Adverse Effects of Toxic Metal Pollution in Rivers on the Physiological Health of Fish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
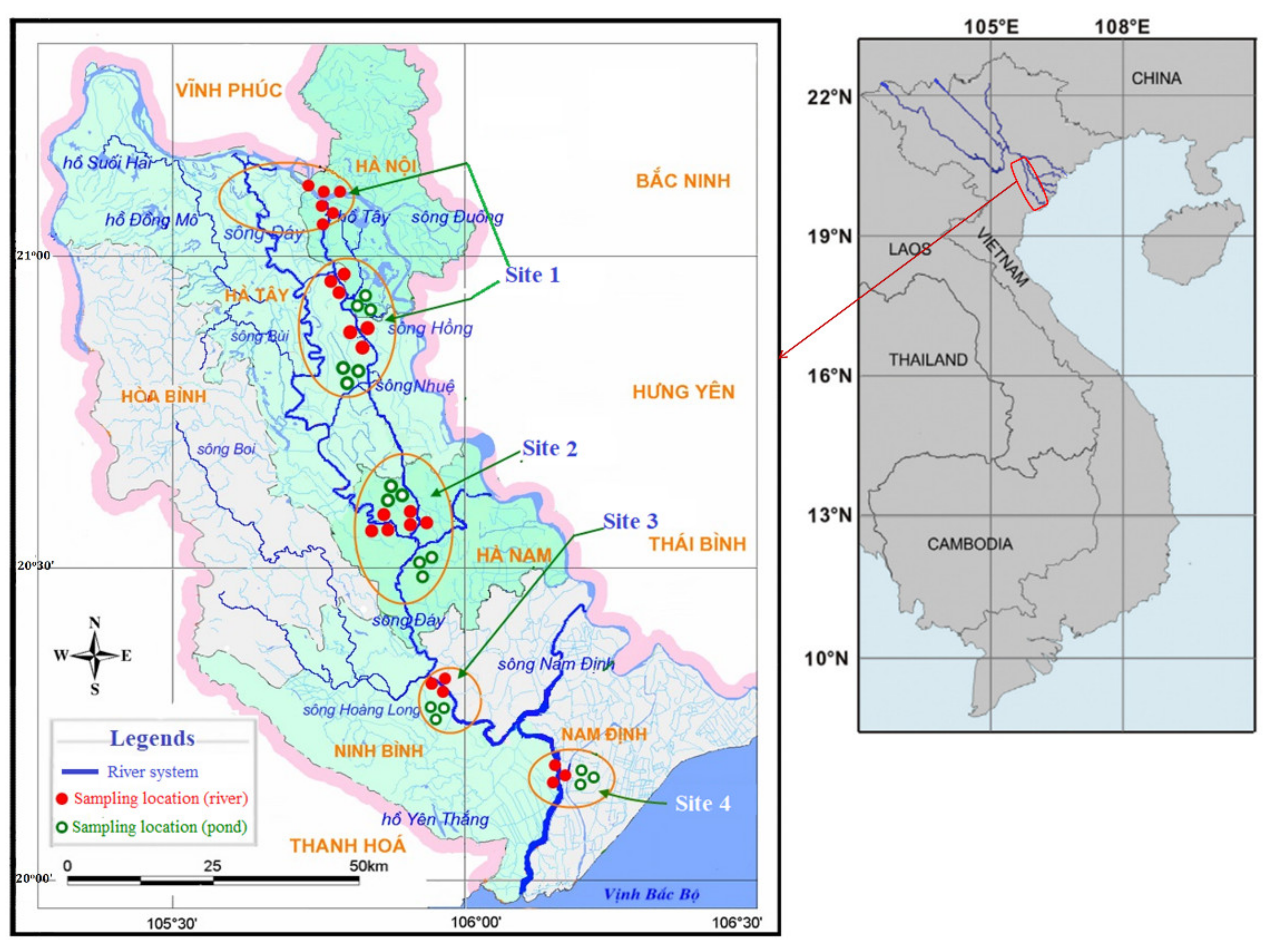
2.1. Study Area, Selected Organisms, and Sampling
2.2. Metal Analysis
2.3. Biomarker Measurements
2.3.1. Glutathione S-Transferases (GSTs) Activity Assay
2.3.2. Glycogen Quantification
2.3.3. Protein Quantification
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
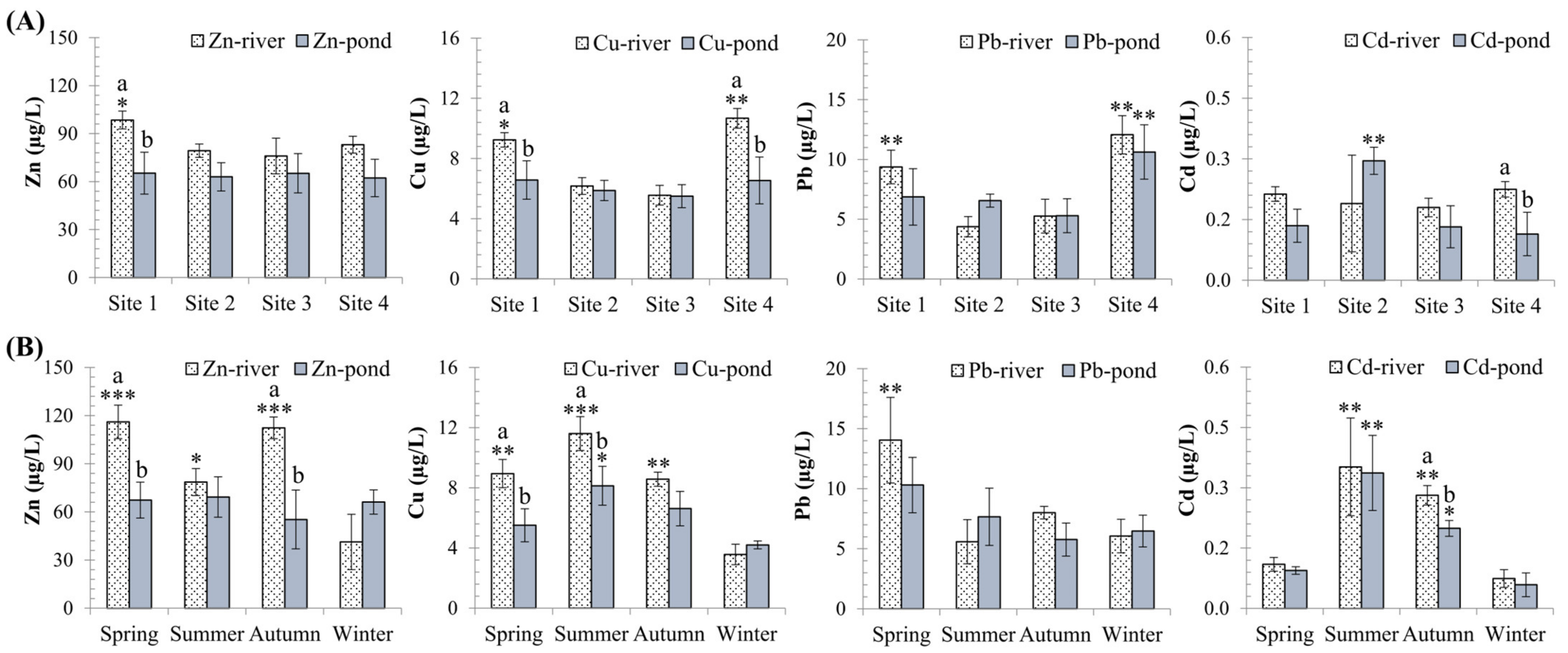
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Metal Pollution in Water
3.2. Metal Accumulation in Fish Tissues
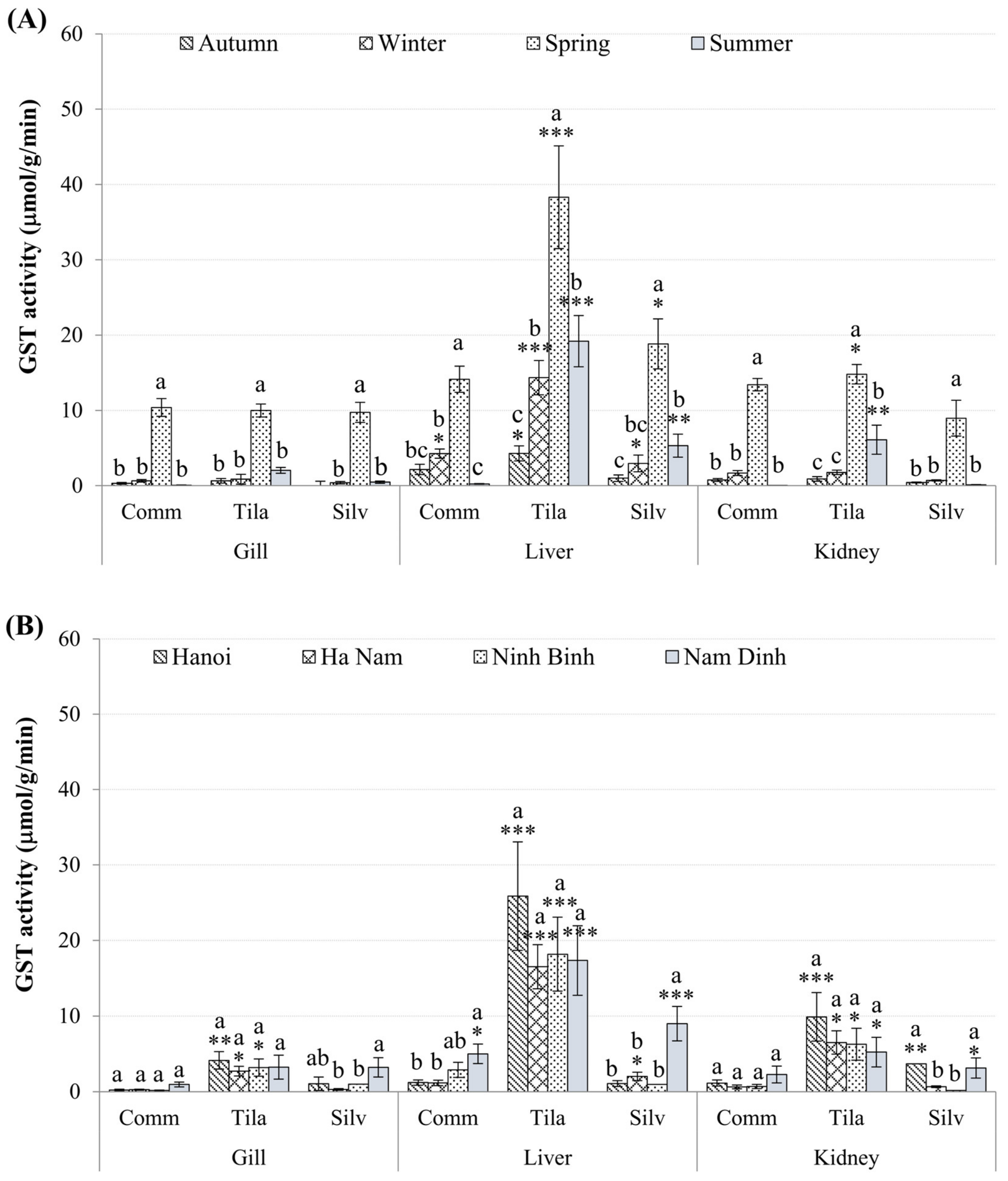
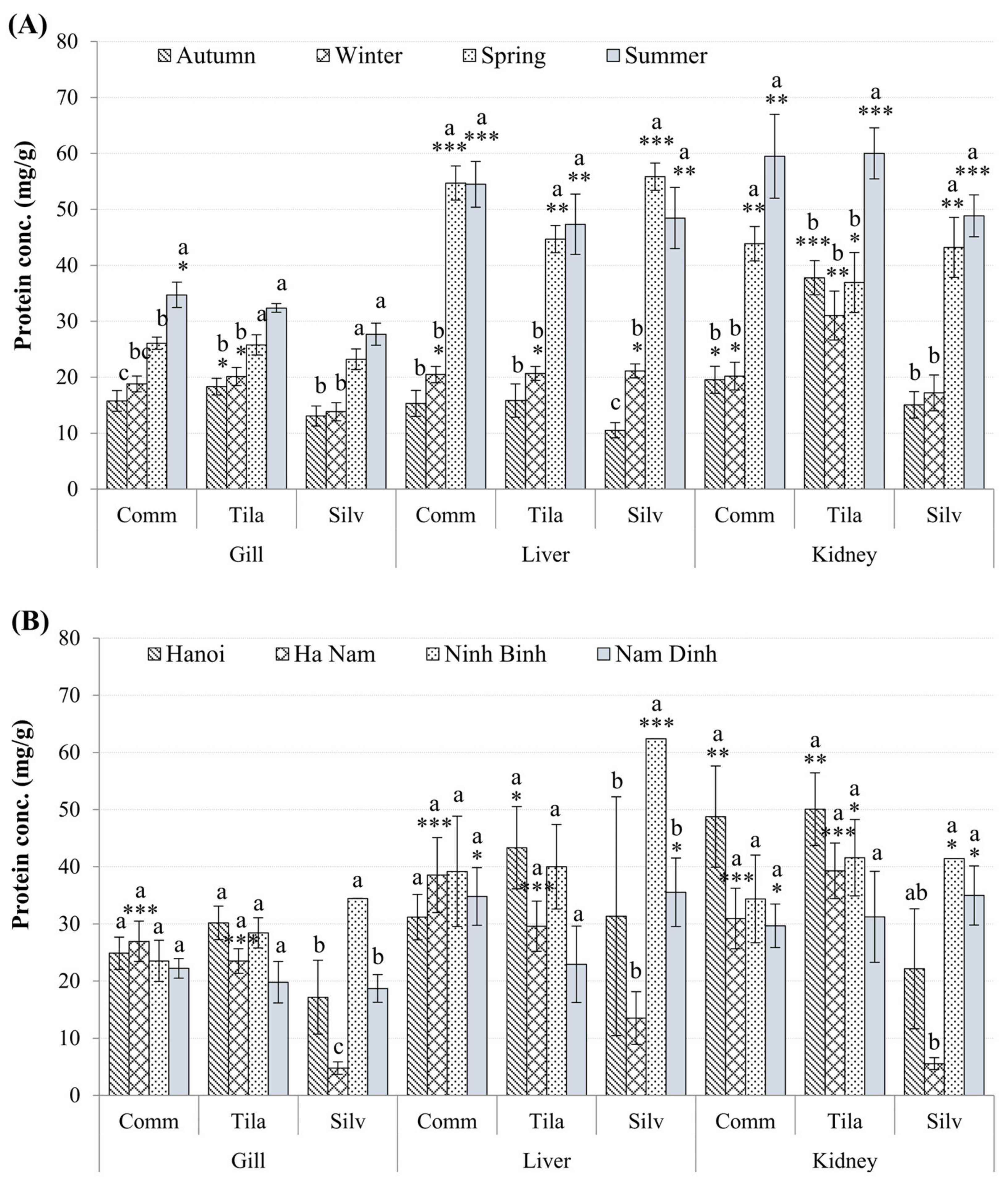
3.3. Biomarkers in Fish Tissues
3.4. Correlation Test Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Metals in Water and Their Bioaccumulation in Fish
4.2. Biomarker Responses in Fish
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, M.; He, Q.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of single and joint toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate, perfluorooctanoic acid, and copper to Carassius auratus using oxidative stress biomarkers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 161, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Feng, M.; Wang, X.; Qin, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Metal accumulation and oxidative stress biomarkers in liver of freshwater fish Carassius auratus following in vivo exposure to waterborne zinc under different pH values. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.T.T.; Gerstmann, S.; Frank, H. Subchronic effects of environment-like cadmium levels on the bivalve Anodonta anatina (Linnaeus 1758): II. Effects on energy reserves in relation to calcium metabolism. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2011, 93, 1802–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, H.M.; Moon, T.W.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Hontela, A. Seasonal variation in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) chronically exposed to metals in the field. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 60, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Modulation of reactive oxygen species in health and disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Iaria, C.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spanò, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Environmental Co-Exposure to Potassium Perchlorate and Cd Caused Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption in Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Capparucci, F.; Lanteri, G.