Characterization Studies on the sugC Gene of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 in Adhesion, Invasion, and Virulence in Mice
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Culture Conditions
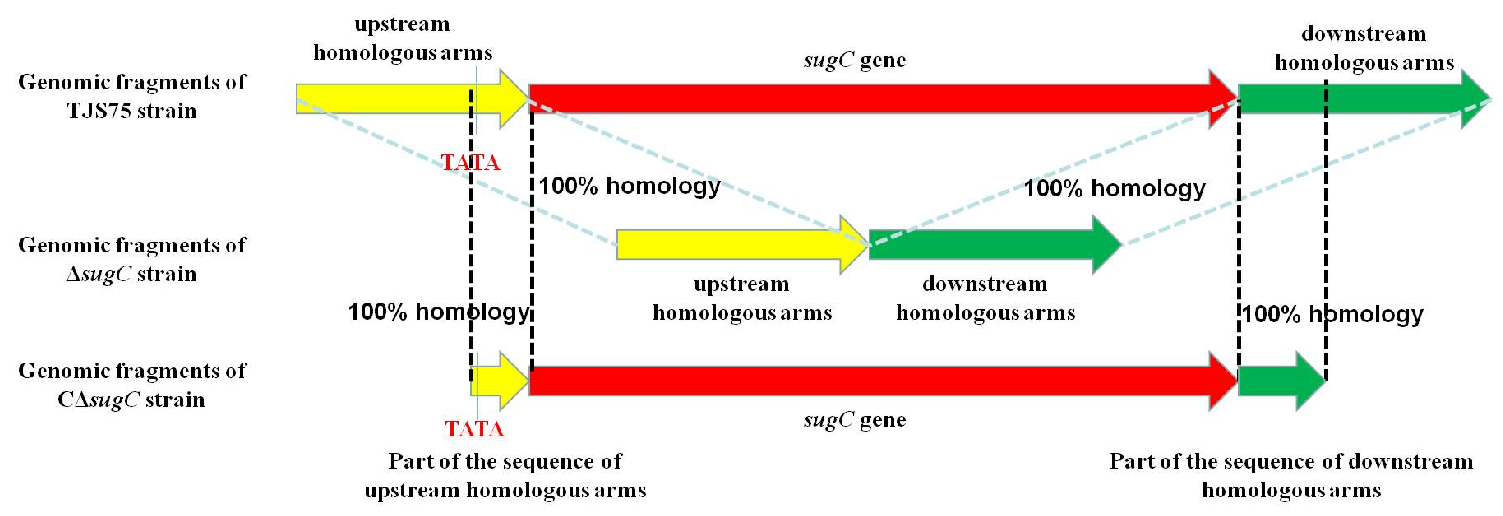
2.2. Construction of sugC Gene Knockout Strain and Complementary Strain
2.3. Cultivation Characteristics
2.4. Growth Curve
2.5. Biochemical Characteristics
2.6. Hemolytic Characteristics
2.7. Characteristics of Adhesion and Invasion
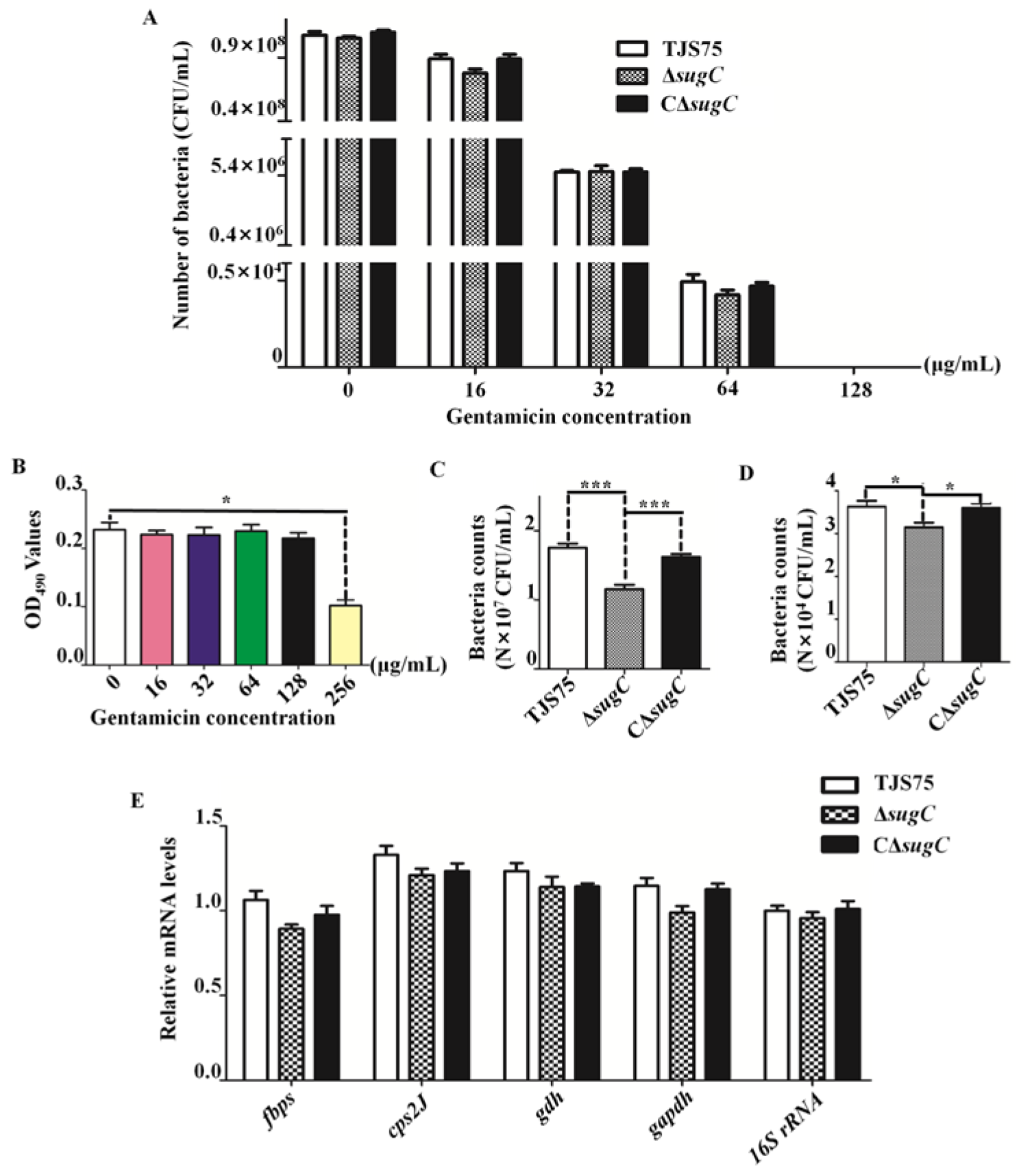
2.7.1. Exploring the Minimum Bactericidal Concentration of GEN for TJS75, ΔsugC and CΔsugC
2.7.2. The Effect of GEN on the Morphology of PK-15 Cells
2.7.3. Bacterial Adherence and Invasion Assays
2.7.4. The Relative Expression of fbps, cps2J, gdh and gapdh
2.8. Animal Pathogenicity Tests
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
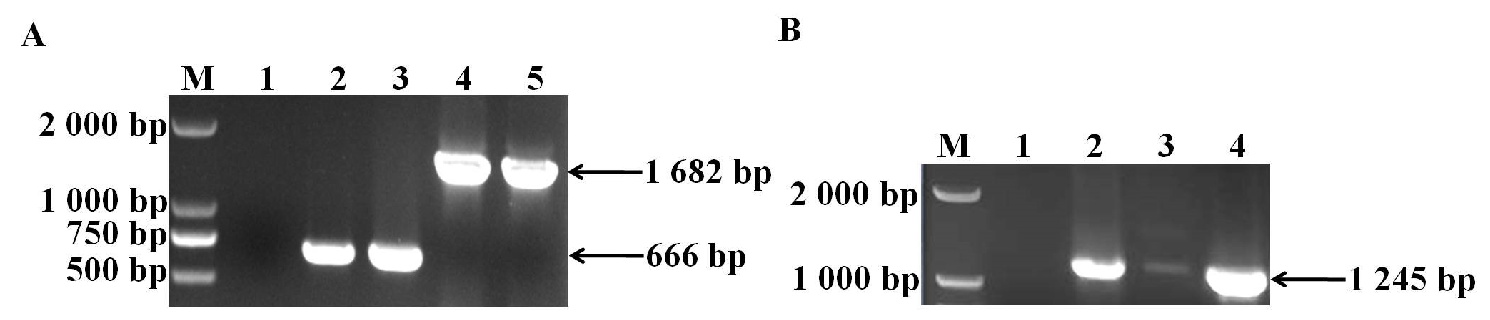
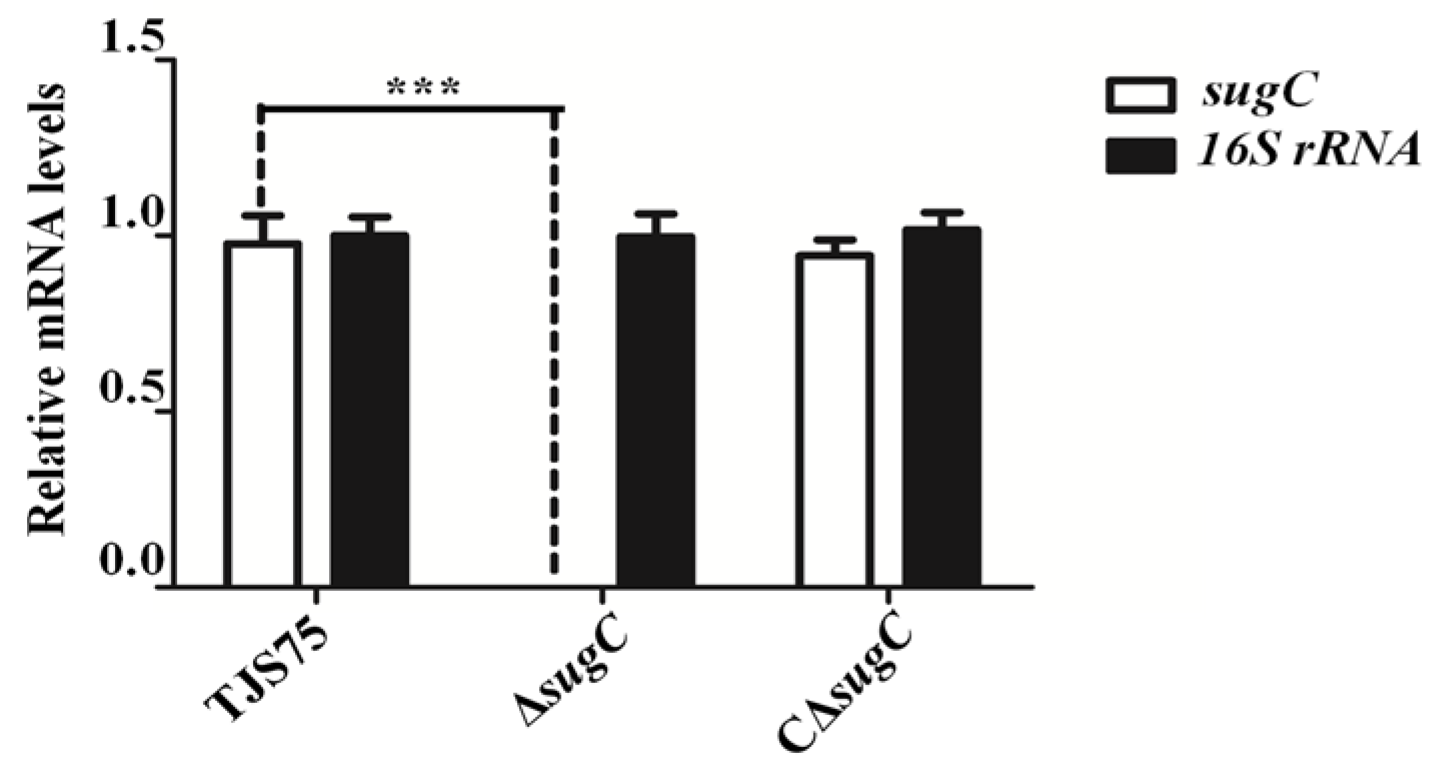
3.1. Identification of sugC Gene Knockout Strain and Complementary Strain
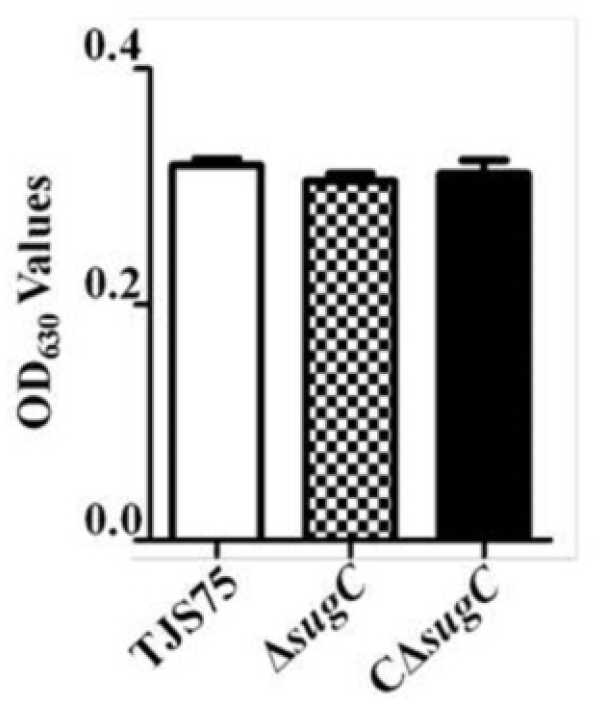
3.2. Observation of the Culture Characteristics of S. suis Strains
3.3. Effect of the sugC Gene on the Biochemical Characteristics of the TJS75 Strain
3.4. Lacking the sugC Gene Does Not Change the Hemolytic Characteristics of the TJS75 Strain
3.5. Knocking Out the sugC Gene Reduces the Adhesion and Invasiveness of TJS75 in PK-15 Cells
3.6. Deletion of the sugC Gene Reduced the Virulence of TJS75 in BALB/c Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Martínez, M.J.; Ornelas, M.A.S.; Amarie, R.E.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Tecles, F.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Escribano, D.; González-Bulnes, A.; Cerón, J.J.; et al. Changes in salivary biomarkers of stress, inflammation, redox status, and muscle damage due to Streptococcus suis infection in pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 1, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Zou, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Gasser, R.B.; Li, J. Predominance of Streptococcus suis ST1 and ST7 in human cases in China, and detection of a novel sequence type, ST658. Virulence 2017, 8, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhou, D.; Yang, K.; Guo, R.; Liang, W.; et al. PerR-regulated manganese import contributes to Oxidative stress defense in Streptococcus suis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0008622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, T.L.; Bayles, D.O. Comparative virulence and antimicrobial resistance distribution of Streptococcus suis isolates obtained from the United States. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1043529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradanas, M.; Poljak, Z.; Fittipaldi, N.; Ricker, N.; Farzan, A. Serotypes, virulence-associated factors, and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus suis isolates recovered from sick and healthy pigs determined by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 742345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Gong, S.; Sun, L.; Yi, L. pdh modulate virulence through reducing stress tolerance and biofilm formation of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Virulence 2019, 10, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, A.; Sun, X.; Jin, M. Screening of virulence-related transcriptional regulators in Streptococcus suis. Genes 2020, 11, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodsant, T.J.; Van Der Putten, B.C.L.; Tamminga, S.M.; Schultsz, C.; Van Der Ark, K.C.H. Identification of Streptococcus suis putative zoonotic virulence factors: A systematic review and genomic meta-analysis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2787–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Roy, A.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Pan, Z.; Yao, H. Role of ClpX and ClpP in Streptococcus suis serotype 2 stress tolerance and virulence. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 223–225, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.A.; Turner, D.P. The role of bacterial ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in pathogenesis and virulence: Therapeutic and vaccine potential. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 171, 105734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.; Daniel, J. The ABC transporter Rv1272c of Mycobacterium tuberculosis enhances the import of long-chain fatty acids in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basavanna, S.; Khandavilli, S.; Yuste, J.; Cohen, J.M.; Hosie, A.H.; Webb, A.J.; Thomas, G.H.; Brown, J.S. Screening of Streptococcus pneumoniae ABC transporter mutants demonstrates that LivJHMGF, a branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter, is necessary for disease pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3412–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosinha, G.M.; Freitas, D.A.