Abstract
Pythium insidiosum causes pythiosis, a fatal infectious disease of humans and animals worldwide. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to improve the clinical outcome of pythiosis. Diagnosis of P. insidiosum relies on immunological, molecular, and proteomic assays. The main treatment of pythiosis aims to surgically remove all affected tissue to prevent recurrent infection. Due to the marked increase in case reports, pythiosis has become a public health concern. Thailand is an endemic area of human pythiosis. To obtain a complete picture of how the pathogen circulates in the environment, we surveyed the presence of P. insidiosum in urban (Bangkok) and rural areas of Thailand. We employed the hair-baiting technique to screen for P. insidiosum in 500 water samples. Twenty-seven culture-positive samples were identified as P. insidiosum by multiplex PCR, multi-DNA barcode (rDNA, cox1, cox2), and mass spectrometric analyses. These environmental strains of P. insidiosum fell into Clade-II and -III genotypes and exhibited a close phylogenetic/proteomic relationship with Thai clinical strains. Biodiversity of the environmental strains also existed in a local habitat. In conclusion, P. insidiosum is widespread in Thailand. A better understanding of the ecological niche of P. insidiosum could lead to the effective prevention and control of this pathogen.
1. Introduction
Pythium insidiosum is a unique pathogenic oomycete that causes the devastating infectious condition, termed “pythiosis”, predominantly in humans, horses, and dogs [1,2,3,4]. The disease is prevalent in tropical and subtropical countries. Affected individuals usually present with an infection of the skin, eye, artery, or internal organ [1,2,3,4]. The pathogenesis mechanism of P. insidiosum has begun to be better understood through genomic and transcriptomic analyses [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Pythiosis possesses a high morbidity and mortality rate, as it is difficult to diagnose and treat the disease. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to improve the clinical outcome of a pythiosis patient. The definitive diagnosis of P. insidiosum cannot rely on the microbiological findings (i.e., colony morphology and zoospore), but requires an immunological [i.e., immunodiffusion, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and immunochromatography], molecular (i.e., sequence homology, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), or proteomic [i.e., matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MALDI-TOF MS)] assay [3,4,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Such the diagnostic tests are not widely available in the clinical laboratories, leading to the delayed diagnosis. Although the antifungal drugs are generally ineffective against the P. insidiosum infection due to the lack of drug-target ergosterol biosynthesis enzymes, success stories of antimicrobial drug use have been occasionally reported [2,4,26,27]. In most cases, the treatment of pythiosis aims to surgically remove all infected tissue [1,2,3,4]. However, a post-surgical recurrent infection is not uncommon due to residual infected tissues [2,4]. Vaccine immunotherapy has been used in the treatment of pythiosis, but it shows limited efficacy [2,4].
Thailand is an endemic area of human pythiosis, and the most affected individuals are farmers [2,4]. Human pythiosis is associated with several hematological disorders (especially thalassemia), in which the underlying mechanism is unknown [2,4,28]. Several case series of human pythiosis (mainly ocular infection) were recently reported from India [29,30,31]. Pythiosis in animals (i.e., horses and dogs) has been mostly diagnosed in other countries, especially Brazil and the United States [1,3,32]. Due to the marked increase in case reports, pythiosis has become a public health concern. As a part of its life cycle, P. insidiosum produces an infective unit, called biflagellate zoospore, in water [33]. Plant materials and animal hairs can attract the organism [34,35,36]. When a swimming zoospore comes in direct contact with an individual, it germinates as hyphae and causes tissue pathology [33,34]. Better understanding the ecological niche of P. insidiosum could lead to the effective prevention and control of this pathogen, especially for those individuals at risk.
Several investigators can isolate P. insidiosum from agricultural or non-residential areas in northern Thailand, Australia, the United States, and Brazil [34,35,36,37,38,39]. To obtain a complete picture of how the pathogen circulates in the environment, we aim to survey the presence of P. insidiosum in a crowded city like Bangkok, as well as rural areas of central and southern Thailand. We employed the hair-baiting technique to isolate P. insidiosum from 500 water samples. Colony morphology was used as a high-throughput screening method, and the culture-positive samples were confirmed by several molecular assays, including multiplex PCR, multi-DNA barcode, and proteomic analyses [4,19,23,40,41,42,43]. We successfully isolated P. insidiosum from Bangkok and other provinces, in which some areas had a notably-high prevalence of the organism. We explored biodiversity, proteomic feature, and phylogenetic relationship of the environmental and clinical strains of P. insidiosum and proposed the use of multi-DNA barcodes for the identification of this pathogen.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Culture Condition
A total of 500 water samples were collected from 100 sample-collection sites in 23 sampling locations (i.e., zoo, public parks, rice fields, and ponds) across 7 provinces of Thailand, which included Bangkok (10 locations; 48 sites; 240 samples), Chonburi (1 location; 3 sites; 15 samples), Chachoengsao (3 locations; 8 sites; 40 samples), Nakhon Pathom (1 location; 12 sites; 60 samples), Kanchanaburi (3 locations; 11 sites; 55 samples), Ratchaburi (4 locations; 13 sites; 65 samples), and Trang (1 location; 5 sites; 25 samples) (Table 1). Five water samples (500 mL/sample) were collected from each sample-collection site using a clean disposable plastic bucket (sampling position: 50–100 cm away from the bank; 5–10 cm depth from the water surface). Each water sample was transferred to a sterile plastic bag containing 5–10 autoclaved 10-cm-long human hairs and left at the ambient temperature overnight. The hairs were removed from the bag by sterile forceps and incubated on Sabouraud dextrose agar (pH 7.2) supplemented with penicillin and streptomycin (100 µg/mL each; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 25 °C for 5 days. A growing, submerged, white-to-colorless colony, which is compatible with P. insidiosum, was subculture onto a freshly-prepared Sabouraud dextrose agar (with or without an overlayed sterile cellophane membrane) and subject to the downstream genomic DNA (gDNA) extraction.

Table 1.
Water sampling locations in central and southern Thailand. The global positioning system (GPS) coordinates, type of water collection sites, number of sites and water samples, and identified organisms are shown in the table.
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
Up to 200 mg of an obtained colony were harvested for gDNA extraction by adapting the salt extraction protocol described by Lohnoo et al. [21]. A hyphal mat was transferred to a 2-mL sterile plastic screw-cap tube containing 1000 mg of glass beads (710–1180 mm in diameter; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and combined with the salt homogenizing buffer (0.4 M NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, and 2 mM EDTA; 400 μL buffer per 100 mg hyphae). To remove carry-over culture agar from the harvested hyphae, the sample tube was boiled at 100 °C for 5 min. The hyphal mat was ruptured by a Tissue Lyzer Retsch MM301 (setting: 2 min at 30 Hz; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and mixed with 45 μL of 20% SDS and 8 μL of 20 mg/mL proteinase K, before an overnight incubation at 56 °C. After well-mixed with 0.3 mL of 6 M NaCl, the sample was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 30 min. The supernatant was collected, combined with an equal volume of isopropanol, stored at −20 °C for 1 h, and centrifuged (10,000× g) at 4 °C for 20 min. After discarding the supernatant, a resulting pellet was collected, washed with 70% ethanol, air dried, and resuspended in 100 μL of Tris-EDTA (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA; pH 8.0). A NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer estimated DNA concentration at 260/280 nm wavelengths (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Multiplex PCR for Identification and Genotyping of P. insidiosum
The established multiplex PCR assay targeting the rDNA sequence was used to identify and genotype P. insidiosum [23]. A 25-μL PCR reaction comprised 50 ng of gDNA template, 0.1 µM of the primer ITS1 (5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3’), 0.07 µM each of the primers R1 (5′-CCTCACATTCTGCCATCTCG-3′), R2 (5′-ATACCGCCAATAGAGGTCAT-3′) and R3 (5′-TTACCCGAAGGCGTCAAAGA-3′), 0.2 mM dNTP, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.65 U Taq polymerase (Thermo Scientific), and 1× buffer with KCl. The reaction was carried out with the following thermal cycling condition: the initial 95 °C denaturation for 5 min, 30 cycles of 95 °C denaturation for 30 s, 59 °C annealing for 30 s and 72 °C extension for 45 s, and the final 72 °C extension for 10 min. The resulting amplicons were assessed for amplicon sizes, using the capillary electrophoresis-based QIAxcel advanced system, DNA screening kit (method AM320), 15–5000 bp alignment markers, and QIAxcel screen gel software (Qiagen). The presence of the 490- and 660-bp (Clade-I genotype), 660-bp (Clade-II genotype), or 800-bp (Clade-III genotype) band(s) indicates P. insidiosum.
2.4. Species Identification by DNA Barcode Analysis
All extracted gDNA samples were recruited for species identification using the rDNA sequence (i.e., the ITS1–5.8S-ITS2 region) as the primary DNA barcode. PCR amplification was carried out in a 50-μL reaction containing 50 ng gDNA template, the universal fungal primers [0.1 µM each of ITS1 and ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′)] [40], 0.2 mM dNTP, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.65 U Taq polymerase (Thermo Scientific), and 1× buffer with KCl. The thermal cycle program included the initial 95 °C denaturation for 5 min, 30 cycles of 95 °C denaturation for 30 s, 55 °C annealing for 30 s, and 72 °C extension for 30 s, and the final 72 °C extension for 10 min.
