Effect of Protein Supplementation on Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adult Patients with Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
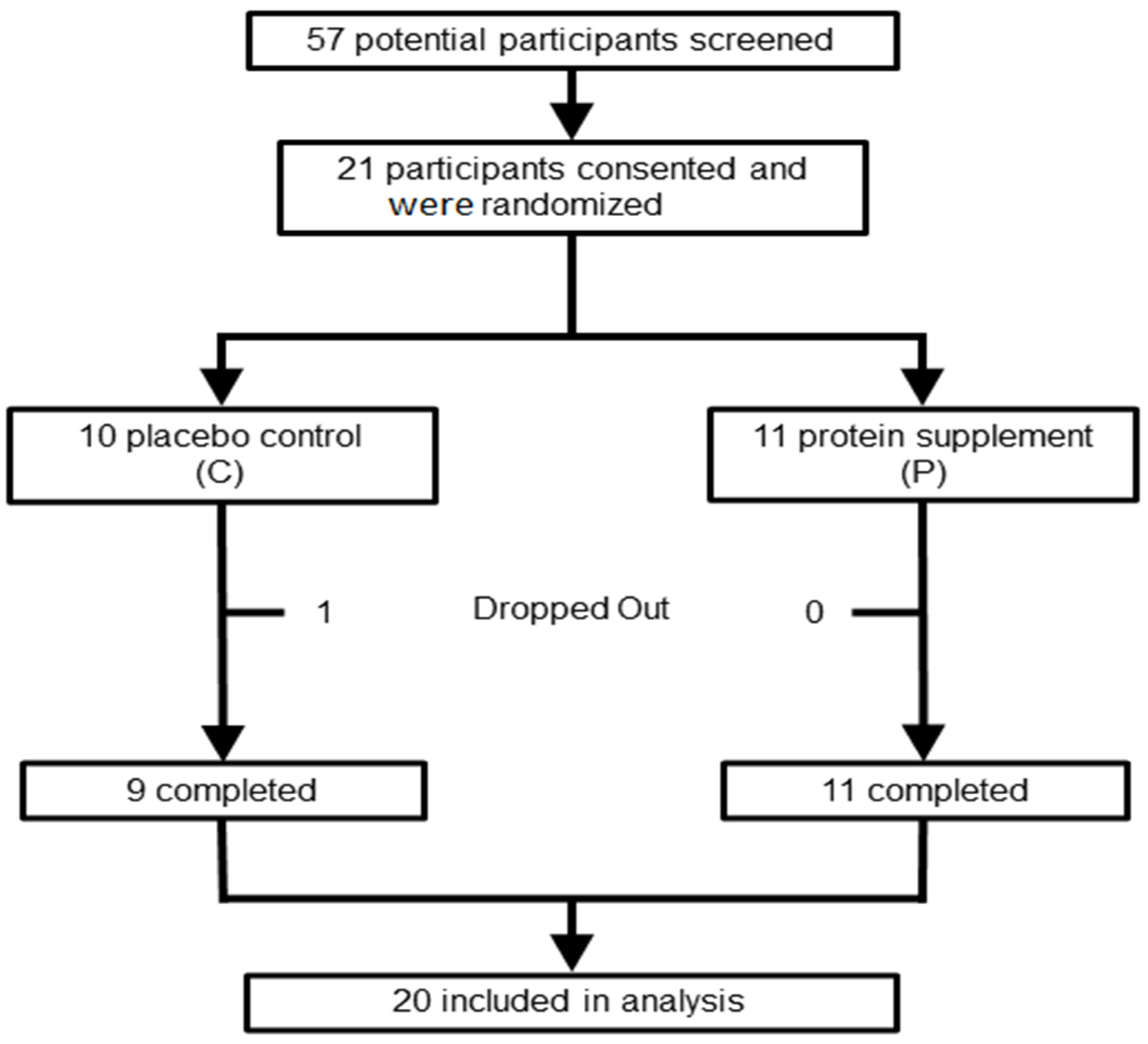
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
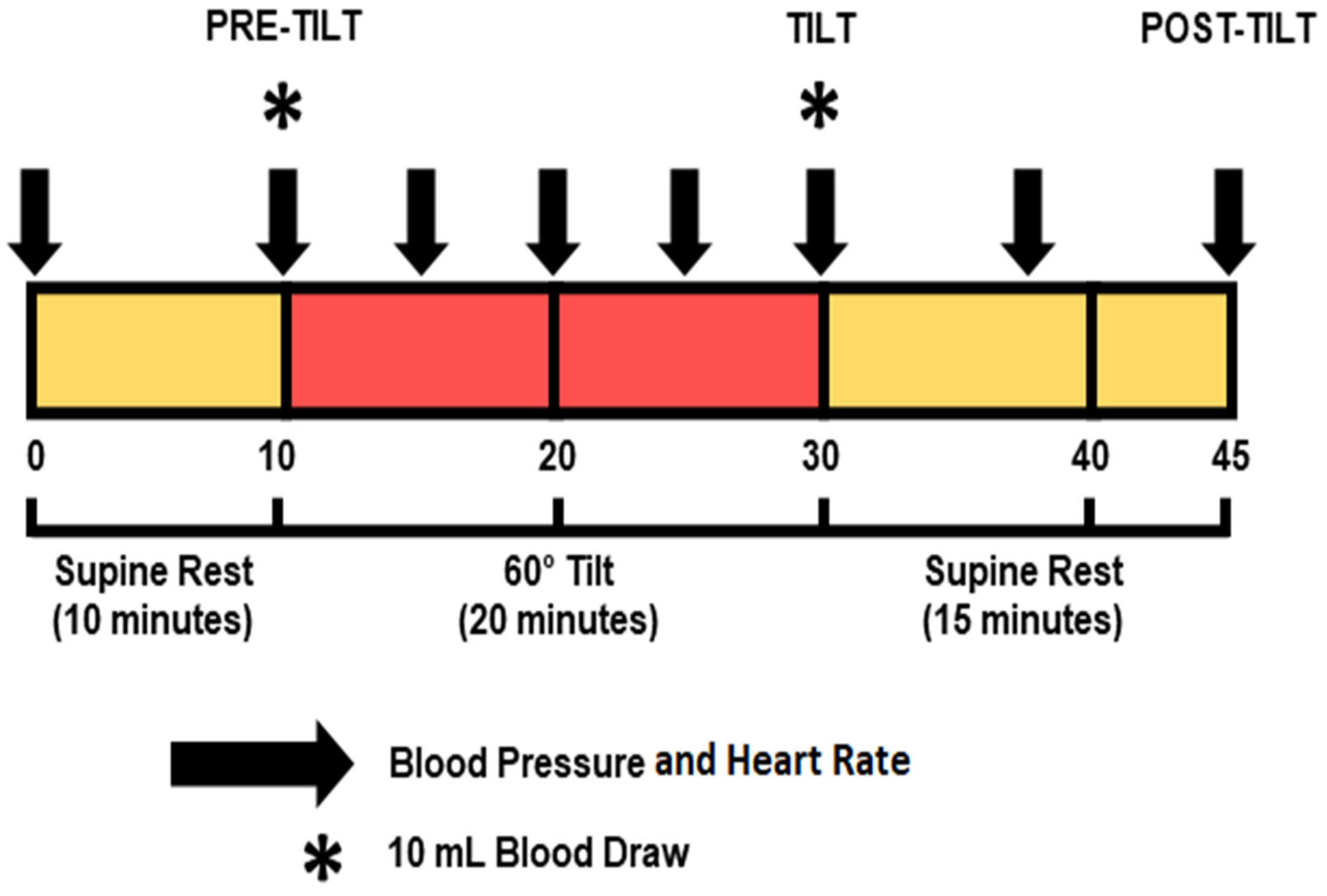
2.2.1. Overview
2.2.2. Dietary Supplementation
2.2.3. Hemodynamic Changes
2.2.4. Biochemical Assessment
2.2.5. Functional Assessment
2.2.6. Body Composition
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
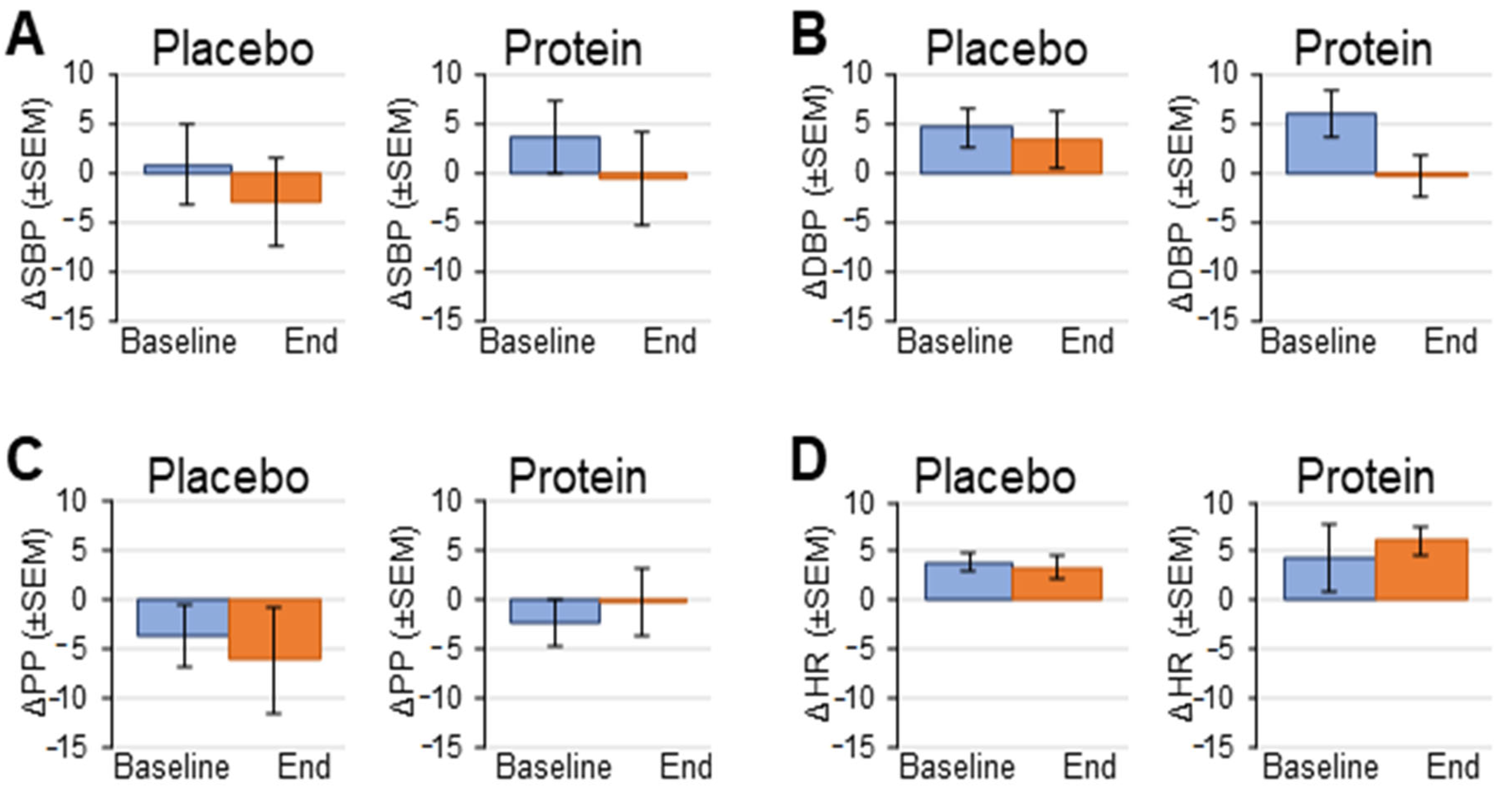
3.2. Hemodynamic Response to Head-Up Tilt Test
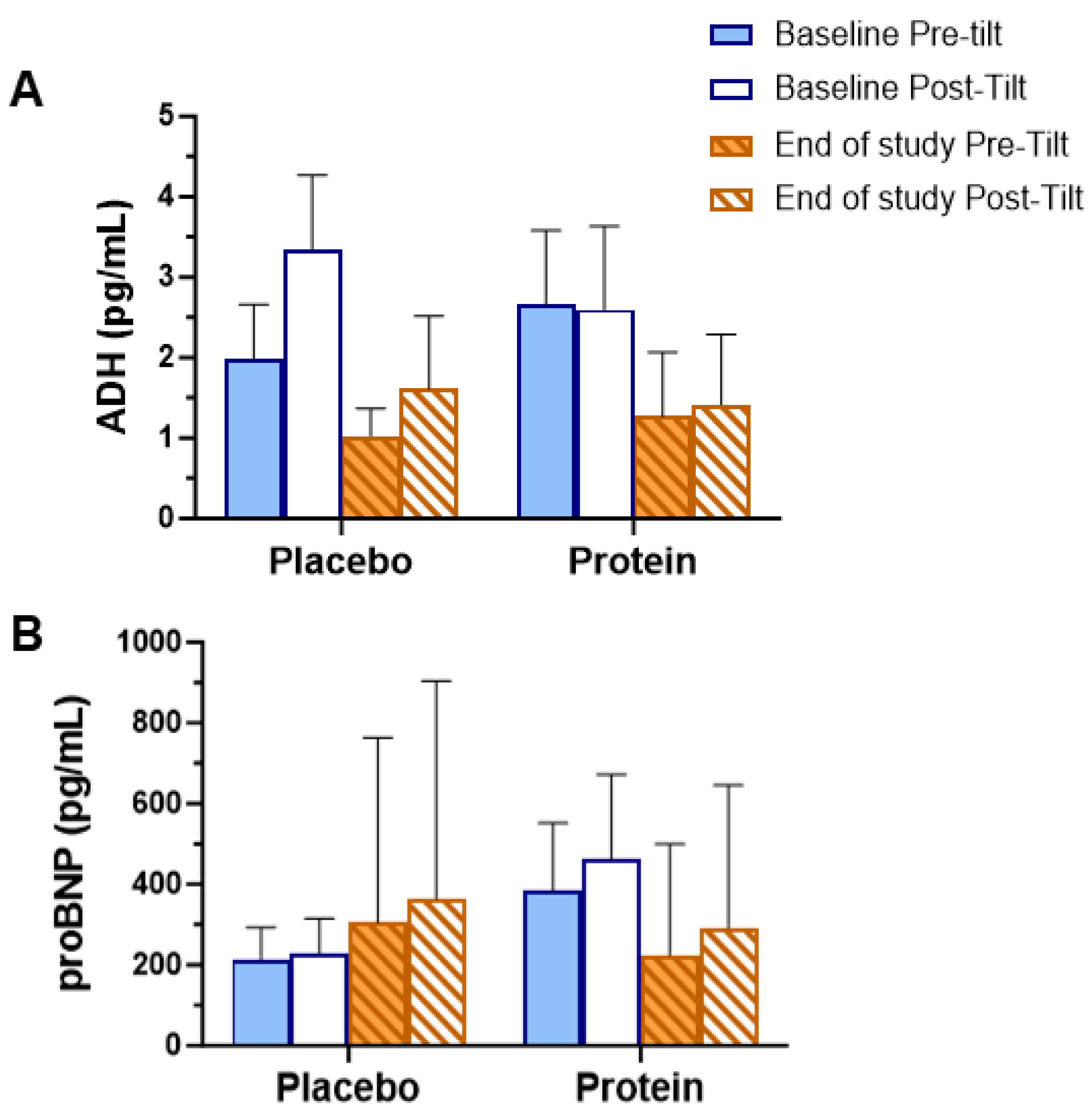
3.3. Biochemical Assessments
3.4. 6 Min Walk Test
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACEI | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ADH | Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) |
| AFib | Atrial fibrillation |
| ARB | Angiotensin II receptor blocker |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CCB | Calcium channel blockers |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HLP | Hyperlipidemia |
| HR | Heart rate |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| OH | Orthostatic hypotension |
| PP | Pulse pressure |
| proBNP | Pro B-type naturetic peptide |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
References
- Wei, J.Y. Age and the cardiovascular system. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hausdorff, J.M.; Edelberg, H.K.; Mitchell, S.L.; Goldberger, A.L.; Wei, J.Y. Increased gait unsteadiness in community-dwelling elderly fallers. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1997, 78, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitz, L.A.; Jonsson, P.V.; Marks, B.L.; Parker, J.A.; Royal, H.D.; Wei, J.Y. Reduced supine cardiac volumes and diastolic filling rates in elderly patients with chronic medical conditions: Implications for postural blood pressure homeostasis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1990, 38, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitz, L.A.; Nyquist, R.P., Jr.; Wei, J.Y.; Rowe, J.W. Postprandial reduction in blood pressure in the elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, K.G.; Wei, J.Y. Clinical implications