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.; Campos, E.; Cravero, S.L.; Rossetti, O.; Splitter, G.; Oliveira, S.C. Identification and characterization of a Brucella abortus ATP-binding cassette transporter homolog to Rhizobium meliloti ExsA and its role in virulence and protection in mice. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5036–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Yang, M.; Hu, P.; Wu, J.; Chen, B.; Hua, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, H.; Xiao, J.; Jin, M. Comparative genomic analysis of Streptococcus suis reveals significant genomic diversity among different serotypes. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, D.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T. Construction and characterization of Streptococcus suis-Escherichia coli shuttle cloning vectors. Plasmid 2001, 45, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Du, D.; Xu, C.; Dai, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Shao, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. SBP2 plays an important role in the virulence changes of different artificial mutants of Streptococcus suis. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 1948–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Guo, X.; Lang, X.; Feng, S. A novel virulence-associated protein, vapE, in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2871–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Fan, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Xue, B.; Zhang, X.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y. Sub-Inhibitory concentrations of amoxicillin and tylosin affect the biofilm formation and virulence of Streptococcus suis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Jiang, X.; Liao, X.; Yue, M.; Li, X.; Fang, W. PrsA contributes to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 pathogenicity by modulating secretion of selected virulence factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Jacques, M.; Beaudoin, M.; Henrichsen, J. Characterization of six new capsular types (23 through 28) of Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2590–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Ji, H.