Pollution Characterization and Environmental Impact Evaluation of Atmospheric Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Method of Systematic Review
2.2. Method of Human Health Risk Assessment
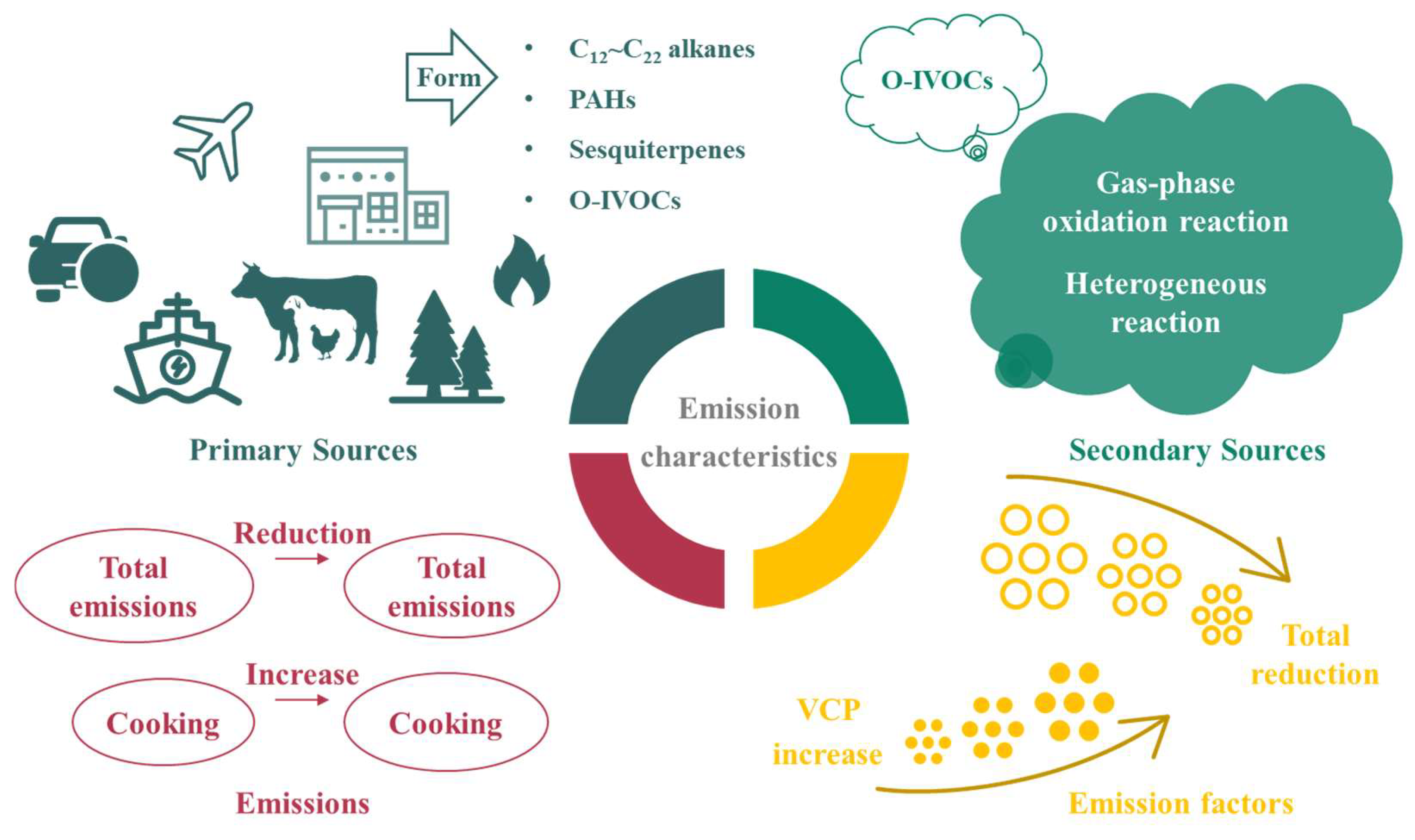
3. Source Characteristics
3.1. Sources and Compositions
3.2. Emission Characteristics
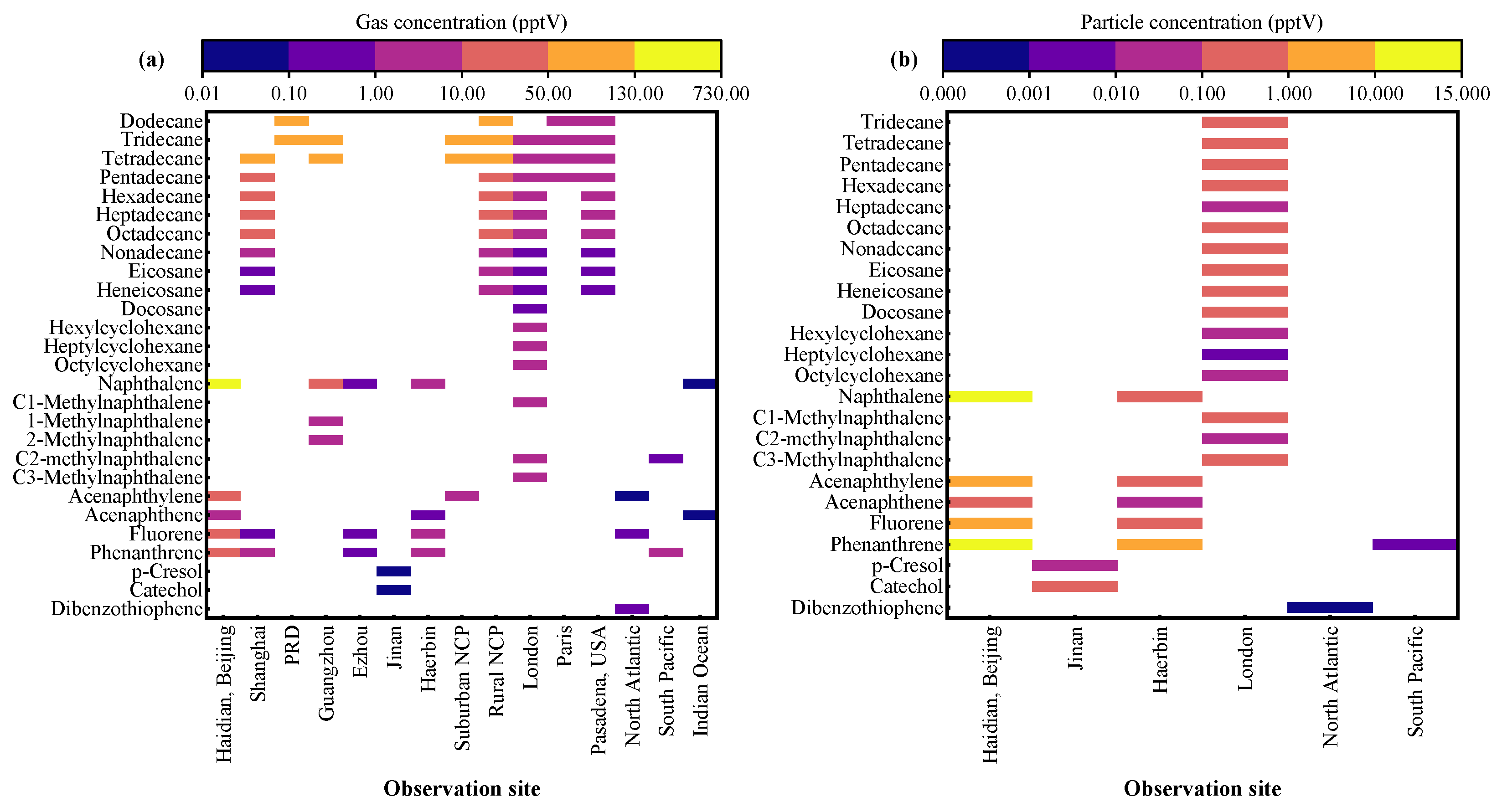
4. Ambient Levels
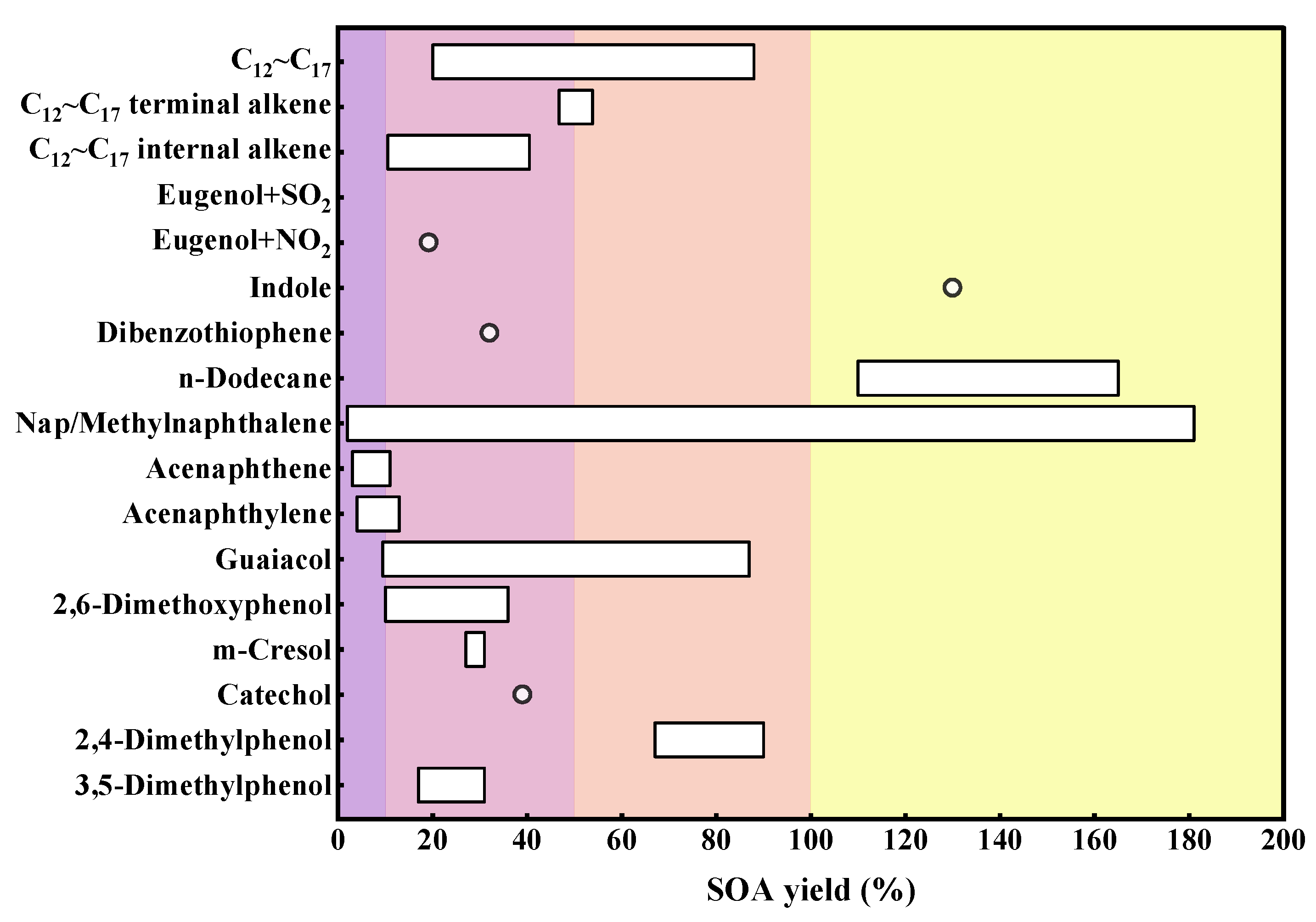
5. Contribution to SOA Formation
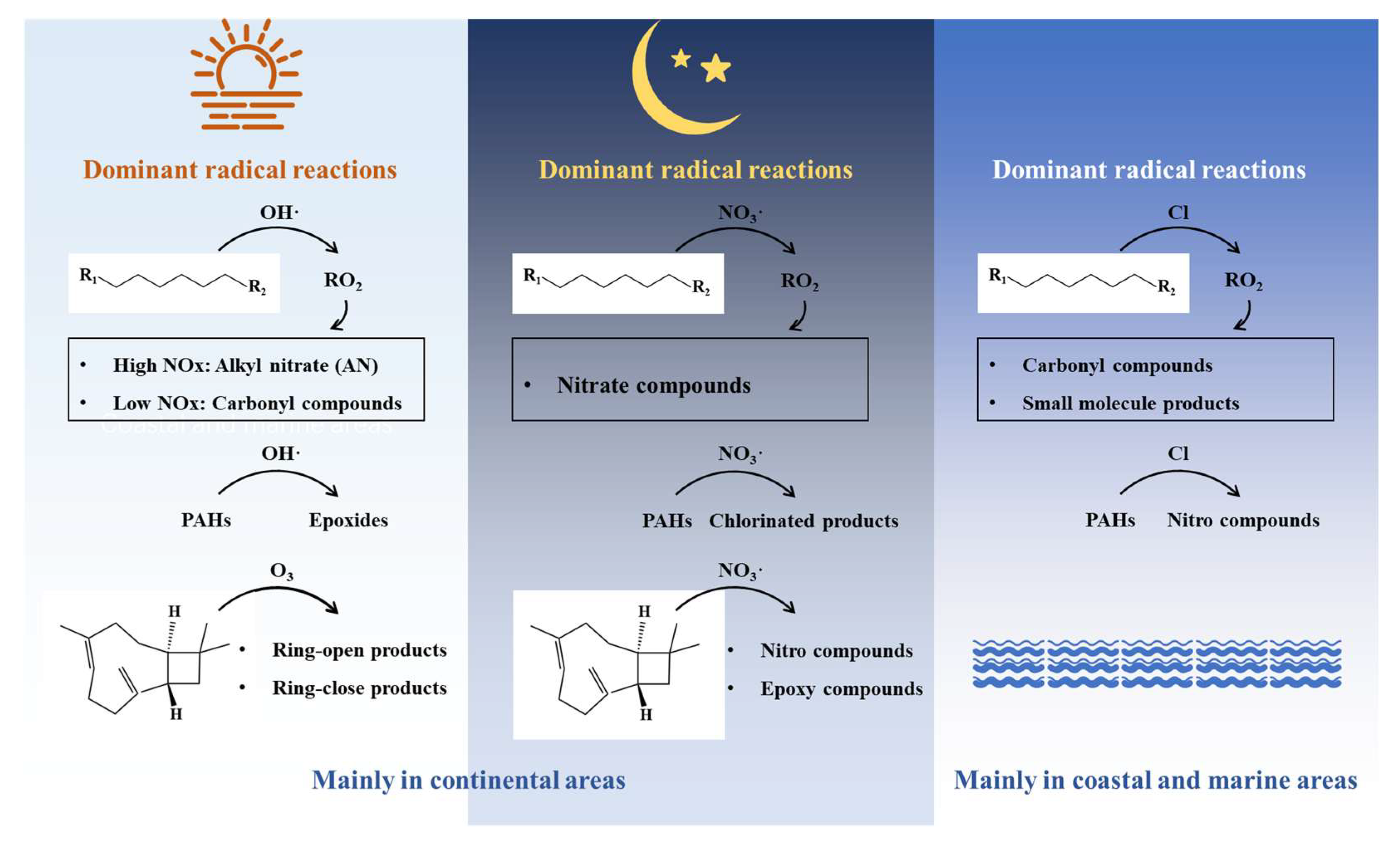
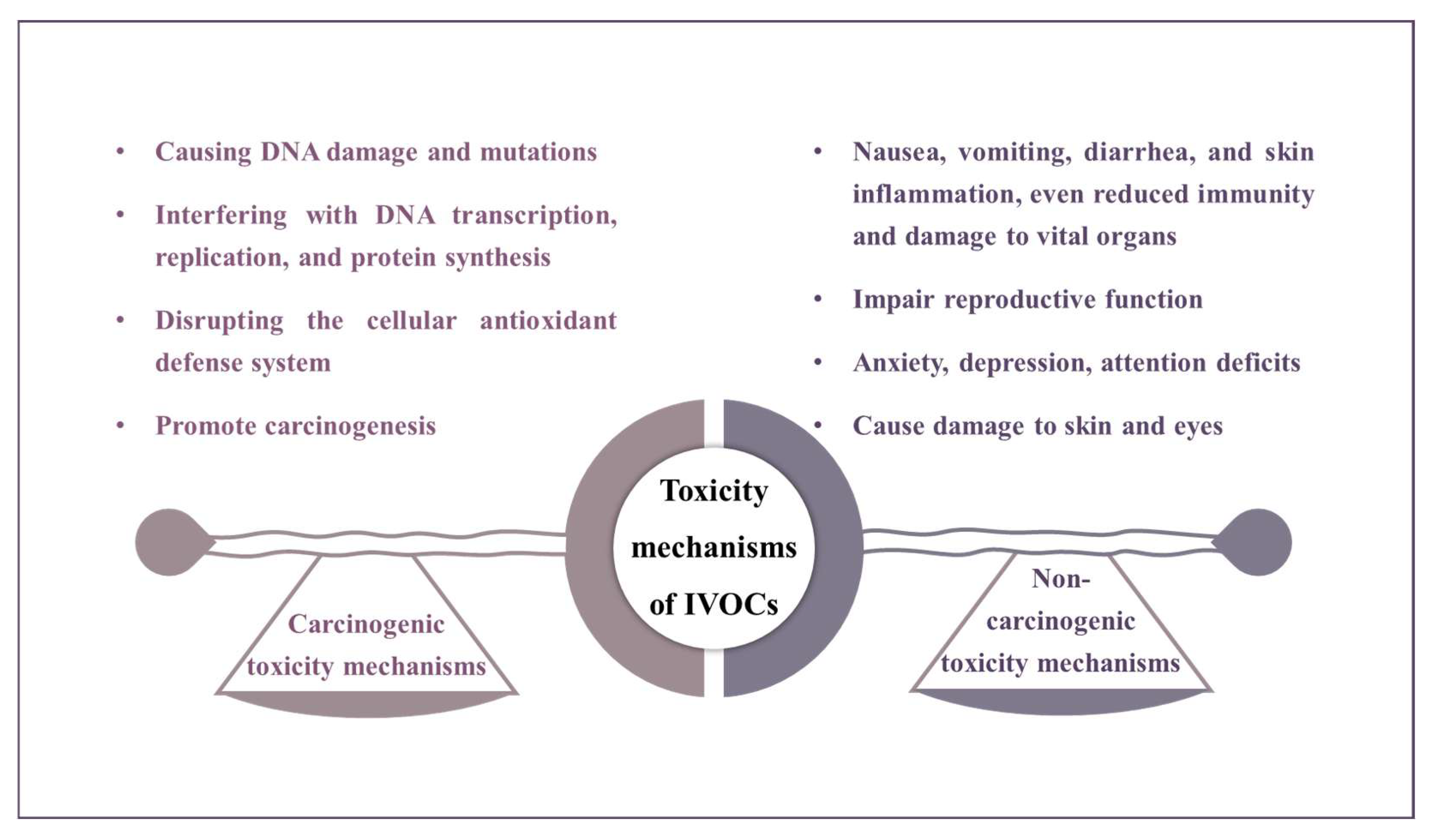
6. Toxicity and Health Risk Assessments
7. Shortcomings and Prospects
8. Conclusions and Implications
8.1. Conclusions
8.2. Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Domingo, N.G.G.; Hunt, N.D.; Gittlin, M.; Colgan, K.K.; Marshall, J.D.; Robinson, A.L.; Azevedo, I.M.L.; Thakrar, S.K.; Clark, M.A.; et al. The food we eat, the air we breathe: A review of the fine particulate matter-induced air quality health impacts of the global food system. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 103004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakidou, M.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Barnes, I.; Dentener, F.J.; Facchini, M.C.; Van Dingenen, R.; Ervens, B.; Nenes, A.; Nielsen, C.J.; et al. Organic aerosol and global climate modelling: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1053–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ulbrich, I.; Alfarra, M.R.; Takami, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. Ubiquity and dominance of oxygenated species in organic aerosols in anthropogenically-influenced Northern hemisphere midlatitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Fung, J.C.H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Chan, C.K.; Lau, A.K.H. Source apportionment of secondary organic aerosols in the Pearl River Delta region: Contribution from the oxidation of semi-volatile and intermediate volatility primary organic aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, P.; Balzarini, A.; Pirovano, G.; Gilardoni, S.; Paglione, M.; Colombi, C.; Gianelle, V.L.; Belie, C.A.; Poluzzi, V.; Lonati, G. Influence of semi- and intermediate-volatile organic compounds (S/IVOC) parameterizations, volatility distributions and aging schemes on organic aerosol modelling in winter conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, K.; Ge, M. Long-chain alkanes in the atmosphere: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.M.; Kroll, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Robinson, A.L. A two-dimensional volatility basis set—Part 2: Diagnostics of organic-aerosol evolution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M.; Shrivastava, M.K.; Weitkamp, E.A.; Sage, A.M.; Grieshop, A.P.; Lane, T.E.; Pierce, J.R.; Pandis, S.N. Rethinking organic aerosols: Semivolatile emissions and photochemical aging. Science 2007, 315, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Qiao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, L.; Lou, S.; Jing, S.; Huang, C.; et al. Characteristics of atmospheric intermediate volatility organic compounds (IVOCs) in winter and summer under different air pollution levels. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.A.; Tkacik, D.S.; de Gouw, J.A.; Gilman, J.B.; Kuster, W.C.; Borbon, A.; Robinson, A.L. Intermediate-volatility organic compounds: A large source of secondary organic aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13743–13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.X.; Donahue, N.M.; Jathar, S.H.; Huang, X.F.; Wu, W.J.; Hao, J.M.; Robinson, A.L. Quantifying the effect of organic aerosol aging and intermediate-volatility emissions on regional-scale aerosol pollution in china. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Fan, C.; Li, J.; Lei, T.; Zhang, W.; Shi, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Lian, C.; et al. Reactions of c12–c14 n-alkylcyclohexanes with cl atoms: Kinetics and secondary organic aerosol formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4859–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Ye, Y.; Pan, T.; Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, H.; Deng, W.; Zhu, M.; et al. Oxidation flow reactor results in a Chinese megacity emphasize the important contribution of S/IVOCs to ambient SOA formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6880–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, C.E.; Gerde, P.; Hanberg, A.; Jernström, B.; Johansson, C.; Kyrklund, T.; Rannug, A.; Törnqvist, M.; Victorin, K.; Westerholm, R. Cancer risk assessment, indicators, and guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the ambient air. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 451–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Song, K.; Gong, Y.; Sheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Yan, S.; Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; et al. Detailed speciation of semi-volatile and intermediate-volatility organic compounds (S/IVOCs) in marine fuel oils using GC × GC-ms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L.; Stanier, C.O.; Pandis, S.N. Coupled partitioning, dilution, and chemical aging of semivolatile organics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinrinade, O.E.; Rosa, A.H. Current levels, sources, and risks of human exposure to PAHs, pbdes and pcbs in south american outdoor air: A critical review. Environ. Res. 2025, 270, 120941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Verma, V.K.; Kumar, S. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in India: Geographical distribution, sources and associated health risk—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Yuan, B.; Wang, C.; Ye, C.; Zhang, S.; Shao, M. Progress in measurements of semi-/intermediate-volatile organic compounds in ambient air. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 4224–4236. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S. Constituents of atmospheric semi-volatile and intermediate volatility organic compounds and their contribution to organic aerosol. Prog. Chem. 2019, 31, 180–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Ge, M. Research progress of intermediate volatility organic compounds. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 2960–2978. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shao, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, W. Roles of semivolatile and intermediate-volatility organic compounds in secondary organic aerosol formation and its implication: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 259–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of Super Fund Remediation and Technology Innovation, Environmental Protection Agency. Risk Assessment Guidance for Super Fund Volume I Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment, EPA-540-r-070-002, OSWER 9285.7-82 January 2009); USA Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ws/t 666-2019; Technical Specifications for Health Risk Assessment of Ambient Air Pollution. National Health Commission of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Wei, D.; Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Primary particulate emissions and secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation from idling diesel vehicle exhaust in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593, 462–469. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yan, C.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of intermediate volatility organic compounds emitted from inland vessels with different influential factors and implication of reduction emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, M.C.; West, J.J.; Jathar, S.H.; Robinson, A.L.; Arunachalam, S. Estimates of non-traditional secondary organic aerosols from aircraft SVOC and IVOC emissions using CMAQ. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6929–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, S.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, K. Organic vapors from residential biomass combustion: Emission characteristics and conversion to secondary organic aerosols. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Feng, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Xie, J.; Huang, G.; Zhu, L.; Hao, J. Differentiated emissions and secondary organic aerosol formation potential of organic vapor from industrial coatings in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Shao, M.; Ling, Z. Emission inventory of semi-volatile and intermediate-volatility organic compounds and their effects on secondary organic aerosol over the Pearl River Delta region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8141–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Helal, W.; Borbon, A.; Sauvage, S.; de Gouw, J.A.; Colomb, A.; Gros, V.; Freutel, F.; Crippa, M.; Afif, C.; Baltensperger, U.; et al. Volatile and intermediate volatility organic compounds in suburban paris: Variability, origin and importance for SOA formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10439–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.H.; Kautzman, K.E.; Chhabra, P.S.; Surratt, J.D.; Chan, M.N.; Crounse, J.D.; Kürten, A.; Wennberg, P.O.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Secondary organic aerosol formation from photooxidation of naphthalene and alkylnaphthalenes: Implications for oxidation of intermediate volatility organic compounds (IVOCs). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, Y.; Chu, W.; Kong, Y.; Chu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of oh radical and SO2 concentrations on photochemical reactions of mixed anthropogenic organic gases. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 10489–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentner, D.R.; Worton, D.R.; Isaacman, G.; Davis, L.C.; Dallmann, T.R.; Wood, E.C.; Herndon, S.C.; Goldstein, A.H.; Harley, R.A. Chemical composition of gas-phase organic carbon emissions from motor vehicles and implications for ozone production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11837–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Luo, S.L.; Huang, X.Q.; Fu, X.W.; Xiao, S.X.; Zeng, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, X.M. Ambient naphthalene and methylnaphthalenes observed at an urban site in the pearl river delta region: Sources and contributions to secondary organic aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 252, 118295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Sawant, A.A.; Jansen, K.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R. Characterization of chemical and particulate emissions from aircraft engines. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4380–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, L.R.; Zielinska, B.; Moosmüller, H. Emissions of levoglucosan, methoxy phenols, and organic acids from prescribed burns, laboratory combustion of wildland fuels, and residential wood combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoneit, B.R.T. Biomass burning—A review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.C.; de Gouw, J.A.; Gilman, J.B.; Jathar, S.H.; Akherati, A.; Cappa, C.D.; Jimenez, J.L.; Lee-Taylor, J.; Hayes, P.L.; McKeen, S.A.; et al. Volatile chemical products emerging as largest petrochemical source of urban organic emissions. Science 2018, 359, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Xu, T.T.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.M.; Cheng, T.T.; Li, X. Seasonal contributions to size-resolved n-alkanes (C8–C40) in the shanghai atmosphere from regional anthropogenic activities and terrestrial plant waxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilberg, A.; Liu, D.Z.; Adamsen, A.P.S.; Hansen, M.J.; Jonassen, K.E.N. Odorant emissions from intensive pig production measured by online proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5894–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Kawamura, K.; Sawano, M. Size distributions and chemical characterization of water-soluble organic aerosols over the Western North Pacific in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.H.; Kreisberg, N.M.; Hohaus, T.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Zhao, Y.; Day, D.A.; Kaser, L.; Karl, T.; Hansel, A.; Teng, A.P.; et al. Speciated measurements of semivolatile and intermediate volatility organic compounds (S/IVOCs) in a pine forest during BEACHON-ROMBAS 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1187–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cai, D.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Molecular characterization of atmospheric organic aerosols in typical megacities in China. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, H.O.T.; Liao, H.; Wu, S.; Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Henze, D.K.; Seinfeld, J.H. Effect of changes in climate and emissions on future sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosol levels in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D01205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Yin, D.; Zhao, B.; Huang, G.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, Z.; et al. Trends of full-volatility organic emissions in china from 2005 to 2019 and their organic aerosol formation potentials. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.-J.; Yin, S.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, X.; Li, L. Emission inventory of intermediate volatility organic compounds from vehicles in the Yangtze River Delta in 2017 and the impact on the formation potential of secondary organic aerosols. Huanjing Kexue 2020, 41, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, J.; Zeng, J.; Xiao, S.; et al. Measurement report: Emissions of intermediate-volatility organic compounds from vehicles under real-world driving conditions in an urban tunnel. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 10005–10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J.; An, J.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Intermediate volatility organic compound emissions from a large cargo vessel operated under real-world conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12934–12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, L.; Li, J.; et al. Concentration, composition and variation of ambient ivocs in Shanghai Port during the G20 Summit. Geochimica 2018, 47, 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Man, H.; Zhao, J.; Huang, W.; Huang, C.; Jing, S.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, D.; He, K.; et al. Voc and ivoc emission features and inventory of motorcycles in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Kong, M.; Chen, K.; Yin, S. The newest emission inventory of anthropogenic full-volatility organic in Central China. Atmos. Res. 2024, 300, 107245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Chang, X.; Huang, L.; Liang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, H.; et al. High-resolution emission inventory of full-volatility organic compounds from cooking in China during 2015–2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 5017–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Presto, A.A.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.A.; Robinson, A.L. Intermediate volatility organic compound emissions from on-road diesel vehicles: Chemical composition, emission factors, and estimated secondary organic aerosol production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11516–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Presto, A.A.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.A.; Robinson, A.L. Intermediate volatility organic compound emissions from on-road gasoline vehicles and small off-road gasoline engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4554–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Lu, Q.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Song, K.; Yu, Y.; Tan, R.; Liu, K.; Shen, R.; Chen, S.; et al. Measurement report: Distinct emissions and volatility distribution of intermediate-volatility organic compounds from on-road chinese gasoline vehicles: Implication of high secondary organic aerosol formation potential. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Zeraati-Rezaei, S.; Xu, H.M.; Harrison, R.M. Characterization of gas and particulate phase organic emissions (C9–C37) from a diesel engine and the effect of abatement devices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11345–11352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, X.e.; Fu, M.; Huang, F.; Man, H.; Deng, F.; Shaikh, A.A.; Wang, X.; Dong, R.; et al. Intermediate-volatility organic compound emissions from nonroad construction machinery under different operation modes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13832–13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Su, P.