of physiological changes in the aging heart. Drugs Aging 2001, 18, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.P.; Wei, J.Y.; Rosa, R.M.; Epstein, F.H.; Rowe, J.W. The effect of age and sodium depletion on cardiovascular response to orthostasis. Hypertension 1986, 8, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsitz, L.A.; Ryan, S.M.; Parker, J.A.; Freeman, R.; Wei, J.Y.; Goldberger, A.L. Hemodynamic and autonomic nervous system responses to mixed meal ingestion in healthy young and old subjects and dysautonomic patients with postprandial hypotension. Circulation 1993, 87, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, A.; Hoang, P.T.S.B.; Sharmin, S.; Reijnierse, E.M.; van Wezel, R.J.; Meskers, C.G.; Maier, A.B. Orthostatic hypotension and falls in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, G.; Wei, J.Y.; Schutzler, S.E.; Coker, K.; Gibson, R.V.; Kirby, M.F.; Ferrando, A.A.; Wolfe, R.R. Daily consumption of a specially formulated essential amino acid-based dietary supplement improves physical performance in older adults with low physical functioning. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K.N.; Li, A. Older adult falls in emergency medicine, 2023 update. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 39, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelik, O.; Feldman, L.; Cohen, N. Heart failure and orthostatic hypotension. Heart Fail Rev. 2016, 21, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitz, L.A.; Pluchino, F.C.; Wei, J.Y.; Rowe, J.W. Syncope in institutionalized elderly: The impact of multiple pathological conditions and situational stress. J. Chronic Dis. 1986, 39, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorowski, A.; Ricci, F.; Sutton, R. Orthostatic hypotension and cardiovascular risk. Kardiol. Pol. 2019, 77, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkar, M.; Medina Inojosa, J.; Liedl, D.; Wysokinski, W.; Houghton, D.E.; Wennberg, P.W.; Lin, G.; Kane, G.; Fischer, K.; Rooke, T.W.; et al. Calf muscle pump function as a predictor of all-cause mortality. Vasc. Med. 2020, 25, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, K.; Çiftçi, S.; Öncü, J.; Doğan, G.M.; Çetinkal, G.; Yıldız, S.S.; Sığırcı, S.; Kılıçkesmez, K.O. Orthostatic hypotension and age-related sarcopenia. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 67, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odiet, J.A.; Boerrigter, M.E.; Wei, J.Y. Carnitine palmitoyl transferase-I activity in the aging mouse heart. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1995, 79, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Camprubi-Robles, M.; Bear, D.E.; Cederholm, T.; Malafarina, V.; Welch, A.A.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Muscle loss: The new malnutrition challenge in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-Y.; Park, S.; Smeets, E.T.H.C.; Schutzler, S.; Azhar, G.; Wei, J.Y.; Ferrando, A.A.; Wolfe, R.R. Consumption of a Specially-Formulated Mixture of Essential Amino Acids Promotes Gain in Whole-Body Protein to a Greater Extent than a Complete Meal Replacement in Older Women with Heart Failure. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.M.; E Miller, M.; A Fielding, R.; Gill, T.M.; Glynn, N.W.; Guralnik, J.M.; King, A.; Newman, A.B.; Manini, T.M.; Marsh, A.P.; et al. Maintenance of Physical Function 1 Year after Exercise Intervention in At-Risk Older Adults: Follow-up from the LIFE Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidossis, L.S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Klein, S.; Wolfe, R.R. Regulation of plasma fatty acid oxidation during low- and high-intensity exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 272, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, M.; Dirksen, A.; Taraborrelli, P.; Panagopolous, D.; Torocastro, M.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B. Orthostatic hypotension in older people: Considerations, diagnosis and management. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, A.W.; Hissen, S.L.; Manabe, K.; Takeda, R.; Washio, T.; Coombs, G.B.; Sanchez, B.; Fu, Q.; Shoemaker, J.K. Age-and sex-related differences in sympathetic vascular transduction and neurohemodynamic balance in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2023, 325, H917–H932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogun, S.; Winzenberg, T.; Wills, K.; Scott, D.; Jones, G.; Aitken, D.; Callisaya, M.L. Prospective