Longitudinal Study of Fecal Microbiota in Calves with or without Diarrhea Episodes before Weaning
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sampling, DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.3. Microbiota in Silico Analysis
3. Results
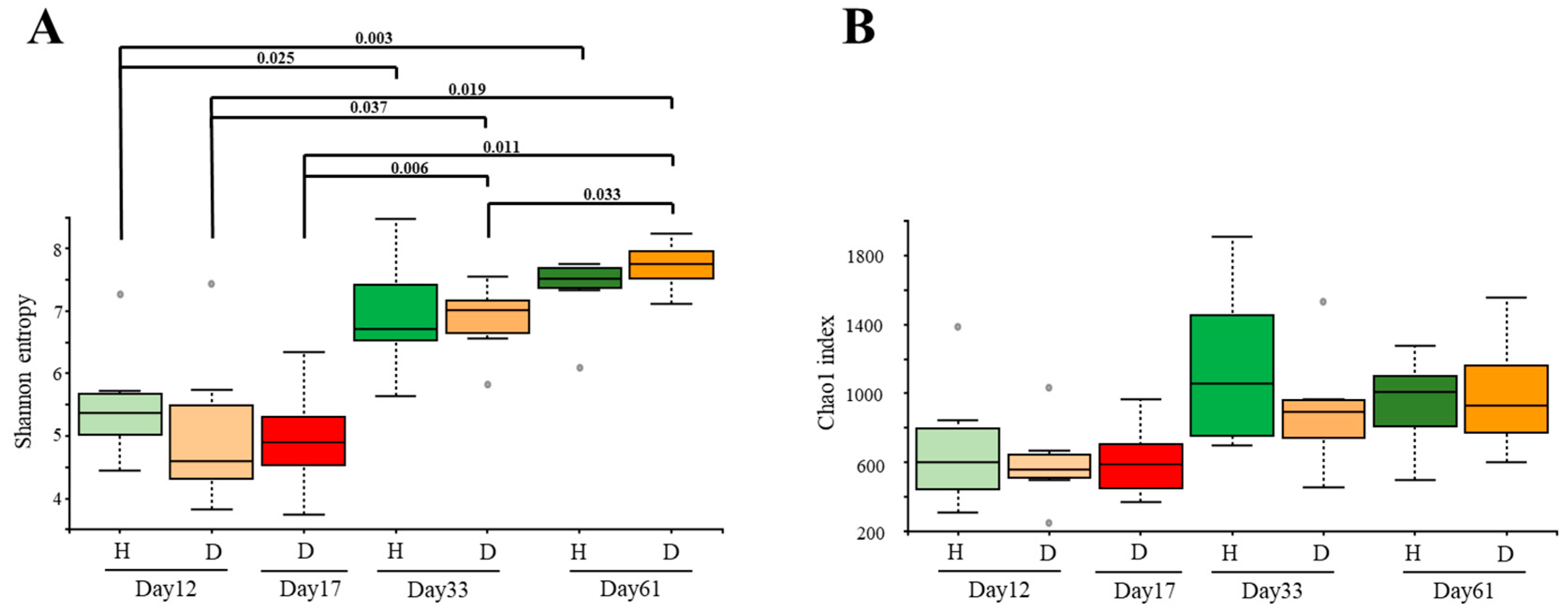
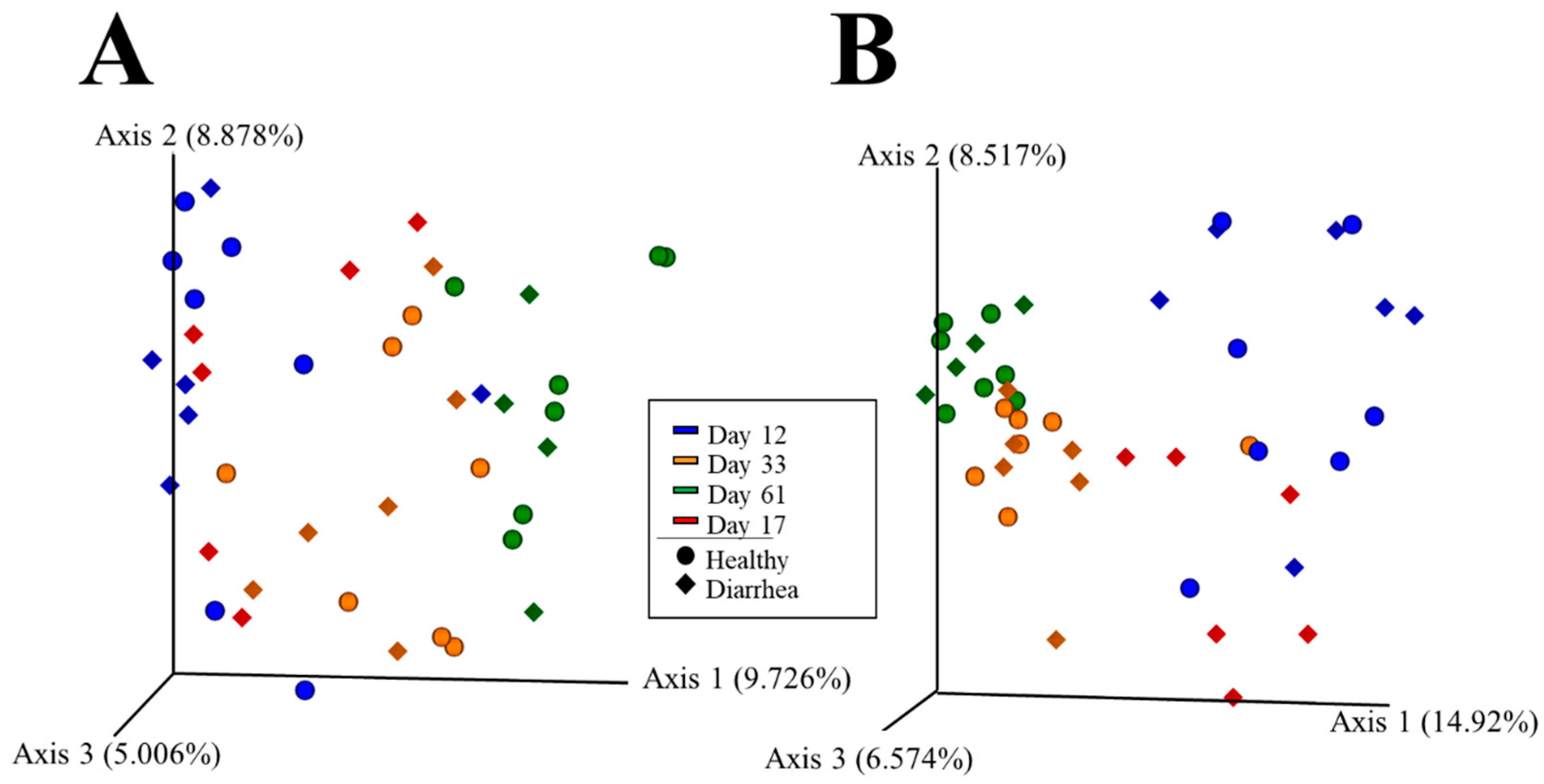
3.1. The Diversity of the Fecal Microbiota Changed through Time but Not according to Health Status
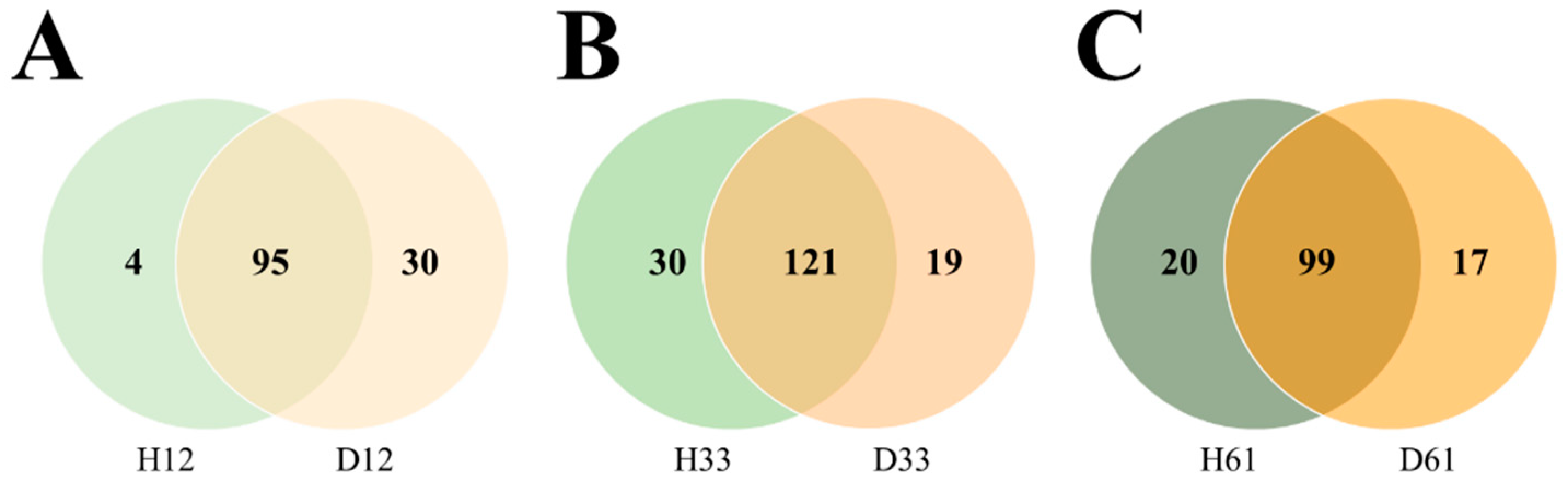
3.2. The Core Microbial Composition Was Different Depending on the Health Status
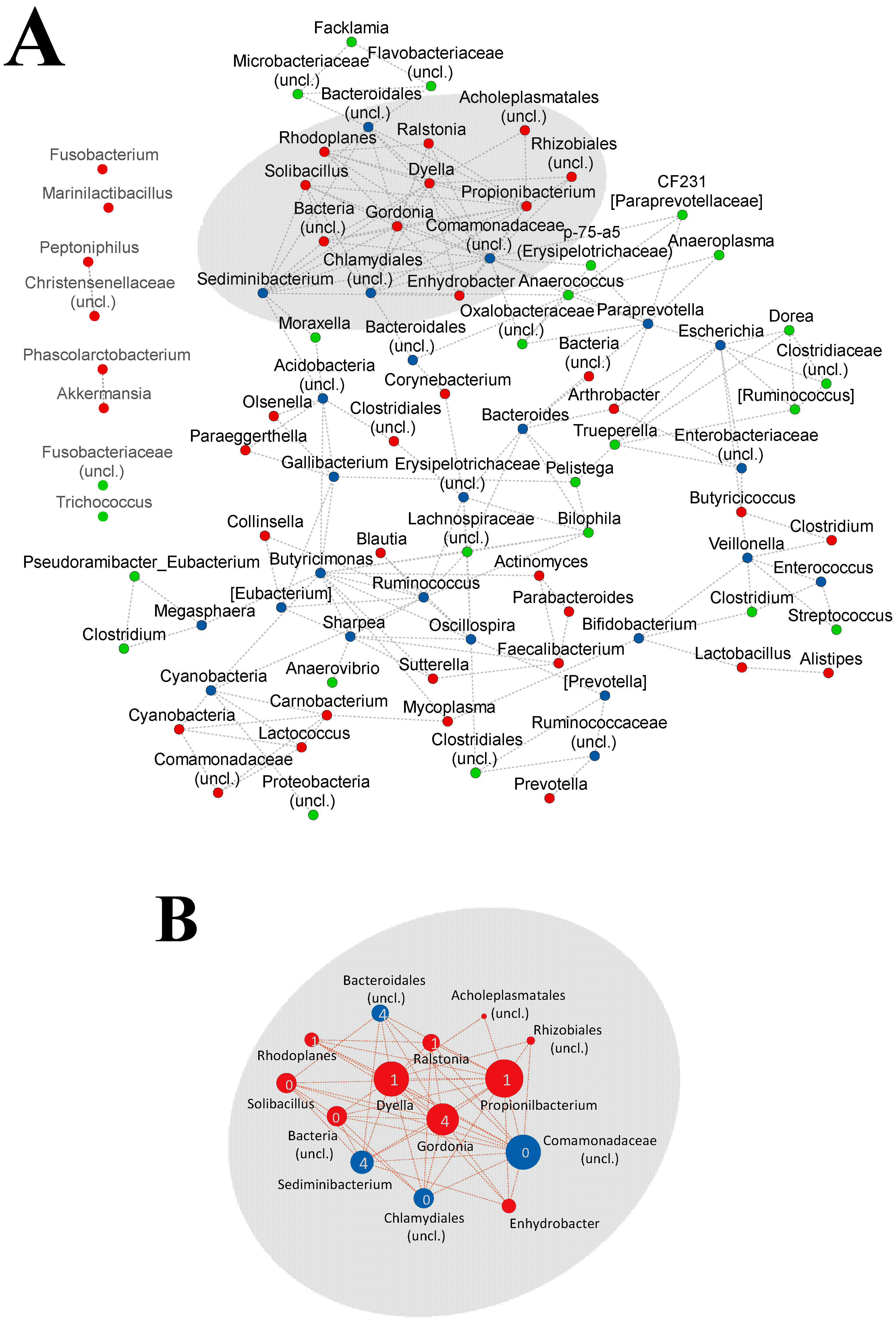
3.3. Animals from Healthy or Disease Groups Showed Different Co-Occurrence Microbial Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, Y.; Yoon, K.-J. An Overview of Calf Diarrhea—Infectious Etiology, Diagnosis, and Intervention. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pempek, J.A.; Watkins, L.R.; Bruner, C.E.; Habing, G.G. A Multisite, Randomized Field Trial to Evaluate the Influence of Lactoferrin on the Morbidity and Mortality of Dairy Calves with Diarrhea. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9259–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.M.; Smith, G.W. Pathophysiology of Diarrhea in Calves. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2009, 25, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.P.; Murinda, S.E.; Jayarao, B.M. Impact of antibiotic use in adult dairy cows on antimicrobial resistance of veterinary and human pathogens: A comprehensive review. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oultram, J.; Phipps, E.; Teixeira, A.G.V.; Foditsch, C.; Bicalho, M.L.; Machado, V.S.; Bicalho, R.C.; Oikonomou, G. Effects of antibiotics (oxytetracycline, florfenicol or tulathromycin) on neonatal calves’ faecal microbial diversity. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Villot, C.; Renaud, D.; Skidmore, A.; Chevaux, E.; Steele, M.; Guan, L.L. Linking perturbations to temporal changes in diversity, stability, and compositions of neonatal calf gut microbiota: Prediction of diarrhea. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for the Prudent Use of Antimicrobials in Veterinary Medicine. Official Journal of the European Union (2015/C 299/04). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/antimicrobial_resistance/docs/2015_prudent_use_guidelines_en.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Barko, P.C.; McMichael, M.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Williams, D.A. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, G.; Teixeira, A.G.V.; Foditsch, C.; Bicalho, M.L.; Machado, V.S.; Bicalho, R.C. Fecal microbial diversity in pre-weaned dairy calves as described by pyrosequencing of metagenomic 16S rDNA. Associations of Faecalibacterium species with health and growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63157. [Google Scholar]
- Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Tang, Z.-Z.; Kemis, J.H.; Kerby, R.L.; Chen, G.; Palloni, A.; Sorenson, T.; Rey, F.E.; Herd, P. Close social relationships correlate with human gut microbiota composition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, M.; Indugu, N.; Vecchiarelli, B.; Redding, L.; Bender, J.; Pappalardo, C.; Leibstein, M.; Toth, J.; Stefanovski, D.; Katepalli, A.; et al. Short communication: Comparison of the fecal bacterial communities in diarrheic and nondiarrheic dairy calves from multiple farms in southeastern Pennsylvania. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7225–7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeno, Y.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Kamagata, Y. rRNA-based analysis to monitor succession of faecal bacterial communities in Holstein calves. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertz, A.F.; Chester-Jones, H. Invited Review: Guidelines for Measuring and Reporting Calf and Heifer Experimental Data. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3577–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 18, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Peddada, S.; Amir, A.; Bittinger, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozupone, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 2017, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16s/23s rRna Sequencing. Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 4, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halko, N.; Martinsson, P.G.; Shkolnisky, Y.; Tygert, M. An Algorithm for the Principal Component Analysis of Large Data Sets. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2010, 33, 2580–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 499. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A Tool for Visualizing High-Throughput Microbial Community Data. GigaScience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. Nouvelles Recherches sur la Distribution Florale. Bull. Société Vaud. Des Sci. Nat. 1908, 44, 223–270. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, T.J. A Method of Establishing Groups of Equal Amplitude in Plant Sociology Based on Similarity of Species Content and Its Application to Analyses of the Vegetation on Danish Commons; I kommission hos E. Munksgaard: København, Demark, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Jari Oksanen, F.; Blanchet, G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Peter, R.; Minchin, R.B.; O’Hara, G.; Simpson, L.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Anderson, M.J. A New Method for Non-Parametric Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, J.J.; Koren, O.; Hugenholtz, P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Walters, W.A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Angenent, L.T.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E. Impact of Training Sets on Classification of High-Throughput Bacterial 16s RRNA Gene Surveys. ISME J. 2012, 6, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Van Treuren, W.; White, R.A.; Eggesbø, M.; Knight, R.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of Composition of Microbiomes: A Novel Method for Studying Microbial Composition. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 27663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Amir, A.; Morton, J.T.; Heller, R.; Arias-Castro, E.; Knight, R. Discrete False-Discovery Rate Improves Identification of Differentially Abundant Microbes. mSystems 2017, 2, e00092-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, M.; Thurimella, K.; Lozupone, C.A. SCNIC: Sparse Correlation Network Investigation for Compositional Data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Qiao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Hou, J.; Hu, M.; Du, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, X. Gut Microbiota and Their Role in Health and Metabolic Disease of Dairy Cow. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 701511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Jöbstl, D.; Schornsteiner, E.; Mann, E.; Wagner, M.; Drillich, M.; Schmitz-Esser, S. Pyrosequencing Reveals Diverse Fecal Microbiota in Simmental Calves during Early Development. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 622. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, F.; Anderson, J.M.; Bharti, R.; Raes, J.; Rosenstiel, P. The Resilience of the Intestinal Microbiota Influences Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmuthuge, N.; Liang, G.; Griebel, P.J.; Guan, L.L. Taxonomic and Functional Compositions of the Small Intestinal Microbiome in Neonatal Calves Provide a Framework for Understanding Early Life Gut Health. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02534-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.F.; Bicalho, M.L.d.S.; Bicalho, R.C. The Bos Taurus Maternal Microbiome: Role in Determining the Progeny Early-Life Upper Respiratory Tract Microbiome and Health. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, Stability and Resilience of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Abenthum, A.; Matthes, J.M.; Kleeberger, D.; Ege, M.J.; Hölzel, C.; Bauer, J.; Schwaiger, K. Development and Genetic Influence of the Rectal Bacterial Flora of Newborn Calves. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 161, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Takeshita, T. The Oral Microbiome and Human Health. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whon, T.W.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, N.