Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Daphnia magna
2.3. Acute Experiments
2.4. Chronic Experiments
2.5. Measurement of Physiological Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Immobilization Toxicity Tests
3.2. Acute Lethality Toxicity Tests
3.3. Damage Caused by MB to D. magna Bodies in Acute Toxicity Tests
3.4. Chronic Toxicity of Methylene Blue in D. magna
3.4.1. Heart Rate and Thoracic Limb Activity
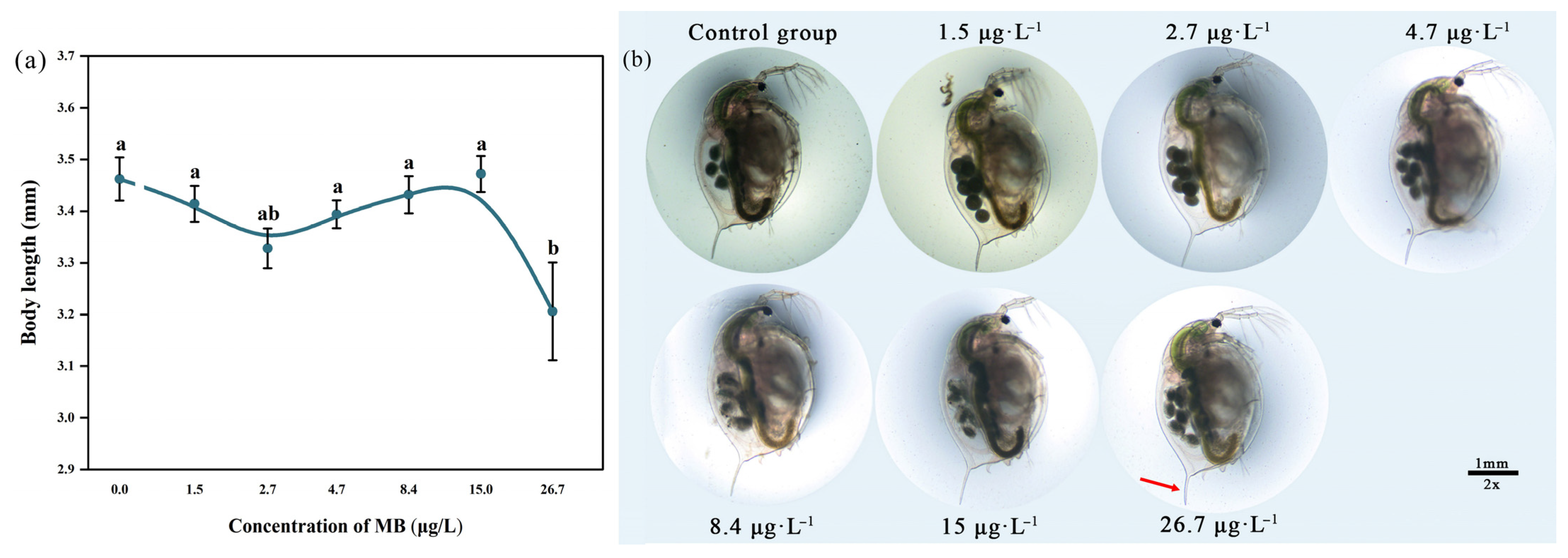
3.4.2. Body Length
3.4.3. Reproduction
3.5. Antioxidant Enzymes, Detoxification Enzymes, and Oxidative Damage Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balarak, D.; Bazzi, M.; Shehu, Z.; Chandrika, K. Application of Surfactant-Modified Bentonite for Methylene Blue Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Orient. J. Chem. 2020, 36, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, H.; Kul, A.R. Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by nonliving lichen (Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf.), as a novel biosorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijinyawa, A.H.; Durga, G.; Mishra, A. A sustainable process for adsorptive removal of methylene blue onto a food grade mucilage: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and equilibrium evaluation. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2019, 21, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarik, I.; Safarikova, M. Detection of low concentrations of malachite green and crystal violet in water. Water Res. 2002, 36, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tran, T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Kumar, P.S.; Din, A.T.; Qazaq, A.S.; Vo, D.V. Green synthesis of Mn3O4 nanoparticles using Costus woodsonii flowers extract for effective removal of malachite green dye. Environ. Res. 2022, 214 Pt 2, 113925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarojini, G.; Babu, S.V.; Rajamohan, N.; Rajasimman, M. Performance evaluation of polymer-marine biomass based bionanocomposite for the adsorptive removal of malachite green from synthetic wastewater. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidian, S.; Taghavi, M.; Kohan, N.A.; Dehghan, A.; Afsharnia, M. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using bismuth oxyiodide from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, L.; Lins, P.; Costa, M.; Almeida, R.; Abud, A.; Soletti, J.; Dotto, G.; Tanabe, E.; Sellaoui, L.; Carvalho, S.; et al. Adsorption of methylene blue on agroindustrial wastes: Experimental investigation and phenomenological modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 141, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosswattaarachchi, A.M.; Cook, T.R. Repurposing the Industrial Dye Methylene Blue as an Active Component for Redox Flow Batteries. Chemelectrochem 2018, 5, 3437–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawagon, C.P.; Amon, R.E.C. Magnetic rice husk ash ‘cleanser’ as efficient methylene blue adsorbent. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, M.A.A.; Sudi, R.M. Valorization of human hair as methylene blue dye adsorbents. Green Process. Synth. 2018, 7, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Du, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. Degradation of methylene blue by natural manganese oxides: Kinetics and transformation products. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlberg, S.T.; Diamant, A.; Ofir, R.; Zilberg, D. Characterization of swim bladder non-inflation (SBN) in angelfish, Pterophyllum scalare (Schultz), and the effect of exposure to methylene blue. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanian, S.