associations of low muscle mass and function with 10-year falls risk, incident fracture and mortality in community-dwelling older adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartholt, K.A.; Lee, R.; Burns, E.R.; Van Beeck, E.F. Mortality from Falls among US Adults Aged 75 Years or Older, 2000–2016. JAMA 2019, 321, 2131–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekfani, T.; Pellicori, P.; Morris, D.A.; Ebner, N.; Valentova, M.; Steinbeck, L.; Wachter, R.; Elsner, S.; Sliziuk, V.; Schefold, J.C.; et al. Sarcopenia in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Impact on muscle strength, exercise capacity and quality of life. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 222, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Holm, H.; Molvin, J.; Bachus, E.; Tasevska-Dinevska, G.; Fedorowski, A.; Jujic, A.; Magnusson, M. Autonomic dysfunction is associated with cardiac remodelling in heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail 2018, 5, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, V.E. Impact of Nutrition on Cardiovascular Function. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vest, A.R.; Chan, M.; Deswal, A.; Givertz, M.M.; Lekavich, C.; Lennie, T.; Litwin, S.E.; Parsly, L.; Rodgers, J.E.; Rich, M.W.; et al. Nutrition, obesity, and cachexia in patients with heart failure: A consensus statement from the Heart Failure Society of America Scientific Statements Committee. J. Cardiac. Fail. 2019, 25, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Colvin, M.M.; Drazner, M.H.; Filippatos, G.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Givertz, M.M.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 2017, 136, e137–e161. [Google Scholar]
- Januzzi, J.L.; Ahmad, T.; Mulder, H.; Coles, A.; Anstrom, K.J.; Adams, K.F.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Fiuzat, M.; Houston-Miller, N.; Mark, D.B.; et al. Natriuretic peptide response and outcomes in chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, M.C.; Phillips, S.M. Supplemental protein in support of muscle mass and health: Advantage whey. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, A8–A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, J.I.; Kim, I.Y.; Wolfe, R.R. Protein consumption and the elderly: What is the optimal level of intake? Nutrients 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Genaro, P.; De Medeiros Pinheiro, M.; Szejnfeld, V.L.; Martini, L.A. Dietary protein intake in elderly women: Association with muscle and bone mass. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbe, A.; Tanimoto, K.; Inaba, Y.; Sakai, S.; Shishikura, K.; Imbe, H.; Tanimoto, Y.; Terasaki, J.; Imagawa, A.; Hanafusa, T. Effects of L-carnitine supplementation on the quality of life in diabetic patients with muscle cramps. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrasawi, M.; Shahar, S.; Manaf, Z.A.; Rajab, N.F.; Kas, D.; Zahara, A. Efficacy of L-carnitine supplementation on frailty status and its biomarkers, nutritional status, and physical and cognitive function among prefrail older adults: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Guthrie, N.; Pezzullo, J.; Sanli, T.; Fielding, R.A.; Bellamine, A. Efficacy of a novel formulation of L-Carnitine, creatine, and leucine on lean body mass and functional muscle strength in healthy older adults: A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Gargante, M.P.; Cristaldi, E.; Colonna, V.; Messano, M.; Koverech, A.; Neri, S.; Vacante, M.; Cammalleri, L.; Motta, M. Acetyl l-carnitine (ALC) treatment in elderly patients with fatigue. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2008, 46, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qu, H.; Yang, Z.; Rong, J.; Cai, W.; Zhou, H. Efficacy and Safety of L-Carnitine Treatment for Chronic Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6274854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.R.; Morin, R.J.; Kiely, D.K.; Gagnon, M.; Azhar, G.; Knight, E.L.; Nelson, J.C.; Lipsitz, L.A. Effects of age and gender on autonomic control of blood pressure dynamics. Hypertension 1999, 33, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, P.; Ricci, F.; Hamrefors, V.; Sutton, R.; Fedorowski, A. Classical and delayed orthostatic hypotension in patients with unexplained syncope and severe orthostatic intolerance. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, W.P., Jr.; Goldstein, D.S. Autonomic uprising: The tilt table test in autonomic medicine. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, A.; Giezenaar, C.; Lange, K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Chapman, I.; Soenen, S. Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Responses following Dietary Protein Intake in Older Men. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; An, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Deng, S. The clinical significance of changes in cTnT, CRP and NT-proBNP levels in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 2947–2954. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, G.; Verma, A.; Robeson, M.S.; Patyal, P.; Nookaew, I.; Sharma, S.; Pangle, A.; Che, Y.; Wolfe, R.R.; Wei, J.Y. Short-Term Ingestion of Essential Amino Acid Based Nutritional Supplements or Whey Protein Improves the Physical Function of Older Adults Independently of Gut Microbiome. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitz, L.A.; Pluchino, F.C.; Wei, J.Y.; Minaker, K.L.; Rowe, J.W. Cardiovascular and norepinephrine responses after meal consumption in elderly (older than 75 years) persons with postprandial hypotension and syncope. Am. J. Cardiol. 1986, 58, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santulli, G.; Iaccarino, G. Adrenergic signaling in heart failure and cardiovascular aging. Maturitas 2016, 93, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control | Protein | All | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Participants | 9 | 11 | 20 |
| Age | |||
| Mean (SE) | 75 (2.5) | 74 (1.7) | 75 (1.4) |
| Median | 75 | 74 | 75 |
| Mode | 75 | 79 | 74 |
| Range | 64–86 | 63–81 | 63–86 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Female | 8 | 9 | 17 |
| Race | |||
| Asian | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| African American | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| White | 8 | 9 | 17 |
| Category | Specific Factor | Control (n = 9) | Protein (n = 11) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD/Stents | 0 | 2 | |
| HTN | 7 | 10 | |
| HLP | 6 | 8 | |
| AFib (stable and controlled) | 0 | 1 | |
| DM | 0 | 2 | |
| Pacemaker/defibrillator | 1 | 1 | |
| COPD/lung diseases | 0 | 1 | |
