Influence of Gallic Acid-Containing Mouth Spray on Dental Health and Oral Microbiota of Healthy Cats—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Mouth Spray
2.2. Study Population and Design
2.3. Gingival Index (GI) and Plaque Index (PI)
2.4. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Gingival Index (GI) and Plaque Index (PI)
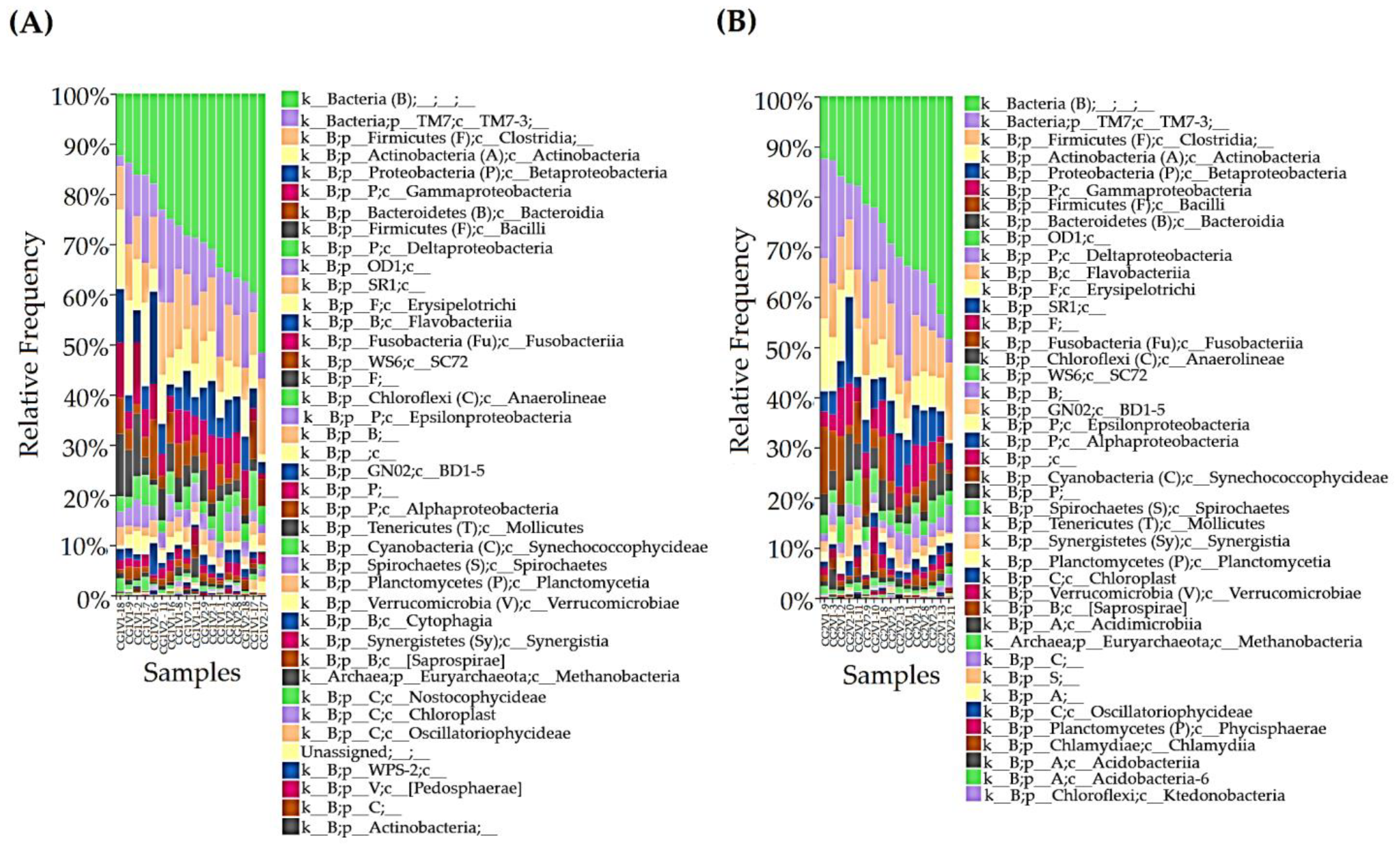
3.2. Oral Microbiome Analysis
3.2.1. Taxonomy Assignment
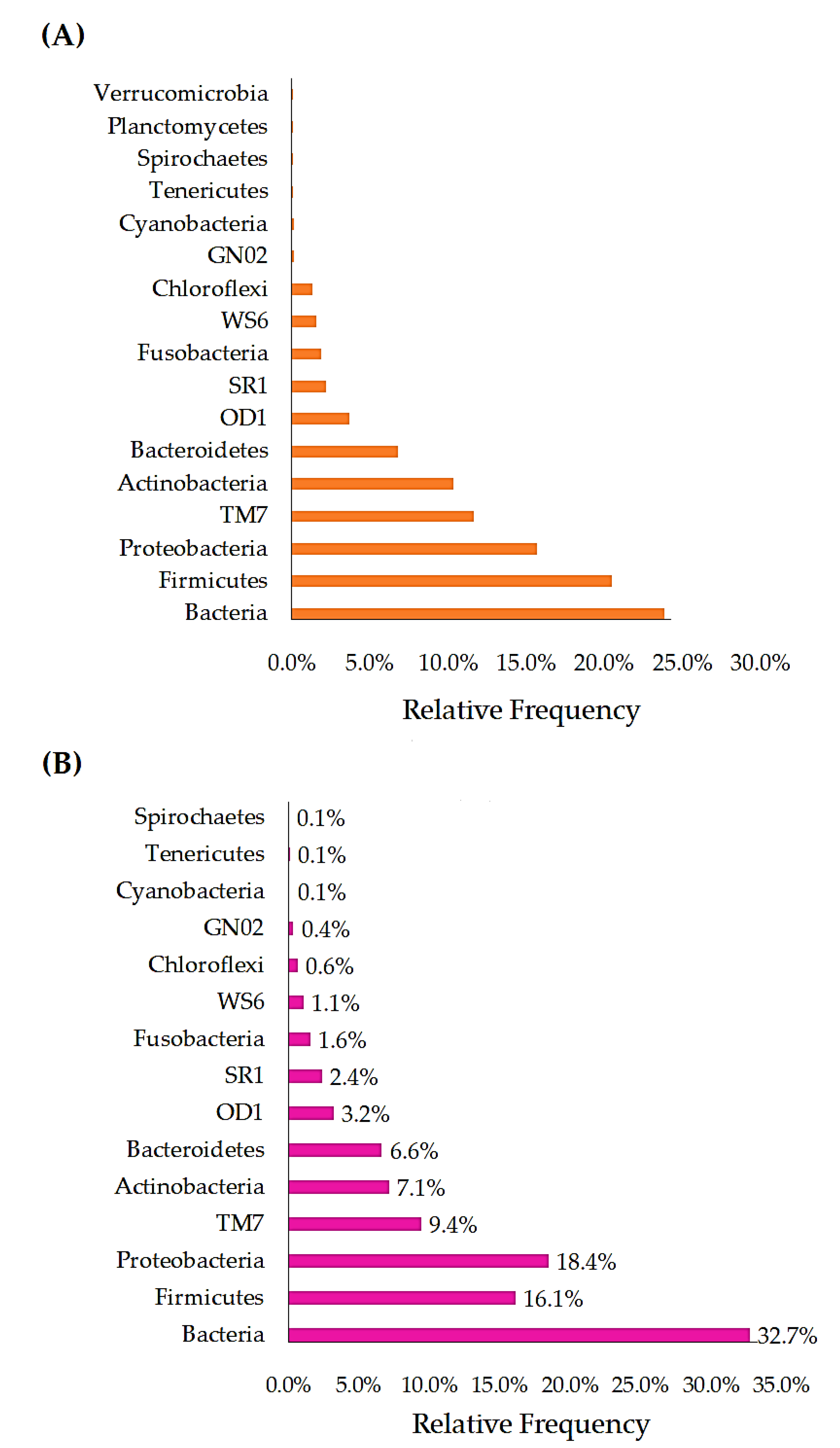
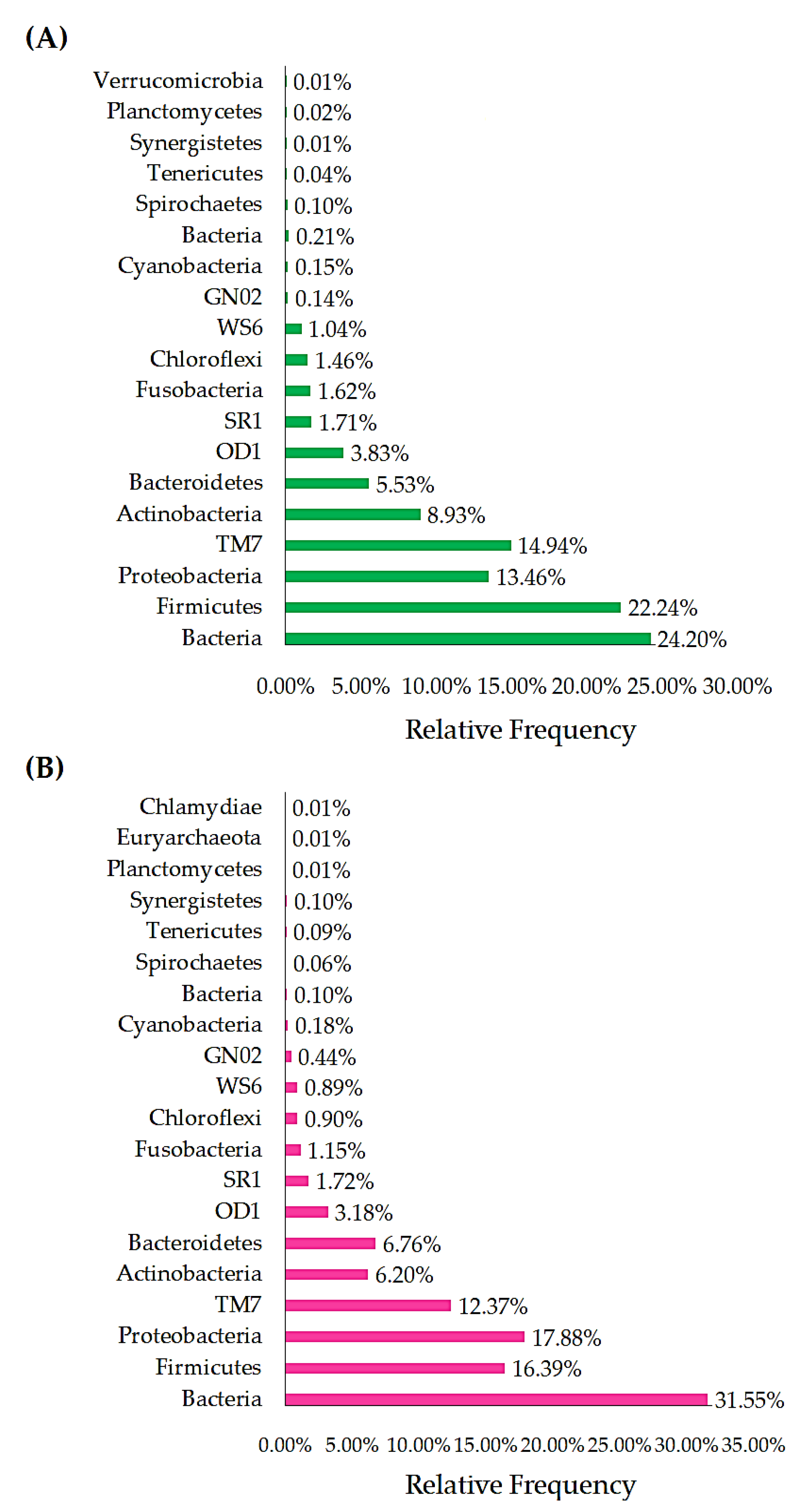
3.2.2. Phylum
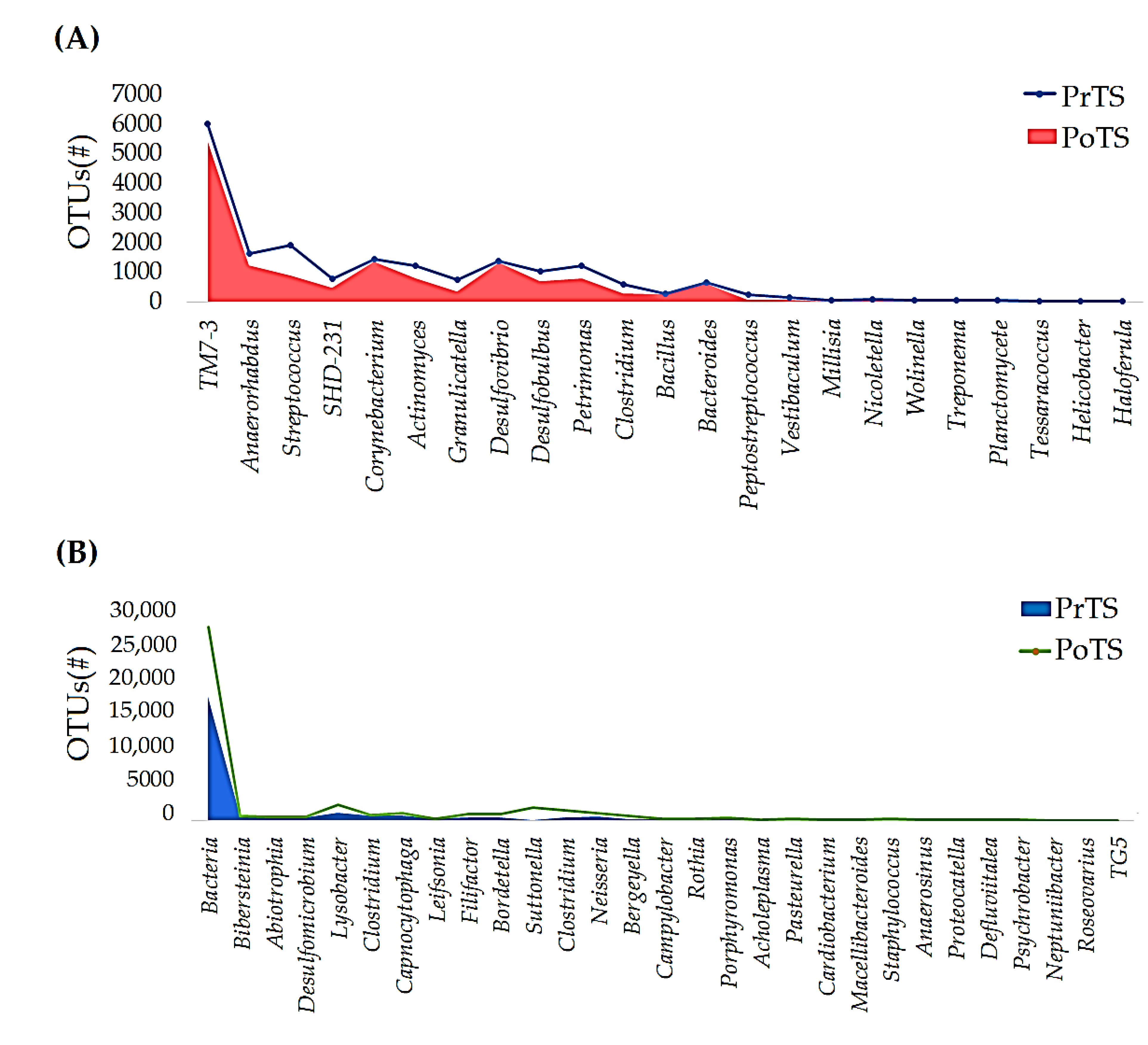
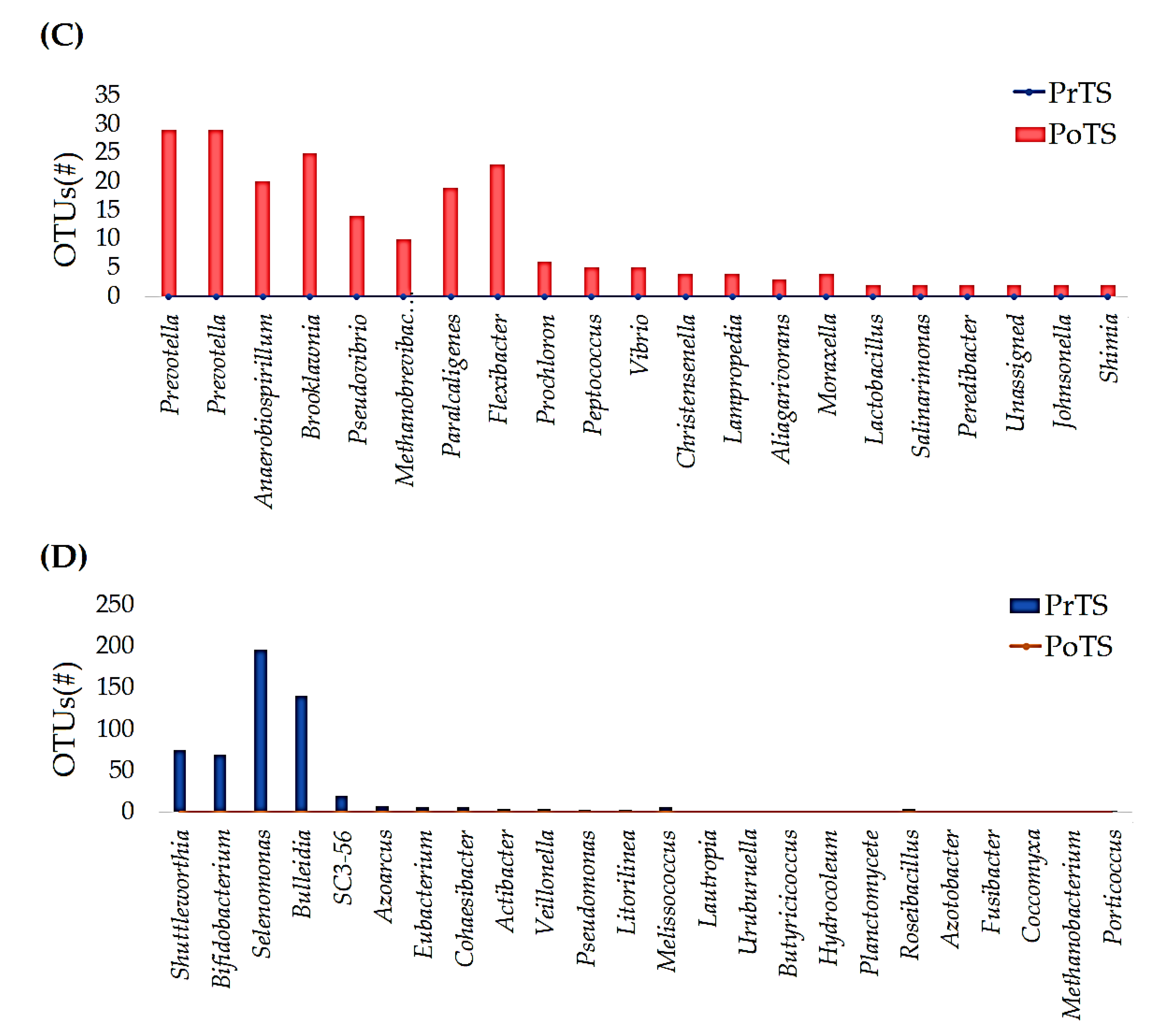
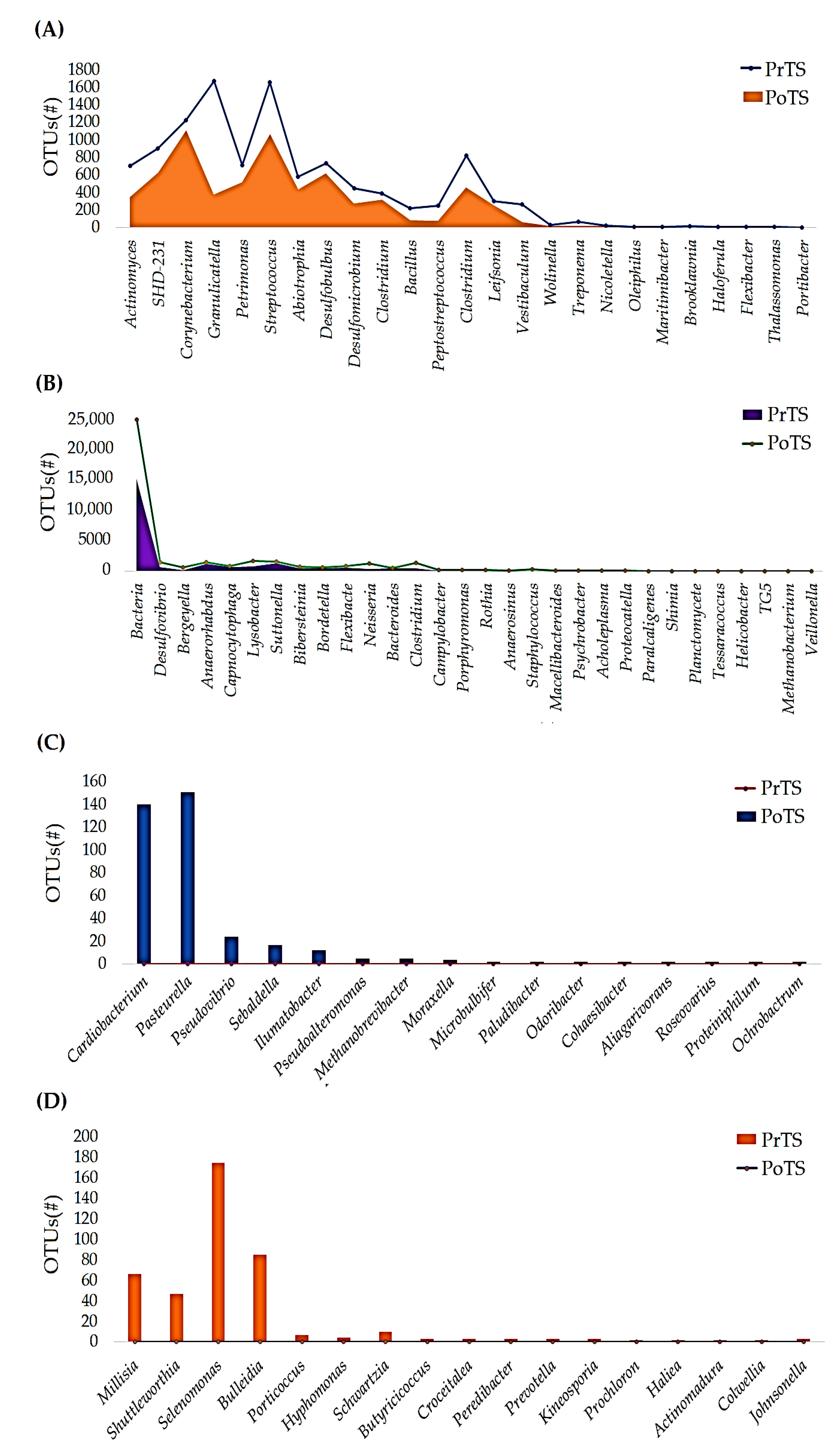
3.2.3. Genus
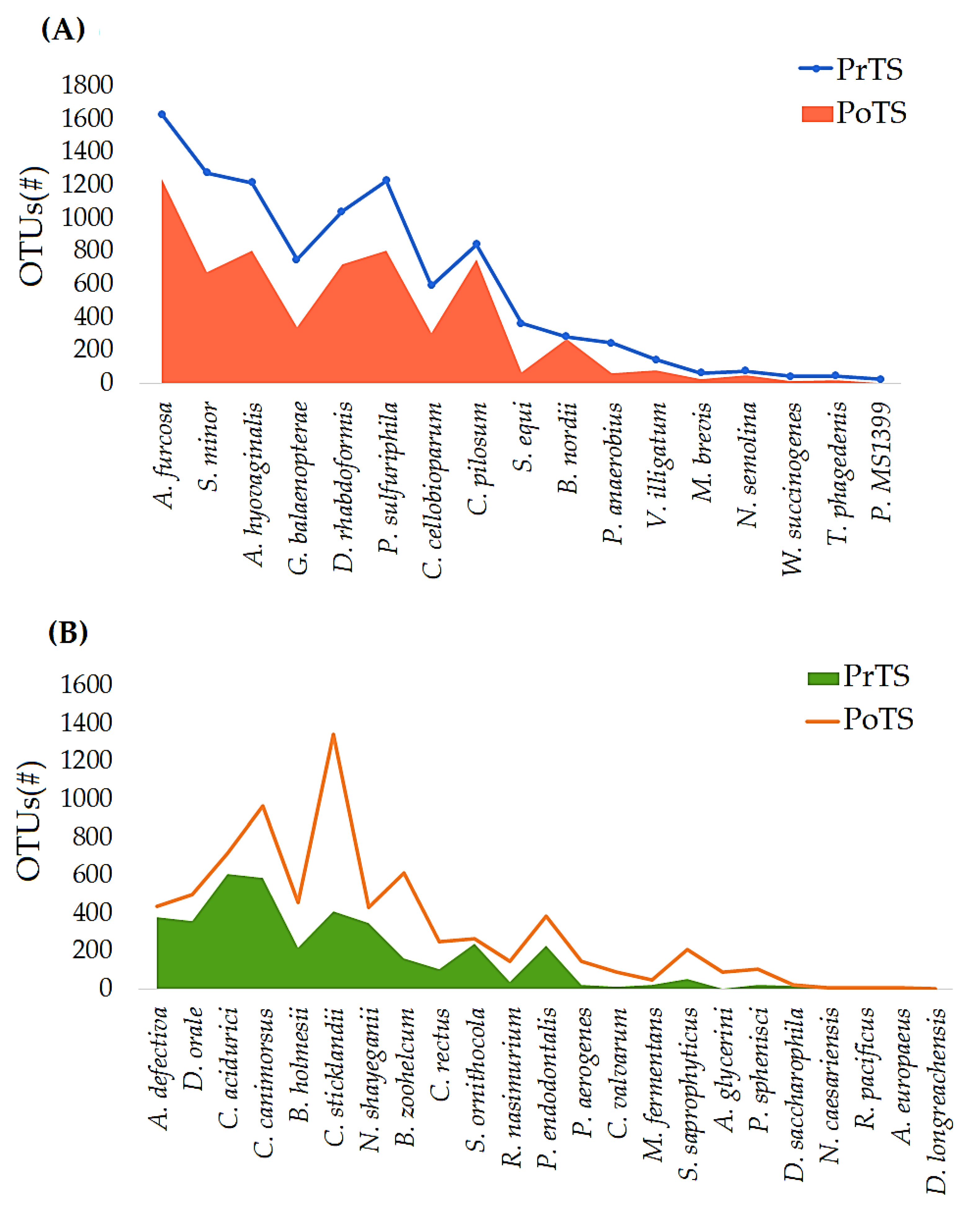
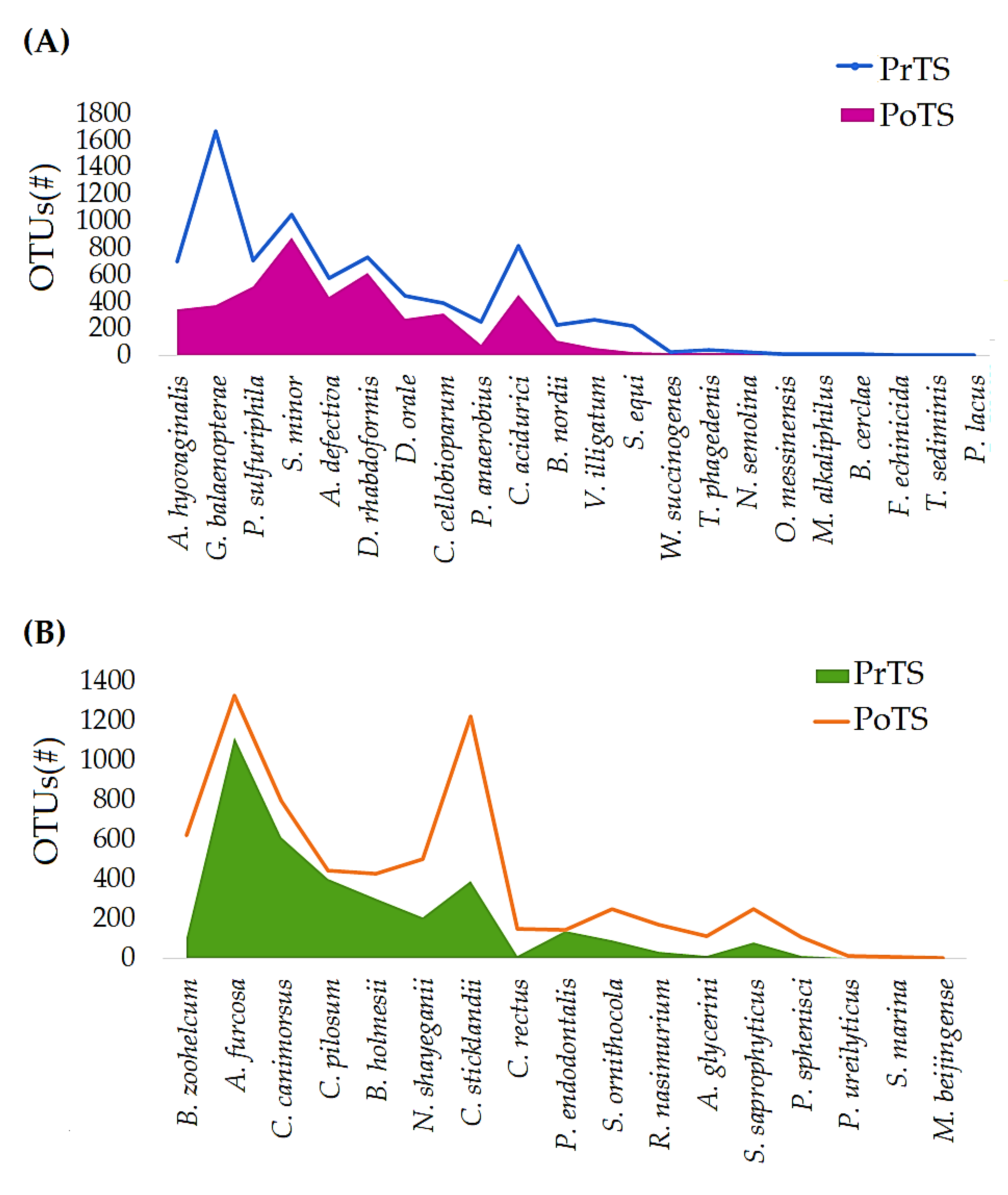
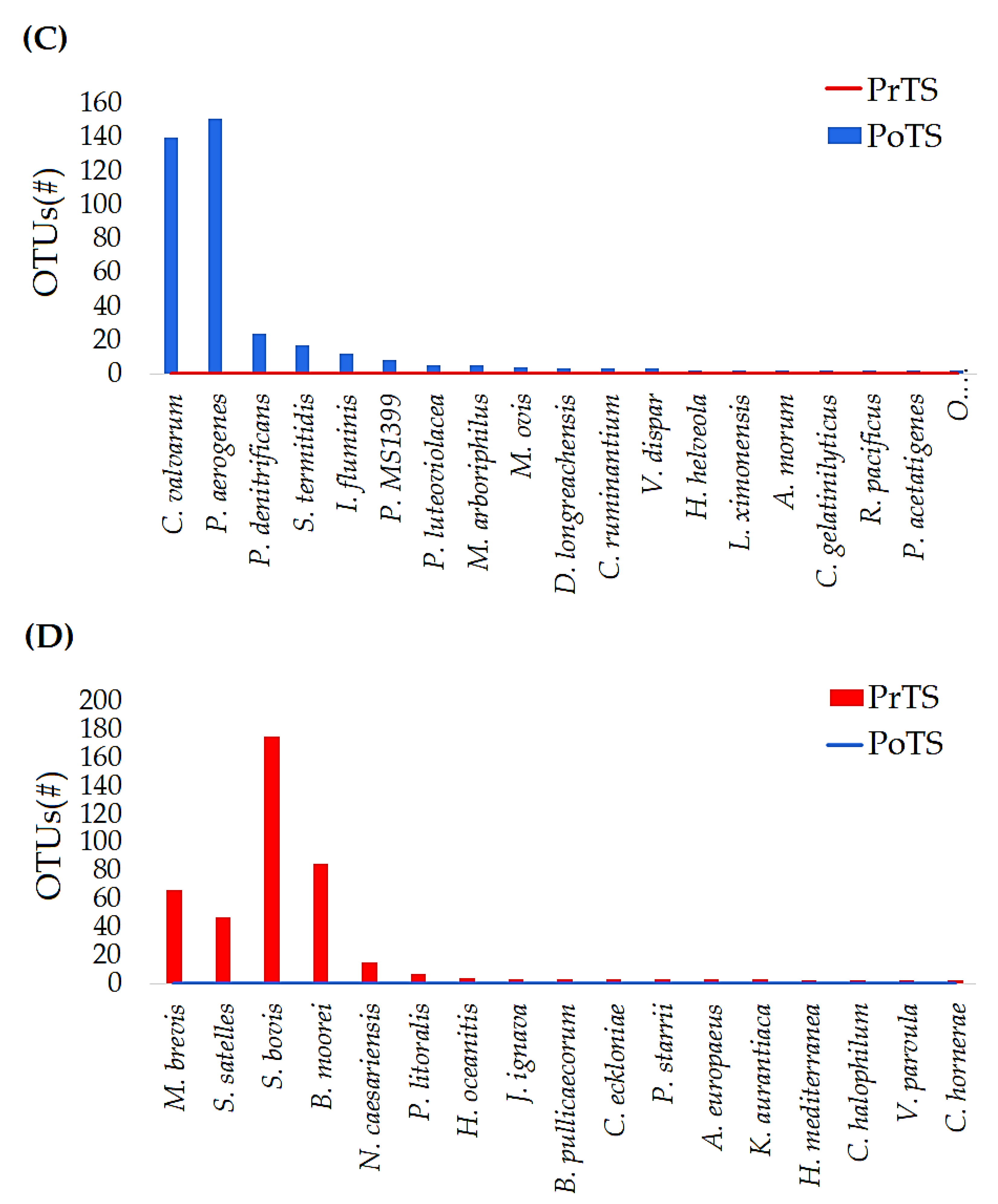
3.2.4. Species
3.3. Refraction Curve Analysis
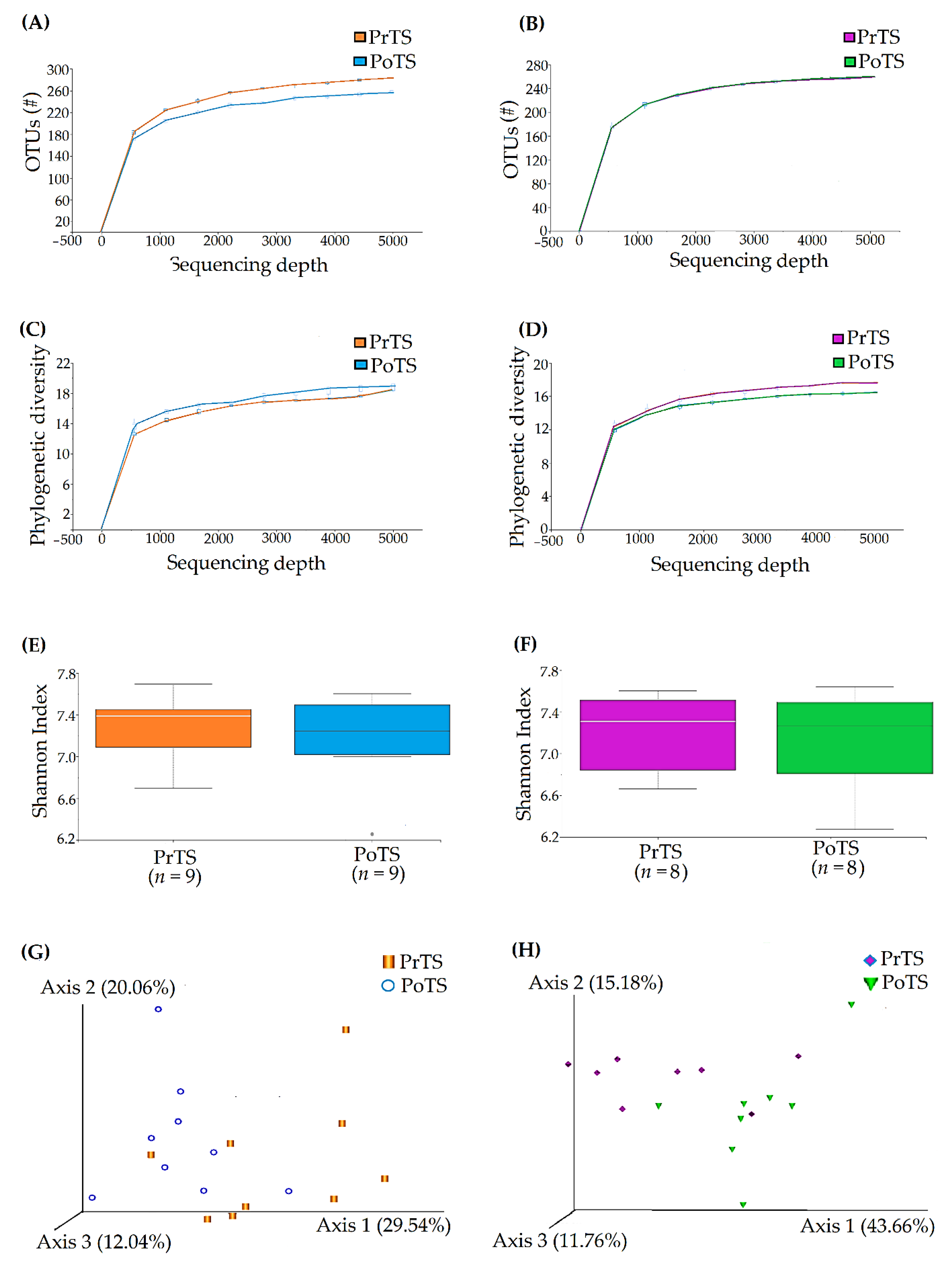
3.3.1. OTUs
3.3.2. Phylogenetic Diversity
3.3.3. Species Richness
3.3.4. Principal Co-ordinates Analysis (PCoA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sedghi, L.; DiMassa, V.; Harrington, A.; Lynch, S.V.; Kapila, Y.L. The oral microbiome: Role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandri, G.; Argentini, C.; Milani, C.; Turroni, F.; Cristina Ossiprandi, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Catching a glimpse of the bacterial gut community of companion animals: A canine and feline perspective. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1708–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskarsson, K.; Puurtinen, A.L.; Penell, J.C. Dental problems and prophylactic care in cats-knowledge and perceptions among Swedish cat owners and communication by veterinary care staff. Animals 2021, 11, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.X.; Fiani, N.; Bicalho, R.C.; Peralta, S. Preliminary functional analysis of the subgingival microbiota of cats with periodontitis and feline chronic gingivostomatitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.; Tutt, C. Periodontal disease in cats: Back to basics--with an eye on the future. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015, 17, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thengchaisri, N.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Sattasathuchana, P. Association of gingivitis with dental calculus thickness or dental calculus coverage and subgingival bacteria in feline leukemia virus- and feline immunodeficiency virus-negative cats. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 81, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.B.; Verstraete, F.J.M.; Arzi, B. An Update on Feline Chronic Gingivostomatitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small. Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, K.E.; Gorrel, C.; Bierer, T.L. Effect of a dental chew on dental substrates and gingivitis in cats. J. Vet. Dent. 2002, 19, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.E. Clinical and microbiological effects of oral zinc ascorbate gel in cats. J. Vet. Dent. 2001, 18, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, J.M.; Gorrel, C.; Markwell, P.J. Effect on canine oral health of adding chlorhexidine to a dental hygiene chew. J. Vet. Dent. 1998, 15, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Hou, Y.; Ai, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Gallic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.S.; Oh, J.S.; Kang, I.C.; Hong, S.J.; Choi, C.H. Inhibitory effect of methyl gallate and gallic acid on oral bacteria. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, O.; Gevrek, F. 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic Acid Attenuates Ligature-Induced Periodontal Disease in Wistar Rats. Antiinflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 20, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, A.T.W. Epigallocatechin gallate and gallic acid affect colonization of abiotic surfaces by oral bacteria. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 120, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Croft, J.; O’Flynn, C.; Deusch, O.; Colyer, A.; Allsopp, J.; Milella, L.; Davis, I.J. A Pyrosequencing investigation of differences in the feline subgingival microbiota in health, gingivitis and mild periodontitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Klein, E.A.; Bennett, M.L.; Croft, J.M.; Harris, S.J.; Marshall-Jones, Z.V. The feline oral microbiome: A provisional 16S rRNA gene-based taxonomy with full-length reference sequences. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakanishi, H.; Furuya, M.; Soma, T.; Hayashiuchi, Y.; Yoshiuchi, R.; Matsubayashi, M.; Tani, H.; Sasai, K. Prevalence of microorganisms associated with feline gingivostomatitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbeck, J.A.; Reiter, A.M.; Pohl, J.C.; Tang, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Linde, A.; Prem, A.; Melgarejo, T. Characterization of oral microbiota in cats: Novel insights on the potential role of fungi in feline chronic gingivostomatitis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Bihan, M.; Yooseph, S.; Methe, B.A. Analyses of the microbial diversity across the human microbiome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.X.; Bicalho, R.C.; Fiani, N.; Lima, S.F.; Peralta, S. The subgingival microbial community of feline periodontitis and gingivostomatitis: Characterization and comparison between diseased and healthy cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolieslager, S.M.; Riggio, M.P.; Lennon, A.; Lappin, D.F.; Johnston, N.; Taylor, D.; Bennett, D. Identification of bacteria associated with feline chronic gingivostomatitis using culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stookey, G.K. Soft rawhide reduces calculus formation in dogs. J. Vet. Dent. 2009, 26, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, M.R. The modified Triadan system: Nomenclature for veterinary