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Combined toxicity of xenobiotics Bisphenol A and heavy metals on zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Toxics 2021, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Brack, W.; Burgess, R.M.; Busch, W.; Escher, B.I.; Focks, A.; Hewitt, M.L.; Jacobsen, B.N.; de Alda, M.L.; Ait-Aissa, S.; et al. Future water quality monitoring: Improving the balance between exposure and toxicity assessments of real-world pollutant mixtures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebe, F.N.; Panemangalore, M. Exposure to low doses of endosulfan and chlorpyrifos modifies endogenous antioxidants in tissues of rats. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2003, 38, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautremepuits, C.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Gendron, A.D.; Fournier, M. Gill and head kidney antioxidant processes and innate immune system responses of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) exposed to different contaminants in the St. Lawrence River. Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Carvalho, C.; Bernusso, V.A.; de Araújo, H.S.S.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Fernandes, M.N. Biomarker responses as indication of contaminant effects in Oreochromis niloticus. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, Q.; Jean, S.; Gandar, A.; Côte, J.; Laffaille, P.; Jacquin, L. Stress responses in fish: From molecular to evolutionary processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donker, M.H. Energy reserves and distribution of metals in populations of the isopod Porcellio scaber from metal-contaminated sites. Funct. Ecol. 1992, 6, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaee, M.; Taheri, S. Metal bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and biochemical alterations in the freshwater snail (Galba truncatula) exposed to municipal sewage. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 7, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, N.S.; EL-Hak, H.N.G.; Ghobashy, M.A.; Mansour, F.A.; Soliman, M.F. Using antioxidant changes in liver and gonads of Oreochromis niloticus as biomarkers for the assessment of heavy metals pollution at Sharkia province, Egypt. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 46, 101863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.N.; Kazama, F.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nishida, K. Application of Material Flow Analysis in assessing nutrient fluxes in Day—Nhue river basin, Vietnam, pp. Southeast Asian Water Environ. 2013, 5, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Nguyen, H.M.; Truong, C.K.; Ahmed, M.B.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.L. Chemical and microbiological risk assessment of urban river water quality in Vietnam. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2559–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MONRE. The Current State of Vietnam Environment in 3 River Basins: Cau, Nhue-Day and Dong Nai River System; National Environmental Report; Environments MoNRE: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Marcussen, H.; Holm, P.E.; Ha, L.T.; Dalsgaard, A. Food safety aspects of toxic element accumulation in fish from wastewater-fed ponds in Hanoi, Vietnam. