Influence of Dexamethasone on the Plasma and Milk Disposition Kinetics of Danofloxacin in Lactating Sheep
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Safety
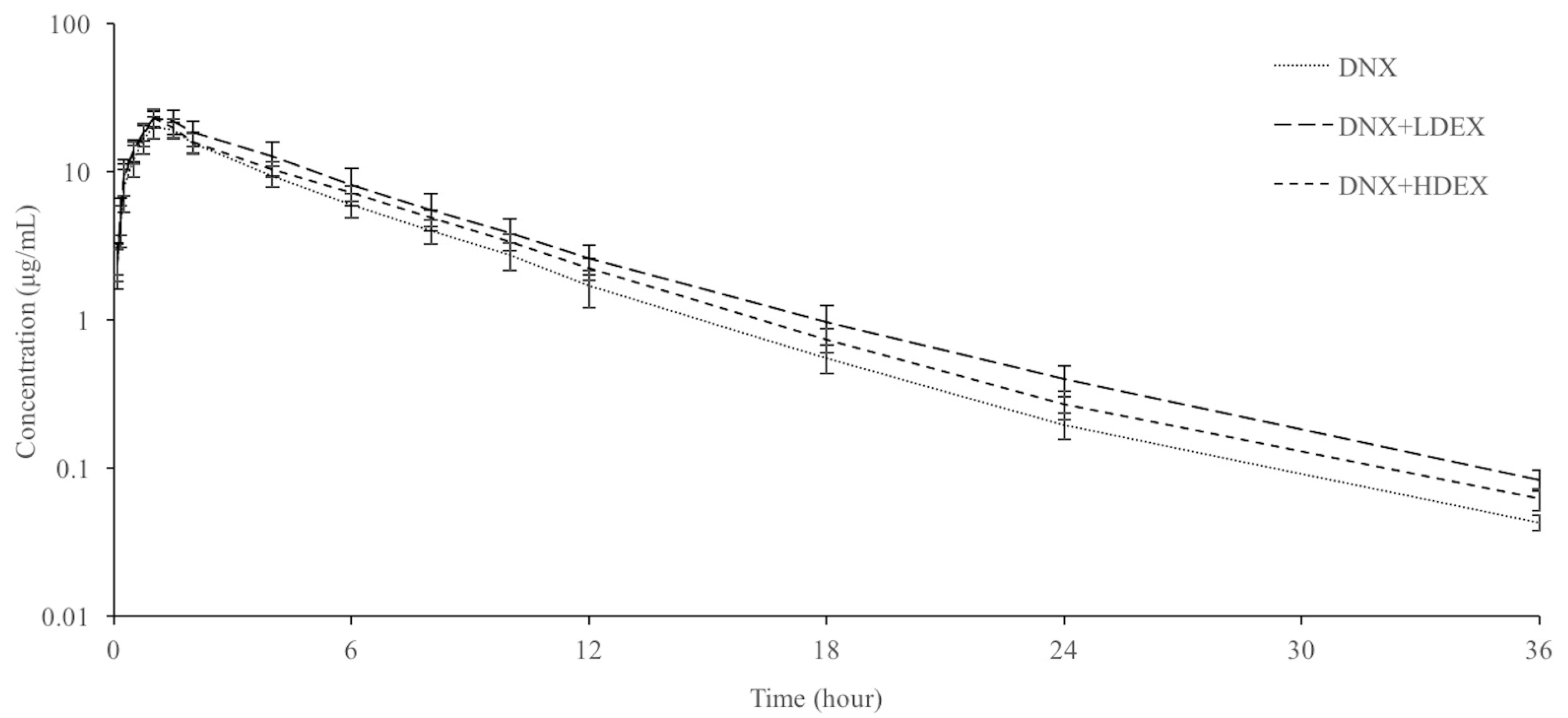
3.2. Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters
3.3. Milk Pharmacokinetic Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giguère, S.; Dowling, P.M. Fluoroquinolones. In Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar]
- Corum, O.; Corum, D.D.; Altan, F.; Er, A.; Cetin, G.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and intramuscular danofloxacin in red-eared slider turtles (Trachemys scripta elegans). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecko, N.; Pokludova, L.; Blahova, J.; Svobodova, Z.; Literak, I. Implications of fluoroquinolone contamination for the aquatic environment-A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S. Veterinary use of new quinolones in Japan. Drugs 1995, 49, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanidou, V.F.; Evaggelopoulou, E.N. Analytical strategies to determine antibiotic residues in fish. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2549–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritova, A.; Dimitrova, D.; Dinev, T.; Moutafchieva, R.; Lashev, L. Comparative pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin, danoflox- acin, and marbofloxacin after intravenous and oral administration in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). J. Avian Med. Surg. 2013, 27, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durna Corum, D.; Corum, O.; Tekeli, I.O.; Turk, E.; Kirgiz, F.C.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of danofloxacin in swan geese (Anser cygnoides) following intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and oral administrations. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 45, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CVMP. Danofloxacin (Extension to All Food Producing Species) Summary Report (6). Committee for Veterinary Medical Products, EMA/MRL/818/02-FINAL. 2002. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/523180851/danofloxacin-extension-all-food-producing-species-summary-report-6-committee-veterinary-medicinal-en (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Brown, S.A. Fluoroquinolones in animal health. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, G. Quinolones: A class of antimicrobial agents. Vet. Med. 2001, 46, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, V.H.J. Glucocorticoids: Mechanisms of action and anti-inflammatory potential in asthma. Med. Inf. 1998, 7, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourpiliadis, C.; Aeddula, N.R. Physiology, Glucocorticoids. In StatPearls, 2023; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- CVMP. Dexamethasone (Extrapolation to Goats), Committee for Medicinal Products For Veterinary Use, EMEA/MRL/874/03-Final. 2004. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/mrl-report/dexamethasone-extrapolation-goats-summary-report-3-committee-veterinary-medicinal-products_en.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Du, Y.; Meng, Y.; Lv, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Su, Z.; Zhao, X. Dexamethasone attenuates LPS-induced changes in expression of urea transporter and aquaporin proteins, ameliorating brain endotoxemia in mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8443. [Google Scholar]
- Aharon, M.A.; Prittie, J.E.; Buriko, K. A review of associated controversies surrounding glucocorticoid use in veterinary emergency and critical care. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2017, 27, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahi, D.; Nggada, H.A.; Ojo, N.A.; Mahre, M.B.; Igbokwe, N.A.; Umaru, B.; Mshelia, G.D. Dexamethasone uses in humans and animals: Public health and socio-economic implications. Kanem J. Med. Sci. 2017, 11, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmeh, A.; Badiei, K.; Pourjafar, M.; Nazıfı, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of insulin and dexamethasone on experimentally Escherichia coli serotype O55: B5 induced endotoxemia in Iranian fat-tailed sheep. Istanb. