Direct Visualization of Fungal Burden in Filamentous Fungus-Infected Silkworms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Media, and Culture Conditions
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Animal Model of Infection
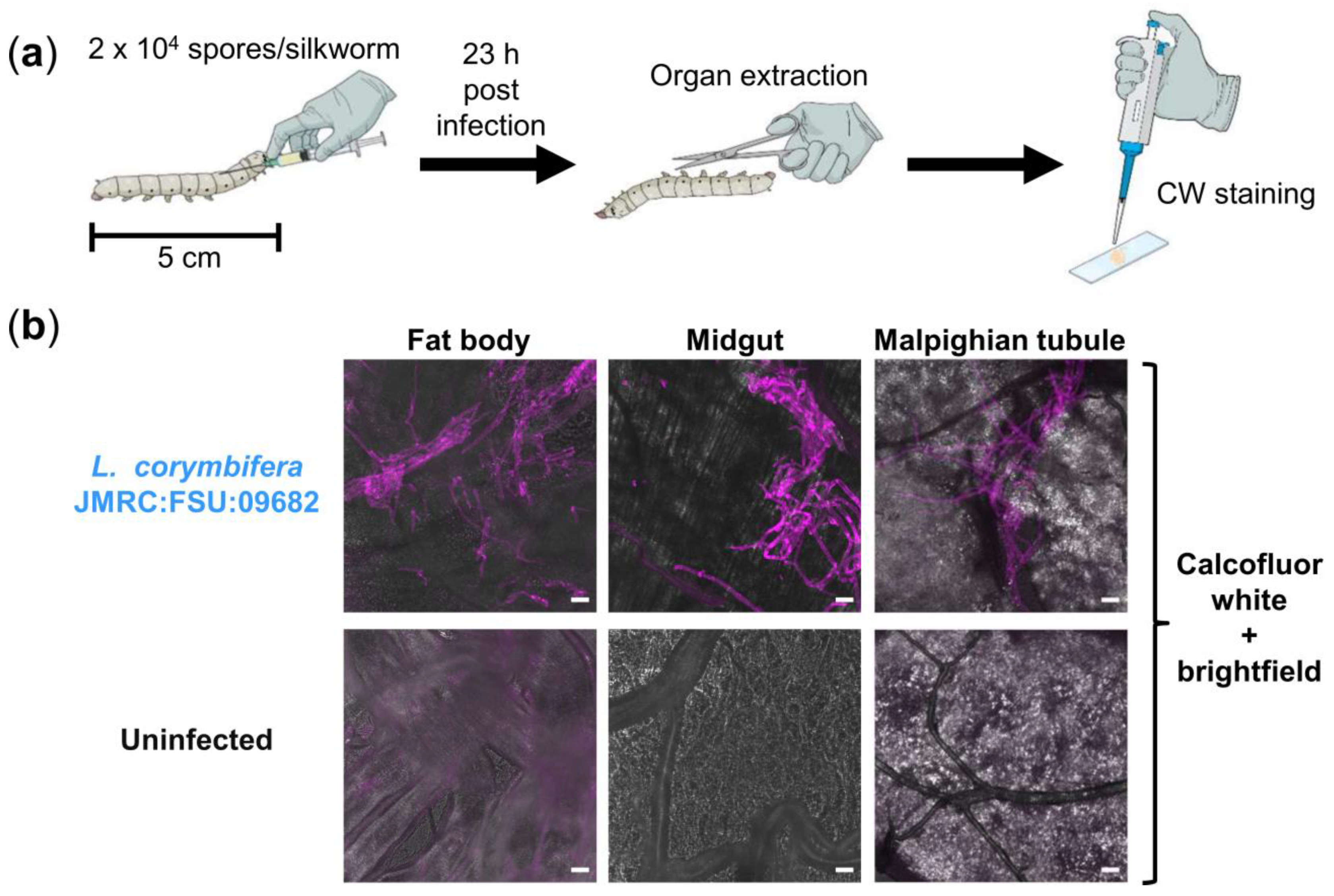
2.4. Visualization of Fungal Growth in Silkworm Hemolymph and Organs
2.5. Antifungal Treatment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of a Silkworm Aspergillus Fumigatus Infection Model to Generate a Robust and Fast In Vivo Read-Out System
3.2. Calcofluor White (CW) Staining Reveals Fungal Burden in Infected Silkworms
3.3. Macroscopical and Microscopical Virulence Comparison of Distinct A. fumigatus Strains
3.4. Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Conventional Antifungals in Silkworms at 34 °C
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden Killers: Human Fungal Infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 165rv113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Köhler, J.R.; Hube, B.; Puccia, R.; Casadevall, A.; Perfect, J.R. Fungi that Infect Humans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, FUNK-0014-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases-Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauwvlieghe, A.F.A.D.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Philips, N.; Verwijs, R.; Vanderbeke, L.; Van Tienen, C.; Lagrou, K.; Verweij, P.E.; Van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Gommers, D.; et al. Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit with Severe Influenza: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnders, B.J.A.; Schauwvlieghe, A.F.A.D.; Wauters, J. Influenza-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Local or Global Lethal Combination? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1764–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xing, X. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Immunocompetent Patients Hospitalised with Influenza A-Related Pneumonia: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmer, T.; Rasch, S.; Spinner, C.; Geisler, F.; Schmid, R.M.; Huber, W. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1428–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanio, A.; Dellière, S.; Fodil, S.; Bretagne, S.; Mégarbane, B. Prevalence of Putative Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e48–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaize, M.; Mayaux, J.; Nabet, C.; Lampros, A.; Marcelin, A.G.; Thellier, M.; Piarroux, R.; Demoule, A.; Fekkar, A. Fatal Invasive Aspergillosis and Coronavirus Disease in an Immunocompetent Patient. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1636–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Arkel, A.L.E.; Rijpstra, T.A.; Belderbos, H.N.A.; van Wijngaarden, P.; Verweij, P.E.; Bentvelsen, R.G. COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2020, 202, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; Wagener, J.; Einsele, H.; Cornely, O.A.; Kurzai, O. Invasive Fungal Infection: New Treatments to Meet New Challenges. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2019, 116, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Moradabadi, A.; Chegini, Z.; Khoshbayan, A.; Didehdar, M. An Overview of the Management of the Most Important Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Blood Malignancies. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2329–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitis, M.; Glavis-Bloom, J.; Mylonakis, E. Invertebrate Models of Fungal Infection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1832, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Sekimizu, K. Silkworm as an Experimental Animal for Research on Fungal Infections. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, N.; Softley, I.; Balfour, A.; Williamson, C.; O’Brien, H.E.; Shetty, A.C.; Bruno, V.M.; Diezmann, S. Tobacco Hornworm (Manduca sexta) Caterpillars as a Novel Host Model for the Study of Fungal Virulence and Drug Efficacy. Virulence 2020, 11, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, H.; Tonoike, A.; Narushima, K.; Horie, R.; Sekimizu, K. Silkworm as a Model Animal to Evaluate Drug Candidate Toxicity and Metabolism. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Panthee, S.; Urai, M.; Hamamoto, H.; Ohwada, T.; Sekimizu, K. Pharmacokinetic Parameters Explain the Therapeutic Activity of Antimicrobial Agents in a Silkworm Infection Model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panthee, S.; Paudel, A.; Hamamoto, H.; Sekimizu, K. Advantages of the Silkworm as an Animal Model for Developing Novel Antimicrobial Agents. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Yamasaki, Y.; Tateyama, Y.; Yamada, T.; Sugita, T. A Novel Silkworm Infection Model with Fluorescence Imaging Using Transgenic Trichosporon asahii Expressing eGFP. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, N.; Takano, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Fugo, H.; Uehara, Y.; Niimi, M. Identification of the Putative Protein Phosphatase Gene Ptc1 as a Virulence-Related Gene Using a Silkworm Model of Candida albicans Infection. Eukaryot. Cell. 2008, 7, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, I.; Kanasaki, R.; Yoshikawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Fujie, A.; Hamamoto, H.; Sekimizu, K. Discovery of a New Antifungal Agent Asp2397 Using a Silkworm Model of Aspergillus fumigatus Infection. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammen, M.P.; Armas, D.; Hughes, F.H.; Hopkins, A.M.; Fisher, C.L.; Resch, P.A.; Rusalov, D.; Sullivan, S.M.; Smith, L.R. First-in-Human Phase 1 Study to Assess Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of a Novel Antifungal Drug, VL-2397, in Healthy Adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00969-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yamada, T.; Abe, S.; Sekimizu, K. An Invertebrate Infection Model for Evaluating Anti-Fungal Agents against Dermatophytosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, J.A.; Gaikwad, Y.B.; Chougale, A.K.; Bhawane, G.P. Curative Effect of Ethanolic Plant Extractives against Beauveria bassiana Infection in Silkworm, Bombyx mori l.: Histopathological Observations on Midgut. Int. J. Anim. Biol. 2015, 1, 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.F.C.; Tavares, J.; Silva, S.A.V.; Alvez, L.F.A.; Loth, E.A.; Brancalhão, R.M.C. Infection of Silkworm Larvae by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Ciência Rural. 2017, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darken, M.A. Applications of Fluorescent Brighteners in Biological Techniques. Science 1961, 133, 1704–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.R.; Käfer, E. Aspergillus Nidulan-an Organism for Detecting a Range of Genetic Damage. In Chemical Mutagens; de Serres, F.J., Hollaender, A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 447–479. [Google Scholar]