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Banaee, M. Effects of exposure to a therapeutic level of methylene blue on antioxidant capacity, haemato-immunological responses and resistance of goldfish, Carassius auratus to Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnipseed, S.B.; Roybal, J.E.; Plakas, S.M.; Pfenning, A.P.; Hurlbut, J.A.; Long, A.R. Determination of methylene blue in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) tissue by liquid chromatography with visible detection. J. Aoac Int. 1997, 80, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S. A comprehensive review on recent developments in bentonite-based materials used as adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 1091–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Do, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kang, M. Fast and highly efficient removal of dye from aqueous solution using natural locust bean gum based hydrogels as adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 143, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forro, L.; Korovchinsky, N.M.; Kotov, A.A. Global diversity of cladocerans (Cladocera; Crustacea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, S.; Ploessl, F.; Bracher, F.; Laforsch, C. Single and combined toxicity of pharmaceuticals at environmentally relevant concentrations in Daphnia magna—A multigenerational study. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarazako, N.; Oda, S. The water flea Daphnia magna (Crustacea, Cladocera) as a test species for screening and evaluation of chemicals with endocrine disrupting effects on crustaceans. Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Cui, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Shi, Z.; Tan, C.; Yang, X. Nano-TiO2 enhances the toxicity of copper in natural water to Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, V.P.; Ventura, M.A.; Amarillo, P.B. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Water and Sediment in Areas of Taal Lake with Heavy Aquaculture Practices Using Allium cepa and Daphnia magna Assay. Philipp. J. Sci. 2022, 151, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, K.; Kaushik, N.K. An assessment of the chronic toxicity of the synthetic pyrethroid, fenvalerate, to Daphnia galeata mendotae, using life tables. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 44, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, S.D. The individual and population effects of tetracycline on Daphnia magna in multigenerational exposure. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpradit, P.; Peerakietkhajorn, S. Disturbances in growth, oxidative stress, energy reserves and the expressions of related genes in Daphnia magna after exposure to ZnO under thermal stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 21, 161682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaye, N.; Musee, N. Effects of Two Antiretroviral Drugs on the Crustacean Daphnia magna in River Water. Toxics 2022, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galhano, V.; Zeumer, R.; Monteiro, M.S.; Knopf, B.; Meisterjahn, B.; Soares, A.M.; Loureiro, S.; Schlechtriem, C.; Lopes, I. Effects of wastewater-spiked nanoparticles of silver and titanium dioxide on survival, growth, reproduction and biochemical markers of Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.S.; Khiew, P.S.; Chiu, W.S.; Tan, Y.F.; Leong, C.O. Polyethyleneimine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as Antifouling Photocatalyst for Wastewater Treatment. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 211: Daphnia Magna Reproduction Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, F.R.; Machado, A.L.; Soares, A.M.; de Oliveira, D.P.; Pestana, J.L. Life history and behavior effects of synthetic and natural dyes on Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Xi, Y.L. Demographic parameters and mixis of three Brachionus angularis Gosse (Rotatoria) strains fed on different algae. Limnologica 2008, 38, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Rongrong, M.; Zongying, Y.; Kun, H. Acute toxicity of prometryn, phoxim, and methylene blue and their histopathological effects on Penaeus vannamei. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Kan, X.; Shi, X.; Fan, X. The acute poisoning function of methyl to Limnodilus hoffineisteri. Nat. Sci. J. Harbin Norm. Univ. 2007, 4, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, Y. Acute toxicity assessment of textile dyes and textile and dye industrial effluents using Daphnia magna bioassay. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2008, 24, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanhere, J.; Gopinathan, R.; Banerjee, J. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Malachite Green on Non-Target Aquatic Organisms: Chlorella Pyrenoidosa and Daphnia magna. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Somogyvári, D.; Kovács, A.W.; Mörtl, M.; Székács, A.; Győri, J. Physiological and metabolic alterations induced by commercial neonicotinoid formulations in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinkey, D.; Lari, E.; Woodman, S.G.; Steinkey, R.; Luong, K.H.; Wong, C.S.; Pyle, G.G. The effects of diltiazem on growth, reproduction, energy reserves, and calcium-dependent physiology in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2019, 232, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Lei, H.; Sun, W.; Li, D.; Dong, W.; Chen, H.; Xie, L. Altered life history traits and transcripts of molting- and reproduction-related genes by cadmium in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, J.M.; Oliveira, F.J.; Airoldi, C.; Filho, E.C.S. Organophilic nickel phyllosilicate for reactive blue dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghan, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.-K. Cardiotoxicity and neurobehavioral effects induced by acrylamide in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Jasieczek, M.; Kosztowny, E. Ketoprofen affects swimming behavior and impairs physiological endpoints of Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Ślaska, B.; Bochra, J.; Gumieniak, K.; Gałek, K. Procaine penicillin alters swimming behaviour and physiological parameters of Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18662–18673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, J.M.; Krijgsman, B.J. Physiological investigations into the heart function of Daphnia. J. Physiol. 1951, 115, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.K.; Wann, K.T.; Matthews, S.B. Lactose causes heart arrhythmia in the water flea Daphnia pulex. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirtle, T.J.; Carr, T.L.; Khurana, T.; Meeker, G. ZD7288 and mibefradil inhibit the myogenic heartbeat in Daphnia magna indicating its dependency on HCN and T-type calcium ion channels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2018, 222, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, H.; Ando, H.; Makioka, T. Myogenic Heartbeat in the Primitive Crustacean Triops longicaudatus. Biol. Bull. 1997, 193, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Yoon, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.D. Mode of action characterization for adverse effect of propranolol in Daphnia magna based on behavior and physiology monitoring and metabolite profiling. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bownik, A.; Kowalczyk, M.; Bańczerowski, J. Lambda-cyhalothrin affects swimming activity and physiological responses of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2018, 216, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Yang, H.; Xia, J.; Zong, Y.; Liu, J. Toxicity of Cu and Cr Nanoparticles to Daphnia magna. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 228, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, E.; Steinkey, D.; Morandi, G.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Giesy, J.P.; Pyle, G.G. Oil sands process-affected water impairs feeding by Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovern, S.B.; Strickler, J.R.; Klaper, R.D. Behavioral and physiological changes in Daphnia magna when exposed to nanoparticle suspensions (titanium dioxide, nano-C60, and C60HxC70Hx). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 12, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Baldwin, L.A. Toxicology rethinks its central belief. Nature 2003, 421, 691–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, K.; Cao, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Combined effects of hypoxia and ammonia to Daphnia similis estimated with life-history traits. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5379–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisseaux, P.; Hopkinson, P.; Santillo, D.; Smith, C.; Garmulewicz, A.; Powell, Z.; Galloway, T. Environmental safety of second and third generation bioplastics in the context of the circular economy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.-D.; Itayama, T.; Ramaraj, R.; Iwami, N.; Shimizu, K.; Dao, T.