Mitophagy Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Injury in Granulosa Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Apoptosis Assay
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.5. Detection of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Intracellular ROS Content
2.6. Measurement of ATP Generation
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
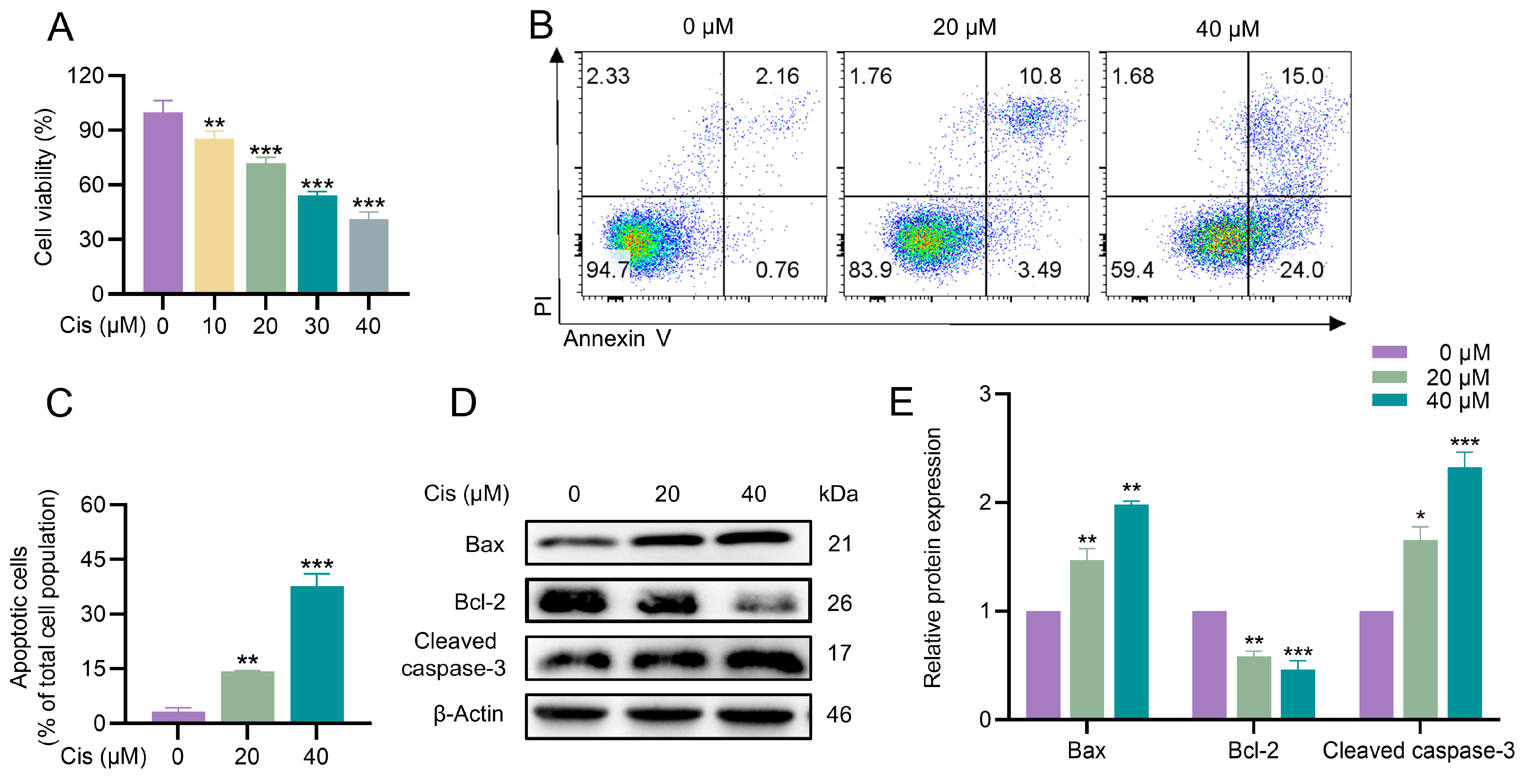
3.1. Cisplatin Inhibited Proliferation and Induced Apoptosis in KGN Cells
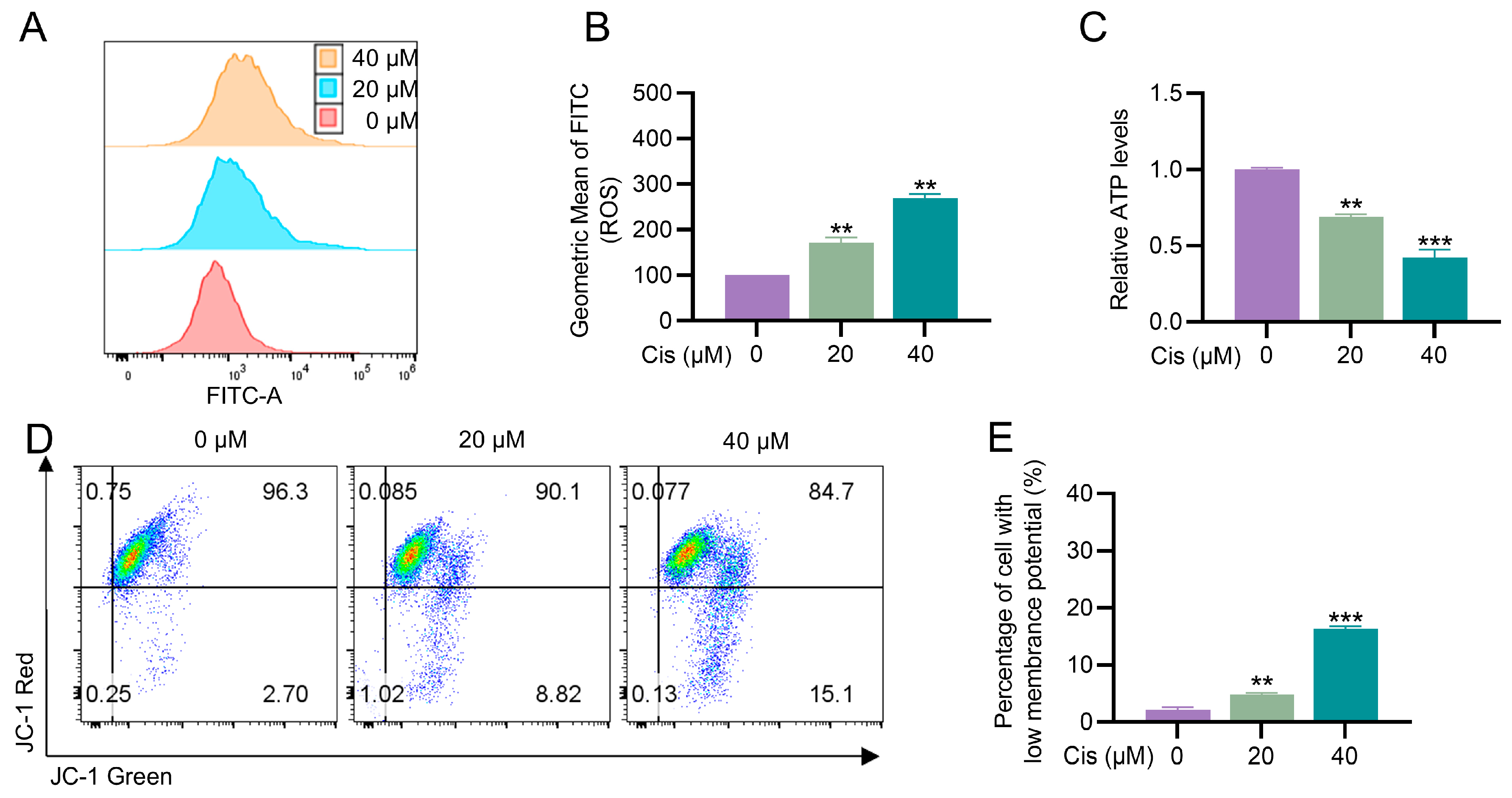
3.2. Cisplatin Caused Mitochondrial Dysfunction in KGN Cells
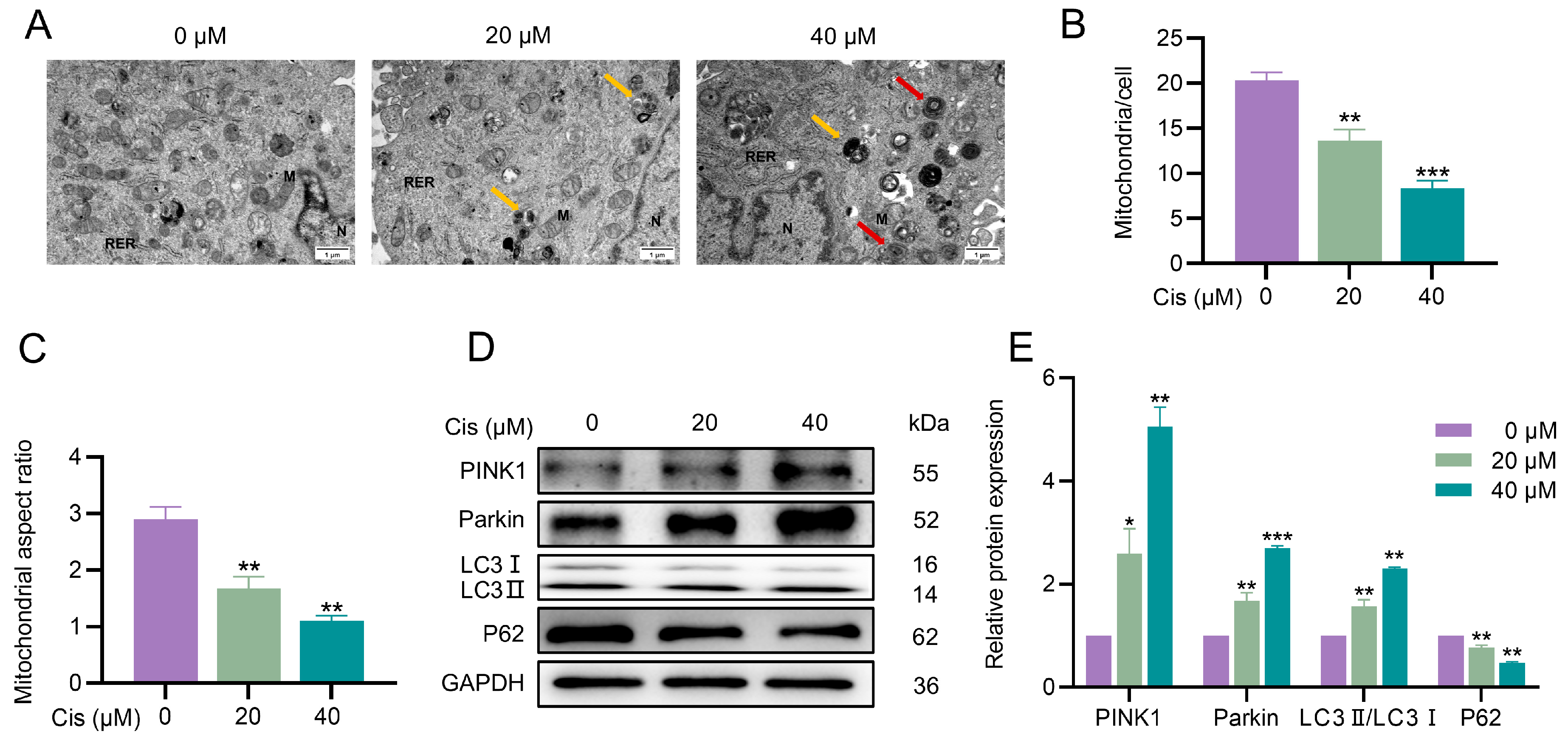
3.3. Cisplatin Induced Mitophagy in KGN Cells
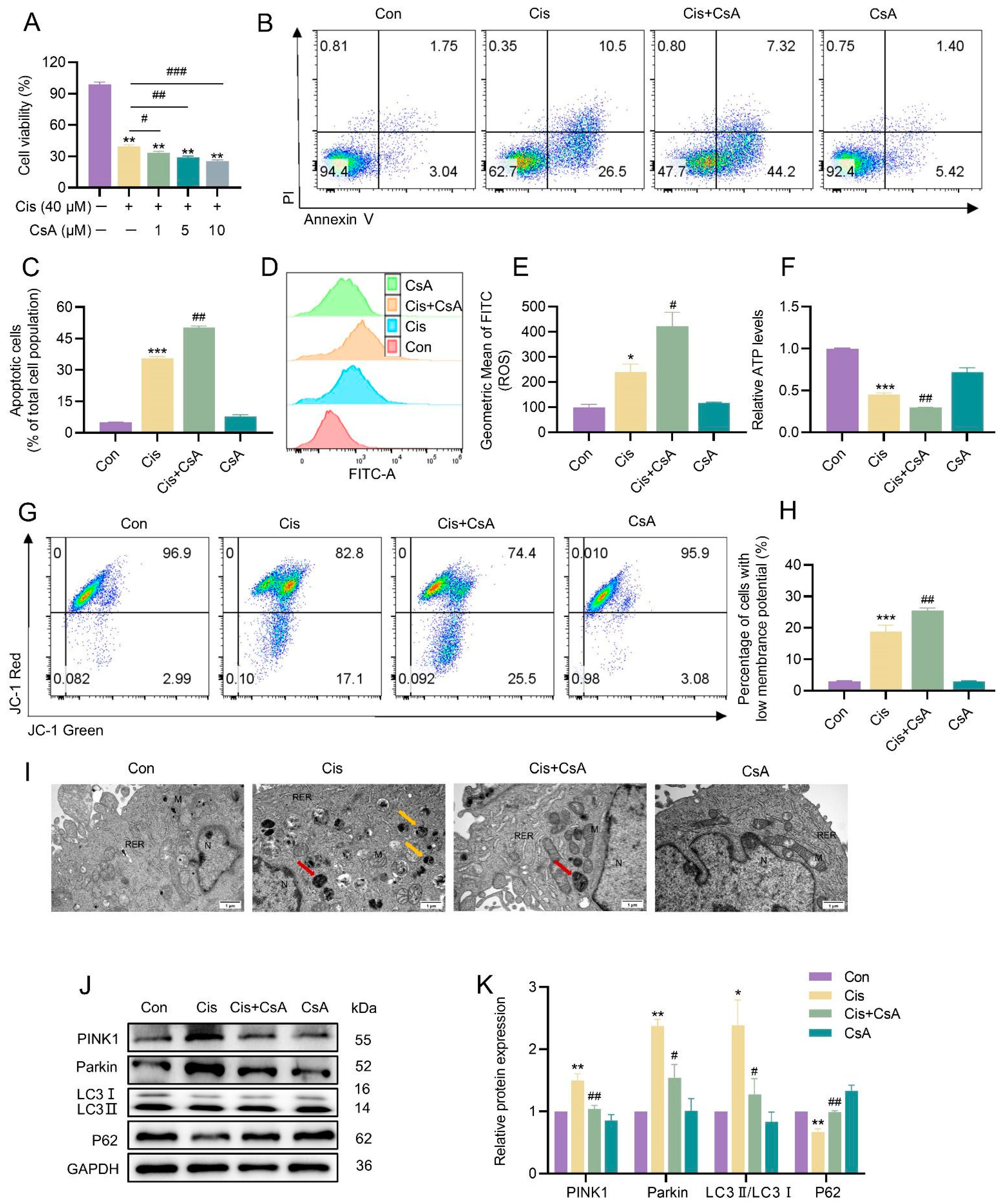
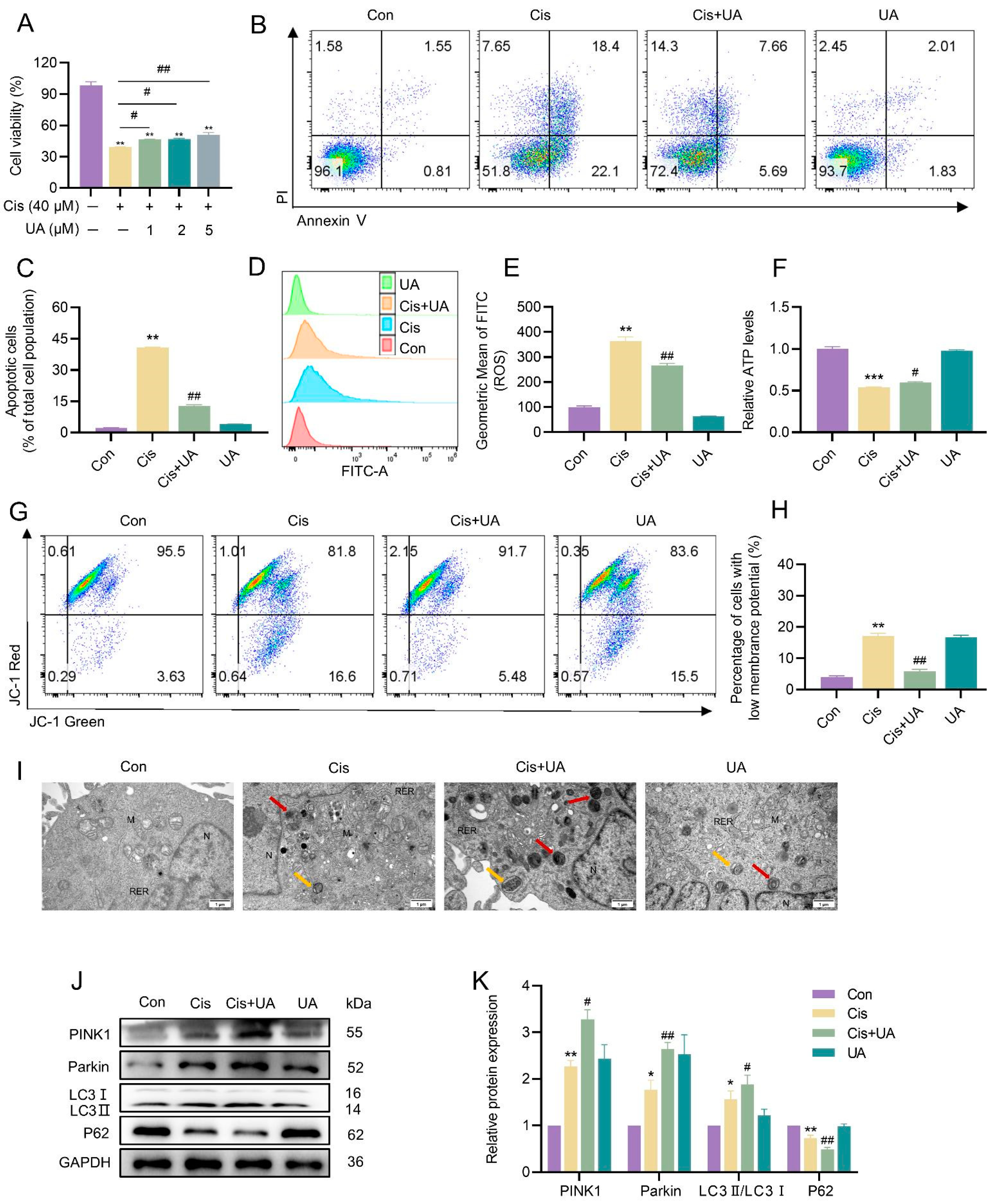
3.4. Mitophagy Served as a Protective Mechanism in the Injury of KGN Cells Caused by Cisplatin
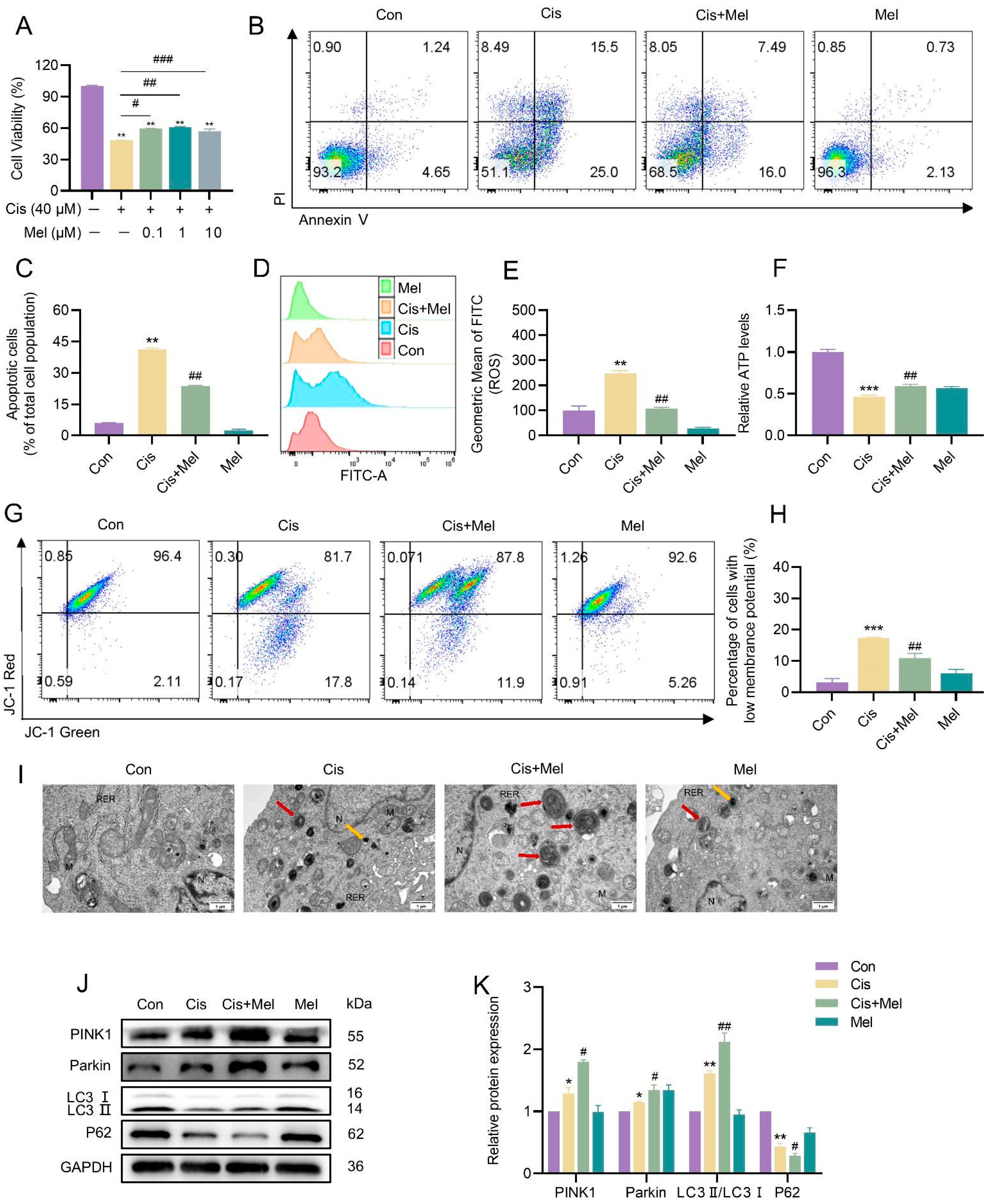
3.5. Melatonin Activated Mitophagy and Attenuated Cisplatin-Induced KGN Cell Damage
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Cai, J.; Chen, G.C.; Zhang, D.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Dong, Z. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is activated in cisplatin nephrotoxicity to protect against kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, N.A.G.; Ferreira, R.S.; dos Santos, A.C. Overview of cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity and ototoxicity, and the protective agents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.R.; Knowlton, N.S.; Thyer, A.C.; Charleston, J.S.; Soules, M.R.; Klein, N.A. A new model of reproductive aging: The decline in ovarian non-growing follicle number from birth to menopause. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 23, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, S.J.; Umair, Z.; Yoon, M.S. Premature Ovarian Insufficiency: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 672890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jancar, N.; Kopitar, A.N.; Ihan, A.; Klun, I.V.; Bokal, E.V. Effect of apoptosis and reactive oxygen species production in human granulosa cells on oocyte fertilization and blastocyst development. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2007, 24, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.T.; Chang, Y.J.; Wei, L.N.; Chen, J.H.; Li, J.J.; Goldsmith, S.; Liang, X.Y. Apoptosis of mural granulosa cells is increased in women with diminished ovarian reserve. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2019, 36, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.H.; Miyano, T. Interaction between growing oocytes and granulosa cells in vitro. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2020, 19, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, B.N.; Mosallanezhad, Z.; Matloob, N.; Davari, M.; Ghobadifar, M.A. The potential role of granulosa cells in the maturation rate of immature human oocytes and embryo development: A co-culture study. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2015, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Zeng, F.; Xu, Q.G.; Ma, J.M. Cryptotanshinone decreases granulosa cell apoptosis and restores ovarian function in mice with premature ovarian failure. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2020, 39, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, G.H.; Meng, M.; Guo, J.; Li, C.X.; Zhu, J.H.; Liu, L.; Wang, L. Adipose-derived stem cells promote the repair of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure by inhibiting granulosa cells apoptosis and senescence. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.L.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, L.H.; Cui, Z.W.; Cheng, F.Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.Y. FGF2 Is Protective Towards Cisplatin-Induced KGN Cell Toxicity by Promoting FTO Expression and Autophagy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 890623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocetta, V.; Ragazzi, E.; Montopoli, M. Mitochondrial Involvement in Cisplatin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrakhmanov, A.; Kulikov, A.V.; Luchkina, E.A.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Gogvadze, V. Involvement of mitophagy in cisplatin-induced cell death regulation. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciarretta, S.; Maejima, Y.; Zablocki, D.; Sadoshima, J. The Role of Autophagy in the Heart. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Reddy, P.H. Defective mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordureau, A.; Paulo, J.A.; Zhang, J.C.; An, H.; Swatek, K.N.; Cannon, J.R.; Harper, J.W. Global Landscape and Dynamics of Parkin and USP30-Dependent Ubiquitylomes in iNeurons during Mitophagic Signaling. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 1124–1142.E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.M.; Li, Z.P.; Zhao, M.Y.; Wang, D.D.; Sun, Z.X.; Yang, L.F. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 84, 101817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Xu, X.G.; An, X.F.; Duan, S.Y.; Huang, Z.M.; Yuan, Y.G. Pink1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy play a protective role in cisplatin induced renal tubular epithelial cells injury. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 350, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yue, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.D. Melatonin therapy for diabetic cardiomyopathy: A mechanism involving Syk-mitochondrial complex I-SERCA pathway. Cell. Signal. 2018, 47, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Pourbarkhordar, V.; Hayes, A.W.; Karimi, G. Melatonin regulates mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy: Cardiovascular protection. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.L.; Zheng, B.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, Y.N.; Sun, H.X.; Zhou, J.J. Melatonin ameliorates excessive PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy by enhancing SIRT1 expression in granulosa cells of PCOS. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E91–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.F.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, X.J.; Liu, S.P.; Liu, H.; Song, P.A. Melatonin alleviates renal injury by activating mitophagy in diabetic nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 889729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, R.O.; Al Jundi, M.; Gubbi, S.; Bompu, M.E.; Sirrs, S.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Hannah-Shmouni, F. Management of mitochondrial diabetes in the era of novel therapies. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Li, N.N.; Shi, K. Melatonin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice: Involvement of PPARα and fatty acid oxidation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 163, 112970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, L.; Rancic, M.; Radovic, M.; Krtinic, D.; Pavlovic, M.; Ilic, B.; Sokolovic, D. Melatonin inhibits apoptosis and oxidative tissue damage in cisplatin-induced pulmonary toxicity in rats. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shan, W.Y.; Li, N.; Zhou, B.; Guo, E.S.; Xia, M.; Sun, C.Y. Melatonin provides protection against cisplatin-induced ovarian damage and loss of fertility in mice. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2021, 42, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, N.; Lopes, F.; Stefansdottir, A.; Rossi, V.; De Felici, M.; Anderson, R.A.; Klinger, F.G. Ovarian damage from chemotherapy and current approaches to its protection. Hum. Reprod. Update 2019, 25, 673–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Schumaker, L.M.; Egorin, M.J.; Zuhowski, E.G.; Guo, Z.M.; Cullen, K.J. Cisplatin preferentially binds mitochondrial DNA and voltage-dependent anion channel protein in the mitochondrial membrane of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Possible role in apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5817–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleih, M.; Böpple, K.; Dong, M.; Gaissler, A.; Heine, S.; Olayioye, M.A.; Essmann, F. Direct impact of cisplatin on mitochondria induces ROS production that dictates cell fate of ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.L.; Chen, G.; Li, W.H.; Kepp, O.; Zhu, Y.S.; Chen, Q. Mitophagy, Mitochondrial Homeostasis, and Cell Fate. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Zhuge, J.R.; Zheng, X.Q.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Xu, T.Z.; Wang, X.Y. Urolithin A-induced mitophagy suppresses apoptosis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via the AMPK signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 150, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.R.; Zhang, M.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Gao, Z.M.; Li, Z.J.; Wu, X.Q. Urolithin A ameliorates obesity-induced metabolic cardiomyopathy in mice via mitophagy activation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, T.G.; Muqit, M.M.K. PINK1 and Parkin: Emerging themes in mitochondrial homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 45, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Long, H.J.; Hou, L.J.; Feng, B.R.; Ma, Z.H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, G.J. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresak, P.; Lapao, A.; Subic, N.; Boya, P.; Elazar, Z.; Simonsen, A. Regulation of PRKN-independent mitophagy. Autophagy 2022, 18, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamacher-Brady, A.; Brady, N.R.; Logue, S.E.; Sayen, M.R.; Jinno, M.; Kirshenbaum, L.A.; Gustafsson, A.B. Response to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury involves Bnip3 and autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.H.; Huang, C.X. Melatonin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via inhibiting oxidative stress, pyroptosis and apoptosis by activating Sirt1/Nrf2 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.Y.; He, M.; Hu, H.B.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ge, Y.; Zeng, Z.H. Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting mitophagy through SIRT3-mediated TFAM deacetylation. Autophagy 2024, 20, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.Q.; Dong, Y.Y.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ding, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Lv, W.F. Melatonin Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis of Bovine Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Promoting Mitophagy via SIRT1/FoxO1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.L.; Shi, X.T.; Xu, X.F.; Zhou, G.X.; Xiong, Y.W.; Yi, S.J.; Wang, H. Melatonin protects against environmental stress-induced fetal growth restriction via suppressing ROS-mediated GCN2/ATF4/BNIP3-dependent mitophagy in placental trophoblasts. Redox Biol. 2021, 40, 101854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Tang, M.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Xue, R. Mitophagy Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Injury in Granulosa Cells. Toxics 2025, 13, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050332
Zhu S, Tang M, Chen J, Li S, Xue R. Mitophagy Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Injury in Granulosa Cells. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050332
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Sihui, Mingge Tang, Jiahua Chen, Shuhang Li, and Rufeng Xue. 2025. "Mitophagy Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Injury in Granulosa Cells" Toxics 13, no. 5: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050332
APA StyleZhu, S., Tang, M., Chen, J., Li, S., & Xue, R. (2025). Mitophagy Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Injury in Granulosa Cells. Toxics, 13(5), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050332