dentistry. J. Vet. Dent. 1991, 8, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennet, P.; Servet, E.; Salesse, H.; Soulard, Y. Evaluation of the Logan & Boyce plaque index for the study of dental plaque accumulation in dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 80, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Sirilun, S.; Juntarachot, N.; Tongpong, P.; Ouparee, W.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Peerajan, S.; Waditee-Sirisattha, R.; Prombutara, P.; Klankeo, P.; et al. Effect of dextranase and dextranase-and-nisin-containing mouthwashes on oral microbial community of healthy adults—A Pilot study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Klein, E.A.; Thompson, E.C.; Blanton, J.M.; Chen, T.; Milella, L.; Buckley, C.M.; Davis, I.J.; Bennett, M.L.; Marshall-Jones, Z.V. The canine oral microbiome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belland, R.; Ojcius, D.M.; Byrne, G.I.I. Focus: Chlamydia. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.Y.M.; Belland, R.J. The chlamydial developmental cycle. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 949–959. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschlag, M.R.; Kohlhoff, S.A.; Gaydos, C.A. Chlamydia pneumoniae. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 9th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, H.C.; Lee, C.; Cheok, Y.Y.; Tan, G.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F. Chlamydiaceae: Diseases in Primary Hosts and Zoonosis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liao, P.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Sindaye, D.; Xin, Z.; Tan, C.; Deng, J.; Yin, Y.; et al. Impact of gallic acid on gut health: Focus on the gut microbiome, immune response, and mechanisms of action. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 580208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Su, W.; Chen, H.; Barberán, A.; Zhao, H.; Yu, M.; Yu, L.; Brookes, P.C.; Schadt, C.W.; Chang, S.X.; et al. Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Turak, A.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Ao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Z. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Inputs on Soil Bacterial Abundance, Diversity, and Community Composition in Chinese Fir Plantations. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnheer, T.; Karygianni, L.; Flury, M.; Belibasakis, G.N. Fusobacterium species and subspecies differentially affect the composition and architecture of supra- and subgingival biofilms models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abusleme, L.; Dupuy, A.K.; Dutzan, N.; Silva, N.; Burleson, J.A.; Strausbaugh, L.D.; Gamonal, J.; Diaz, P.I. The subgingival microbiome in health and periodontitis and its relationship with community biomass and inflammation. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Carvalho, T.T.; Manchope, M.F.; Artero, N.A.; Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Fattori, V.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in pain and inflammation: Mechanisms of action, pre-clinical and clinical data, and pharmaceutical development. Molecules 2020, 25, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobo, F. Infections Caused by Anaerobic Microorganisms. In Encyclopedia of Infection and Immunity, 1st ed.; Rezaei, N., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 614–627. ISBN 9780323903035. [Google Scholar]
- Sogodogo, E.; Drancourt, M.; Grine, G. Methanogens as emerging pathogens in anaerobic abscesses. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda, C.; García-Márquez, S.; Santos, Y. Detection of Flexibacter maritimus in fish tissue using nested PCR amplification. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 26, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, A.M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van den Broeck, W.; Bossier, P.; Decostere, A. Columnaris disease in fish: A review with emphasis on bacterium-host interactions. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, M.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Cui, C.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L. 16S rDNA analysis of periodontal plaque in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and periodontitis patients. J. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 9, 1324725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduin, C.M.; Hol, C.; Fleer, A.; van Dijk, H.; van Belkum, A. Moraxella catarrhalis: From emerging to established pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oba, P.M.; Carroll, M.Q.; Alexander, C.; Valentine, H.; Somrak, A.J.; Keating, S.C.J.; Sage, A.M.; Swanson, K.S. Microbiota populations in supragingival plaque, subgingival plaque, and saliva habitats of adult dogs. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.J.; Facklam, R.R. Granulicatella and Abiotrophia species from human clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3520–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, W.L.; Wade, W.G.; Boden, R.; Kelly, D.P.; Wood, A.P. Facultative methylotrophs from the human oral cavity and methylotrophy in strains of Gordonia, Leifsonia, and Microbacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 2011, 193, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgeon, A.; Pinder, S.L.; Costa, M.C.; Weese, J.S. Characterization of the oral microbiota of healthy cats using next-generation sequencing. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, V.L.; Hinckley, L.; Gilbert, K.; Risatti, G.R.; Londoño, A.S.; Smyth, J.A. Actinomyces hyovaginalis-associated lymphadenitis in a Nubian goat. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2009, 21, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langendijk, P.S.; Kulik, E.M.; Sandmeier, H.; Meyer, J.; van der Hoeven, J.S. Isolation of Desulfomicrobium orale sp. nov. and Desulfovibrio strain NY682, oral sulfate-reducing bacteria involved in human periodontal disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payette, F.; Charlebois, A.; Fairbrother, J.H.; Beauchamp, G.; Leclere, M. Nicoletella semolina in the airways of healthy horses and horses with severe asthma. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographic | Control | Treatment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n; %) | 11 (55) | 7 (35) | 0.341 * |
| Female (n; %) | 9 (45) | 13 (65) | |
| Weight (Kg; Mean ± SD) | 4.46 ± 1.07 | 4.23 ± 1.00 | 0.285 ** |
| Age (Year; Mean ± SD) | 5.00 ± 1.67 | 4.64 ± 1.68 | 0.622 ** |
| Para-Meters | Tooth Code | Median (Interquartile Range: Q3–Q1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treatment | ||||||
| Pre (Day 0) | Post (Day 42) | Comparison * p-Value | Pre (Day 0) | Post (Day 42) | Comparison * p-Value | ||
| GI | 104 | 1 (2) | 0.5 (1) | 0.1255 | 0 (1) | 0 (1) | 0.2334 |
| 108 | 2 (0.5) | 1 (2) | 0.0053 (−) | 2 (1) | 0.5 (1) | 0.0003 (−) | |
| 204 | 0.5 (2) | 1 (1) | 0.8162 | 0 (2) | 0 (1) | 0.3223 | |
| 208 | 2 (0) | 1 (1) | 0.0539 | 2 (1) | 1 (2) | 0.0111 (−) | |
| 304 | 1 (2) | 0 (1) | 0.0843 | 0 (1) | 0 (0.5) | 0.0327 (−) | |
| 309 | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1.00 | 1 (2) | 0 (1.5) | 0.0122 (−) | |
| 404 | 1 (1.5) | 0 (1.5) | 0.4401 | 0 (1) | 0 (0) | 0.4705 | |
| 409 | 1 (1) | 1 (1.5) | 0.0766 | 1 (2) | 0 (1) | 0.0196 (−) | |
| PI | 104 | 1 (1.5) | 1.5 (1) | 0.0231 (+) | 1 (2) | 1 (1) | 0.0497 (−) |
| 108 | 2 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.7243 | 3 (1) | 1.5 (1.5) | 0.0154 (−) | |
| 204 | 1 (2) | 2 (2) | 0.0237 (+) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1) | 0.0084 (−) | |
| 208 | 2 (2) | 3 (1) | 0.1968 | 3 (1) | 3 (1) | 0.9319 | |
| 304 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.0155 (+) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0) | 0.0257 (−) | |