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, Y. Emission of intermediate volatility organic compounds from a ship main engine burning heavy fuel oil. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 84, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shang, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, G.; et al. Intermediate volatile organic compound emissions from residential solid fuel combustion based on field measurements in Rural China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5689–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Sha, Q.e.; Bi, L.; Yu, Y.; Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, J. Development and uncertainty analysis of intermediate volatility organic compounds ivocs emission inventories from mobile sources in Guangdong Province. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2022, 42, 408–418. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Ling, Z.; Liu, H.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. A gridded emission inventory of semi-volatile and intermediate volatility organic compounds in china. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.L.; Yang, C.; Cao, X.-L. Intermediate volatile organic compounds in canadian residential air in winter: Implication to indoor air quality. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; Zhou, L.; Shi, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; et al. Temperature effects on optical properties and chemical composition of secondary organic aerosol derived from n-dodecane. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8123–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, L.; Yang, Z.; Tchinda, N.T.; Li, J.; Li, K. Contrasting impacts of humidity on the ozonolysis of monoterpenes: Insights into the multi-generation chemical mechanism. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 10809–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Tao, S.; Yang, Y.F.; Dou, H.; Yang, Y.; Coveney, R.M. Inhalation exposure of traffic police officers to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) during the winter in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Li, Q.B.; Luo, Y.M.; Ding, Q.; Xi, L.M.; Ma, J.M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Cheng, C.L. Characteristics and sources of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 165, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Yuan, B.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, S.H.; Qi, J.P.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Hu, W.W.; Chen, W.; Ye, C.S.; et al. Measurements of higher alkanes using NO+ chemical ionization in PTR-ToF-MS: Important contributions of higher alkanes to secondary organic aerosols in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14123–14138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.H.; Liu, H.X.; Wang, Z.G.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhan, C.L.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Zheng, J.R.; Yao, R.Z.; Cao, J.J. Atmospheric concentrations and air-soil exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in typical urban-rural fringe of Wuhan-Ezhou region, Central China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.F.; Lu, C.Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.W.; Yang, L.X.; Xue, L.K.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, W.X. Nitrated phenols and the phenolic precursors in the atmosphere in Urban Jinan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Li, Y.F.; Qi, H.; Sun, D.Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, D.G. Seasonal variations of sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to a Northeastern Urban City, China. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.X.; Alam, M.S.; Stark, C.; Harrison, R.M. Composition and emission factors of traffic-emitted intermediate volatility and semi-volatile hydrocarbons (C10–C36) at a street canyon and urban background sites in central London, UK. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 231, 117448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gaya, B.; Fernández-Pinos, M.C.; Morales, L.; Méjanelle, L.; Abad, E.; Piña, B.; Duarte, C.M.; Jiménez, B.; Dachs, J. High atmosphere-ocean exchange of semivolatile aromatic hydrocarbons. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, Y. Potential deterioration of ozone pollution in coastal areas caused by marine-emitted halogens: A case study in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Sha, Q.e.; Zheng, J. Measurement-based intermediate volatility organic compound emission inventory from on-road vehicle exhaust in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Xu, R.; Kong, M.; Zhang, R. Research progress on sampling analysis and field observation of intermediate volatility organic compounds in the urban atmosphere. Environ. Chem. 2023, 44, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S.; Cai, S.; Guo, F.; Gui, P.; Huang, G.; Wu, D.; Han, L.; et al. Full-volatility emission framework corrects missing and underestimated secondary organic aerosol sources. One Earth 2022, 5, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Che, H.; Lv, T.; Wu, B.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, Z. Real-world emission characteristics of semivolatile/intermediate-volatility organic compounds originating fromnonroad constructionmachinery in the working process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z. A case study of investigating secondary organic aerosol formation pathways in beijing using an observation-based SOA box model. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, L.C.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Harley, R.A.; Miguel, A.H.; Hering, S.V.; Hammond, S.K. Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in motor vehicle fuels and exhaust emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Ikemori, F.; Ramasamy, S.; Iijima, A.; Kumagai, K.; Fushimi, A.; Fujitani, Y.; Chatani, S.; Tanabe, K.; Takami, A.; et al. Formation of secondary organic aerosol tracers from anthropogenic and biogenic volatile organic compounds under varied NOx and oxidant conditions. Atmos. Environ. X 2022, 14, 100169. [Google Scholar]
- Presto, A.A.; Miracolo, M.A.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Secondary organic aerosol formation from high-NOx photo-oxidation of low volatility precursors: n-Alkanes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza, C.L.; Craven, J.S.; Yee, L.D.; Coggon, M.M.; Schwantes, R.H.; Shiraiwa, M.; Zhang, X.; Schilling, K.A.; Ng, N.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; et al. Secondary organic aerosol yields of 12-carbon alkanes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1423–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.B.; Ziemann, P.J. Effects of molecular structure on aerosol yields from oh radical-initiated reactions of linear, branched, and cyclic alkanes in the presence of NOx. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambe, A.T.; Onasch, T.B.; Croasdale, D.R.; Wright, J.P.; Martin, A.T.; Franklin, J.P.; Massoli, P.; Kroll, J.H.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Brune, W.H.; et al. Transitions from functionalization to fragmentation reactions of laboratory secondary organic aerosol (SOA) generated from the OH oxidation of alkane precursors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5430–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.B.; Ziemann, P.J. Products and mechanism of secondary organic aerosol formation from reactions of n-alkanes with OH radicals in the presence of NOx. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9229–9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.E.; Ziemann, P.J.; Griffin, R.J.; Lim, Y.B.; Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Modeling SOA formation from oh reactions with C8–C17 n-alkanes. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8015–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkacik, D.S.; Presto, A.A.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Secondary organic aerosol formation from intermediate-volatility organic compounds: Cyclic, linear, and branched alkanes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8773–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Ruiz, L.H. Chlorine-initiated oxidation of n-alkanes under high NOx conditions: Insights into secondary organic aerosol composition and volatility using a FIGAERO-CIMS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discussions 2018, 18, 15535–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, J.