- Punt, P.J.; van den Hondel, C.A. Transformation of Filamentous Fungi Based on Hygromycin B and Phleomycin Resistance Markers. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 216, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubodera, T.; Yamashita, N.; Nishimura, A. Pyrithiamine Resistance Gene (ptrA) of Aspergillus oryzae: Cloning, Characterization and Application as a Dominant Selectable Marker for Transformation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartze, V.U.; Hoffmann, K.; Nyilasi, I.; Papp, T.; Vágvölgyi, C.; de Hoog, S.; Voigt, K.; Jacobsen, I.D. Lichtheimia Species Exhibit Differences in Virulence Potential. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraibooj, K.; Park, H.R.; Dahse, H.M.; Skerka, C.; Voigt, K.; Figge, M.T. Virulent Strain of Lichtheimia corymbifera Shows Increased Phagocytosis by Macrophages as Revealed by Automated Microscopy Image Analysis. Mycoses 2014, 57, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brady, D.; Saviane, A.; Romoli, O.; Tettamanti, G.; Sandrelli, F.; Cappellozza, S. Oral Infection In A Germ-Free Bombyx mori Model. In Immunity in Insects; Sandrelli, F., Tettamanti, G., Eds.; Springer Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 217–231. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, D.R.; Clark, K.D. Bombyx mori and Aedes aegypti form Multi-Functional Immune Complexes that Integrate Pattern Recognition, Melanization, Coagulants, and Hemocyte Recruitment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.D.; Lu, Z.; Strand, M.R. Regulation of Melanization by Glutathione in the Moth Pseudoplusia includens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, S. Theory of the Growth of Silkworm Larvae and Its Application. JARQ 1982, 15, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Fraczek, M.G.; Bromley, M.; Buied, A.; Moore, C.B.; Rajendran, R.; Rautemaa, R.; Ramage, G.; Denning, D.W.; Bowyer, P. The cdr1B Efflux Transporter is Associated with Non-Cyp51a-Mediated Itraconazole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Hoffmann, K.; de Hoog, G.S.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Voigt, K.; Bibashi, E.; Walther, G. Species Recognition and Clinical Relevance of the Zygomycetous genus Lichtheimia (syn. Absidia pro parte, Mycocladus). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2154–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajiwara, H.; Itou, Y.; Imamaki, A.; Nakamura, M.; Mita, K.; Ishizaka, M. Proteomic Analysis of Silkworm Fat Body. J. Insect. Biotechnol. Sericol. 2006, 75, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto, H.; Horie, R.; Sekimizu, K. Pharmacokinetics of Anti-Infectious Reagents in Silkworms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; van Rhijn, N.; Fraczek, M.; Gsaller, F.; Davies, E.; Carr, P.; Gago, S.; Fortune-Grant, R.; Rahman, S.; Gilsenan, J.M.; et al. The Negative Cofactor 2 Complex is a Key Regulator of Drug Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Rhijn, N.; Furukawa, T.; Khan, S.; Papastamoulis, P.; Fortune-Grant, R.; Rattray, M.; Bromley, M.; Bignell, E. Genetically Distinct Transcriptional Circuits Drive Stress-Adaptation and Host Cytotoxicity in the Major Mould Pathogen of the Human Lung. In Proceedings of the 9th Advances Against Aspergillosis and Mucormycosis Conference (AAAM 2020), Lugano, Switzerland, 