Exposure to Molybdate Results in Metabolic Disorder: An Integrated Study of the Urine Elementome and Serum Metabolome in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Animal Experiment
2.3. Histological Examination
2.4. Analysis of Elementome in Urine
2.5. Analysis of Metabolome in Serum
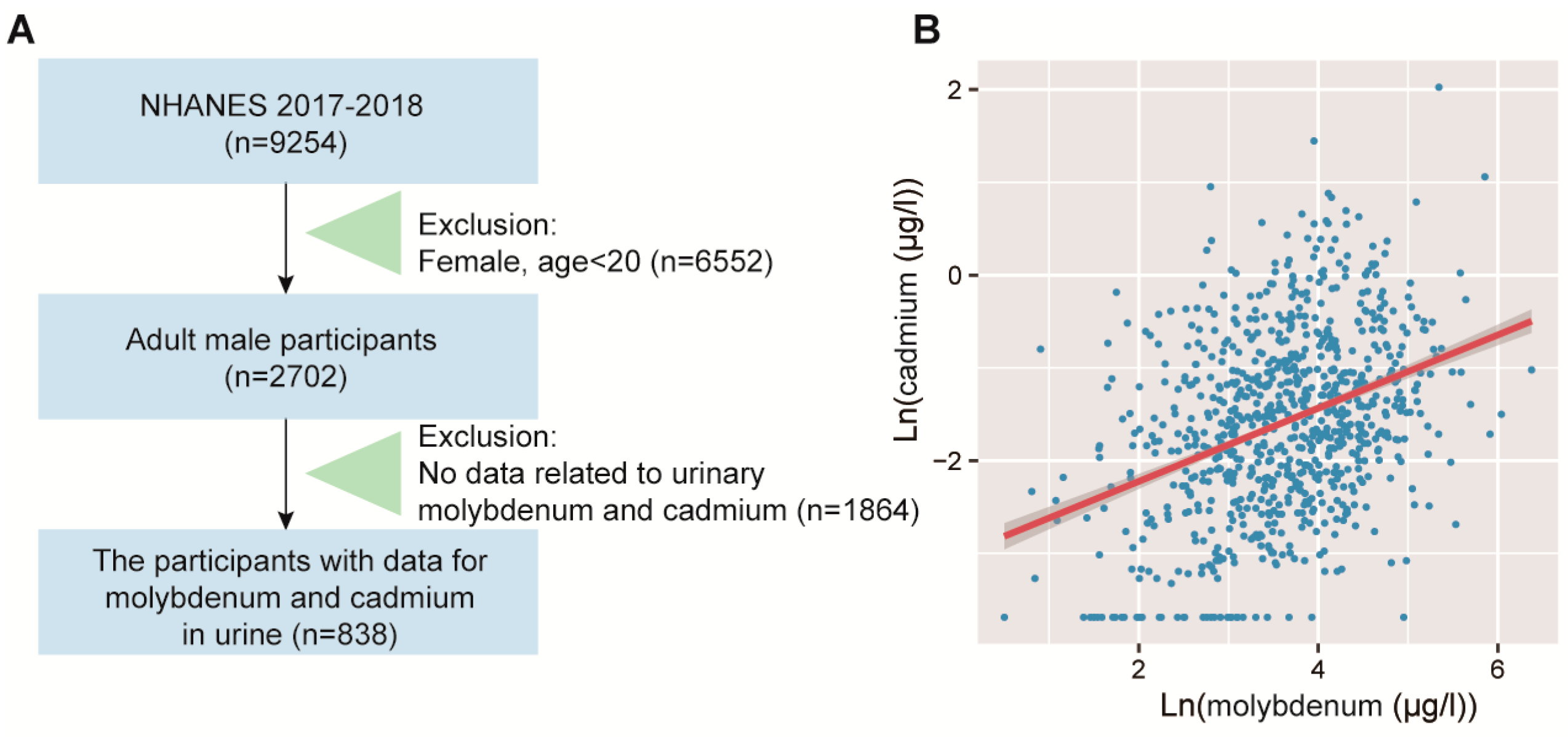
2.6. Human NHANES Population Study
2.7. Assessment of Molybdenum and Cadmium Exposure in NHANES
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Molybdate Exposure on Body Weight, Organ Coefficients, and Histopathological Examination in Mice
3.2. The Effect of Molybdate Exposure on the Serum Metabolome in Mice
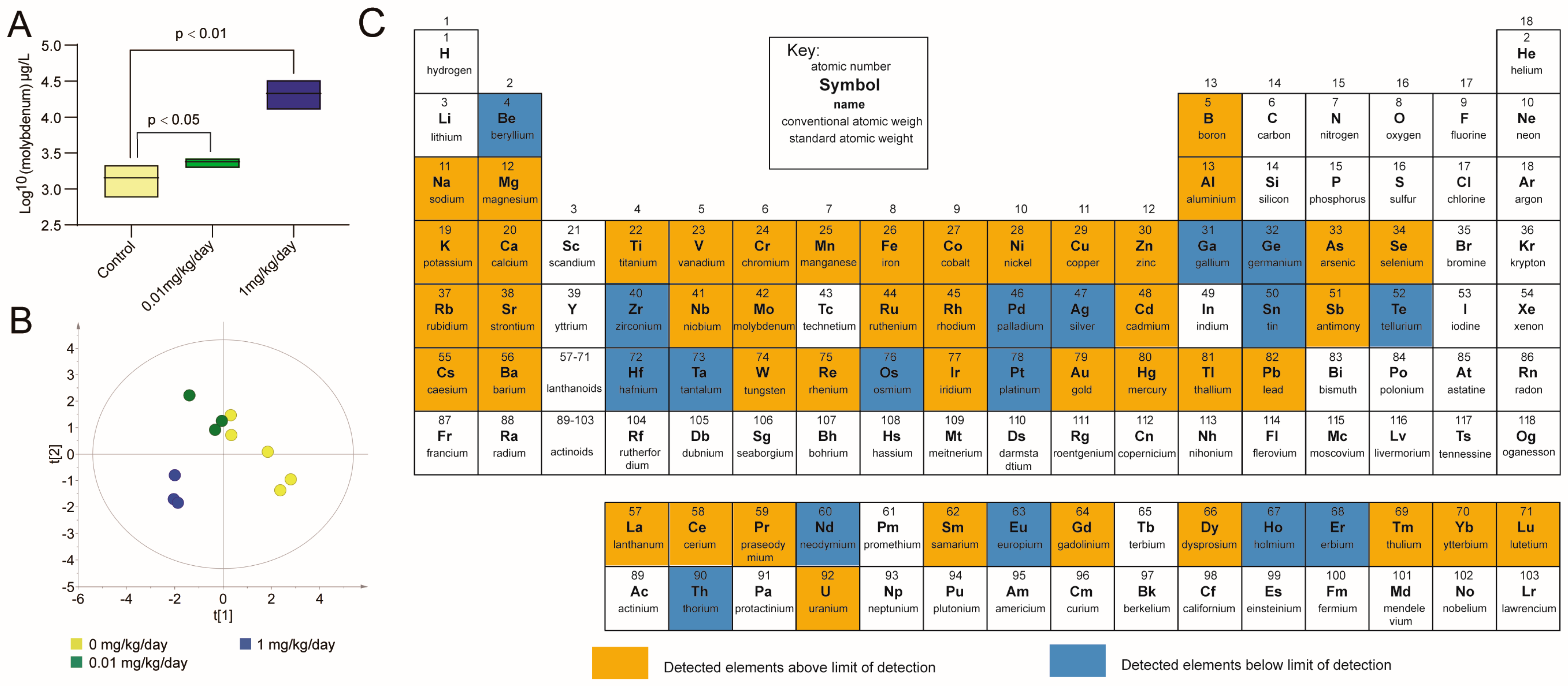
3.3. Molybdate Exposure Increased the Urinary Molybdenum Content and Affected the Urine Elementome in Mice
3.4. Validation of the Positive Correlation between Urinary Molybdenum and Cadmium in Humans
3.5. Correlation between Urinary Cadmium and Differential Serum Metabolites in Mice
4. Discussion
4.1. The Direct Effects of Molybdate Exposure on Serum Metabolome
4.2. The Effects of Molybdate Exposure on Urine Elementome
4.3. The Indirect Effects of Molybdate on Serum Metabolome through Urine Elementome
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Himoto, T.; Masaki, T. Current Trends of Essential Trace Elements in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobańska, Z.; Zapór, L.; Szparaga, M.; Stępnik, M. Biological effects of molybdenum compounds in nanosized forms under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2020, 33, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani Yengejeh, S.; Liu, J.; Kazemi, S.A.; Wen, W.; Wang, Y. Effect of Structural Phases on Mechanical Properties of Molybdenum disulfide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5994–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, M.; Murcia, M.; Soler-Blasco, R.; Casas, M.; Zubero, B.; Riutort-Mayol, G.; Gil, F.; Olmedo, P.; Grimalt, J.O.; Amorós, R.; et al. Exposure to metals and metalloids among pregnant women from Spain: Levels and associated factors. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafford, J.M.; Lambert, C.E.; Zyskowski, J.A.; Engfehr, C.L.; Fletcher, O.J.; Clark, S.L.; Tiwary, A.; Gulde, C.M.; Sample, B.E. Dietary toxicity of soluble and insoluble molybdenum to northern bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnlund, J.R.; Keyes, W.R.; Peiffer, G.L. Molybdenum absorption, excretion, and retention studied with stable isotopes in young men at five intakes of dietary molybdenum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.R.H.; El-Atawy, R.H.; Ghoneim, A.M.; El-Ghor, A.A. Induction of fetal abnormalities and genotoxicity by molybdenum nanoparticles in pregnant female mice and fetuses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 23950–23962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxicological Profile for Molybdenum; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) Toxicological Profiles: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=1482&tid=289 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Pi, S.; Wei, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Li, G.; Nie, G.; Hu, G. Cadmium and molybdenum co-exposure triggers autophagy via CYP450s/ROS pathway in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Singh, S.P. Effects of molybdenum on fertility of male rats. Biometals 2002, 15, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G.; Belaidi, A.A. Molybdenum in human health and disease. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013, 13, 415–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A. Reading e-journal article pdf files—Turn your laptop into an electronic book. Anaesth Intensive Care 2006, 34, 519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dumas, M.E. Metabolome 2.0: Quantitative genetics and network biology of metabolic phenotypes. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhifd, M.; Beger, R.; Flynn, T.; Guo, L.; Harris, G.; Hogberg, H.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Kamp, H.; Kleensang, A.; Maertens, A.; et al. Quality assurance of metabolomics. ALTEX 2015, 32, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ding, X.; Shi, R.; Thorne, R.F.; Zhang, X.D.; Hu, W.; Wu, M. CircACC1 Regulates Assembly and Activation of AMPK Complex under Metabolic Stress. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 157–173.e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, F.C.; Collao, V.; Bhattacharya, S.K. High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Lipidomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2625, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Alonso, M.; Prieto Montaña, F.; Miranda, M.; Castillo, C.; Hernández, J.; Luis Benedito, J. Interactions between toxic (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and nutritional essential (Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Se, Zn) elements in the tissues of cattle from NW Spain. Biometals 2004, 17, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Xing, C.; Huang, A.; Zhuang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G.; Mao, Y.; Cao, H. Molybdenum Induces Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage in Kidney of Goats. Biol. Trace Elem Res. 2020, 197, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, R.R.; Kruse, T. Cell biology of molybdenum in plants and humans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.L.; Li, S.; Qin, C.B.; Zhu, Z.X.; Hu, W.P.; Yang, L.P.; Lu, R.H.; Li, W.J.; Nie, G.X. Intestinal microbiota and lipid metabolism responses in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) following copper exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y. Iron Metabolism in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C. Magnesium and disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission Scientific Committee on Food. Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Molybdenum; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, G.D.; Keith, S.; Faroon, O.; Buser, M.; Ingerman, L.; Hard, C.; Citra, M.J.; Nguyen, A.; Klotzbach, J.M.; Diamond, G.L. Toxicological profile for molybdenum: Draft for public comment. 2017. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/46170 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Bernasconi, L.; Brolli, B.; Negro, A.; Zoino, J.L.; Schicchi, A.; Petrolini, V.M.; Lonati, D.; Ronchi, A.; Locatelli, C.A. Accidental ingestion of sodium molybdate at the workplace followed by short-term biomonitoring. Med. Lav. 2022, 113, e2022015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaoui, M.; Fiette, L. Histopathology procedures: From tissue sampling to histopathological evaluation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 691, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Dehli Villanger, G.; Aase, H.; Xia, Y. Identifying a critical window of maternal metal exposure for maternal and neonatal thyroid function in China: A cohort study. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M.K.; Arain, A.L.; Shao, J.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.; Lozoff, B.; Meeker, J.D. Distribution and predictors of 20 toxic and essential metals in the umbilical cord blood of Chinese newborns. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tang, R.; Fu, G.; Xu, B.; Zhu, P.; Qiao, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, B.; Qin, Y.; Lu, C.; et al. Association of exposure to phenols and idiopathic male infertility. J. Hazard Mater. 2013, 250–251, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, T.; Feng, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, K.; Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, M. A metabolomic study on the gender-dependent effects of maternal exposure to fenvalerate on neurodevelopment in offspring mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Song, Q.; Liang, Q.; Liang, M.; Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Lowe, S.; et al. Combined exposure to multiple metals on cardiovascular disease in NHANES under five statistical models. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sevillano, M.A.; García-Barrera, T.; Navarro, F.; Gailer, J.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L. Use of elemental and molecular-mass spectrometry to assess the toxicological effects of inorganic mercury in the mouse Mus musculus. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5853–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendawy, A.O.; Khattab, M.S.; Sugimura, S.; Sato, K. Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid as a Supplement on Animal Performance, Iron Status, and Immune Response in Farm Animals: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Koda, A.; Nozawa, N.; Ota, U.; Kondo, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Kamiya, A.; Miyashita, K.; Itoh, H.; Nakajima, M.; et al. Combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid and ferrous ion reduces plasma glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. FEBS Open Bio. 2016, 6, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z.; Djaldetti, M. 5-Aminolevulinic acid stimulation of porphyrin and hemoglobin synthesis by uninduced Friend erythroleukemic cells. Cell Differ. 1979, 8, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modec, B.; Dolenc, D.; Kasunic, M. Complexation of molybdenum(V) with glycolic acid: An unusual orientation of glycolato ligand in {Mo2O4}2+ complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-González, E.R.; Jackman, J.A.; Yoon, B.K.; Mokrzecka, N.; Cho, N.J. pH-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Glycolic Acid: Implications for Anti-Acne Formulations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.T.; Su, W.C.; Chen, Q.X.; Shen, D.Y.; Zhuang, J.X. The inhibitory kinetics and mechanism of glycolic acid on lipase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsai, Y.S.; Chang, C.S.; Kuo, T.C.; Yao, W.J.; Shieh, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Kuo, P.H. The metabolome profiling and pathway analysis in metabolic healthy and abnormal obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw, S.C.; Wong, Z.Z.; Anderson, R.; Martins da Silva, S. l-carnitine and l-acetylcarnitine supplementation for idiopathic male infertility. Reprod. Fertil. 