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2013, 39, 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sendzik, J.; Shakibaei, M.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Lode, H.; Stahlmann, R. Synergistic effects of dexamethasone and quinolones on human-derived tendon cells. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, J.W.; Roland, P.S.; Lee, K.H. Ciprofloxacin 0.3% + dexamethasone 0.1% for the treatment for otitis media. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2013, 14, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, F.; Corum, O.; Yildiz, R.; Eser Faki, H.; Ider, M.; Ok, M.; Uney, K. Intravenous pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin following simultaneous administration with flunixin meglumine or diclofenac in sheep. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 43, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durna Corum, D.; Corum, O.; Yildiz, R.; Eser Faki, H.; Ider, M.; Cetin, G.; Uney, K. Influences of tolfenamic acid and flunixin meglumine on the disposition kinetics of levofloxacin in sheep. Acta Vet. Hung. 2020, 68, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, G.; Durna Corum, D.; Corum, O.; Atik, O.; Coskun, D.; Uney, K. Effect of ketoprofen and tolfenamic acid on intravenous pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in sheep. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 44, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ural, M.N.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetic behavior and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic integration of danofloxacin following single or co-administration with meloxicam in healthy lambs and lambs with respiratory infections. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballent, M.; Lifschitz, A.; Virkel, G.; Sallovitz, J.; Maté, L.; Lanusse, C. In vivo and ex vivo assessment of the interaction between ivermectin and danofloxacin in sheep. Vet. J. 2012, 192, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Otero, J.A.; Barrera, B.; Prieto, J.G.; Merino, G.; Alvarez, A.I. Inhibition of ABCG2/BCRP transporter by soy isoflavones genistein and daidzein: Effect on plasma and milk levels of danofloxacin in sheep. Vet. J. 2013, 196, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real, R.; Egido, E.; Pérez, M.; Gonzalez-Lobato, L.; Barrera, B.; Prieto, J.G.; Merino, G. Involvement of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in the secretion of danofloxacin into milk: Interaction with ivermectin. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corum, O.; Altan, F.; Yildiz, R.; Ider, M.; Ok, M.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin and danofloxacin in premature calves. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uney, K.; Corum, D.D.; Marín, P.; Coskun, D.; Terzi, E.; Badillo, E.; Corum, O. Effect of body size on plasma and tissue pharmacokinetics of danofloxacin in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 2024, 14, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shem-Tov, M.; Ziv, G.; Glickman, A.; Saran, A. Pharmacokinetics and penetration of danofloxacin from the blood into the milk of ewes. Vet. Res. 1997, 28, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero, E.; Cárceles, C.M.; Fernandez-Varon, E.; Marin, P.; Benchaoui, H. Pharmacokinetics of danofloxacin 18% in lactating sheep and goats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, L.O.; Farrell, D.E.; Cope, C.V.; Baker, J.D.; Myers, M.J. The effect of endotoxin and dexamethasone on enrofloxacin pharmacokinetic parameters in swine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, F.S.; Landoni, M.F.; Lees, P. Pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD), and PK-PD integration of danofloxacin in sheep biological fluids. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, O.; Dik, B.; Er, A. Effect of single dose dexamethasone (0.1 mg/kg) on white blood cell counts and serum glucose levels in healthy ewes. Eurasian J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 32, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKellar, Q.A.; Gibson, I.F.; McCormack, R.Z. Pharmacokinetics and tissue disposition of danofloxacin in sheep. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1998, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, P.L.; Bousquet-Melou, A. Plasma clearance. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uney, K.; Durna Corum, D.; Terzi, E.; Corum, O. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of carprofen in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) broodstock. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corum, O.; Uney, K.; Coskun, D.; Durna Corum, D.; Cetin, G.; Elmas, M. Plasma and milk pharmacokinetics and estimated milk withdrawal time of tolfenamic acid in lactating sheep. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e70047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.G. Lactation and drugs. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2007, 17, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, B.; González-Lobato, L.; Otero, J.A.; Real, R.; Prieto, J.G.; Álvarez, A.I.; Merino, G. Effects of triclabendazole on secretion of danofloxacin and moxidectin into the milk of sheep: Role of triclabendazole metabolites as inhibitors of the ruminant ABCG2 transporter. Vet. J. 2013, 198, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstegen, R.H.; Ito, S. Drugs in lactation. J. Obstet Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.; Kim, M.K.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.; Cho, J.Y.; Yu, K.S.; Lim, K.S. Effects of dexamethasone coadministered with oseltamivir on the pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir in healthy volunteers. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villikka, K.; Kivistö, K.T.; Neuvonen, P.J. The effect of dexamethasone on the pharmacokinetics of triazolam. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 83, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, T.E. Interaction of dexamethasone with phenytoin. Pharmacotherapy 1991, 11, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, O.; Durna Corum, D.; Atik, O.; Eser Faki, H.; Altan, F.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of danofloxacin in chukar partridge (Alectoris chukar) following intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and oral administrations. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO 2025. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/w8338e/w8338e07.htm#:~:text=Peak%20danofloxacin%20concentrations%20in%20plasma,higher%20than%20that%20in%20faeces (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Johnson, D.B.; Lopez, M.J.; Kelley, B. Dexamethasone. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482130/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Narang, V.S.; Fraga, C.; Kumar, N.; Shen, J.; Throm, S.; Stewart, C.F.; Waters, C.M. Dexamethasone increases expression and activity of multidrug resistance transporters at the rat blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tainturier, D.; Alvinerie, M.; Brandon, R.A.; Toutain, P.L. Dexamethasone concentrations in bovine blood plasma and milk after intravenous injection. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, M.M.; Molina, A.J.; Merino, G.; Prieto, J.G.; Alvarez, A.I. Interaction of enrofloxacin with breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2): Influence of flavonoids and role in milk secretion in sheep. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardimci, S.B.; Sakin, F.; Corum, O. Pharmacokinetics, tissue residues, and withdrawal times of florfenicol in chukar partridges (Alectoris chukar). J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. 2019. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/other/answer-request-european-commission-updating-scientific-advice-impact-public-health-animal-health-use_en.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- WHO. List of Medically Important Antimicrobials a Risk Management Tool for Mitigating Antimicrobial Resistance Due to Non-Human Use. 2019. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/gcp/who-mia-list-2024-lv.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2025).