The secondary DNA barcode sequences (i.e., cox1 and cox2) were also amplified from gDNA samples of P. insidiosum and another Pythium spp. A PCR amplification was set up in a 50-μL reaction, containing 100 ng gDNA template, the oomycete-specific cox1 primers [0.2 μM each of OomCox-I_Levup (5′-TCAWCWMGATGGCTTTTTTCAAC-3′) and OomCox-I_Levlo (5′-CYTCHGGRTGWCCRAAAAACCAAA-3′)] [42] or cox2 primers [0.4 μM each of FM58 (5′-CCACAAATTTCACTACATTGA-3′) and FM66 (5′-TAGGATTTCAAGATCCTGC-3′)] [41], 0.2 mM dNTP, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1.25 U Taq DNA polymerase (Thermo Scientific), and 1× buffer with KCl. The thermal cycle settings included the initial 94 °C denaturation for 5 min, 30 (cox1) or 35 (cox2) cycles of 94 °C denaturation for 30 (cox1) or 60 (cox2) s, 52 °C annealing for 30 (cox1) or 60 (cox2) s, and 72 °C extension for 45 (cox1) or 60 (cox2) s, and the final extension at 72 °C for 10 min.
All PCR products were checked using the QIAxcel advanced system (as mentioned above). The PCR products were cleaned using a PCR purification kit (Qiagen) and sequenced using a corresponding primer set, such as ITS1/ITS4 (rDNA), OomCox-I_Levup/OomCox-I_Levlo (cox1), and FM58/FM66 (cox2). The obtained sequence was BLAST searched against the NCBI nucleotide database (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi accessed on 16 January 2021). The BLAST search cutoff for species identification was set at 98.5% identity [43].
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
The obtained rDNA, cox1, and cox2 sequences of each of the P. insidiosum strains and outgroup organisms were concatenated and subject to phylogenetic analysis, using the online bioinformatics tool at (http://www.phylogeny.fr accessed on 16 January 2021) [44]. The “one-click” default setting [44] executed multiple sequence alignment using MUSCLE (v3.8.31) [45], sequence curation using GBlocks (v0.91b) [46], phylogenetic relationship analysis using PhyML (v3.0) [47] and branch assessment using a LRT test [48], and phylogenetic tree construction using TreeDyn (v198.3) [49].
2.6. Mass Spectrometric Analysis and Dendrogram
Selected organisms (i.e., a colony without bacterial contamination) isolated from the environment (i.e., P. insidiosum, Pythium catenulatum, and Pythium rhizo-oryzae) (Table 1 and Table 2), P. insidiosum strain Pi35 isolated from a patient with pythiosis (positive control) and Candida parapsilosis strain ATCC 22019 (negative control) were recruited for MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Each organism was subcultured in a glass Petri dish containing 10 mL Sabouraud dextrose broth and incubated at 37 °C for 5–7 days. Proteins were extracted from these organisms using the established protocol [19] with some modifications. Briefly, a harvested organism (100 mg) was transferred to a sterile microtube, washed 5 times with 1 mL of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) grade water (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA), and centrifuged (16,600× g) at 4 °C for 5 min to remove the supernatant. The organism was mixed with 300 µL of LC-MS grade water before vortexing and adding 900 µL of absolute EtOH (Merck). The sample mixture underwent another round of vortexing, centrifugation, and supernatant removal. A resulting pellet was dried at 37 °C for 30 min and resuspended with equal volumes (up to 100 µL) of 70% formic acid (Merck) and acetonitrile (Merck). The supernatant (containing extracted proteins) was collected by centrifugation and kept at −30 °C until use.

Table 2.
Twenty-seven strains of P. insidiosum successfully isolated from 5 provinces in Thailand. Sampling locations (with GPS coordinates), water sources, strain IDs, sequence homology analyses, and species-level identification and biotyping (based on DNA barcodes, multiplex PCR, and mass spectrometry) are summarized in the Table.
The extracted protein (0.5 µL) was placed on a ground steel target plate (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA, USA) (8 replicates), air-dried, and layered with 0.5 µL of 5 mg/mL α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid in 70% acetonitrile and 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid. An ultrafleXtreme mass spectrometer and the FlexControl software version 3.0 (Bruker Daltonics), using the previously-described setting [19], generated mass spectra from the extracted proteins. The MALDI-TOF MS analysis matched the generated mass spectra of each organism against the supplemented Bruker MALDI Biotyper database DB4613 (Bruker Daltonics), containing the main spectral profiles (MSP) of 4274 bacteria, 331 fungi, 7 archaea, 1 green alga, and 13 P. insidiosum strains [19]. Mass spectrum similarity was transformed into an identification score by the MALDI Biotyper software version 3.0 (Bruker Daltonics). A score of 2.00 or higher indicates a reliable species-level identification, while that fall between 1.70–1.99 indicates a reliable genus-level identification. A lower score (<1.70) means an unreliable organism identification. The MATLAB software version 7.1 (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) generated a dendrogram of all P. insidiosum isolates tested, by using the distance values (for each pair of P. insidiosum MSPs) calculated by the MALDI Biotyper software [19].
2.7. Data Availability
The rDNA, cox1, and cox2 sequences of the P. insidiosum strains used in this study have been deposited in the GenBank/DDBJ databases (see the accession numbers in Table 2 and Table 3). The rDNA, cox1, and cox2 sequences of the P. rhizo-oryzae strain RCB01 (accessions: LC556053, LC553639, and LC553641, respectively) and the P. catenulatum strain RM9-06 (accessions: LC556067, LC553640, and LC553642, respectively), used as an outgroup in the phylogenetic analysis, have been deposited in the same databases.

Table 3.
Twenty-two clinical strains of P. insidiosum used for proteomic and phylogenetic analyses in this study. The table contains strain IDs, reference IDs, affected hosts (i.e., humans or animals), country of origins, mass spectrometry-based prototypes, and GenBank accessions (i.e., rDNA, cox1, and cox2).
3. Results
3.1. Screening the Colony Morphology of P. insidiosum Isolated from Water Samples
Water samples were collected from 100 water collection sites [i.e., rice fields, irrigation channels, and ponds (in a zoo, public recreation parks, and countryside areas); 5 samples/site] in 10 urban (i.e., Bangkok) and 13 rural (i.e., 5 central and 1 southern provinces) sampling locations (Table 1). All 23 locations were depicted in Figure 1 (also available online at https://microreact.org/project/nv2faGXa2rahFjUHKd5QQN access on 16 January 2021 [50]). Human hairs, used to bait P. insidiosum in a water sample, were incubated at room temperature on a Sabouraud agar plate supplemented with the antibacterial agents. From the total of 500 water samples, 446 (89.2%) showed different bacterial growths and various fungal colonies (with or without spores or color pigments), while 54 (10.8%) exhibited no growth on the agar plates. Among them, 64 samples (12.8%) provided a white-to-colorless, non-sporulation, submerged colony, which is compatible with the gross morphology of P. insidiosum. Each suspected P. insidiosum colony was subcultured on a new Sabouraud agar plate for gDNA extraction. The obtained gDNA samples were used for species identification, biotyping, and phylogenetic analysis (see below).
