Antifungal Efficacy of Luliconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid-Carrier Gel in an Animal Model of Dermatophytosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of LCZ-NLC NPs
2.2. Gel Preparation
2.3. In Vitro Drug Skin Absorption and Retention
2.4. Selection of Fungi
2.5. Preparation of Dermatophyte Suspension for Animal Inoculation
2.6. In Vivo Animal Study
2.7. Preparation Method of Tinea Corporis in Guinea Pigs
2.8. Evaluation of Treatment
2.9. Mycological Examination
2.10. Histopathology Analysis
2.11. In Vivo Skin Irritation Studies
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
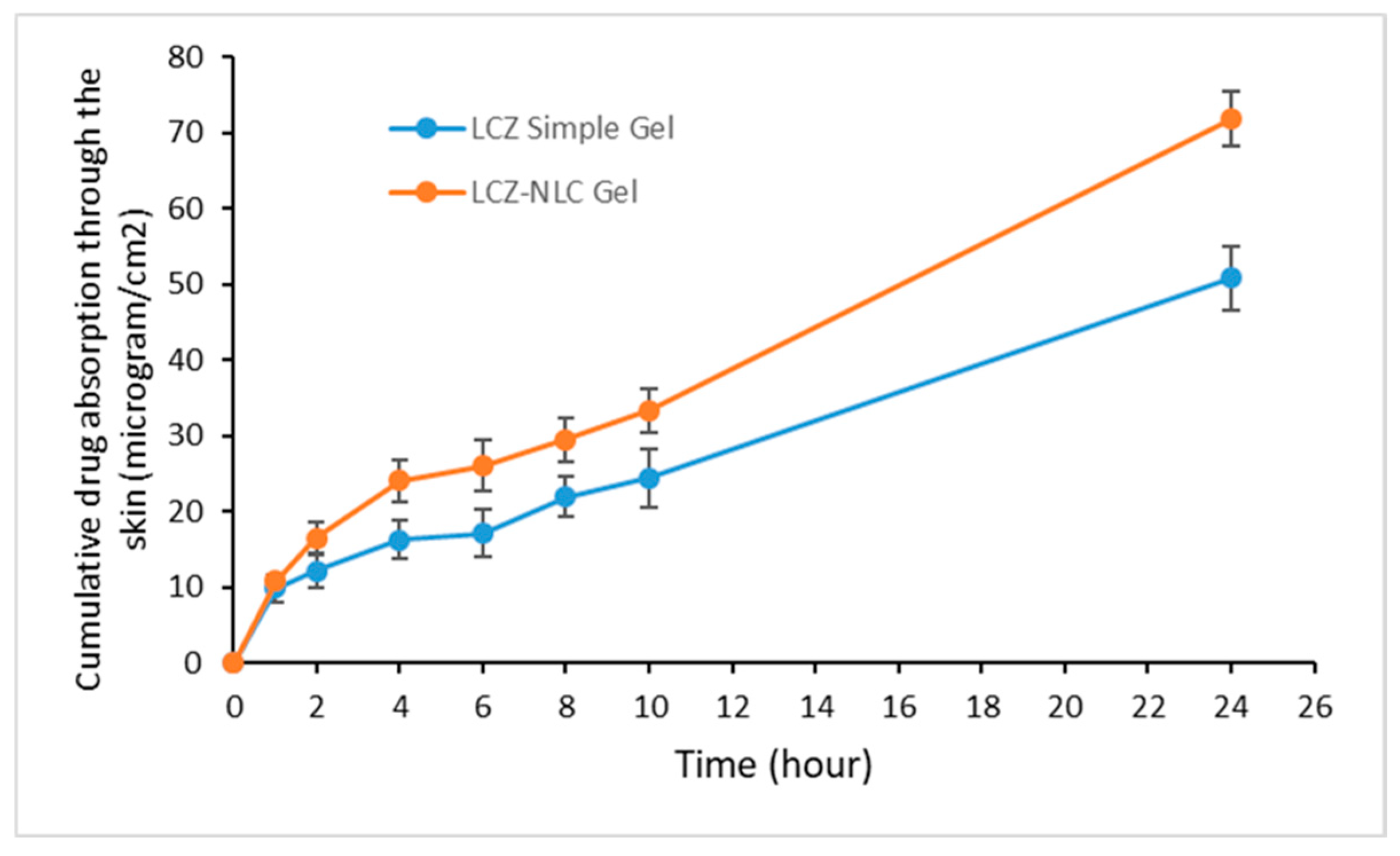
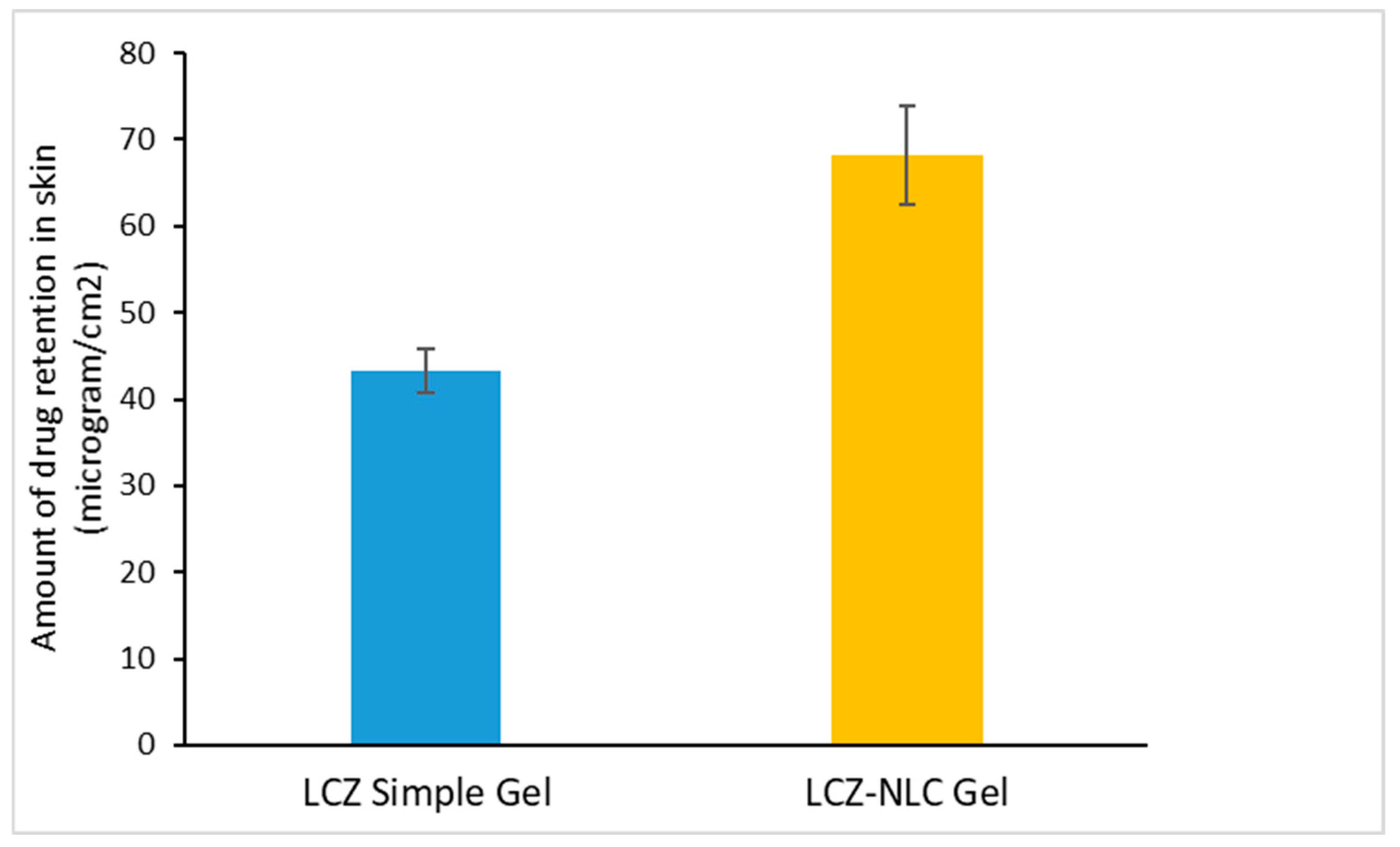
3.1. Analysis of Drug Absorption and Retention in Gel Formulations
3.2. Animals
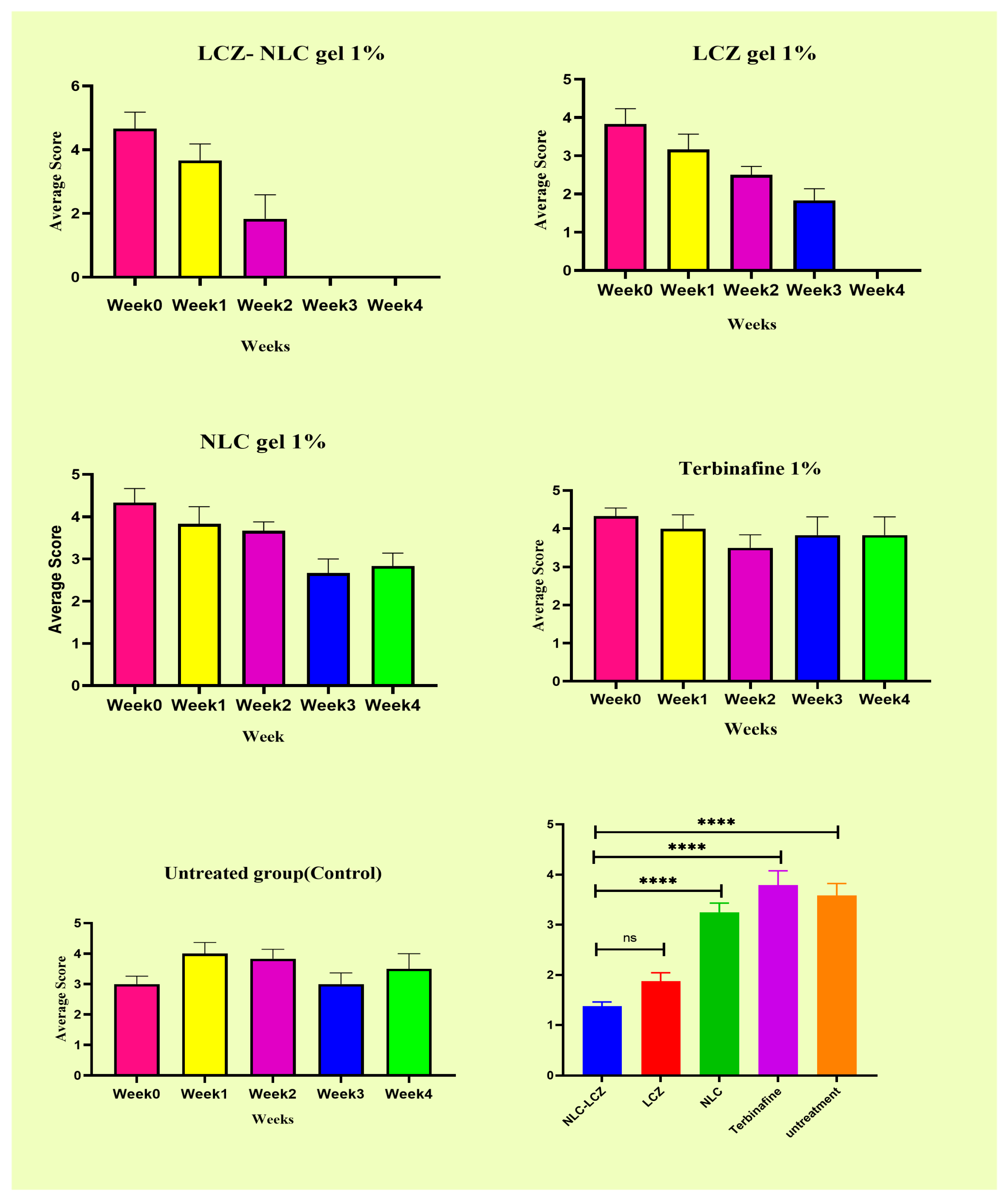
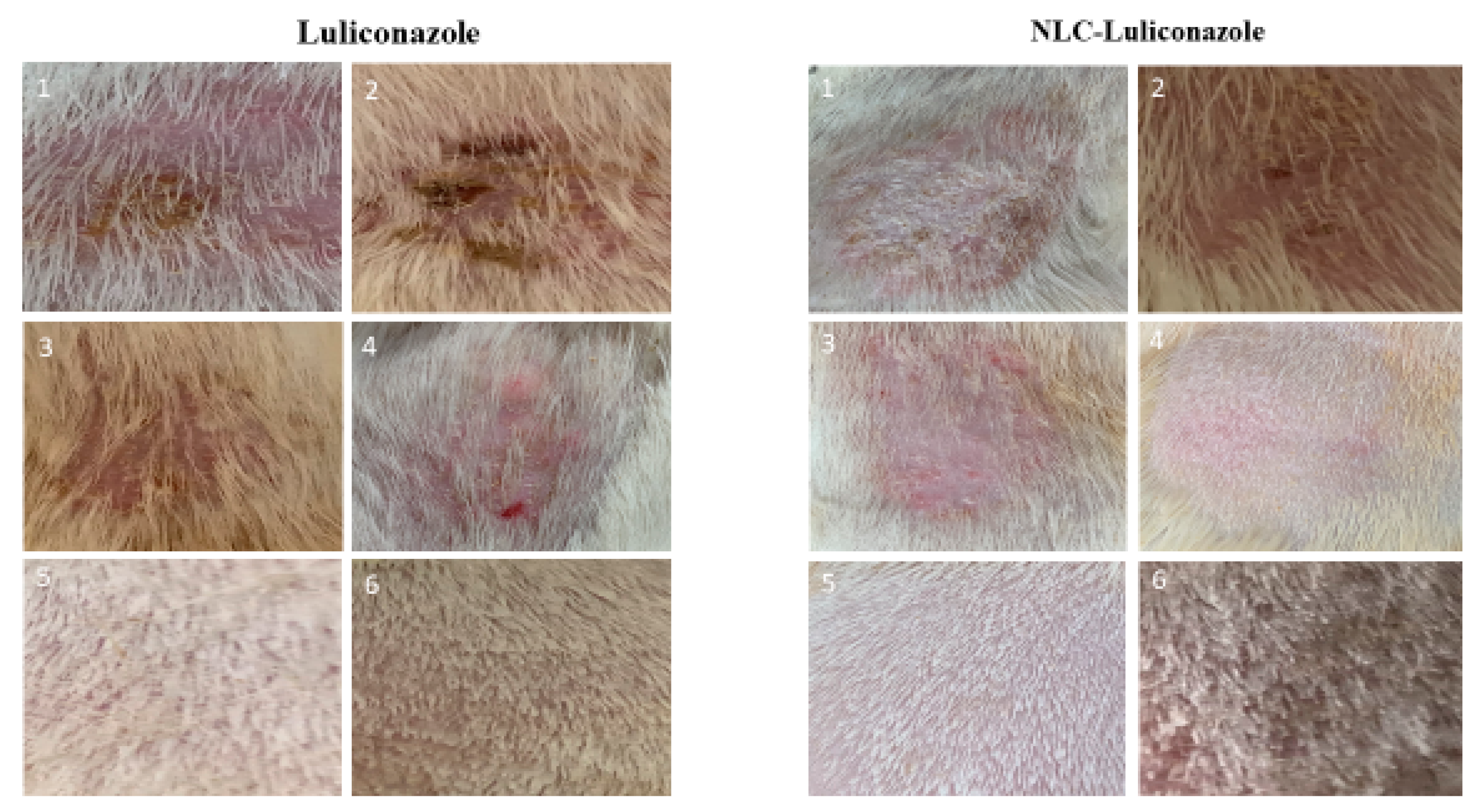
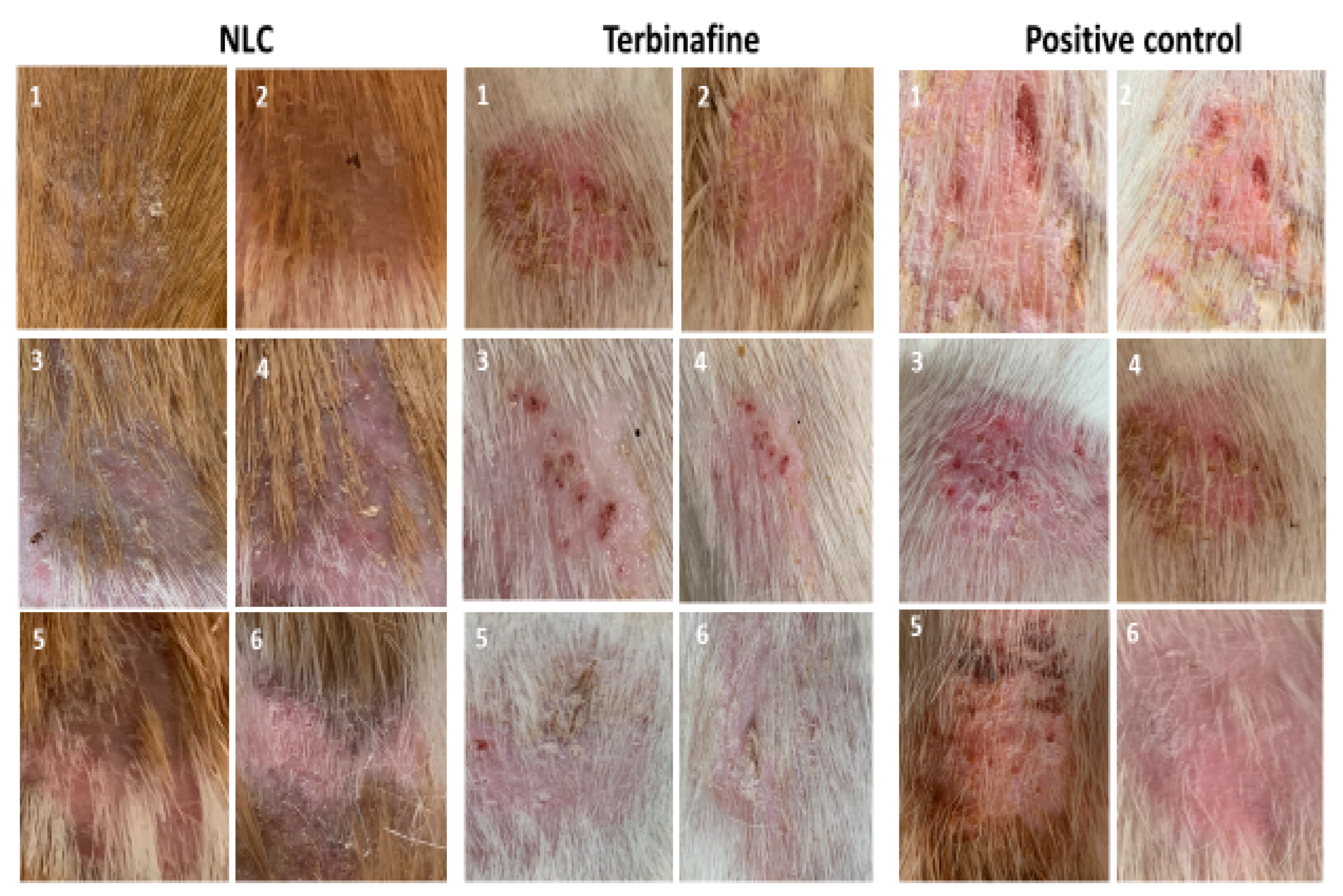
3.3. Efficacy of LCZ-NLC 1% Gel, LCZ 1% Gel, and Terbinafine 1%: A Clinical and Mycological Evaluation in Guinea Pig Models
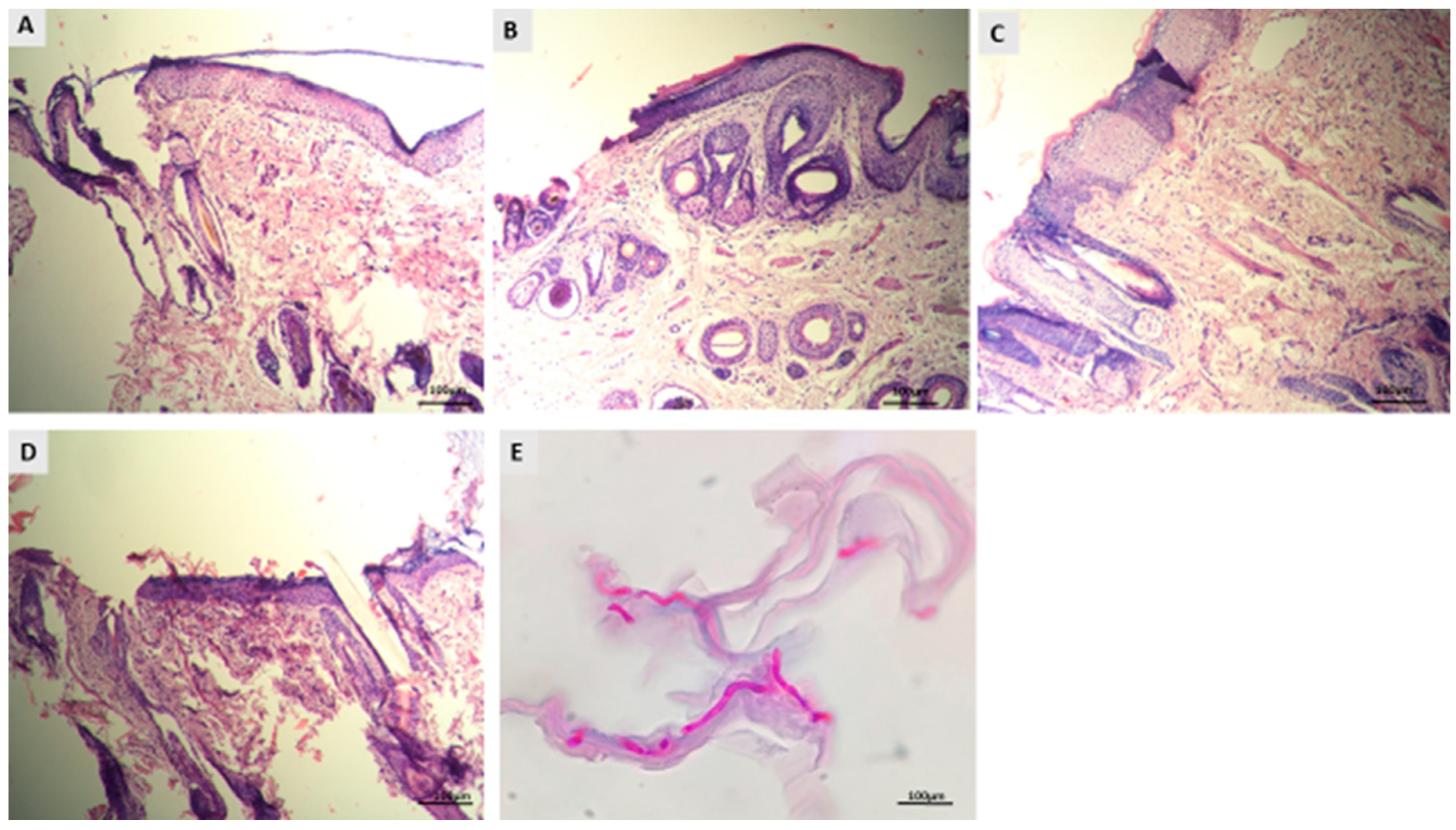
3.4. Histopathological Evaluation of Dermatophytosis in Guinea Pigs
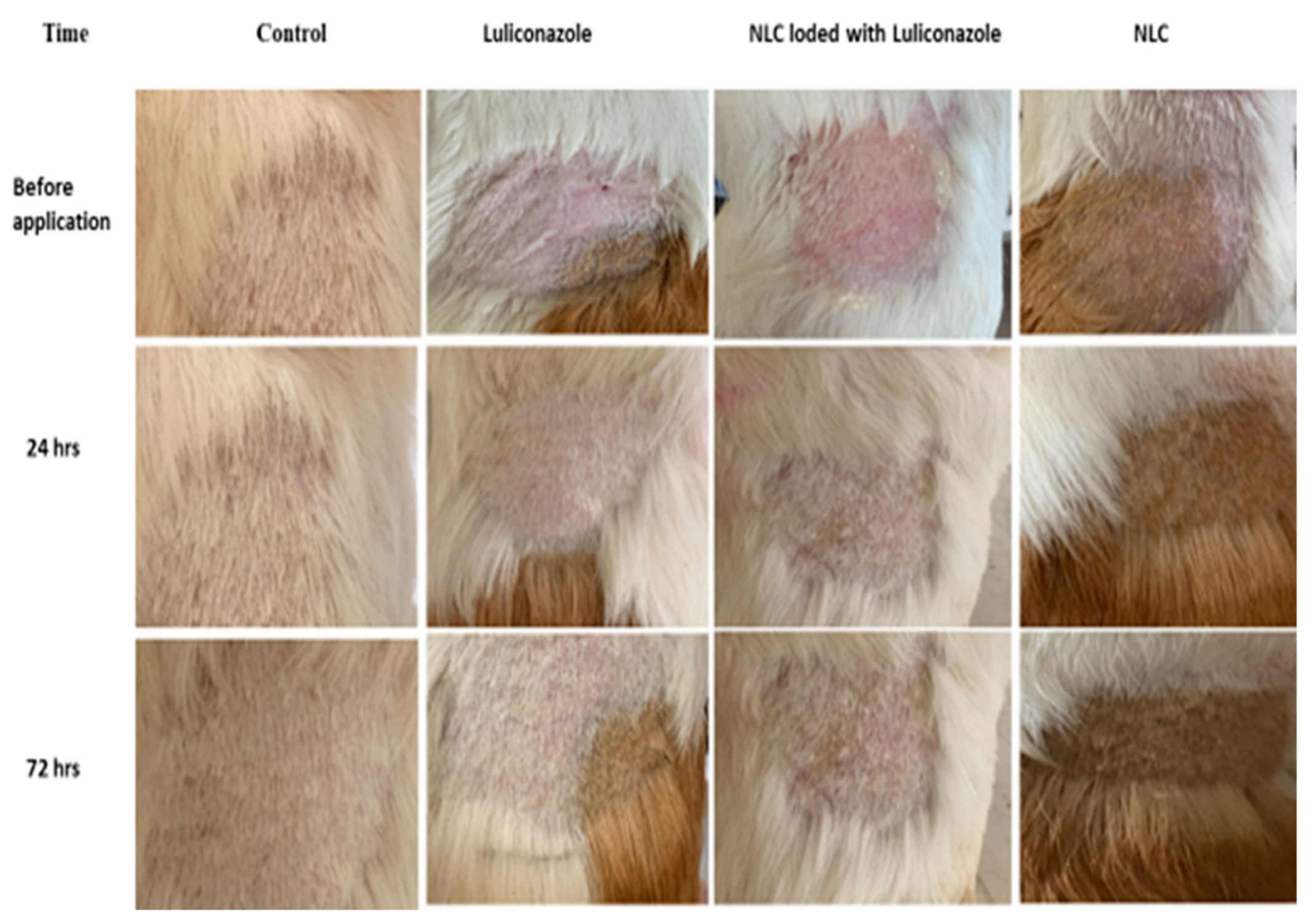
3.5. Skin Irritation Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seebacher, C.; Bouchara, J.-P.; Mignon, B. Updates on the epidemiology of dermatophyte infections. Mycopathologia 2008, 166, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havlickova, B.; Czaika, V.A.; Friedrich, M. Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses 2008, 51, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Doh, J.Y.; Han, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, J.H.; Bang, C.H.