Molecular Mechanism of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Lung Injury Mediated by the Ras/Rap Signaling Pathway in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Ethics
2.2. PFOS Sample Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Animal and Exposure Protocol
2.4. RNA-Seq
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Determination of MEK and ERK Protein Expression Levels
2.7. Determination of ICAM-1 and VEGFa Protein Expression Levels
2.8. Measurement of Inflammatory Factors in BALF
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
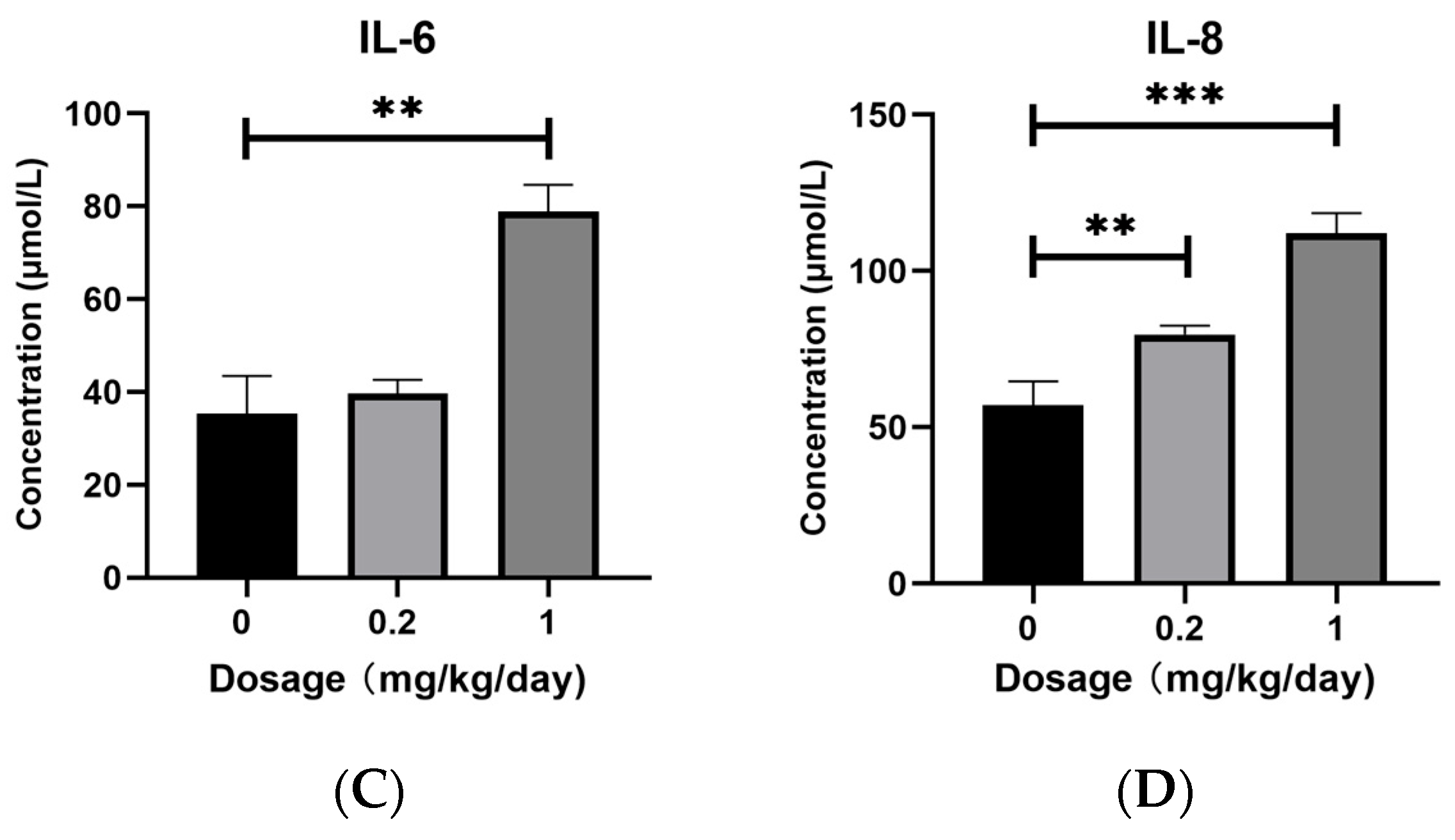
3.1. Effects of PFOS Exposure on Inflammatory Factors Expression
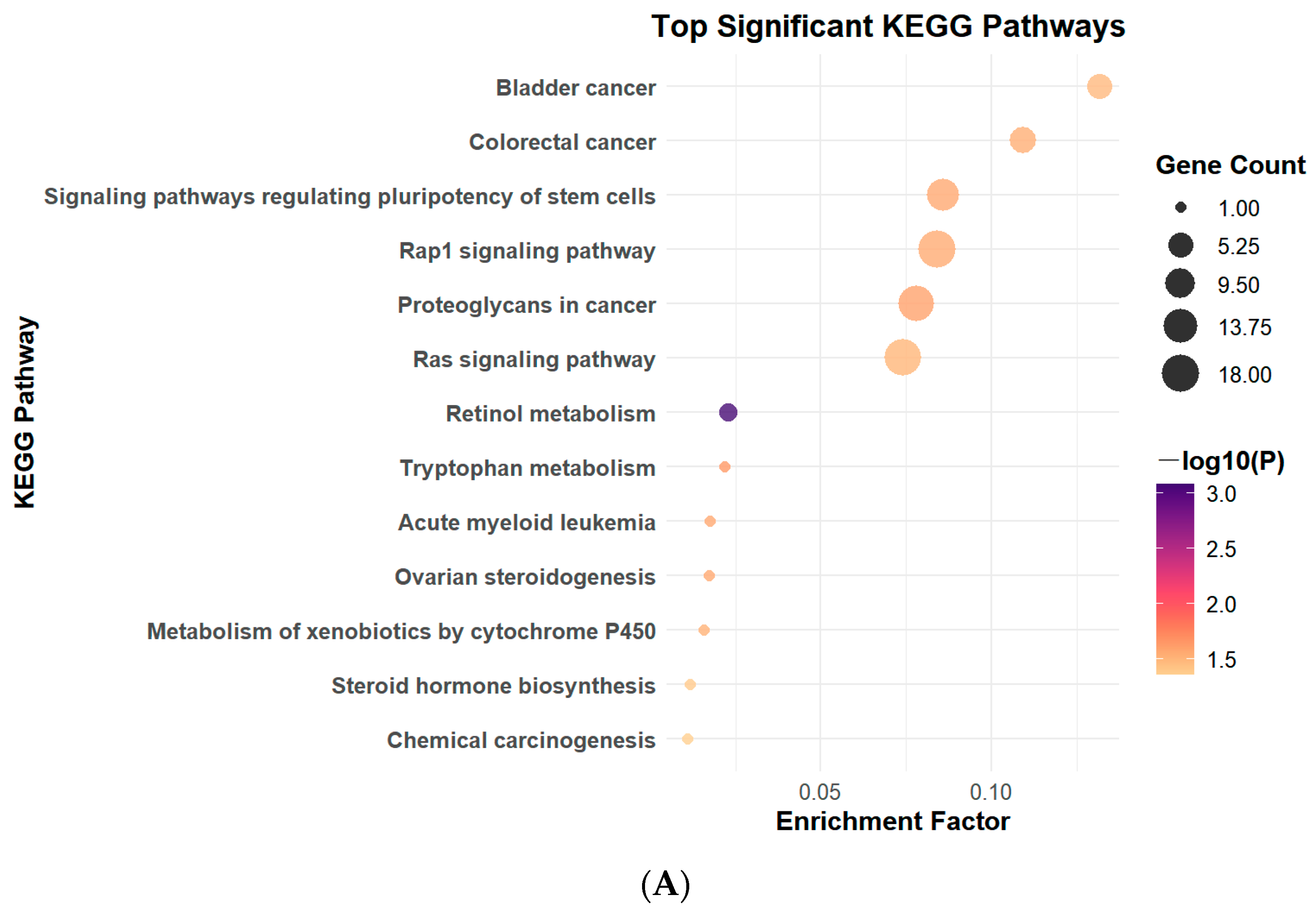
3.2. PFOS Exposure Leads to Changes in Signaling Pathways
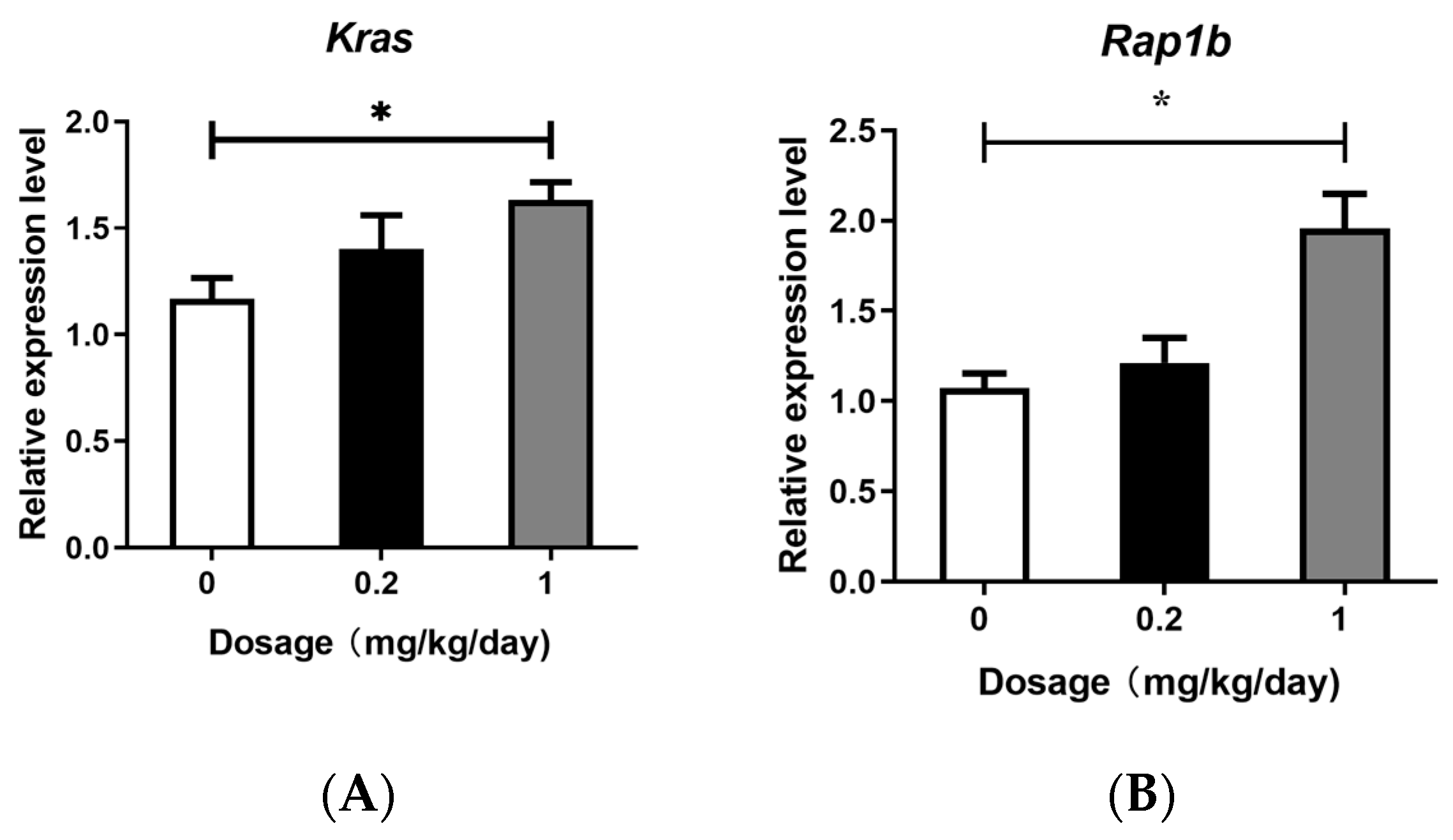
3.3. Effects of PFOS Exposure on Gene Expression
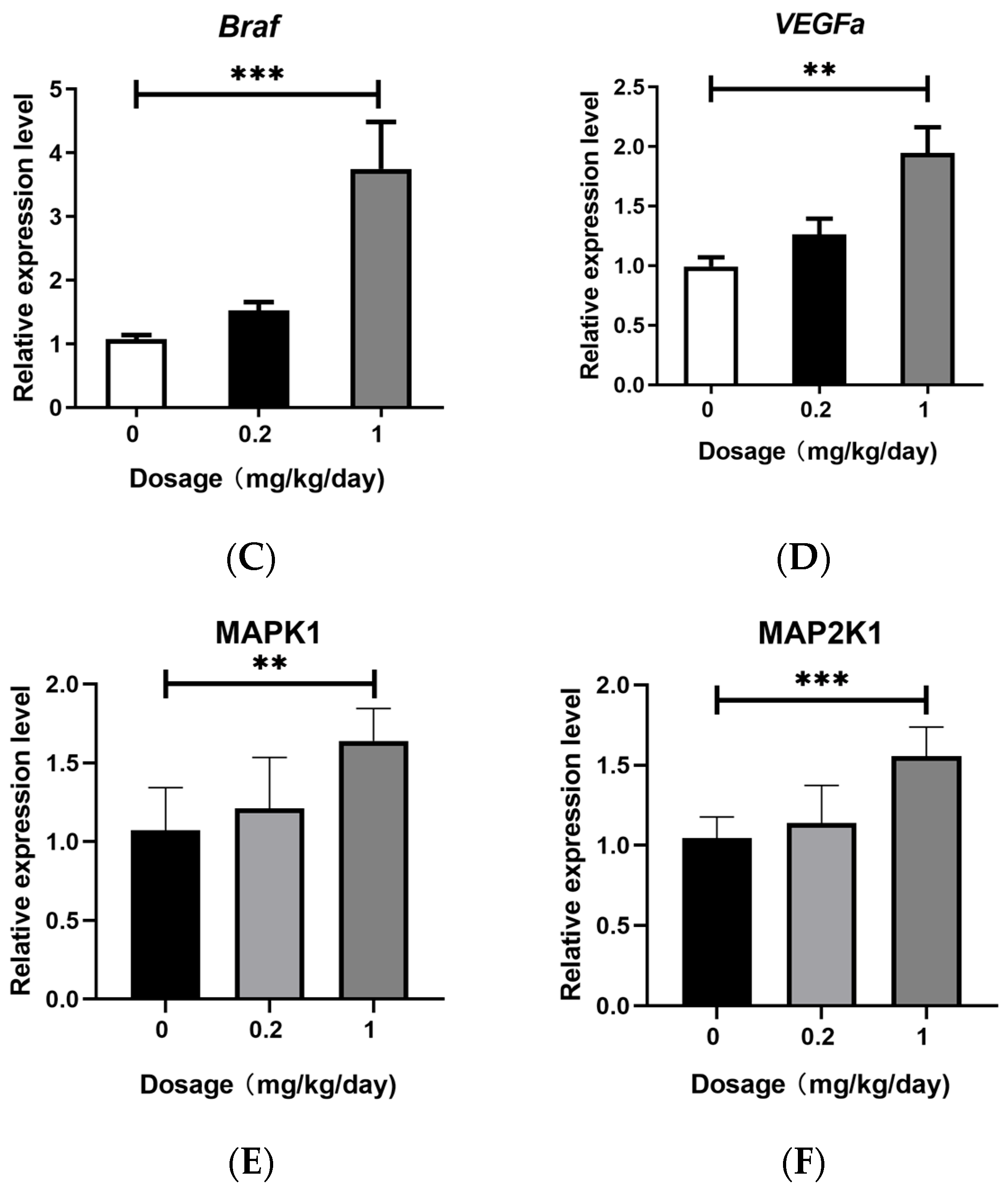
3.4. Effects of PFOS Exposure on Downstream Signaling Pathway
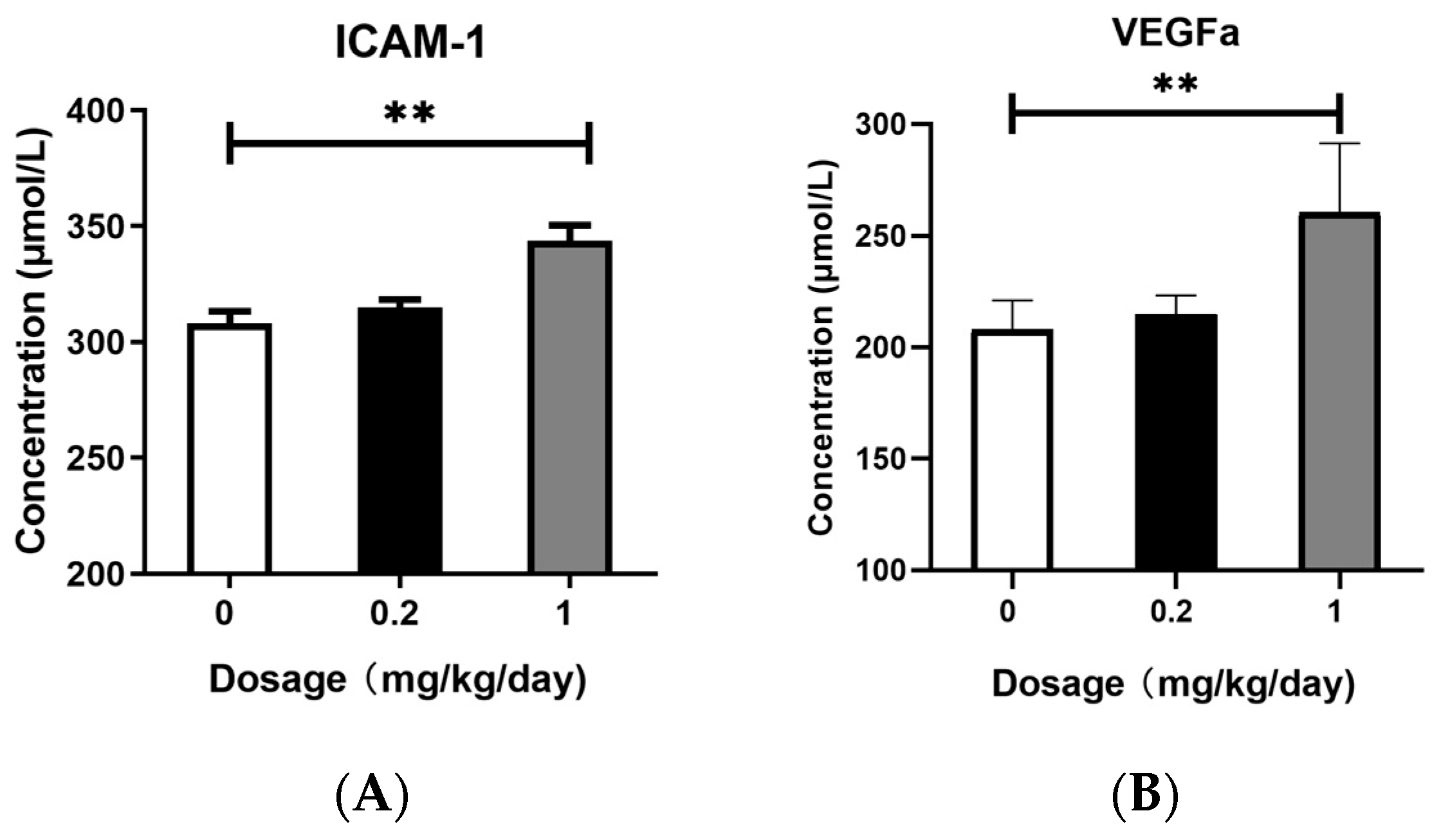
3.5. Effects of PFOS Exposure on ICAM-1 and VEGFa Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, J.M. Enhancing Regulations to Reduce Exposure to PFAS—Federal Action on “Forever Chemicals”. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1924–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Spyrou, A.; Tzamaria, A.; Efthimiou, I.; Triantafyllidis, V. Current state of knowledge of environmental occurrence, toxic effects, and advanced treatment of PFOS and PFOA. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Geng, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, F.; Kannan, K.; et al. Perfluorinated compounds in human blood, water, edible freshwater fish, and seafood in China: Daily intake and regional differences in human exposures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, K.; Li, X.; Tang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, N.; Cai, Z.