27–29 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, C.; Colabardini, A.C.; Chiaratto, J.; Pardeshi, L.; de Castro, P.A.; Ferreira Filho, J.A.; Silva, L.P.; Rocha, M.C.; Malavazi, I.; Costa, J.H.; et al. Aspergillus fumigatus Transcription Factors Involved in The Caspofungin Paradoxical Effect. mBio 2020, 11, e00816-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, L.N.A.; Pardeshi, L.; Dong, Z.; Tan, K.; Steenwyk, J.L.; Colabardini, A.C.; Ferreira Filho, J.A.; de Castro, P.A.; Silva, L.P.; Preite, N.W.; et al. The Aspergillus fumigatus Transcription Factor RglT is Important for Gliotoxin Biosynthesis and Self-Protection, and Virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, D.; Miura, D.; Shimizu, K.; Paul, S.; Ohba, A.; Gonoi, T.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K.; Shintani, T.; Moye-Rowley, W.S.; et al. A Novel Zn2-Cys6 Transcription Factor AtrR Plays a Key Role in an Azole Resistance Mechanism of Aspergillus fumigatus by Co-Regulating Cyp51a and Cdr1b Expressions. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrettl, M.; Beckmann, N.; Varga, J.; Heinekamp, T.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Jöchl, C.; Moussa, T.A.; Wang, S.; Gsaller, F.; Blatzer, M.; et al. HapX-Mediated Adaption to Iron Starvation is Crucial for Virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Gravelat, F.N.; Chiang, L.Y.; Chen, D.; Vanier, G.; Ejzykowicz, D.E.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Nierman, W.C.; Sheppard, D.C.; Filler, S.G. Aspergillus fumigatus Acum Regulates Both Iron Acquisition and Gluconeogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, M.C.; Fabri, J.H.; Franco de Godoy, K.; Alves de Castro, P.; Hori, J.I.; Ferreira da Cunha, A.; Arentshorst, M.; Ram, A.F.; van den Hondel, C.A.; Goldman, G.H.; et al. Aspergillus fumigatus MADS-Box Transcription Factor rlmA is Required for Regulation of the Cell Wall Integrity and Virulence. G3 (Bethesda) 2016, 6, 2983–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cramer, R.A.J.; Perfect, B.Z.; Pinchai, N.; Park, S.; Perlin, D.S.; Asfaw, Y.G.; Heitman, J.; Perfect, J.R.; Steinbach, W.J. Calcineurin Target CrzA Regulates Conidial Germination, Hyphal Growth, and Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bok, J.W.; Chung, D.; Balajee, S.A.; Marr, K.A.; Andes, D.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frisvad, J.C.; Kirby, K.A.; Keller, N.P. GliZ, a Transcriptional Regulator of Gliotoxin Biosynthesis, Contributes to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6761–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugui, J.A.; Pardo, J.; Chang, Y.C.; Zarember, K.A.; Nardone, G.; Galvez, E.M.; Müllbacher, A.; Gallin, J.I.; Simon, M.M.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. Gliotoxin is a Virulence Factor of Aspergillus fumigatus: gliP Deletion Attenuates Virulence in Mice Immunosuppressed with Hydrocortisone. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriani, F.M.; Malavazi, I.; da Silva Ferreira, M.E.; Savoldi, M.; Von Zeska Kress, M.R.; de Souza Goldman, M.H.; Loss, O.; Bignell, E.; Goldman, G.H. Functional Characterization of the Aspergillus fumigatus CRZ1 Homologue, CrzA. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 1274–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Cuesta, I.; Walther, G.