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Hu, F.; et al. Contribution of the Rgg transcription regulator to metabolism and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, Approved Standard, 4th ed.; CLSI document VET01-A4; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, Y.; Bullerman, L.B. Cytotoxicity of Fusarium mycotoxins to mammalian cell cultures as determined by the MTT bioassay. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wei, R.; Li, R.; Zhao, D.; Ge, M.; Yao, Q.; Yu, X. The XRE family transcriptional regulator SrtR in Streptococcus suis is involved in Oxidant tolerance and virulence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Gao, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, P.; Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Ren, Y.; et al. Fpr2 exacerbates Streptococcus suis-induced streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome via attenuation of neutrophil recruitment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1094331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoulou, F.L.; Kerr, I.D. ABC transporter research: Going strong 40 years on. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Tampé, R. Structural and mechanistic principles of ABC transporters. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 605–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orelle, C.; Mathieu, K.; Jault, J.M. Multidrug ABC transporters in bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, V.G.; Ween, M.P.; McDevitt, C.A. The role of ATP-binding cassette transporters in bacterial pathogenicity. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 919–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kistler, H.C.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y. A fungal ABC transporter FgAtm1 regulates iron homeostasis via the transcription factor cascade FgAreA-HapX. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalscheuer, R.; Weinrick, B.; Veeraraghavan, U.; Besra, G.S.; Jr, W.R.J. Trehalose-recycling abc transporter lpqy-suga-sugb-sugc is essential for virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21761–21766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu-Sait, M.R.; Koliwer-Brandl, H.; Stewart, J.A.; Swarts, B.M.; Jacobsen, M.; Ioerger, T.R.; Kalscheuer, R. PPE51 mediates uptake of trehalose across the mycomembrane of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, A.