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Reveals Occupational Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Relates to Oxidative Stress, Fatty Acid beta-Oxidation Disorder, and Kidney Injury in a Manufactory in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9800–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Tam, C.H.T.; Wong, K.K.; Ozaki, R.; Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Metzger, B.E.; Chow, E.; Tam, W.H.; Wong, C.K.C.; Ma, R.C.W. Epidemic-specific association of maternal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and their components with maternal glucose metabolism: A cross-sectional analysis in a birth cohort from Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besis, A.; Botsaropoulou, E.; Samara, C.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Hanssen, L.; Huber, S. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in air-conditioner filter dust of indoor microenvironments in Greece: Implications for exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, N.; Ramhøj, L.; Lykkebo, C.A.; Kugathas, I.; Poulsen, R.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Evrard, B.; Darde, T.A.; Axelstad, M.; Bahl, M.I.; et al. PFOS-induced thyroid hormone system disrupted rats display organ-specific changes in their transcriptomes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørli, J.B.; Låg, M.; Ekeren, L.; Perez-Gil, J.; Haug, L.S.; Da Silva, E.; Matrod, M.N.; Gützkow, K.B.; Lindeman, B. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) modify lung surfactant function and pro-inflammatory responses in human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2020, 62, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Aris, I.M.; Fleisch, A.F.; Lin, P.D.; Nichols, A.R.; Oken, E.; Hivert, M.F. Associations of Prenatal Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Exposures with Offspring Adiposity and Body Composition at 16-20 Years of Age: Project Viva. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Tang, P.; Fan, H.; Song, Y.; Liang, J.; Huang, H.; Pan, D.; Mo, M.; LeiLei; Lin, M.; et al. Association between maternal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and serum markers of liver function during pregnancy in China: A mixture-based approach. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.R.F. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.Y.; Aris, A.Z. Environmental impacts, exposure pathways, and health effects of PFOA and PFOS. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhuge, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, G. Oxidative stress and Cx43-mediated apoptosis are involved in PFOS-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 2022, 478, 153283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, Y.; An, Q.; Yang, X.; Yin, S.; Ma, L.Q.; Liu, W. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to emerging and legacy per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances: Levels and transfer in maternal serum, cord serum, and breast milk. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, Q.Y.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Leng, J.; Tang, N.J. Associations between exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and birth outcomes: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.T.; Wong, A.Y.-M.; Feng, S.; Wong, C.K.-C. Effects of In Utero Exposure to Perfluorooctane Sulfonate on Placental Functions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 16050–16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Almerick, T.; Boncan, D.; Wan, H.T.; Chan, T.F.; Zhang, E.L.; Lai, K.P.; Wong, C.K.-C. Hepatic metabolism gene expression and gut microbes in offspring, subjected to in-utero PFOS exposure and postnatal diet challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Eliot, M.N.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Kelsey, K.T.; Fore, R.; Langevin, S.; Buckley, J.; Chen, A.; Lanphear, B.P.; Cecil, K.M.; et al. Gestational Perfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure and DNA Methylation at Birth and 12 Years of Age: A Longitudinal Epigenome-Wide Association Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 037005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, H.B.; Larose, T.L.; Oien, T.; Sandanger, T.M.; Odland, J.O.; van de Bor, M.; Jacobsen, G.W. Prenatal exposure to persistent organic pollutants and child overweight/obesity at 5-year follow-up: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Health 2018, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakis, N.; David, V.C.; Jin, R.; Margetaki, K.; Valvi, D.; Siskos, A.P.; Maitre, L.; Garcia, E.; Varo, N.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances Associated With Increased Susceptibility to Liver Injury in Children. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1758–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, I.H.; Timmermann, C.A.G.; Nielsen, F.; Schoeters, G.; Johnk, C.; Kyhl, H.B.; Host, A.; Jensen, T.K. Association between prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and asthma in 5-year-old children in the Odense Child Cohort. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, A.M.; Webster, G.M.; Yolton, K.; Calafat, A.M.; Muckle, G.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and neurobehavior in US children through 8 years of age: The HOME study. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hong, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Li, H.; Cai, Z. The Role of Fecal Microbiota in Liver Toxicity Induced by Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Male and Female Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 67009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.C.; Wan, H.T.; Lee, W.K.; Lam, T.K.Y.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Lai, K.P.; Wong, C.K.C. Effects of In Utero PFOS Exposure on Epigenetics and Metabolism in Mouse Fetal Livers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14892–14903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, L.E.L.; Yamada, M.; Ford, J.; Owens, G.; Prow, T.; Juhasz, A. Health-related toxicity of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Comparison to legacy PFOS and PFOA. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M.; Sun, Q. Associations between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposures and Blood Lipid Levels among Adults-A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 56001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.M.; Fleisch, A.F.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Woo Baidal, J.A.; Pardo, L.; Webster, T.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Oken, E.; Sagiv, S.K. Early life exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and mid-childhood lipid and alanine aminotransferase levels. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, L.Y.; Qin, X.D.; Ye, X.Y.; Yu, S.; Bao, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.B.; Bloom, M.S.; Jalava, P.; et al. Perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate exacerbate airway inflammation in asthmatic mice and in vitro. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Xin, L.; Jiang, F. Maternal PFOS exposure in mice induces hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in adult female offspring: Involvement of microbiome-gut-liver axis and autophagy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Qiu, L.; Huang, J.; Dong, T.; Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Wang, S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) disrupts testosterone biosynthesis via CREB/CRTC2/StAR signaling pathway in Leydig cells. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Sho, M.; Adachi, M.; Huang, C.L.; Iki, K.; Kanehiro, H.; Hisanaga, M.; Nakano, H.; Miyake, M. The association of K-ras gene mutation and vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer 2001, 92, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarpia, L.; Lippman, S.M.; El-Naggar, A.K. Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, I.; Salazar, J.; Arqueros, C.; Andres, M.; Sebio, A.; Majem, M.; Szafranska, J.; Martinez, E.; Paez, D.; Lopez-Pousa, A.; et al. KRAS genetic variant as a prognostic factor for recurrence in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Jiang, R.; Huang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Rui, D.; Liao, X.; Ling, Z. Inhibition of lung cancer cells and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signal transduction by ectonucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase-7 (ENTPD7). Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, U.; Wang, M.; Hu, J. Targeting Aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiller, C.; Blanchard, M.P.; Pertuit, M.; Thirion, S.; Enjalbert, A.; Barlier, A.; Gerard, C. Ras and Rap1 govern spatiotemporal dynamic of activated ERK in pituitary living cells. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Hwang, J.