Isolation and Characterization of Aerobic and Facultative Anaerobic 17β-Estradiol Degrading Bacteria in Paddy Soils and Their Potential Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Medium Chemicals
2.2. Enrichment, Isolation, and Identification of E2 Removal Strains
2.3. Study of Removal Properties
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Preliminary Screening of E2-Degrading Bacteria
3.2. Impact of Diverse Environmental Parameters on E2 Degradation
3.3. Genomic Analysis of the Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Zhou, J.L.; Wilding, A. Simultaneous determination of endocrine disrupting phenolic compounds and steroids in water by solid-phase extraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1022, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapper, M.A.; Kolanczyk, R.C.; LaLone, C.A.; Denny, J.S.; Ankley, G.T. Conversion of Estrone to 17β-Estradiol: A Potential Confounding Factor in Assessing Risks of Environmental Estrogens to Fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Williams, R.J.; Matthiessen, P. The potential steroid hormone contribution of farm animals to freshwaters, the United Kingdom as a case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanselman, T.A.; Graetz, D.A.; Wilkie, A.C. Manure-Borne estrogens as potential environmental contaminants: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5471–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, M.E.; Holstege, D.M.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Aerobic versus Anaerobic Microbial Degradation of Etofenprox in a California Rice Field Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, R.A.; Tomco, P.L.; Howard, M.W.; Schempp, T.T.; Stewart, D.J.; Stacey, P.M.; Ball, D.B.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Aerobic versus Anaerobic Microbial Degradation of Clothianidin under Simulated California Rice Field Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7059–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Lin, H.; Lin, X.; Mo, J.; Chen, C.; Dai, X.; Liao, D.; Gao, C.; Li, Y. Occurrence and distribution of natural and synthetic progestins, androgens, and estrogens in soils from agricultural production areas in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sparks, D.L.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Tian, K.; Zhou, D.; Meng, F.; Zhang, H.; Huo, H. Genomics analysis of the steroid estrogen-degrading bacterium Serratia nematodiphila DH-S01. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, H.; Kan, J.