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2007, 12, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcussen, H.; Joergensen, K.; Holm, P.E.; Brocca, D.; Simmons, R.W.; Dalsgaard, A. Element contents and food safety of water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forssk.) cultivated with wastewater in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 139, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuong, N.T.; Yoneda, M.; Ikegami, M.; Takakura, M. Source discrimination of heavy metals in sediment and water of To Lich River in Hanoi City using multivariate statistical approaches. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8065–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toan, L.Q.; Sinh, D.X.; Nguyen-Viet, H.; Long, N.H.; Duc, P.P. Assessment on lead and cadmium pollution in tilapia and water spinach cultivated in Nhue River related to human health risk in Hanam. J. Pract. Med. 2014, 5, 130–134. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/53937 (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Ngo, H.T.T.; Tran, L.A.T.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Le, T.T.; Gao, Y. Metal Pollution and Bioaccumulation in the Nhue-Day River Basin, Vietnam: Potential Ecological and Human Health Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 13425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenaers, S.; Vergauwen, L.; Hagenaars, A.; Vanhaecke, L.; AbdElgawad, H.; Asard, H.; Covaci, A.; Bervoets, L.; Knapen, D. Prioritization of contaminated watercourses using an integrated biomarker approach in caged carp. Water Res. 2016, 99, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferases: The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimo, T.J.; Damschen, E.D.; Rada, R.G.; Monroe, E.M. Nonlethal evaluation of the physiological health of unionid mussels: Methods for biopsy and glycogen analysis. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1998, 17, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayeva, L.; Mamytova, N.; Beisenova, R.; Tazitdinova, R.; Abzhalelov, A.; Akhayeva, A. Studying the self-cleaning ability of water bodies and watercounts of Arshalyn district of Akmola region. J. Environ. Manag. Tour. 2020, 11, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Furuichi, T.; Hai, H.T.; Tanaka, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in river water of Hanoi, Vietnam using multivariate analyses. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, J.; Thomas, K.V. A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.R.; Walker, P.A.; Glover, C.N. Nutritive metal uptake in teleost fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, O.; Jacquillet, G.; Tauc, M.; Cougnon, M.; Poujeol, P. Effect of heavy metals on, and handling by, the kidney. Nephron Physiol. 