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R. Recent proceedings on prevalence and pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2019, 32, 473–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kong, D.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zang, Y.; Hao, H.; Jiang, Y. Interaction of fibrinogen and muramidase-released protein promotes the development of Streptococcus suis meningitis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greeff, A.; Buys, H.; Verhaar, R.; Dijkstra, J.; Van Alphen, L.; Smith, H.E. Contribution of fibronectin-binding protein to pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brassard, J.; Gottschalk, M.; Quessy, S. Cloning and purification of the Streptococcus suis serotype 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and its involvement as an adhesin. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Fu, S.; Liu, M.; Jin, M.; Liu, J.; Bei, W.; Chen, H. Cloning, expression and characterization of a cell wall surface protein, 6-phosphogluconate-dehydrogenase, of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type and Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| TJS75 | / | S. suis serotype 2 virulence strain isolated from diseased pigs in Tianjin in 2015 (Accession: CP095162.1) |
| ΔsugC | / | TJS75 strain with sugC gene knocked out |
| CΔsugC | / | Complementary strain of ΔsugC; SpcR |
| E. coli DH5α | / | For cloning of recombinant plasmids |
| pSET4s [16] | / | S. suis temperature-sensitive suicide vector |
| pSET2 | / | E. coli–S. suis shuttle vector; SpcR |
| pSET4s-ΔsugC | / | Recombinant vector with background of pSET4s, designed to knock out sugC gene; SpcR |
| pSET2-sugC | / | pSET2 containing complete sugC gene and its promoter; SpcR |
| S1 | TACTACTTACCTCCGTATTGCA | Detecting full length of sugC gene |
| S2 | TGATTACCTTTAACGATAT | |
| L1 | GAAGCTGCAGTCAAAGAAGACATATACCCAAG 1 | Detecting upstream homologous arms of sugC gene |
| L2 | GAGGTGTGATTGCTCAAAGATAT | |
| R1 | TAGCCACGTTACACACCTC | Detecting downstream homologous arms of sugC gene |
| R2 | CCCCCCGGGCGAAGCTGAACGTGGCTAT | |
| CΔsugC-F | CCCCGGGTATATGATGAAGGCTACCAGCAACCACA | sugC gene and its upstream promoter carrying relevant restriction enzyme sites at both ends |
| CΔsugC-R | GCTGCAGGAAATTAAAGACTTTGCAAGCAGCGT | |