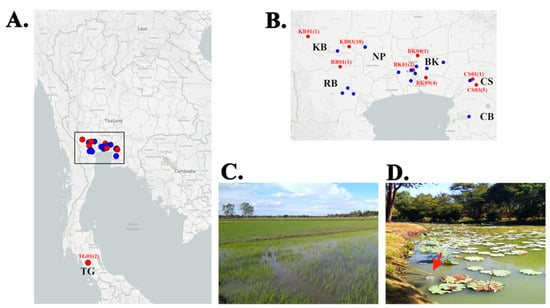
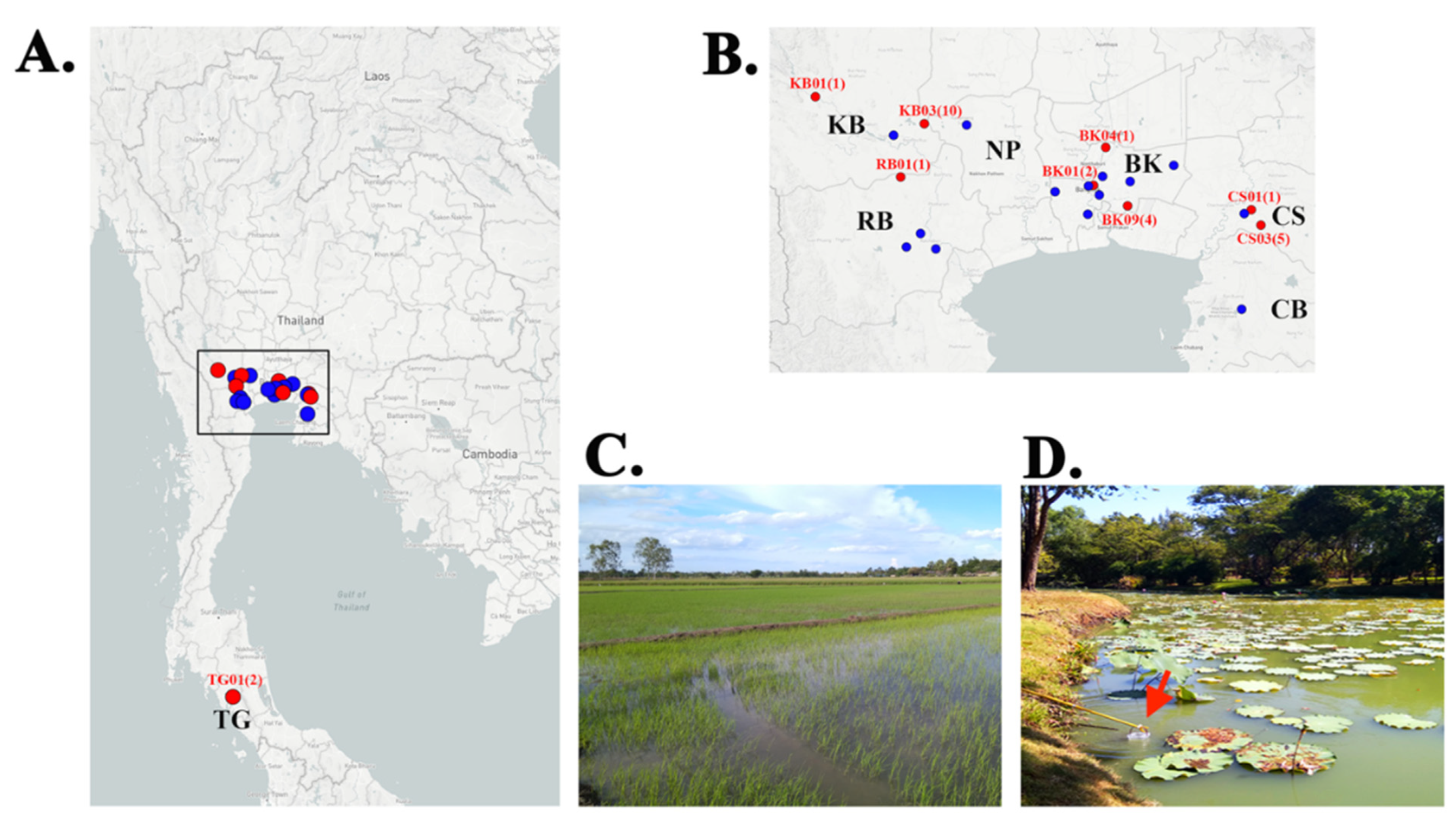
Figure 1.
Geographic distribution of the P. insidiosum-positive locations in Thailand. (A) The map of Thailand shows 23 sampling locations (i.e., zoo, public parks, rice fields, and ponds) across 7 central and southern provinces of Thailand, which include Bangkok (BK; 10 locations: BK01-10), Chonburi (CB; 1 location: CB01), Chachoengsao (CS; 3 locations: CS01-03), Nakhon Pathom (NP; 1 location: NP01), Kanchanaburi (KB; 3 locations: KB01-03), Ratchaburi (RB; 4 locations: RB01-04), and Trang (TG; 1 location: TG01). (B) An enlarged map demonstrates the sampling locations shown in the box in Figure 1A. The P. insidiosum-positive locations (i.e., KB01, BK01, and CS01) are indicated in red. The number in each parenthesis is the number of P. insidiosum strain(s) successfully isolated from the corresponding location. (C) The location KB03 is a rice field, where 10 strains of P. insidiosum (strain IDs: KCB01–CB10) have been isolated. (D) The location BK09 is a pond in a public park in Bangkok, in which 4 strains of P. insidiosum (strain IDs: RM9-02–RM9-05) have been recovered (the arrow indicates a clean disposable plastic bucket used to collect water sample).
3.2. Identification and Genotyping of P. insidiosum by Multiplex PCR and DNA Barcodes
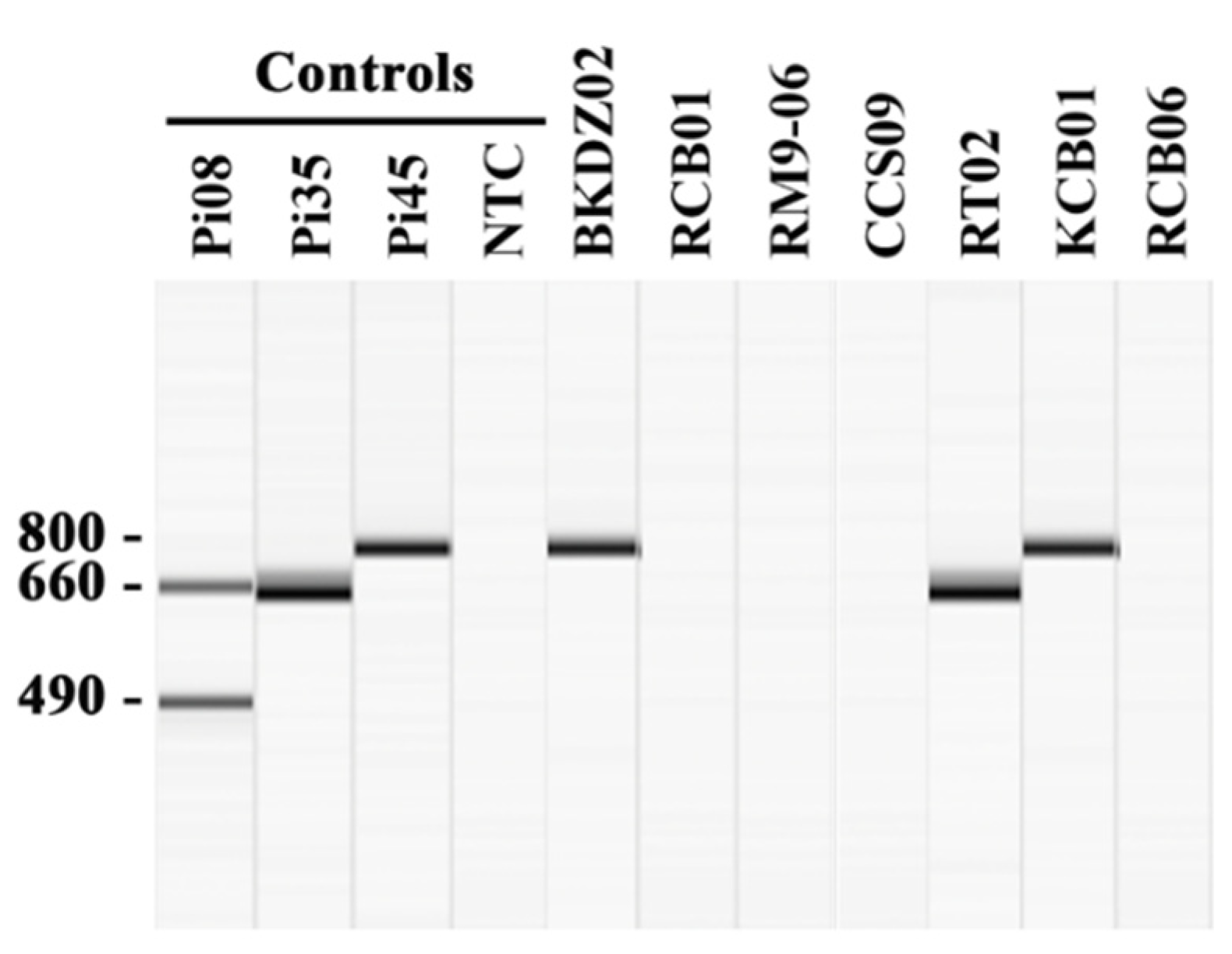
All 64 extracted gDNA samples were initially analyzed by the established P. insidiosum-specific multiplex PCR [23]. The assay can identify and genotype P. insidiosum in 27 samples (Table 2): 70.4% (n = 19) of which provided only the 660-bp band (Clade-II genotype), such as the sample RT02, while the rest, 29.6% (n = 8), provided only the 800-bp band (Clade-III genotype), such as the samples BKDZ02 and KCB01 (Figure 2). The other 37 gDNA samples (i.e., RCB01, RM9-06, CCS-09, and RCB06) provided no PCR product (Figure 2). The species identifications of all samples were then performed by DNA barcode analysis (see below).