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Oh, B.H.; Kim, M.H. Structural basis of inactivation of Ras and Rap1 small GTPases by Ras/Rap1-specific endopeptidase from the sepsis-causing pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 18110–18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Zankov, D.P.; Kurokawa-Seo, M.; Ogita, H. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Exerts Diverse Cellular Effects via Small G Proteins, Rho and Rap. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, R.C.; Cheng, K.; Ring, B.Z.; Su, L. Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, V.; Castellone, M.D.; De Vita, G.; Cirafici, A.M.; Hershman, J.M.; Guerrero, C.; Fusco, A.; Melillo, R.M.; Santoro, M. RET/papillary thyroid carcinoma oncogenic signaling through the Rap1 small GTPase. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.I.; Castro-Perez, E.; Prabhakar, K.; Block, L.; Longley, B.J.; Wisinski, J.A.; Kimple, M.E.; Setaluri, V. EPAC-RAP1 Axis-Mediated Switch in the Response of Primary and Metastatic Melanoma to Cyclic AMP. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.R.; Adjei, A.A. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2006, 1, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, G. Targeting the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-P.; Ferrara, N. OncogenicrasFails to Restore anin VivoTumorigenic Phenotype in Embryonic Stem Cells Lacking Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 254, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.M.; Wiesolek, H.L.; Sumagin, R. ICAM-1: A master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Moon, S.-O.; Park, S.K.; Chae, S.W.; Koh, G.Y. Angiopoietin-1 Reduces VEGF-Stimulated Leukocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells by Reducing ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-Selectin Expression. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, S.J.; Shum, A.J.; Lee, R.L.; Takei, F.; Gold, M.R. The Rap GTPases Regulate Integrin-mediated Adhesion, Cell Spreading, Actin Polymerization, and Pyk2 Tyrosine Phosphorylation in B Lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12009–12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Sequence of Primer (5′→3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| C57 BL/6J Mice | ||
| Rap-1b | TGCAGGAACGGAGCAATTCA | GTCGACTGTGCTGTGATGGA |
| Braf | AGTGGTACCCGCAAGATGTG | TGGTTTCTTCTCTCCATCCTGA |
| Vegfa | CGGGCCTCGGTTCCA | GCAGCCTGGGACCACTTG |
| Kras | GACACGAAACAGGCTCAGGA | GCATCGTCAACACCCTGTC |
| Mapk1 | CCCAAGTGATGAGCCCATTG | CTTACACCATCTCTCCCTTGCT |
| Map2k1 | CACCAGAGGGAAGCTTGAGAT | GCCTCCAGGTTGGTCCTCTC |
| β-Actin | CACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCC | TCATCCATGGCGAACTGGTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; He, J.; Ma, C.; Xue, J. Molecular Mechanism of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Lung Injury Mediated by the Ras/Rap Signaling Pathway in Mice. Toxics 2025, 13, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040320
Peng J, He J, Ma C, Xue J. Molecular Mechanism of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Lung Injury Mediated by the Ras/Rap Signaling Pathway in Mice. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040320
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jianhao, Jinfei He, Chenglong Ma, and Jiangdong Xue. 2025. "Molecular Mechanism of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Lung Injury Mediated by the Ras/Rap Signaling Pathway in Mice" Toxics 13, no. 4: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040320
APA StylePeng, J., He, J., Ma, C., & Xue, J. (2025). Molecular Mechanism of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Lung Injury Mediated by the Ras/Rap Signaling Pathway in Mice. Toxics, 13(4), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040320






