Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Yingtan City, Jiangxi Province, China: A Principal Component Analysis–Positive Matrix Factorization Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
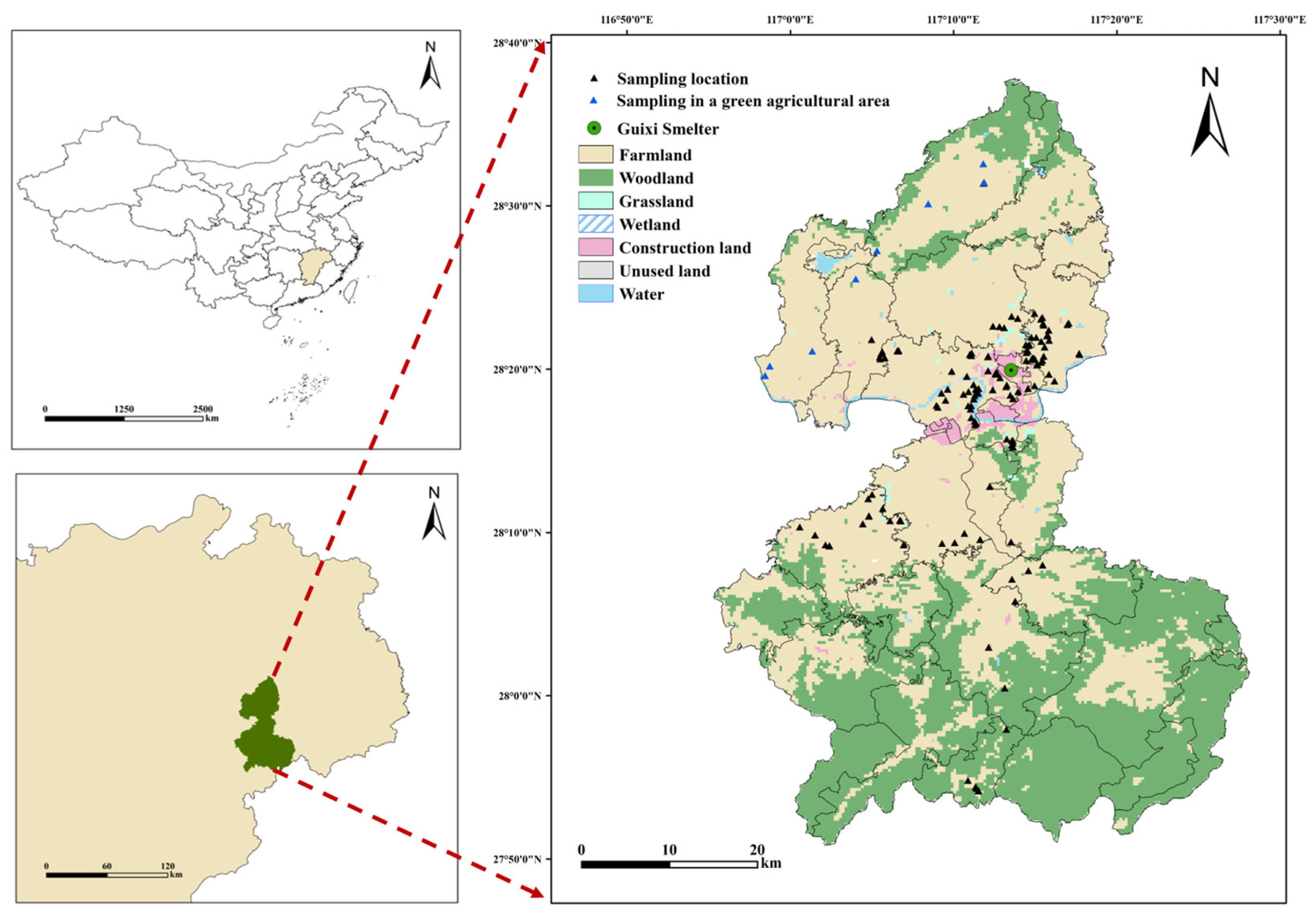
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Field Investigation
2.3. Analysis of PTEs
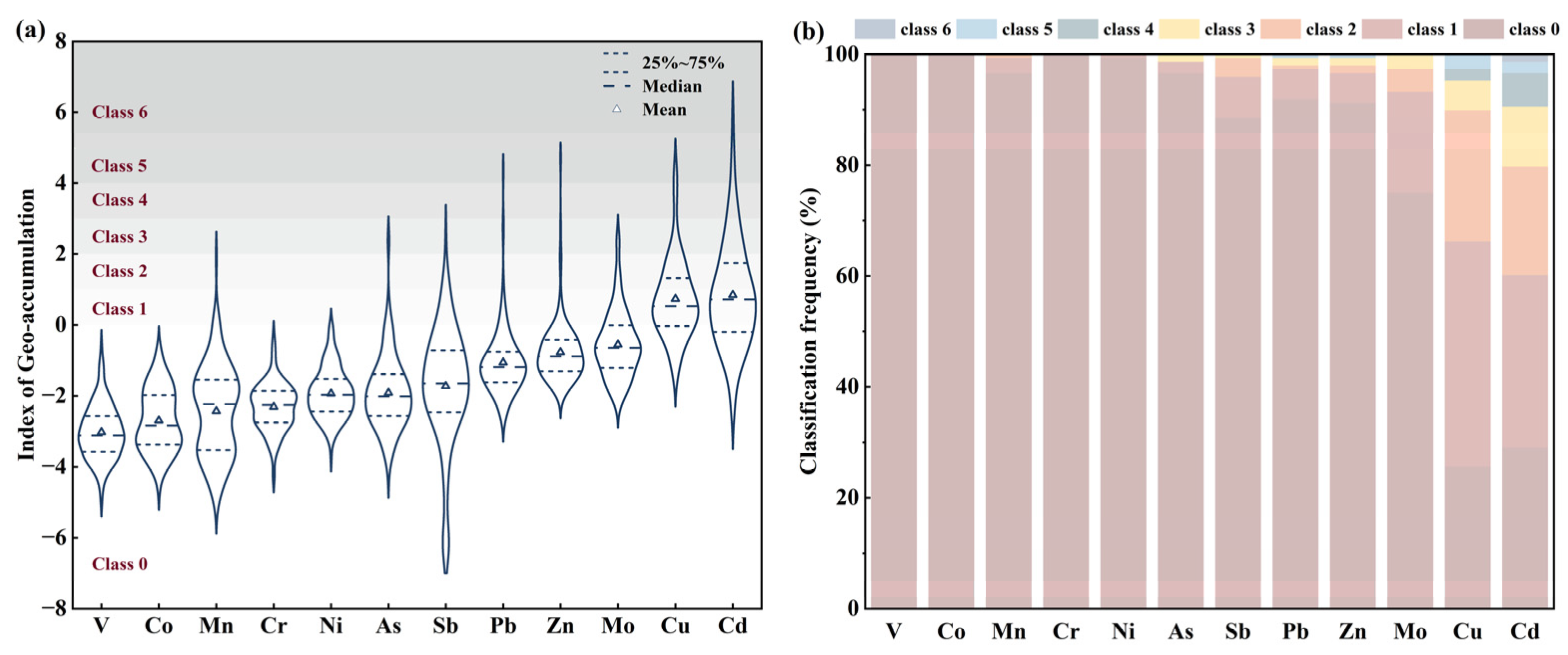
2.4. Index of Geo-Accumulation
2.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.6. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of PTEs in Soil
3.2. Assessment of Soil PTs Contamination
3.3. Source Apportionment of Soil PTEs
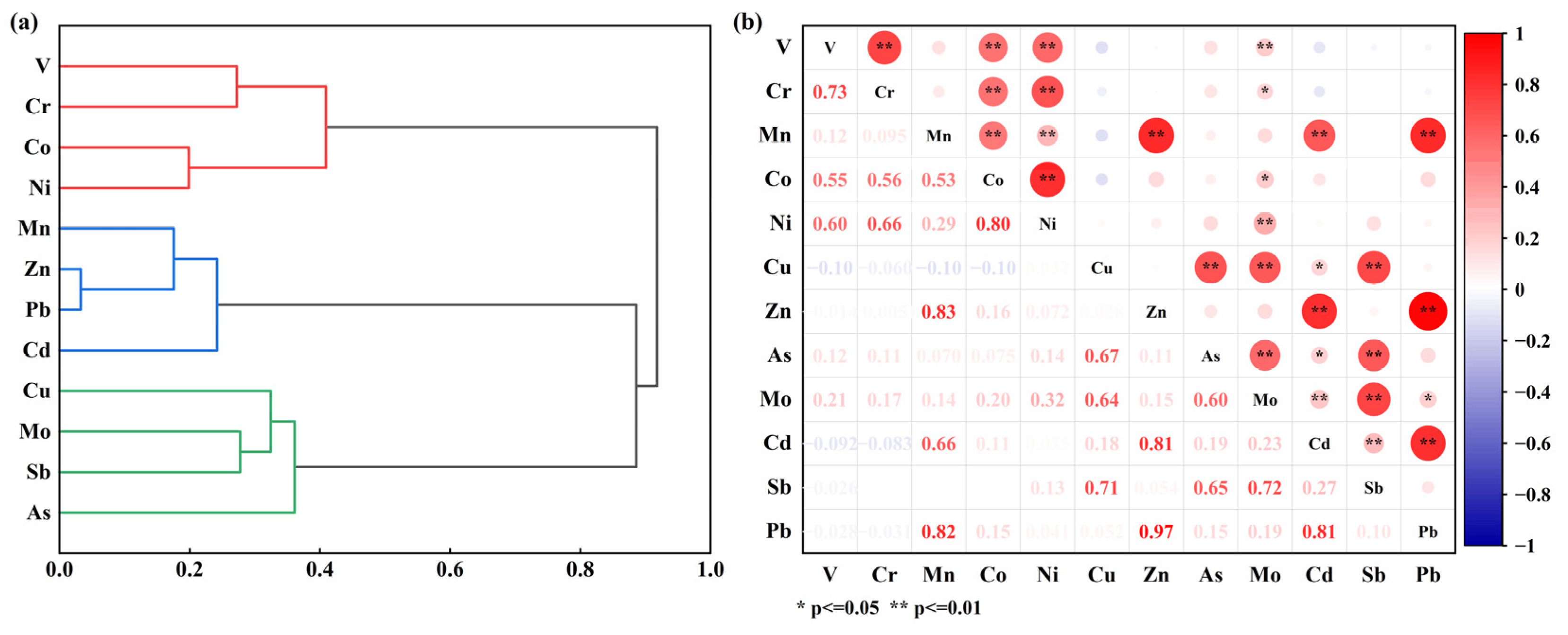
3.3.1. Homology Analysis of Soil PTEs
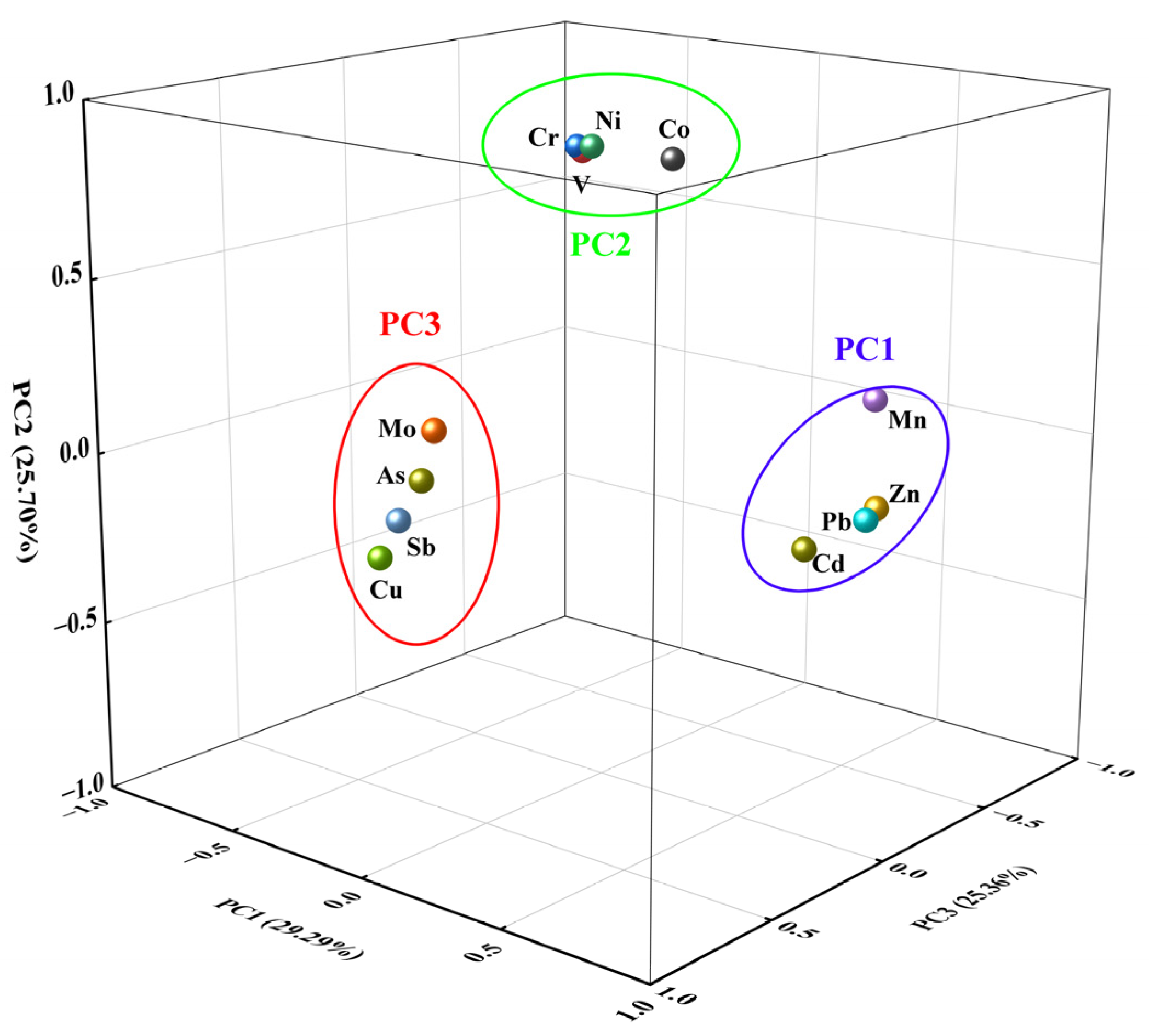
3.3.2. PCA Analysis of Soil PTEs
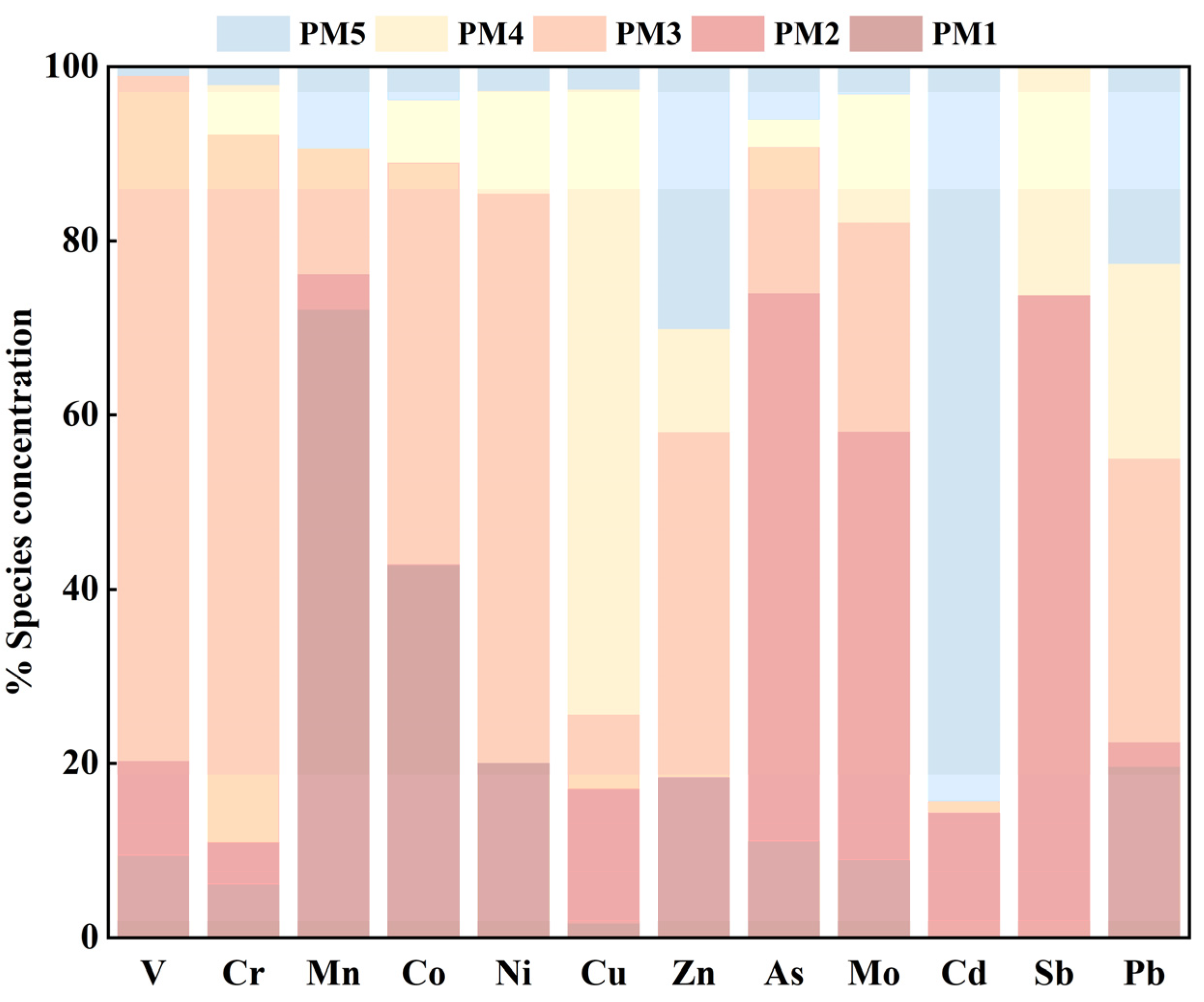
3.3.3. PMF Analysis of Soil PTEs
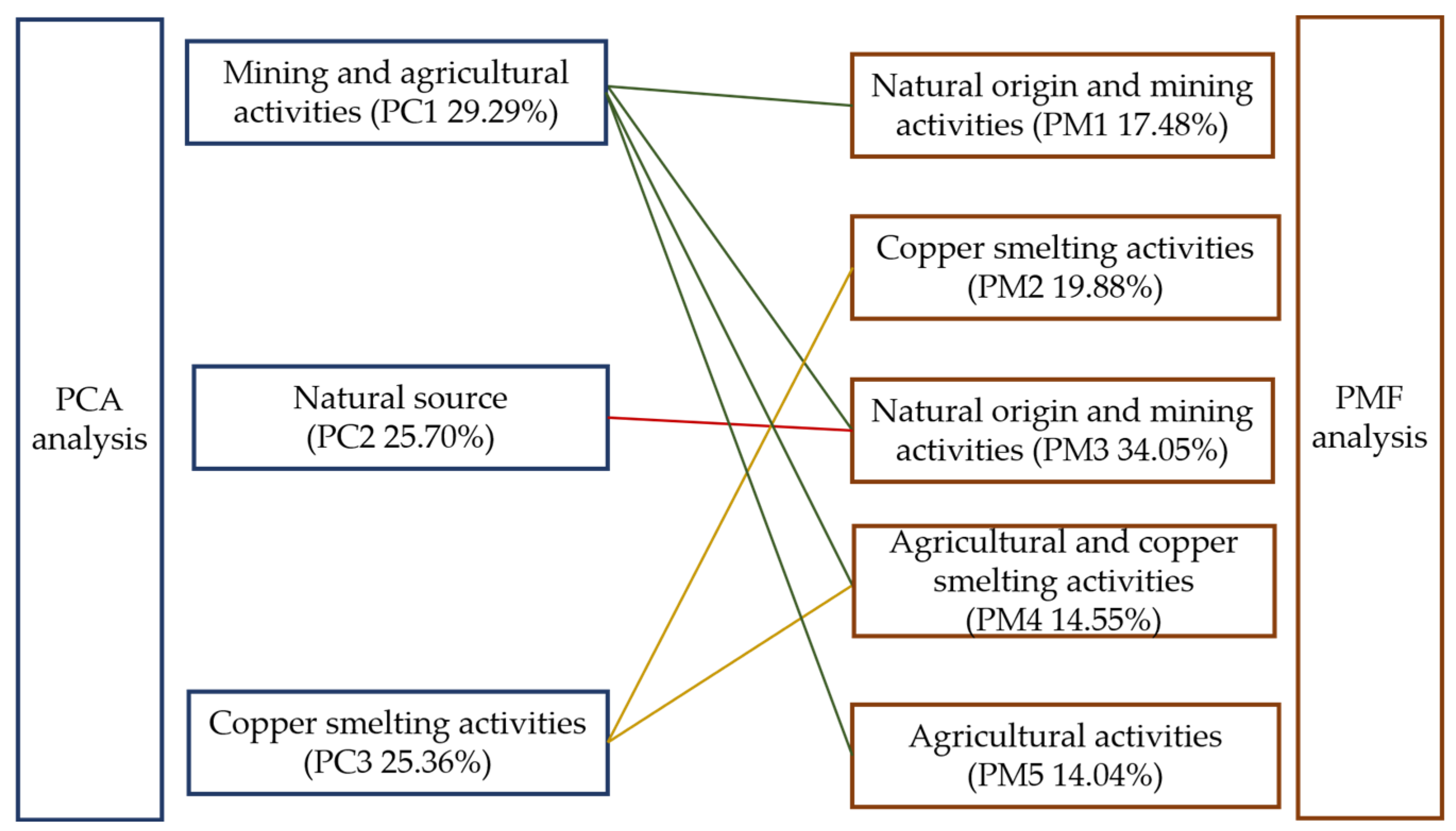
3.3.4. Integrating PCA-PMF with Field Survey
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.B.; Wang, M.; Li, S.S.; Zheng, H.; Lei, X.Q.; Sun, X.Y.; Wang, L.F. Current status of and discussion on farmland heavy metal pollution prevention in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2019, 26, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection; Ministry of Land and Resources. National Soil Pollution Status Survey Bulletin. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/foot/site1/20140417/782bcb88840814ba158d01.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Zhao, J.X.; Yin, P.C.; Yue, R.; Wang, M.P.; Shi, R. Research progress of status, source, restoration technique of heavy metals pollution in cropland of China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 19–21+26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, R. Soil pollution survey and management in Taiwan of China. Soils 2018, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.A.; He, K.L.; Sun, Z.H.; Chen, G.; Zheng, H.F. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in the agricultural soils of an industrializing region and associated model uncertainty. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.R.; Ji, Y.K.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.N.; Fu, Y.; Liu, S.T.; Ma, J.Q. Source-oriented comprehensive assessment framework for identifying priority heavy metals in agricultural soils. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bai, Z.X.; Bo, W.H.; Lin, J.; Yang, J.J.; Chen, T. Analysis and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil in China: A Meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.F.; Lou, Z.H.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.Q.; Lv, X.N. Source analysis and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of different cultivated land qualities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130942. [Google Scholar]
- NI, Z.Y.; Xie, G.X.; Zhang, M.K. Effects of Acidification on Bioavailability of Cadmium and Lead in Cultivated Land Soil and Their Accumulation in Agricultural Products. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2017, 29, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Pang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, D.; Hu, M.; Xu, L.; Liu, T.; Sun, W.; Yu, H.Y. Controlling factors of heavy metal(loid) accumulation in rice: Main and interactive effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 42357–42371. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, W.; Bai, C.; Xu, C.; Ye, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, L. Cadmium, arsenic, and mineral nutrients in rice and potential risks for human health in South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 76842–76852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L. Research on the Content and Distribution of Heavy Metals in the Soil of a Vegetable Base Site. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, H. Early warning research on the probability of soil heavy metal risk in county agricultural land based on environmental capacity. Resour. Environ. Yangtze River Basin 2020, 29, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, J.; Henríquez-Hernández, Z.Z.W.L.A. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils: Sources, Influencing Factors, and Remediation Strategies. Toxics 2024, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Tian, Z. Study on atmospheric heavy metal deposition by environmental tracers surrounding copper smelting. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiong, L.; Xiaoqing, O.U.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, M. Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Contents in Facility Agriculture of Guangxi. Asian Agric. Res. 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Sources Analysis of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil and Rice in an Industrial Area in Hunan Province, China. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.H.; Li, G.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, S.C.; Cui, J.H.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, Q. Investigating factors influencing the PMF model:A case study of source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils near a lead-zinc ore. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Diakite, M.L.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Source apportionment based on the comparative approach of two receptor models in a large-scale region in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56696–56710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Sun, Q.; Wadood, S.A.; Guo, B. Source identification and spatial distribution of arsenic and heavy metals in agricultural soil around Hunan industrial estate by positive matrix factorization model, principle components analysis and geo statistical analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Zhou, Y. Trace Metal Pollution in Topsoil Surrounding the Xiangtan Manganese Mine Area (South-Central China): Source Identification, Spatial Distribution and Assessment of Potential Ecological Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, D.; Petrović, S.; Relić, D.; Mihajlidi-Zelić, A. Applying receptor models Unmix and PMF on real data set of elements in PM for sources evaluation of the sea coastal side region (Southeast Adriatic Sea). Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2013, 2013, 4941–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.P.; Xie, M.J. Characteristics of lead enrichment in the soil from a typical peri-urban agricultural area of the southern Jiangsu and source appointment based on the PCA-PMF method. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, S. Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements Based on PCA and PMF Model in Black Soil Area of Hailun City, Northeast China. Toxics 2024, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2012; National Food Safety Standard—Limits of Contaminants in Food. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- HJ 803-2016; Soil and Sediment-Determination of Aqua Regia Extracts of 12 Metal Elements-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the Reople’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Müller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.P.; Wang, Q.Z.; Guan, Q.Y.; Ma, Y.R.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal pollution levels, source apportionment and risk assessment in dust storms in key cities in Northwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 422, 126878. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Y.; Lu, X.W.; Lei, K. A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: Contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaman, R.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.R.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.F.; Hu, C.H.; Wu, G.L.; Chen, M. Combination of PCA and PMF to apportion the sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Poyang during the wet season. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 964–976. [Google Scholar]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.X. Trace elements in PM2.5 in Shandong Province: Source identification and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 558–577. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-research/positive-matrix-factorization-model-environmental-data-analyses (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the Reople’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Wang, H.Z.; Liu, D.Y.; Lv, Y.F.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Huang, L.; Zhu, L. Ecological and health risk assessments of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils around a petroleum refining plant in China: A quantitative method based on the improved hybrid model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Zhao, R.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Ye, C. Ecological risk assessment and pollution characteristic analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Xingkai Lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Gao, Y.X. Pollution characteristics and source identification of heavy metals in farmland soils around a tailing pond in Zhejiang Province. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.J.; Ren, W.; Luo, Q.; Ma, J. Evaluation and their sources of heavy metals in uncultivated saline-alkaline soil in the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2019, 36, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, W.C.; Liu, W.Q.; Ma, L.Y.; Ming, C.H.; Chen, J.B.; Yuan, W. Analysis of heavy metal sources and ecological health risk assessment in typical non-ferrous metal smelting sites. Earth Environ. 2024, 52, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Meng, W.; Liu, N.T.; Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 964–977. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Yu, C.L.; Wang, L.P.; Song, J.J.; Sun, L.W.; Qian, J.; Sun, M.H. Heavy metal sources and ecological risk assessment of typical lead-zinc mining areas in Hebei Province. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2024, 43, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Research progress on soil heavy metal pollution and ecological restoration technology in lead-zinc mining areas. China Strateg. Emerg. Ind. 2024, 32, 122–124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Tang, Y.Y.; Chen, M.; Pan, Y.X. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in lead-zinc area based on APCS-MLR and PMF. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Zhao, T.; Gao, Y.; Sun, R.G. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of a typical lead-zinc mining Area in Guizhou Province. Earth Environ. 2022, 50, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the Reople’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1996.
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Guo, T.; Ding, H.; Liu, X. Source analysis of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil in a mining area based on a small watershed scale. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Dong, Q.Q. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Lalin River basin. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.H.; Mustafa, A.-R.A.; El-Sheikh, A.A. Geochemistry and spatial distribution of selected heavy metals in surface soil of Sohag, Egypt: A multivariate statistical and GIS approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, J.; Ziyath, A.M.; Bostrom, T.E.; Bekessy, L.K.