2005, 99, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.C. Effect of dietary copper exposure on accumulation, growth and hematological parameters of the juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 58, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avenant-Oldewage, A.; Marx, H.M. Bioaccumulation of chromium, copper and iron in the organs and tissues of Clarias gariepinus in the Olifants River, Kruger National Park. Water SA 2000, 26, 569–582. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, E.O.; Adelowo, O.A.; Ajimoko, Y.R. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) from Nigeria Ogun River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2007, 4, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilbudak, B.; Erdem, C. Cadmium accumulation in gill, liver, kidney and muscle tissues of common carp, Cyprinus carpio, and Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 92, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canli, M.; Atli, G. The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.; Behr, E.R.; Knorr, C.D.L.; Vendruscolo, D.S.; Flores, E.M.; Dressler, V.L.; Baldisserotto, B. Metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species from different trophic levels in a subtropical Brazilian river. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.T.; Jeng, S.S. Comparative zinc concentrations in tissues of common carp and other aquatic organisms. Zool. Stud. 1998, 37, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sunjog, K.; Kolarević, S.; Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Višnjić-Jeftić, Ž.; Gačić, Z.; Lenhardt, M.; Vuković-Gačić, B. Seasonal variation in metal concentration in various tissues of the European chub (Squalius cephalus L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 9232–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ravikumar, B.; Bai, G.; Li, X. Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, G.; Triendl, M.; Hofer, R. Seasonal patterns of metal accumulation in Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) from an oligotrophic Alpine lake related to temperature. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, Z.B.; Capelli, N.; Laffray, X.; Elise, G.; Ayadi, H.; Aleya, L. Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water, sediment and roach tissues in a landfill draining system pond (Etueffont, France). Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.R.J.; Rosa, R.M.; Moraes, J.; Campos, E.; Logullo, C.; Vaz, I.D.S., Jr.; Masuda, A. Relationship between glutathione S-transferase, catalase, oxygen consumption, lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in eggs and larvae of Boophilus microplus (Acarina: Ixodidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupkin, A.C.; Menone, M.L. Changes in the activities of glutathione-S-transferases, glutathione reductase and catalase after exposure to different concentrations of cadmium in Australoheros facetus (Cichlidae, Pisces). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2013, 8, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, F.; Hummel, H.