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Xiong, G.; Hu, Z. A novel 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in Rhodococcus sp. P14 for transforming 17β-estradiol to estrone. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2017, 276, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Zhuang, W.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Reinhard, M.; Hoon, L.T.; Tay, J.-H. Characterization of estrogen-degrading bacteria isolated from an artificial sandy aquifer with ultrafiltered secondary effluent as the medium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Peng, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, Q.; Pratush, A.; Xiong, G.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. A novel dehydrogenase 17β-HSDx from Rhodococcus sp. P14 with potential application in bioremediation of steroids contaminated environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horinouchi, M.; Hayashi, T.; Kudo, T. Steroid degradation in Comamonas testosteroni. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 129, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Peng, W.; Fu, Y.; Deng, Z.; Lin, S.; Liang, R. Identification of a 17β-estradiol-degrading Microbacterium hominis SJTG1 with high adaptability and characterization of the genes for estrogen degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 444, 130371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Wang, P.; Kang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, K.; Huo, H. Genomic analysis of a new estrogen-degrading bacterial strain, Acinetobactersp. DSSKY-A-001. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019, 2804134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, C.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, B. Biodegradation of dibutyl phthalate by the new strain Acinetobacter baumannii DP-2. Toxics 2022, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Sultan, S.; Kertesz, M. Bacterial community analysis of cypermethrin enrichment cultures and bioremediation of cypermethrin contaminated soils. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 55, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, R.; Commichau, F.M.; Benndorf, D.; Hertel, R.; Holzer, K.; Hoelzle, L.E.; Mardoukhi, M.S.Y.; Noack, L.E.; Martienssen, M. Biodegradation of selected aminophosphonates by the bacterial isolate Ochrobactrum sp. BTU1. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 280, 127600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Xue, J. Oil degradation ability difference and microbial community successions by Ochrobactrum and Shewanella in different oil-polluted seawater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xue, C.