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L. Antifungal Susceptibility Profile of Human-Pathogenic Species of Lichtheimia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3058–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawamoto, M.; Jouraku, A.; Toyoda, A.; Yokoi, K.; Minakuchi, Y.; Katsuma, S.; Fujiyama, A.; Kiuchi, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Shimada, T. High-Quality Genome Assembly of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 107, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorjão, A.L.; Oliveira, L.D.; Scorzoni, L.; Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.A.; Cristina, A.P.M.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Junqueira, J.C. From Moths to Caterpillars: Ideal Conditions for Galleria mellonella Rearing for in Vivo Microbiological Studies. Virulence 2018, 9, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Fukunaga, D.H.; Shimizu, K.; Kawamoto, S.; Sekimizu, K. Quantitative Evaluation of Cryptococcal Pathogenesis and Antifungal Drugs Using a Silkworm Infection Model with Cryptococcus neoformans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monod, M.; Paris, S.; Sarfati, J.; Jaton-Ogay, K.; Ave, P.; Latgé, J.P. Virulence of Alkaline Protease-Deficient Mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1993, 106, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierman, W.C.; Pain, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Arroyo, J.; Berriman, M.; Abe, K.; Archer, D.B.; Bermejo, C.; et al. Genomic Sequence of the Pathogenic and Allergenic Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 2005, 438, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staib, F.; Mishra, S.K.; Rajendran, C.; Voigt, R.; Steffen, J.; Neumann, K.H.; Hartmann, C.A.; Heins, G. A Notable Aspergillus from a Mortal Aspergilloma of the Lung. New Aspects of the Epidemiology, Serodiagnosis and Taxonomy of Aspergillus fumigatus. Zent. Bakteriol. Abt. Orig. Med. Mikrobiol. Infekt. Parasitol. 1980, 247, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, V.M.; Mackenzie, D.W. Mycelial Antigens from Two Strains of Aspergillus fumigatus: An Analysis by Two-Dimensional Immunoelectrophoresis. Mycoses 1980, 23, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuzzi, M.; van Rhijn, N.; Krappmann, S.; Bowyer, P.; Bromley, M.J.; Bignell, E.M. On the Lineage of Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates in Common Laboratory Use. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, C.H.; Beattie, S.R.; Fuller, K.K.; McGurk, E.A.; Tang, Y.W.; Hohl, T.M.; Obar, J.J.; Cramer, R.A.J. Heterogeneity among Isolates Reveals that Fitness in Low Oxygen Correlates with Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence. mBio 2016, 7, e01515–e01516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, K.K.; Cramer, R.A.; Zegans, M.E.; Dunlap, J.C.; Loros, J.J. Aspergillus fumigatus Photobiology Illuminates the Marked Heterogeneity between Isolates. mBio 2016, 7, e01517-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kingsbury, J.M.; Heitman, J.; Pinnell, S.R. Calcofluor White Combination Antifungal Treatments for Trichophyton rubrum and Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singara Charya, M.A. Fungi: An Overview. In Plant Biology and Biotechnology; Bahadur, B., Venkat Rajam, M., Sahijram, L., Krishnamurthy, K., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 197–215. [Google Scholar]