| qsugC-F | CTACTTACCTCCGTATTGCATAATG | Relative quantitative detection of sugC gene |
| qsugC-R | CCATGTTATTGATGATGTCGTGACT | |
| q16S rRNA-F | GGCGTGCCTAATACATG | Relative quantitative detection of internal reference genes |
| q16S rRNA-R | GCTATGAGGCAGGTT | |
| qgdh-F | CGGCGGTGGTAAAGGTGGTT | Relative quantitative detection of gdh gene |
| qgdh-R | CGTCAAGTGAAGGTCCGATGTG | |
| qfbps-F | TGCCATTTGCCAATAGCCCTGAA | Relative quantitative detection of fbps gene |
| qfbps-R | TCCCGCTCCGCCTTATCCTG | |
| qcps2J-F | GTTACTTGCTACTTTTGATGG | Relative quantitative detection of cps2J gene |
| qcps2J-R | TTTTCATTTCCTAAGTCTCG | |
| qgapdh-F | GTTTGATGACTACAATCCTCGGTTAC | Relative quantitative detection of gapdh gene |
| qgapdh-R | GCTTTAGCAGCACCAGTTGAG |
| Dose (CFU/mL) | Strain and Number of Mice | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJS75 | ΔsugC | CΔsugC | Control (0.9% NaCl) | |
| 1 × 109 | 10 | 10 | 10 | / 1 |
| 1 × 108 | 10 | 10 | 10 | / |
| 1 × 107 | 10 | 10 | 10 | / |
| 1 × 106 | 10 | 10 | 10 | / |
| Total | 40 | 40 | 40 | 10 |
| Dose (CFU/mL) | Initial Time of Onset (h) | Initial Time of Death (h) | Duration of Onset (h) | Morbidity Rate % | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJS75 | ΔsugC | CΔsugC | TJS75 | ΔsugC | CΔsugC | TJS75 | ΔsugC | CΔsugC | TJS75 | ΔsugC | CΔsugC | |
| 1.0 × 109 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1.0 × 108 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 132 | 132 | 132 | 100 | 80 | 100 |
| 1.0 × 107 | 12 | 24 | 12 | 48 | 0 | 24 | 132 | 132 | 132 | 80 | 40 | 80 |
| 1.0 × 106 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 60 | 0 | 60 | 24 | 12 | 36 | 60 | 20 | 60 |
| Dose (CFU/mL) | Number of Dead Mice/Total Mice | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJS75 | ΔsugC | CΔsugC | |||||||
| 1.0 × 109 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 |
| 1.0 × 108 | 6/10 | 7/10 | 5/10 | 4/10 | 4/10 | 4/10 | 7/10 | 7/10 | 7/10 |
| 1.0 × 107 | 4/10 | 4/10 | 4/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 4/10 | 4/10 | 4/10 |
| 1.0 × 106 | 2/10 | 2/10 | 2/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 2/10 | 2/10 | 2/10 |
| Mean LD50 value | 2.15 × 107 CFU | 1.47 × 108 CFU | 1.75 × 107 CFU | ||||||
| Group | Dose (CFU/mL) | Dying Mice | Average Bacterial Count | Survivors | Average Bacterial Count | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Blood | Brain | Lungs | Heart Blood | Brain | Lungs | ||||
