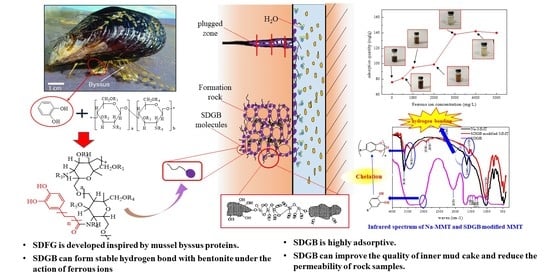
Wellbore Stability through Novel Catechol-Chitosan Biopolymer Encapsulator-Based Drilling Mud
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Orthogonal Experiment of SDGB
2.2. Characterization of SDGB
2.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Characterization Test
2.2.2. NMR Hydrogen Spectroscopy (HNMR) Analysis
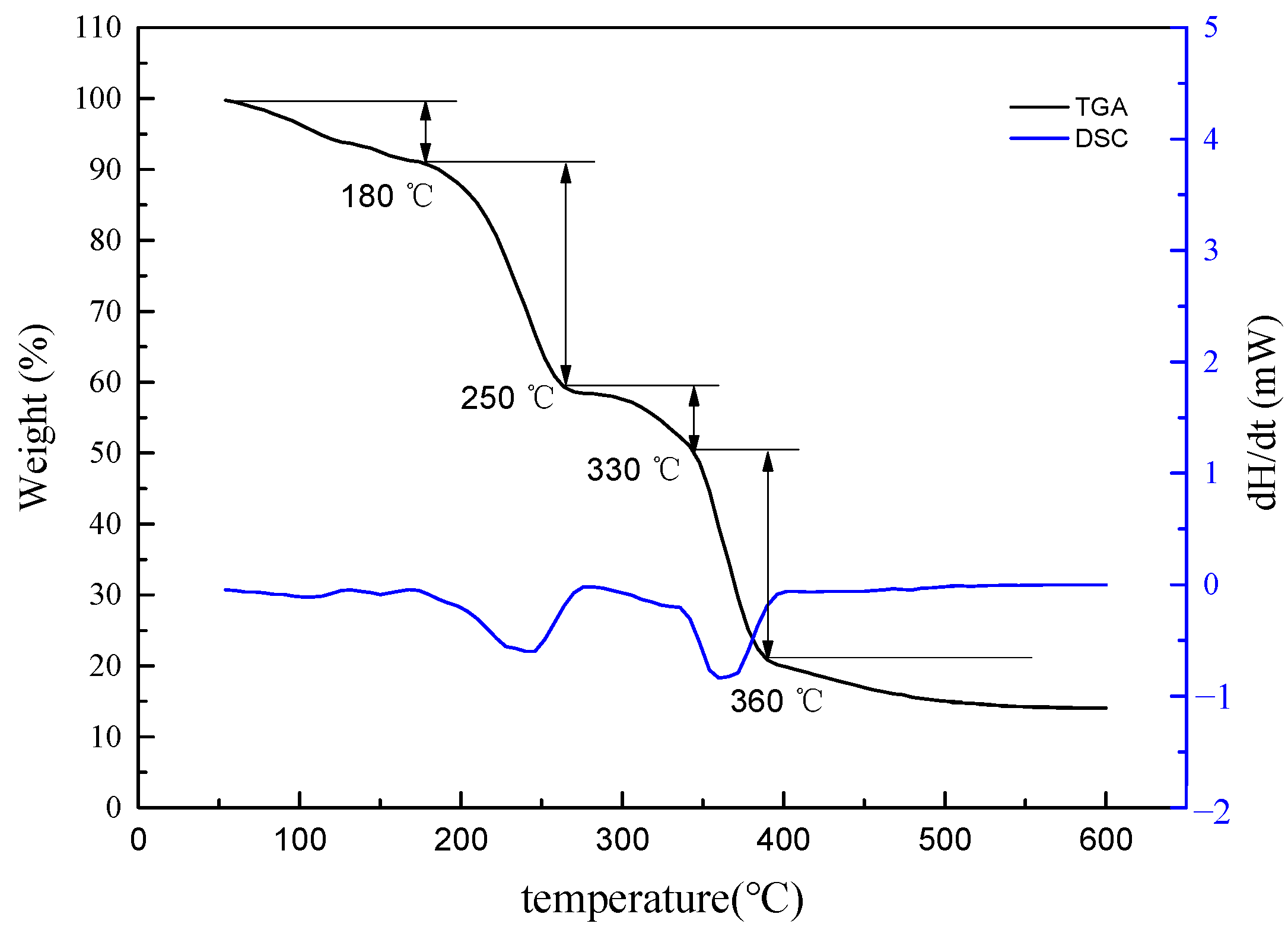
2.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.2.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Test
2.3. Evaluation of Improving Borehole Stability
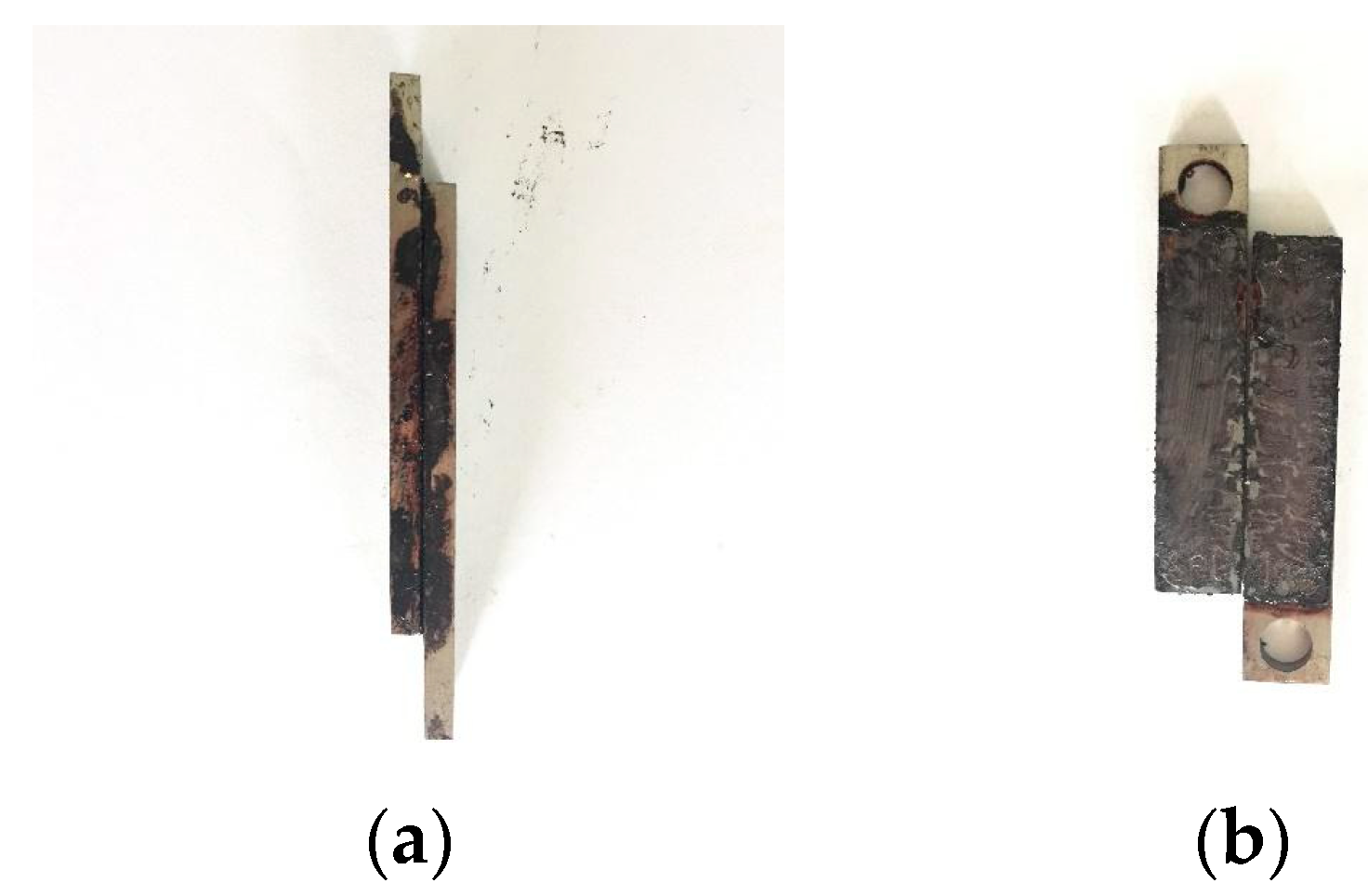
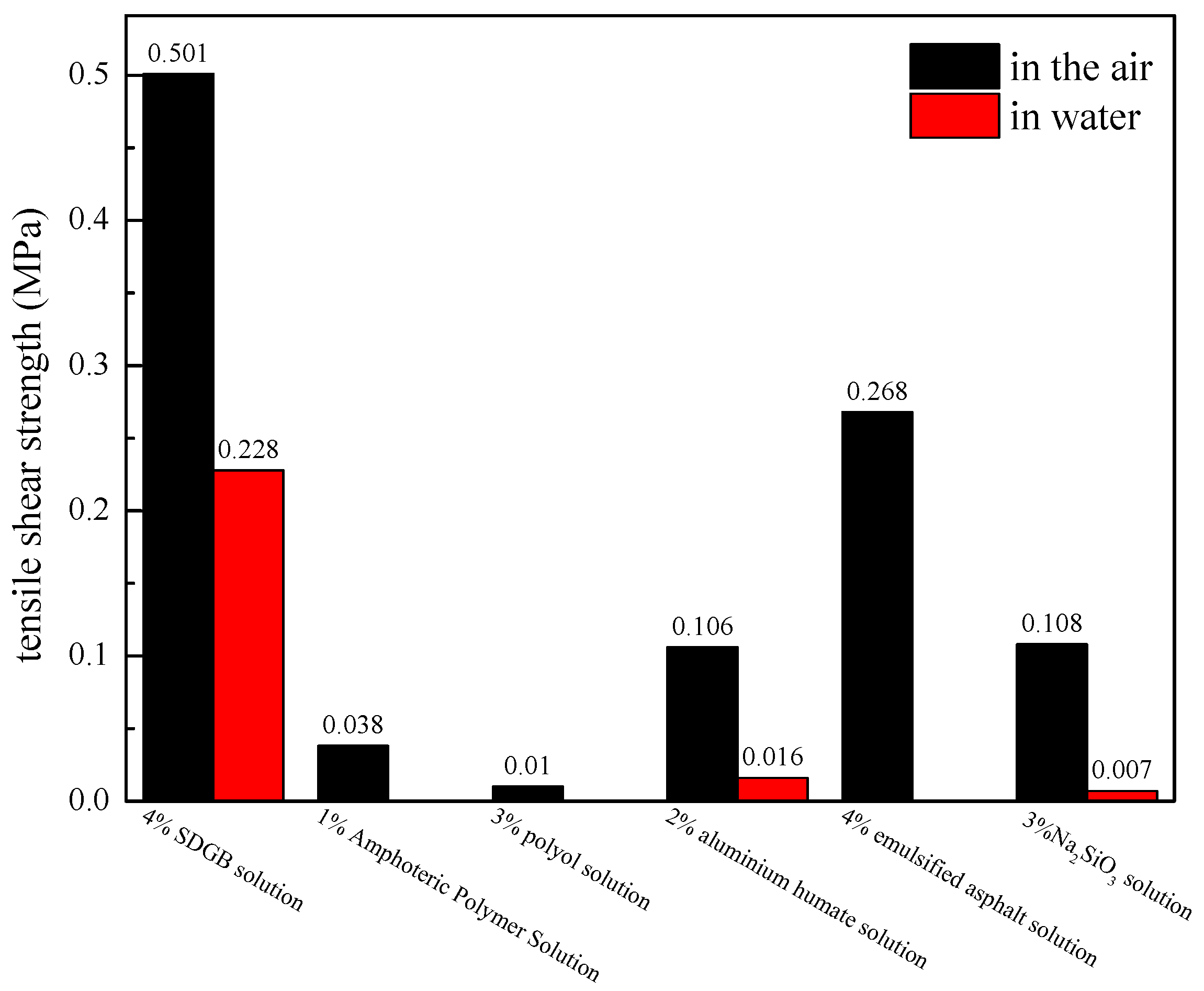
2.3.1. Tensile Shear Strength Test
2.3.2. Uniaxial Compressive Strength Test
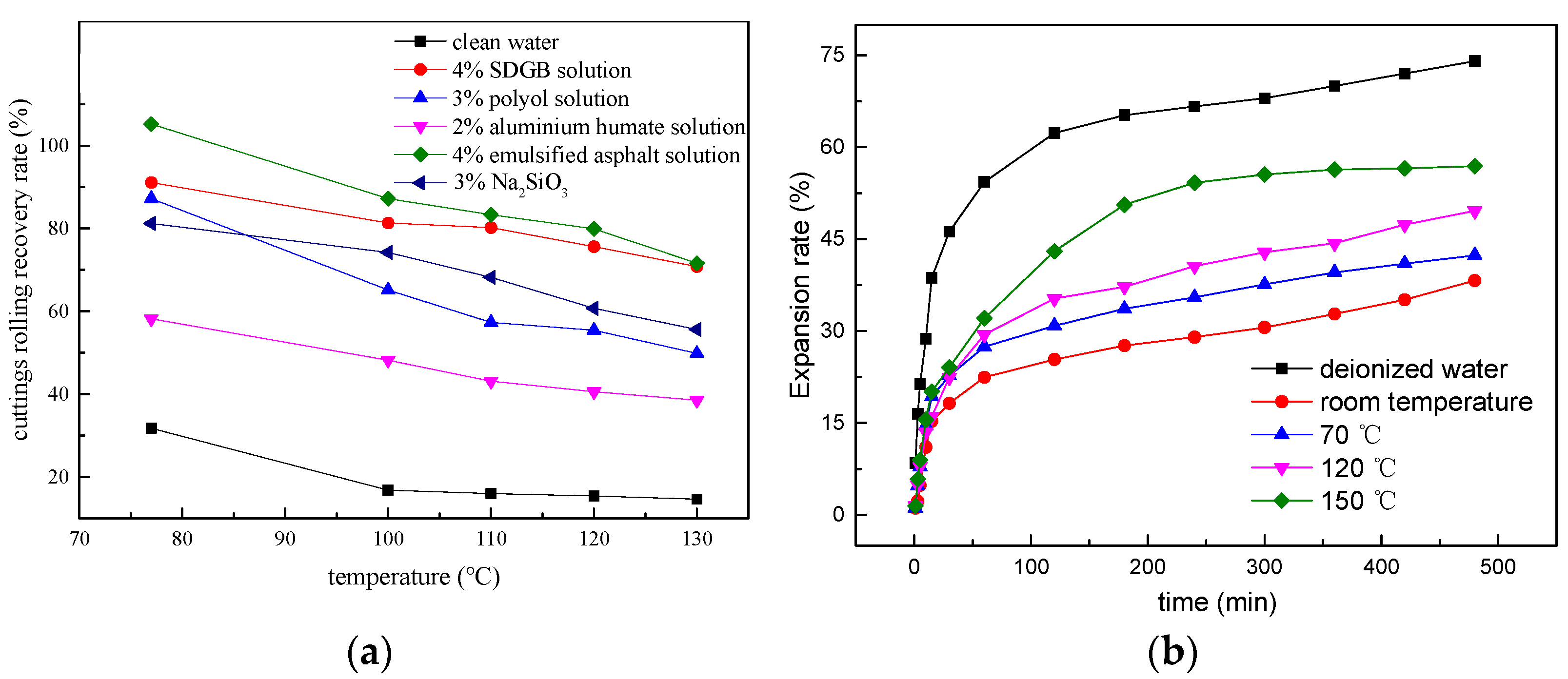
2.3.3. Inhibitory Shale Hydration Test
2.3.4. Hydroscopicity Test
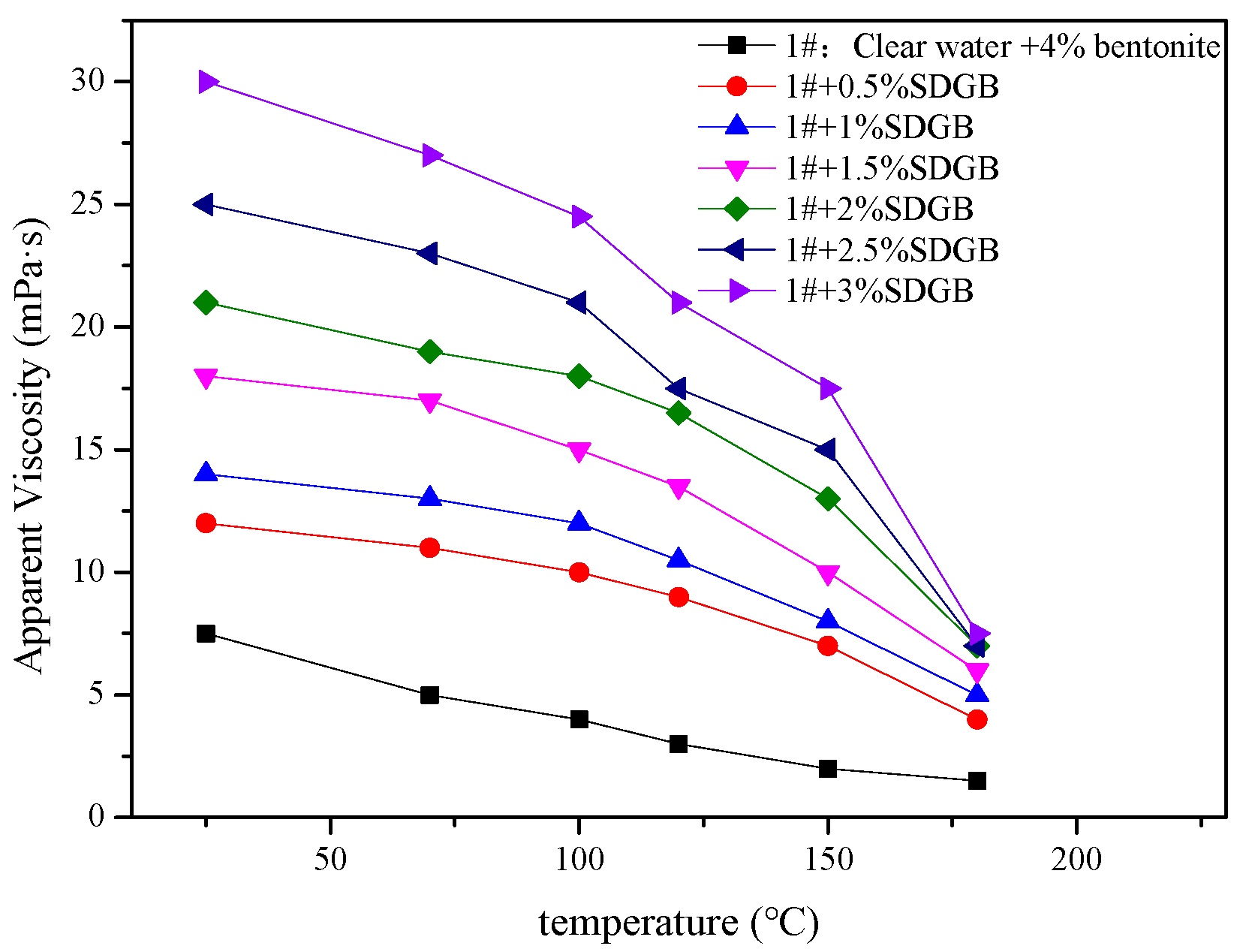
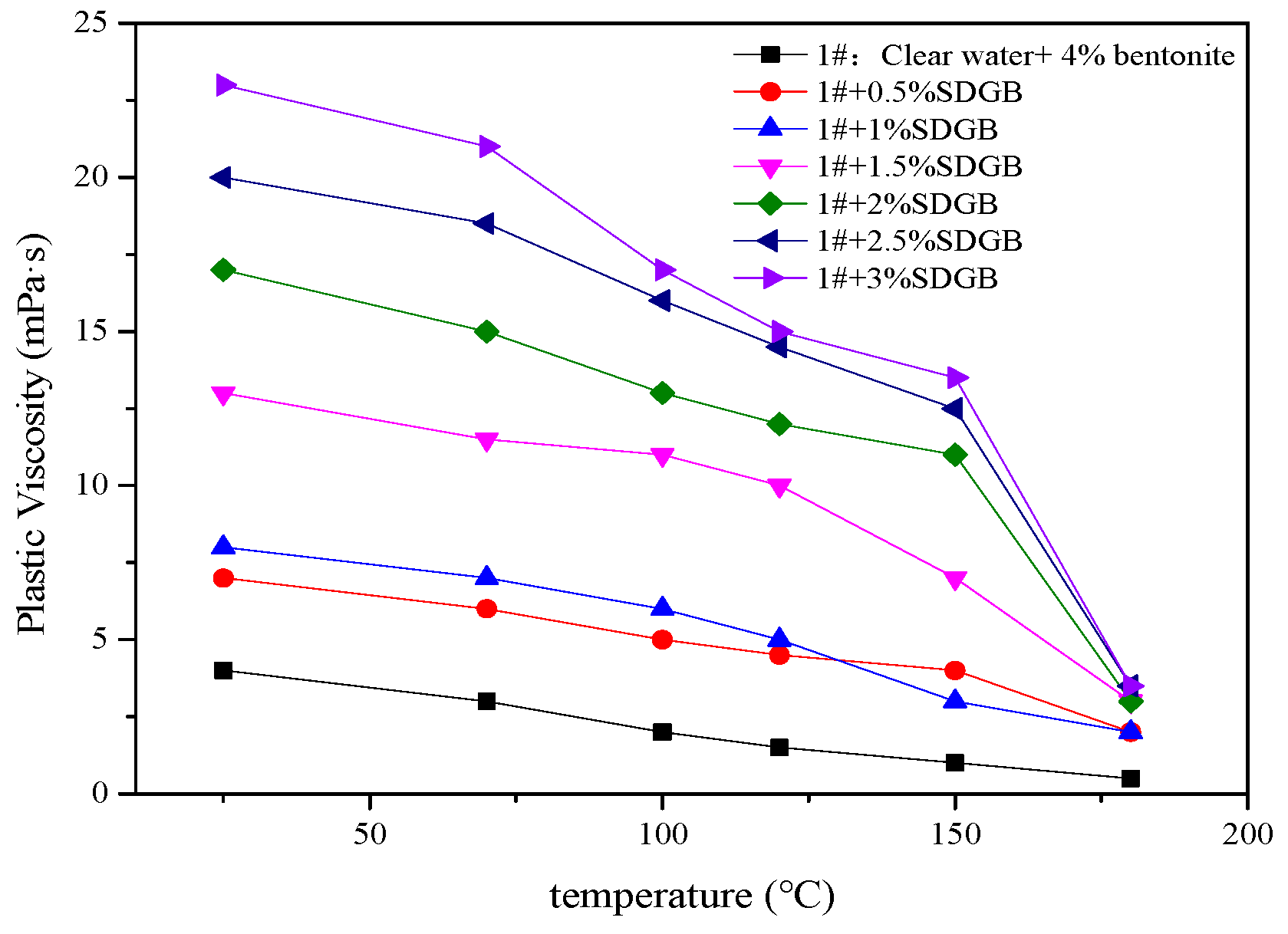
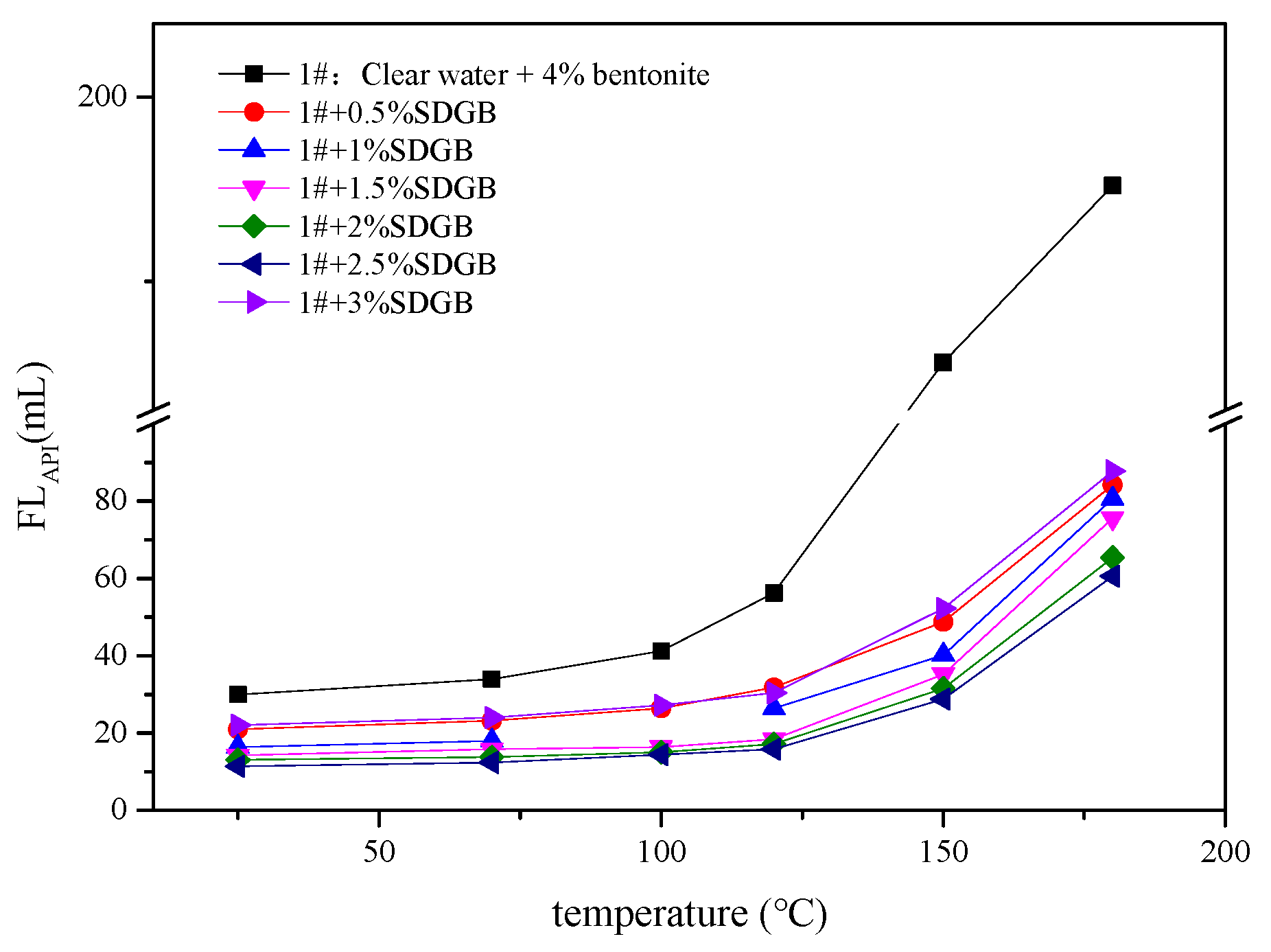
2.3.5. Compatibility Evaluation in Drilling Fluid
2.4. Mechanism of SDGB
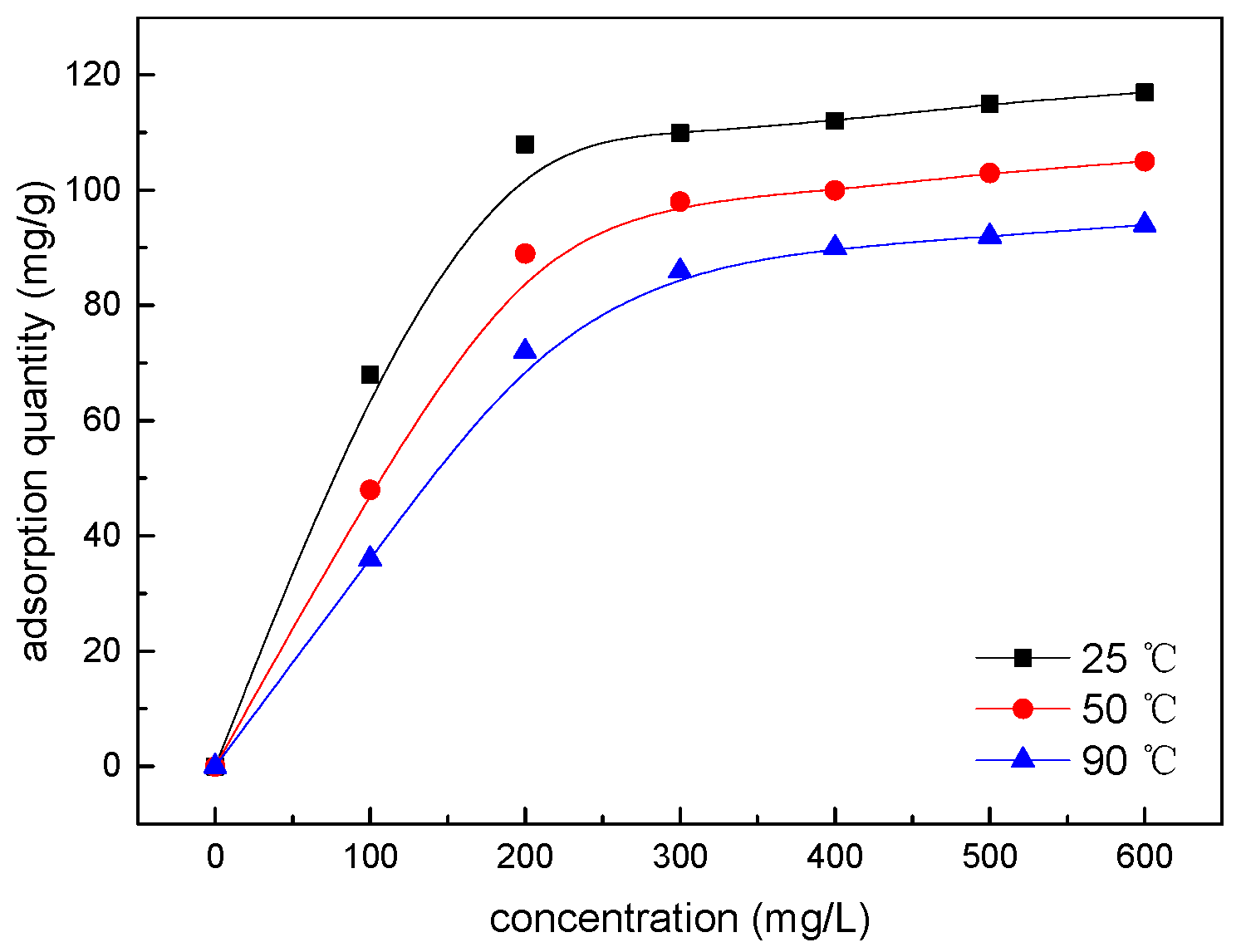
2.4.1. Adsorption Isotherm Test
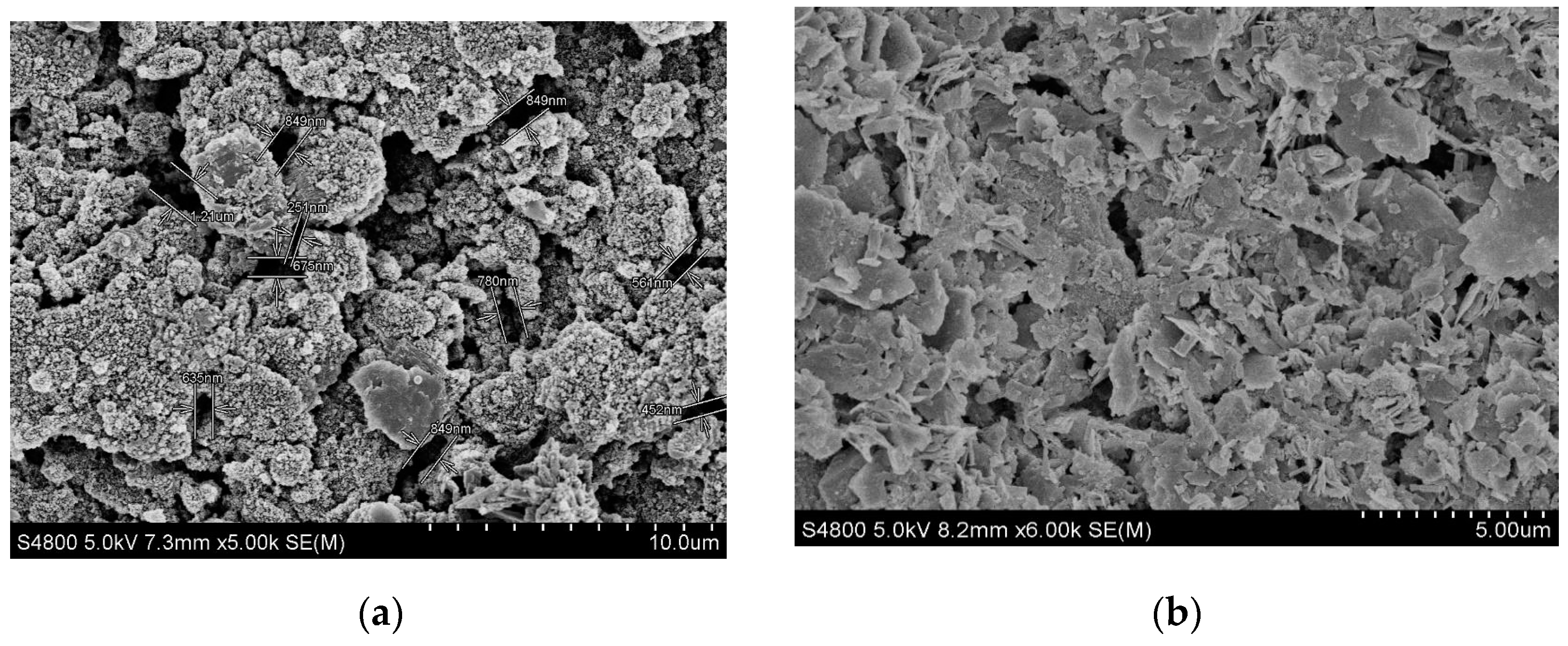
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Test
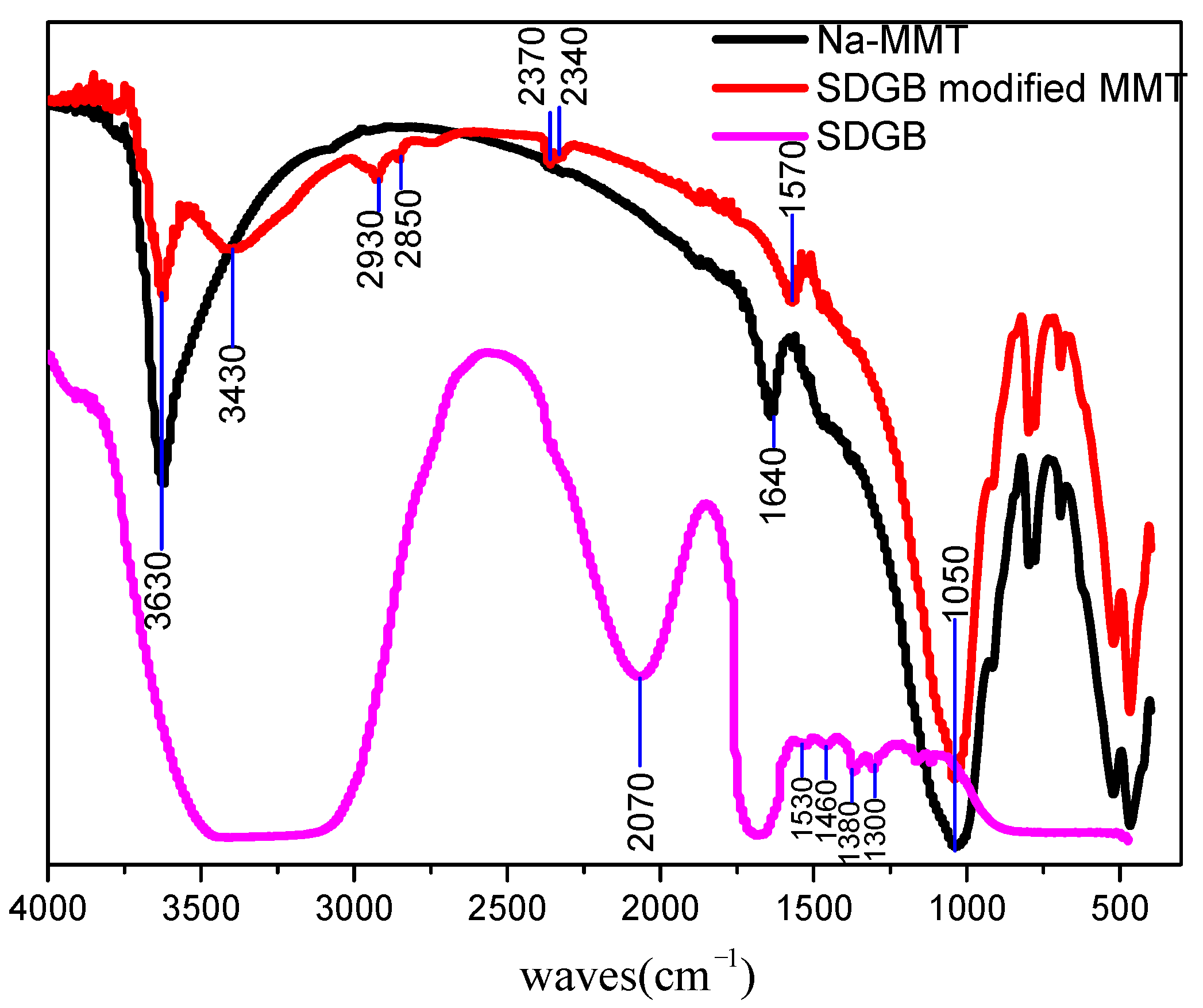
2.4.3. FT-IR Test
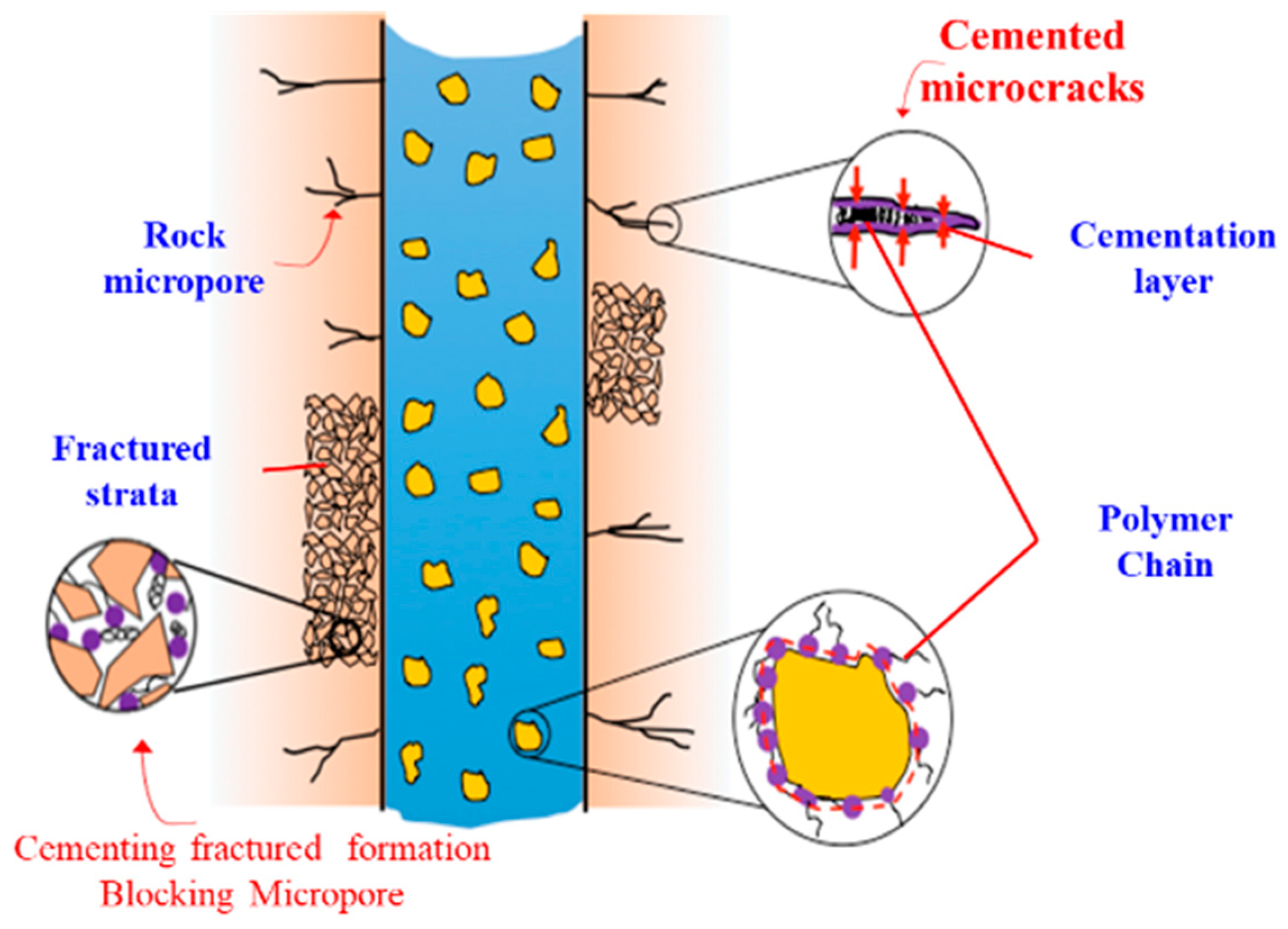
2.4.4. Summary and Analysis of Mechanism
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
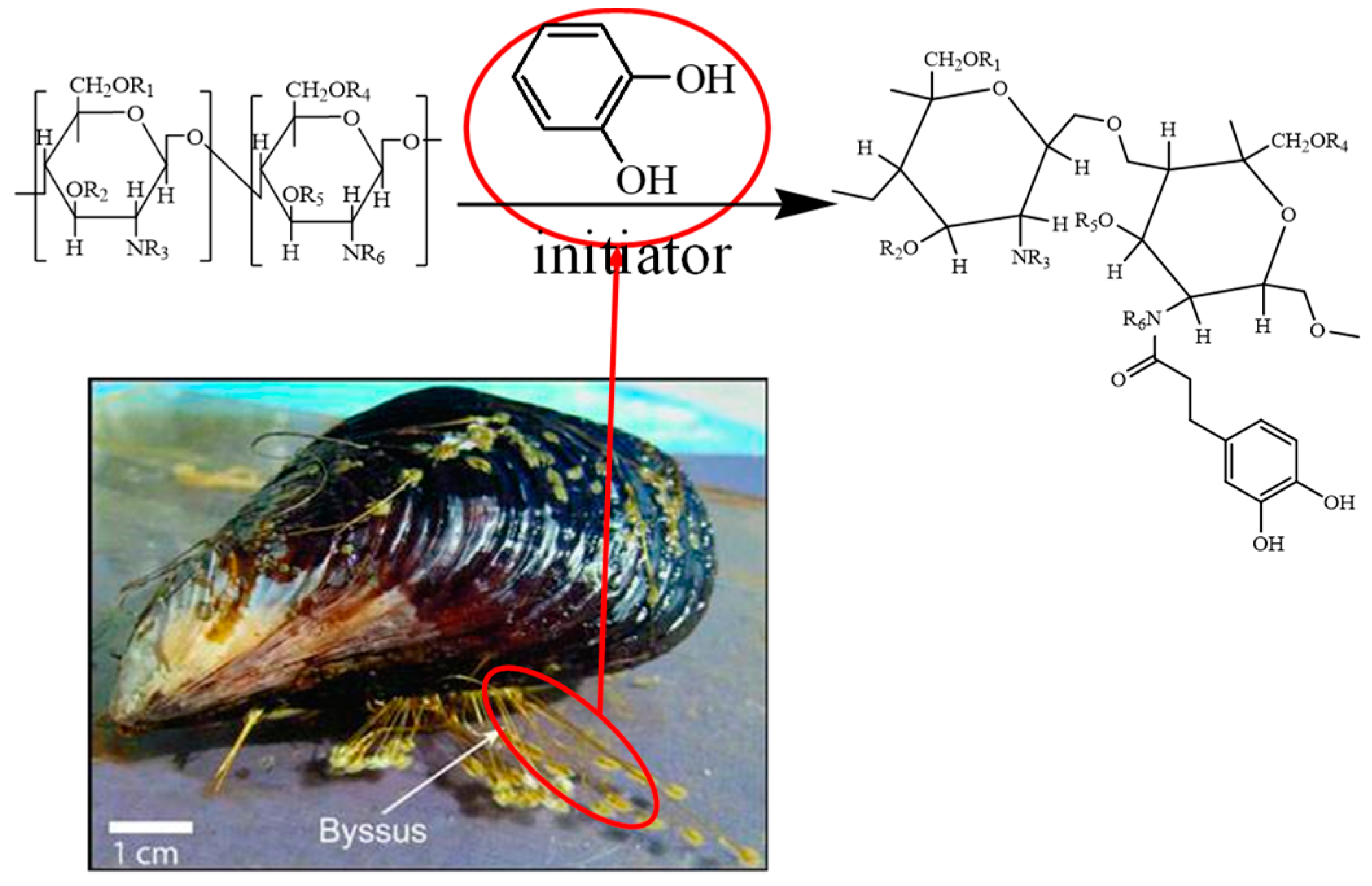
4.2.1. Synthesis of Catechol-Chitosan Biopolymer Encapsulators
4.2.2. Tensile Shear Strength Test
4.2.3. Cuttings Hot-Rolling Dispersion Test
4.2.4. Characterization of SDGB
4.2.5. Core Uniaxial Compressive Strength Test
4.2.6. The Hydroscopicity Test
4.2.7. Scanning Electron Microscope Test
4.2.8. Adsorption Isotherm Test
4.2.9. Rheological and Filtration Testing of Drilling Fluids