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Larroux, C.; Sukhotin, A. Trace metals and variations of antioxidant enzymes in Arctic bivalve populations. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1998, 35, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.A.; Pinheiro, T.; Santos, M.C.; da Luz Mathias, M.; Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Viegas-Crespo, A.M. Response of antioxidant enzymes in freshwater fish populations (Leuciscus alburnoides complex) to inorganic pollutants exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 280, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, P.S.; Rani, A.U. Cadmium-induced antioxidant defense mechanism in freshwater teleost Oreochromis mossambicus (Tilapia). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 56, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lara, E.; Toribio, F.; Lopez-Barea, J.; Barcena, J.A. Glutathione-S-transferase isoenzyme patterns in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) exposed to environmental contaminants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. Endocrinol. 1996, 113, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, L.L.; Da Rosa, C.E.; Leite, A.M.; Moraes, L.; Pires, W.V.; Pinho, G.L.L.; Martins, A.M.G.; Robaldo, R.B.; Nery, L.E.M.; Monserrat, J.M.; et al. Biomarkers in croakers Micropogonias furnieri (Teleostei: Sciaenidae) from polluted and non-polluted areas from the Patos Lagoon estuary (Southern Brazil): Evidences of genotoxic and immunological effects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Vicente, J.J.; Gravato, C.; Guilhermino, L.; Galindo-Riaño, M.D. Oxidative stress biomarkers in Senegal sole, Solea senegalensis, to assess the impact of heavy metal pollution in a Huelva estuary (SW Spain): Seasonal and spatial variation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 75, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.L.; Posser, T.; Mattos, J.J.; Sánchez-Chardi, A.; Trevisan, R.; Oliveira, C.S.; Carvalho, P.S.M.; Leal, R.B.; Marques, M.R.F.; Bainy, A.C.D.; et al. Biochemical alterations in juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to zinc: Glutathione reductase as a target. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pi, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, P.; Liu, D.; Zhang, T. Effects of cadmium exposure on metal accumulation and energy metabolism of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaut, V.; Daelemans, O.; Sinha, A.K.; De Boeck, G.; Bervoets, L. A multibiomarker approach for evaluating environmental contamination: Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) transplanted along a gradient of metal pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.; Reddy, M.V.; Radhakrishnaiah, K. Impact of copper on the oxidative metabolism of the fry of common carp, Cyprinus carpio (Linn.) at different pH. J. Environ. Biol. 2008, 29, 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Klerks, P.L. Fitness cost of resistance to cadmium in the least killifish (Heterandria formosa). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomin, M.; Jorge, M.B.; Bianchini, A. Effects of copper exposure on the energy metabolism in juveniles of the marine clam Mesodesma mactroides. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, H.; Blust, R. Stress responses and changes in protein metabolism in carp Cyprinus carpio during cadmium exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 48, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretto, A.; Loro, V.L.; Morsch, V.M.; Moraes, B.S.; Menezes, C.; Santi, A.; Toni, C. Alterations in carbohydrate and protein metabolism in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.J.; Baldisserotto, B.; Wood, C.M. Tissue-specific cadmium and metallothionein levels in rainbow trout chronically acclimated to waterborne or dietary cadmium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenji, D.; Micic, B.; Sipos, S.; Miljanovic, B.; Teodorovic, I.; Kaisarevic, S. Fish biomarkers from a different perspective: Evidence of adaptive strategy of Abramis brama (L.) to chemical stress. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| C. carpio | H. molitrix | O. niloticus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gills | Livers | Kidneys | Gills | Livers | Kidneys | Gills | Livers | Kidneys | |
| Zn concentration (mg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Spring | 227 ± 29 aA | 189 ± 60 bA | 303 ± 71 bA | 30 ± 6.5 aA | 44 ± 6.7 aA | 37 ± 8.2 abA | 29 ± 3.4 abA | 31 ± 2.9 aA | 47 ± 4.1 aA |
| Summer | 183 ± 23 aB | 85 ± 12 aA | 230 ± 42 abB | 30 ± 3.2 aA | 41 ± 7.6 aA | 31 ± 1.5 aA | 28 ± 1.6 aA | 38 ± 3.7 aA | 63 ± 12 abB |
| Autumn | 133 ± 28 aA | 88 ± 15 aA | 140 ± 18 aA | 22 ± 1.7 aA | 46 ± 8.3 aB | 29 ± 5.0 aAB | 27 ± 2.3 aA | 32 ± 2.8 aA | 46 ± 9.0 aAB |
| Winter | 200 ± 21 aAB | 109 ± 14 abA | 236 ± 38 abB | 32 ± 8.8 aA | 58 ± 6.6 aB | 49 ± 10.4 bB | 38 ± 4.9 abA | 36 ± 3.0 aA | 91 ± 15 bB |
| Average | 190 ± 25 | 118 ± 25 | 227 ± 42 | 28 ± 5.1 | 47 ± 7.3 | 37 ± 6.3 | 30 ± 3.1 | 34 ± 3.1 | 62 ± 10 |
| Cu concentration (mg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Spring | 1.7 ± 0.21 aA | 16.1 ± 7.1 abB | 6.2 ± 1.5 abB | 2.0 ± 0.37 abA | 34 ± 14 aB | 2.9 ± 0.43 aA | 2.3 ± 0.14 aA | 204 ± 37 bC | 5.2 ± 0.48 aB |
| Summer | 3.5 ± 0.21 bA | 16.8 ± 1.9 abB | 10.7 ± 1.3 bAB | 4.5 ± 0.89 bA | 31 ± 6.7 aC | 8.8 ± 0.69 bB | 3.6 ± 0.16 bA | 100 ± 13 aC | 13 ± 2.2 bB |
| Autumn | 1.5 ± 0.15 aA | 12.0 ± 2.5 aB | 4.0 ± 0.41 aA | 0.93 ± 0.08 aA | 23 ± 7.9 aB | 1.7 ± 0.27 aA | 1.3 ± 0.10 aA | 80 ± 18 aC | 3.5 ± 0.52 aB |
| Winter | 1.2 ± 0.11 aA | 24 ± 5.6 bC | 4.4 ± 0.36 aB | 1.3 ± 0.19 aA | 21 ± 6.8 aC | 3.6 ± 0.68 abB | 1.7 ± 0.19 aA | 101 ± 10 aC | 5.7 ± 0.63 aB |
| Average | 1.9 ± 0.17 | 17 ± 4.2 | 6.3 ± 0.91 | 2.2 ± 0.38 | 27 ± 8.8 | 4.3 ± 0.52 | 2.2 ± 0.15 | 121 ± 20 | 6.9 ± 1.0 |
