Dural Changes Induced by an Ultrasonic Bone Curette in an Excised Porcine Spinal Cord
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
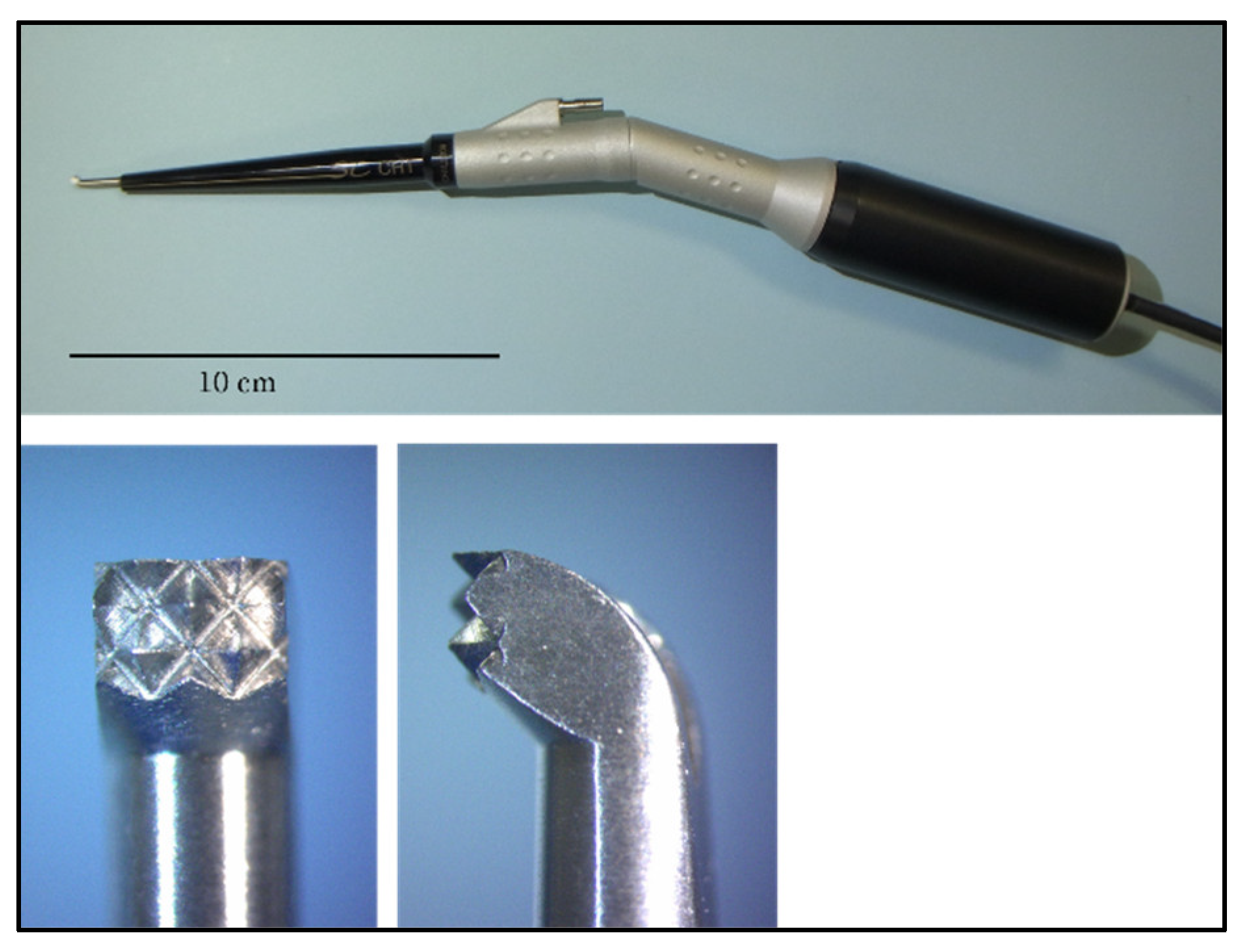
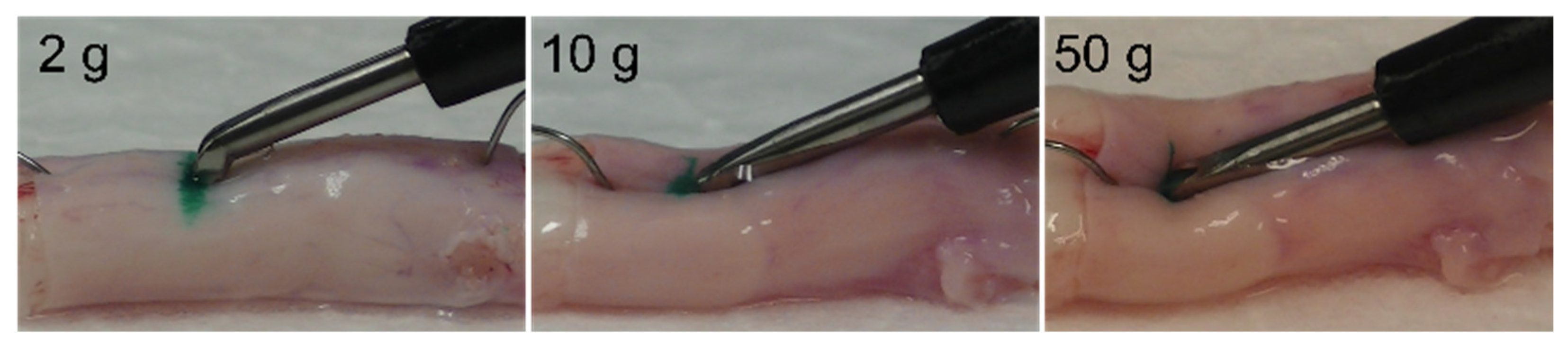
2.1. Experiment 1
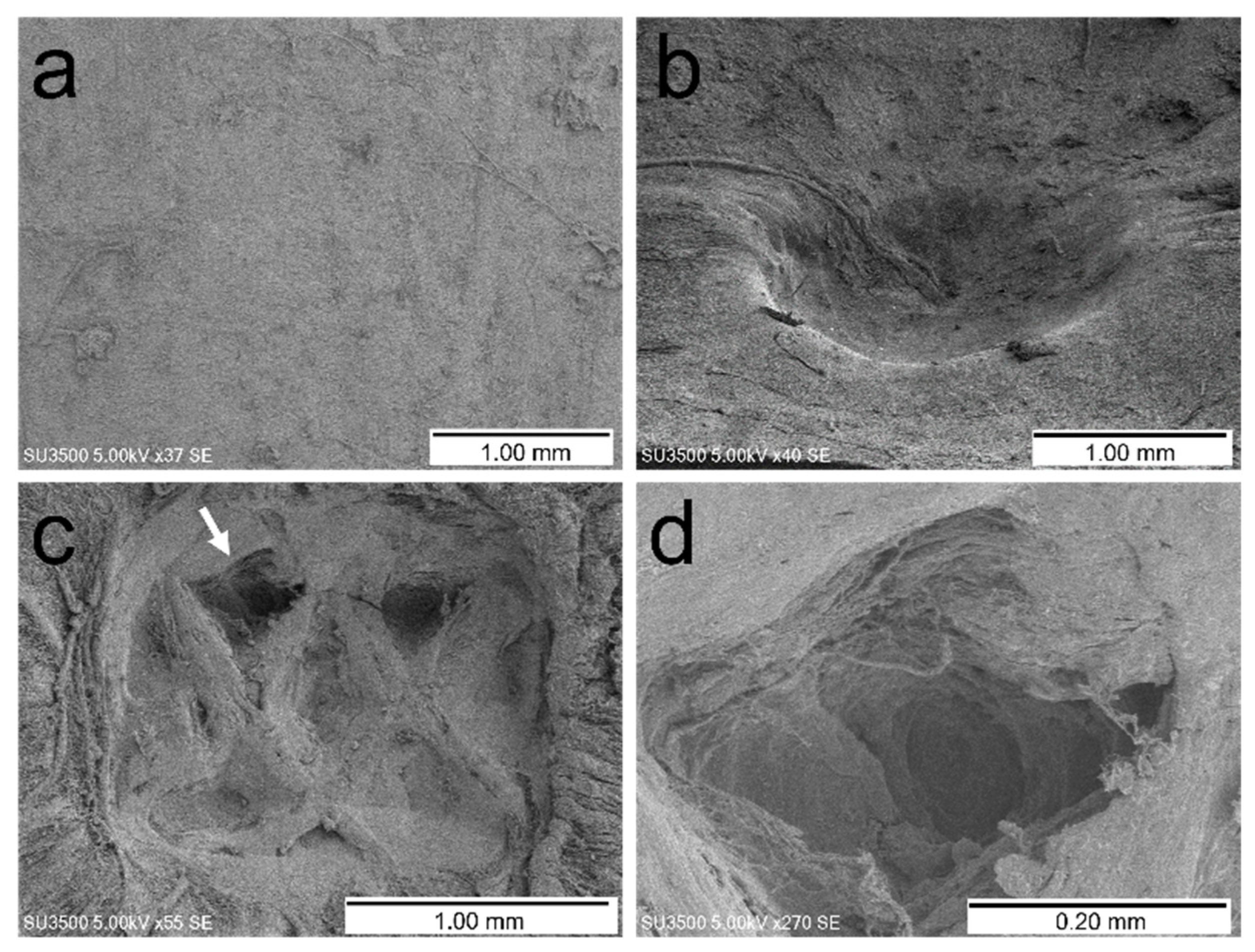
2.2. Evaluation Using a Scanning Electron Microscope and Stereomicroscope
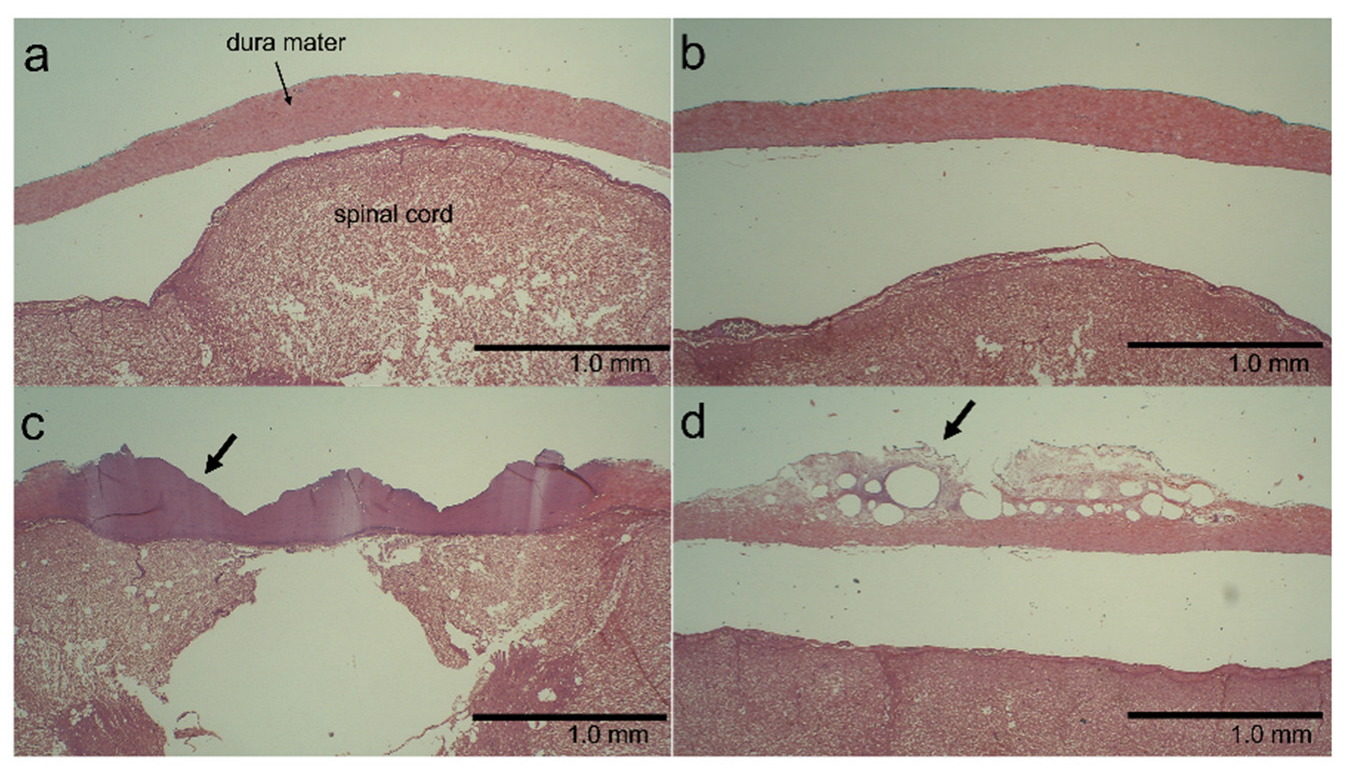
2.3. Histological Examination
2.4. Experiment 2
2.5. Untreated Specimens
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the Spinal Cord When Pressed by the Ultrasonic Bone Curette
3.2. Dural Changes Induced by Ultrasonic Vibration
3.3. Dural Changes When the Spinal Cord Is Pressed without Ultrasonic Vibration
3.4. Histological Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moon, R.D.C.; Srikandarajah, N.; Clark, S.; Wilby, M.J.; Pigott, T.D. Primary lumbar decompression using ultrasonic bone curette compared to conventional technique. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 35, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, D.; Spadola, M.; Berger, C.; Glauser, G.; Mahmoud, A.F.; O’Malley, B.; Malhotra, N.R. Novel approach using ultrasonic bone curettage and transoral robotic surgery for en bloc resection of cervical spine chordoma: Case report. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 30, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Xu, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Qi, M.; Shen, X.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Ultrasonic Bone Curette-assisted Dome-like Laminoplasty in the Treatment of Cervical Ossification of Longitudinal Ligament. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Uchikado, H.; Kim, S.D.; Mahadewa, T.; Inoue, T.; Mizuno, J. Ultrasonic bone curettes in spinal surgery. Int. Congr. Ser. 2004, 1259, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastelli, M.M., Jr.; Pinheiro-Neto, C.D.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Wang, E.W.; Snyderman, C.H.; Gardner, P.A. Application of ultrasonic bone curette in endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: Technical note. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2014, 75, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadeishi, H.; Suzuki, A.; Yasui, N.; Satou, Y. Anterior clinoidectomy and opening of the internal auditory canal using an ultrasonic bone curette. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Marukawa, K.; Shimada, M.; Yamamoto, E. Use of the Sonopet ultrasonic curettage device in intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzino-Demo, P.; Boffano, P.; Tanteri, G.; Gerbino, G. The use of an ultrasonic bone curette in the surgery of jaw tumors involving the inferior alveolar nerve. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, e100–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wladis, E.J. Ultrasonic instruments in orbital surgery: A major review. Orbit 2022, 41, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toombs, J.P.; Bauer, M.S. Intervertebral disc disease. In Textbook of Small Animal Surgery, 2nd ed.; Slatter, D., Ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 1070–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, S.R.; de Costa, R. Crevical vertebral Column and Spinal Cord. In Veterinary Surgery: Small Animal Expert Consult, 2nd ed.; Johnston, S.A., Tobias, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 438–485. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, C.W.; Fossum, T.W. Thoracolumbar Spine. In Small Animal Surgery, 5th ed.; Fossum, T.W., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1404–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Crovace, A.M.; Luzzi, S.; Lacitignola, L.; Fatone, G.; Lucifero, A.G.; Vercellotti, T.; Crovace, A. Minimal invasive piezoelectric osteotomy in neurosurgery: Technic, applications, and clinical outcomes of a retrospective case series. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, S. Effect of Ultrasonic Osteotome on Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Spinal Surgery: A System Review and Meta-Analysis. Comput. Math Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 9548142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Kim, S.D.; Mizuno, J.; Ohara, Y.; Ito, K. Technical advantages of an ultrasonic bone curette in spinal surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2005, 2, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bydon, M.; Macki, M.; Xu, R.; Ain, M.C.; Ahn, E.S.; Jallo, G.I. Spinal decompression in achondroplastic patients using high-speed drill versus ultrasonic bone curette: Technical note and outcomes in 30 cases. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2014, 34, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onen, M.R.; Yuvruk, E.; Akay, S.; Naderi, S. The reliability of the ultrasonic bone scalpel in cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A comparative study of 46 patients. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazer, D.B.; Yaşar, B.; Rosberg, H.E.; Akbaş, A. Technical aspects on the use of ultrasonic bone shaver in spine surgery: Experience in 307 patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8428530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Luo, D.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J. Safety and efficacy of cervical laminoplasty using a piezosurgery device compared with a high-speed drill. Medicine 2016, 95, e4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, Z.; Yu, X.; Song, R.; Huang, W. Use of ultrasonic device in cervical and thoracic laminectomy: A retrospective comparative study and technical note. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Ishizaka, S.; Sasaki, T.; Miyahara, T.; Horiuchi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Shigeta, H.; Hongo, K. Safe and minimally invasive laminoplastic laminotomy using an ultrasonic bone curette for spinal surgery: Technical note. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Isu, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Isobe, M.; Kogure, K. Surgical pitfalls of an ultrasonic bone curette (SONOPET) in spinal surgery. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, ONS390–ONS393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bydon, M.; Xu, R.; Papademetriou, K.; Sciubba, D.M.; Wolinsky, J.P.; Witham, T.F.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Jallo, G.; Bydon, A. Safety of spinal decompression using an ultrasonic bone curette compared with a high-speed drill: Outcomes in 337 patients. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 18, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ohnmeiss, D.; Lieberman, I.H. Use of an ultrasonic osteotome device in spine surgery: Experience from the first 128 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 2845–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahfoudh, R.; Qattan, E.; Ellenbogen, J.R.; Wilby, M.; Barrett, C.; Pigott, T. Applications of the ultrasonic bone cutter in spinal surgery--our preliminary experience. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 28, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshettry, V.R.; Jiang, X.; Chotai, S.; Ammirati, M. Optic nerve surface temperature during intradural anterior clinoidectomy: A comparison between high-speed diamond burr and ultrasonic bone curette. Neurosurg. Rev. 2014, 37, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Wanibuchi, M.; Minamida, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Mikami, T.; Fujishige, M.; Yamamura, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Mikuni, N. Heat generation by ultrasonic bone curette comparing with high-speed drill. Acta Neurochir 2018, 160, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.R.; Gruener, A.M.; Kum, C.; McCulley, T.J. Temperature changes associated with bone drilling in an orbital model: Comparison of ultrasonic bone curette and conventional high-speed rotational drill. Orbit 2019, 38, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, C.; Goldberg, R.A.; Rubino, G. Unilateral blindness after ipsilateral prophylactic transcranial optic canal decompression for fibrous dysplasia. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 126, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, N.; Miwa, T.; Mukai, Y.; Takenaka, S.; Makino, T.; Fuji, T. Potential risk of thermal damage to cervical nerve roots by a high-speed drill. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2009, 91, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambay, B.S.; Walmsley, A.D. Investigations into the use of an ultrasonic chisel to cut bone. Part 1: Forces applied by clinicians. J. Dent. 2000, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mae, T.; Nakata, K.; Kumai, T.; Ishibashi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Ohori, T.; Hirose, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Characteristics of ultrasound device: A new technology for bone curettage and excavation. J. Exp. Orthop. 2019, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Henmi, A.; Takahashi, T.; Sasano, Y. Experimental comparison of the performance of cutting bone and soft tissue between piezosurgery and conventional rotary instruments. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsuna, F.; Harata, S.; Yoshimura, N. Influence of the ultrasonic surgical aspirator on the dura and spinal cord. An electrohistologic study. Spine 1991, 16, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, S.; Okada, Y.; Iseki, H.; Hori, T.; Takakura, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Nagata, H. Thermological study of drilling bone tissue with a high-speed drill. Neurosurgery 2000, 46, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Scale Display (g) | Spinal Dural Covering | n | No. of Specimens with Dural Changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration | Dural Indentation (Depressions or Blade Marks) | Discoloration | |||