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.L.; Ge, X.L. Aqueous-phase production of secondary organic aerosols from oxidation of dibenzothiophene (DBT). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoui, M.; Leungsakul, S.; Kamens, R.M. Gas and particle products distribution from the reaction of β-caryophyllene with ozone. J. Atmos. Chem. 2003, 45, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.H.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Wang, W.X. Theoretical study on NO3-initiated oxidation of acenaphthene in the atmosphere. Can. J. Chem. 2008, 86, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Shi, X.G.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Hu, J.T.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, W.X. Mechanistic and kinetic studies on the OH-initiated atmospheric oxidation of fluoranthene. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; He, M.X. Mechanisms and kinetic parameters for the gas-phase reactions of anthracene and pyrene with Cl atoms in the presence of NOx. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17345–17353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Li, L.J.; Tang, P.; Cocker, D.R. SOA formation from photooxidation of naphthalene and methylnaphthalenes with m-xylene and surrogate mixtures. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 180, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Jang, E.; Alam, M.S.; Dang, J. Mechanisms of reactivity of benzo(a)pyrene and other PAH inferred from field measurements. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Yi, Y.Y.; Huo, X.X.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, Q.Z. Understanding the atmospheric fate of triphenylene: The oxidation mechanism initiated by OH radicals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 785, 139158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.Y.; Buchholz, A.; Li, Z.J.; Song, J.W.; Vallon, M.; Jiang, F.; Möhler, O.; Leisner, T.; Saathoff, H. Volatility of secondary organic aerosol from β-caryophyllene ozonolysis over a wide tropospheric temperature range. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8965–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Wu, Y.; Liang, L.; Zhang, R. The formation and evolution of secondary organic aerosol during haze events in beijing in wintertime. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 139158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.F.; Day, D.A.; Palm, B.B.; Yatavelli, R.L.N.; Chan, A.H.; Kaser, L.; Cappellin, L.; Hayes, P.L.; Cross, E.S.; Carrasquillo, A.J.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of atmospheric organic carbon at a forested site. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Wei, Z.; Chen, M.; Meng, H.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X. Aging effects on the toxicity alteration of different types of organic aerosols: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Ge, T.; Huang, C.; Luo, Z.; Ou, S.; Zheng, J. Research progress on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Formation, deleterious effects and control technologies. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Wu, J.; Turco, R.P.; Winer, A.M.; Atkinson, R.; Arey, J.; Paulson, S.E.; Lurmann, F.W.; Miguel, A.H.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A. Naphthalene distributions and human exposure in a Southern California. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, T.; Chang, F.; Meng, Z. Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons pollution characteristics in PM2.5 in two districts of Xi’an city from 2016 to 2018. J. Hyg. Res. 2020, 49, 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Yang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhan, E.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y. Pollution and carcinogenic risk of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Ji’nan. J. Environ. Health 2014, 31, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Fromme, H.; Sysoltseva, M.; Achten, C.; Bühl, T.; Röhl, C.; Leubner, S.; Gerull, F.; Gessner, A.; Kraft, M.; Burghardt, R.