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Characterisation of atmospheric deposited particles during a dust storm in urban areas of Eastern Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J. Present situation and prospects of technologies for remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated soil around Jiangxi Guixi Smelter. World Environ. 2016, 161, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.X.; Zou, X.H.; Pan, X.L.; Cai, W.D.; Luo, Y.Q. Analysis and evaluation on heavy metal pollution condition of soil in farmland around Guixi Smelting Factory. Jiangxi Sci. 2012, 30, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Gong, X.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Zeng, H.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Li, Z.L.; Zheng, L. Ecological risk assessment and pollution analysis on the heavy metals contaminated soil around Guixi smeltery. J. Nanchang Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 39, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, Z.H.; Qi, Y.H.; Zhang, X.T. Determination of Re, Mo and Se in copper smelting waste by indutively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Anhui Chem. Ind. 2011, 37, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Yuan, L.C.; Huang, L.Q.; Xu, Z.F. Trend and recovery of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in copper smelting. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2019, 10, 13–19+27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.; Zeng, G.; Gao, X.; Zhong, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; He, X.; Fang, Y. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.S.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Chen, S.B. An overview of current status of copper pollution in soil and remediation efforts in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Huang, T.H.; Chen, J.; Zhong, F.L.; Shi, J.C.; Xu, J.M. Safe utilization of farmland soil with cadmium pollution: Strategies and deliberations. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.) 2019, 45, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.G.; Wu, H.W.; Liu, J. Evolution of heavy metal contents of three soils under long-term fertilizations. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Liang, T.Z.; Feng, D.L.; Diao, L.Y.; Liang, M.Z. Research on trace element copper application in aquaculture. J. Guangxi Agric. 2019, 34, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.Y.; Zhang, W.L. Advances of epidemiological study on population exposure and health hazard of environmental cadmium pollution. J. Environ. Hyg. 2019, 9, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.L.; Wang, Y.G.; Yu, D.; Li, X.J.; Yue, J.P. Effects of heavy metals on variation in bacterial communities in farmland soil of tailing dam collapse area. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matse, D.T.; Geretharan, T.; van Gorp, E.F.; Anderson, S.; Jeyakumar, P.; Anderson, C.W.N. The Potential Impact of Long-Term Copper Fungicide Sprays on Soil Health in Avocado Orchards. Environments 2024, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class | Igeo Value | Soil Quality |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Igeo ≤ 0 | Practically uncontaminated |
| 1 | 0 < Igeo ≤ 1 | Uncontaminated to moderately contaminated |
| 2 | 1 < Igeo ≤ 2 | Moderately contaminated |
| 3 | 2 < Igeo ≤ 3 | Moderately to heavily contaminated |
| 4 | 3 < Igeo ≤ 4 | Heavily contaminated |
| 5 | 4 < Igeo ≤ 5 | Heavily to extremely contaminated |
| 6 | Igeo > 5 | Extremely contaminated |
| Mean of All Soil (1) (mg·kg−1 d.w.) | Minimum (1) (mg·kg−1 d.w.) | Maximum (1) (mg·kg−1 d.w.) | Variation Coefficient | Soil Background Value in Jiangxi Province (2) (mg·kg−1) | Risk Screening Value (3) (mg·kg−1) | Average of the Igeo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | 137.88 | 14.63 | 1861.00 | 1.31 | 328.00 | - | −2.43 |
| Zn | 89.62 | 25.81 | 2717.60 | 2.56 | 69.40 | 200.00 | −0.77 |
| Cu | 76.30 | 10.23 | 739.05 | 1.39 | 20.30 | 50.00 | 0.73 |
| Pb | 35.56 | 7.47 | 990.83 | 2.48 | 32.30 | 80.00 | −1.06 |
| V | 20.58 | 4.59 | 96.76 | 0.65 | 95.80 | - | −3.02 |
| Cr | 15.47 | 3.49 | 57.14 | 0.51 | 45.90 | 250.00 | −2.31 |
| As | 8.57 | 1.13 | 116.05 | 1.60 | 14.90 | 30.00 | −1.91 |
| Ni | 8.42 | 2.13 | 28.55 | 0.57 | 18.90 | 60.00 | −1.93 |
| Co | 3.21 | 0.66 | 11.36 | 0.65 | 11.50 | - | −2.70 |
| Sb | 0.90 | 0.02 | 9.92 | 1.26 | 1.15 | - | −1.73 |
| Mo | 0.66 | 0.16 | 4.19 | 0.98 | 0.50 | - | −0.56 |
| Cd | 0.59 | 0.03 | 10.85 | 2.00 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.84 |