| 2 | No covering | 4 | 0 (0) | 3 (75) | 1 (25) |
| Cotton covering | 4 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| 10 | No covering | 4 | 0 (0) | 4 (100) | 4 (100) |
| Cotton covering | 4 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) * | 0 (0) * | |
| 50 | No covering | 4 | 0 (0) | 4 (100) | 4 (100) |
| Cotton covering | 4 | 0 (0) | 4 (100) § | 4 (100) § | |
| Scale Display (g) | Spinal Dural Covering | n | No. of Specimens with Dural Changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration | Dural Indentation (Depressions or Blade Marks) | Discoloration | |||
| 2 | No covering | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Cotton covering | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| 10 | No covering | 3 | 0 (0) | 3 (100) * | 0 (0) |
| Cotton covering | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| 50 | No covering | 3 | 0 (0) | 3 (100) * | 0 (0) |
| Cotton covering | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ota, R.; Iwaki, E.; Sakai, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Sekiguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Naganobu, K. Dural Changes Induced by an Ultrasonic Bone Curette in an Excised Porcine Spinal Cord. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110601
Ota R, Iwaki E, Sakai K, Haraguchi T, Kaneko Y, Sekiguchi S, Yamaguchi R, Naganobu K. Dural Changes Induced by an Ultrasonic Bone Curette in an Excised Porcine Spinal Cord. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(11):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110601
Chicago/Turabian StyleOta, Rizou, Eri Iwaki, Kentaro Sakai, Tomohiro Haraguchi, Yasuyuki Kaneko, Satoshi Sekiguchi, Ryoji Yamaguchi, and Kiyokazu Naganobu. 2022. "Dural Changes Induced by an Ultrasonic Bone Curette in an Excised Porcine Spinal Cord" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 11: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110601
APA StyleOta, R., Iwaki, E., Sakai, K., Haraguchi, T., Kaneko, Y., Sekiguchi, S., Yamaguchi, R., & Naganobu, K. (2022). Dural Changes Induced by an Ultrasonic Bone Curette in an Excised Porcine Spinal Cord. Veterinary Sciences, 9(11), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110601