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Isolation and identification of 17β-estradiol degrading bacteria and its degradation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, T. Isolation and characterization of a new highly effective 17β-estradiol-degrading Gordonia sp. strain R9. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Yin, C.; Peng, W.; Deng, Z.; Lin, S.; Liang, R. Characterization of an 17β-estradiol-degrading bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia SJTL3 tolerant to adverse environmental factors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Johansen, A.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, Z. Biodegradation of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) by Bacillus sp. LUNF1 and characterization of a novel hydrolase capable of catalyzing PAEs. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, S.; Lin, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Barceló, D.; Zheng, H. Efficient degradation of tylosin by Klebsiella oxytoca TYL-T1. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Szarka, G.; Hegyesi, N.; Wang, Y.; Sui, X.; Pukánszky, B. Quantitative analysis of factors determining the enzymatic degradation of poly(lactic acid). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harthern-Flint, S.L.; Dolfing, J.; Mrozik, W.; Meynet, P.; Eland, L.E.; Sim, M.; Davenport, R.J. Experimental and Genomic Evaluation of the Oestrogen Degrading Bacterium Rhodococcus equi ATCC13557. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 670928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Meng, Q.; Li, S.; Chang, M.; Meng, F.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Qiu, Q.; Shao, J.; Huo, H. Mechanism of 17β-estradiol degradation by Rhodococcus equi via the 4,5-seco pathway and its key genes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Tian, K.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, S.; Jin, S.; Huo, H. Genome Analysis of Rhodococcus Sp. DSSKP-R-001: A Highly Effective β-Estradiol-Degrading Bacterium. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 3505428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Li, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Tian, K.; Chang, M.; Li, S.; Zhou, D.; Huo, H. Study on the estradiol degradation gene expression and resistance mechanism of Rhodococcus R-001 under low-temperature stress. Chemosphere 2024, 358, 142146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, B.; Wille, K.; Noppe, H.; De Brabander, H.; Van de Wiele, T.