Detection of Morphine and Opioids in Fingernails: Immunohistochemical Analysis and Confirmation with Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Matrices
2.1.2. Antibodies
2.1.3. Reagents for Immunohistochemistry
2.1.4. Chemicals and Reagents for UHPLC Analysis
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin Embedding
Antibody and Peroxidase Marking
2.2.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
Extraction Procedure in Nail and Hair Matrices
Acid Hydrolysis and Extraction Procedure in Blood Matrix
Derivatization
2.2.3. Hr-LC and GC-MS Parameters
Hair and Nail Analysis and Quantification by UHPLC-HRMS
Blood Analysis and Quantification by GC-MS
2.2.4. Validation
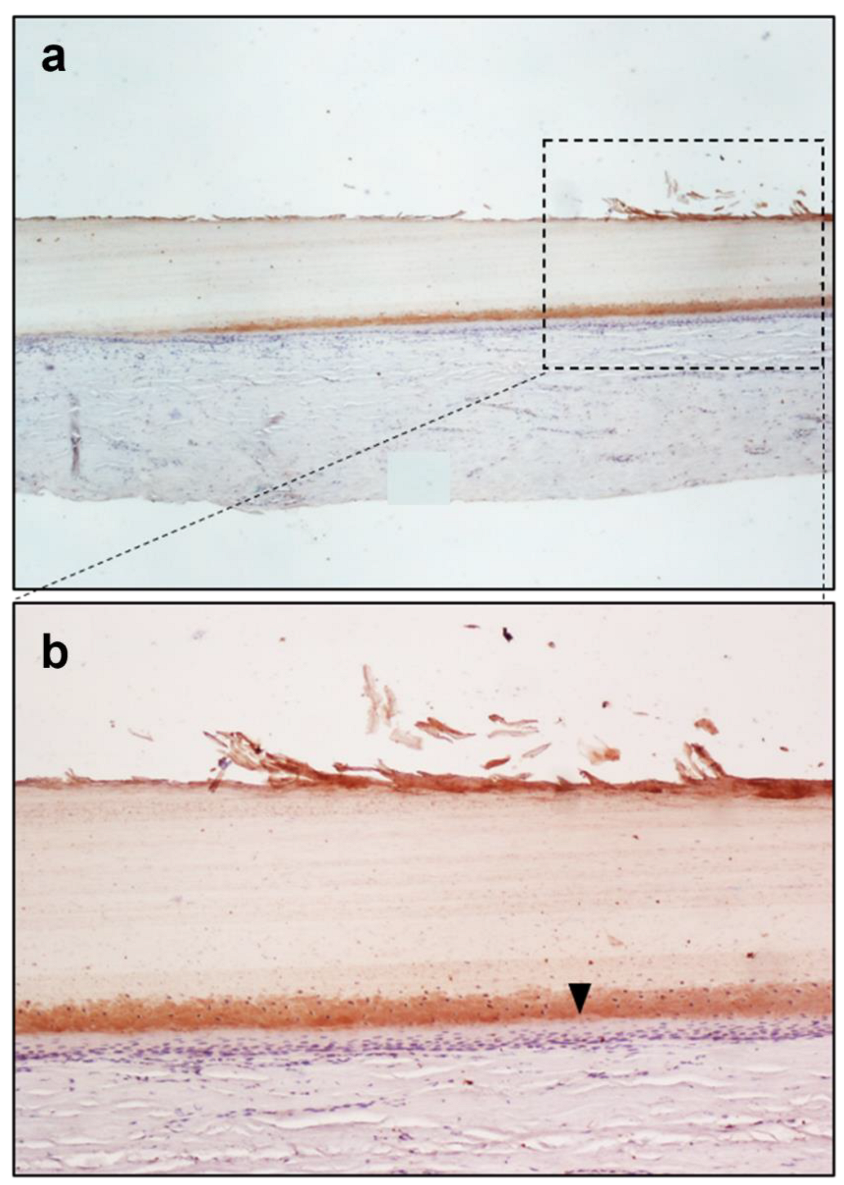
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumgartner, M.R. Nails: An adequate alternative matrix in forensic toxicology for drug analysis? Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2189–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeri, A.; Pichini, S.; Pacifici, R.; Zuccaro, P.; Lopez, A. Drugs in nails: Physiology, pharmacokinetics and forensic toxicology. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 38, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, I.; Jones, J.; Jones, M.; Lewis, D.; Negrusz, A. Detection of Drugs in Nails: Three Year Experience. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lesnikova, I.; Schreckenbach, M.N.; Kristensen, M.P.; Papanikolaou, L.L.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S. Usability of Immunohistochemistry in Forensic Samples with Varying Decomposition. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2018, 39, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.M.; Hao, C.Y.; Wang, L. An immunohistochemical study on the distribution in organs in cases with morphine poisoning. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 18, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, I.M.; Dimke, H.; Frische, S. A single simple procedure for dewaxing, hydration and heat-induced epitope retrieval (HIER) for immunohistochemistry in formalin fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Eur. J. Histochem. 2015, 59, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowe, A.R.; Yue, W. Semi-quantitative Determination of Protein Expression using Immunohistochemistry Staining and Analysis: An Integrated Protocol. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronstrand, R.; Forsman, M.; Roman, M. Quantitative analysis of drugs in hair by UHPLC high resolution mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 283, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassoni, G.; Cacaci, C.; Zampi, M.; Froldi, R. Bile analysis in heroin overdose. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 1405–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moffat, A.C.; Osselton, M.D.; Widdop, B.; Watts, J. Clarke’s Analysis of Drugs and Poisons, IV ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2011; Volume II, pp. 1734–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Cippitelli, M.; Mirtella, D.; Ottaviani, G.; Tassoni, G.; Froldi, R.; Cingolani, M. Toxicological Analysis of Opiates from Alternative Matrices Collected from an Exhumed Body. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 63, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Working Group for Forensic Toxicology. Scientific Working Group for Forensic Toxicology (SWGTOX) standard practices for method validation in forensic toxicology. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 452–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usagawa, T.; Itoh, Y.; Hifumi, E.; Takeyasu, A.; Nakahara, Y.; Uda, T. Characterization of morphine-specific monoclonal antibodies showing minimal cross-reactivity with codeine. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 157, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassoni, G.; Mirtella, D.; Zampi, M.; Ferrante, L.; Cippitelli, M.; Cognigni, E.; Froldi, R.; Cingolani, M. Hair analysis in order to evaluate drug abuse in driver’s license regranting procedures. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 244, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumba, V.A.; Ziavrou, K.S.; Vougiouklakis, T. Hair as a biological indicator of drug use, drug abuse or chronic exposure to environmental toxicants. Int. J. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryczynski, J.; Schwartz, R.P.; Mitchell, S.G.; O’Grady, K.E.; Ondersma, S.J. Hair drug testing results and self-reported drug use among primary care patients with moderate-risk illicit drug use. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 141, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harkey, M.R. Anatomy and physiology of hair. Forensic Sci. Int. 1993, 63, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Han, E.; In, S.; Choi, H.; Chung, H.; Chung, K.H. Analysis of pubic hair as an alternative specimen to scalp hair: A contamination issue. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 206, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Yang, W.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.; Kim, E.; Lim, M.; Chung, H. Correlation of methamphetamine results and concentrations between head, axillary, and pubic hair. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 147, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelle, D.; Yegles, M.; Neels, H.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Doncker, M.; Maudens, K.; Covaci, A.; Crunelle, C.L. Nail analysis for the detection of drugs of abuse and pharmaceuticals: A review. Forensic Toxicol. 2015, 33, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahs, A.B.; Bolla, S.R. Histology, Nail. In StatPearls 2021; StatPearls Publishing Copyright© 2021; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.H.; Kopan, R. Long-range, nonautonomous effects of activated Notch1 on tissue homeostasis in the nail. Dev. Biol. 2003, 263, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalasinsky, K.S.; Magluilo, J., Jr.; Schaefer, T. Study of drug distribution in hair by infrared microscopy visualization. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1994, 18, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gygi, S.P.; Joseph, R.E., Jr.; Cone, E.J.; Wilkins, D.G.; Rollins, D.E. Incorporation of codeine and metabolites into hair. Role of pigmentation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1996, 24, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perrin, C.; Michiels, J.F.; Boyer, J.; Ambrosetti, D. Melanocytes Pattern in the Normal Nail, With Special Reference to Nail Bed Melanocytes. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2018, 40, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, C.; Langbein, L.; Schweizer, J. Expression of hair keratins in the adult nail unit: An immunohistochemical analysis of the onychogenesis in the proximal nail fold, matrix and nail bed. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achten, G.; André, J.; Laporte, M. Nails in light and electron microscopy. Semin. Dermatol. 1991, 10, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett, A.; Spearman, R.I. The histochemistry of the human nail. Arch. Dermatol. 1966, 94, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, A.; Spearman, R.I.; Hardy, J.A. The histochemistry of keratinization. Br. J. Dermatol. 1959, 71, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.; Raul, J.S.; Ameline, A. The use of multiple keratinous matrices (head hair, axillary hair, and toenail clippings) can help narrowing a period of drug exposure: Experience with a criminal case involving 25I-NBOMe and 4-MMC. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| TIME | PHASE A (%) | PHASE B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–0.5 | 98 | 2 |