| TJS75 | 1.0 × 108 | 4 | 3.40 × 106 | 1.10 × 105 | 5.10 × 105 | 4 | 1.10 × 103 | 1.40×101 | 3.0 × 101 |
| 1.0 × 107 | 2 | 4.90 × 105 | 5.40 × 104 | 6.40 × 104 | 6 | 4.80 × 101 | 4 | 1 | |
| 1.0 × 106 | 1 | 5.80 × 104 | 1.30 × 102 | 8.40 × 101 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| ΔsugC | 1.0 × 108 | 1 | 7.80 × 104 | 6.30 × 102 | 3.80 × 101 | 6 | 5.20 × 102 | 9 | 1.40 × 101 |
| 1.0 × 107 | 0 | / * | / | / | 10 | 1.50 × 101 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1.0 × 106 | 0 | / | / | / | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| CΔsugC | 1.0 × 108 | 3 | 8.60 × 106 | 7.10 × 104 | 4.90 × 105 | 3 | 3.20 × 102 | 4 | 6.70 × 101 |
| 1.0 × 107 | 1 | 3.80 × 105 | 1.70 × 103 | 4.50 × 104 | 6 | 2.60 × 101 | 4 | 0 | |
| 1.0 × 106 | 1 | 5.70 × 104 | 4.10 × 102 | 5.90 × 101 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Li, C.; Tian, X.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Ren, W.; Chi, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Characterization Studies on the sugC Gene of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 in Adhesion, Invasion, and Virulence in Mice. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090447
Dong Z, Li C, Tian X, Guo X, Li X, Ren W, Chi J, Zhang L, Li F, Zhu Y, et al. Characterization Studies on the sugC Gene of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 in Adhesion, Invasion, and Virulence in Mice. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(9):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090447
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zhimin, Cheng Li, Xiangxue Tian, Xiaoran Guo, Xiuli Li, Weike Ren, Jingjing Chi, Li Zhang, Fuqiang Li, Yao Zhu, and et al. 2024. "Characterization Studies on the sugC Gene of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 in Adhesion, Invasion, and Virulence in Mice" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 9: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090447
APA StyleDong, Z., Li, C., Tian, X., Guo, X., Li, X., Ren, W., Chi, J., Zhang, L., Li, F., Zhu, Y., Zhang, W., & Yan, M. (2024). Characterization Studies on the sugC Gene of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 in Adhesion, Invasion, and Virulence in Mice. Veterinary Sciences, 11(9), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090447