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. 17α-ethinylestradiol cometabolism by bacteria degrading estrone, 17β-estradiol and estriol. Biodegradation 2008, 19, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratush, A.; Ye, X.; Yang, Q.; Kan, J.; Peng, T.; Wang, H.; Huang, T.; Xiong, G.; Hu, Z. Biotransformation strategies for steroid estrogen and androgen pollution. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2385–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-P.; Lee, T.-H.; Goh, K.-S.; Chu, K.-H.; Wang, P.-H.; Ismail, W.; Shih, C.-J.; Chiang, Y.-R. Biochemical Mechanisms and Catabolic Enzymes Involved in Bacterial Estrogen Degradation Pathways. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 712–724.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajka, C.P.; Londry, K.L. Anaerobic biotransformation of estrogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnow, P.; Tralau, T.; Luch, A. Chemical activation of estrogen and aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathways and their interaction in toxicology and metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
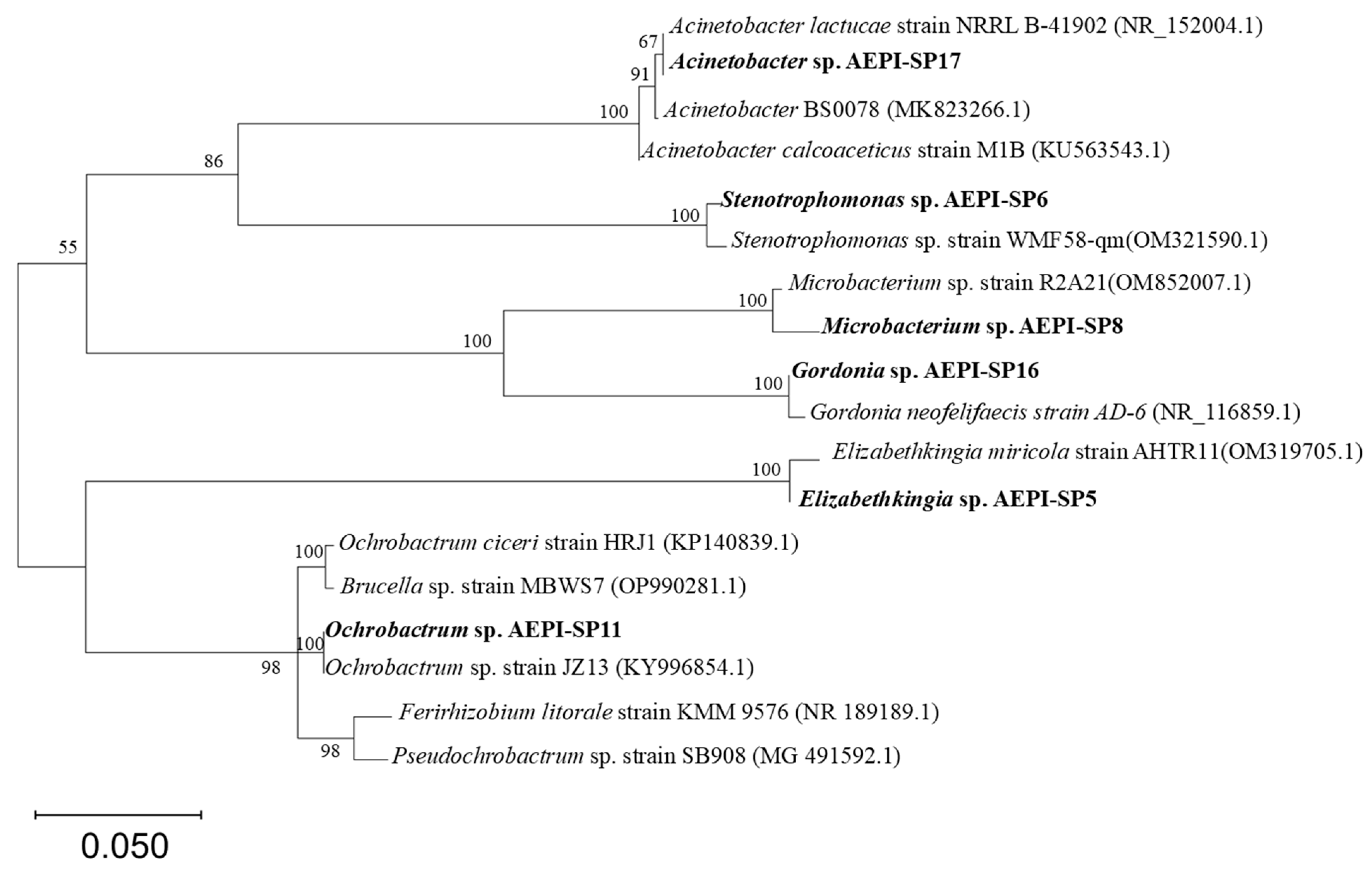
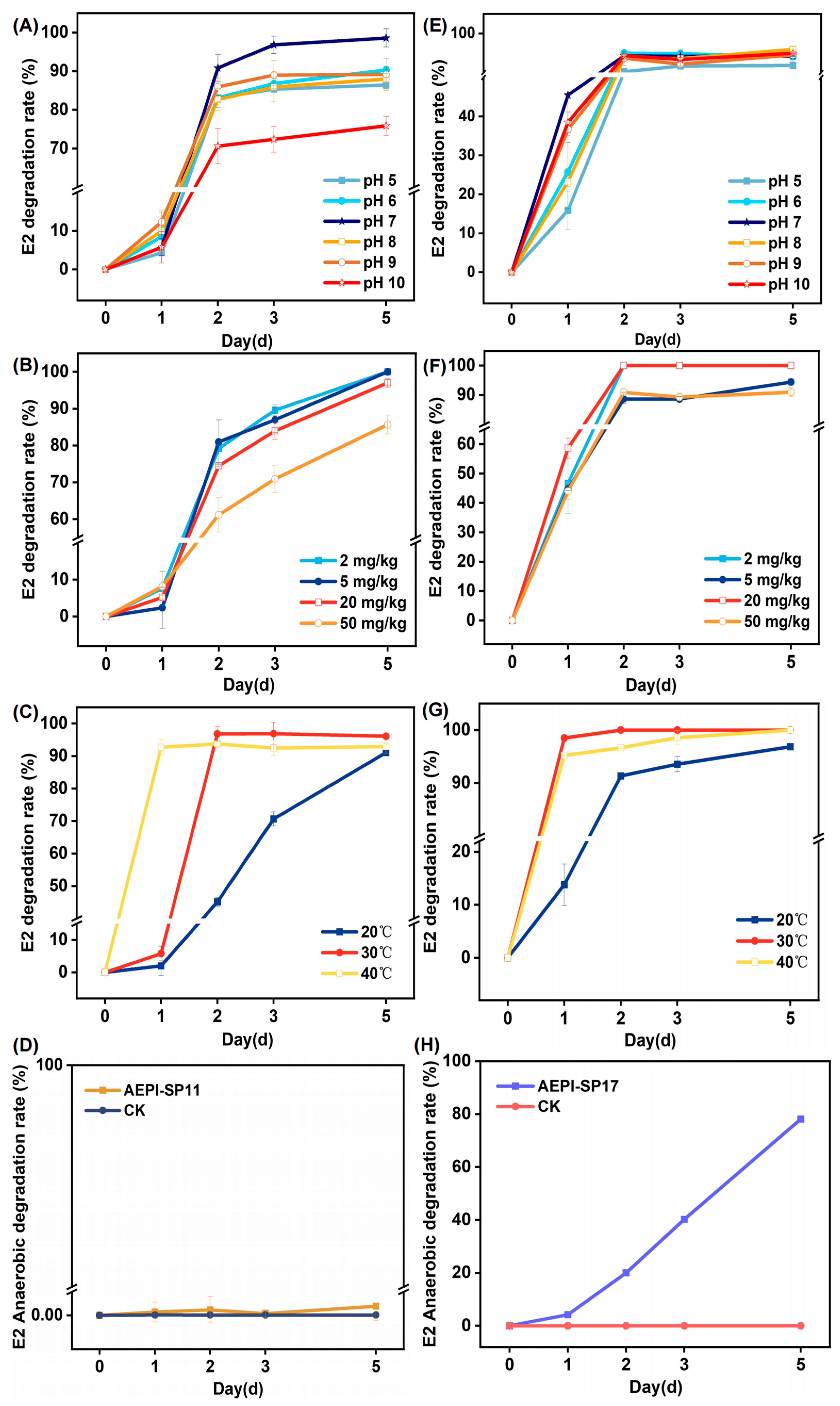
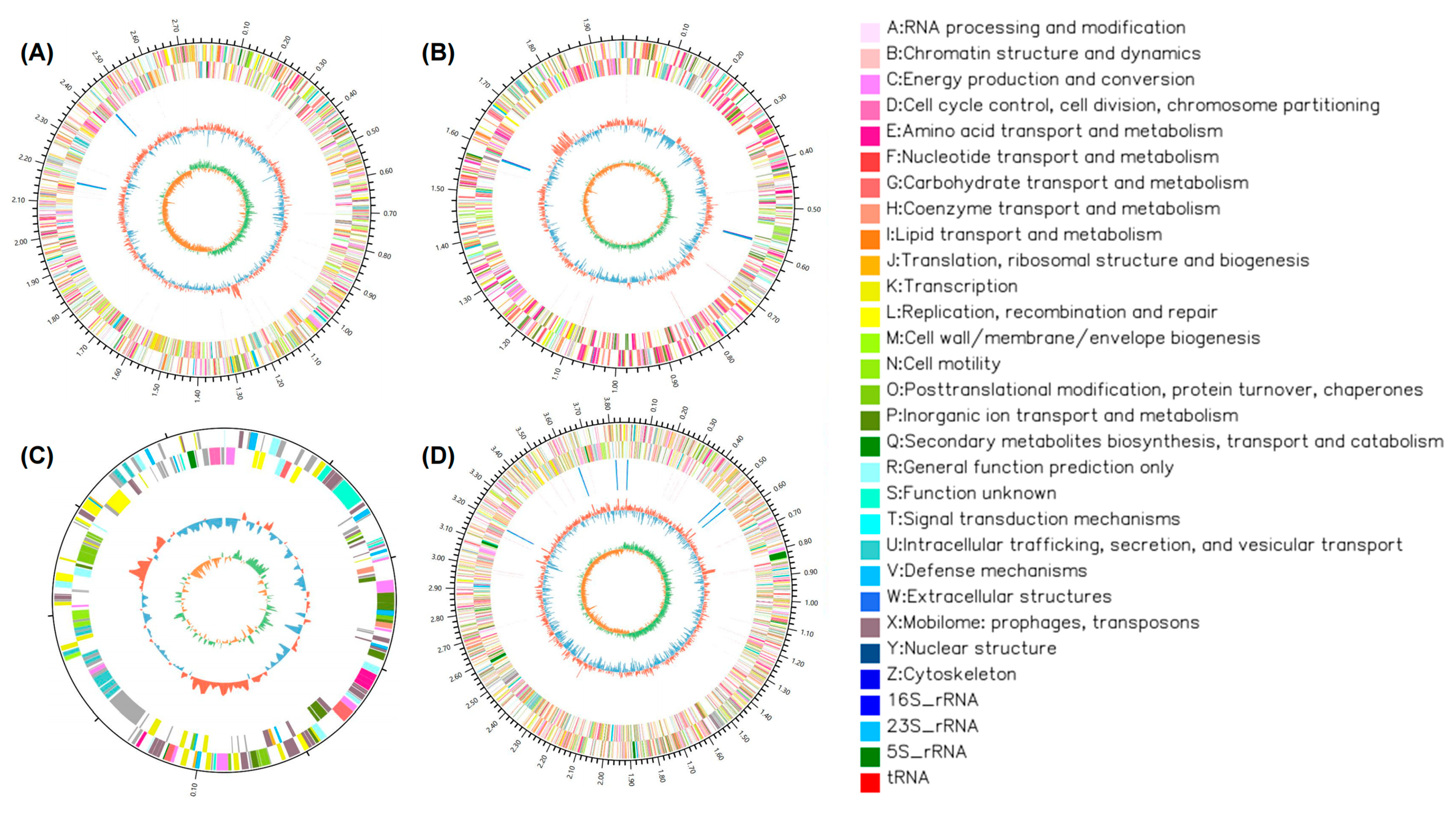
| Bacterium | Degradation Rate ± SD |
|---|---|
| Elizabethkingia sp. AEPI-SP5 | 55.21% ± 0.89% |
| Stenotrophomonas sp. AEPI-SP6 | 44.72% ± 1.63% |
| Microbacterium sp. AEPI-SP8 | 71.44% ± 6.33% |
| Ochrobactrum sp. AEPI-SP11 | 96.11% ± 0.15% |
| Gordonia sp. AEPI-SP16 | 72.4% ± 4.17% |
| Acinetobacter sp. AEPI-SP17 | 96.85% ± 0.20% |
| CK | 3.32% ± 0.52% |
| Category | Locus_Tag of AEPI-SP11 | Locus_Tag of AEPI-SP17 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDRs | gene0523, gene2386, gene3106 | gene0105, gene1660, gene2526, gene0276, gene0746, gene0856, gene0950, gene1228, gene1362 | short-chain dehydrogenase |
| HSDs | gene2019 | 3-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | |
| gene2887 | 7-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | ||
| gene4471 | 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | ||
| gene3055 | 3alpha (or 20beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | ||
| Di-/monooxygenases | gene0510 | gene0214 | quercetin 2,3-dioxygenase |
| gene0389 | ring-cleaving dioxygenase MhqA | ||
| gene3388 | gene0970 | NAD(P)H-dependent flavin oxidoreductase | |
| gene3713 | aromatic compound catabolic process | ||