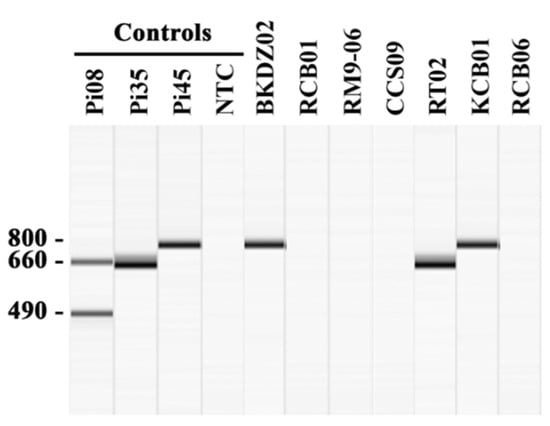
Figure 2.
Identification and genotyping of P. insidiosum by multiplex PCR. The multiplex PCR amplifies the rDNA sequence from a gDNA sample extracted from water-isolated P. insidiosum-suspected colonies. The amplicon sizes are assessed by using the capillary electrophoresis-based QIAxcel advanced system (Qiagen) (see the methods). The positive controls include gDNA samples extracted from P. insidiosum strains Pi08 (Clade-I genotype; amplicons: 490- and 660-bp bands), Pi35 (Clade-II genotype; amplicon: 660-bp band), and Pi45 (Clade-III genotype; amplicon: 800-bp band). The PCR reaction with no gDNA template serves as the negative control [no template control (NTC)]. The multiplex PCR results of 7 randomly-selected P. insidiosum-suspected organisms (IDs: BKDZ02, RCB01, RM9-06, CCS09, RT02, KCB01, and RCB06) are shown in the Figure.
The fungal universal primers ITS1 and ITS4 [40] amplified the primary DNA barcode (rDNA sequence) from all 64 gDNA samples (Table 4). The sequence homology analysis using BLAST search against the GenBank database showed that the best-matched organism was P. insidiosum in 27 samples (5.4% of all 500 water samples), Pythium catenulatum in 16 samples (3.2%), Pythium rhizo-oryzae in 8 samples (1.6%), Pythium inflatum in 1 sample (0.2%), unspecified Pythium species in 5 samples (1.0%), and a fungus (i.e., Sclerotium hydrophilum, Mucor amphibiorum, and Pezizomycetes species) in 3 samples (0.6%) (Table 1). The gDNA samples of 4 organisms (Strain IDs: RT01, CCS06, KCB13, and KCB14; Table 4) repeatedly reported poor-quality sequencing chromatograms and were excluded from the BLAST search analysis. The rDNA sequences of the 27 water-isolated P. insidiosum strains (average length: 850 bp; range: 639-909 bp) showed the average sequence identity of 99.7% (range: 98.0–100.0%) (Table 2). One of these strains (ID: BKDZ02) best matched P. insidiosum at 98.0% identity which was slightly lower than the species-level cutoff value (98.5% identity) [43].

Table 4.
A list of 64 culture-positive samples that show a white-to-colorless, non-sporulation, submerged colony, which is compatible with the gross morphology of P. insidiosum. The table includes sample collection locations and sites, organism identities, strain IDs, percent sequence identities, DNA barcode-based genotypes (i.e., Clade I, II, and III), multiplex PCR results (i.e., positive or negative; Clade I, II, and III), and GenBank accessions of DNA barcodes (i.e., rDNA, cox1, and cox2).
Two secondary DNA barcodes (i.e., cox1 and cox2) were employed for the P. insidiosum identification. The P. insidiosum strain KCB12 was lost, and thus excluded from the cox1 and cox2 barcoding analysis. Two primer pairs (i.e., OomCox-I_Levup/OomCox-I_Levlo [42] and FM58/FM66 [41]) respectively amplified a partial coding sequence of cox1 and cox2 from 26 water-isolated P. insidiosum strains (Table 2). The average sequence lengths of cox1 and cox2 were 690 bp (range: 656–696 bp) and 585 bp (range: 555–586 bp), respectively. BLAST search against the GenBank database best matched P. insidiosum in all 26 samples, with the average sequence identity of 98.1% (range: 94.1–100.0%) for cox1 and 100.0% for cox2 (Table 2). The percent identities of the cox1 sequences from 8 P. insidiosum strains (i.e., BKDZ01, BKDZ02, KCB01, KCB03, KCB04, KCB06, KCB08, and KCB09; mean, 94.3%; range: 94.1–94.4%) fell below the species-level cutoff value (98.5%) (Table 2).
3.3. Geographic Distribution of the P. insidiosum-Positive Water Samples
Twenty-seven P. insidiosum-positive water samples were derived from 9 sampling locations (39.1% of all 23 locations), covering 12 water collection sites (12.0% of all 100 sites), including 4 ponds in a zoo and two public parks (25.9% of all positive samples) in Bangkok metropolis, and 4 ponds (14.8%) and 4 rice fields (59.3%) in 4 countryside provinces (i.e., Kanchanaburi, Chachoengsao, Trang, and Ratchaburi) (Table 1 and Table 2; Figure 1). No P. insidiosum-positive samples were obtained from 2 provinces: Chonburi and Nakhon Pathom. Some P. insidiosum strains were co-isolated from the same water collection site, for example, 10 strains (IDs: KCB01–KCB10) from the Rice field#3 in Kanchanaburi (Figure 1C), 4 strains (IDs: RM9-02–RM9-05) from the Pond#4 in Bangkok (Figure 1D), and 3 strains (IDs: CCS03–CCS05) from the Rice field#1, and 2 strains (IDs: CCS07 and CCS08) from the Rice field#2 in Chachangsao (Table 2).
3.4. Phylogenetic Relationship among the Water-Isolated and Clinical Strains of P. insidiosum
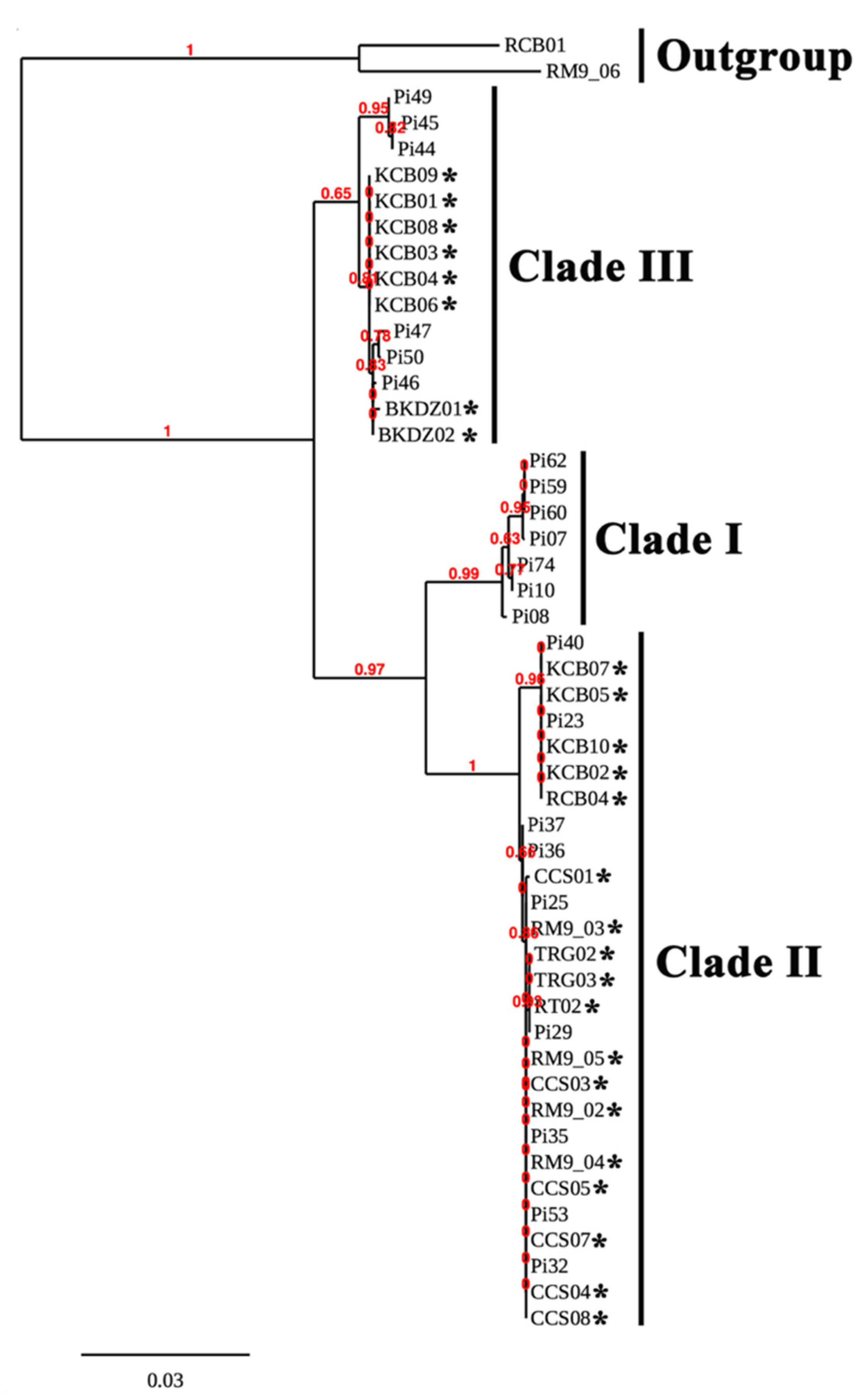
The rDNA, cox1, and cox2 sequences of 26 water-isolated (Table 2) and 22 reference (Table 3) strains of P. insidiosum and 2 outgroup organisms (i.e., P. rhizo-oryzae strain RCB01 and P. catenulatum strain RM9-06) were aligned, trimmed, and concatenated into a 1737 bp-long sequence. These rDNA-cox1-cox2 combined sequences were subject to the construction of a maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic tree (Figure 3). The branch support values were calculated based on the LRT test [48]. The phylogenetic tree divided 48 strains of P. insidiosum into 3 groups: Clade-I, Clade-II, and Clade-III (Figure 3; Table 2 and Table 3). The water-isolated P. insidiosum strains only located in Clade-II (n = 18) and Clade-III (n = 8) genotypes (Figure 3; Table 2). Water from several sample collection sites (i.e., Pond#4, Rice Field#1, Rice Field#2, and Rice Field#3) contained more than one strain of P. insidiosum (Table 2). All 4 P. insidiosum strains (i.e., RM9-02, RM9-03, RM9-04, and RM9-05) isolated from Pond#3 in Bangkok, and 5 P. insidiosum strains isolated from Rice Field#1 (i.e., CCS03, CCS04 and CCS05) and Rice Field#2 (i.e., CCS07 and CCS08) in Chachoengsao province were grouped in Clade-II genotype (Figure 3). On the other hand, 10 P. insidiosum strains isolated from Rice Field#3 in Kanchanaburi province were assigned to both Clade-II (i.e., strains KCB02, KCB05, KCB07 and KCB10) and Clade-III (i.e., strains KCB01, KCB03, KCB04, KCB06, KCB08 and KCB09) genotypes (Figure 3).
