Significant Biotransformation of Arsenobetaine into Inorganic Arsenic in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Exposure Diets and Experimental Design
2.3. Total Arsenic Determination
2.4. Arsenic Speciation Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
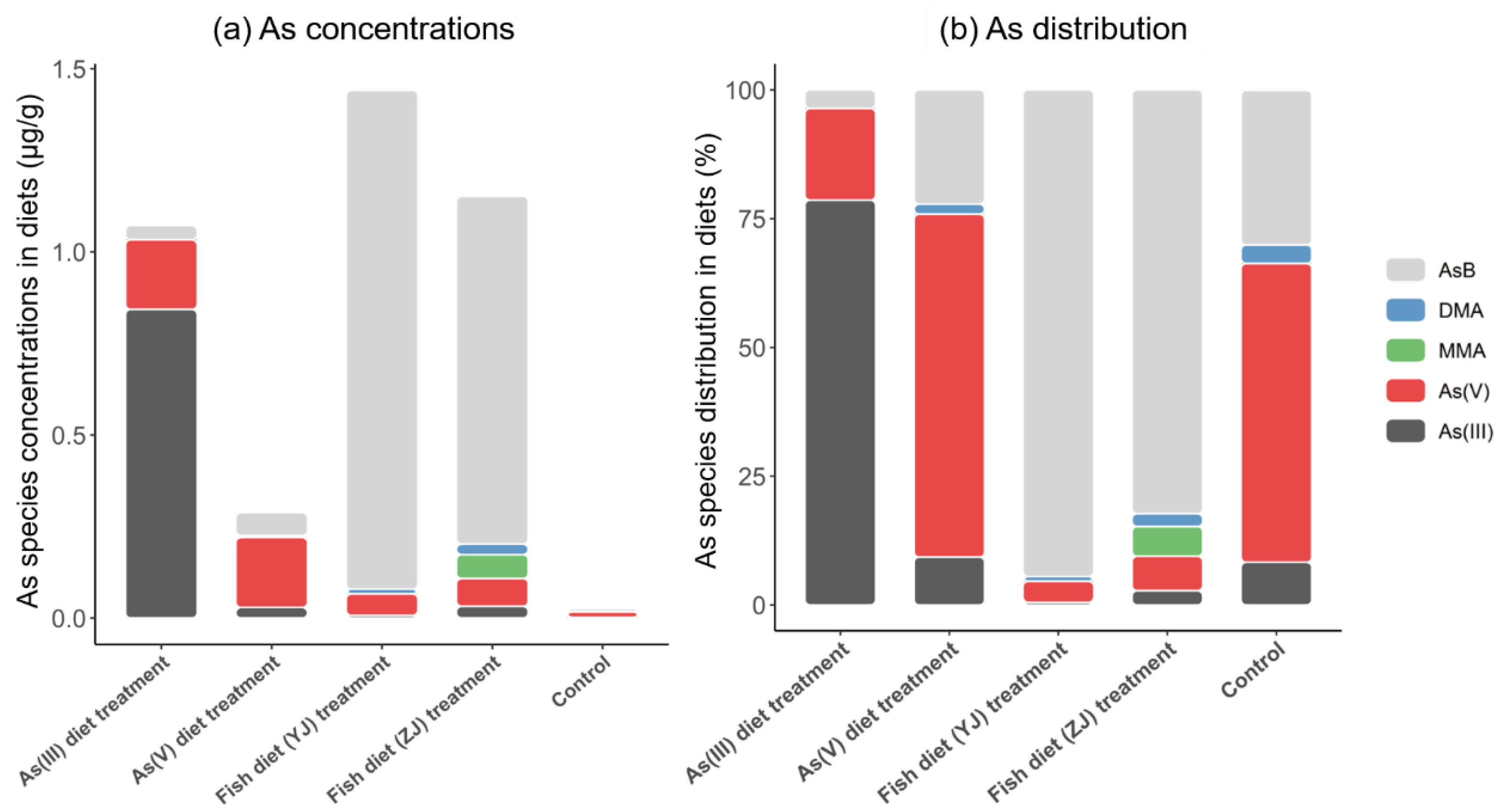
3.1. Total Arsenic Content and Arsenic Speciation in Diets
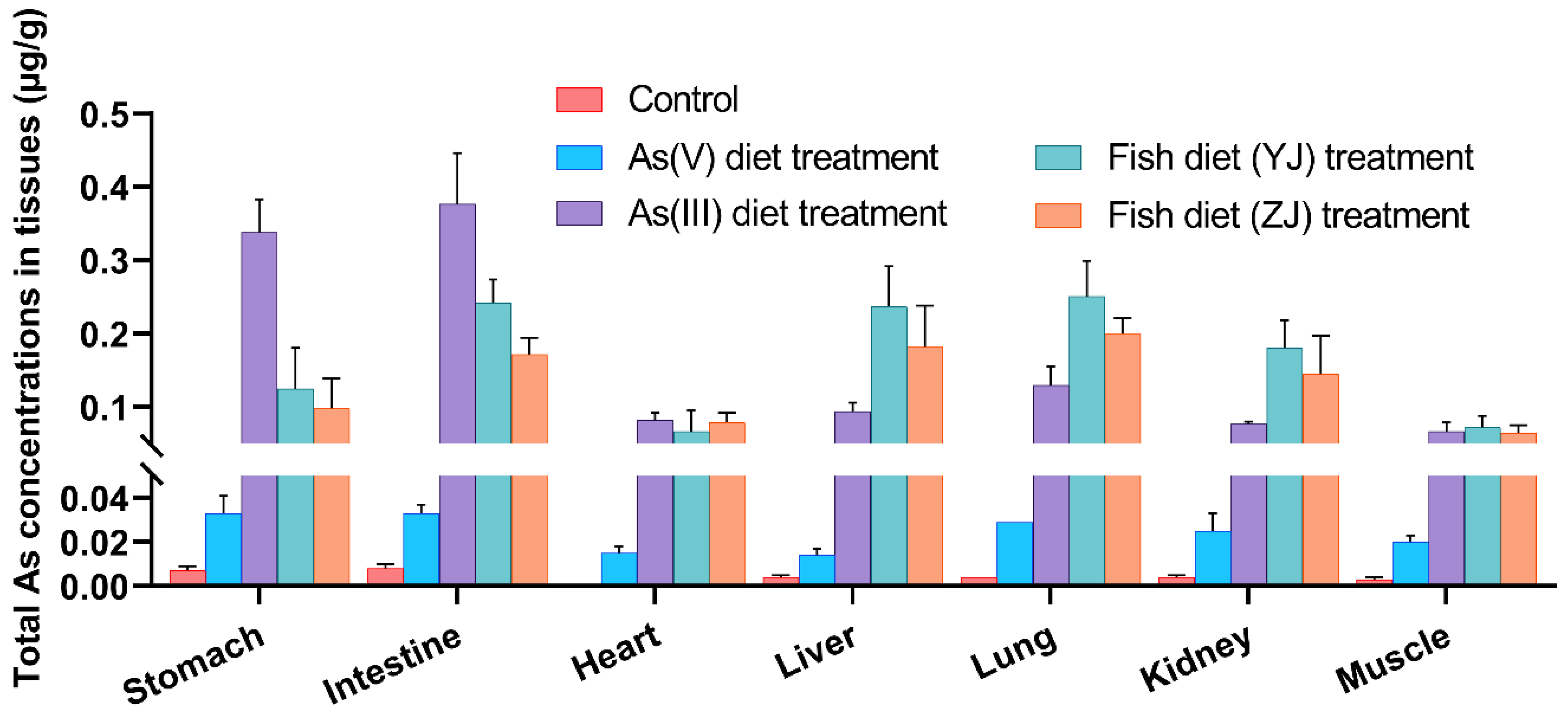
3.2. Differential Bioaccumulation in Various Internal Organs
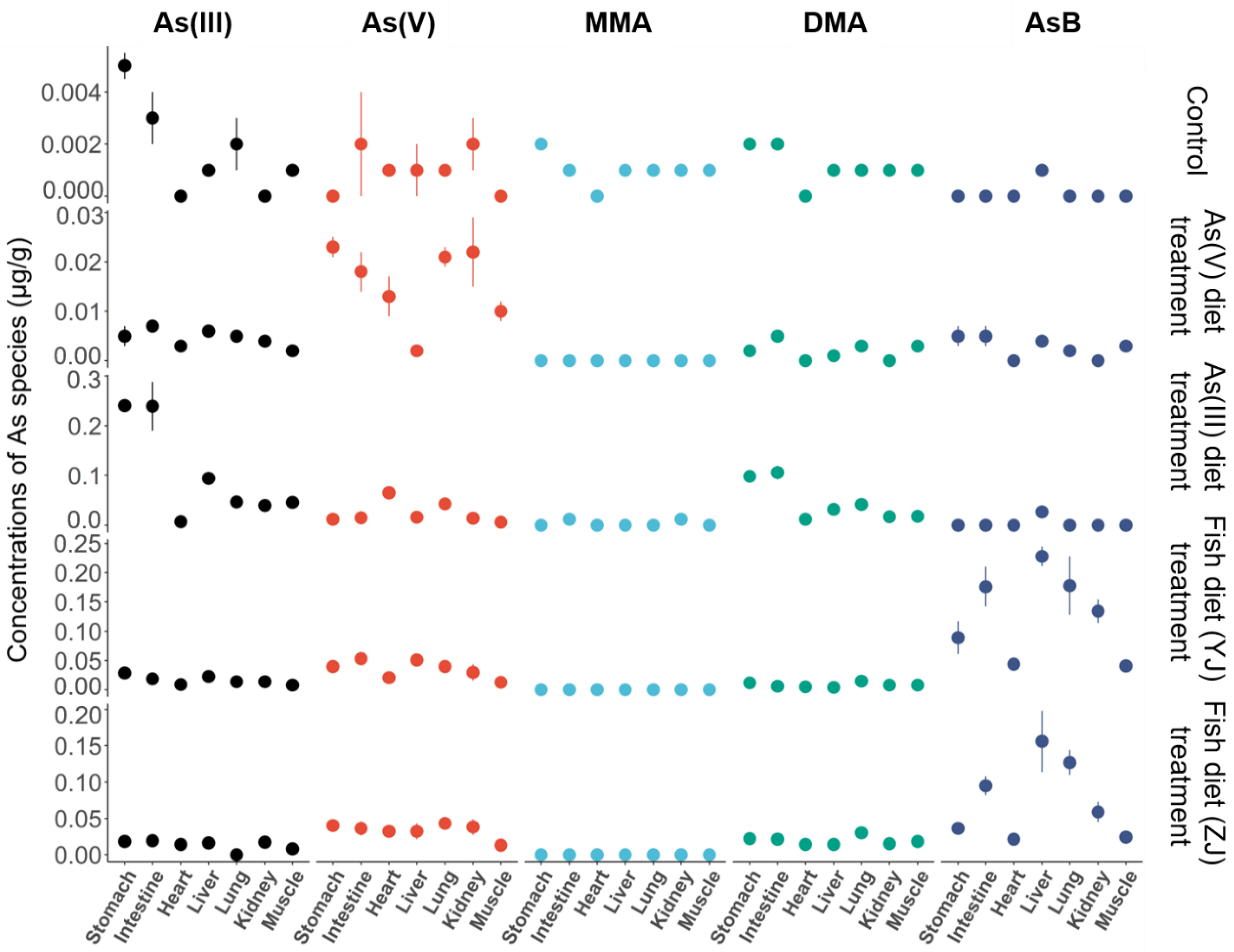
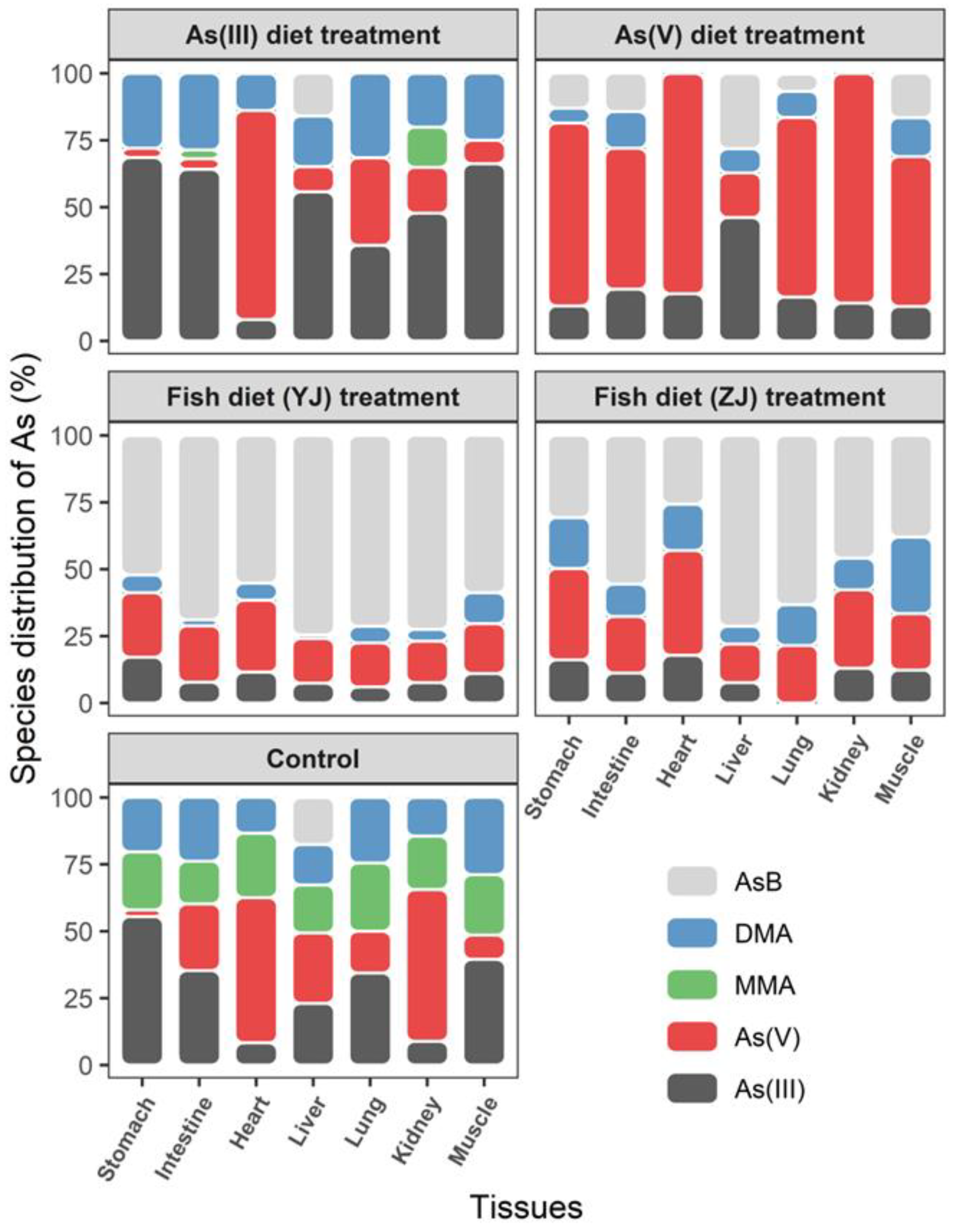
3.3. Arsenic Species Bioaccumulation and Biotransformation in Mice
3.4. Potential Toxicological Risks of Different Arsenic Forms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Backer, L.; Haskell, J.; Belova, A.; Greco, S.L. Estimated burden of disease from arsenic in drinking water supplied by domestic wells in the United States. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, W.X. Large-scale spatial and interspecies differences in trace elements and stable isotopes in marine wild fish from Chinese waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, D.J.; Naujokas, M.F.; Bradham, K.D.; Cowden, J.; Heacock, M.; Henry, H.F.; Lee, J.S.; Thomas, D.J.; Thompson, C.; Tokar, E.J.; et al. Arsenic and Environmental Health: State of the Science and Future Research Opportunities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moe, B.; Peng, H.Y.; Lu, X.F.; Chen, B.W.; Chen, L.W.L.; Gabos, S.; Li, X.F.; Le, X.C. Comparative cytotoxicity of fourteen trivalent and pentavalent arsenic species determined using real-time cell sensing. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 49, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.; Wang, W.X. Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.Q.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, H.X.; Zhang, L. Biotransformation and detoxification of inorganic arsenic in Bombay oyster Saccostrea cucullata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 158, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Aureli, F.; Raggi, A.; Cubadda, F. Arsenic speciation in freshwater fish: Focus on extraction and mass balance. Talanta 2010, 81, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, R.; Francesconi, K.A.; Kienzl, N.; Soeroes, C.; Fodor, P.; Varadi, L.; Raml, R.; Goessler, W.; Kuehnelt, D. Arsenic speciation in freshwater organisms from the river Danube in Hungary. Talanta 2006, 69, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, V.; Goodale, B.; Raab, A.; Schwerdtle, T.; Reimer, K.; Conklin, S.; Karagas, M.R.; Francesconi, K.A. Human exposure to organic arsenic species from seafood. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hao, X.; He, L.; He, W.; Chen, J. The study of lead content distribution in Chinese seafood and its oral bioavailability in mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Biotransformation of inorganic arsenic in a marine herbivorous fish Siganus fuscescens after dietborne exposure. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, J.; Krupp, E.M. Critical review or scientific opinion paper: Arsenosugars–A class of benign arsenic species or justification for developing partly speciated arsenic fractionation in foodstuffs? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvonga, C.; Rimmer, C.A.; Yu, L.L.; Lee, S.B. Organoarsenicals in Seafood: Occurrence, Dietary Exposure, Toxicity, and Risk Assessment Considerations–A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, B.M.; Moore, T.; Conklin, S.D.; Creed, J.T.; Wolf, D.C.; Thomas, D.J. Tissue distribution and urinary excretion of dimethylated arsenic and its metabolites in dimethylarsinic acid- or arsenate-treated rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wu, S.L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Smith, K.R.; Yao, X.H.; Gao, H.W. Global impact of atmospheric arsenic on health risk: 2005 to 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13975–13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Wang, J.H.; Yan, B.; Miao, A.J.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.Q. Progresses and emerging trends of arsenic research in the past 120 years. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1306–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, E.M.; Hughes, M.F.; Adair, B.M.; Highfill, J.H.; Crecelius, E.A.; Clewell, H.J.; Yager, J.W. Tissue distribution and urinary excretion of inorganic arsenic and its methylated metabolites in C57BL6 mice following subchronic exposure to arsenate in drinking water. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 232, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M. Mechanisms of arsenic biotransformation. Toxicology 2002, 181, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, W.R.; Mcbride, B.C.; Manji, H.; Reglinski, J. The metabolism of methylarsine oxide and sulfide. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1989, 3, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.F.; Devesa, V.; Adair, B.M.; Styblo, M.; Kenyon, E.M.; Thomas, D.J. Tissue dosimetry, metabolism and excretion of pentavalent and trivalent monomethylated arsenic in mice after oral administration. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 208, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marafante, E.; Vahter, M. The effect of methyltransferase inhibition on the metabolism of [74As] in mice and rabbits. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1984, 148, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marafante, E.; Vahter, M.; Norin, H.; Envall, J.; Sandstrom, M.; Christakopoulos, A. Biotransformation of dimethylarsinic acid in mouse, hamster and man. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1987, 7, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yoshida, K.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Inoue, Y.; Endo, G. Methylation and demethylation of dimethylarsinic acid in rats following chronic oral exposure. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 10, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiobara, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Animal species difference in the uptake of dimethylarsinous acid (DMA(III)) by red blood cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.T.; Katagiri, A.; Sakuma, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Ohmichi, M. Distributions and chemical forms of arsenic after intravenous administration of dimethylarsinic and monomethylarsonic acids to rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.T.; Mandal, B.K.; Katagiri, A.; Sakuma, Y.; Kawakami, A.; Ogra, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sei, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Anzai, K.; et al. Dimethylthioarsenicals as arsenic metabolites and their chemical preparations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, M.; Ulven, S.M.; Meltzer, H.M.; Alexander, J. Arsenic in the human food chain, biotransformation and toxicology–Review focusing on seafood arsenic. J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.Q.; Song, D.D.; Du, S.; Zhang, L. Arsenic speciation in wild marine organisms and a health risk assessment in a subtropical bay of China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 626, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Marafante, E.; Dencker, L. Metabolism of arsenobetaine in mice, rats and rabbits. Sci. Total Environ. 