| gene3714 | gene1645 | 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate catabolic | |
| gene0182 | gene0066 | catechol 2,3-dioxygenase | |
| gene0919 | estradiol dioxygenase family | ||
| gene1646 | protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase activity | ||
| gene0064 | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | ||
| gene1669, gene2535 | aromatic ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase subunit alpha, beta | ||
| Other dehydrogenases | gene0007 | phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase | |
| gene0129 | gene1670 | (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein] | |
| gene0257 | gene2157 | enoyl-(acyl carrier protein) reductase | |
| gene0535 | gene1808 | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier protein] reductase | |
| gene2241 | gene0509 | NAD(P)-dependent dehydrogenase, short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase family | |
| gene2477 | gene1361 | NADP-dependent 3-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase | |
| gene2386 | gene3069 | retinol dehydrogenase | |
| gene2517 | 2-hydroxycyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA dehydrogenase | ||
| gene1789 | 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Yang, S.; Ju, H.; Wang, C.; Ye, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, M. Isolation and Characterization of Aerobic and Facultative Anaerobic 17β-Estradiol Degrading Bacteria in Paddy Soils and Their Potential Mechanisms. Toxics 2025, 13, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040292
Li W, Yang S, Ju H, Wang C, Ye H, Ma X, Wang Y, Bai M. Isolation and Characterization of Aerobic and Facultative Anaerobic 17β-Estradiol Degrading Bacteria in Paddy Soils and Their Potential Mechanisms. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040292
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenxin, Shuo Yang, Hanye Ju, Chunyu Wang, Huike Ye, Xiaodong Ma, Yaqiong Wang, and Mohan Bai. 2025. "Isolation and Characterization of Aerobic and Facultative Anaerobic 17β-Estradiol Degrading Bacteria in Paddy Soils and Their Potential Mechanisms" Toxics 13, no. 4: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040292
APA StyleLi, W., Yang, S., Ju, H., Wang, C., Ye, H., Ma, X., Wang, Y., & Bai, M. (2025). Isolation and Characterization of Aerobic and Facultative Anaerobic 17β-Estradiol Degrading Bacteria in Paddy Soils and Their Potential Mechanisms. Toxics, 13(4), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040292






