Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase 1 of Echinococcus multilocularis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites
2.2. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of FBA Genes
2.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction and Prokaryotic Expression of EmFBA1
2.5. Preparation of Polyclonal Antibodies against EmFBA1
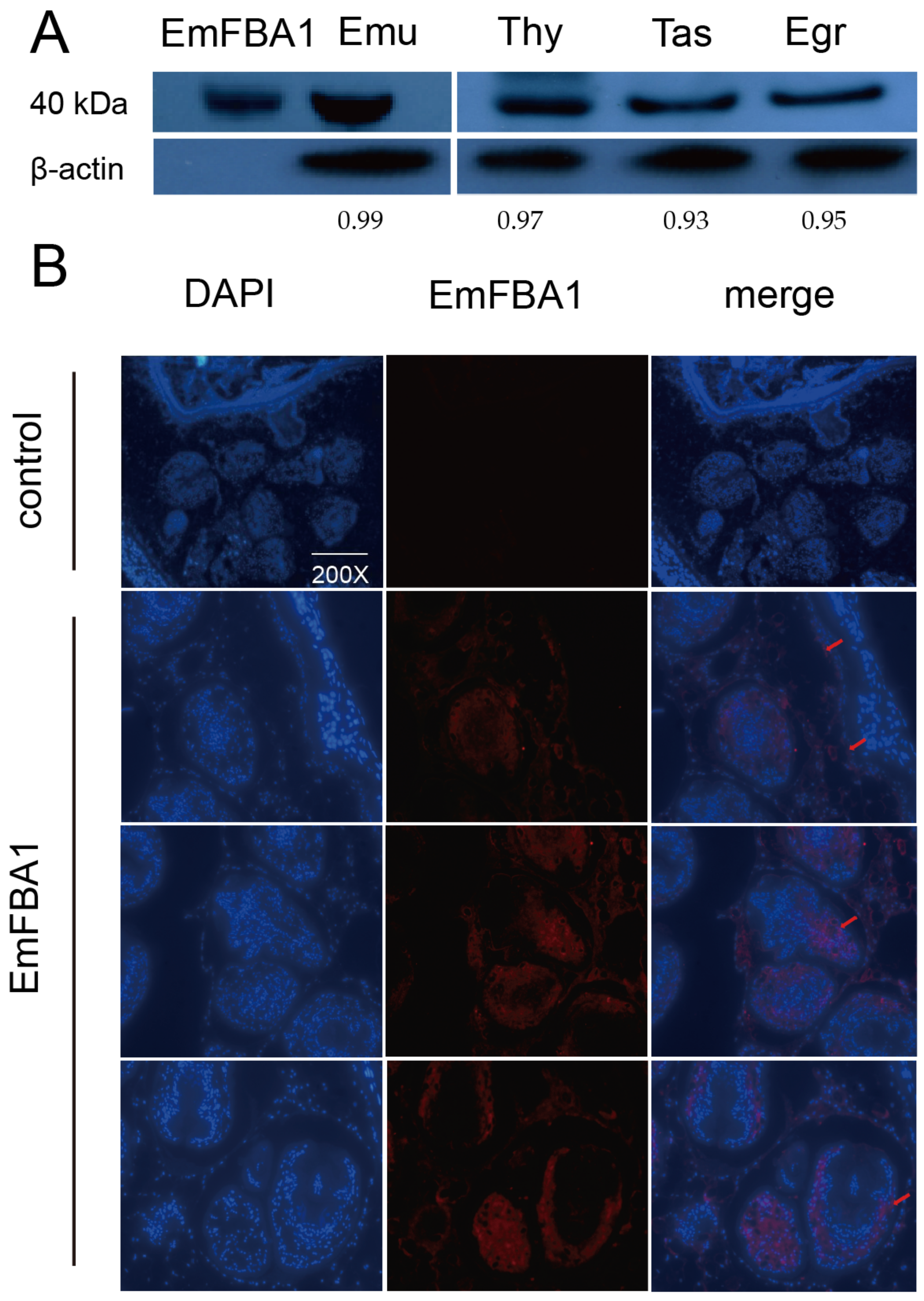
2.6. Immunofluorescence and Western Blotting
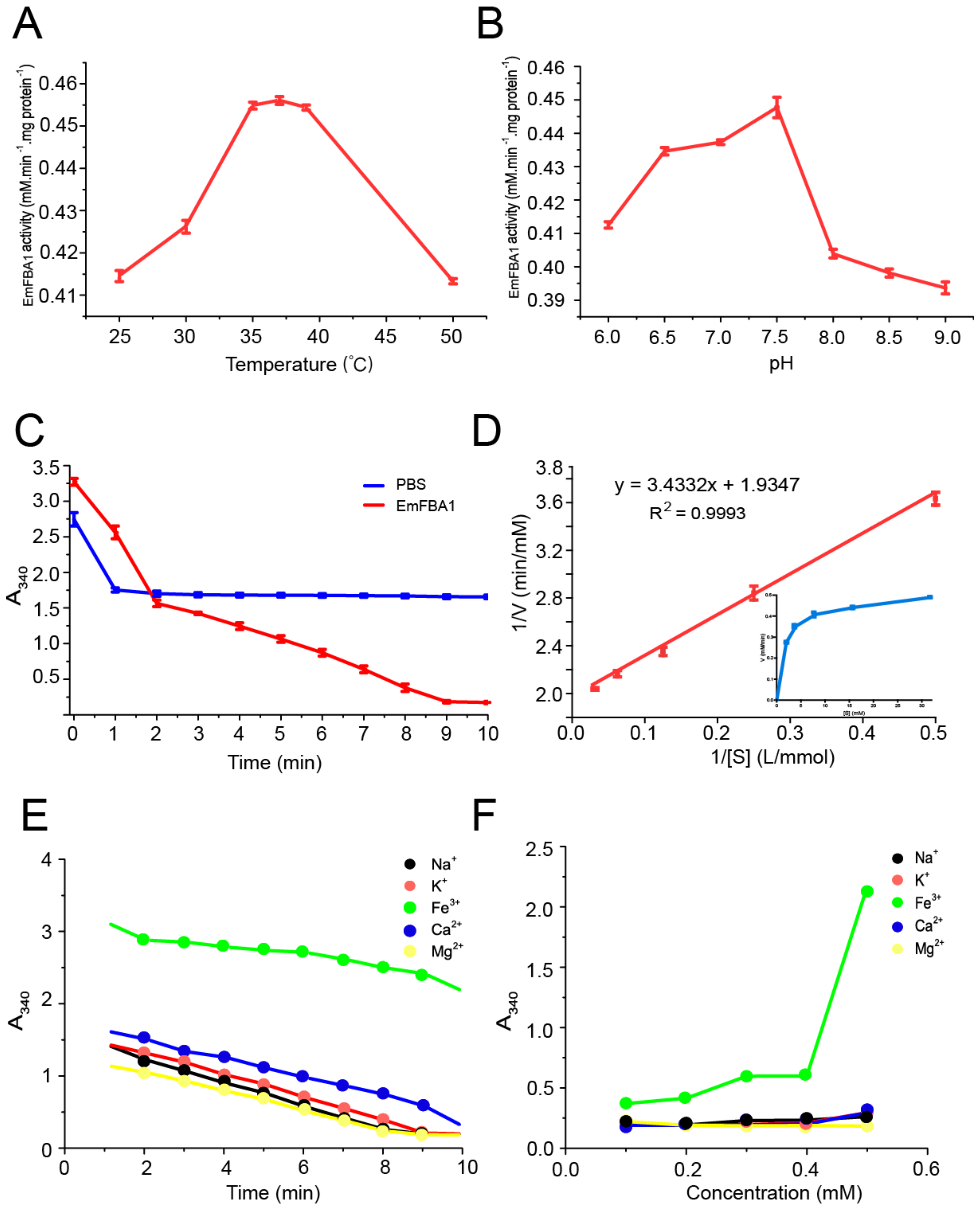
2.7. Determination of Enzyme Kinetics
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of fba Genes in Echinococcus Species
3.2. Localization of EmFBA1
3.3. Enzyme Kinetics of EmFBA1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deplazes, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Torgerson, P.R.; Harandi, M.F.; Romig, T.; Antolová, D.; Schurer, J.M.; Lahmar, S.; Cringoli, G.; et al. Global Distribution of Alveolar and Cystic Echinococcosis; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 95, pp. 315–493. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00075-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.-D.; Chen, K.-F.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Yang, K.-M.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.-X.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Meng, T.; Ma, Z.; et al. Two-stage hepatectomy for multiple giant alveolar echinococcosis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, J.; Thompson, R.C. Historical Aspects of Echinococcosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schweiger, A.; Ammann, R.W.; Candinas, D.; Clavien, P.-A.; Eckert, J.; Gottstein, B.; Halkic, N.; Muellhaupt, B.; Prinz, B.M.; Reichen, J.; et al. Human Alveolar Echinococcosis after Fox Population Increase, Switzerland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.M.; Borges, N.; Pagán, J.P.; Castaño-Cerezo, S.; Csonka, L.N.; Goodner, B.W.; Reynolds, K.A.; Gonçalves, L.G.; Argandoña, M.; Nieto, J.J.; et al. Fructose metabolism in Chromohalobacter salexigens: Interplay between the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas and Entner–Doudoroff pathways. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovářová, J.; Nagar, R.; Faria, J.; Ferguson, M.A.J.; Barrett, M.P.; Horn, D. Gluconeogenesis using glycerol as a substrate in bloodstream-form Trypanosoma brucei. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma aldolase is required for metabolism but dispensable for host-cell invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3567–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, N.; Pandey, V.C.; Dutta, G.P.; Ghatak, S. Levels of FDP-aldolase enzyme activity in Plasmodium knowlesi parasitized monkey erythrocytes. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1986, 24, 502–504. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, M.; Diab, T.; Hammam, O.; Karim, A.; Medhat, A.; Khela, M.; El-Dabaa, E. Protective and Anti-Pathology Effects of Sm Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase-Based DNA Vaccine against Schistosoma mansoni by Changing Route of Injection. Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, C.; Tong, M.; Zhang, P.; Cai, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, M. Molecular Characterization of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate Aldolase From Trichinella spiralis and Its Potential in Inducing Immune Protection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzatto, K.R.; Monteiro, K.M.; Paredes, R.; Paludo, G.P.; da Fonsêca, M.M.; Galanti, N.; Zaha, A.; Ferreira, H. Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and enolase from Echinococcus granulosus: Genes, expression patterns and protein interactions of two potential moonlighting proteins. Gene 2012, 506, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, T.; Zhu, S.; Dong, H.; Ming, Z. Protein extract from head-foot tissue of Oncomelania hupensis promotes the growth and development of mother sporocysts of Schistosoma japonicum via upregulation of parasite aldolase gene. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Mao, L.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Hou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, X. Identification and molecular characterization of exosome-like vesicles derived from the Taenia asiatica adult worm. Acta Trop. 2019, 198, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, S.A.; Martin, S.R.; Howell, S.A.; Grainger, M.; Moon, R.W.; Green, J.L.; Holder, A.A. The Binding of Plasmodium falciparum Adhesins and Erythrocyte Invasion Proteins to Aldolase Is Enhanced by Phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, L.; Hopp, C.S.; Muthinja, J.M.; Frischknecht, F.; Bosch, J.; Muthmja, J.M. Discovery of Plasmodium (M)TRAP–Aldolase Interaction Stabilizers Interfering with Sporozoite Motility and Invasion. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odongo, S.; Sterckx, Y.G.J.; Stijlemans, B.; Pillay, D.; Baltz, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Magez, S. An Anti-proteome Nanobody Library Approach Yields a Specific Immunoassay for Trypanosoma congolense Diagnosis Targeting Glycosomal Aldolase. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Xie, H.; Zhu, S.; Liao, D.; Zhan, T.; Liu, D. Cloning, expression, and partial characterization of FBPA from Schistosoma japonicum, a molecule on that the fluke may develop nutrition competition and immune evasion from human. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, R.G.; Hurdayal, R.; Choveaux, D.; Przyborski, J.M.; Coetzer, T.; Goldring, J.D. Plasmodium glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: A potential malaria diagnostic target. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 179, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Su, M.; Guo, A.; Ding, J.; Yang, J.; Xiang, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, S.; Ayaz, M.; et al. Regulatory effects of Echinococcus multilocularis extracellular vesicles on RAW264.7 macrophages. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 235, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.S.; Song, I.-S.; Shin, T.H.; Chung, S.-J.; Shim, C.-K.; Song, S.; Chung, Y.B. Kinetic analysis about the bidirectional transport of 1-anilino-8-naphthalene sulfonate (ANS) by isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2003, 26, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yan, M.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, N.; Gu, X.; Xie, Y.; Lai, W.; Jing, B.; et al. Molecular characterization of triosephosphate isomerase from Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmann, B.; Spiliotis, M.; Müller, J.; Scholl, S.; Müller, N.; Gottstein, B.; Hemphill, A. Echinococcus multilocularis phosphoglucose isomerase (EmPGI): A glycolytic enzyme involved in metacestode growth and parasite–host cell interactions. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanstra, J.R.; Kerkhoven, E.J.; van Tuijl, A.; Blits, M.; Wurst, M.; van Nuland, R.; Albert, M.-A.; Michels, P.A.M.; Bouwman, J.; Clayton, C.; et al. A domino effect in drug action: From metabolic assault towards parasite differentiation. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 79, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanstra, J.R.; Gerding, A.; Dolga, A.M.; Sorgdrager, F.; Buist-Homan, M.; Du Toit, F.; Faber, K.N.; Holzhütter, H.-G.; Szoor, B.; Matthews, K.R.; et al. Targeting pathogen metabolism without collateral damage to the host. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voronin, D.; Schnall, E.; Grote, A.; Jawahar, S.; Ali, W.; Unnasch, T.R.; Ghedin, E.; Lustigman, S. Pyruvate produced by Brugia spp. via glycolysis is essential for maintaining the mutualistic association between the parasite and its endosymbiont, Wolbachia. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008085. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, C. Gluconeogenesis in Cancer: Function and Regulation of PEPCK, FBPase, and G6Pase. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.-C.; Yang, L.; Bi, H.; Ai, X. Genome-wide analysis of the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) gene family and functional characterization of FBA7 in tomato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 108, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, T.J.; Sibley, L.D. Aldolase forms a bridge between cell surface adhesins and the actin cytoskeleton in apicomplexan parasites. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, Y.-K.; Ueno, A.; Terkawi, M.A.; Aboge, G.O.; Junya, Y.; Igarashi, M.; Kim, J.-Y.; Hong, Y.-C.; Chung, D.-I.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Actin polymerization mediated by Babesia gibsoni aldolase is required for parasite invasion. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bian, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Xie, Z.; Sun, H.; Jia, F.; Liang, P.; Zhou, C.; He, L.; et al. Molecular and biochemical characterizations of three fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases from Clonorchis sinensis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 194, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, C.M.; Elissondo, M.C.; Cumino, A.C.; Chisari, A.; Denegri, G.M. Primary cell culture of Echinococcus granulosus developed from the cystic germinal layer: Biological and functional characterization. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompipak, J.; Senawong, T.; Jokchaiyaphum, K.; Siriwes, K.; Nuchadomrong, S.; Laha, T.; Sripa, B.; Senawong, G. Characterization and localization of Opisthorchis viverrini fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 66, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, S.A.; Martin, S.R.; Grainger, M.; Howell, S.A.; Green, J.L.; Holder, A.A. Plasmodium falciparum aldolase and the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of certain apical organellar proteins promote actin polymerization. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 197, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Lan, T.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Kandil, O.M.; Ayaz, M.; Luo, X.; Song, H.; et al. Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase 1 of Echinococcus multilocularis. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9010004
He X, Zhang J, Sun Y, Lan T, Guo X, Wang X, Kandil OM, Ayaz M, Luo X, Song H, et al. Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase 1 of Echinococcus multilocularis. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xuedong, Jing Zhang, Yue Sun, Tianyan Lan, Xiaola Guo, Xiaoqiang Wang, Omnia M. Kandil, Mazhar Ayaz, Xuenong Luo, Houhui Song, and et al. 2022. "Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase 1 of Echinococcus multilocularis" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9010004
APA StyleHe, X., Zhang, J., Sun, Y., Lan, T., Guo, X., Wang, X., Kandil, O. M., Ayaz, M., Luo, X., Song, H., & Zheng, Y. (2022). Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase 1 of Echinococcus multilocularis. Veterinary Sciences, 9(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9010004