- Renwick, J.; Reeves, E.P.; Wientjes, F.B.; Kavanagh, K. Translocation of Proteins Homologous to Human Neutrophil P47phox and P67phox to the Cell Membrane in Activated Hemocytes of Galleria mellonella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyrsl, P.; Cíz, M.; Kubala, L.; Lojek, A. Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Hemocytes Do Not Produce Reactive Oxygen Metabolites as a Part of Defense Mechanisms. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2004, 49, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Hamamoto, H.; Kamimura, M.; Sekimizu, K. Activation of the Silkworm Cytokine by Bacterial and Fungal Cell Wall Components via a Reactive Oxygen Species-Triggered Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laniado-Laborin, R.; Cabrales-Vargas, M.N. Amphotericin B: Side Effects and Toxicity. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2009, 26, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Lewis, R.E. How I Treat Mucormycosis. Blood 2011, 118, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekersky, I.; Fielding, R.M.; Dressler, D.E.; Lee, J.W.; Buell, D.N.; Walsh, T.J. Pharmacokinetics, Excretion, and Mass Balance of Liposomal Amphotericin B (AmBisome) and Amphotericin B Deoxycholate in Humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Knockout Gene ID | Generic Name | Virulence in Silkworm Model (Compared to WT *) | Data from Mouse Infection Models (with References) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virulence in Mouse Model (Compared to WT *) | Mouse Model | Infectious Dose | |||
| AFUB_030360 | hapB | Strongly attenuated | Strongly attenuated [41] | Leukopenic | Unknown |
| AFUB_014000 | - | Attenuated | Attenuated [41] | ||
| AFUB_026340 | rfeC | Attenuated | Slightly attenuated [41] | ||
| AFUB_009970 | cbfA | Slightly attenuated | Unchanged [42] | IN, 1 × 105 | |
| AFUB_058240 | nctC | Slightly attenuated | Avirulent [42] | ||
| AFUB_091020 | fhdA | Slightly attenuated | Unchanged [42] | ||
| AFUB_008610 | rglT | Slightly attenuated | Strongly attenuated [43] | ||
| AFUB_029870 | nctA | Unchanged | Unchanged [40] | Leukopenic | IN, 5 × 105 |
| Non-neutropenic | IN, 7 × 106 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Wolf, A.-K.; Thusek, S.; Heinekamp, T.; Bromley, M.; Krappmann, S.; Terpitz, U.; Voigt, K.; Brakhage, A.A.; Beilhack, A. Direct Visualization of Fungal Burden in Filamentous Fungus-Infected Silkworms. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020136
Yu Y, Wolf A-K, Thusek S, Heinekamp T, Bromley M, Krappmann S, Terpitz U, Voigt K, Brakhage AA, Beilhack A. Direct Visualization of Fungal Burden in Filamentous Fungus-Infected Silkworms. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(2):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020136
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yidong, Ann-Katrin Wolf, Sina Thusek, Thorsten Heinekamp, Michael Bromley, Sven Krappmann, Ulrich Terpitz, Kerstin Voigt, Axel A. Brakhage, and Andreas Beilhack. 2021. "Direct Visualization of Fungal Burden in Filamentous Fungus-Infected Silkworms" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 2: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020136
APA StyleYu, Y., Wolf, A.-K., Thusek, S., Heinekamp, T., Bromley, M., Krappmann, S., Terpitz, U., Voigt, K., Brakhage, A. A., & Beilhack, A. (2021). Direct Visualization of Fungal Burden in Filamentous Fungus-Infected Silkworms. Journal of Fungi, 7(2), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020136