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Ong, S.H.; Azeemuddin, M.; Goodman, H. A wellbore stability model for formations with anisotropic rock strengths. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 96, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shen, H.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, J.; Dong, X.; Luo, S. Nanoscale laponite as a potential shale inhibitor in water-based drilling fluid for stabilization of wellbore stability and mechanism study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33252–33259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauder, T.; Barbarick, K.; Ippolito, J.; Shanahan, J.; Ayers, P. Soil properties affecting wheat yields following drilling-fluid application. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianshou, M.; Ping, C. Study of meso-damage characteristics of shale hydration based on CT scanning technology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, P. Hydration-phase diagrams and friction of montmorillonite under laboratory and geologic conditions, with implications for shale compaction, slope stability, and strength of fault gouge. Tectonophysics 1984, 107, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidug, W.; Wong, S.W. Hydration swelling of water-absorbing rocks: A constitutive model. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1996, 20, 403–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadizadeh, S.R.; Moslemizadeh, A.; Dezaki, A.S. A novel nonionic surfactant for inhibiting shale hydration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 118, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, Y.; Li, G.; Li, P.; Deng, Y. Theoretical simulation and experimental evaluation of the effect of hydration on the shale rock strength. Drill. Prod. Technol. 2010, 33, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Huang, W. Minimization shale hydration with the combination of hydroxyl-terminated PAMAM dendrimers and KCl. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8484–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Yin, T.; Liu, K.; Guo, Q. Water-soluble complexes of an acrylamide copolymer and ionic liquids for inhibiting shale hydration. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, S. Mechanisms of shale hydration and water block removal. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.; Walker, T.; Jiang, G. Environmentally acceptable water-base mud can prevent shale hydration and maintain borehole stability. SPE Drill. Completion 1995, 10, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z. Synthesis and characterization of nano-SiO2@ octadecylbisimidazoline quaternary ammonium salt used as acidizing corrosion inhibitor. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 61, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baoyou, R.; Xiaolin, P.; Cheng, C.; Chuan, M. Experimental study on improving the formation pressure-bearing capacity by using nano-drilling fluid. Oil Drill. Prod. Technol. 2018, 40, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Xu, C.; Tang, L.; Li, S.; Li, D. Constructing a tough shield around the wellbore: Theory and method for lost-circulation control. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Liang, Y. Application of wellbore strengthening drilling fluid technology in Lingshui gas field. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Chengdu, China, 23–25 April 2021; p. 012190. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Bao, D.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, J. Mechanisms of wellbore strengthening and new advances in lost circulation control with dense pressure bearing zone. Drill. Fluid Completion Fluid 2018, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, F. Application of core-shell structural acrylic resin/nano-SiO2 composite in water based drilling fluid to plug shale pores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 55, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, B.B.; van Oort, E.; Daigle, H. How do nanoparticles stabilize shale? SPE Drill. Completion 2019, 34, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtarmanesh, S.; Shahrabi, M.A.; Atashnezhad, A. Improvement of wellbore stability in shale using nanoparticles. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 112, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, J. Improving the shale stability with nano-silica grafted with hyperbranched polyethyleneimine in water-based drilling fluid. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 83, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Jalalifar, H.; Apourvari, S.N.; Sakebi, M.R. Mechanistic study of improvement of wellbore stability in shale formations using a natural inhibitor. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 181, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkhalil, H.; Nakhaee, A. Effect of nano ZnO on wellbore stability in shale: An experimental investigation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 173, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z. Novel micro and nano particle-based drilling fluids: Pioneering approach to overcome the borehole instability problem in shale formations. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Brisbane, Australia, 9–11 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, C.M.; Zhang, R.; Chenevert, M.; Sharma, M. High-performance water-based mud using nanoparticles for shale reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 12–14 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, P.; Chen, Z. Experimental study on the application of an ionic liquid as a shale inhibitor and inhibitive mechanism. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 150, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, W.; Cao, J. Poly (oxypropylene)-amidoamine modified bentonite as potential shale inhibitor in water-based drilling fluids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Jin, J.; Lv, K.; Li, H.; Rong, K.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X. Use of silicone quaternary ammonium salt for hydrophobic surface modification to inhibit shale hydration and mechanism study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 341, 117369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sheng, J.J.; Fu, L. Application of polyether amine, poly alcohol or KCl to maintain the stability of shales containing Na-smectite and Ca-smectiteShifeng Zhang et al. Maintaining stability of shale with Na-, Ca-smectite. Clay Miner. 2018, 53, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.D. Design and development of quaternary amine compounds: Shale inhibition with improved environmental profile. In Proceedings of the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 20–22 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J.A.; Hamadamin, A.B.; Ahmed, S.M.; Mahmood, B.S.; Sajadi, S.M.; Manshad, A.K. Synergistic Effect of Nanoinhibitive Drilling Fluid on the Shale Swelling Performance at High Temperature and High Pressure. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 1996–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, R.F. Membrane Forming In-Situ Polymerization for Water Based Drilling Fluids. U.S. Patent 7279445B2, 9 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schlemmer, R.; Friedheim, J.; Growcock, F.; Bloys, J.; Headley, J.; Polnaszek, S. Chemical osmosis, shale, and drilling fluids. SPE Drill. Completion 2003, 18, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, R.; Friedheim, J.; Growcock, F.; Bloys, J.; Headley, J.; Polnaszek, S. Membrane efficiency in shale-an empirical evaluation of drilling fluid chemistries and implications for fluid design. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 26–28 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Albooyeh, M.; Kivi, I.R.; Ameri, M. Promoting wellbore stability in active shale formations by water-based muds: A case study in Pabdeh shale, Southwestern Iran. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 56, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Luo, P.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, J.; Kuang, X.; Wang, D. Application of a new family of organosilicon quadripolymer as a fluid loss additive for drilling fluid at high temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Feng, X. A new experimental methodology to investigate formation damage in clay-bearing reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 143, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, S.; He, W. Fighting wellbore instability: Customizing drilling fluids based on laboratory studies of shale-fluid interactions. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Asia Pacific Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition, Tianjin, China, 9–11 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.P.; Richards, B.G.; Rahman, S. Managing physico-chemical wellbore instability in shales with the chemical potential mechanism. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 28–31 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, W.; Fan, X.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Y. A review of the shale wellbore stability mechanism based on mechanical–chemical coupling theories. Petroleum 2015, 1, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kord Forooshani, P.; Lee, B.P. Recent approaches in designing bioadhesive materials inspired by mussel adhesive protein. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Rho, J.; Messersmith, P.B. Facile conjugation of biomolecules onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Ni, K.; Wei, D.; Ren, Y. Fe3+-induced oxidation and coordination cross-linking in catechol–chitosan hydrogels under acidic pH conditions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37377–37384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Chiou, Y.-M.; Orville, A.M.; Miller, M.A.; Lipscomb, J.D.; Que, L., Jr. X-ray absorption spectroscopic studies of the Fe (II) active site of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. Implications for the extradiol cleavage mechanism. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 6649–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, T.J. Mussel byssus and biomolecular materials. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Factor Level | Mole Ratio of Catechol/Chitosan | Initiator Concentration * /% | Time /h | Temperature /°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:1 | 5 | 8 | 10 |
| 2 | 1:2 | 7 | 10 | 25 |
| 3 | 1:3 | 10 | 12 | 40 |
| Num. | Monomer Ratio | Initiator Concentration /% | Time /h | Temperature /°C | Rolling Recovery /% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:1 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 75.1 | |
| 2 | 1:1 | 7 | 10 | 25 | 73.6 | |
| 3 | 1:1 | 10 | 12 | 40 | 67.5 | |
| 4 | 1:2 | 5 | 10 | 40 | 74.6 | |
| 5 | 1:2 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 78.9 | |
| 6 | 1:2 | 10 | 8 | 25 | 75.1 | |
| 7 | 1:3 | 5 | 12 | 25 | 73.4 | |
| 8 | 1:3 | 7 | 8 | 40 | 74.3 | |
| 9 | 1:3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 78.4 | |
| Level | k1 | 0.721 | 0.744 | 0.748 | 0.775 | - |
| k2 | 0.762 | 0.756 | 0.755 | 0.74 | - | |
| k3 | 0.754 | 0.737 | 0.733 | 0.721 | - | |
| R | 0.041 | 0.019 | 0.023 | 0.053 | - | |