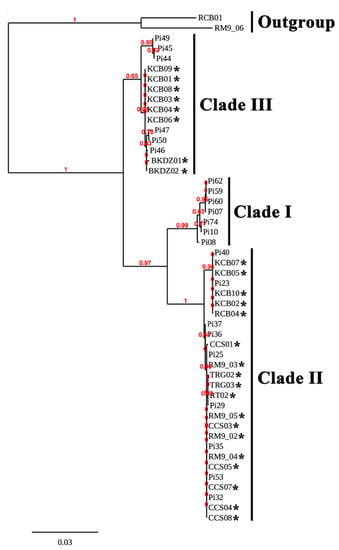
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic relationship of water-isolated and clinical strains of P. insidiosum. The rDNA-cox1-cox2 concatenated sequences of 26 water-isolated (Table 2) and 22 clinical (Table 3) strains of P. insidiosum and 2 outgroup organisms (i.e., P. rhizo-oryzae strain RCB01 and P. catenulatum strain RM9-06) are recruited for the construction of a maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic tree. The branch support values are calculated based on the aLRT test. Asterisks indicate water-isolated strains of P. insidiosum.
3.5. Mass Spectrometric Analysis and Proteotyping of P. insidiosum
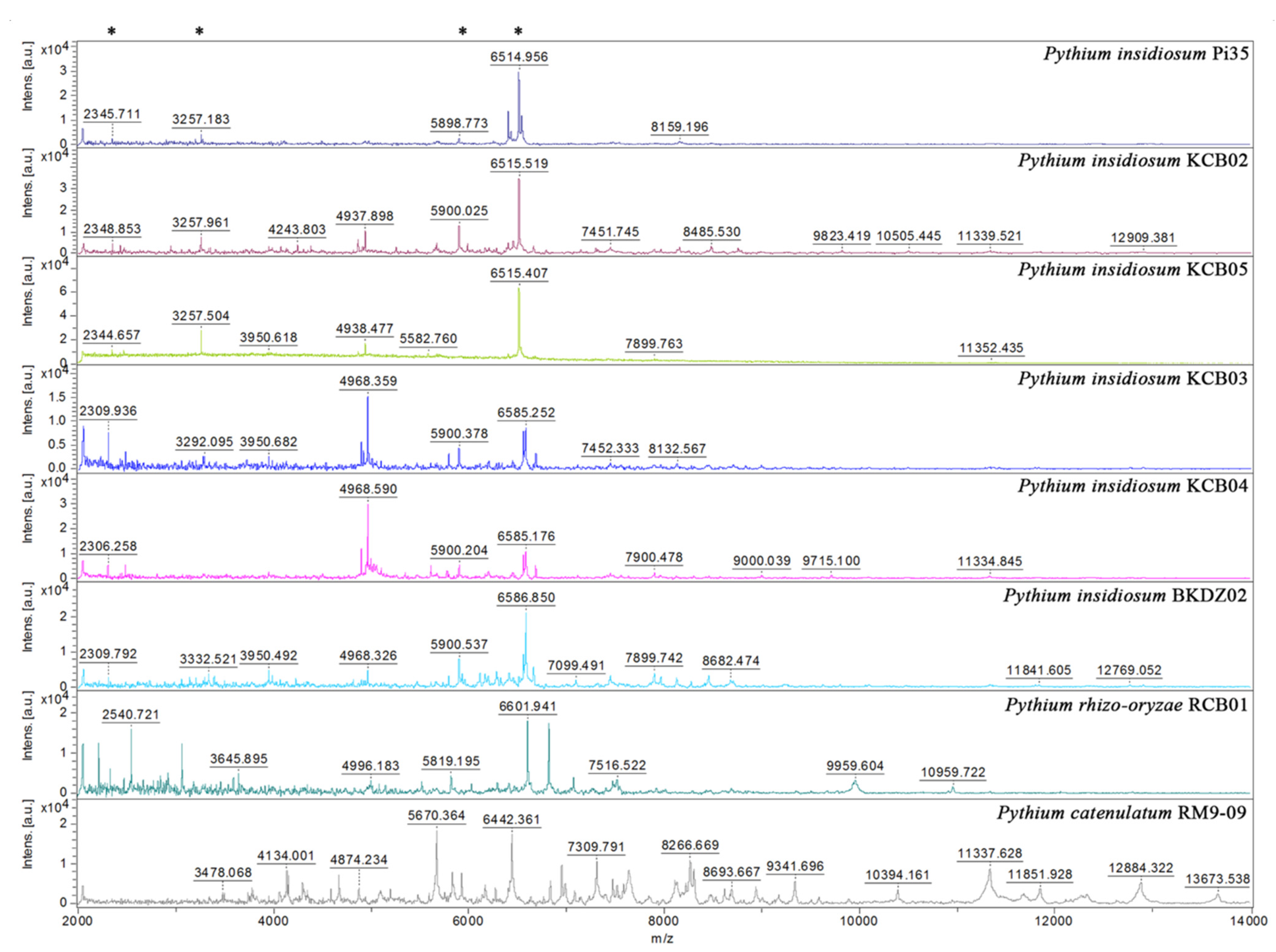
MALDI-TOF MS generated mass spectra from 10 selected water-isolated P. insidiosum strains (9 from Rice Field#3 and one from the zoo; Table 2), 2 non-insidiosum Pythium species (i.e., P. rhizo-oryzae strain RCB01 and P. catenulatum strain RM9-09), the P. insidiosum strain Pi35 (positive control), and the C. parapsilosis strain ATCC 22019 (negative control) (Figure 4). The obtained mass spectra were subject to the species-level identification by searching through the supplemented MALDI Biotyper DB4613 database (Bruker Daltonics), containing 4626 MSPs of various organisms, including 331 fungi and 13 P. insidiosum strains [19]. The mass spectrometric analysis assigned all organisms as “P. insidiosum” (identification scores: 2.149–2.490), except P. rhizo-oryzae strain RCB01 (score: 1.573), P. catenulatum strain RM9-09 (score: 1.483) (Table 2), and the negative control (which matched the C. parapsilosis strain ATCC 22019 THL; score: 2.214).
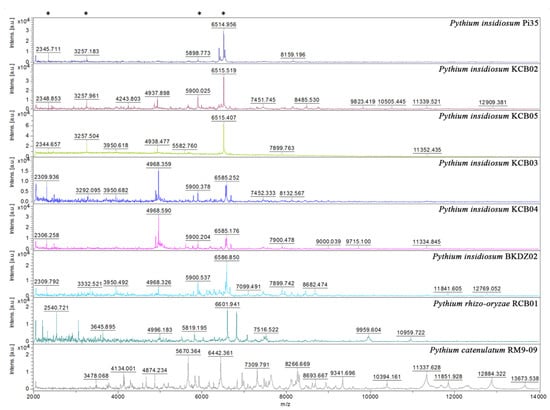
Figure 4.
