Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Clinical Outcomes, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity and Impact on Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Manifestations
2.1. Brief History of the First Reported Manifestations of Chronic N2O Exposure
2.2. Common Symptoms and Signs
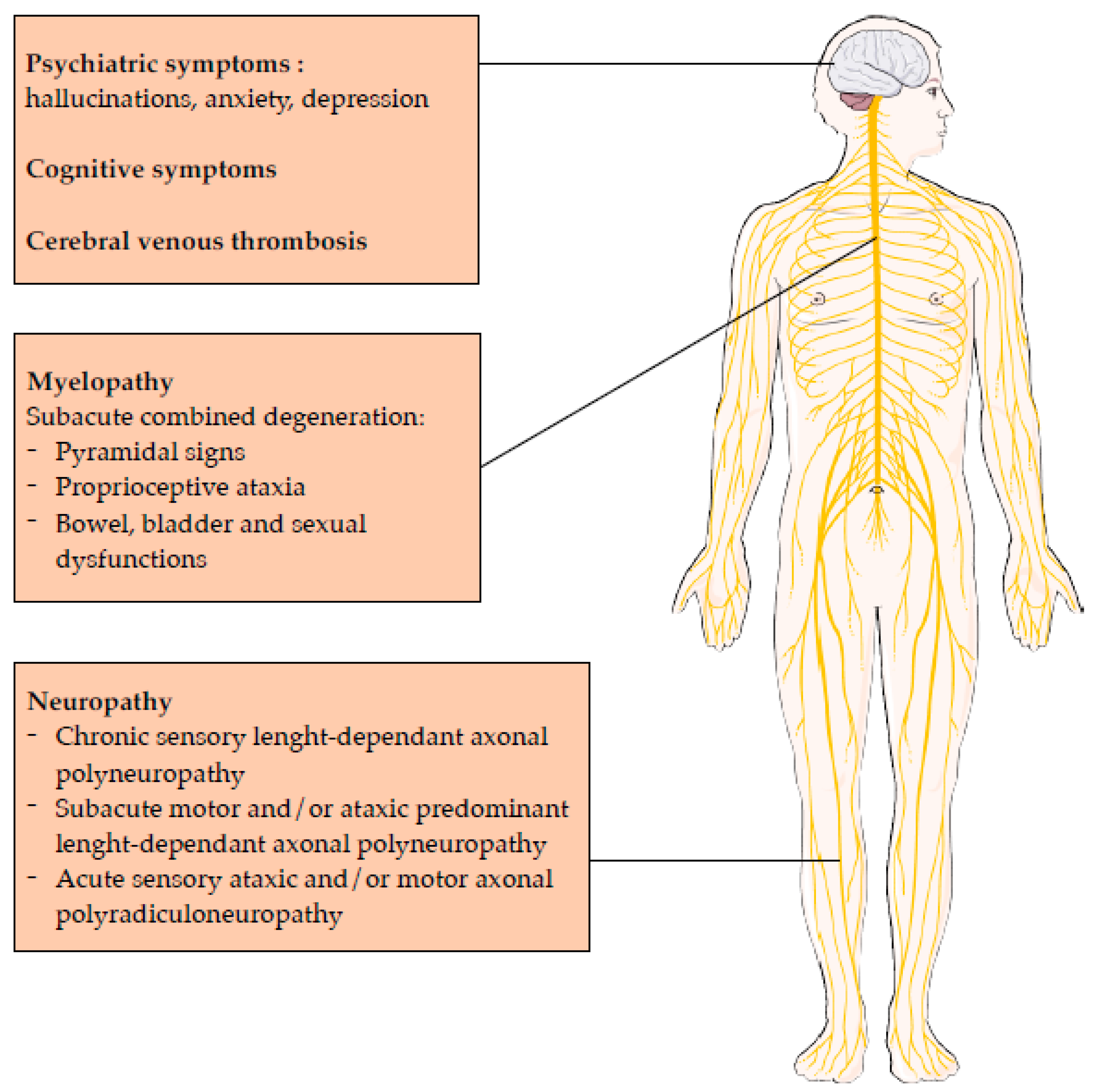
2.3. Central Nervous System Involvement
2.4. Peripheral Nervous System Involvement
- More motor and sensory nerve injury in the lower limbs compared to the upper limbs,
- More motor nerve injury than sensory nerve injury in the lower limbs,
- More demyelinating features in the sensory and motor nerves of the upper limbs, with a marked motor predominance.