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.H. Risk factors of dermatophytosis among Korean adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.; Jackson, B.R.; Chiller, T.; Beer, K.D. Estimation of direct healthcare costs of fungal diseases in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, R.; Kimura, U.; Kakurai, M.; Hiruma, J.; Kamata, H.; Suga, Y.; Harada, K. Trichophyton indotineae sp. nov.: A new highly terbinafine-resistant anthropophilic dermatophyte species. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, A.; Vinay, K.; Dogra, S. Emergence of recalcitrant dermatophytosis in India. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Gupta, A.; Sardana, K.; Sethia, K.; Panesar, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Ghadlinge, M. A prospective study on patterns of topical steroids self-use in dermatophytoses and determinants predictive of cutaneous side effects. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Sabater, A.; Normand, A.-C.; Bidaud, A.-L.; Cremer, G.; Foulet, F.; Brun, S.; Bonnal, C.; Aït-Ammar, N.; Jabet, A.; Ayachi, A. Terbinafine resistance in dermatophytes: A French multicenter prospective study. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.B.; Panda, S.; Nenoff, P.; Singal, A.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Uhrlass, S.; Das, A.; Bisherwal, K.; Shaw, D.; Vasani, R. The unprecedented epidemic-like scenario of dermatophytosis in India: I. Epidemiology, risk factors and clinical features. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2021, 87, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Nanjoh, Y.; Toga, T.; Pillai, R.; Jo, W.; Tsuboi, R. Luliconazole Retention in Stratum Corneum and Prevention of Fungal Infection in a Guinea Pig Tinea Pedis Model. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Abastabar, M.; Al-Hatmi, A.M.; Vafaei Moghaddam, M.; De Hoog, G.S.; Haghani, I.; Aghili, S.R.; Shokohi, T.; Hedayati, M.T.; Daie Ghazvini, R.; Kachuei, R. Potent activities of luliconazole, lanoconazole, and eight comparators against molecularly characterized Fusarium species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00009-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokoohi, G.R.; Badali, H.; Mirhendi, H.; Ansari, S.; Rezaei-Matehkolaei, A.; Ahmadi, B.; Vaezi, A.; Alshahni, M.M.; Makimura, K. In vitro activities of luliconazole, lanoconazole, and efinaconazole compared with those of five antifungal drugs against melanized fungi and relatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00635-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghi, N.; Shokohi, T.; Badali, H.; Makimura, K.; Rezaei-Matehkolaei, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Didehdar, M.; Haghani, I.; Abastabar, M. In vitro activity of new azoles luliconazole and lanoconazole compared with ten other antifungal drugs against clinical dermatophyte isolates. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abastabar, M.; Rahimi, N.; Meis, J.F.; Aslani, N.; Khodavaisy, S.; Nabili, M.; Rezaei-Matehkolaei, A.; Makimura, K.; Badali, H. Potent activities of novel imidazoles lanoconazole and luliconazole against a collection of azole-resistant and-susceptible Aspergillus fumigatus strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6916–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, A.; Abastabar, M.; Keighobadi, M.; Emami, S.; Fakhar, M.; Teshnizi, S.H.; Makimura, K.; Rezaei-Matehkolaei, A.; Mirzaei, H. Promising antileishmanial activity of novel imidazole antifungal drug luliconazole against Leishmania major: In vitro and in silico studies. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, R.K.; Nakamura, N.; Tavakkol, A. Luliconazole: A review of a new antifungal agent for the topical treatment of onychomycosis. Mycoses 2014, 57, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, S131–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.D.