1983, 30, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Concha, G. Role of metabolism in arsenic toxicity. Pharm. Toxicol. 2001, 89, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, H.; Kaise, T.; Yamamura, Y. Metabolism and excretion of orally administered arsenobetaine in the hamster. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1986, 36, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, C.F.; Brima, E.I.; Jenkins, R.O. Biotransformation of arsenobetaine by microorganisms from the human gastrointestinal tract. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2015, 20, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, K.; Kuroda, K.; Inoue, Y.; Chen, H.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, G. Metabolites of arsenobetaine in rats: Does decomposition of arsenobetaine occur in mammals? Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, C.; Raab, A.; Williams, P.N.; Deacon, C.; Haris, P.I.; Meharg, A.A.; Feldmann, J. Accumulation or production of arsenobetaine in humans? J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Nordin, J.Z.; O’Loughlin, A.; Gustafsson, Y.; Corso, G.; Mäger, I.; Vader, P.; Lee, Y.; Sork, H.; Seow, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z. Speciation analysis of six arsenic species in marketed shellfish: Extraction optimization and health risk assessment. Food. Chem. 2018, 244, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, J.D.; Brown, J.W.N.I. Measurement of arsenic species in infant rice cereals by liquid chromatography inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 3, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenyon, E.M.; Del Razo, L.M.; Hughes, M.F. Tissue distribution and urinary excretion of inorganic arsenic and its methylated metabolites in mice following acute oral administration of arsenate. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 85, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Jin, Y.; Lv, X.; Sun, G. Distribution and speciation of arsenic by transplacental and early life exposure to inorganic arsenic in offspring rats. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2010, 134, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, N.; Li, X. Advances in Understanding How Heavy Metal Pollution Triggers Gastric Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7825432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusdottir, S.; Heinken, A.; Kutt, L.; Ravcheev, D.A.; Bauer, E.; Noronha, A.; Greenhalgh, K.; Jager, C.; Baginska, J.; Wilmes, P.; et al. Generation of genome-scale metabolic reconstructions for 773 members of the human gut microbiota. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nurchi, V.M.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Crisponi, G.; Alexander, J.; Bjorklund, G.; Aaseth, J. Arsenic Toxicity: Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Agents. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Cao, W.; Wei, P.; Li, T.; Weng, W. Speciation transformation of arsenic in abalone viscera hydrolysate fraction: In vitro digestion and in vivo metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Gao, S.; Xia, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, A.; Ji, S. Study of the accumulation and distribution of arsenic species and association with arsenic toxicity in rats after 30 days of oral realgar administration. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 247, 111576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.M.O.; Grotto, D.; Batista, B.L.; Barbosa, F.J. Distribution of arsenic and oxidative stress in mice after rice ingestion. J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Xue, J.; Tu, P.; Lai, Y.; Ru, H.; Lu, K. Gut microbiome disruption altered the biotransformation and liver toxicity of arsenic in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Montalvo, E.A.; Valenzuela, O.L.; Sanchez-Pena, L.C.; Albores, A.; Del Razo, L.M. Dose-dependent urinary phenotype of inorganic arsenic methylation in mice with a focus on trivalent methylated metabolites. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; Xiang, R.; Pei, Y. (1)H NMR-based metabonomics study on the toxicity alleviation effect of other traditional Chinese medicines in Niuhuang Jiedu tablet to realgar (As2S2). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, K.T. Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: Modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2001, 172, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, S.F.; Hasan, M.S.; Yang, Z.; Stevens, A.W.; Brett, J.; Peng, Z. Feeding Arsenic-Containing Rice Bran to Growing Pigs: Growth Performance, Arsenic Tissue Distribution, and Arsenic Excretion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M. Species-Differences in the metabolism of arsenic compounds. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 8, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehnelt, D.; Goessler, W. Organoarsenic compounds in the terrestrial environment. In Organometallic Compounds in the Environment; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 223–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.X. Arsenic bioaccumulation in a marine juvenile fish Terapon jarbua. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.F.; Kenyon, E.M.; Edwards, B.C.; Mitchell, C.T.; Razo, L.M.D.; Thomas, D.J. Accumulation and metabolism of arsenic in mice after repeated oral administration of arsenate. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 191, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Martinez-Castillo, M.; Quintana-Perez, J.C.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.G.; Tamay-Cach, F.; Valenzuela-Limon, O.L.; Garcia-Montalvo, E.A.; Hernandez-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2020, 110, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.; Maity, J.P.; Jean, J.S.; Liu, C.C.; Liu, C.W.; Bundschuh, J.; Lu, H.Y. Health risks for human intake of aquacultural fish: Arsenic bioaccumulation and contamination. J. Environ. Sci. Health Toxic Hazard. Substain. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaise, T.; Yamauchi, H.; Horiguchi, Y.; Tani, T.; Watanabe, S.; Hirayama, T.; Fukui, S. A comparative study on acute toxicity of methylarsonic acid, dimethylarsinic acid and trimethylarsine oxide in mice. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1989, 3, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popowich, A.; Zhang, Q.; Le, X.C. Arsenobetaine: The ongoing mystery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, K.; Zhang, W. Significant Biotransformation of Arsenobetaine into Inorganic Arsenic in Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020091
Zhang J, Ye Z, Huang L, Zhao Q, Dong K, Zhang W. Significant Biotransformation of Arsenobetaine into Inorganic Arsenic in Mice. Toxics. 2023; 11(2):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020091
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jichao, Zijun Ye, Liping Huang, Qianyu Zhao, Kaige Dong, and Wei Zhang. 2023. "Significant Biotransformation of Arsenobetaine into Inorganic Arsenic in Mice" Toxics 11, no. 2: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020091
APA StyleZhang, J., Ye, Z., Huang, L., Zhao, Q., Dong, K., & Zhang, W. (2023). Significant Biotransformation of Arsenobetaine into Inorganic Arsenic in Mice. Toxics, 11(2), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020091