| Medications | ACEI/ARB | 6 | 5 |
| Beta Blockers | 4 | 2 | |
| CCB | 4 | 3 | |
| Diuretic | 2 | 2 | |
| Anti-arrhythmic | 0 | 0 | |
| Nitrates | 1 | 0 | |
| Statins | 5 | 4 | |
| Other | Fall | 1 | 2 |
| Dizziness | 1 | 3 |
| Baseline | End of Study | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Tilt | Tilt | Post-Tilt | Pre-Tilt | Tilt | Post-Tilt | |
| Placebo Control | ||||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 135 ± 5 | 130 ± 8 | 137 ± 5 | 132 ± 6 | 125 ± 7 | 136 ± 6 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80 ± 2 | 80 ± 4 | 87 ± 4 | 79 ± 3 | 84 ± 2 † | 84 ± 4 |
| PP (mmHg) | 54 ± 4 | 50 ± 5 | 50 ± 6 | 53 ± 4 | 47 ± 5 | 52 ± 3 |
| HR (beats/min) | 62 ± 2 | 69 ± 3 | 63 ± 3 | 70 ± 3 * | 77 ± 6 | 68 ± 4 |
| Protein Supplement | ||||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 132 ± 4 | 132 ± 5 | 132 ± 6 | 136 ± 6 | 132 ± 7 | 132 ± 7 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 77 ± 4 | 80 ± 4 | 79 ± 5 | 83 ± 4 | 82 ± 4 | 81 ± 4 |
| PP (mmHg) | 56 ± 2 | 52 ± 3 | 52 ± 3 | 53 ± 3 | 50 ± 3 | 50 ± 4 |
| HR (beats/min) | 71 ± 4 ‡ | 75 ± 5 | 64 ± 4 | 72 ± 4 | 78 ± 3 | 70 ± 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azhar, G.; Pangle, A.K.; Coker, K.; Sharma, S.; Wei, J.Y. Effect of Protein Supplementation on Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adult Patients with Heart Failure. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020042
Azhar G, Pangle AK, Coker K, Sharma S, Wei JY. Effect of Protein Supplementation on Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adult Patients with Heart Failure. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzhar, Gohar, Amanda K. Pangle, Karen Coker, Shakshi Sharma, and Jeanne Y. Wei. 2025. "Effect of Protein Supplementation on Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adult Patients with Heart Failure" Geriatrics 10, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020042
APA StyleAzhar, G., Pangle, A. K., Coker, K., Sharma, S., & Wei, J. Y. (2025). Effect of Protein Supplementation on Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adult Patients with Heart Failure. Geriatrics, 10(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020042





