di Servizi per il Mercato Agricolo Alimentare. scheda_di_settore_OLIO_aprile_2020. Available online: http://www.ismeamercati.it/olio-oliva (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Piarulli, L.; Savoia, M.A.; Taranto, F.; D’Agostino, N.; Sardaro, R.; Girone, S.; Gadaleta, S.; Fucili, V.; De Giovanni, C.; Montemurro, C. A Robust DNA Isolation Protocol from Filtered Commercial Olive Oil for PCR-Based Fingerprinting. Foods 2019, 8, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R. NMR Studies on Italian PDO Olive Oils and their Potential in Olive-Tree-Derived Products Characterization. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Community. Commission Regulation (EC) No 182/2009 of 6 March 2009 amending Regulation (EC) No 1019/2002 on marketing standards for olive oil. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 63, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- European Community. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 29/2012 of 13 January 2012 on marketing standards for olive oil. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, 12, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- El Riachy, M.; Bou-Mitri, C.; Youssef, A.; Andary, R.; Skaff, W. Chemical and sensorial characteristics of olive oil produced from the Lebanese olive variety ‘Baladi’. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Coco, L.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P. NMR-metabolomic study on monocultivar and blend salento EVOOs including some from secular olive trees. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Coco, L.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis of monovarietal EVOOs as a tool for modulating Coratina-based blends. Foods 2014, 3, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis as possible tool to assess cultivars, from specific geographical areas, in EVOOs. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Papadia, P.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P. Harvest year effects on Apulian EVOOs evaluated by 1H NMR based metabolomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Zelasco, S.; Salimonti, A.; Conforti, F.L.; Biagianti, A.; Barbini, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. Traceability of “Tuscan PGI” extra virgin olive oils by 1H NMR metabolic profiles collection and analysis. Metabolites 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.P. High resolution NMR characterization of olive oils in terms of quality, authenticity and geographical origin. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongai, D.; Sabatini, N.; Del Coco, L.; Perri, E.; Del Re, P.; Simone, N.; Marchegiani, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR and multivariate analysis for geographic characterization of commercial extra virgin olive oil: A possible correlation with climate data. Foods 2017, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacchi, R.; Mannina, L.; Fiordiponti, P.; Barone, P.; Paolillo, L.; Patumi, M.; Segre, A. Characterization of Italian extra virgin olive oils using 1H-NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3947–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.; Brescia, M.A.; Liuzzi, V.; Reniero, F.; Guillou, G.; Ghelli, S.; van der Meer, P. Characterization of Italian olive oils based on analytical and nuclear magnetic resonance determinations. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, M.a.D.; Ruiz, A. High resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance in the study of edible oils and fats. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, R.; Addeo, F.; Paolillo, L. 1H and 13C NMR of virgin olive oil. An overview. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1997, 35, S133–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahov, G. Application of NMR to the study of olive oils. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1999, 4, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.P.; Segre, A. Olive oil as seen by NMR and chemometrics. Spectrosc. Eur. 2003, 15, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- D’Imperio, M.; Mannina, L.; Capitani, D.; Bidet, O.; Rossi, E.; Bucarelli, F.M.; Quaglia, G.B.; Segre, A. NMR and statistical study of olive oils from Lazio: A geographical, ecological and agronomic characterization. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. Tunisian extra virgin olive oil traceability in the EEC market: Tunisian/Italian (Coratina) EVOOs blend as a case study. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghisoni, S.; Lucini, L.; Angilletta, F.; Rocchetti, G.; Farinelli, D.; Tombesi, S.; Trevisan, M. Discrimination of extra-virgin-olive oils from different cultivars and geographical origins by untargeted metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; D’Imperio, M.; Capitani, D.; Rezzi, S.; Guillou, C.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Vilchez, M.A.D.M.; Fernaández, A.H.; Thomas, F.; Aparicio, R. 1H NMR-based protocol for the detection of adulterations of refined olive oil with refined hazelnut oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11550–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Mondelli, D.; Mezzapesa, G.N.; Miano, T.; De Pascali, S.A.; Girelli, C.R.; Fanizzi, F.P. Protected Designation of Origin extra virgin olive oils assessment by nuclear magnetic resonance and multivariate statistical analysis: “Terra di Bari”, an Apulian (Southeast Italy) case study. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscopo, A.; De Bruno, A.; Zappia, A.; Ventre, C.; Poiana, M. Characterization of monovarietal olive oils obtained from mills of Calabria region (Southern Italy). Food Chem. 2016, 213, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanteri, S.; Armanino, C.; Perri, E.; Palopoli, A. Study of oils from Calabrian olive cultivars by chemometric methods. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarisi, C.; Di Stasio, M.; La Cara, F.; Nazzaro, M.; Siano, F.; Coppola, R.; Volpe, F.; De Mattia, A.; Grazia Volpe, M. Shelf-life of extra virgin olive oils from Southern Italy. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 10, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.E. A User’s Guide to Principal Components; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 587. [Google Scholar]
- Kettaneh, N.; Berglund, A.; Wold, S. PCA and PLS with very large data sets. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2005, 48, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triba, M.N.; Le Moyec, L.; Amathieu, R.; Goossens, C.; Bouchemal, N.; Nahon, P.; Rutledge, D.N.; Savarin, P. PLS/OPLS models in metabolomics: The impact of permutation of dataset rows on the K-fold cross-validation quality parameters. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, S.; Eriksson, L.; Trygg, J.; Kettaneh, N. The PLS Method–Partial Least Squares Projections to Latent Structures–and Its Applications in Industrial RDP (Research, Development, and Production); Umeå University: Umeå, Sweden, 2004; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chem. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccard, J.; Rutledge, D.N. A consensus orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) strategy for multiblock Omics data fusion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 769, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Byrne, T.; Johansson, E.; Trygg, J.; Vikström, C. Multi-and Megavariate Data Analysis Basic Principles and Applications; Umetrics Academy: Malmo, Sweden, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock, Å.M.; Wheelock, C.E. Trials and tribulations of ‘omics data analysis: Assessing quality of SIMCA-based multivariate models using examples from pulmonary medicine. Mol. BioSyst. 2013, 9, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barison, A.; Pereira da Silva, C.W.; Campos, F.R.; Simonelli, F.; Lenz, C.A.; Ferreira, A.G. A simple methodology for the determination of fatty acid composition in edible oils through 1H NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariello, M.; Contursi, A.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Piccinin, E.; De Santis, S.; Piglionica, M.; Spaziante, A.F.; Sabbà, C.; Villani, G.; Moschetta, A. Extra-Virgin Olive Oil from Apulian Cultivars and Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, A.A.; Gill, S.S.; Abbas, Z.K.; Naeem, M. Plant Biodiversity: Monitoring, Assessment and Conservation; CABI: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pacetti, D.; Scortichini, S.; Boarelli, M.C.; Fiorini, D. Simple and rapid method to analyse squalene in olive oils and extra virgin olive oils. Food Control 2019, 102, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favati, F.; Condelli, N.; Galgano, F.; Caruso, M.C. Extra virgin olive oil bitterness evaluation by sensory and chemical analyses. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, V.; Karkoula, E.; Magiatis, P.; Melliou, E.; Kotsiras, A.; Mouroutoglou, C. Correlation of Oleocanthal and Oleacein Concentration with Pungency and Bitterness in “Koroneiki“ Virgin olive oil. In Proceedings of the II International Symposium on Horticulture in Europe 1099, Angers, France, 25 September 2015; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Aracama, A.; Goicoechea, E.; Guillén, M.D. Direct study of minor extra-virgin olive oil components without any sample modification. 1H NMR multisupression experiment: A powerful tool. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of Samples | Cultivar | Origin | Harvesting Period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocultivar | 74 | Coratina | Apulia (Italy) | 2012/2013; 2013/2014 |
| 10 | Ogliarola Barese | Apulia (Italy) | 2012/2013; 2013/2014 | |
| 15 | Cima di Mola | Apulia (Italy) | 2013/2014 | |
| 10 | Carolea | Calabria (Italy) | 2012/2013; 2015/2016 | |
| 14 | Cellina di Nardò | Apulia (Italy) | 2012/2013 | |
| 3 | Rossanese | Calabria (Italy) | 2012/2013 | |
| 100% Italian BLEND | 38 | Ogliarola Barese + Coratina + Carolea + Cima di Mola + Rossanese + Cellina di Nardò | Apulia (Italy); Calabria (Italy) | 2016/2017 |
| 74 | Ogliarola Barese + Coratina + Carolea + Cima di Mola + Rossanese + Cellina di Nardò | Apulia (Italy); Calabria (Italy) | 2017/2018 | |
| 80 | Ogliarola Barese + Coratina + Carolea + Cima di Mola + Rossanese + Cellina di Nardò | Apulia (Italy); Calabria (Italy) | 2018/2019 | |
| 49 | Ogliarola Barese + Coratina + Carolea + Cima di Mola + Rossanese + Cellina di Nardò | Apulia (Italy); Calabria (Italy) | 2019/2020 |
| N° of Samples | Coratina | Ogliarola | Cima di Mola | Carolea | Cellina | Rossanese | Coratina & Cellina | No Class (Ypred ≤ 0.65) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| training set | Coratina | 74 | 74 | |||||||
| Ogliarola | 10 | 0 | 10 | |||||||
| Cima di Mola | 15 | 14 | 1 | |||||||
| Carolea | 10 | 10 | ||||||||
| Cellina | 14 | |||||||||
| Rossanese | 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| prediction set | 2016/2017 | 38 | 33 | 1 | 4 | |||||
| 2017/2018 | 74 | 63 | 11 | |||||||
| 2018/2019 | 80 | 24 | 20 | 17 | 19 | |||||
| 2019/2020 | 49 | 1 | 9 | 38 | 1 |
| NMR Experiment | N° of Samples | Coratina | Sweeteners | No Class (Ypred ≤ 0.65) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H zg | training set | Coratina | 74 | 74 | ||
| Sweeteners | 52 | 0 | 52 | |||
| prediction set | 100% Italian EVOO blends | 233 | 130 | 3 | 100 | |
| 1H noesygpps | training set | Coratina | 74 | 74 | ||
| Sweeteners | 52 | 0 | 52 | |||
| prediction set | 100% Italian EVOO blends | 233 | 80 | 9 | 144 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Girelli, C.R.; Calò, F.; Angilè, F.; Mazzi, L.; Barbini, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR Spectroscopy to Characterize Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oil Blends, Using Statistical Models and Databases Based on Monocultivar Reference Oils. Foods 2020, 9, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121797
Girelli CR, Calò F, Angilè F, Mazzi L, Barbini D, Fanizzi FP. 1H NMR Spectroscopy to Characterize Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oil Blends, Using Statistical Models and Databases Based on Monocultivar Reference Oils. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121797
Chicago/Turabian StyleGirelli, Chiara Roberta, Francesca Calò, Federica Angilè, Lucia Mazzi, Daniele Barbini, and Francesco Paolo Fanizzi. 2020. "1H NMR Spectroscopy to Characterize Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oil Blends, Using Statistical Models and Databases Based on Monocultivar Reference Oils" Foods 9, no. 12: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121797
APA StyleGirelli, C. R., Calò, F., Angilè, F., Mazzi, L., Barbini, D., & Fanizzi, F. P. (2020). 1H NMR Spectroscopy to Characterize Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oil Blends, Using Statistical Models and Databases Based on Monocultivar Reference Oils. Foods, 9(12), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121797