| Pb concentration (mg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Spring | 0.73 ± 0.11 aA | 0.39 ± 0.05 abA | 1.6 ± 0.36 bB | 1.1 ± 0.34 bA | 0.76 ± 0.12 abA | 1.2 ± 0.56 bA | 0.77 ± 0.09 bA | 0.93 ± 0.13 abA | 1.1 ± 0.16 abA |
| Summer | 0.57 ± 0.04 aA | 0.75 ± 0.06 bA | 1.2 ± 0.17 bB | 0.74 ± 0.16 abA | 1.58 ± 0.57 bA | 1.6 ± 0.63 bA | 0.62 ± 0.04 bA | 1.4 ± 0.22 bB | 1.3 ± 0.21 bB |
| Autumn | 0.50 ± 0.08 aA | 0.23 ± 0.05 aA | 0.29 ± 0.06 aA | 0.31 ± 0.05 aA | 0.29 ± 0.07 aA | 0.25 ± 0.06 aA | 0.61 ± 0.08 abA | 0.45 ± 0.08 aA | 1.2 ± 0.29 bB |
| Winter | 0.48 ± 0.10 aA | 0.24 ± 0.04 aA | 0.33 ± 0.05 aA | 0.28 ± 0.04 aA | 0.28 ± 0.04 aA | 0.27 ± 0.08 aA | 0.31 ± 0.04 aA | 0.63 ± 0.14 aA | 0.59 ± 0.11 aA |
| Average | 0.57 ± 0.084 | 0.40 ± 0.049 | 0.86 ± 0.16 | 0.61 ± 0.15 | 0.73 ± 0.20 | 0.85 ± 0.33 | 0.58 ± 0.063 | 0.86 ± 0.14 | 1.0 ± 0.19 |
| Cd concentration (μg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Spring | 6.3 ± 2.6 aA | 98 ± 42 aA | 220 ± 68 aA | 4.0 ± 2.4 aA | 46 ± 32 aA | 116 ± 54 aA | 4.3 ± 1.7 aA | 211 ± 40 aA | 373 ± 72 aA |
| Summer | 89 ± 9.3 aA | 105 ± 10 aA | 435 ± 65 aA | 60 ± 10 aA | 97 ± 36 aA | 162 ± 25 aA | 71 ± 6.8 aA | 269 ± 44 aA | 311 ± 43 aA |
| Autumn | 5.9 ± 1.0 aA | 16 ± 2.3 aA | 99 ± 13 aA | 5.9 ± 2.0 aA | 23 ± 6.0 aA | 113 ± 33 aA | 8.8 ± 1.8 aA | 82 ± 18 aA | 219 ± 49 aA |
| Winter | 3.1 ± 1.0 aA | 30 ± 4.2 aA | 158 ± 25 aA | 6.2 ± 3.6 aA | 52 ± 29 aA | 305 ± 86 aA | 2.9 ± 0.5 aA | 165 ± 33 aA | 234 ± 57 aA |
| Average | 25 ± 3.5 | 62 ± 15 | 288 ± 43 | 19 ± 4.6 | 54 ± 2.6 | 174 ± 49 | 22 ± 2.7 | 182 ± 34 | 284 ± 55 |
| C. carpio | H. molitrix | O. niloticus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gills | Livers | Kidneys | Gills | Livers | Kidneys | Gills | Livers | Kidneys | |
| Zn concentration (mg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Site 1 | 222 ± 19 aA | 114 ± 14 abB | 168 ± 19 bAB | 21 ± 5.1 bA | 31 ± 4.4 bA | 22 ± 1.8 bA | 37 ± 4.6 aB | 37 ± 3.2 aB | 72 ± 12 aA |
| Site 2 | 145 ± 26 bAB | 82 ± 15 abB | 206 ± 45 abA | 22 ± 2.8 bB | 54 ± 7.5 aA | 40 ± 6.1 aAB | 32 ± 2.9 abB | 42 ± 4.9 aAB | 62 ± 13 abA |
| Site 3 | 156 ± 29 aA | 59 ± 9.5 bB | 142 ± 30 bA | 31 ± 3.8 aA | 34 ± 5.5 abA | 35 ± 6.4 aA | 26 ± 1.3 bC | 34 ± 2.1 abB | 48 ± 4.6 bA |
| Site 4 | 196 ± 21 aAB | 132 ± 22 aB | 313 ± 40 aA | 28 ± 2.8 abB | 45 ± 5.1 aA | 36 ± 5.8 aAB | 25 ± 2.4 bB | 28 ± 1.4 bB | 77 ± 17 aA |
| Average | 184 ± 13 | 109 ± 11.5 | 243 ± 25 | 27 ± 2.3 | 56 ± 10 | 50 ± 13.8 | 35 ± 3.5 | 42 ± 4.1 | 83 ± 10.8 |
| Cu concentration (mg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Site 1 | 2.2 ± 0.27 aC | 18 ± 2.5 abA | 6.5 ± 0.94 aB | 1.2 ± 0.28 cB | 7.4 ± 2.8 bA | 1.8 ± 0.12 cB | 2.5 ± 0.30 aC | 124 ± 18 aA | 6.4 ± 1.2 bB |
| Site 2 | 2.6 ± 0.32 aC | 22 ± 4.7 aA | 6.6 ± 1.1 aB | 1.3 ± 0.23 cC | 22 ± 2.7 abA | 3.6 ± 0.89 bB | 2.7 ± 0.48 aC | 113 ± 13 aA | 8.3 ± 2.1 abB |