| Mn (Dalton) | Mw (Dalton) | Mp (Dalton) | Mz (Dalton) | Mz+1 (Dalton) | Polydispersity Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25,974 | 33,424 | 17,339 | 46,291 | 66,870 | 1.66731 |
| Quartz | Plagioclase | Calcite | Hematite | Clay Mineral |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 53 |
| Kaolinite | Chlorite | Illite | Illte/Smectite | Interlayer Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 2 | 97 | 75 |
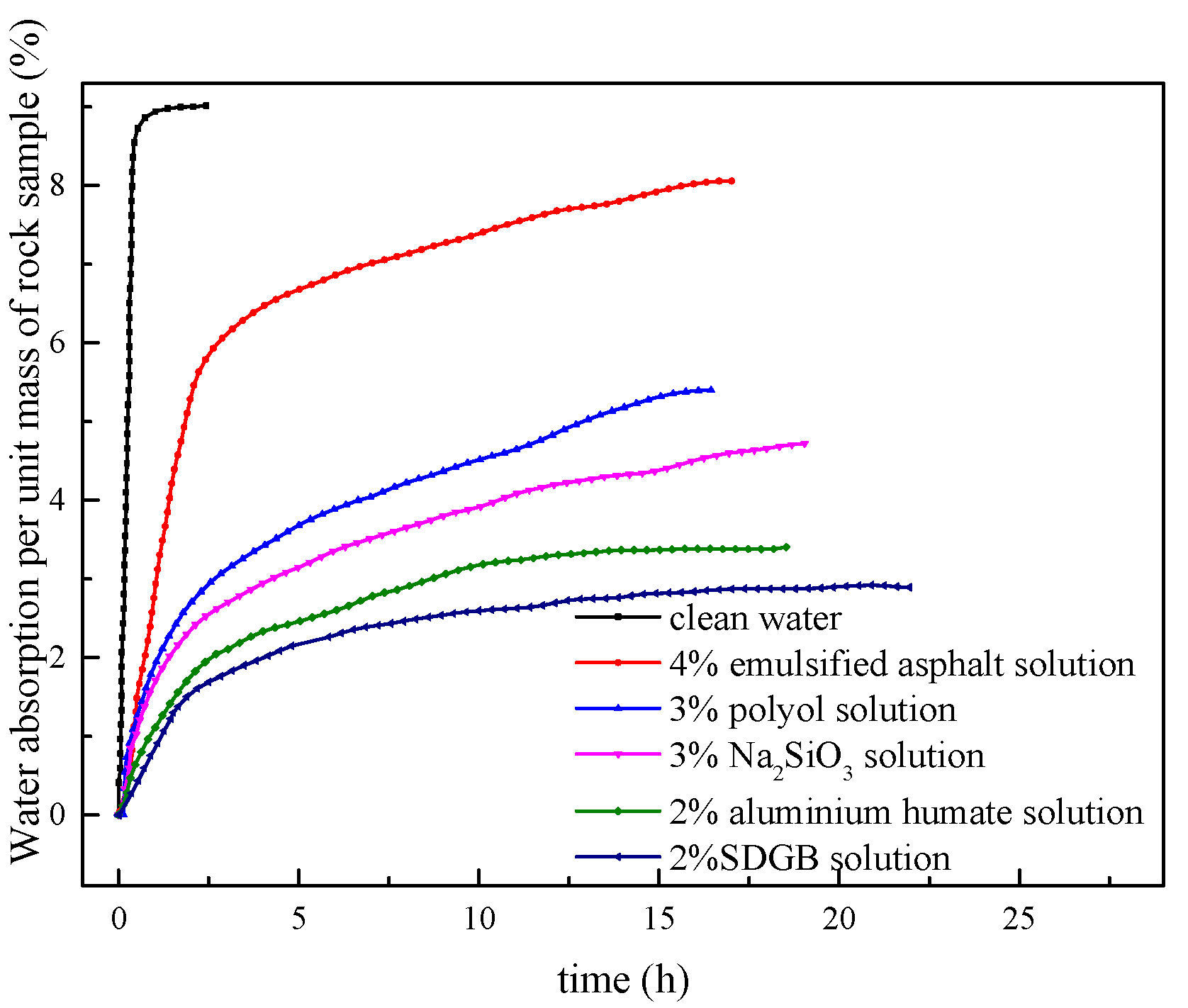
| Wellbore Stabilizer | Water Absorption of Rock Core (%) | Water Absorption Reduction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Clean water | 9.10 | 0 |
| 4% emulsified asphalt solution | 8.05 | 11.53 |
| 3% polyol solution | 5.38 | 40.88 |
| 3% Na2SiO3 solution | 4.70 | 48.35 |
| 2% aluminium humate solution | 3.24 | 64.40 |
| 2% SDGB solution | 2.75 | 69.78 |
| Clean water | 9.10 | 0 |
| 4% emulsified asphalt solution | 8.05 | 11.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Kang, Y.; Guo, B. Wellbore Stability through Novel Catechol-Chitosan Biopolymer Encapsulator-Based Drilling Mud. Gels 2022, 8, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050307
Tang Z, Qiu Z, Zhong H, Kang Y, Guo B. Wellbore Stability through Novel Catechol-Chitosan Biopolymer Encapsulator-Based Drilling Mud. Gels. 2022; 8(5):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050307
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhichuan, Zhengsong Qiu, Hanyi Zhong, Yujie Kang, and Baoyu Guo. 2022. "Wellbore Stability through Novel Catechol-Chitosan Biopolymer Encapsulator-Based Drilling Mud" Gels 8, no. 5: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050307
APA StyleTang, Z., Qiu, Z., Zhong, H., Kang, Y., & Guo, B. (2022). Wellbore Stability through Novel Catechol-Chitosan Biopolymer Encapsulator-Based Drilling Mud. Gels, 8(5), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050307