- Chronic sensory length-dependent axonal polyneuropathy,
- Subacute motor and/or ataxic predominant length-dependent axonal polyneuropathy,
- Acute sensory ataxic and/or motor axonal polyradiculoneuropathy.
2.5. Prognosis of Central and Neurological Nervous System Involvement
2.6. Other Presentations
3. Pharmacological Effects
3.1. Dependence Producing Potential of Nitrous Oxide
3.2. Anaesthesia
3.3. Analgesia
3.4. Anxiolytic Effect
3.5. Anti-depressant Effect
4. Laboratory Medicine
4.1. Direct N2O Measurement
4.2. Impact on Metabolism
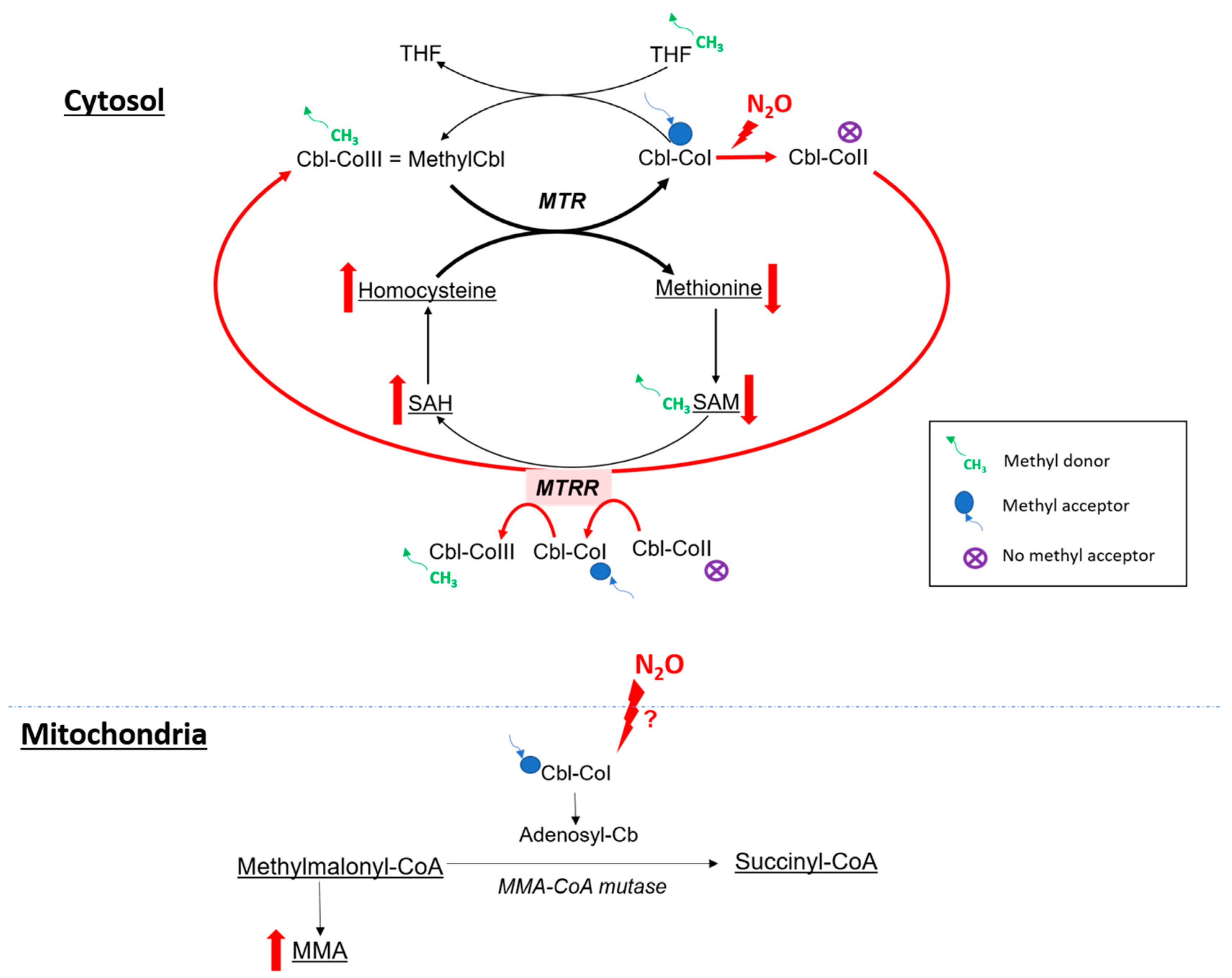
4.2.1. Cobalamin and One Carbon Metabolism
4.2.2. N2O and Oxidative Stress
4.2.3. Homocysteine and Oxidative Stress
4.3. Indirect Biomarkers of N2O Intoxication
4.3.1. Vitamin B12
4.3.2. Plasma Homocysteine
4.3.3. Plasma MMA
4.3.4. Plasma Methionine
4.3.5. Oxidative Stress Markers
4.3.6. Others Biological Parameters to Consider
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- (PDF) Recreational Use of Nitrous Oxide: A Growing Concern for Europe. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366138268_Recreational_use_of_nitrous_oxide_a_growing_concern_for_Europe (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Lassen, H.C.; Henriksen, E.; Neukirch, F.; Kristensen, H.S. Treatment of tetanus; severe bone-marrow depression after prolonged nitrous-oxide anaesthesia. Lancet 1956, 270, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sund Kristensen, H.; Berthelsen, P.G. Risus sardonicus and laughing gas–when nitrous oxide lost its innocence. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1994, 38, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layzer, R.B. Myeloneuropathy after prolonged exposure to nitrous oxide. Lancet 1978, 2, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layzer, R.B.; Fishman, R.A.; Schafer, J.A. Neuropathy following abuse of nitrous oxide. Neurology 1978, 28, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastak, J.T. Nitrous oxide and its abuse. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1991, 122, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, N.Y.; Silbert, P.L.; Erber, W.N.; Rijks, C.J. “Nanging”: Another cause of nitrous oxide neurotoxicity. Med. J. Aust. 1997, 166, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstock, A.R.; Ferris, J.A. Nitrous oxide causes peripheral neuropathy in a dose dependent manner among recreational users. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berling, E.; Fargeot, G.; Aure, K.; Tran, T.H.; Kubis, N.; Lozeron, P.; Zanin, A. Nitrous oxide-induced predominantly motor neuropathies: A follow-up study. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortanier, E.; Berling, E.; Zanin, A.; Guillou, A.L.; Micaleff, J.; Nicolas, G.; Lozeron, P.; Attarian, S. How to distinguish Guillain-Barré syndrome from nitrous oxide-induced neuropathy: A 2-year, multicentric, retrospective study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 3296–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, J.; Weng, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Chang, T.-S.; Sung, J.-Y.; Lin, C.S.-Y. Elucidating Unique Axonal Dysfunction Between Nitrous Oxide Abuse and Vitamin B12 Deficiency. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, G.; Blair, C.; Lu, Z.; Yogendran, S.; Offord, J.; Sutherland, E.; Barnes, S.; Palavra, N.; Cremer, P.; Bolitho, S.; et al. Nitrous oxide-induced myeloneuropathy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3938–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gernez, E.; Deheul, S.; Tard, C.; Joncquel, M.; Douillard, C.; Grzych, G. Plasma Methionine and Clinical Severity in Nitrous Oxide Consumption. Toxics 2022, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzych, G.; Deheul, S.; Gernez, E.; Davion, J.-B.; Dobbelaere, D.; Carton, L.; Kim, I.; Guichard, J.C.; Girot, M.; Humbert, L.; et al. Comparison of biomarker for diagnosis of nitrous oxide abuse: Challenge of cobalamin metabolic parameters, a retrospective study. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, D.; Zou, Y.; Yu, X.; Ji, Y.; Wang, C.; Lv, X.; Zhou, N.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K.; et al. Key Characteristics of Nitrous Oxide-Induced Neurological Disorders and Differences Between Populations. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 627183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; de Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Xu, R.; Feng, F.; Kan, W.; Ding, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; et al. Clinical epidemiological characteristics of nitrous oxide abusers: A single-center experience in a hospital in China. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J. Nitrous oxide-related neurological disorders: Clinical, laboratory, neuroimaging, and electrophysiological findings. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Yu, M.; Zheng, D.; Gao, H.; Li, W.; Ma, Y. Electrophysiologic Characteristics of Nitrous-Oxide-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy: A Retrospective Study of 76 Patients. J. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 19, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Ba, F.; Bi, G.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, W. The sharp rise of neurological disorders associated with recreational nitrous oxide use in China: A single-center experience and a brief review of Chinese literature. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Electrodiagnostic Characteristics of Nitrous Oxide-Induced Neuropathy in Taiwan-PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27567448/ (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Yu, M.; Qiao, Y.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Gao, H.; Zheng, D.; Ma, Y. Analysis of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors in 110 patients with nitrous oxide abuse. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussalah, A.; Julien, M.; Levy, J.; Hajjar, O.; Franczak, C.; Stephan, C.; Laugel, E.; Wandzel, M.; Filhine-Tresarrieu, P.; Green, R.; et al. Global Burden Related to Nitrous Oxide Exposure in Medical and Recreational Settings: A Systematic Review and Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Kang, L.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Hu, F.; Lu, W.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Q.Y.; Dang, J. Acute nitrous oxide-induced neuropathy mimicking Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2022, 27, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garakani, A.; Jaffe, R.J.; Savla, D.; Welch, A.K.; Protin, C.A.; Bryson, E.O.; McDowell, D.M. Neurologic, psychiatric, and other medical manifestations of nitrous oxide abuse: A systematic review of the case literature. Am. J. Addict. 2016, 25, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Otmani, H.; El Moutawakil, B.; Moutaouakil, F.; Gam, I.; Rafai, M.A.; Slassi, I. [Postoperative dementia: Toxicity of nitrous oxide]. Encephale 2007, 33, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabat, A.; Hardouin, J.; Courtière, A. Nitrous oxide impairs selective stages of working memory in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 364, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, M.C.; Wijnhoven, A.M.; Maessen, G.C.; Blankensteijn, S.R.; van der Heyden, M.A.G. Does vitamin B12 deficiency explain psychiatric symptoms in recreational nitrous oxide users? A narrative review. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, W.; Pariente, A.; Mijahed, R. Extensive Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Secondary to Recreational Nitrous Oxide Abuse. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 51, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulkadi, S.; Peters, B.; Vliegen, A.-S. Thromboembolic complications of recreational nitrous oxide (ab)use: A systematic review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 54, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, D.; Agrawal, A.; Gupta, S.; Bajaj, S. Recreational Nitrous Oxide Abuse Causing Ischemic Stroke in a Young Patient: A Rare Case Report. Cureus 2018, 10, e3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacny, J.P.; Lichtor, J.L.; Coalson, D.W.; Apfelbaum, J.L.; Flemming, D.; Foster, V. Time course of effects of brief inhalations of nitrous oxide in normal volunteers. Addiction 1994, 89, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohrn, C.S.; Lichtor, J.; Coalson, D.W.; Uitvlugt, A.; de Wit, H.; Zacny, J.P. Reinforcing effects of extended inhalation of nitrous oxide in humans. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1993, 31, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dj, W.; Jp, Z. Within- and between-subject variability in the reinforcing and subjective effects of nitrous oxide in healthy volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2001, 64, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dj, W.; Jp, Z. Analysis of the reinforcing and subjective effects of different doses of nitrous oxide using a free-choice procedure. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2002, 66, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.; Capps, B.; Hall, W. Addiction Neurobiology: Ethical and Social Implications; EMCDDA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, K.; Das, R.K.; Kamboj, S.K. The Subjective Response to Nitrous Oxide is a Potential Pharmaco-Endophenotype for Alcohol Use Disorder: A Preliminary Study with Heavy Drinkers. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillman, M.A. Mini-Review: A Brief History of Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Use in Neuropsychiatry. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2019, 11, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G. Nitrous oxide, an opioid addictive agent. Review of the evidence. Am. J. Med. 1986, 81, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, S.; Kroon, E.; Colyer-Patel, K.; Cousijn, J. Does nitrous oxide addiction exist? An evaluation of the evidence for the presence and prevalence of substance use disorder symptoms in recreational nitrous oxide users. Addiction 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lonkhuyzen, J.J.N.; van der Ben, L.; Koot, I.S.v.D.H.; de Lange, D.W.; van Riel, A.J.; Hondebrink, L. High Incidence of Signs of Neuropathy and Self-Reported Substance Use Disorder for Nitrous Oxide in Patients Intoxicated with Nitrous Oxide. Eur. Addict. Res. 2023, 29, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radparvar, S. The Clinical Assessment and Treatment of Inhalant Abuse. Perm. J. 2023, 27, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, B.W.; Bleckwenn, M. Concepts and correlations relevant to general anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2002, 89, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.D.; Weimann, J.; Maze, M. Biologic effects of nitrous oxide: A mechanistic and toxicologic review. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, S.K.; Kohno, T.; Ikoma, M.; Yamakura, T.; Baba, H. Nitrous oxide inhibits glutamatergic transmission in spinal dorsal horn neurons. Pain 2008, 134, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.J.; Honoré, E. Properties and modulation of mammalian 2P domain K+ channels. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M.A. Nitrous oxide for relief of labor pain: A systematic review. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 186, S110–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamura, S.; Obara, M.; Takeda, K.; Maze, M.; Hanaoka, K. Corticotropin-releasing factor mediates the antinociceptive action of nitrous oxide in rats. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, A.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Liu, J. The role of the dynorphin/κ opioid receptor system in anxiety. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, C. 30 years of dynorphins--new insights on their functions in neuropsychiatric diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y.; Guo, T.; Orii, R.; Maze, M.; Fujinaga, M. Brain stem opioidergic and GABAergic neurons mediate the antinociceptive effect of nitrous oxide in Fischer rats. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouil, D.E.; Quock, R.M. Advances in understanding the actions of nitrous oxide. Anesth. Prog. 2007, 54, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakura, T.; Harris, R.A. Effects of gaseous anesthetics nitrous oxide and xenon on ligand-gated ion channels. Comparison with isoflurane and ethanol. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagele, P.; Duma, A.; Kopec, M.; Gebara, M.A.; Parsoei, A.; Walker, M.; Janski, A.; Panagopoulos, V.N.; Cristancho, P.; Miller, J.P.; et al. Nitrous Oxide for Treatment-Resistant Major Depression: A Proof-of-Concept Trial. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmoe, M.C.; Janski, A.M.; Zorumski, C.F.; Nagele, P.; Palanca, B.J.; Conway, C.R. Ketamine and nitrous oxide: The evolution of NMDA receptor antagonists as antidepressant agents. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 412, 116778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkholm, C.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF—A key transducer of antidepressant effects. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantamäki, T.; Yalcin, I. Depression and antidepressant action-from molecules to networks. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, M.J.; Latto, I.P.; Rosen, M. Analysis of nitrous oxide concentrations in whole blood: An evaluation of an equilibration technique. Br. J. Anaesth. 1973, 45, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanitre, E.; Rackow, H.; Greene, L.T.; Klonymus, D.; Epstein, R.M. Uptake and excretion of subanesthetic concentrations of nitrous oxide in man. Anesthesiology 1962, 23, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, S.; Stenqvist, O.; Bengtsson, A.; Houltz, E.; Bengtson, J.P. Nitrous oxide elimination and diffusion hypoxia during normo- and hypoventilation. Br. J. Anaesth. 1993, 71, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Gagliano-Candela, R.; Strisciullo, G.; Colucci, A.P.; Strada, L.; Laviola, D.; Goldoni, M.; Mutti, A. Nitrous oxide determination in postmortem biological samples: A case of serial fatal poisoning in a public hospital. J. Forensic Sci. 2010, 55, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusler, H. Quantitative analysis of common anaesthetic agents. J. Chromatogr. 1985, 340, 273–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, V.; Riazzi, B.S.; Matthews, R.G. In vitro inactivation of methionine synthase by nitrous oxide. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 15823–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Osborne, M.L.; Kolhouse, J.F.; Binder, M.J.; Podell, E.R.; Utley, C.S.; Abrams, R.S.; Allen, R.H. Nitrous oxide has multiple deleterious effects on cobalamin metabolism and causes decreases in activities of both mammalian cobalamin-dependent enzymes in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 67, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaddon, A.; Regland, B.; Hudson, P.; Davies, G. Functional vitamin B(12) deficiency and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2002, 58, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guéant, J.-L.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.-M.; Oussalah, A.; Zuily, S.; Rosenberg, I. Hyperhomocysteinemia in Cardiovascular Diseases: Revisiting Observational Studies and Clinical Trials. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 123, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.; Rodriguez-Guéant, R.-M.; Oussalah, A.; Jeannesson, E.; Wahl, D.; Ziuly, S.; Guéant, J.-L. Cardiovascular manifestations of intermediate and major hyperhomocysteinemia due to vitamin B12 and folate deficiency and/or inherited disorders of one-carbon metabolism: A 3.5-year retrospective cross-sectional study of consecutive patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutilainen, S.; Morrow, J.D.; Roberts, L.J.; Alfthan, G.; Alho, H.; Nyyssönen, K.; Salonen, J.T. Enhanced in vivo lipid peroxidation at elevated plasma total homocysteine levels. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van den Berg, M.; Boers, G.H.; Franken, D.G.; Blom, H.J.; Van Kamp, G.J.; Jakobs, C.; Rauwerda, J.A.; Kluft, C.; Stehouwert, C.D. Hyperhomocysteinaemia and endothelial dysfunction in young patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 25, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauls, D.L.; Wolberg, A.S.; Hoffman, M. Elevated plasma homocysteine leads to alterations in fibrin clot structure and stability: Implications for the mechanism of thrombosis in hyperhomocysteinemia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrońska-Nofer, T.; Nofer, J.-R.; Jajte, J.; Dziubałtowska, E.; Szymczak, W.; Krajewski, W.; Wąsowicz, W.; Rydzyński, K. Oxidative DNA damage and oxidative stress in subjects occupationally exposed to nitrous oxide (N2O). Mutat. Res. 2012, 731, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, A.; Kozlov, A.V. Biological Activities of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species: Oxidative Stress versus Signal Transduction. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Grasso, M.; Fidilio, A.; Torrisi, S.A.; Musso, N.; Geraci, F.; Tropea, M.R.; Privitera, A.; Tascedda, F.; Puzzo, D.; et al. Antioxidant Activity of Fluoxetine and Vortioxetine in a Non-Transgenic Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 809541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, K.; Nehmé, J.; Bourdon, E.; Pivert, G.; Friguet, B.; Delcayre, C.; Delabar, J.-M.; Janel, N. Cystathionine beta synthase deficiency promotes oxidative stress, fibrosis, and steatosis in mice liver. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambooy, S.; Heida, A.; Joschko, C.; Nakladal, D.; van Buiten, A.; Kloosterhuis, N.; Huijkman, N.; Gerding, A.; van de Sluis, B.; Henning, R.; et al. Selective Hepatic Cbs Knockout Aggravates Liver Damage, Endothelial Dysfunction and ROS Stress in Mice Fed a Western Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontiera, M.S.; Stabler, S.P.; Kolhouse, J.F.; Allen, R.H. Regulation of methionine metabolism: Effects of nitrous oxide and excess dietary methionine. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1994, 5, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, E.; Bennis, A.; Diesnis, R.; Niguet, J.P.; Grzych, G. Awareness of health care related to nitrous oxide abuse for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N2O-Induced Neuropathy | Guillain-Barré Syndrome | |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | ||
| Upper limb weakness | Less frequent | More frequent |
| Numbness in the limbs | Common | Less frequent |
| Babinski sign | Common | Absent |
| Diffuse hyporeflexia/areflexia | Less frequent | Common |
| Ataxia | Frequent | Less frequent |
| Apallesthaesia | Common | Less frequent |
| Cranial nerve involvement | Uncommon | Frequent |
| Respiratory distress | Uncommon | Frequent |
| Swallowing problems | Absent | Frequent |
| Electrophysiological characteristics | ||
| Conduction blocks | Uncommon | Frequent |
| Decrease in CMAP amplitude (upper limbs) | Less frequent | Frequent |
| Decrease in CMAP amplitude (lower limbs) | Frequent | Less frequent |
| Decrease in SNAP amplitude (lower limbs) | Frequent | Absent |
| Decrease in SCV | Possible | Uncommon |
| Absent F waves | Frequent | Less frequent |
| Property | System | Receptor Target |
|---|---|---|
| Anesthesia | Glutamatergic inhibition | NMDA receptor (AMPA and kaitine) inhibition |
| Cholinergic inhibition | Nicotinic Acetyl Choline receptor inhibition | |
| Analgesia | Opioidergic activation (+GABAergic inhibition) | Kappa opioid receptor activation |
| Noradrenergic activation | α1- and α2B adrenoreceptors activation | |
| Anti-depressive effects | Glutamatergic inhibition | NDMA receptor inhibition |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gernez, E.; Lee, G.R.; Niguet, J.-P.; Zerimech, F.; Bennis, A.; Grzych, G. Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Clinical Outcomes, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity and Impact on Metabolism. Toxics 2023, 11, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120962
Gernez E, Lee GR, Niguet J-P, Zerimech F, Bennis A, Grzych G. Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Clinical Outcomes, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity and Impact on Metabolism. Toxics. 2023; 11(12):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120962
Chicago/Turabian StyleGernez, Emeline, Graham Robert Lee, Jean-Paul Niguet, Farid Zerimech, Anas Bennis, and Guillaume Grzych. 2023. "Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Clinical Outcomes, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity and Impact on Metabolism" Toxics 11, no. 12: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120962
APA StyleGernez, E., Lee, G. R., Niguet, J.-P., Zerimech, F., Bennis, A., & Grzych, G. (2023). Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Clinical Outcomes, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity and Impact on Metabolism. Toxics, 11(12), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120962