Comparison of mass spectra from P. insidiosum and non-insidiosum Pythium species. Four mass spectra are generated from P. insidiosum strains inhabited in the same rice field (IDs: KCB02, KCB03, KCB04, and KCB05). One each of the mass spectra is derived from P. insidiosum strain BKDZ02 (from a zoo in Bangkok), P. rhizo-oryzae strain RCB01 (from a pond in Ratchaburi province), and P. catenulatum strain RM9-09 (from a pond in Bangkok). The P. insidiosum strain Pi35 (from a pythiosis patient) is included as a reference organism. The Y-axis shows mass intensity, while the X-axis represents the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). Asterisks indicate the prominent m/z peaks that share among different strains of P. insidiosum.
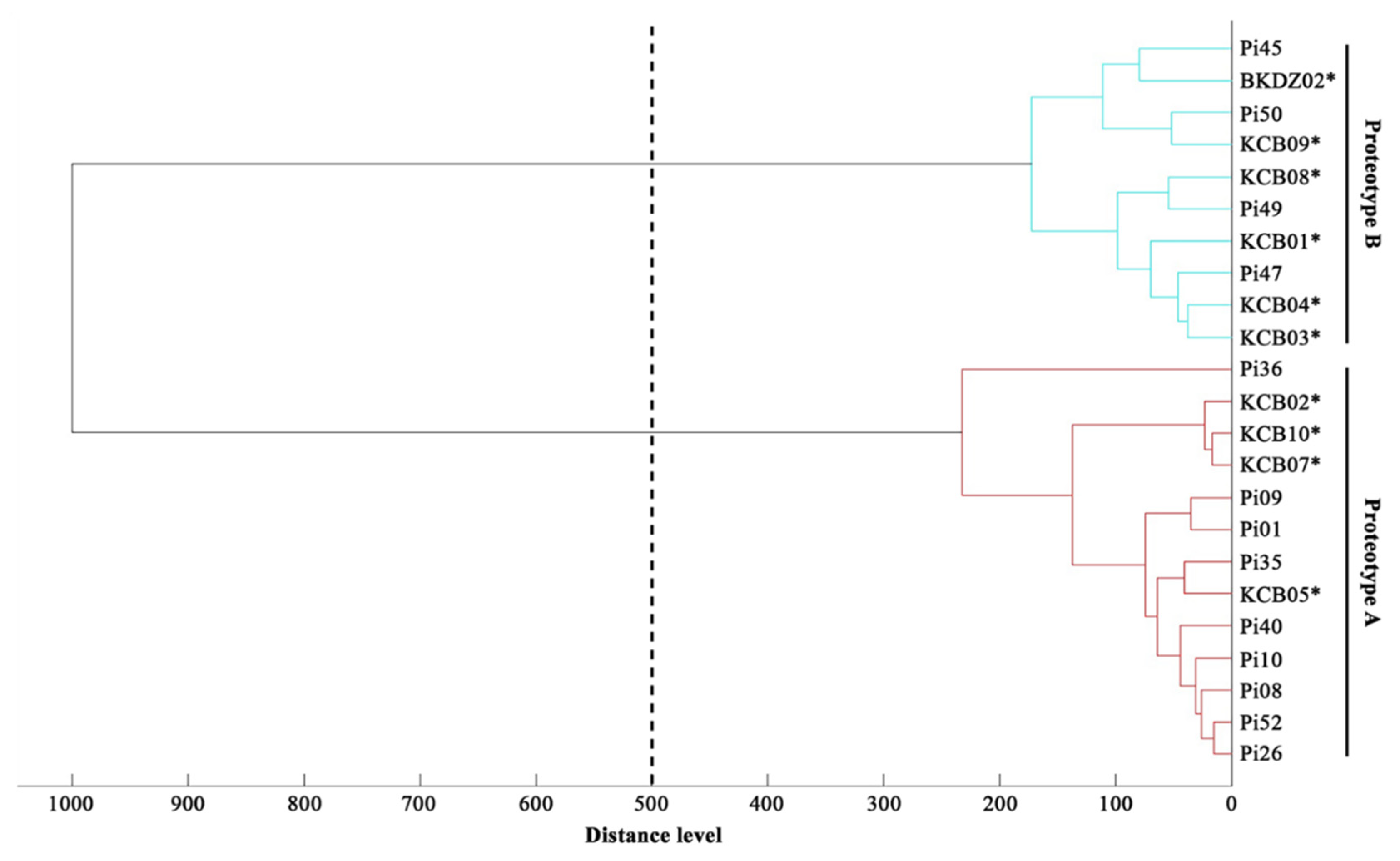
The MALDI Biotyper software constructed a dendrogram based on the MSPs of 10 water-isolated P. insidiosum strains (4 Clade-II and 6 Clade-III genotype strains; Table 2) and 13 P. insidisoum reference strains from the previous study [4 Clade-I genotype strains (i.e., Pi01, Pi08, Pi09, and Pi10); 5 Clade-II genotype strains (i.e., Pi26, Pi35, Pi36, Pi40, and Pi52); and 4 Clade-III genotype strains (i.e., Pi45, Pi47, Pi49, and Pi50)] [19]. By using the distance value of 500 as the cut-off value [51], the dendrogram divided P. insidisoum into 2 groups: Proteotype-A (including all Clade-I and -II genotype strains) and Proteotype-B (including all Clade-III genotype strains) (Table 2 and Table 3; Figure 5).
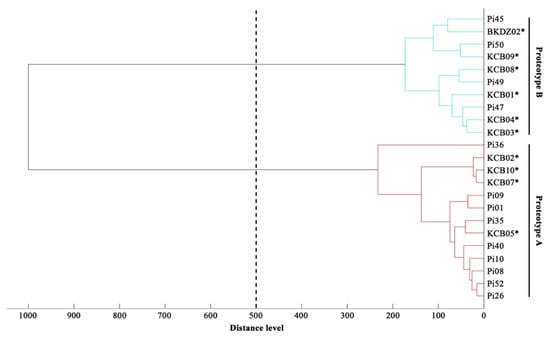
Figure 5.
Proteomic dendrogram of water-isolated and clinical strains of P. insidiosum. The main spectral profiles (MSP) of 10 water-isolated (4 Clade-II and 6 Clade-III genotype strains; Table 2) and 13 clinical (4 Clade-I, 5 Clade-II, and 4 Clade-III genotype strains; Table 3) strains of P. insidiosum are recruited for the construction of a dendrogram. The distance value of 500 is used as the cut-off value for proteotyping of the organisms. Asterisks indicate water-isolated strains of P. insidiosum.
4. Discussion
We surveyed the presence of P. insidiosum in urban and rural watery areas of Thailand, using the hair-baiting technique [35]. A total of 500 water samples were collected from 100 sites (i.e., ponds and rice fields) in 7 central and southern provinces of the country (Figure 1). Cultures of most water samples (89.2%) showed growing bacterial and fungal colonies. Among them, 64 samples (12.8%) provided a white-to-colorless, non-sporulation, submerged colony, which is compatible with the gross morphology of P. insidiosum. Such morphologies are not specific to P. insidiosum, as they are observed in several microorganisms. Nevertheless, recognition of the colony characteristics can facilitate the screening of P. insidiosum through a vast number of water samples. Multiplex PCR [23] identified P. insidiosum in 27 out of 64 colony screening-positive samples (Table 2 and Table 4). The identity of P. insidiosum was confirmed by DNA barcode analyses (i.e., rDNA, cox1, and cox2) [40,41,42,43]. rDNA is the most common barcode used to identify an organism at the species level [40,43]. However, rDNA failed to assign P. insidiosum in one of 27 PCR-positive samples (sequence identity cutoff: 98.5%) (Table 2), indicating that the current rDNA database had a limitation in identifying this organism. The secondary barcodes (cox1 and cox2) were then employed [41,42,43]. cox2 identified P. insidiosum in all 27 PCR-positive samples (sequence identity: 100%), whereas cox1 detected the organism only in 19 PCR-positive samples (sequence identity: 99.3–100.0%) (Table 2). The ineffectiveness of cox1 in the identification of P. insidiosum was due to the limited cox1 database in GenBank, as only 4 cox1 sequences of this species (accessions: JQ305799, HQ708612, HQ708611, and AP014838) were available at the time of analysis. As the final result, the colony screening, multiplex PCR, and DNA barcode analyses co-identified P. insidiosum in 27 out of 500 water samples (detection rate: 5.4%) (Table 2).