-S.; Pham, T.-L.; Maseda, H. Chronic ecotoxicology and statistical investigation of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin to Daphnia magna under extendedly long-term exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.E.; Roslev, P. Behavioral responses and starvation survival of Daphnia magna exposed to fluoxetine and propranolol. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, E.; Villarroel, M.; Andreu, E.; Ferrando, M. Disturbances in energy metabolism of Daphnia magna after exposure to tebuconazole. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, A.; Tišler, T.; Erjavec, B.; Pintar, A. Antioxidant responses and whole-organism changes in Daphnia magna acutely and chronically exposed to endocrine disruptor bisphenol A. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 86, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wei, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Acute toxicity and responses of antioxidant systems to dibutyl phthalate in neonate and adult Daphnia magna. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Fu, Y.; Dong, S.; Ma, Y.; Meng, H.; Guo, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Psychoactive drugs citalopram and mirtazapine caused oxidative stress and damage of feeding behavior in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.; Blake-Kalff, M.; Davies, E. Detoxification of xenobiotics by plants: Chemical modification and vacuolar compartmentation. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, L.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L. Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage of three task-specific ionic liquids ([C2NH2MIm] BF4,[MOEMIm] BF4, and [HOEMIm] BF4) to zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Koedrith, P.; Seo, Y.R. Ecotoxicogenomic Approaches for Understanding Molecular Mechanisms of Environmental Chemical Toxicity Using Aquatic Invertebrate, Daphnia Model Organism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12261–12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Xie, N.; Ma, H.; Dai, Y.; Xu, B.; Lin, Q.; Huang, H. Acute toxicity test of copper iron mixture, metrifonate, methylene blue and povidone-iodine on summerlings of Megalobrama terminalis. Fish. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2020, 47, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Qu, J.; Zhou, F. Study on the acute toxicity of methylene blue to young Rhodeus Ocellatus. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2010, 37, 131–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rifici, L.M.; Cherry, D.S.; Farris, J.L.; Cairns, J., Jr. Acute and subchronic toxicity of methylene blue to larval fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas): Implications for aquatic toxicity testing. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, K.S. Toxicity of some chemical therapeutics to the commercial shrimp, Penaeus californiensis. Aquaculture 1976, 7, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willford, W.A.; USDOI, FWS, Bur Sport Fish Wildl. Invest Fish Control No.18, Resourc Publ No. 35: 10 (1966) as Cited in the ECOTOX Database. 28 November 2022. [Google Scholar]










| Chemical Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | CAS Registry Number | Solubility (g/L) | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloro-3,7-bis(dimethylamino) phenothiazine-5-buzz-trishydrate | C16H18CIN3S·3 (H2O) | 373.9 | 7220-79-3 | 50 (20 °C) |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Wen, M.; Ji, G. Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna. Toxics 2023, 11, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070594
Li S, Cui Y, Wen M, Ji G. Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna. Toxics. 2023; 11(7):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070594
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuhui, Yixin Cui, Min Wen, and Gaohua Ji. 2023. "Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna" Toxics 11, no. 7: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070594
APA StyleLi, S., Cui, Y., Wen, M., & Ji, G. (2023). Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna. Toxics, 11(7), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070594