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles for parenteral delivery of actives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Zimmer, A.; Pardeike, J. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for pulmonary application: A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Trabado, J.; Diebold, Y.; Sanchez, A. Designing lipid nanoparticles for topical ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcês, A.; Amaral, M.; Lobo, J.S.; Silva, A.C. Formulations based on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for cutaneous use: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Badran, M.M.; Ali, H.M.; Abdel-Bakky, M.S.; El-Bagory, I. Fatty alcohol containing nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) for progesterone oral delivery: In vitro and ex vivo studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratabadi, M.; Barogh, R.E.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Ebrahimnejad, P.; Haghani, I.; Akhtari, J.; Hajheydari, Z.; Abastabar, M. Formulation, characterization, and in vitro antifungal efficacy of luliconazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (LCZ-NLCs) against a panel of resistant fungal strains. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Akbari, J.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Babaei, A.; Eghbali, M.; Sanaee, A.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Omidi, M. Eco-friendly preparation, characterization, evaluation of anti-melanogenesis/antioxidant effect and in vitro/in vivo safety profile of kojic acid loaded niosome as skin lightener preparation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2023, 34, 1952–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Akbari, J.; Hajheydari, Z.; Goodarzi, A.; Rostamkalaei, S.S.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Rahimnia, S.M. Green formulation of spironolactone loaded chitosan-coated nano lipid carrier for treatment of acne vulgaris: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Mousavi, S.N.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Rahimnia, S.M. Evaluation of an innovative, green, and eco-friendly baclofen-loaded niosome (Baclosome) formulation for pain management by transdermal delivery. Nanomed. J. 2025, 12, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Wei, Y.-X.; Lai, K.-M.; He, Z.-D.; Zhang, H.-J. In vivo antifungal activity of dipyrithione against Trichophyton rubrum on guinea pig dermatophytosis models. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudramurthy, S.M.; Shankarnarayan, S.A.; Dogra, S.; Shaw, D.; Mushtaq, K.; Paul, R.A.; Narang, T.; Chakrabarti, A. Mutation in the squalene epoxidase gene of Trichophyton interdigitale and Trichophyton rubrum associated with allylamine resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02522-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, B.K.; Asawa, S.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dwivedy, K.; Tilak, R.; Dubey, N.K. In vitro and in situ efficacy of Cymbopogon khasans sobti, Cyperus scariosus r. Br. and their combination against two important dermatophytes. J. Sci. Res. 2023, 67, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Nanjoh, Y.; Kaneda, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Tsuboi, R. Short-term therapy with luliconazole, a novel topical antifungal imidazole, in guinea pig models of tinea corporis and tinea pedis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3138–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council, N.R. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Flecknell, P.A.; Richardson, C.A.; Popovic, A.; Carpenter, R.E.; Brunson, D.B. Anesthesia and immobilization of small mammals. In Essentials of Small Animal Anesthesia and Analgesia, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2011; pp. 300–325. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, D.; Bharti, S. Luliconazole for the treatment of fungal infections: An evidence-based review. Core Evid. 2014, 9, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalvand, M.; Hashemi, S.J.; Bayat, M. Effect of fluconazole and terbinafine nanoparticles on the treatment of dermatophytosis induced by Trichophyton mentagrophytes in guinea pig. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghate, V.M.; Lewis, S.A.; Prabhu, P.; Dubey, A.; Patel, N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for the topical delivery of tretinoin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezanejad Gatabi, Z.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Saeedi, M. Vitamin K (Menadione)-incorporated chitosan/alginate hydrogel as a novel product for periorbital hyperpigmentation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2024, 35, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Egea, M.; Garcia, M.; Souto, E. Design and ocular tolerance of flurbiprofen loaded ultrasound-engineered NLC. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monod, M.; Feuermann, M.; Yamada, T. Terbinafine and itraconazole resistance in dermatophytes. In Dermatophytes and Dermatophytoses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 415–429. [Google Scholar]
- Niwano, Y.; Tabuchi, T.; Kanai, K.; Hamaguchi, H.; Uchida, K.; Yamaguchi, H. Therapeutic efficacy of lanoconazole ointment in guinea pig model of tinea corporis, a comparative study with ointment and cream preparations. Jpn. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, H. Animal Model for Superficial Mycosis. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 2009, 50, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, L.K.; Oliveira, C.; Ferri, P.H.; Oliveira Júnior, J.G.d.; Souza Júnior, A.H.d.; Fernandes, O.d.F.L.; Silva, M.d.R.R. Antimicrobial activity of Hyptis ovalifolia towards dermatophytes. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2003, 98, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Siddiqui, N. Antifungal activity of some essential oil isolates. Pharmazie 1992, 47, 467–468. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, K. Surfactants and percutaneous absorption. Predict. Percutaneous Penetration 1990, 1, 148–162. [Google Scholar]
- Songkro, S. An overview of skin penetration enhancers: Penetration enhancing activity, skin irritation potential and mechanism of action. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 31, 299–321. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Akbari, J.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Ahmadi, F.; Mojaveri, M.R.; Ahmadipour, S.; Hashemi, S.M.H. Green formulation of Menadione-loaded niosome as a skin-lightening preparation: In vitro/In vivo safety evaluation on Wistar rat. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 14, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansagra, H.; Mallick, S. Microemulsion-based antifungal gel of luliconazole for dermatophyte infections: Formulation, characterization and efficacy studies. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 46, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Shanthi, N.; Mahato, A.K.; Soni, S.; Rajnikanth, P. Preparation of luliconazole nanocrystals loaded hydrogel for improvement of dissolution and antifungal activity. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebrahimi Barogh, R.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Nosratabadi, M.; Maleki, A.; Khosravi Ebrahimi, F.; Yahyazade, Z.; Haghani, I.; Ebrahimnejad, P.; Saeedi, M.; Armstrong-James, D.; et al. Antifungal Efficacy of Luliconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid-Carrier Gel in an Animal Model of Dermatophytosis. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040324
Ebrahimi Barogh R, Rahimnia SM, Nosratabadi M, Maleki A, Khosravi Ebrahimi F, Yahyazade Z, Haghani I, Ebrahimnejad P, Saeedi M, Armstrong-James D, et al. Antifungal Efficacy of Luliconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid-Carrier Gel in an Animal Model of Dermatophytosis. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(4):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040324
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbrahimi Barogh, Robab, Seyyed Mobin Rahimnia, Mohsen Nosratabadi, Abolfazl Maleki, Fatemeh Khosravi Ebrahimi, Zahra Yahyazade, Iman Haghani, Pedram Ebrahimnejad, Majid Saeedi, Darius Armstrong-James, and et al. 2025. "Antifungal Efficacy of Luliconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid-Carrier Gel in an Animal Model of Dermatophytosis" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 4: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040324
APA StyleEbrahimi Barogh, R., Rahimnia, S. M., Nosratabadi, M., Maleki, A., Khosravi Ebrahimi, F., Yahyazade, Z., Haghani, I., Ebrahimnejad, P., Saeedi, M., Armstrong-James, D., Abastabar, M., & Badali, H. (2025). Antifungal Efficacy of Luliconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid-Carrier Gel in an Animal Model of Dermatophytosis. Journal of Fungi, 11(4), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040324