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons including dibenzopyrenes in indoor air samples from schools and residences in Germany. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korunov, A.O.; Khalikov, I.S.; Surnin, V.A. Seasonal variation and spatial distribution of the content of benzo(a)pyrene in the atmospheric air in the Russian Federation. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2021, 90, 2670–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.A.; Atia, N.N. Atmospheric concentrations, gaseous-particulate distribution, and carcinogenic potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Assiut, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8059–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tanabe, K.; Koyano, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Study on size distribution of 8 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in airborne suspended particulates indoor and outdoor. J. West China Univ. Med. Sci. 1994, 25, 442–446. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Definitions | Values | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA | Contaminant concentration in air | μg·m−3 | |
| ET | Exposure time | 3.7 | h/d |
| EF | Exposure frequency | 365 | d/y |
| ED | Exposure duration | 78.6 | y |
| AT | Averaging time | 78.6 × 365 × 24 | h |
| RfC | Reference concentration | mg·m−3 |
| IVOC Precursors | SOA Tracers | Indicator for Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Nap | 4-nitrophthalic acid | PAHs |
| 4-nitro-1-naphthol | ||
| 2,4-dinitro-1-naphthol | ||
| Phthalic acid | ||
| β-caryophyllene | β-caryophyllinic acid | Sesquiterpenes |
| Toxicity Parameters | Nap | BaP | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| IARC Carcinogenic Classes | Possibly carcinogenic to humans | Carcinogenic to humans | |
| Reference Concentration (RfC) | 3.0 × 10−3 | 2.0 × 10−6 | mg m−3 |
| Inhalation Unit Risk (IUR) | 3.4 × 10−5 | 6.0 × 10−4 | (μg·m−3)−1 |
| Reference Dose (RfD) | 2.0 × 10−2 | 3.0 × 10−4 | mg kg−1 day−1 |
| Oral Slope Factor (CSFo) | 0.12 | 1 | mg kg−1 day−1 |
| Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs) | 0.2 | 0.2 | μg L−1 |
| Median Lethal Dose (LD50) (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) | 150 | 250 | mg kg−1 |
| Nap (ng·m−3) | Sampling Location | ECR (×10−6) | HQ | BaP (ng·m−3) | Sampling Location | ECR (×10−6) | HQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3879.4 [67] | Haidian, Beijing | 20.33 | 0.20 | 52.58 [67] | Haidian, Beijing | 4.86 | 4.05 |
| 38.5 [72] | Harbin Winter | 0.20 | 0.00 | 4.61 [72] | Harbin Winter | 0.43 | 0.36 |
| 174 [69] | PRD | 0.91 | 0.01 | 1.33 [105] | Lianhu, Xi’an | 0.12 | 0.10 |
| 224 [69] | Rural NCP | 1.17 | 0.01 | 2.04 [106] | Jinan, China | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| 596 [107] | Classroom, German | 3.12 | 0.03 | 155 [108] | Svirsk, Russia | 14.34 | 11.95 |
| 378.6 [109] | Assiut, Egypt | 1.98 | 0.02 | 73.6 [109] | Assiut, Egypt | 6.81 | 5.67 |
| 41 [74] | North Atlantic | 0.21 | 0.00 | 2.91 [110] | Tokyo, Japan | 0.27 | 0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Nie, Y.; Gao, X.; Yan, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H. Pollution Characterization and Environmental Impact Evaluation of Atmospheric Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040318
Yan Y, Nie Y, Gao X, Yan X, Ji Y, Li J, Li H. Pollution Characterization and Environmental Impact Evaluation of Atmospheric Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040318
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yongxin, Yan Nie, Xiaoshuai Gao, Xiaoyu Yan, Yuanyuan Ji, Junling Li, and Hong Li. 2025. "Pollution Characterization and Environmental Impact Evaluation of Atmospheric Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review" Toxics 13, no. 4: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040318
APA StyleYan, Y., Nie, Y., Gao, X., Yan, X., Ji, Y., Li, J., & Li, H. (2025). Pollution Characterization and Environmental Impact Evaluation of Atmospheric Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review. Toxics, 13(4), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040318