| Elements | Component | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| V | −0.06 | 0.84 | 0.02 |
| Cr | −0.07 | 0.85 | 0.03 |
| Mn | 0.89 | 0.27 | −0.06 |
| Co | 0.23 | 0.85 | −0.01 |
| Ni | 0.07 | 0.88 | 0.14 |
| Cu | −0.02 | −0.13 | 0.89 |
| Zn | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| As | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.83 |
| Mo | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.83 |
| Cd | 0.87 | −0.08 | 0.21 |
| Sb | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.89 |
| Pb | 0.97 | −0.01 | 0.08 |
| Eigenvalues | 4.00 | 2.88 | 2.76 |
| Variance contribution ratio % | 29.29 | 25.70 | 25.36 |
| Cumulative contribution ratio % | 29.29 | 54.98 | 80.34 |
| Elements | R2 | Intercept | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|
| V | 0.68 | 6.92 | 0.60 |
| Cr | 0.85 | 1.82 | 0.85 |
| Mn | 0.64 | 58.86 | 0.47 |
| Co | 0.88 | 0.62 | 0.72 |
| Ni | 0.68 | 2.88 | 0.62 |
| Cu | 0.86 | 12.21 | 0.76 |
| Zn | 0.76 | 47.95 | 0.19 |
| As | 0.63 | 3.91 | 0.38 |
| Mo | 0.70 | 0.17 | 0.63 |
| Cd | 0.87 | 0.02 | 0.89 |
| Sb | 0.80 | 0.04 | 0.80 |
| Pb | 0.59 | 18.45 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Han, R. Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Yingtan City, Jiangxi Province, China: A Principal Component Analysis–Positive Matrix Factorization Method. Toxics 2025, 13, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040267
Chen S, Wang H, Han R. Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Yingtan City, Jiangxi Province, China: A Principal Component Analysis–Positive Matrix Factorization Method. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040267
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shaoting, Hongmei Wang, and Ruiming Han. 2025. "Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Yingtan City, Jiangxi Province, China: A Principal Component Analysis–Positive Matrix Factorization Method" Toxics 13, no. 4: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040267
APA StyleChen, S., Wang, H., & Han, R. (2025). Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Yingtan City, Jiangxi Province, China: A Principal Component Analysis–Positive Matrix Factorization Method. Toxics, 13(4), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040267