| Site 3 | 2.2 ± 0.46 aC | 12 ± 3.7 abA | 6.1 ± 1.2 aB | 3.8 ± 3.2 aB | 35 ± 7.1 aA | 9.5 ± 3.1 aB | 2.3 ± 0.35 aC | 98 ± 25 aA | 6.8 ± 1.1 abB |
| Site 4 | 2.2 ± 0.41 aC | 12 ± 2.3 bA | 4.9 ± 0.78 aB | 2.0 ± 0.38 bB | 27 ± 6.5 aA | 4.4 ± 0.94 abB | 2.7 ± 0.44 aC | 106 ± 26 aA | 11 ± 2.8 aB |
| Average | 2.3 ± 0.20 | 20 ± 3.1 | 6.4 ± 0.60 | 1.8 ± 0.24 | 20 ± 3.1 | 4.1 ± 0.63 | 2.6 ± 0.22 | 107 ± 15.5 | 8.9 ± 1.8 |
| Pb concentration (mg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Site 1 | 0.54 ± 0.07 aA | 0.41 ± 0.07 abA | 0.67 ± 0.16 abA | 0.29 ± 0.20 bA | 0.10 ± 0.05 bA | 0.12 ± 0.03 cA | 0.69 ± 0.09 aA | 0.97 ± 0.13 aA | 0.87 ± 0.09 abA |
| Site 2 | 0.52 ± 0.07 aA | 0.54 ± 0.08 aA | 0.64 ± 0.14 bA | 0.31 ± 0.04 bA | 0.32 ± 0.07 abA | 0.32 ± 0.07 bA | 0.58 ± 0.07 aB | 0.76 ± 0.12 abAB | 1.3 ± 0.25 abA |
| Site 3 | 0.45 ± 0.12 aA | 0.50 ± 0.14 aA | 0.93 ± 0.23 aA | 0.5 ± 0.01 abB | 0.68 ± 0.15 aAB | 1.0 ± 0.13 aA | 0.50 ± 0.08 aA | 0.58 ± 0.12 bA | 0.80 ± 0.16 bA |
| Site 4 | 0.63 ± 0.07 aA | 0.45 ± 0.09 aA | 0.83 ± 0.18 aA | 0.75 ± 0.16 aA | 0.73 ± 0.12 aA | 0.72 ± 0.17 abA | 0.67 ± 0.20 aB | 0.74 ± 0.17 abAB | 1.6 ± 0.42 aA |
| Average | 0.57 ± 0.05 | 0.47 ± 0.045 | 0.90 ± 0.12 | 0.56 ± 0.17 | 0.53 ± 0.08 | 0.53 ± 0.33 | 0.63 ± 0.09 | 0.88 ± 0.10 | 1.3 ± 0.24 |
| Cd concentration (μg kg−1 wet weight) | |||||||||
| Site 1 | 28 ± 8.9 aB | 48 ± 12 bB | 203 ±51 bA | 4.5 ± 2.5 cC | 12 ± 1.0 bB | 125 ±6.0 bA | 37 ± 14 aC | 195 ± 32 abB | 402 ±85 aA |
| Site 2 | 34 ± 10 aC | 70 ± 17 abB | 189 ± 37 bA | 21 ± 8.0 bB | 47 ± 13 aB | 186 ± 47 aA | 30 ± 9.0 aB | 255 ± 40 aA | 320 ± 50 abA |
| Site 3 | 8.9 ± 6.0 bC | 31 ± 8.2 bB | 196 ± 55 bA | 50 ± 9.8 aB | 54 ± 7.5 aB | 200 ± 61 aA | 17 ± 6.0 bC | 123 ± 27 bB | 204 ± 37 bA |
| Site 4 | 12 ± 4.5 bC | 97 ± 23 aB | 461 ± 115 aA | 19 ± 6.3 bC | 58 ± 17 aB | 148 ± 42 abA | 29 ± 13 abC | 124 ± 31 bB | 259 ± 65 bA |
| Average | 25 ± 5.3 | 70 ± 10 | 259 ± 83 | 24 ± 6.1 | 49 ± 9.8 | 162 ± 27 | 23 ± 4.6 | 190 ± 22 | 308 ± 33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ngo, H.T.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, D.Q. Adverse Effects of Toxic Metal Pollution in Rivers on the Physiological Health of Fish. Toxics 2022, 10, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090528
Ngo HTT, Nguyen TD, Nguyen TTH, Le TT, Nguyen DQ. Adverse Effects of Toxic Metal Pollution in Rivers on the Physiological Health of Fish. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090528
Chicago/Turabian StyleNgo, Huong Thi Thuy, Thanh Dinh Nguyen, Tien Thi Hanh Nguyen, Thao Thanh Le, and Dinh Quoc Nguyen. 2022. "Adverse Effects of Toxic Metal Pollution in Rivers on the Physiological Health of Fish" Toxics 10, no. 9: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090528
APA StyleNgo, H. T. T., Nguyen, T. D., Nguyen, T. T. H., Le, T. T., & Nguyen, D. Q. (2022). Adverse Effects of Toxic Metal Pollution in Rivers on the Physiological Health of Fish. Toxics, 10(9), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090528