-R.; Sung, H.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, W.; Kim, P.S.; Hyun, D.-W.; Seong, H.J.; et al. Calf Diarrhea Caused by Prolonged Expansion of Autochthonous Gut Enterobacteriaceae and Their Lytic Bacteriophages. mSystems 2021, 6, e00816-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, D.L.; Cerutti, L.; Gürtler, A.; Griener, T.; Zelazny, A.; Emler, S. Performance and Application of 16S RRNA Gene Cycle Sequencing for Routine Identification of Bacteria in the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00053-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, M.J.; Jalanka, J.; Pessa-Morikawa, T.; Kokkonen, T.; Satokari, R.; Hynönen, U.; Iivanainen, A.; Niku, M. The Composition of the Perinatal Intestinal Microbiota in Cattle. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hang, B.P.T.; Wredle, E.; Dicksved, J. Analysis of the Developing Gut Microbiota in Young Dairy Calves—Impact of Colostrum Microbiota and Gut Disturbances. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Thaiss, C.A.; Elinav, E. Dysbiosis and the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balootaki, P.A.; Amin, M.; Haghparasti, F.; Rokhbakhsh-Zamin, F. Isolation and Detection of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae and Its Distribution in Humans and Animals by Phenotypical and Molecular Methods in Ahvaz-Iran in 2015. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 42, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Risely, A. Applying the Core Microbiome to Understand Host–Microbe Systems. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A.; Bienhold, C.; Chatzinotas, A.; Gallien, L.; Gobet, A.; Kurm, V.; Küsel, K.; Rillig, M.C.; Rivett, D.W.; Salles, J.F.; et al. Where Less May Be More: How the Rare Biosphere Pulls Ecosystems Strings. ISME J. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.D.; Neufeld, J.D. Ecology and Exploration of the Rare Biosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchado, M.S.; Lauber, M.; Reitmeier, S.; Kacprowski, T.; Baumbach, J.; Haller, D.; List, M. Network Analysis Methods for Studying Microbial Communities: A Mini Review. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2687–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Calf ID | Farm of Origin | Group | Age at Sampling (Days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reception | Disease | First Month | Second Month | |||
| 1 | 1 | Healthy | 15 | Not sampled | 35 | 63 |
| 4 | 2 | Healthy | 7 | Not sampled | 34 | 62 |
| 5 | 3 | Healthy | 8 | Not sampled | 35 | 63 |
| 6 | 4 | Diarrhea | 11 | 18 | 31 | 59 |
| 7 | 5 | Healthy | 14 | Not sampled | 34 | 62 |
| 8 | 6 | Healthy | 13 | Not sampled | 33 | 61 |
| 9 | 6 | Healthy | 12 | Not sampled | 32 | 60 |
| 15 | 7 | Diarrhea | 11 | 16 | 31 | 59 |
| 22 | 8 | Diarrhea | 12 | 16 | 32 | 60 |
| 25 | 5 | Diarrhea | 13 | 17 | 33 | 61 |
| 26 | 9 | Healthy | 11 | Not sampled | 31 | 59 |
| 28 | 5 | Diarrhea | 10 | 16 | 30 | 62 * |
| 79 | 6 | Diarrhea | 13 | 17 | 33 | 60 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obregon-Gutierrez, P.; Bague-Companys, J.; Bach, A.; Aragon, V.; Correa-Fiz, F. Longitudinal Study of Fecal Microbiota in Calves with or without Diarrhea Episodes before Weaning. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090463
Obregon-Gutierrez P, Bague-Companys J, Bach A, Aragon V, Correa-Fiz F. Longitudinal Study of Fecal Microbiota in Calves with or without Diarrhea Episodes before Weaning. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(9):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090463
Chicago/Turabian StyleObregon-Gutierrez, Pau, Jaume Bague-Companys, Alex Bach, Virginia Aragon, and Florencia Correa-Fiz. 2022. "Longitudinal Study of Fecal Microbiota in Calves with or without Diarrhea Episodes before Weaning" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 9: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090463
APA StyleObregon-Gutierrez, P., Bague-Companys, J., Bach, A., Aragon, V., & Correa-Fiz, F. (2022). Longitudinal Study of Fecal Microbiota in Calves with or without Diarrhea Episodes before Weaning. Veterinary Sciences, 9(9), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090463