| 309 | 1 (2) | 2 (1) | 0.0699 (+) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1) | 0.0298 (−) | |
| 404 | 1 (1) | 1 (0.5) | 0.0004 (+) | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 0.3173 | |
| 409 | 1 (2) | 1 (1) | 0.251 (+) | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | 0.0375 (−) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaiyasut, C.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Bharathi, M.; Tansrisook, C.; Peerajan, S.; Chaiyasut, K.; Khongtan, S.; Tanongpitchayes, K.; Thongma, N.; Chawnan, N.; et al. Influence of Gallic Acid-Containing Mouth Spray on Dental Health and Oral Microbiota of Healthy Cats—A Pilot Study. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070313
Chaiyasut C, Sivamaruthi BS, Bharathi M, Tansrisook C, Peerajan S, Chaiyasut K, Khongtan S, Tanongpitchayes K, Thongma N, Chawnan N, et al. Influence of Gallic Acid-Containing Mouth Spray on Dental Health and Oral Microbiota of Healthy Cats—A Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(7):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070313
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaiyasut, Chaiyavat, Bhagavathi Sundaram Sivamaruthi, Muruganantham Bharathi, Chawin Tansrisook, Sartjin Peerajan, Khontaros Chaiyasut, Suchanat Khongtan, Kittidaj Tanongpitchayes, Nichaphat Thongma, Natcha Chawnan, and et al. 2022. "Influence of Gallic Acid-Containing Mouth Spray on Dental Health and Oral Microbiota of Healthy Cats—A Pilot Study" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 7: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070313
APA StyleChaiyasut, C., Sivamaruthi, B. S., Bharathi, M., Tansrisook, C., Peerajan, S., Chaiyasut, K., Khongtan, S., Tanongpitchayes, K., Thongma, N., Chawnan, N., & Thongkorn, K. (2022). Influence of Gallic Acid-Containing Mouth Spray on Dental Health and Oral Microbiota of Healthy Cats—A Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences, 9(7), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070313