2020, 1, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Kashkooli, S.; Amini, M.R.; Shahinfar, H.; Djafarian, K.; Clark, C.C.T.; Shab-Bidar, S. The effects of L-carnitine supplementation on lipid concentrations inpatients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2020, 12, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, L.A.; Heath, S.H.; Hagen, T.M. Acetyl-L-carnitine supplementation reverses the age-related decline in carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) activity in interfibrillar mitochondria without changing the L-carnitine content in the rat heart. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2012, 133, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, F.; Xing, C.; Hu, G.; Cao, H. Effects of Different Levels of Molybdenum on Rumen Microbiota and Trace Elements Changes in Tissues from Goats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 174, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G.; Mendel, R.R. Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis and molybdenum enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Nie, G.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Dai, X.; Liao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Cao, H.; Xing, C.; et al. Molybdenum and cadmium co-induce oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 383, 121157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, J.K.; Panchal, H.; Saraf, P. Cadmium as a testicular toxicant: A Review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Cao, H.; Dai, X.; Xing, C.; Xu, X.; Nie, G.; Zhang, C. Molybdenum and Cadmium exposure influences the concentration of trace elements in the digestive organs of Shaoxing duck (Anas platyrhyncha). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, J.D.; Rossano, M.G.; Protas, B.; Diamond, M.P.; Puscheck, E.; Daly, D.; Paneth, N.; Wirth, J.J. Cadmium, lead, and other metals in relation to semen quality: Human evidence for molybdenum as a male reproductive toxicant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umerska, A.; Cassisa, V.; Matougui, N.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Eveillard, M.; Saulnier, P. Antibacterial action of lipid nanocapsules containing fatty acids or monoglycerides as co-surfactants. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spink, C.H. Differential scanning calorimetry. Methods Cell Biol. 2008, 84, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Generating the Blood Exposome Database Using a Comprehensive Text Mining and Database Fusion Approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 97008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat Yemiş, G.; Delaquis, P. Natural Compounds With Antibacterial Activity Against Cronobacter spp. in Powdered Infant Formula: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 595964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Weik, T.; Roider, G.; Summer, B.; Thomsen, M. Influence of Surface Coating on Metal Ion Release: Evaluation in Patients With Metal Allergy. Orthopedics 2016, 39, S24–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucovic, D.; Kulas, J.; Mirkov, I.; Popovic, D.; Zolotarevski, L.; Despotovic, M.; Kataranovski, M.; Aleksandra, P.A. Oral Cadmium Intake Enhances Contact Allergen-induced Skin Reaction in Rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Metabolite | 0.01 mg/kg/day | 1 mg/kg/day | 0, 0.01, 1 mg/kg/day a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | p | Fold Change | p | r | p | |