P. insidiosum can be isolated from swampy areas in several countries across the world (i.e., Thailand, Australia, the United States, and Brazil) [34,35,36,37,38,39]. Recently, Jara et al. successfully isolated P. insidiosum throughout the study area in the Chincoteague National Wildlife Refuge in Virginia, the United States [39]. Based on an ecological niche model framework, they predicted that the warm weather during June and August is more suitable for the organism than the cold weather during December and March [39]. In Thailand, Supabandhu et al. successfully isolated 59 P. insidiosum strains from 325 water samples collected from agricultural areas (i.e., rice fields, irrigation channels, and water reservoirs) in northern Thailand [35]. They reported the isolate-per-sample (IPS) value of 59/325 or 0.18. The current study reported the IPS value of 27/500 or 0.05, which was calculated based on the P. insidiosum-positive samples collected from urban areas (i.e., zoo and public parks; 7 isolates per 300 samples) and agricultural areas (i.e., ponds and rice fields; 20 isolates per 200 samples) in central and southern Thailand (Table 1). The IPS value of Supabandhu et al. (0.18) was 3.4-fold higher than that of our study (0.05). In our study, the IPS value of agricultural areas (20/200 or 0.10) was 5-time higher than that of urban areas (7/300 or 0.02). P. insidiosum may be more prevalent in the northern part than the other parts of Thailand. On the other hand, the low prevalence may due to sampling biases, as 48% of the water samples were collected from the urban areas. Taken together, we learned that: (i) P. insidiosum is widespread in Thailand (and perhaps in neighborhood countries where cases are not yet reported); (ii) the organism presents in the crowded city, i.e., Bangkok; and (iii) the pathogen is more prevalent in the agricultural habitats. The higher prevalence of P. insidiosum in the agricultural areas was consistent with the fact that the majority of Thai patients with pythiosis were farmers living all over the country [2,35]. An individual who exposes to the ecological niche of P. insidiosum could become at risk of the infection.
P. insidiosum is classified into 3 genotypes, in association with its geographic origins (i.e., Clade-I genotype in Americas, Clade-II genotype in Asia and Australia, and Clade-III genotype in Thailand) [52,53]. The multiplex PCR has the ability to not only detect P. insidiosum, but also genotype this organism into Clade-I, -II, or -III strains, simply based on size and number of the amplicons [23]. This amplification technique correctly assigned 27 water-isolated P. insidiosum strains into Clade-II (n = 19) and Clade-III (n = 8) genotypes, which were in agreement with the phylogenetic findings (Table 2; Figure 3). Biodiversity of the Thai water-isolated strains of P. insidiosum (n = 26; Table 2), in relation to the human and animal strains from different geographic areas (n = 22; Table 3), was assessed by phylogenetic and proteomic approaches. Using the rDNA-cox1-cox2 concatenated sequences, P. insidiosum can be grouped into 3 phylogenetic clades, as expected (Figure 3). The Thai water-isolated strains were restricted to only Clade-II and Clade-III (Table 2; Figure 3). This finding suggests that the major circulating strains of P. insidiosum in the Thai environment are the Clade-II and Clade-III genotypes, which are the typical genotypes of the pathogen isolated from all Thai patients [23,53]. Until 2020, a clade Ath (equivalent to Clade-I) strain of P. insidiosum was isolated from the first dog with pythiosis in Thailand [54]. Such information suggests that the Clade-I strains might also circulate in Thailand, but to a much lesser extent than the Clade-II and -III strains.
We initially explored the proteome-based biodiversity of the P. insidiosum isolated from water (n = 10), humans (n = 6), and animals (n = 3) (Table 2 and Table 3). Unlike the phylogenetic approach, the mass spectrometry-derived dendrogram divided these isolates into only 2 groups: proteotype-A (comprising Clade-I and -II genotypes) and proteotype-B (comprising only Clade-III genotypes) (Figure 5). Hence, the proteomic method exhibited less discrimination power for bio-diversifying P. insidiosum than the phylogenetic approach. Nine of the water-isolated strains were from the same sample collection site (Rice Field#3) and can be grouped into 2 subpopulations: proteotype-A/genotype Clade-II (n = 4) and proteotype-B/genotype Clade-III (n = 5) (Table 2; Figure 5). The proteomic (Figure 5) and phylogenetic (Figure 3) analyses demonstrated the marked biodiversity of the P. insidiosum subpopulation inhabiting a local environment.
In conclusion, we successfully isolated P. insidiosum from the urban and rural areas (including the city of Bangkok), using the hair-baiting technique. The identity of the organism was confirmed by multiplex PCR, DNA barcoding, and proteomic analysis. The combination of rDNA and cox2 barcodes showed superior performance for the identification of P. insidiosum, while the cox1 barcode cannot assign a species to some strains due to the lack of a comprehensive dataset in GenBank. Proteomic and phylogenetic analyses revealed subpopulations and biodiversity (i.e., proteotype-A/genotype Clade-II and proteotype-B/genotype Clade-III) of the water-isolated P. insidiosum strains in a local area. P. insidiosum is ubiquitous in Thailand and only the Clade-II and Clade-III genotypes (the typical genotypes that infect Thai patients) circulate in the environment (i.e., rice fields and ponds). Better understanding the ecological niches of P. insidiosum can lead to a proper measure to reduce the exposure of an individual at risk to the pathogen, and thus prevent pythiosis.
Author Contributions
Z.M.H.: methodology, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft; A.L.: methodology; W.P.: methodology; C.Y.: methodology; T.L.: methodology; W.Y.: methodology; Y.K.: methodology; P.P.: methodology; P.S.-C.: methodology; T.R.: methodology; P.J.: methodology; C.J.: methodology; P.C.: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing; T.K.: funding acquisition, conceptualization, supervision, methodology, formal analysis, resources, visualization, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial supports were obtained from Thailand Research Fund (for Theerapong Krajaejun; grant numbers: RSA6280092); Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University (for Theerapong Krajaejun; grant number: CF_61007 and CF_63008); Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University (a Doctoral Student Competency Scholarship for Zin Mar Htun); and Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Kasetsart University (a Cooperative Social Responsibility Program of Veterinary Practice—2018 grant for Chompoonek Yurayart).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University (approval number: MURA2018/537).
References
- Mendoza, L.; Ajello, L.; McGinnis, M.R. Infection Caused by the Oomycetous Pathogen Pythium Insidiosum. J. Mycol. Med. 1996, 6, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Krajaejun, T.; Sathapatayavongs, B.; Pracharktam, R.; Nitiyanant, P.; Leelachaikul, P.; Wanachiwanawin, W.; Chaiprasert, A.; Assanasen, P.; Saipetch, M.; Mootsikapun, P.; et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Analyses of Human Pythiosis in Thailand. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaastra, W.; Lipman, L.J.; de Cock, A.W.; Exel, T.K.; Pegge, R.B.; Scheurwater, J.; Vilela, R.; Mendoza, L. Pythium Insidiosum: An Overview. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitasombat, M.N.; Jongkhajornpong, P.; Lekhanont, K.; Krajaejun, T. Recent Update in Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Pythiosis. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rujirawat, T.; Patumcharoenpol, P.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Lerksuthirat, T.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Suriyaphol, P.; Grenville-Briggs, L.J.; Garg, G.; Kittichotirat, W.; et al. Draft Genome Sequence of the Pathogenic Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum Strain Pi-S, Isolated from a Patient with Pythiosis. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00574-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujirawat, T.; Patumcharoenpol, P.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Kumsang, Y.; Payattikul, P.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Suriyaphol, P.; Reamtong, O.; Garg, G.; et al. Probing the Phylogenomics and Putative Pathogenicity Genes of Pythium Insidiosum by Oomycete Genome Analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittichotirat, W.; Patumcharoenpol, P.; Rujirawat, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Krajaejun, T. Draft Genome and Sequence Variant Data of the Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum Strain Pi45 from the Phylogenetically-Distinct Clade-III. Data Brief. 2017, 15, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajaejun, T.; Kittichotirat, W.; Patumcharoenpol, P.; Rujirawat, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W. Data on Whole Genome Sequencing of the Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum Strain CBS 101555 from a Horse with Pythiosis in Brazil. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patumcharoenpol, P.; Rujirawat, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Vanittanakom, N.; Kittichotirat, W.; Krajaejun, T. Draft Genome Sequences of the Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum Strain CBS 573.85 from a Horse with Pythiosis and Strain CR02 from the Environment. Data Brief. 2018, 16, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajaejun, T.; Lerksuthirat, T.; Garg, G.; Lowhnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Khositnithikul, R.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Suriyaphol, P.; Ranganathan, S.; Sullivan, T.D. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Pathogenicity and Evolutionary History of the Pathogenic Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum. Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajaejun, T.; Khositnithikul, R.; Lerksuthirat, T.; Lowhnoo, T.; Rujirawat, T.; Petchthong, T.; Yingyong, W.; Suriyaphol, P.; Smittipat, N.; Juthayothin, T.; et al. Expressed Sequence Tags Reveal Genetic Diversity and Putative Virulence Factors of the Pathogenic Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajaejun, T.; Kittichotirat, W.; Patumcharoenpol, P.; Rujirawat, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W. Draft Genome Sequence of the Oomycete Pythium Destruens Strain ATCC 64221 from a Horse with Pythiosis in Australia. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindayok, T.; Piromsontikorn, S.; Srimuang, S.; Khupulsup, K.; Krajaejun, T. Hemagglutination Test for Rapid Serodiagnosis of Human Pythiosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeratijarut, A.; Karnsombut, P.; Aroonroch, R.; Srimuang, S.; Sangruchi, T.; Sansopha, L.; Mootsikapun, P.; Larbcharoensub, N.; Krajaejun, T. Evaluation of an In-House Immunoperoxidase Staining Assay for Histodiagnosis of Human Pythiosis. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2009, 40, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keeratijarut, A.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Sriwanichrak, K.; Krajaejun, T. A Peptide ELISA to Detect Antibodies against Pythium Insidiosum Based on Predicted Antigenic Determinants of Exo-1,3-β-Glucanase. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2013, 44, 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Keeratijarut, A.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Nampoon, U.; Lerksuthirat, T.; Onpaew, P.; Chongtrakool, P.; Krajaejun, T. PCR Amplification of a Putative Gene for Exo-1, 3-β-Glucanase to Identify the Pathogenic Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum. Asian Biomed. 2014, 8, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeratijarut, A.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Rujirawat, T.; Srichunrusami, C.; Onpeaw, P.; Chongtrakool, P.; Brandhorst, T.T.; Krajaejun, T. Detection of the Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum by Real-Time PCR Targeting the Gene Coding for Exo-1,3-β-Glucanase. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajaejun, T.; Imkhieo, S.; Intaramat, A.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. Development of an Immunochromatographic Test for Rapid Serodiagnosis of Human Pythiosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajaejun, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Jittorntam, P.; Srimongkol, A.; Kumsang, Y.; Yingyong, W.; Rujirawat, T.; Reamtong, O.; Mangmee, S. Assessment of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Identification and Biotyping of the Pathogenic Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 77, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareonsirisuthigul, T.; Khositnithikul, R.; Intaramat, A.; Inkomlue, R.; Sriwanichrak, K.; Piromsontikorn, S.; Kitiwanwanich, S.; Lowhnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Chaiprasert, A.; et al. Performance Comparison of Immunodiffusion, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Immunochromatography and Hemagglutination for Serodiagnosis of Human Pythiosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohnoo, T.; Jongruja, N.; Rujirawat, T.; Yingyon, W.; Lerksuthirat, T.; Nampoon, U.; Kumsang, Y.; Onpaew, P.; Chongtrakool, P.; Keeratijarut, A.; et al. Efficiency Comparison of Three Methods for Extracting Genomic DNA of the Pathogenic Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2014, 97, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Intaramat, A.; Sornprachum, T.; Chantrathonkul, B.; Chaisuriya, P.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Jongruja, N.; Kumsang, Y.; Sandee, A.; Chaiprasert, A.; et al. Protein A/G-Based Immunochromatographic Test for Serodiagnosis of Pythiosis in Human and Animal Subjects from Asia and Americas. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rujirawat, T.; Sridapan, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Kumsang, Y.; Sae-Chew, P.; Tonpitak, W.; Krajaejun, T. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism-Based Multiplex PCR for Identification and Genotyping of the Oomycete Pythium Insidiosum from Humans, Animals and the Environment. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2017, 54, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.; Vilela, R.; Kettler, N.; Chilvers, M.I.; Mendoza, L. Identification of Pythium Insidiosum Complex by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, Z.M.; Rotchanapreeda, T.; Rujirawat, T.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Kumsang, Y.; Sae-Chew, P.; Payattikul, P.; Yurayart, C.; Limsivilai, O.; et al. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for Identification of Pythium Insidiosum. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerksuthirat, T.; Sangcakul, A.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Rujirawat, T.; Krajaejun, T. Evolution of the Sterol Biosynthetic Pathway of Pythium Insidiosum and Related Oomycetes Contributes to Antifungal Drug Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02352-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolanda, H.; Krajaejun, T. Review of Methods and Antimicrobial Agents for Susceptibility Testing against Pythium Insidiosum. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathapatayavongs, B.; Leelachaikul, P.; Prachaktam, R.; Atichartakarn, V.; Sriphojanart, S.; Trairatvorakul, P.; Jirasiritham, S.; Nontasut, S.; Eurvilaichit, C.; Flegel, T. Human Pythiosis Associated with Thalassemia Hemoglobinopathy Syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 159, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasika, R.; Lalitha, P.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Rameshkumar, G.; Prajna, N.V.; Srinivasan, M. Pythium Keratitis in South India: Incidence, Clinical Profile, Management, and Treatment Recommendation. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 67, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appavu, S.P.; Prajna, L.; Rajapandian, S.G.K. Genotyping and Phylogenetic Analysis of Pythium Insidiosum Causing Human Corneal Ulcer. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Iyer, G.; Srinivasan, B.; Benurwar, S.; Agarwal, M.; Narayanan, N.; Lakshmipathy, M.; Radhika, N.; Rajagopal, R.; Krishnakumar, S.; et al. Clinical Profile, Risk Factors and Outcome of Medical, Surgical and Adjunct Interventions in Patients with Pythiuminsidiosum Keratitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, C.E.P.; Ubiali, D.G.; Pescador, C.A.; Zanette, R.A.; Santurio, J.M.; Marques, L.C. Epidemiological Survey of Equine Pythiosis in the Brazilian Pantanal and Nearby Areas: Results of 76 Cases. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2014, 34, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.; Hernandez, F.; Ajello, L. Life Cycle of the Human and Animal Oomycete Pathogen Pythium Insidiosum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.I. Investigations into the Biology of Three “phycomycotic” Agents Pathogenic for Horses in Australia. Mycopathologia 1983, 81, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supabandhu, J.; Fisher, M.C.; Mendoza, L.; Vanittanakom, N. Isolation and Identification of the Human Pathogen Pythium Insidiosum from Environmental Samples Collected in Thai Agricultural Areas. Med. Mycol. 2008, 46, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presser, J.W.; Goss, E.M. Environmental Sampling Reveals that Pythium Insidiosum Is Ubiquitous and Genetically Diverse in North Central Florida. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanittanakom, N.; Szekely, J.; Khanthawong, S.; Sawutdeechaikul, P.; Vanittanakom, P.; Fisher, M.C. Molecular Detection of Pythium Insidiosum from Soil in Thai Agricultural Areas. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, C.G.; Fonseca, A.O.S.; Valente, J.S.S.; Braga, C.Q.; Sallis, E.S.V.; Azevedo, M.I.; Weiblen, C.; Santurio, J.M.; Botton, S.A.; Pereira, D.I.B. Isolamento e Caracterização de Espécies de Pythium de Ambientes Aquáticos No Estado Do Rio Grande Do Sul e Avaliação Da Patogenicidade Em Modelo Experimental. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2017, 37, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jara, M.; Holcomb, K.; Wang, X.; Goss, E.M.; Machado, G. The Potential Distribution of Pythium Insidiosum in the Chincoteague National Wildlife Refuge, Virginia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 640339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, F.N. Phylogenetic Relationships among Some Pythium Species Inferred from Sequence Analysis of the Mitochondrially Encoded Cytochrome Oxidase II Gene. Mycologia 2000, 92, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robideau, G.P.; de Cock, A.W.A.M.; Coffey, M.D.; Voglmayr, H.; Brouwer, H.; Bala, K.; Chitty, D.W.; Désaulniers, N.; Eggertson, Q.A.; Gachon, C.M.M.; et al. DNA Barcoding of Oomycetes with Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I and Internal Transcribed Spacer. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevakumar, S.; Sridhar, K.R. Diagnosis of Pythium by Classical and Molecular Approaches. In Pythium; Rai, M., Abd-Elsalam, K.A., Ingle, A.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 200–224. ISBN 978-0-429-29640-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny. Fr: Robust Phylogenetic Analysis for the Non-Specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castresana, J. Selection of Conserved Blocks from Multiple Alignments for Their Use in Phylogenetic Analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A Simple, Fast, and Accurate Algorithm to Estimate Large Phylogenies by Maximum Likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O. Approximate Likelihood-Ratio Test for Branches: A Fast, Accurate, and Powerful Alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevenet, F.; Brun, C.; Bañuls, A.-L.; Jacq, B.; Christen, R. TreeDyn: Towards Dynamic Graphics and Annotations for Analyses of Trees. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argimón, S.; Abudahab, K.; Goater, R.J.E.; Fedosejev, A.; Bhai, J.; Glasner, C.; Feil, E.J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Yeats, C.A.; Grundmann, H.; et al. Microreact: Visualizing and Sharing Data for Genomic Epidemiology and Phylogeography. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.; Freiwald, A.; Maier, T.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Kostrzewa, M.; Geider, K. Classification and Identification of Bacteria by Mass Spectrometry and Computational Analysis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurko, A.M.; Mendoza, L.; Lévesque, C.A.; Désaulniers, N.L.; de Cock, A.W.A.M.; Klassen, G.R. A Molecular Phylogeny of Pythium Insidiosum. Mycol. Res. 2003, 107, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiprasert, A.; Krajaejun, T.; Pannanusorn, S.; Prariyachatigul, C.; Wanachiwanawin, W.; Sathapatayavongs, B.; Juthayothin, T.; Smittipat, N.; Vanittanakom, N.; Chindamporn, A. Pythium Insidiosum Thai Isolates: Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis. Asian Biomed. 2009, 3, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Chindamporn, A.; Kammarnjessadakul, P.; Kesdangsakonwut, S.; Banlunara, W. A Case of Canine Cutaneous Pythiosis in Thailand. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).