| Parameter | DNX | DNX + LDEX | DNX + HDEX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | |||
| t1/2ʎz (h) | 5.20 (4.95–5.41) | 5.30 (5.09–5.53) | 5.36 (5.06–5.66) |
| AUC0–24 (h*µg/mL) | 8.88 (8.31–10.62) | 8.62 (7.60–9.85) | 9.30 (8.35–10.76) |
| AUC0–∞ (h*µg/mL) | 9.26 (8.69–11.01) | 8.99 (7.97–10.23) | 9.71 (8.74–11.22) |
| AUCextrap (%) | 4.03 (3.50–4.55) | 4.20 (3.89–4.54) | 4.06 (3.46–4.64) |
| MRT0–∞ (h) | 6.53 (6.06–7.00) | 6.65 (6.43–6.89) | 6.79 (6.58–7.00) |
| ClT (L/h/kg) | 0.65 (0.55–0.69) | 0.67 (0.59–0.75) | 0.62 (0.53–0.69) |
| Vdss (L/kg) | 4.23 (3.53–4.83) | 4.44 (3.78–5.19) | 4.20 (3.70–4.56) |
| C0.08 h (µg/mL) | 3.06 (2.80–3.40) | 2.88 (2.46–3.38) | 2.97 (2.68–3.24) |
| Milk | |||
| t1/2ʎz (h) | 4.30 (4.08–4.55) b | 4.65 (4.44–4.98) a | 4.85 (4.58–5.15) a |
| AUC0–24 (h*µg/mL) | 98.04 (78.65–117.44) b | 111.96 (92.13–129.92) ab | 127.00 (97.50–165.83) a |
| AUC0–last (h*µg/mL) | 99.25 (79.64–118.81) b | 113.64 (93.44–131.95) ab | 129.37 (99.15–153.87) a |
| AUC0–∞ (h*µg/mL) | 99.52 (79.85–119.10) b | 114.06 (93.73–132.42) ab | 129.95 (99.65–153.87) a |
| AUCextrap (%) | 0.27 (0.23–0.37) | 0.44 (0.35–0.53) | 0.36 (0.31–0.44) |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 20.61 (17.94–24.15) b | 23.74 (19.84–28.26) ab | 24.93 (21.39–28.04) a |
| Tmax (h) | 1.00 (1.00–1.50) | 1.00 (1.00–1.50) | 1.00 (1.00–1.50) |
| AUC0–∞ milk/AUC0–∞ plasma | 10.75 (9.13–13.11) b | 12.69 (9.16–16.20) a | 13.38 (9.85–19.38) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uney, K.; Yildiz, R.; Durna Corum, D.; Ider, M.; Corum, O. Influence of Dexamethasone on the Plasma and Milk Disposition Kinetics of Danofloxacin in Lactating Sheep. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030210
Uney K, Yildiz R, Durna Corum D, Ider M, Corum O. Influence of Dexamethasone on the Plasma and Milk Disposition Kinetics of Danofloxacin in Lactating Sheep. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030210
Chicago/Turabian StyleUney, Kamil, Ramazan Yildiz, Duygu Durna Corum, Merve Ider, and Orhan Corum. 2025. "Influence of Dexamethasone on the Plasma and Milk Disposition Kinetics of Danofloxacin in Lactating Sheep" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030210
APA StyleUney, K., Yildiz, R., Durna Corum, D., Ider, M., & Corum, O. (2025). Influence of Dexamethasone on the Plasma and Milk Disposition Kinetics of Danofloxacin in Lactating Sheep. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030210