| 5-aminolevulinic acid | 1.145 | 0.100 | 1.100 | 0.041 * | 0.691 | 0.019 * |
| norvaline | 0.828 | 0.195 | 0.763 | 0.026 * | −0.573 | 0.066 |
| pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid | 0.397 | 0.000 * | 0.504 | 0.011 * | −0.473 | 0.142 |
| estriol | 13.253 | 0.066 | 8.636 | 0.042 * | 0.309 | 0.355 |
| glycolic acid | 2.458 | 0.056 | 2.422 | 0.008 * | 0.882 | 0.000 * |
| l-acetylcarnitine | 1.446 | 0.145 | 1.600 | 0.045 * | 0.682 | 0.021 * |
| biotin | 1.790 | 0.033 * | 1.783 | 0.043 * | 0.473 | 0.142 |
| 2,3-dihydroxypropyl octanoate | 1.406 | 0.041 * | 1.732 | 0.035 * | 0.636 | 0.035 * |
| Element | 0.01 mg/kg/day | 1 mg/kg/day | 0, 0.01, 1 mg/kg/day c | LOD b (μg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | p | Fold Change | p | r | p | ||
| Boron | 2.106 | 0.028 * | 1.566 | 0.089 | 0.409 | 0.212 | 2.12 |
| Vanadium | 1.969 | 0.008 * | 1.472 | 0.120 | 0.145 | 0.670 | 0.03 |
| Cobalt | 1.798 | 0.036 * | 1.244 | 0.230 | 0.027 | 0.937 | 0.01 |
| Arsenic | 1.931 | 0.032 * | 1.376 | 0.197 | 0.382 | 0.247 | 0.04 |
| Cadmium | 1.000 | NA a | 25.578 | 0.000 * | 0.786 | 0.004 * | 0.08 |
| Gold | 0.533 | 0.296 | 0.192 | 0.037 * | −0.477 | 0.138 | 0.01 |
| Element | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | β (95%CI) | p | No. | β (95%CI) | p | No. | β (95%CI) | p | |
| Cadmium | 838 | 0.39 (0.32, 0.46) | p < 0.01 | 838 | 0.44 (0.38, 0.50) | p < 0.01 | 822 | 0.47 (0.41, 0.52) | p < 0.01 |
| Metabolite | Cadmium | |
|---|---|---|
| r | p | |
| 5-aminolevulinic acid | 0.025 | 0.942 |
| glycolic acid | 0.176 | 0.606 |
| l-acetylcarnitine | 0.413 | 0.207 |
| 2,3-dihydroxypropyl octanoate | 0.782 | 0.004 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, K.; Tang, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Guan, Y.; Huang, R.; Duan, J.; Liu, Z.; Ji, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Exposure to Molybdate Results in Metabolic Disorder: An Integrated Study of the Urine Elementome and Serum Metabolome in Mice. Toxics 2024, 12, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040288
Zhou K, Tang M, Zhang W, Chen Y, Guan Y, Huang R, Duan J, Liu Z, Ji X, Jiang Y, et al. Exposure to Molybdate Results in Metabolic Disorder: An Integrated Study of the Urine Elementome and Serum Metabolome in Mice. Toxics. 2024; 12(4):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040288
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Kun, Miaomiao Tang, Wei Zhang, Yanling Chen, Yusheng Guan, Rui Huang, Jiawei Duan, Zibo Liu, Xiaoming Ji, Yingtong Jiang, and et al. 2024. "Exposure to Molybdate Results in Metabolic Disorder: An Integrated Study of the Urine Elementome and Serum Metabolome in Mice" Toxics 12, no. 4: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040288
APA StyleZhou, K., Tang, M., Zhang, W., Chen, Y., Guan, Y., Huang, R., Duan, J., Liu, Z., Ji, X., Jiang, Y., Hu, Y., Zhang, X., Zhou, J., & Chen, M. (2024). Exposure to Molybdate Results in Metabolic Disorder: An Integrated Study of the Urine Elementome and Serum Metabolome in Mice. Toxics, 12(4), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040288