| 0.5–10 | 0 | 100 |
| 10–12 | 0 | 100 |
| 12–13 | 98 | 2 |
| 13–15 | 98 | 2 |
| Hair | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Substances | Linearity Range | R2 | LOQ(LOD) |
| Morphine | 0.05–5 (ng/mg) | 0.9933 | 0.05 (0.02) (ng/mg) |
| MAM | 0.05–5 (ng/mg) | 0.9897 | 0.05 (0.02) (ng/mg) |
| Nail | |||
| Morphine | 0.05–5(ng/mg) | 0.9942 | 0.05 (0.02) (ng/mg) |
| MAM | 0.05–5 (ng/mg) | 0.9853 | 0.05 (0.02) (ng/mg) |
| Blood | |||
| Morphine | 0.5–500 (ng/mL) | 0.9959 | 0.5 (0.2) (ng/mL) |
| Fingernail matrix | Area | Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Subject A (Figure 1) | 1,228,800 | 19.695 |
| Subject B (Figure 2) | 1,228,800 | 26.049 |
| Subject C (Figure 5) | 1,228,800 | 2.252 |
| Subject A matrix | Instrument | Morphine | 6-MAM | Codeine | Methadone | EDDP |
| Blood | GC-MS | 472 ng/ml | Negative | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Scalp hair | UHPLC | 3.64 ng/mg | 1.42 ng/mg | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Fingernail | UHPLC | 0.35 ng/mg | 0.43 ng/mg | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Subject B matrix | Instrument | Morphine | 6-MAM | Codeine | Methadone | EDDP |
| Blood | GC-MS | 360 ng/ml | Negative | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Pubic hair | UHPLC | 1.60 ng/mg | 0.44 ng/mg | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Fingernail | UHPLC | 1.23 ng/mg | 1.18 ng/mg | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Subject C matrix | Instrument | Morphine | 6-MAM | Codeine | Methadone | EDDP |
| Blood | GC-MS | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Pubic hair | UHPLC | 2.2 ng/mg | 4.43 ng/mg | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Fingernail | UHPLC | Negative | 1.03 ng/mg | Negative | Negative | Negative |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scendoni, R.; Bury, E.; Buratti, E.; Froldi, R.; Cippitelli, M.; Mietti, G.; Cingolani, M. Detection of Morphine and Opioids in Fingernails: Immunohistochemical Analysis and Confirmation with Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Toxics 2022, 10, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080420
Scendoni R, Bury E, Buratti E, Froldi R, Cippitelli M, Mietti G, Cingolani M. Detection of Morphine and Opioids in Fingernails: Immunohistochemical Analysis and Confirmation with Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Toxics. 2022; 10(8):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080420
Chicago/Turabian StyleScendoni, Roberto, Emanuele Bury, Erika Buratti, Rino Froldi, Marta Cippitelli, Gianmario Mietti, and Mariano Cingolani. 2022. "Detection of Morphine and Opioids in Fingernails: Immunohistochemical Analysis and Confirmation with Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Toxics 10, no. 8: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080420
APA StyleScendoni, R., Bury, E., Buratti, E., Froldi, R., Cippitelli, M., Mietti, G., & Cingolani, M. (2022). Detection of Morphine and Opioids in Fingernails: Immunohistochemical Analysis and Confirmation with Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Toxics, 10(8), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080420







